The Cano-eMLST Program: An Approach for the Calculation of Canonical Extended Multi-Locus Sequence Typing, Making Comparison of Genetic Differences Among Bunches of Bacterial Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
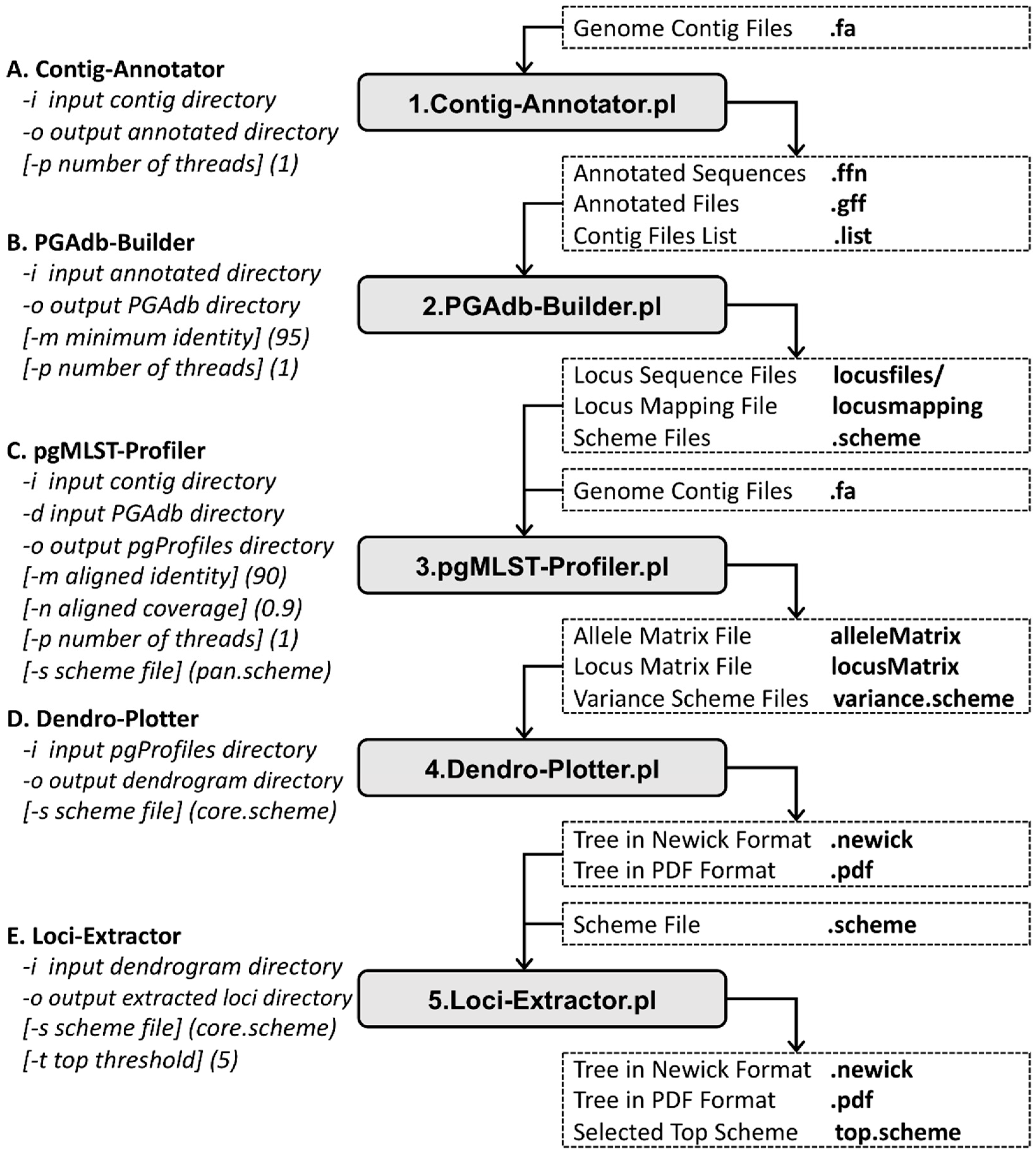
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Contig Annotator
2.2. PGAdb Builder
2.3. pgMLST Profiler
2.4. Dendro Plotter
2.5. Loci Extractor
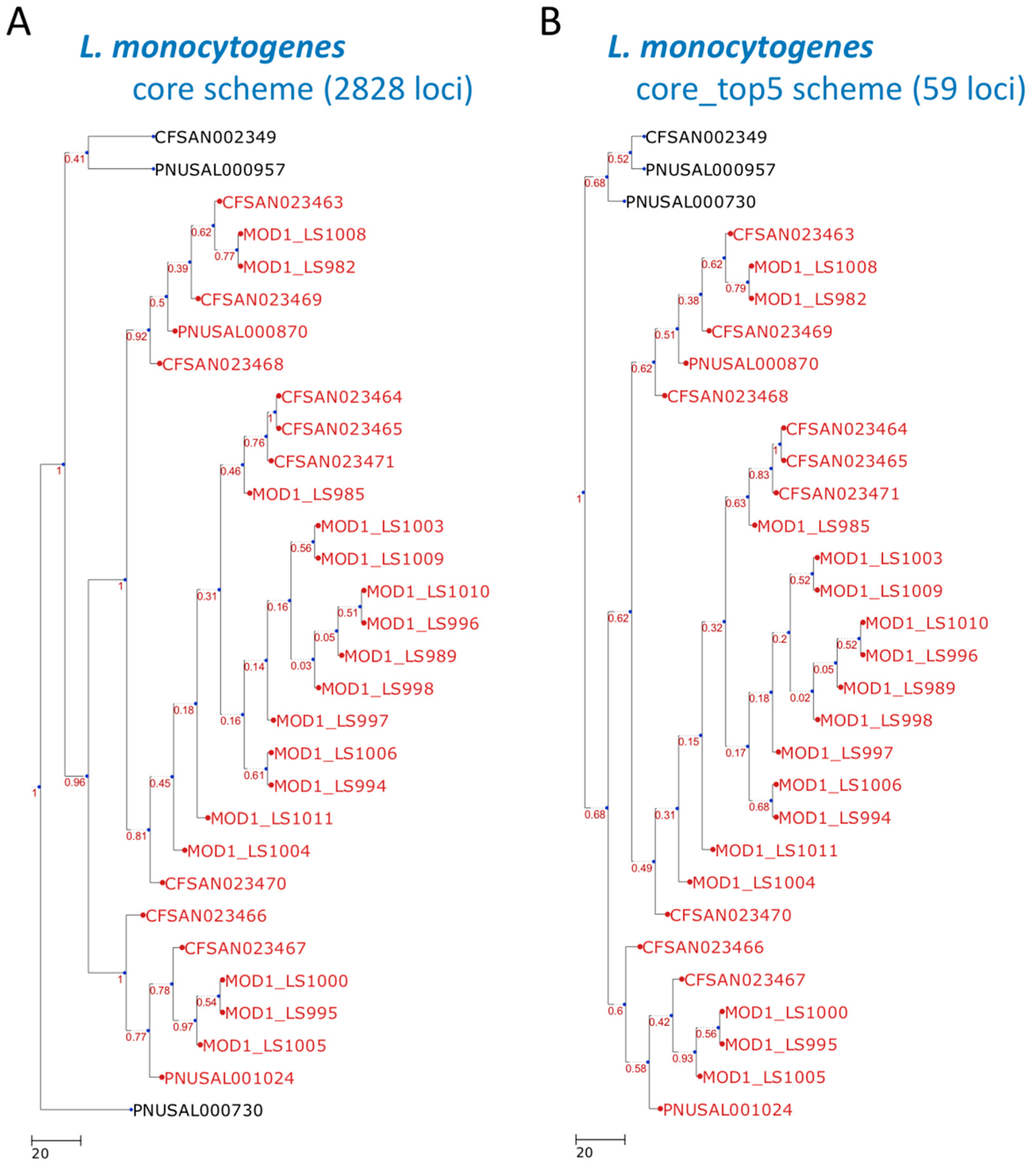
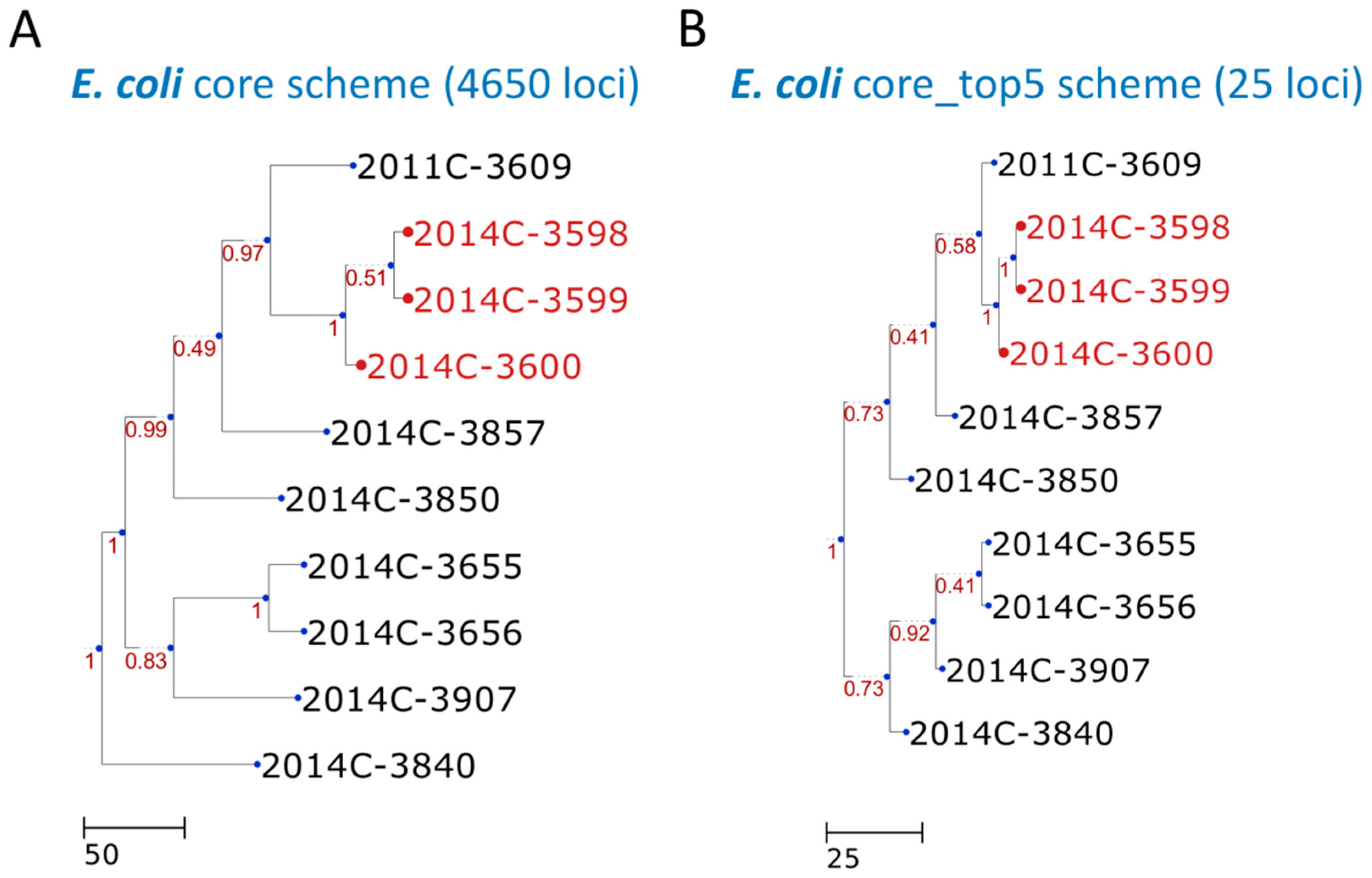
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swaminathan, B.; Barrett, T.J.; Hunter, S.B.; Tauxe, R.V. PulseNet: The molecular subtyping network for foodborne bacterial disease surveillance, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, B.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Ng, L.K.; Lukinmaa, S.; Kam, K.M.; Rolando, S.; Gutierrez, E.P.; Binsztein, N. Building PulseNet International: An interconnected system of laboratory networks to facilitate timely public health recognition and response to foodborne disease outbreaks and emerging foodborne diseases. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2006, 3, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.Y.; Watanabe, H.; Terajima, J.; Li, C.C.; Liao, J.C.; Tung, S.K.; Chiou, C.S. Multilocus Variable-Number Tandem Repeat Analysis for Molecular Typing of Shigella sonnei. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3574–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxrud, D.; Pederson-Gulrud, K.; Wotton, J.; Medus, C.; Lyszkowicz, E.; Besser, J.; Bartkus, J.M. Comparison of multiple-locus variable-number tandem repeat analysis, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and phage typing for subtype analysis of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.S. Multilocus variable-number tandem repeat analysis as a molecular tool for subtyping and phylogenetic analysis of bacterial pathogens. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 10, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.S.; Izumiya, H.; Thong, K.L.; Larsson, J.T.; Liang, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Koh, X.P. A simple approach to obtain comparable Shigella sonnei MLVA results across laboratories. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluytmans-van den Bergh, M.F.; Rossen, J.W.; Bruijning-Verhagen, P.C.; Bonten, M.J.; Friedrich, A.W.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; Willems, R.J.; Kluytmans, J.A. Whole-Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing of Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2919–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingry, L.C.; Rowe, L.A.; Respicio-Kingry, L.B.; Beard, C.B.; Schriefer, M.E.; Petersen, J.M. Whole genome multilocus sequence typing as an epidemiologic tool for Yersinia pestis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 84, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, P.G.; Prior, K.; Harmsen, D.; Seifert, H. Development and evaluation of a core genome multilocus typing scheme for whole-genome sequence-based typing of Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bletz, S.; Janezic, S.; Harmsen, D.; Rupnik, M.; Mellmann, A. Defining and Evaluating a Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Genome-Wide Typing of Clostridium difficile. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01987-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Been, M.; Pinholt, M.; Top, J.; Bletz, S.; Mellmann, A.; van Schaik, W.; Brouwer, E.; Rogers, M.; Kraat, Y.; Bonten, M.; et al. Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for High- Resolution Typing of Enterococcus faecium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3788–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran-Gilad, J.; Prior, K.; Yakunin, E.; Harrison, T.G.; Underwood, A.; Lazarovitch, T.; Valinsky, L.; Luck, C.; Krux, F.; Agmon, V.; et al. Design and application of a core genome multilocus sequence typing scheme for investigation of Legionnaires‘ disease incidents. Euro Surveill. 2015, 20, 21186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppitsch, W.; Pietzka, A.; Prior, K.; Bletz, S.; Fernandez, H.L.; Allerberger, F.; Harmsen, D.; Mellmann, A. Defining and Evaluating a Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for Whole-Genome Sequence-Based Typing of Listeria monocytogenes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, T.A.; Diel, R.; Harmsen, D.; Rothganger, J.; Walter, K.M.; Merker, M.; Weniger, T.; Niemann, S. Whole-genome-based Mycobacterium tuberculosis surveillance: A standardized, portable, and expandable approach. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medini, D.; Donati, C.; Tettelin, H.; Masignani, V.; Rappuoli, R. The microbial pan-genome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timme, R.E.; Rand, H.; Shumway, M.; Trees, E.K.; Simmons, M.; Agarwala, R.; Davis, S.; Tillman, G.E.; Defibaugh-Chavez, S.; Carleton, H.A.; et al. Benchmark datasets for phylogenomic pipeline validation, applications for foodborne pathogen surveillance. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Serra, F.; Bork, P. ETE 3: Reconstruction, Analysis, and Visualization of Phylogenomic Data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.F.; Foulds, L.R. Comparison of Phylogenetic Trees. Math. Biosci. 1981, 53, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Nielsen, E.M.; Kaas, R.S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. Evaluation of whole genome sequencing for outbreak detection of Salmonella enterica. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.C.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielbasa, S.M.; Wan, R.; Sato, K.; Horton, P.; Frith, M.C. Adaptive seeds tame genomic sequence comparison. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 1 | Import ETE toolkit and scikit-learn library |
| 2 | Read newick tree file to be traversal |
| 3 | for each node in tree: |
| 4 | if node is leaf: |
| 5 | continue |
| 6 | (subtree_1, subtree_2) = get_children (node) |
| 7 | if (leaf_amount(subtree_1) < 3 and leaf_amount(subtree_2) < 3): |
| 8 | continue |
| 9 | (class_1, class_2) = (subtree_1, subtree_2) |
| 10 | Informative loci selected by feature importance |
| 11 | Non-redundant merge of the informative loci |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.-Y.; Lin, J.-W.; Chen, C.-C. The Cano-eMLST Program: An Approach for the Calculation of Canonical Extended Multi-Locus Sequence Typing, Making Comparison of Genetic Differences Among Bunches of Bacterial Strains. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7040098
Liu Y-Y, Lin J-W, Chen C-C. The Cano-eMLST Program: An Approach for the Calculation of Canonical Extended Multi-Locus Sequence Typing, Making Comparison of Genetic Differences Among Bunches of Bacterial Strains. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(4):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7040098
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yen-Yi, Ji-Wei Lin, and Chih-Chieh Chen. 2019. "The Cano-eMLST Program: An Approach for the Calculation of Canonical Extended Multi-Locus Sequence Typing, Making Comparison of Genetic Differences Among Bunches of Bacterial Strains" Microorganisms 7, no. 4: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7040098
APA StyleLiu, Y.-Y., Lin, J.-W., & Chen, C.-C. (2019). The Cano-eMLST Program: An Approach for the Calculation of Canonical Extended Multi-Locus Sequence Typing, Making Comparison of Genetic Differences Among Bunches of Bacterial Strains. Microorganisms, 7(4), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7040098





