World-Wide Variation in Incidence of Staphylococcus aureus Associated Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Meta-Regression
Abstract
1. Introduction
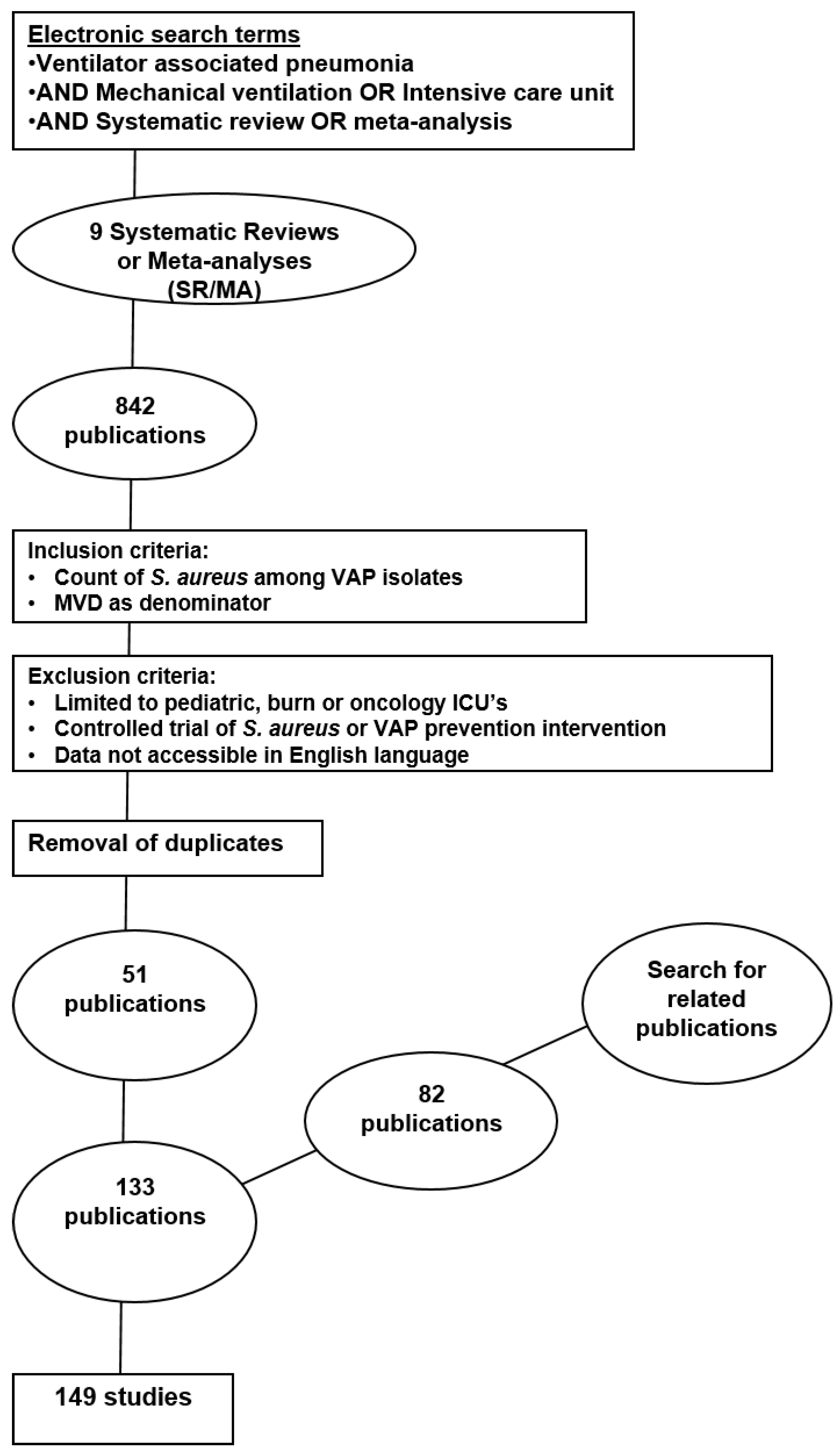
2. Methods
Availability of Data and Materials
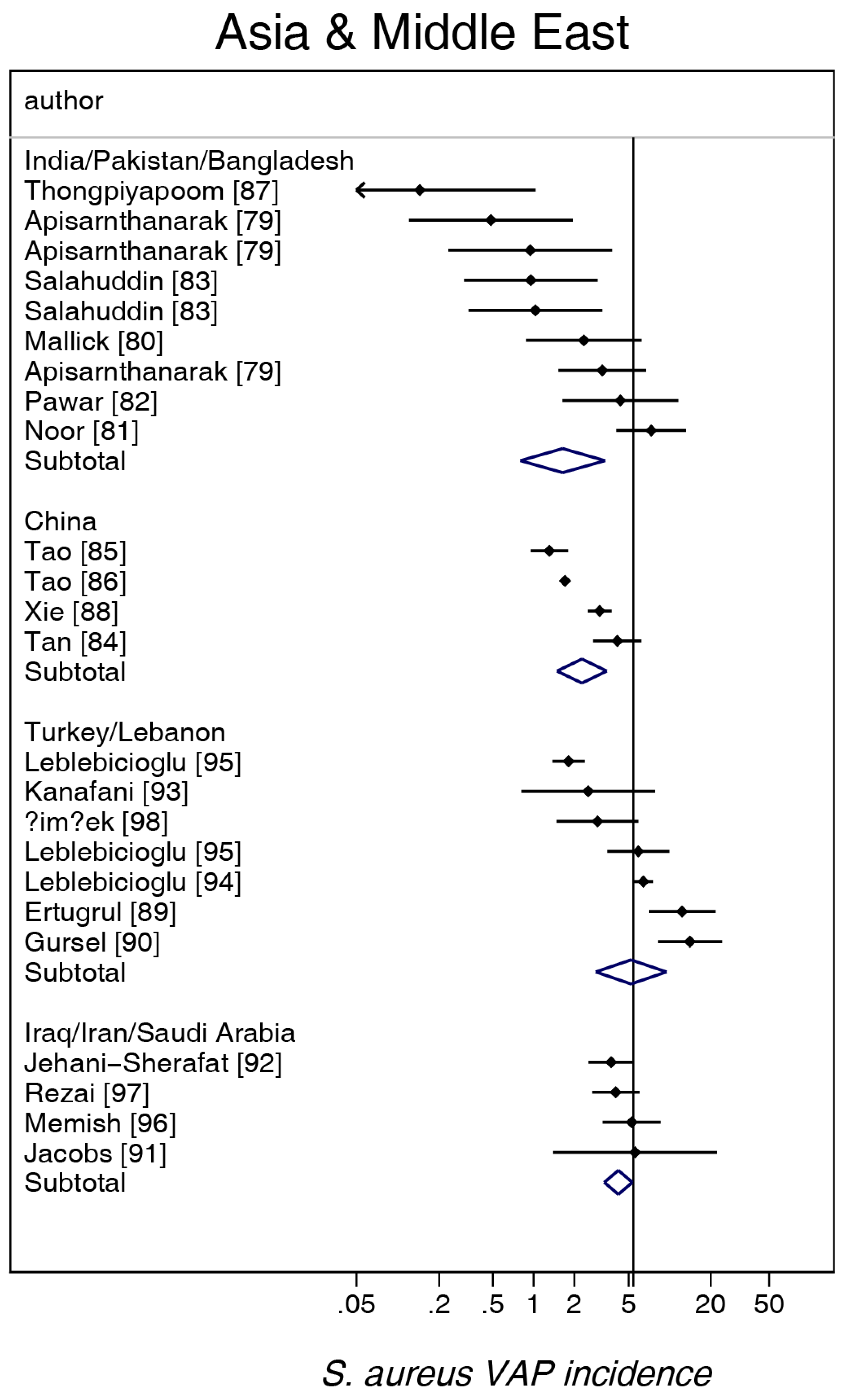
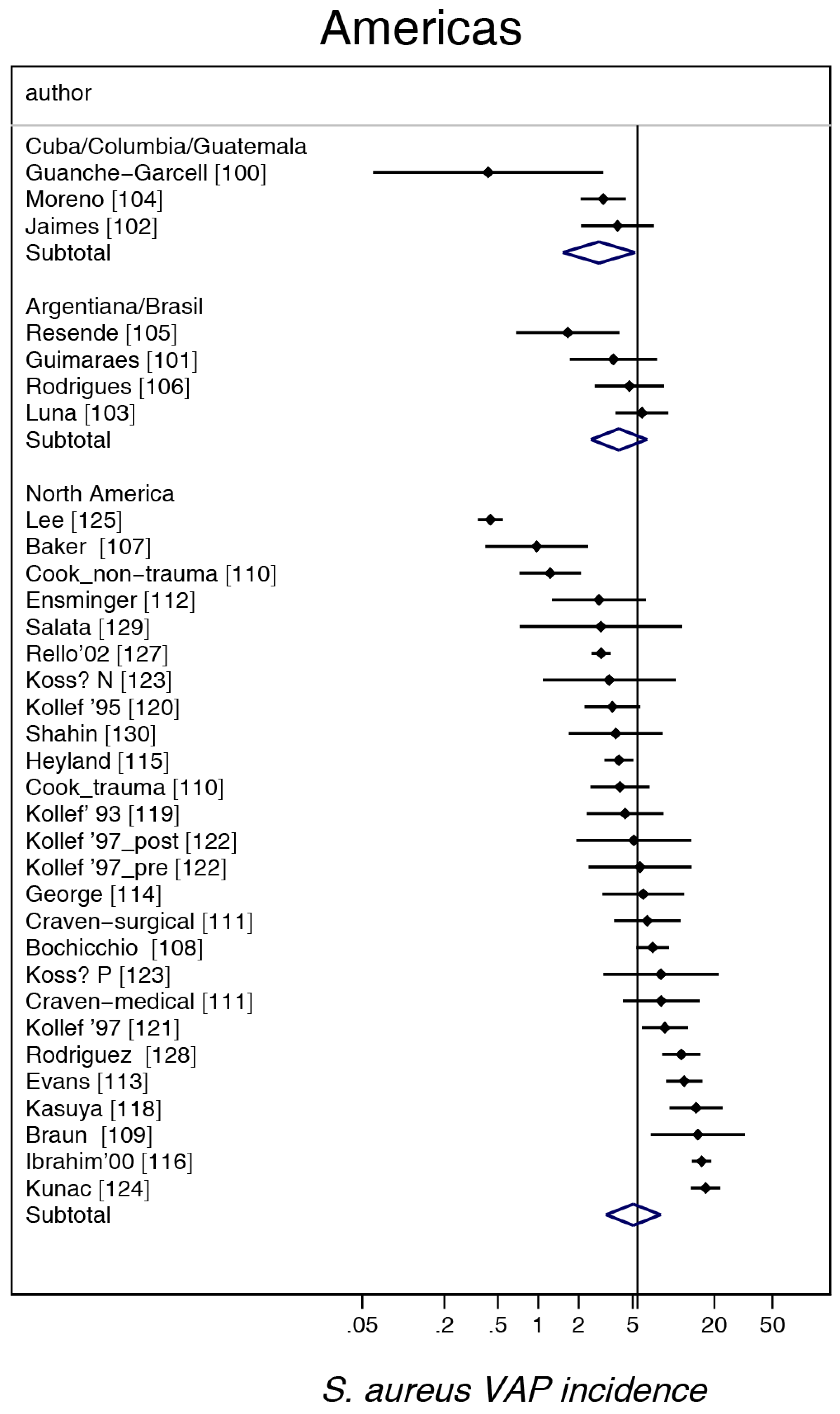
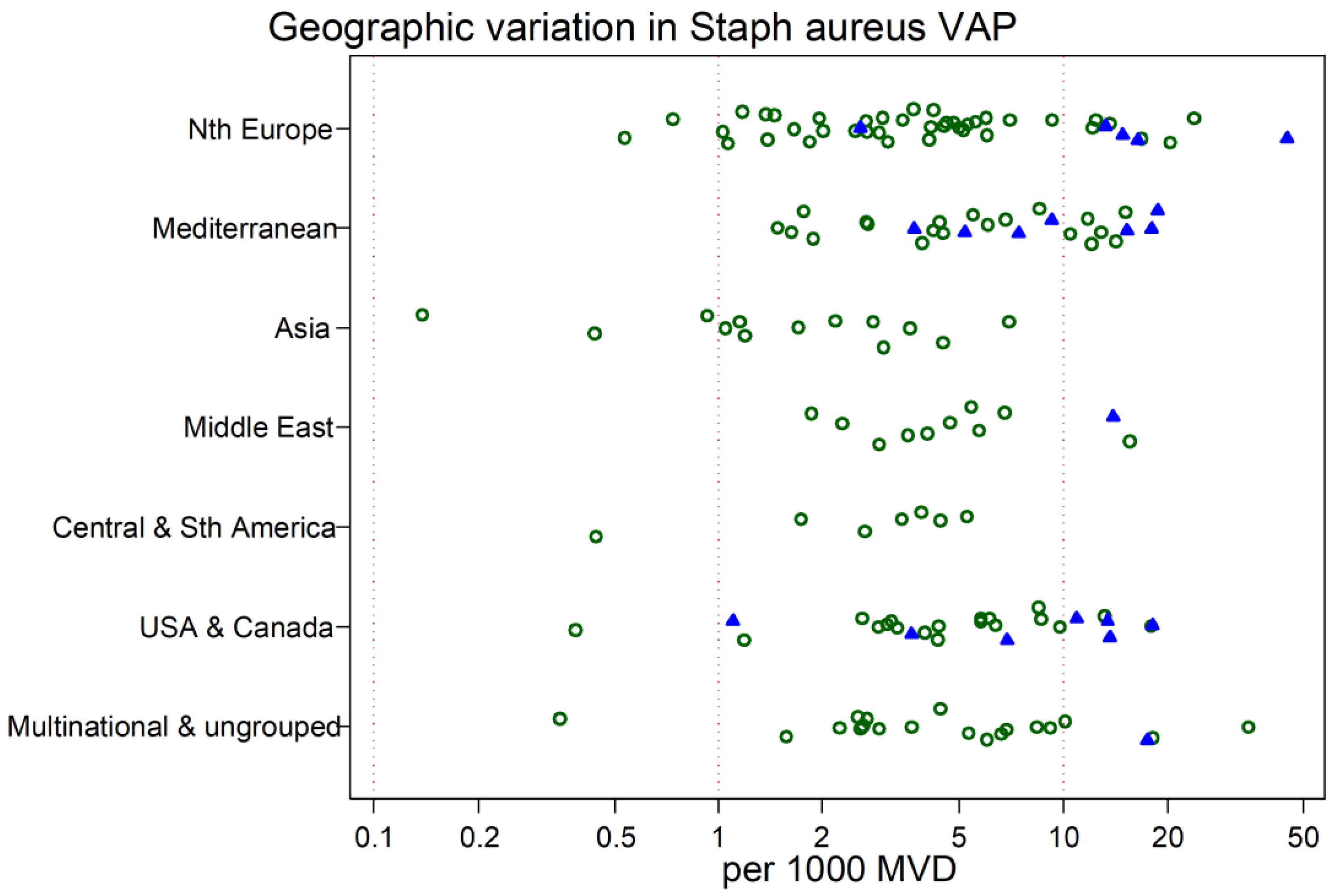
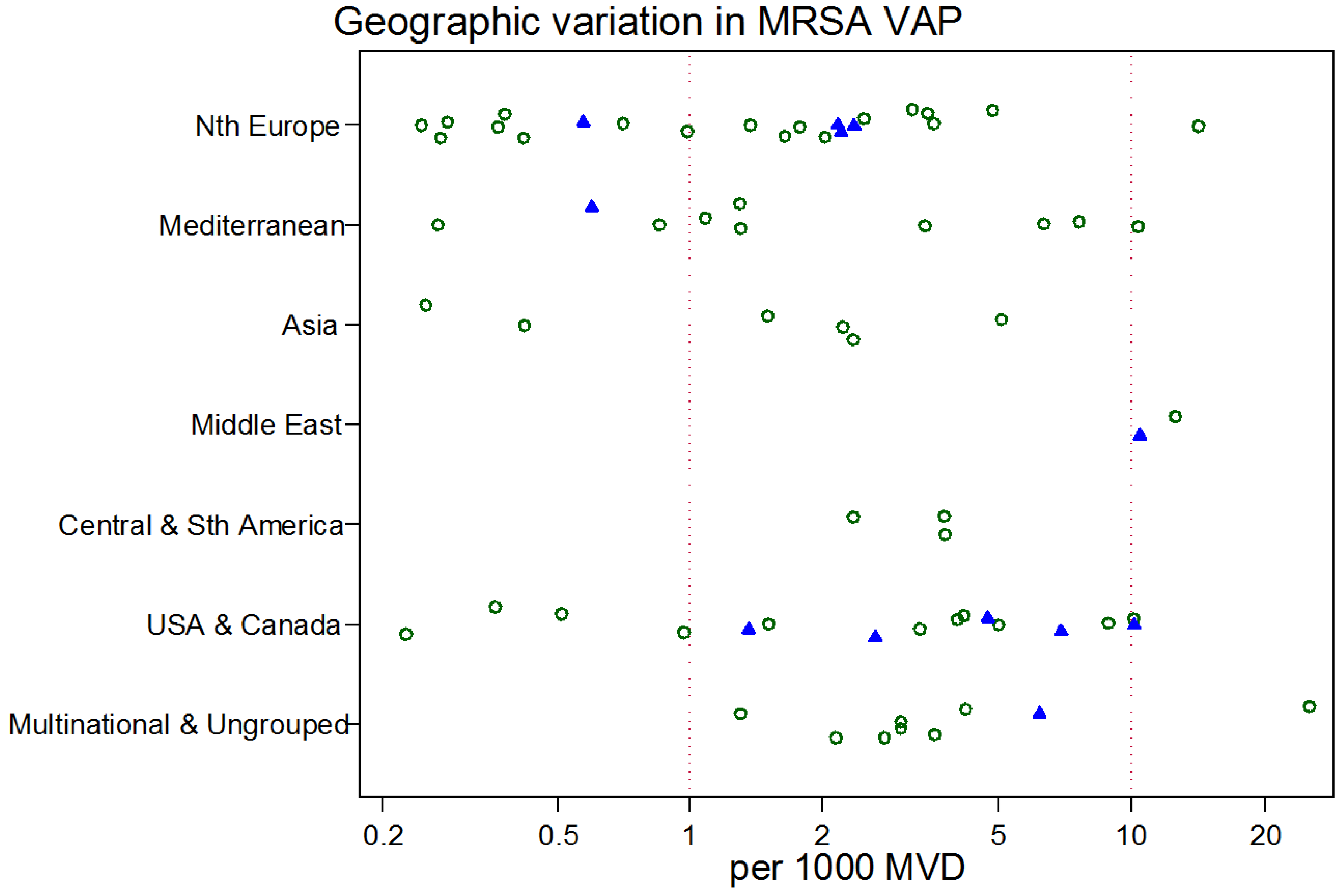
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blot, S.; Koulenti, D.; Dimopoulos, G.; Martin, C.; Komnos, A.; Krueger, W.A.; Spina, G.; Armaganidis, A.; Rello, J.; EU-VAP Study Investigators. Prevalence, risk factors, and mortality for ventilator-associated pneumonia in middle-aged, old, and very old critically ill patients. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevret, S.; Hemmer, M.; Carlet, J.; Langer, M. Incidence and risk factors of pneumonia acquired in intensive care units. Results from a multicenter prospective study on 996 patients. European Cooperative Group on Nosocomial Pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 1993, 19, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollef, M.H.; Chastre, J.; Fagon, J.Y.; François, B.; Niederman, M.S.; Rello, J.; Torres, A.; Vincent, J.L.; Wunderink, R.G.; Go, K.W.; et al. Global prospective epidemiologic and surveillance study of ventilator-associated pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magret, M.; Amaya-Villar, R.; Garnacho, J.; Lisboa, T.; Diaz, E.; DeWaele, J.; Deja, M.; Manno, E.; Rello, J.; et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in trauma patients is associated with lower mortality: Results from EU-VAP study. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2010, 69, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, V.D.; Maki, D.G.; Salomao, R.; Moreno, C.A.; Mehta, Y.; Higuera, F.; Cuellar, L.E.; Arikan, O.A.; Abouqal, R.; Leblebicioglu, H. Device-associated nosocomial infections in 55 intensive care units of 8 developing countries. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, V.D.; Rodrigues, C.; Madani, N.; Mitrev, Z.; Ye, G.; Salomao, R.; Ulger, F.; Guanche-Garcell, H.; Kanj, S.S.; Cuéllar, L.E.; et al. Effectiveness of a multidimensional approach for prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia in adult intensive care units from 14 developing countries of four continents: Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A’court, C.H.; Garrard, C.S.; Crook, D.; Bowler, I.; Conlon, C.; Peto, T.; Anderson, E. Microbiological lung surveillance in mechanically ventilated patients, using non-directed bronchial lavage and quantitative culture. Q. J. Med. 1993, 86, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekaert, M.; Timsit, J.F.; Vansteelandt, S.; Depuydt, P.; Vésin, A.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Decruyenaere, J.; Clec’h, C.; Azoulay, E.; Benoit, D. Attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A reappraisal using causal analysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercault, N.; Wolf, M.; Runge, I.; Fleury, J.C.; Boulain, T. Intrahospital transport of critically ill ventilated patients: A risk factor for ventilator-associated pneumonia—A matched cohort study. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 2471–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrouane, Y.; Daudenthun, I.; Riegel, B.; Emery, M.N.; Martin, G.; Krivosic, R.; Grandbastien, B. Early onset pneumonia in neurosurgical intensive care unit patients. J. Hosp. Infect. 1998, 40, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstain, C.; Azoulay, E.; De Lassence, A.; Cohen, Y.; Costa, M.A.; Mourvillier, B.; Descorps-Declere, A.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Thuong, M.; Schlemmer, B.; et al. Sedation, sucralfate, and antibiotic use are potential means for protection against early-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bregeon, F.; Papazian, L.; Visconti, A.; Gregoire, R.; Thirion, X.; Gouin, F. Relationship of microbiologic diagnostic criteria to morbidity and mortality in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia. JAMA 1997, 277, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronchard, R.; Albaladejo, P.; Brezac, G.; Geffroy, A.; Seince, P.F.; Morris, W.; Branger, C.; Marty, J. Early onset pneumonia: Risk factors and consequences in head trauma patients. Anesthesiologists 2004, 100, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastre, J.; Trouillet, J.L.; Vuagnat, A.; Joly-Guillou, M.L.; Clavier, H.; Dombret, M.C.; Gibert, C. Nosocomial pneumonia in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daschner, F.; Kappstein, I.; Schuster, F.; Scholz, R.; Bauer, E.; Jooβens, D.; Just, H. Influence of disposable (‘Conchapak’) and reusable humidifying systems on the incidence of ventilation pneumonia. J. Hosp. Infect. 1988, 11, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duszyńska, W.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Dragan, B.; Węgrzyn, P.; Mazur, A.; Wojtyra, P.; Tomala, A.; Kübler, A. Ventilator-associated pneumonia monitoring according to the INICC project at one centre. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2015, 47, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagon, J.Y.; Chastre, J.; Domart, Y.; Trouillet, J.L.; Pierre, J.; Darne, C.; Gibert, C. Nosocomial pneumonia in patients receiving continuous mechanical ventilation. Prospective analysis of 52 episodes with use of a protected specimen brush and quantitative culture techniques. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacouin, A.; Barbarot, N.; Camus, C.; Salomon, S.; Isslame, S.; Marque, S.; Lavoué, S.; Donnio, P.Y.; Thomas, R.; Le Tulzo, Y. Late-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia in nontrauma intensive care unit patients. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 109, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Chevret, S.; Arlet, G.; Marie, O.; Rouveau, M.; Popoff, N.; Schlemmer, B. Oropharyngeal or gastric colonization and nosocomial pneumonia in adult intensive care unit patients. A prospective study based on genomic DNA analysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georges, H.; Leroy, O.; Guery, B.; Alfandari, S.; Beaucaire, G. Predisposing factors for nosocomial pneumonia in patients receiving mechanical ventilation and requiring tracheotomy. Chest 2000, 118, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giard, M.; Lepape, A.; Allaouchiche, B.; Guerin, C.; Lehot, J.J.; Robert, M.O.; Fournier, G.; Jacques, D.; Chassard, D.; Gueugniaud, P.Y.; et al. Early-and late-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia acquired in the intensive care unit: Comparison of risk factors. J. Crit. Care 2008, 23, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruson, D.; Hilbert, G.; Vargas, F.; Valentino, R.; Bebear, C.; Allery, A.; Bebear, C.; Gbikpi-benissan, G.E.; Cardinaud, J.P. Rotation and restricted use of antibiotics in a medical intensive care unit: Impact on the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruson, D.; Hilbert, G.; Vargas, F.; Valentino, R.; Bui, N.; Pereyre, S.; Bebear, C.; Bebear, C.M.; Gbikpi-Benissan, G. Strategy of antibiotic rotation: Long-term effect on incidence and susceptibilities of Gram-negative bacilli responsible for ventilator-associated pneumonia. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerin, C.; Girard, R.; Chemorin, C.; De Varax, R.; Fournier, G. Facial mask noninvasive mechanical ventilation reduces the incidence of nosocomial pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 1997, 23, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugonnet, S.; Uçkay, I.; Pittet, D. Staffing level: A determinant of late-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyllienmark, P.; Gardlund, B.; Persson, J.O.; Ekdahl, K. Nosocomial pneumonia in the ICU: A prospective cohort study. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 39, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaillette, E.; Nseir, S. Relationship between inhaled β2-agonists and ventilator-associated pneumonia: A cohort study. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlenberg, A.; Schwab, F.; Behnke, M.; Geffers, C.; Gastmeier, P. Pneumonia associated with invasive and noninvasive ventilation: An analysis of the German nosocomial infection surveillance system database. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolpa, M.; Walaszek, M.; Gniadek, A.; Wolak, Z.; Dobros, W. Incidence, Microbiological Profile and Risk Factors of Healthcare-Associated Infections in Intensive Care Units: A 10 Year Observation in a Provincial Hospital in Southern Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepelletier, D.; Roquilly, A.; Mahe, P.J.; Loutrel, O.; Champin, P.; Corvec, S.; Naux, E.; Pinaud, M.; Lejus, C.; Asehnoune, K. Retrospective analysis of the risk factors and pathogens associated with early-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia in surgical-ICU head-trauma patients. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2010, 22, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyt, C.E.; Guérin, V.; Combes, A.; Trouillet, J.L.; Ayed, S.B.; Bernard, M.; Gibert, C.; Chastre, J. Procalcitonin kinetics as a prognostic marker of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnason, S.; Kristinsson, K.G.; Stefansson, T.; Erlendsdottir, H.; Jonsdottir, K.; Kristjansson, M.; Gudmundsson, S. Risk factors and outcome in ICU-acquired infections. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2008, 52, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahul, P.; Auboyer, C.; Jospe, R.; Ros, A.; Guerin, C.; el Khouri, Z.; Galliez, M.; Dumont, A.; Gaudin, O. Prevention of nosocomial pneumonia in intubated patients respective role of mechanical subglottic secretions drainage and stress ulcer prophylaxis. Intensive Care Med. 1992, 18, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowicz, P.; Wolff, M.; Djedaini, K.; Cohen, Y.; Chastre, J.; Delclaux, C. Multicenter prospective study of ventilator-associated pneumonia during acute respiratory distress syndrome. Incidence, prognosis, and risk factors. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, F.; Franceschini, B.; Berger, P.; Arnal, J.M.; Gainnier, M.; Sainty, J.M.; Papazian, L. Early antibiotic treatment for BAL-confirmed ventilator-associated pneumonia: A role for routine endotracheal aspirate cultures. Chest 2005, 127, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moine, P.; Timsit, J.F.; De Lassence, A.; Troché, G.; Fosse, J.P.; Alberti, C.; Cohen, Y. Mortality associated with late-onset pneumonia in the intensive care unit: Results of a multi-center cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myny, D.; Depuydt, P.; Colardyn, F.; Blot, S. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in a tertiary care ICU analysis of risk factors for acquisition and mortality. Acta Clin. Belg. 2005, 60, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguile-Makao, M.; Zahar, J.R.; Français, A.; Tabah, A.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Allaouchiche, B.; Goldgran-Toledano, D.; Azoulay, E.; Adrie, C.; Jamali, S.; et al. Attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia: Respective impact of main characteristics at ICU admission and VAP onset using conditional logistic regression and multi-state models. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.L.; Røder, B.; Magnussen, P.; Engquist, A.; Frimodt-møller, N. Nosocomial pneumonia in an intensive care unit in a Danish university hospital: Incidence, mortality and etiology. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 24, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nseir, S.; Di Pompeo, C.; Soubrier, S.; Cavestri, B.; Jozefowicz, E.; Saulnier, F.; Durocher, A. Impact of ventilator-associated pneumonia on outcome in patients with COPD. Chest 2005, 128, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papazian, L.; Bregeon, F.; Thirion, X.; Gregoire, R.; Saux, P.; Denis, J.P.; Perin, G.; Charrel, J.; Dumon, J.F.; Affray, J.P.; et al. Effect of ventilator-associated pneumonia on mortality and morbidity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reusser, P.; Zimmerli, W.; Scheidegger, D.; Marbet, G.A.; Buser, M.; Gyr, K. Role of gastric colonization in nosocomial infections and endotoxemia: A prospective study in neurosurgical patients on mechanical ventilation. J. Infect. Dis. 1989, 160, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stéphan, F.; Mabrouk, N.; Decailliot, F.; Delclaux, C.; Legrand, P. Ventilator-associated pneumonia leading to acute lung injury after trauma: Importance of Haemophilus influenzae. Anesthesiology 2006, 104, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timsit, J.F.; Chevret, S.; Valcke, J.; Misset, B.; Renaud, B.; Goldstein, F.W.; Vaury, P.; Carlet, J. Mortality of nosocomial pneumonia in ventilated patients: Influence of diagnostic tools. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouillet, J.L.; Chastre, J.; Vuagnat, A.; Joly-Guillou, M.L.; Combaux, D.; Dombret, M.C.; Gibert, C. Ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by potentially drug-resistant bacteria. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhems, P.; Bénet, T.; Voirin, N.; Januel, J.M.; Lepape, A.; Allaouchiche, B.; Argaud, L.; Chassard, D.; Guérin, C. Early-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia incidence in intensive care units: A surveillance-based study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhamme, K.M.; De Coster, W.; De Roo, L.; De Beenhouwer, H.; Nollet, G.; Verbeke, J.; Demeyer, I.; Jordens, P. Pathogens in early-onset and late-onset intensive care unit–acquired pneumonia. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2007, 28, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woske, H.J.; Röding, T.; Schulz, I.; Lode, H. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in a surgical intensive care unit Epidemiology, etiology and comparison of three bronchoscopic methods for microbiological specimen sampling. Crit. Care 2001, 5, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahar, J.R.; Nguile-Makao, M.; Français, A.; Schwebel, C.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Goldgran-Toledano, D.; Azoulay, E.; Thuong, M.; Jamali, S.; Cohen, Y.; et al. Predicting the risk of documented ventilator-associated pneumonia for benchmarking: Construction and validation of a score. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 2545–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Lerma, F. ICU-acquired Pneumonia Study Group. Modification of empiric antibiotic treatment in patients with pneumonia acquired in the intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, M.; Moro, M.L.; Capelli, O.; De Blasi, R.A.; D’Errico, R.R.; Conti, G.; Bufi, M.; Gasparetto, A. Risk factors for early onset pneumonia in trauma patients. Chest 1994, 105, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolopoulou, E.; Bakakos, P.; Katostaras, T.; Gregorakos, L. Incidence and risk factors for ventilator-associated pneumonia in 4 multidisciplinary intensive care units in Athens, Greece. Respir. Care 2003, 48, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouza, E.; Pérez, A.; Muñoz, P.; Perez, M.J.; Rincón, C.; Sánchez, C.; Martín-Rabadán, P.; Riesgo, M.; Cardiovascular Infection Study Group. Ventilator-associated pneumonia after heart surgery: A prospective analysis and the value of surveillance. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 1964–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcanti, M.; Ferrer, M.; Ferrer, R.; Morforte, R.; Garnacho, A.; Torres, A. Risk and prognostic factors of ventilator-associated pneumonia in trauma patients. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cendrero, J.A.; Solé-Violán, J.; Benitez, A.B.; Catalán, J.N.; Fernández, J.A.; Santana, P.S.; de Castro, F.R. Role of different routes of tracheal colonization in the development of pneumonia in patients receiving mechanical ventilation. Chest 1999, 116, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaari, A.; El Habib, M.; Ghdhoun, H.; Algia, N.B.; Chtara, K.; Hamida, C.B.; Chelly, H.; Bahloul, M.; Bouaziz, M. Does low-dose hydrocortisone therapy prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia in trauma patients? Am. J. Ther. 2015, 22, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Latorre, F.J.; Pont, T.; Ferrer, A.; Rosselló, J.; Palomar, M.; Planas, M. Pattern of tracheal colonization during echanical ventilation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewig, S.; Torres, A.; El-Ebiary, M.; Fàbregas, N.; Hernandez, C.; Gonzalez, J.; Nicolas, J.M.; Soto, L. Bacterial colonization patterns in mechanically ventilated patients with traumatic and medical head injury. Incidence, risk factors, and association with ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortal, J.; Giannella, M.; Pérez, M.J.; Barrio, J.M.; Desco, M.; Bouza, E.; Muñoz, P. Incidence and risk factors for ventilator-associated pneumonia after major heart surgery. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, J.; Peñafiel, A.; Marsé, P.; Jordá, R.; Raurich, J.M.; Mata, F. Incidence of gastroesophageal reflux and aspiration in mechanically ventilated patients using small-bore nasogastric tubes. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2000, 24, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, P.A.; Torres, A.; Rodríguez-Roisin, R.O.; Aznar, R.; Gatell, J.M.; Agusti-Vidal, A. Incidence and etiology of pneumonia acquired during mechanical ventilation. Crit. Care Med. 1989, 17, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallel, H.; Chelly, H.; Bahloul, M.; Ksibi, H.; Dammak, H.; Chaari, A.; Hamida, C.B.; Rekik, N.; Bouaziz, M. The effect of ventilator-associated pneumonia on the prognosis of head trauma patients. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2005, 59, 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Piazza, O.; Iasiello, A.; PapaIanni, C.; De Robertis, E.; Servillo, G.; Rossano, F.; Tufano, R. Incidence of antimicrobial-resistant ventilator-associated pneumonia: An eighteen-month survey. Panminerva Med. 2005, 47, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raineri, E.; Crema, L.; Dal Zoppo, S.; Acquarolo, A.; Pan, A.; Carnevale, G.; Albertario, F.; Candiani, A. Rotation of antimicrobial therapy in the intensive care unit: Impact on incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, P.; Lopez-Ferraz, C.; Gordon, M.; Gimeno, A.; Villarreal, E.; Ruiz, J.; Menendez, R.; Torres, A. From starting mechanical ventilation to ventilator-associated pneumonia, choosing the right moment to start antibiotic treatment. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, J.; Quintana, E.; Ausina, V.; Castella, J.; Luquin, M.; Net, A.; Prats, G. Incidence, etiology, and outcome of nosocomial pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients. Chest 1991, 100, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, J.; Ausina, V.; Castella, J.; Net, A.; Prats, G. Nosocomial respiratory tract infections in multiple trauma patients: Influence of level of consciousness with implications for therapy. Chest 1992, 102, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, J.; Sonora, R.; Jubert, P.; Artigas, A.; Rué, M.; Vallés, J. Pneumonia in intubated patients: Role of respiratory airway care. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, J.; Lorente, C.; Diaz, E.; Bodi, M.; Boque, C.; Sandiumenge, A.; Santamaria, J.M. Incidence, etiology, and outcome of nosocomial pneumonia in ICU patients requiring percutaneous tracheotomy for mechanical ventilation. Chest 2003, 124, 2239–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincón-Ferrari, M.D.; Flores-Cordero, J.M.; Leal-Noval, S.R.; Murillo-Cabezas, F.; Cayuelas, A.; Muñoz-Sánchez, M.A.; Sánchez-Olmedo, J.I. Impact of ventilator-associated pneumonia in patients with severe head injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2004, 57, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Santana, S.E.; García, A.J.; Esteban, A.N.; Guerra, L.; Alvarez, B.E.; Corcia, S.A.; Gudin, J.; Martinez, A.; Quintana, E.; Armengol, S. ICU pneumonias: A multi-institutional study. Crit. Care Med. 1987, 15, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofianou, D.C.; Constandinidis, T.C.; Yannacou, M.; Anastasiou, H.; Sofianos, E. Analysis of risk factors for ventilator-associated pneumonia in a multidisciplinary intensive care unit. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2000, 19, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamayo, E.; Álvarez, F.J.; Martínez-Rafael, B.; Bustamante, J.; Bermejo-Martin, J.F.; Fierro, I.; Eiros, J.M.; Castrodeza, J.; Heredia, M.; Gómez-Herreras, J.I.; et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia is an important risk factor for mortality after major cardiac surgery. J. Crit. Care 2012, 27, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artigas, A.T.; Dronda, S.B.; Vallés, E.C.; Marco, J.M.; Usón, M.C.; Figueras, P.; Suarez, F.J.; Hernandez, A. Risk factors for nosocomial pneumonia in critically ill trauma patients. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Aznar, R.; Gatell, J.M.; Jiménez, P.; González, J.; Ferrer, A.; Celis, R.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R. Incidence, risk, and prognosis factors of nosocomial pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1990, 142, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urli, T.; Perone, G.; Acquarolo, A.; Zappa, S.; Antonini, B.; Candiani, A. Surveillance of infections acquired in intensive care: Usefulness in clinical practice. J. Hosp. Infect. 2002, 52, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles, J.; Pobo, A.; Garcia-Esquirol, O.; Mariscal, D.; Real, J.; Fernandez, R. Excess ICU mortality attributable to ventilator-associated pneumonia: The role of early vs. late onset. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violan, J.S.; Sanchez-Ramirez, C.; Mujica, A.P.; Cendrero, J.C.; Fernandez, J.A.; de Castro, F.R. Impact of nosocomial pneumonia on the outcome of mechanically-ventilated patients. Crit. Care 1998, 2, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apisarnthanarak, A.; Pinitchai, U.; Thongphubeth, K.; Yuekyen, C.; Warren, D.K.; Zack, J.E.; Warachan, B.; Fraser, V.J. Effectiveness of an educational program to reduce ventilator-associated pneumonia in a tertiary care center in Thailand: A 4-year study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallick, U.K.; Faruq, M.O.; Ahsan, A.A.; Fatema, K.; Ahmed, F.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Islam, M.; Sultana, A. Spectrum of Early Onset and Late Onset Ventilator Associated Pneumonia (VAP) in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Bangladesh: A Prospective Cohort Study. Bangladesh Crit. Care J. 2015, 3, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Noor, A.; Hussain, S.F. Risk factors associated with development of ventilator-associated pneumonia. J. Coll. Phys. Surg. Pak. 2005, 15, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, M.; Mehta, Y.; Khurana, P.; Chaudhary, A.; Kulkarni, V.; Trehan, N. Ventilator-associated pneumonia: Incidence, risk factors, outcome, and microbiology. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2003, 17, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahuddin, N.; Zafar, A.; Sukhyani, L.; Rahim, S.; Noor, M.F.; Hussain, K.; Siddiqui, S.; Islam, M.; Husain, S.J. Reducing ventilator-associated pneumonia rates through a staff education programme. J. Hosp. Infect. 2004, 57, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Zhu, S.; Yan, D.; Chen, W.; Chen, R.; Zou, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Farmakiotis, D.; Mylonakis, E. Candida spp. airway colonization: A potential risk factor for Acinetobacter baumannii ventilator-associated pneumonia. Sabouraudia 2016, 54, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Hu, B.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Gao, X.; He, L. Device-associated infection rates in 398 intensive care units in Shanghai, China: International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC) findings. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e774–e780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Hu, B.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; He, L. Impact of a multidimensional approach on ventilator-associated pneumonia rates in a hospital of Shanghai: Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium. J. Crit. Care 2012, 27, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongpiyapoom, S.; Narong, M.N.; Suwalak, N.; Jamulitrat, S.; Intaraksa, P.; Boonrat, J.; Kasatpibal, N.; Unahalekhaka, A. Device-associated infections and patterns of antimicrobial resistance in a medical-surgical intensive care unit in a university hospital in Thailand. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2004, 87, 819–824. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.S.; Xiong, W.; Lai, R.P.; Liu, L.; Gan, X.M.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, M.; Lou, Y.X.; Fu, X.Y.; Wang, H.F.; et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in intensive care units in Hubei Province, China: A multicentre prospective cohort survey. J. Hosp. Infect. 2011, 78, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertugrul, B.M.; Yildirim, A.; Ay, P.; Oncu, S.; Cagatay, A.; Cakar, N.; Ertekin, C.; Ozsut, H.; Eraksoy, H.; Calangu, S. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in surgical emergency intensive care unit. Saudi Med. J. 2006, 27, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gursel, G.; Aydogdu, M.; Nadir Ozis, T.; Tasyurek, S. Comparison of the value of initial and serial endotracheal aspirate surveillance cultures in predicting the causative pathogen of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 42, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, S.; Chang, R.W.; Lee, B.; Bartlett, F.W. Continuous enteral feeding: A major cause of pneumonia among ventilated intensive care unit patients. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1990, 14, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahani-Sherafat, S.; Razaghi, M.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Tajeddin, E.; Seyedjavadi, S.; Rashidan, M.; Alebouyeh, M.; Rostampour, M.; Haghi, A.; Sayarbayat, M.; et al. Device-associated infection rates and bacterial resistance in six academic teaching hospitals of Iran: Findings from the International Nocosomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC). J. Infect. Public Health 2015, 8, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanafani, Z.A.; Kara, L.; Hayek, S.; Kanj, S.S. Ventilator-associated pneumonia at a tertiary-care center in a developing country: Incidence, microbiology, and susceptibility patterns of isolated microorganisms. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2003, 24, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leblebicioglu, H.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Arıkan, Ö.A.; Özgültekin, A.; Yalcin, A.N.; Koksal, I.; Usluer, G.; Sardan, Y.C.; Ulusoy, S. Device-associated hospital-acquired infection rates in Turkish intensive care units. Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC). J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 65, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblebicioglu, H.; Yalcin, A.N.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Koksal, I.; Sirmatel, F.; Unal, S.; Turgut, H.; Ozdemir, D.; Ersoz, G.; Uzun, C.; et al. Effectiveness of a multidimensional approach for prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia in 11 adult intensive care units from 10 cities of Turkey: Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC). Infection 2013, 41, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memish, Z.A.; Cunningham, G.; Oni, G.A.; Djazmati, W. The incidence and risk factors of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a Riyadh hospital. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2000, 21, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezai, M.S.; Bagheri-Nesami, M.; Nikkhah, A.; Bayg, A.H. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of ventilator-associated Pneumonia in 18 hospitals of Iran. Running title: Ventilator-associated pneumonia in Iran. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res. 2016, 7, 936–946. [Google Scholar]
- Şimşek, S.; Yurtseven, N.; Gercekogalu, H.; Izgi, F.; Sohtorik, Ü.; Canik, S.; Özler, A. Ventilator-associated pneumonias in a cardiothoracic surgery centre postoperative intensive care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2001, 47, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, D.E.; Hershow, R.C.; Ramirez, C.A.; Weinstein, R.A. Control of nosocomial infections in an intensive care unit in Guatemala City. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guanche-Garcell, H.; Morales-Perez, C.; Rosenthal, V.D. Effectiveness of a multidimensional approach for the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia in an adult intensive care unit in Cuba: Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC). J. Infect. Public Health 2013, 6, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, M.M.; Rocco, J.R. Prevalence of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a university hospital and prognosis for the patients affected. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2006, 32, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes, F.; De La Rosa, G.; Gómez, E.; Múnera, P.; Ramírez, J.; Castrillón, S. Incidence and risk factors for ventilator-associated pneumonia in a developing country Where is the difference? Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, C.M.; Blanzaco, D.; Niederman, M.S.; Matarucco, W.; Baredes, N.C.; Desmery, P.; Palizas, F.; Menga, G.; Rios, F.; Apezteguia, C. Resolution of ventilator-associated pneumonia: Prospective evaluation of the clinical pulmonary infection score as an early clinical predictor of outcome. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, C.A.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Olarte, N.; Gomez, W.V.; Sussmann, O.; Agudelo, J.G.; Rojas, C.; Osorio, L.; Linares, C.; Valderrama, A.; et al. Device-associated infection rate and mortality in intensive care units of 9 Colombian hospitals: Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium. Infect. Control 2006, 27, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, M.M.; Monteiro, S.G.; Callegari, B.; Figueiredo, P.M.; Monteiro, C.R.; Monteiro-Neto, V. Epidemiology and outcomes of ventilator-associated pneumonia in northern Brazil: An analytical descriptive prospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, P.M.; Neto, C.; Santos, L.R.; Knibel, M.F. Ventilator-associated pneumonia: Epidemiology and impact on the clinical evolution of ICU patients. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2009, 35, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.M.; Meredith, J.W.; Haponik, E.F. Pneumonia in intubated trauma patients. Microbiology and outcomes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochicchio, G.V.; Joshi, M.; Bochicchio, K.; Tracy, K.; Scalea, T.M. A time-dependent analysis of intensive care unit pneumonia in trauma patients. J. Trauma 2004, 56, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, S.R.; Levin, A.B.; Clark, K.L. Role of corticosteroids in the development of pneumonia in mechanically ventilated head-trauma victims. Crit. Care Med. 1986, 14, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.; Norwood, S.; Berne, J. Ventilator-associated pneumonia is more common and of less consequence in trauma patients compared with other critically ill patients. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2010, 69, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, D.E.; Kunches, L.M.; Lichtenberg, D.A.; Kollisch, N.R.; Barry, M.A.; Heeren, T.C.; McCabe, W.R. Nosocomial infection and fatality in medical and surgical intensive care unit patients. Arch. Intern. Med. 1988, 148, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensminger, S.A.; Wright, R.S.; Baddour, L.M.; Afess, B. Suspected ventilator-associated pneumonia in cardiac patients admitted to the coronary care unit. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2006, 81, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, H.L.; Zonies, D.H.; Warner, K.J.; Bulger, E.M.; Sharar, S.R.; Maier, R.V.; Cuschieri, J. Timing of intubation and ventilator-associated pneumonia following injury. Arch. Surg. 2010, 145, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, D.L.; Falk, P.S.; Wunderink, R.G.; Leeper Jr, K.V.; Meduri, G.U.; Steere, E.L.; Glen Mayhall, C. Epidemiology of ventilator-acquired pneumonia based on protected bronchoscopic sampling. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyland, D.K.; Cook, D.J.; Griffith, L.; Keenan, S.P.; Brun-Buisson, C. The attributable morbidity and mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia in the critically ill patient. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, E.H.; Ward, S.; Sherman, G.; Kollef, M.H. A comparative analysis of patients with early-onset vs late-onset nosocomial pneumonia in the ICU setting. Chest 2000, 117, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, E.H.; Hill, C.; Fraser, V.; Kollef, M.H. The Occurrence Of Ventilator-associated Pneumonia (vap) In A Community Hospital: Risk Factors And Clinical Outcomes. Chest 2000, 118, 555–561. [Google Scholar]
- Kasuya, Y.; Hargett, J.L.; Lenhardt, R.; Heine, M.F.; Doufas, A.G.; Remmel, K.S.; Ramirez, J.A.; Akça, O. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill stroke patients: Frequency, risk factors, and outcomes. J. Crit. Care 2011, 26, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollef, M.H. Ventilator-associated pneumonia. A multivariate analysis. JAMA 1993, 270, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollef, M.H.; Silver, P.; Murphy, D.M.; Trovillion, E. The effect of late-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia in determining patient mortality. Chest 1995, 108, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollef, M.H.; Vlasnik, J.O.; Sharpless, L.; Pasque, C.; Murphy, D.; Fraser, V. Scheduled change of antibiotic classes: A strategy to decrease the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollef, M.H.; Shapiro, S.D.; Von Harz, B.; Prentice, D.; John, R.S.; Silver, P.; Trovillion, E. Patient transport from intensive care increases the risk of developing ventilator-associated pneumonia. Chest 1997, 112, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koss, W.G.; Khalili, T.M.; Lemus, J.F.; Chelly, M.M. Nosocomial pneumonia is not prevented by protective contact isolation in the surgical intensive care unit. Am. Surg. 2001, 67, 1140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kunac, A.; Sifri, Z.C.; Mohr, A.M.; Horng, H.; Lavery, R.F.; Livingston, D.H. Bacteremia and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Marker for Contemporaneous Extra-Pulmonic Infection. Surg. Infect. 2014, 15, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Walker, V.; Chen, L.F.; Sexton, D.J.; Anderson, D.J. The epidemiology of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a network of community hospitals: A prospective multicenter study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2013, 34, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lowy, F.D.; Carlisle, P.S.; Adams, A.; Feiner, C. The incidence of nosocomial pneumonia following urgent endotracheal intubation. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1987, 8, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rello, J.; Ollendorf, D.A.; Oster, G.; Vera-Llonch, M.; Bellm, L.; Redman, R.; Kollef, M.H. Epidemiology and outcomes of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a large US database. Chest 2002, 122, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.L.; Gibbons, K.J.; Bitzer, L.G.; Dechert, R.E.; Steinberg, S.M.; Flint, L.M. Pneumonia: Incidence, risk factors, and outcome in injured patients. J. Trauma 1991, 31, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salata, R.A.; Lederman, M.M.; Shlaes, D.M.; Jacobs, M.R.; Eckstein, E.; Tweardy, D.; Toossi, Z.; Chmielewski, R.; Marino, J.; King, C.H. Diagnosis of nosocomial pneumonia in intubated, intensive care unit patients. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987, 135, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shahin, J.; Bielinski, M.; Guichon, C.; Flemming, C.; Kristof, A.S. Suspected ventilator-associated respiratory infection in severely ill patients: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boots, R.J.; Phillips, G.E.; George, N.; Faoagali, J.L. Surveillance culture utility and safety using low-volume blind bronchoalveolar lavage in the diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Respirology 2008, 13, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cade, J.F.; McOwat, E.; Siganporia, R.; Keighley, C.; Presneill, J.; Sinickas, V. Uncertain relevance of gastric colonization in the seriously ill. Intensive Care Med. 1992, 18, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potgieter, P.D.; Linton, D.M.; Oliver, S.; Forder, A.A. Nosocomial infections in a respiratory intensive care unit. Crit. Care Med. 1987, 15, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chastre, J.; Fagon, J.Y. Ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 867–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulenti, D.; Lisboa, T.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Krueger, W.; Macor, A.; Sole-Violan, J.; Diaz, E.; Topeli, A.; DeWaele, J.; Carneiro, A.; et al. Spectrum of practice in the diagnosis of nosocomial pneumonia in patients requiring mechanical ventilation in European intensive care units. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 2360–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollef, M.H.; Shorr, A.; Tabak, Y.P.; Gupta, V.; Liu, L.Z.; Johannes, R.S. Epidemiology and outcomes of healthcare-associated pneumonia. Results from a large US database of culture-positive pneumonia. Chest 2005, 128, 3854–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, J.; Torres, A.; Ricart, M.; Valles, J.; Gonzalez, J.; Artigas, A.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R. Ventilator-associated pneumonia by Staphylococcus aureus. Comparison of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive episodes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulenti, D.; Tsigou, E.; Rello, J. Nosocomial pneumonia in 27 ICUs in Europe: Perspectives from the EU-VAP/CAP study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.C. World-wide variation in incidence of Acinetobacter associated ventilator-associated pneumonia: A meta-regression. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, J.; Sa-Borges, M.; Correa, H.; Leal, S.R.; Baraibar, J. Variations in etiology of ventilator-associated pneumonia across four treatment sites: Implications for antimicrobial prescribing practices. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.C. Severe Burns: Pathogenesis and Prevention of Infection. In Recent Clinical Techniques, Results, and Research in Wounds; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Safdar, N.; Dezfulian, C.; Collard, H.R.; Saint, S. Clinical and economic consequences of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 2184–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, H.R.; Saint, S.; Matthay, M.A. Prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia: An evidence-based systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melsen, W.G.; Rovers, M.M.; Bonten, M.J. Ventilator-associated pneumonia and mortality: A systematic review of observational studies. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arabi, Y.; Al-Shirawi, N.; Memish, Z.; Anzueto, A. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in adults in developing countries: A systematic review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Chen, B.; Li, W.; Yan, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y. Ventilator-associated pneumonia after cardiac surgery: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 3148–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, M.; Kääriäinen, M.; Kyngäs, H. Effectiveness of educational programmes in preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2013, 84, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Jin, A.; Wang, W.; Chen, R.; Zhan, S. Incidence, temporal trend and factors associated with ventilator-associated pneumonia in mainland China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrafiotis, M.; Siempos, I.I.; Ntaidou, T.K.; Falagas, M.E. Attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Tubercul. Lung Dis. 2011, 15, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruíz, M.; Torres, A.; Ewig, S.; Marcos, M.A.; Alcón, A.; LLedó, R.; Asenjo, M.A.; Maldonado, A. Noninvasive versus invasive microbial investigation in ventilator-associated pneumonia: Evaluation of outcome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.C. Unusually High Incidences of Staphylococcus aureus Infection within Studies of Ventilator Associated Pneumonia Prevention Using Topical Antibiotics: Benchmarking the Evidence Base. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.C. Ventilator Associated Pneumonia prevention methods using topical antibiotics: Herd protection or herd peril? Chest 2014, 146, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.C. The perfidious effect of topical placebo: A calibration of Staphylococcus aureus Ventilator Associated Pneumonia incidence within Selective Digestive Decontamination (SDD) studies versus the broader evidence base. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4524–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
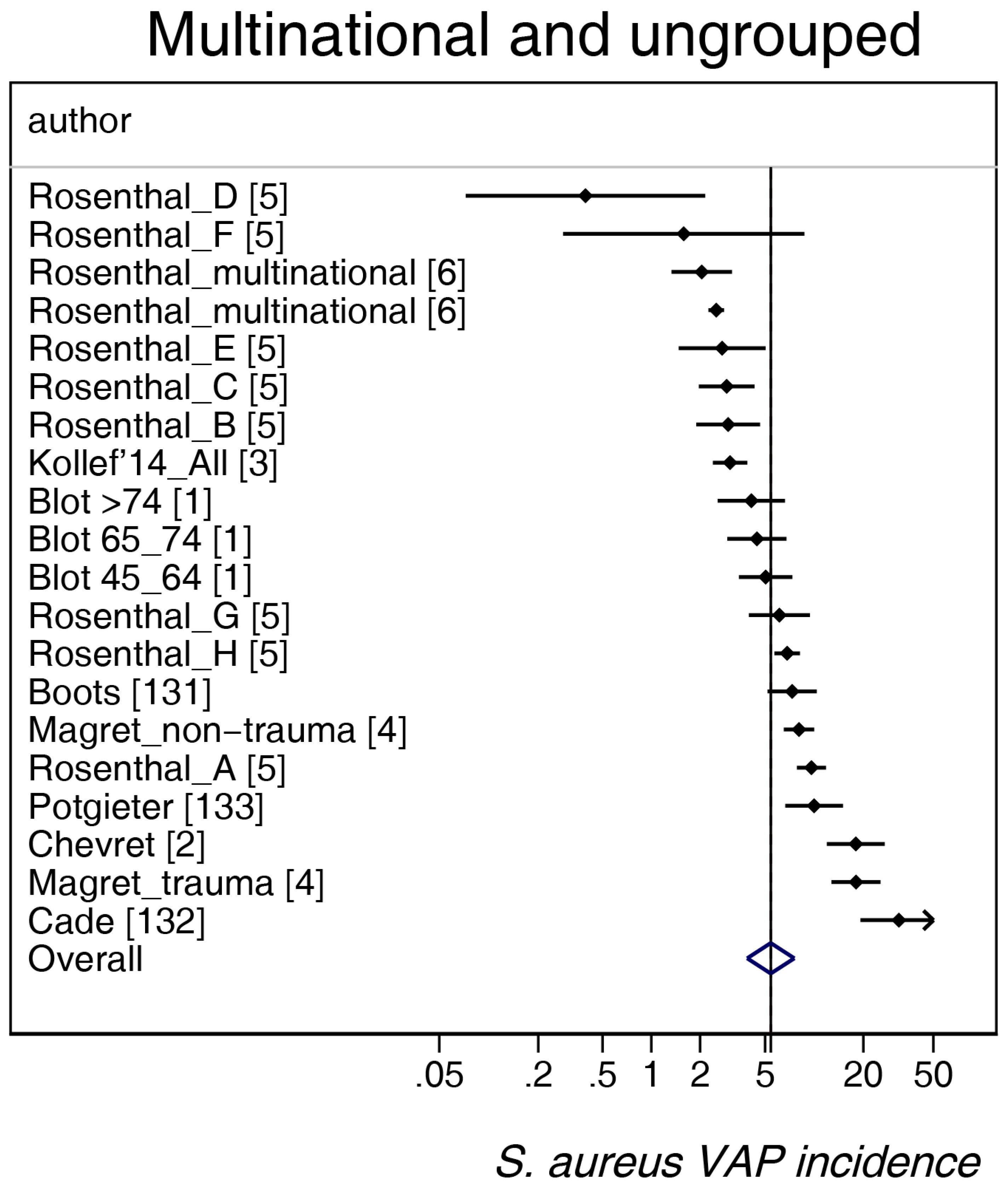
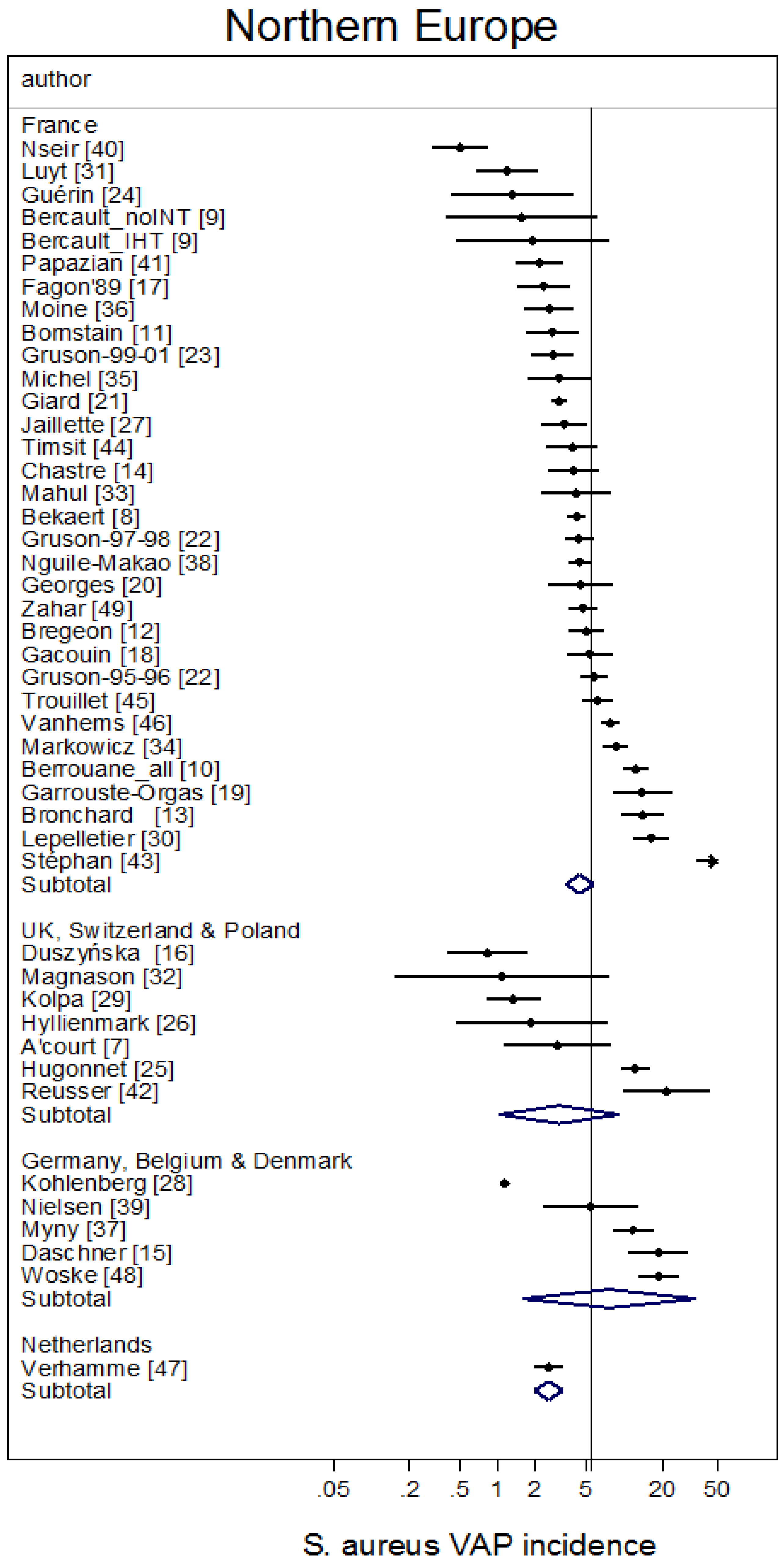
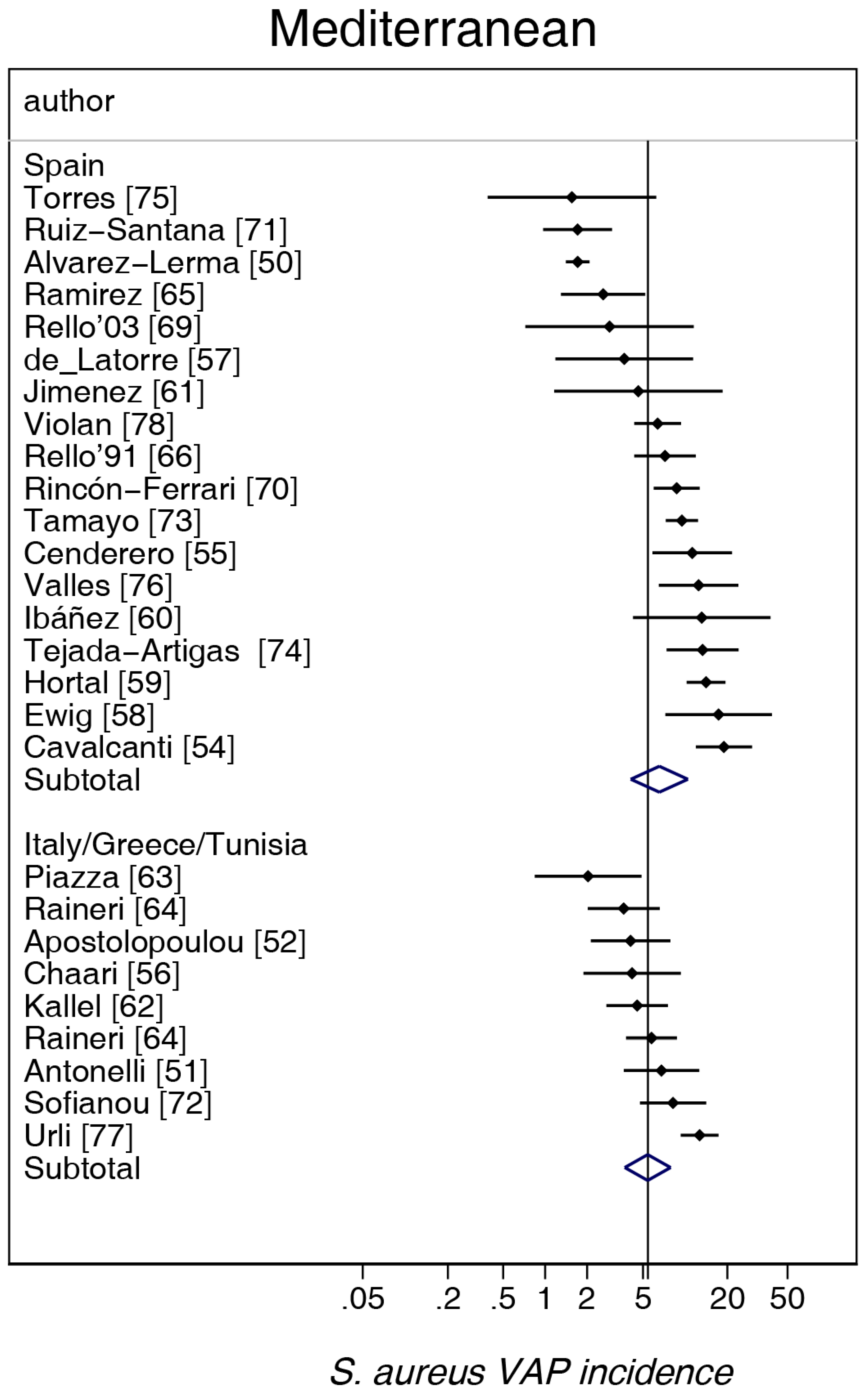

| Multinational and Ungrouped | Northern Europe b | Mediterranean c | Asia d | Middle East e | Central and South America f | USA/Canada g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources [ref] | [1,2,3,4,5,6,131,132,133] | [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] | [50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78] | [79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88] | [89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98] | [99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106] | [107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130] |
| Number of groups | 20 | 45 | 27 | 13 | 11 | 7 | 26 |
| Trauma ICUs h | 1 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| Bronchoscopic sampling i | 2 | 27 | 16 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 10 |
| Intervention period j | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Study publication year (range) | 1987–2014 | 1988–2018 | 1987–2016 | 2003–2016 | 1990–2017 | 2003–2013 | 1986–2014 |
| Numbers of patients per study group; median (IQR) | 1194; 411–2339 | 439; 175–1004 | 184; 101–318 | 618; 344–1076 | 448; 92–2584 | 274; 180–712 | 327; 223–521 |
| Duration of MV (days); median (IQR) | 7.4; 5–9.2 | 10.7; 8.0–13 | 8.0; 7–11 | 6.0; 2.5–9 | 9.8; 8.9–13.5 | 9.6; 7.6–10 | 6.0; 5–8 |
| VAP incidence per 1000 MV days | |||||||
| mean | 25.0 | 17.8 | 26.8 | 18.2 | 24.0 | 21.8 | 20.5 |
| 95% CI | 20.7–30.2 | 14.0–22.4 | 20.9–34.1 | 14.3–23.1 | 18.2–31.2 | 13.6–34.8 | 14.0–30.6 |
| S. aureus VAP incidence per 1000 MV days | |||||||
| mean | 5.4 | 4.4 | 6.1 | 2.1 | 4.9 | 3.5 | 5.1 |
| 95% CI | 3.9–7.5 | 3.2–6.1 | 4.4–8.5 | 1.5–3.0 | 3.3–7.3 | 2.4–5.0 | 3.2–8.0 |
| MRSA VAP incidence per 1000 MV days k | |||||||
| mean | 3.7 | 1.4 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 2.5 | ||
| 95% CI | 2.2–6.1 | 0.8–2.5 | 1.1–4.5 | 0.9–3.3 | 1.2–5.3 | ||
| n | 9 | 22 | 10 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 16 |
| Overall VAP | S. aureus VAP | MRSA VAP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | Coefficient b | 95% CI | p | Coefficient b | 95% CI | p | Coefficient b | 95% CI | p |
| Multinational and Ungrouped (reference group) | +3.60 | +3.12–+4.08 | +2.16 | +1.54–+2.79 | +1.99 | +0.68–+3.31 | |||
| Geographic region | |||||||||
| Northern Europe | −0.37 | −0.73–−0.01 | 0.05 | −0.27 | −0.74–+0.20 | 0.26 | −1.09 | −1.97–−0.21 | 0.02 |
| Mediterranean | −0.06 | −0.45–+0.34 | 0.78 | −0.12 | −0.63–+0.39 | 0.64 | −0.69 | −1.71–+0.33 | 0.18 |
| Asia | −0.23 | −0.69–+0.22 | 0.32 | −0.79 | −1.4–−0.18 | 0.01 | −0.75 | −1.95–+0.45 | 0.21 |
| Middle East | −0.04 | −0.51–+0.43 | 0.87 | −0.04 | −0.65–+0.56 | 0.88 | +0.95 | −0.66–+2.56 | 0.24 |
| Central and South America | −0.08 | −0.61–+0.44 | 0.76 | −0.45 | −1.17–+0.28 | 0.23 | −0.22 | −1.60–+1.16 | 0.75 |
| USA and Canada | −0.35 | −0.75–+0.05 | 0.08 | −0.33 | −0.83–+0.18 | 0.20 | −0.62 | −1.53–+0.29 | 0.18 |
| Trauma c | +0.38 | +0.07–+0.68 | 0.02 | +0.82 | +0.43–+1.21 | 0.001 | +0.29 | −0.43–+1.00 | 0.42 |
| Year of publication d | −0.01 | −0.03–+0.01 | 0.065 | −0.02 | −0.04–−0.01 | 0.04 | −0.02 | −0.06–+0.02 | 0.26 |
| Mode of diagnosis e | −0.07 | −0.31–+0.16 | 0.53 | +0.01 | −0.30–+0.31 | 0.95 | +0.13 | −0.44–+0.70 | 0.65 |
| Intervention period f | −0.35 | −0.74–+0.04 | 0.075 | −0.50 | −1.03–+0.04 | 0.068 | −0.54 | −1.67–+1.58 | 0.34 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hurley, J.C. World-Wide Variation in Incidence of Staphylococcus aureus Associated Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Meta-Regression. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6010018
Hurley JC. World-Wide Variation in Incidence of Staphylococcus aureus Associated Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Meta-Regression. Microorganisms. 2018; 6(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleHurley, James C. 2018. "World-Wide Variation in Incidence of Staphylococcus aureus Associated Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Meta-Regression" Microorganisms 6, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6010018
APA StyleHurley, J. C. (2018). World-Wide Variation in Incidence of Staphylococcus aureus Associated Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Meta-Regression. Microorganisms, 6(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6010018





