Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy is Ineffective as an Adjuvant to Daptomycin with Rifampicin Treatment in a Murine Model of Staphylococcus aureus in Implant-Associated Osteomyelitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolate
2.2. Generation of Pathogenic Challenge
2.3. Murine Model
2.3.1. Study Design
2.3.2. Experimental Murine Model
2.4. Animal Welfare
2.5. Protocol for In Vivo Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
2.6. Antibiotic Treatment
2.7. Post Mortem Analysis
2.8. Serologicalbone Formation and Resorption Biomarkers
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
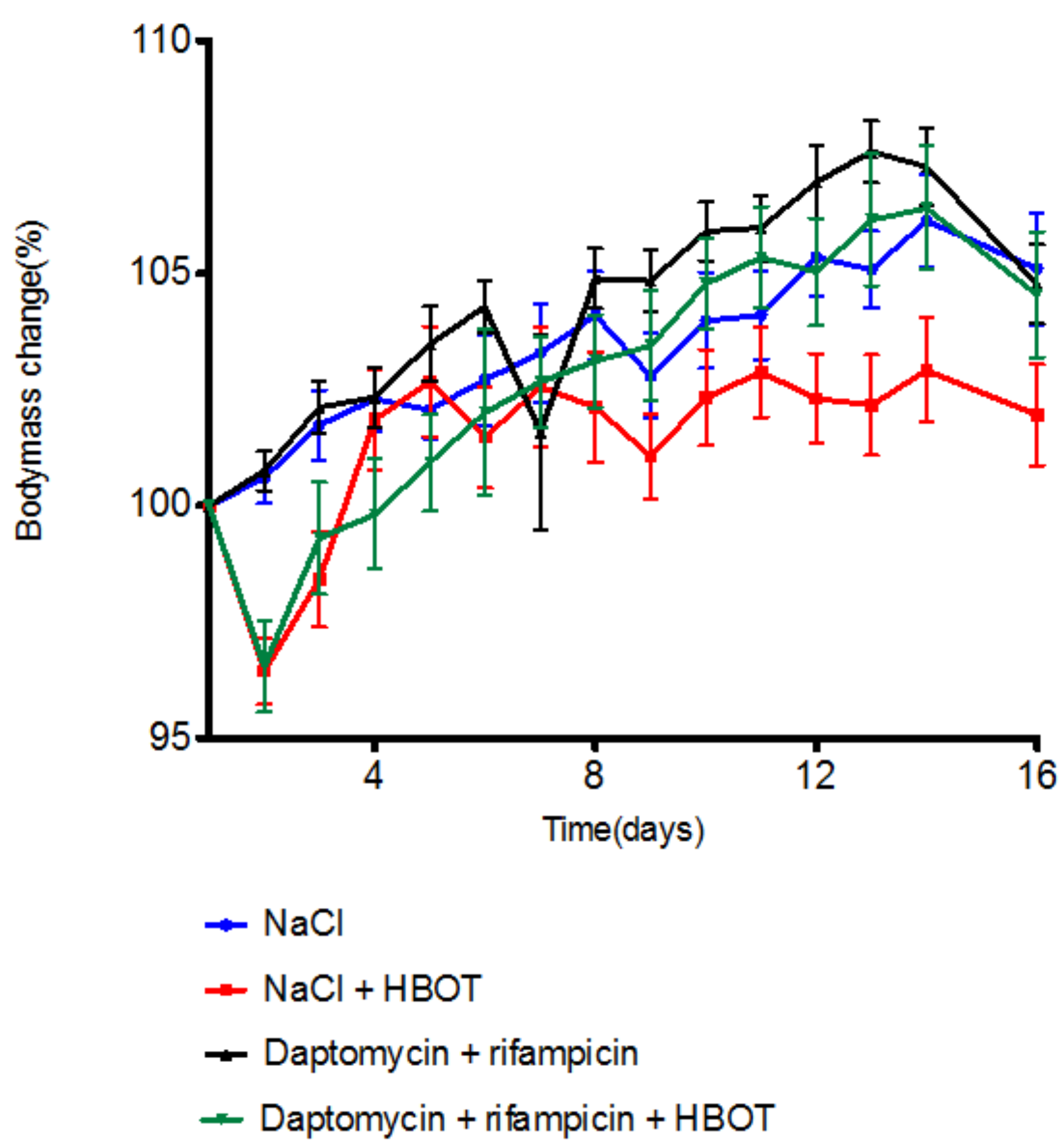
3.1. HBOT Leads to Initial Loss in Body Mass, but Animals Regain Mass within Days
3.2. HBOT Treatment Reduces Abscess Signs
3.3. HBOT Treatment Does Not Improve the Outcome from Antibiotic Therapy
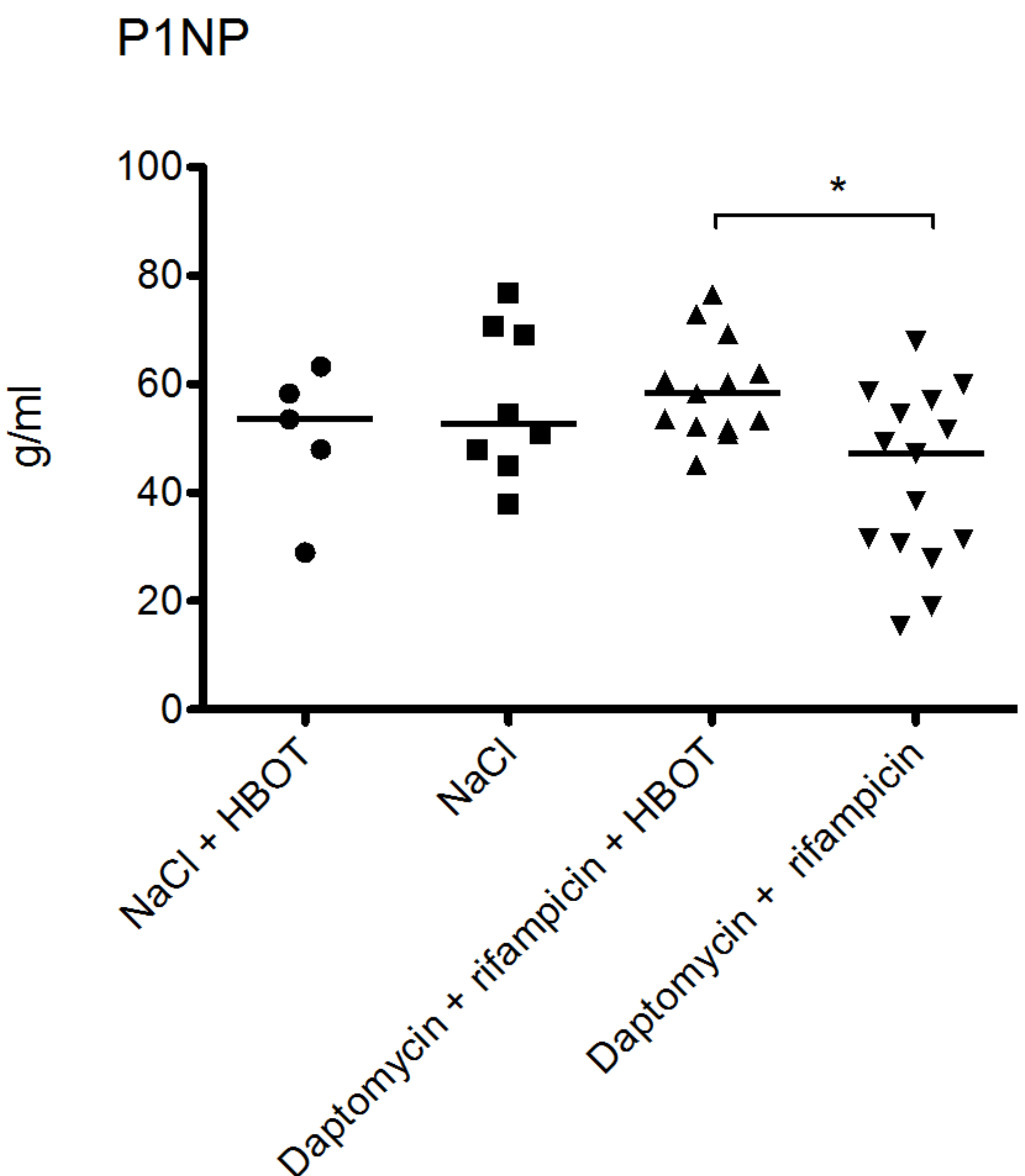
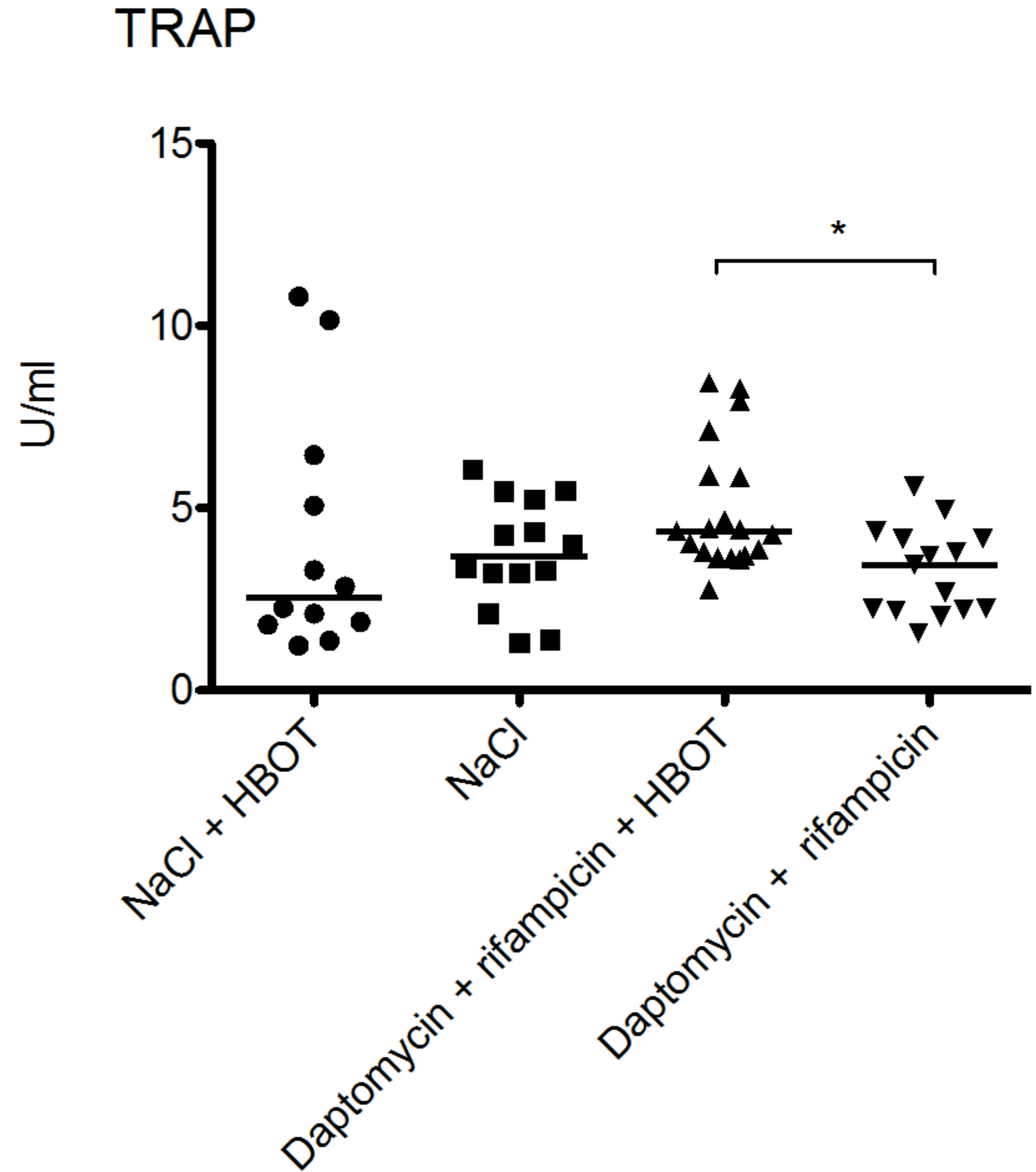
3.4. HBOT Leads to Elevated Bone Turnover in Animals Treated with Antibiotics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arciola, C.R.; An, Y.H.; Campoccia, D.; Donati, M.E.; Montanaro, L. Etiology of implant orthopedic infections: A survey on 1027 clinical isolates. Int. J. Artif Organs 2005, 28, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brady, R.A.; Leid, J.G.; Calhoun, J.H.; Costerton, J.W.; Shirtliff, M.E. Osteomyelitis and the role of biofilms in chronic infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 52, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal biofilms. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 322, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Watson, H.; Schmier, J.K.; Parvizi, J. Economic burden of periprosthetic joint infection in the United States. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, H.; Fenstad, A.M.; Hallan, G.; Havelin, L.I.; Furnes, O.; Overgaard, S.; Pedersen, A.B.; Karrholm, J.; Garellick, G.; Pulkkinen, P.; et al. Increasing risk of prosthetic joint infection after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2012, 83, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundtoft, P.H.; Pedersen, A.B.; Schonheyder, H.C.; Moller, J.K.; Overgaard, S. One-year incidence of prosthetic joint infection in total hip arthroplasty: A cohort study with linkage of the danish hip arthroplasty register and danish microbiology databases. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, K.F.; Vuong, C.; Otto, M. Staphylococcus quorum sensing in biofilm formation and infection. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beenken, K.E.; Dunman, P.M.; McAleese, F.; Macapagal, D.; Murphy, E.; Projan, S.J.; Blevins, J.S.; Smeltzer, M.S. Global gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 4665–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izano, E.A.; Amarante, M.A.; Kher, W.B.; Kaplan, J.B. Differential roles of poly-n-acetylglucosamine surface polysaccharide and extracellular DNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A.; Ochsner, P.E. Prosthetic-joint infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic implant-associated infection. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the united states from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tande, A.J.; Patel, R. Prosthetic joint infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 302–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Bassi, G.L.; Coenye, T.; Donelli, G.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Hola, V.; Imbert, C.; Kirketerp-Moller, K.; et al. ESCMID guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of biofilm infections 2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, S1–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, J.T.; Guckian, J.C.; Glass, D.L.; Reinarz, J.A. Therapy with hyperbaric oxygen for experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in rabbits. J. Infect. Dis. 1978, 138, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esterhai, J.L., Jr.; Clark, J.M.; Morton, H.E.; Smith, D.W.; Steinbach, A.; Richter, S.D. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen exposure on oxygen tension within the medullary canal in the rabbit tibial osteomyelitis model. J. Orthop. Res. 1986, 4, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbles, P.M.; Edelsberg, J.S. Hyperbaric-oxygen therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, V.; Reichert, B.; Simanowski, H.J.; Scholz, H.C. Therapy with hyperbaric oxygen and cefazolin for experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in rats. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 1999, 26, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shandley, S.; Matthews, K.P.; Cox, J.; Romano, D.; Abplanalp, A.; Kalns, J. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in a mouse model of implant-associated osteomyelitis. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, N.B. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: 1999 Committee Report; Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society: Kensington, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Knighton, D.R.; Halliday, B.; Hunt, T.K. Oxygen as an antibiotic. The effect of inspired oxygen on infection. Arch. Surg 1984, 119, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, S.R. Oxidative stress is fundamental to hyperbaric oxygen therapy. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, D.; van Bruggen, R.; Meischl, C. Oxidative killing of microbes by neutrophils. Microbes. Infect. 2003, 5, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, J.T.; Brown, G.L.; Guckian, J.C.; Wells, C.H.; Reinarz, J.A. A mechanism for the amelioration by hyperbaric oxygen of experimental staphylococcal osteomyelitis in rabbits. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 142, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolpen, M.; Mousavi, N.; Sams, T.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Ciofu, O.; Moser, C.; Kuhl, M.; Hoiby, N.; Jensen, P.O. Reinforcement of the bactericidal effect of ciprofloxacin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm by hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niska, J.A.; Shahbazian, J.H.; Ramos, R.I.; Francis, K.P.; Bernthal, N.M.; Miller, L.S. Vancomycin-rifampin combination therapy has enhanced efficacy against an experimental Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5080–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Manso, D.; del Prado, G.; Ortiz-Perez, A.; Manrubia-Cobo, M.; Gomez-Barrena, E.; Cordero-Ampuero, J.; Esteban, J. In vitro susceptibility to antibiotics of staphylococci in biofilms isolated from orthopaedic infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 41, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldoni, D.; Haschke, M.; Rajacic, Z.; Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A. Linezolid alone or combined with rifampin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in experimental foreign-body infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, A.K.; Baldoni, D.; Haschke, M.; Rentsch, K.; Schaerli, P.; Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A. Efficacy of daptomycin in implant-associated infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Importance of combination with rifampin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2719–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergidis, P.; Rouse, M.S.; Euba, G.; Karau, M.J.; Schmidt, S.M.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Patel, R. Treatment with linezolid or vancomycin in combination with rifampin is effective in an animal model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus foreign body osteomyelitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh-Mghir, A.; Muller-Serieys, C.; Dinh, A.; Massias, L.; Cremieux, A.C. Adjunctive rifampin is crucial to optimizing daptomycin efficacy against rabbit prosthetic joint infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4589–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, N.P.; Skovdal, S.M.; Meyer, R.L.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Fuursted, K.; Petersen, E. Rifampicin-containing combinations are superior to combinations of vancomycin, linezolid and daptomycin against Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infection in vivo and in vitro. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, N.P.; Meyer, R.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Fuursted, K.; Petersen, E. A modified chronic infection model for testing treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms on implants. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y.; Yanagihara, K.; Yamada, K.; Migiyama, Y.; Nagaoka, K.; Morinaga, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Imamura, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Miyazaki, T.; et al. In vivo efficacy of daptomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a mouse model of hematogenous pulmonary infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2841–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsemakers, W.J.; Emanuel, N.; Cohen, O.; Reichart, M.; Potapova, I.; Schmid, T.; Segal, D.; Riool, M.; Kwakman, P.H.; de Boer, L.; et al. A doxycycline-loaded polymer-lipid encapsulation matrix coating for the prevention of implant-related osteomyelitis due to doxycycline-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Control. Release 2015, 209, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contie, S.; Voorzanger-Rousselot, N.; Litvin, J.; Bonnet, N.; Ferrari, S.; Clezardin, P.; Garnero, P. Development of a new elisa for serum periostin: Evaluation of growth-related changes and bisphosphonate treatment in mice. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2010, 87, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohanski, M.A.; Dwyer, D.J.; Hayete, B.; Lawrence, C.A.; Collins, J.J. A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 2007, 130, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobritz, M.A.; Belenky, P.; Porter, C.B.; Gutierrez, A.; Yang, J.H.; Schwarz, E.G.; Dwyer, D.J.; Khalil, A.S.; Collins, J.J. Antibiotic efficacy is linked to bacterial cellular respiration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8173–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, J.N.; Alder, J.; Thorne, G.M.; Tally, F.P. Daptomycin: A lipopeptide antibiotic for the treatment of serious gram-positive infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, H.A.; Smerdon, G.; Fox, S.W. Osteoclastic resorptive capacity is suppressed in patients receiving hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergidis, P.; Schmidt-Malan, S.M.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Patel, R. Comparative activities of vancomycin, tigecycline and rifampin in a rat model of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmon, D.R.; Berbari, E.F.; Berendt, A.R.; Lew, D.; Zimmerli, W.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Rao, N.; Hanssen, A.; Wilson, W.R. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, e1–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| − | + | ++ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl + HBOT | 5 | 9 | 6 |
| NaCl | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| Daptomyicin + rifampicin + HBOT | 7 | 11 | 2 |
| Daptomyicin + rifampicin | 4 | 12 | 4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jørgensen, N.P.; Hansen, K.; Andreasen, C.M.; Pedersen, M.; Fuursted, K.; Meyer, R.L.; Petersen, E. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy is Ineffective as an Adjuvant to Daptomycin with Rifampicin Treatment in a Murine Model of Staphylococcus aureus in Implant-Associated Osteomyelitis. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms5020021
Jørgensen NP, Hansen K, Andreasen CM, Pedersen M, Fuursted K, Meyer RL, Petersen E. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy is Ineffective as an Adjuvant to Daptomycin with Rifampicin Treatment in a Murine Model of Staphylococcus aureus in Implant-Associated Osteomyelitis. Microorganisms. 2017; 5(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms5020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleJørgensen, Nis Pedersen, Kasper Hansen, Caroline Marie Andreasen, Michael Pedersen, Kurt Fuursted, Rikke L. Meyer, and Eskild Petersen. 2017. "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy is Ineffective as an Adjuvant to Daptomycin with Rifampicin Treatment in a Murine Model of Staphylococcus aureus in Implant-Associated Osteomyelitis" Microorganisms 5, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms5020021
APA StyleJørgensen, N. P., Hansen, K., Andreasen, C. M., Pedersen, M., Fuursted, K., Meyer, R. L., & Petersen, E. (2017). Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy is Ineffective as an Adjuvant to Daptomycin with Rifampicin Treatment in a Murine Model of Staphylococcus aureus in Implant-Associated Osteomyelitis. Microorganisms, 5(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms5020021








