Scorpion Venom-Derived Peptides: A New Weapon Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peptide Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Bacterial Strains
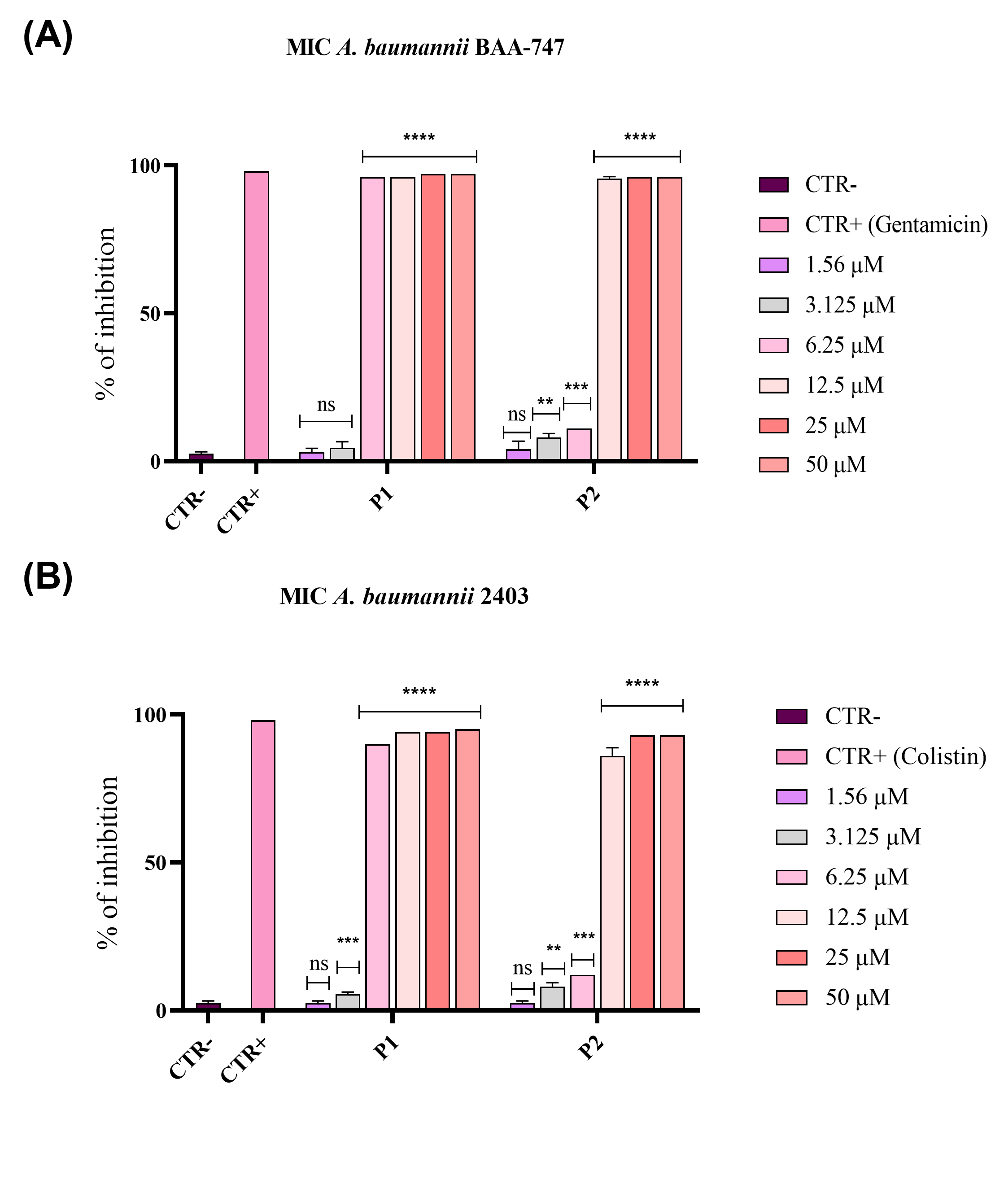
2.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC80) and Minimal Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) Determination
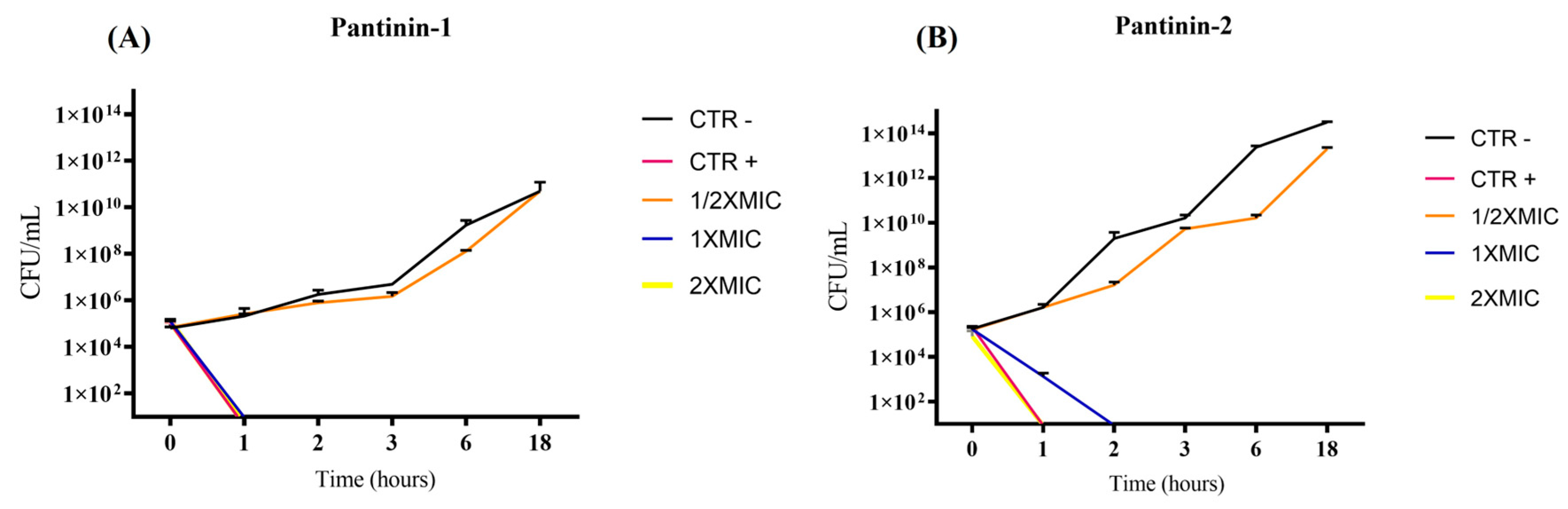
Time-Kill Kinetic Assay
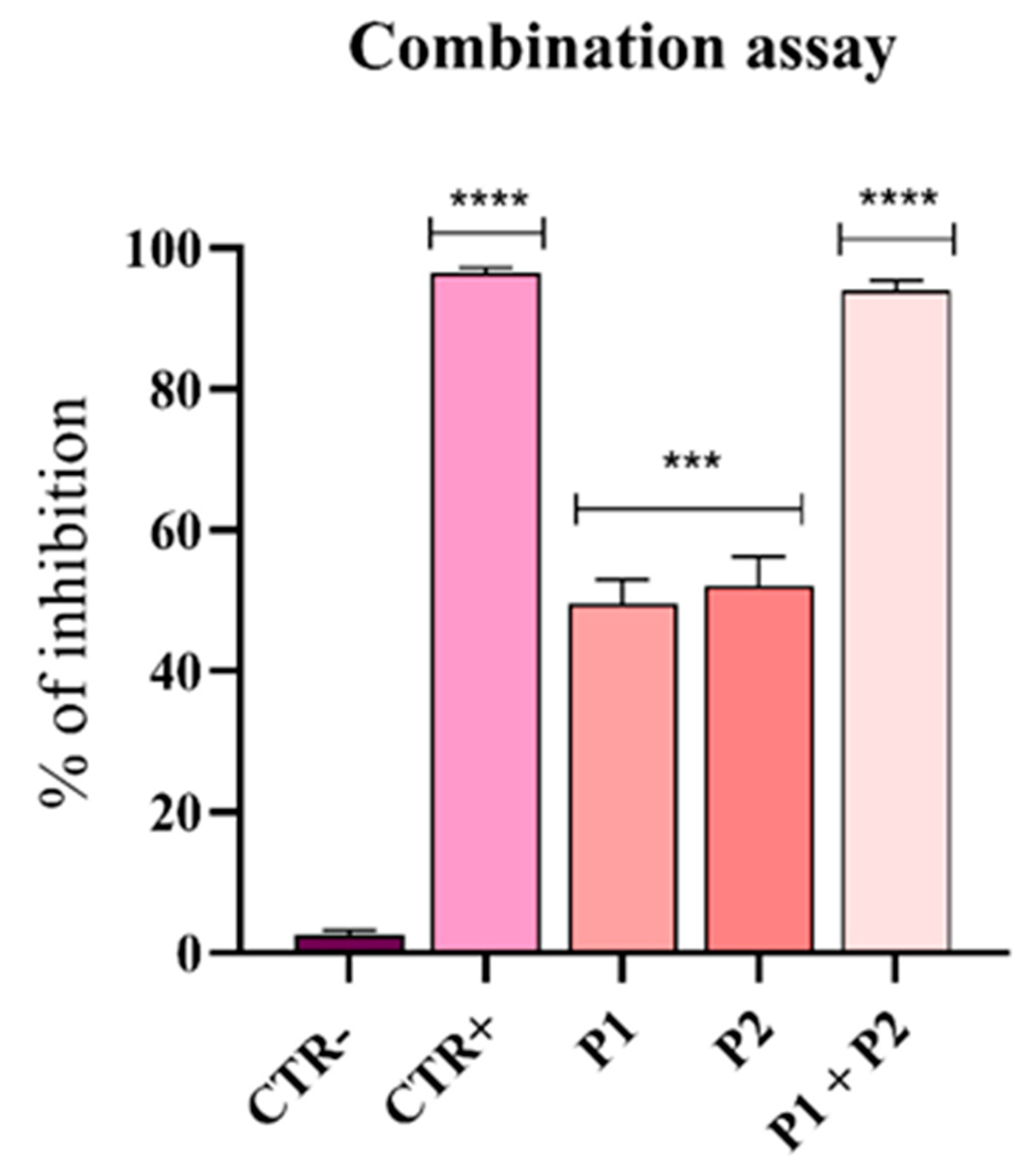
2.4. Synergism Assay
2.5. Antibiofilm Activity
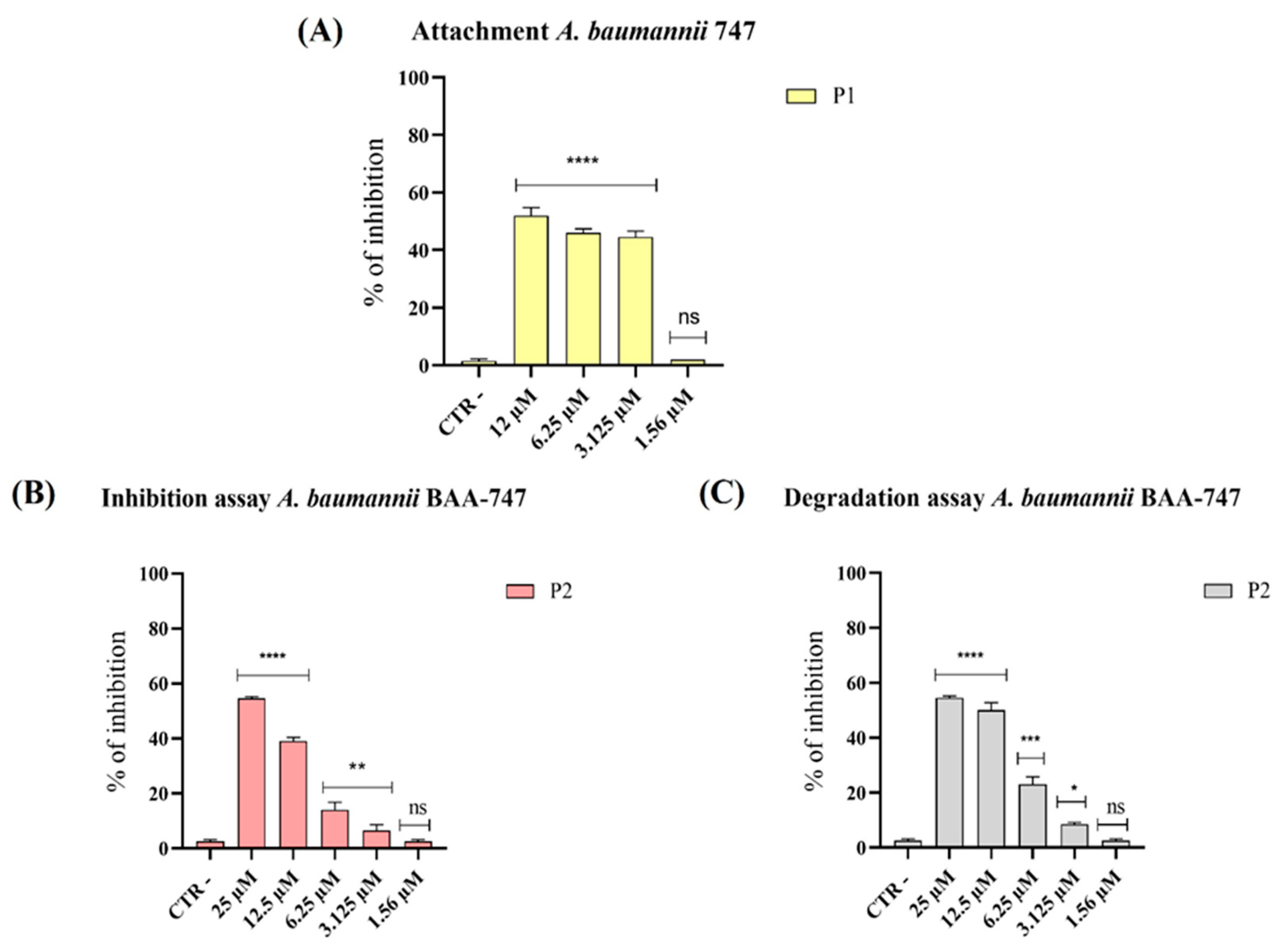
2.5.1. Biofilm Adhesion and Maturation
2.5.2. Biofilm Degradation
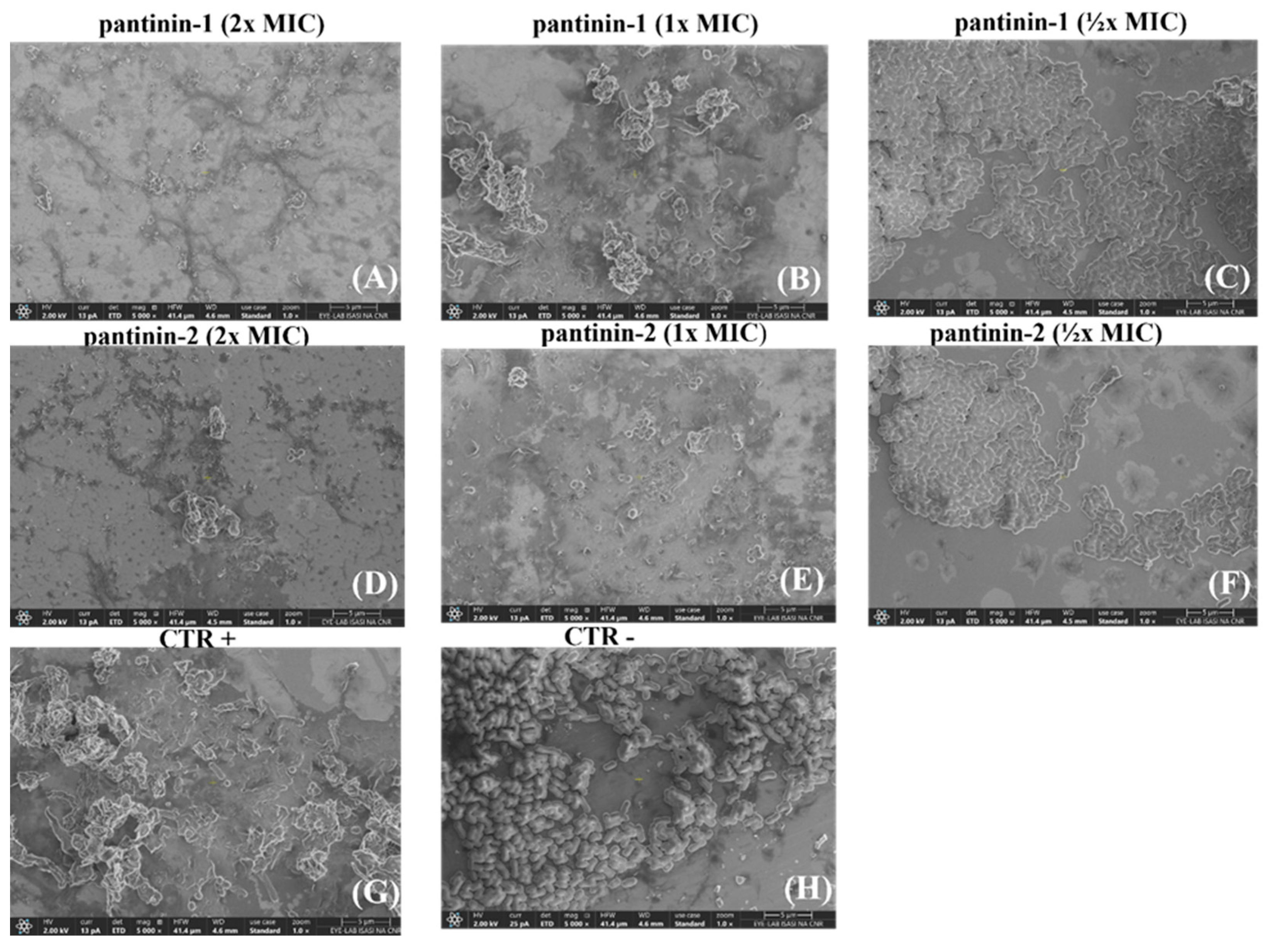
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
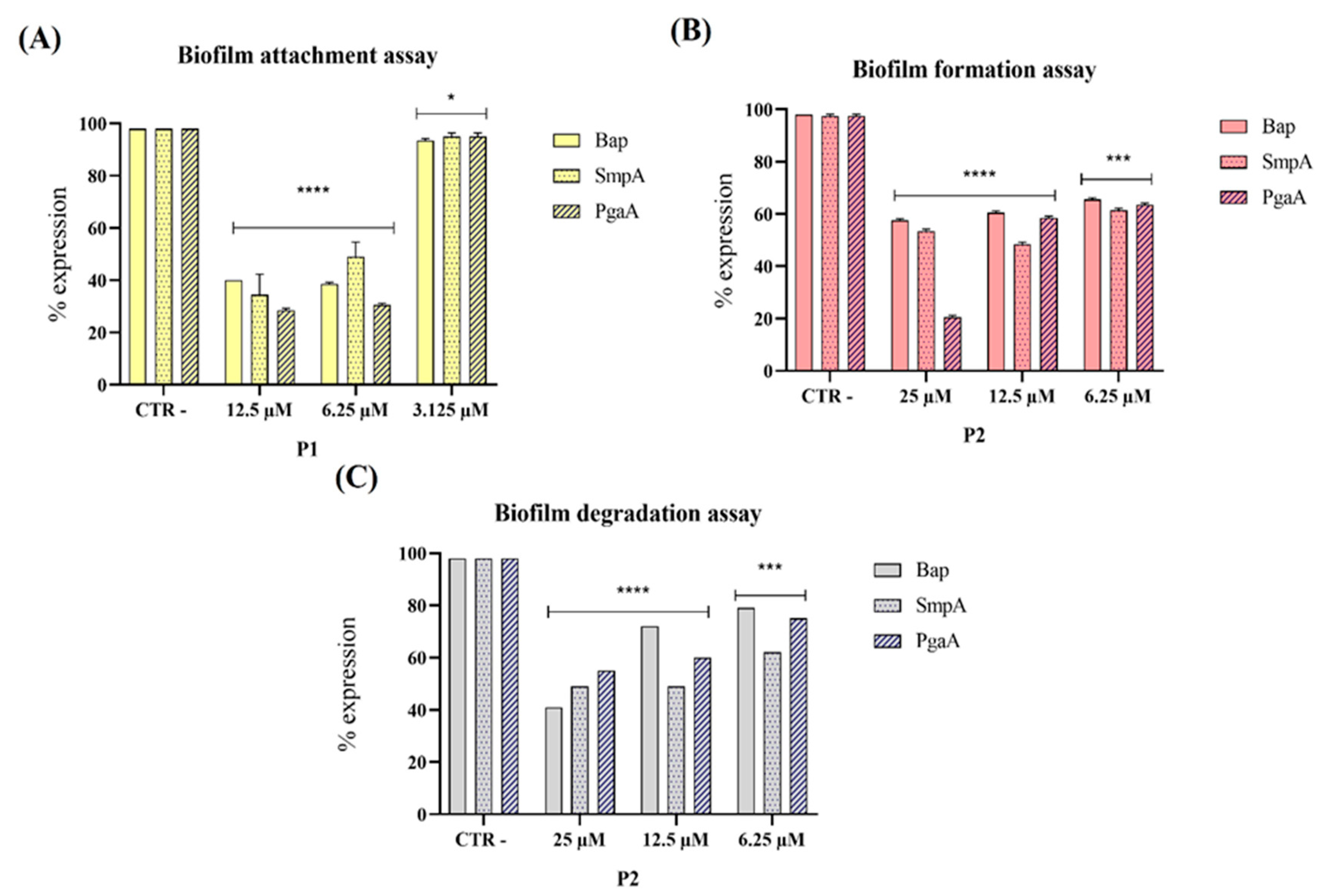
2.7. Molecular Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity
3.2. Effect of Pantinins on Different Stages of Biofilm Formation
3.3. Evaluation of Virulence Gene Expression
3.4. The Effects of Pantinin-1 and Pantinin-2 on the Integrity of A. baumannii Surface
3.5. Synergistic Effect of Pantinins Against A. Baumannii
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A. baumannii | Acinetobacter baumannii |
| AMPs | Antimicrobial Peptides |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MBC | Minimal Bactericidal Concentration |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| CV | Crystal Violet |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| HaCaT | Human Keratinocyte Cell Line |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulphoxide |
| CTR+ | Positive Control |
| CTR− | Negative Control |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| FBS | Bovine Fetal Serum |
| MH | Müller–Hinton |
| LB | Luria–Bertani |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization–Time of Flight |
| EUCAST | European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| CFU | Colony-Forming Unit |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| O/N | Overnight |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| RT | Reverse Transcription |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| CRAB | Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii |
| MDR | Multidrug-Resistant |
| XDR | Extensively Drug-Resistant |
| PDR | Pan-Drug-Resistant |
| VAP | Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia |
| PNAG | Poly-β-(1-6)-N-acetylglucosamine |
| ST | Sequence Type |
References
- Pipito, L.; Rubino, R.; D’Agati, G.; Bono, E.; Mazzola, C.V.; Urso, S.; Zinna, G.; Distefano, S.A.; Firenze, A.; Bonura, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens: A Retrospective Epidemiological Study at the University Hospital of Palermo, Italy. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daruka, L.; Czikkely, M.S.; Szili, P.; Farkas, Z.; Balogh, D.; Grezal, G.; Maharramov, E.; Vu, T.H.; Sipos, L.; Juhasz, S.; et al. ESKAPE pathogens rapidly develop resistance against antibiotics in development in vitro. Nat. Microbiol. 2025, 10, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhalil, A.D.; Barakat, S.A.; Mansour, A.; Al-Shami, N.; Naseef, H. ESKAPE Pathogens: Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns, Risk Factors, and Outcomes a Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study of Hospitalized Patients in Palestine. Infect. Drug Resist. 2024, 17, 3813–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.W.K.; Millar, B.C.; Moore, J.E. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 80, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE pathogens: Antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, H. Virulence Factors and Pathogenicity Mechanisms of Acinetobacter baumannii in Respiratory Infectious Diseases. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampatakis, T.; Tsergouli, K.; Behzadi, P. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Virulence Factors, Molecular Epidemiology and Latest Updates in Treatment Options. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalauskiene, G.V.; Malciene, L.; Stankevicius, E.; Radzeviciene, A. Unseen Enemy: Mechanisms of Multidrug Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-Negative ESKAPE Pathogens. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jiang, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhong, L.; Zhou, M.; Xie, S.; et al. Emergence and global spread of a dominant multidrug-resistant clade within Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyenuga, N.; Cobo-Díaz, J.F.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Alexa, E.-A. Overview of Antimicrobial Resistant ESKAPEE Pathogens in Food Sources and Their Implications from a One Health Perspective. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denissen, J.; Reyneke, B.; Waso-Reyneke, M.; Havenga, B.; Barnard, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, W. Prevalence of ESKAPE pathogens in the environment: Antibiotic resistance status, community-acquired infection and risk to human health. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 244, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, K.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Rajabnia, M.; Halaji, M. Effects of Curcumin on Biofilm Production and Associated Gene in Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Hospitalized Patients. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. 2025, 14, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yi, X.; Du, R.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q. Scorpion venom peptides enhance immunity and survival in Litopenaeus vannamei through antibacterial action against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1551816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. APD3: The antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1087–D1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.; Sahl, H.G. Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlapuu, M.; Hakansson, J.; Ringstad, L.; Bjorn, C. Antimicrobial Peptides: An Emerging Category of Therapeutic Agents. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanis, E.; Aguilar, F.; Banaei, N.; Dean, F.B.; Villarreal, A.; Alanis, M.; Lozano, K.; Bullard, J.M.; Zhang, Y. A rationally designed antimicrobial peptide from structural and functional insights of Clostridioides difficile translation initiation factor 1. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0277323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cane, C.; Tammaro, L.; Duilio, A.; Di Somma, A. Investigation of the Mechanism of Action of AMPs from Amphibians to Identify Bacterial Protein Targets for Therapeutic Applications. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.H.; Kim, K.H.; Ki, M.R.; Pack, S.P. Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Biomedical Applications: A Review. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.C.; Zhou, L.; Shi, W.; Luo, X.; Zhang, L.; Nie, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Cao, B.; Cao, H. Three new antimicrobial peptides from the scorpion Pandinus imperator. Peptides 2013, 45, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R.; Zannella, C.; Della Marca, R.; Chianese, A.; Di Clemente, L.; Monti, A.; Doti, N.; Cacioppo, F.; Iovane, V.; Montagnaro, S.; et al. Expanding the Antiviral Spectrum of Scorpion-Derived Peptides Against Toscana Virus and Schmallenberg Virus. Pathogens 2025, 14, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.; Zannella, C.; Chianese, A.; Acconcia, C.; Monti, A.; Della Marca, R.; Pagnini, U.; Montagnaro, S.; Doti, N.; Isernia, C.; et al. Pantinin-Derived Peptides against Veterinary Herpesviruses: Activity and Structural Characterization. ChemMedChem 2025, 20, e202500333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.; Della Marca, R.; Chianese, A.; Monti, A.; Donadio, F.; Esposito, E.; Doti, N.; Zannella, C.; Galdiero, M.; De Filippis, A. The inhibitory potential of three scorpion venom peptides against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pnemoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1569719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrayess, R.A.; Mohallal, M.E.; Mobarak, Y.M.; Ebaid, H.M.; Haywood-Small, S.; Miller, K.; Strong, P.N.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A. Scorpion Venom Antimicrobial Peptides Induce Caspase-1 Dependant Pyroptotic Cell Death. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 788874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, M. Acinetobacter baumannii: An evolving and cunning opponent. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1332108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, F.; Dell’Annunziata, F.; Folliero, V.; Foglia, F.; Marca, R.D.; Zannella, C.; De Filippis, A.; Franci, G.; Galdiero, M. Cupferron impairs the growth and virulence of Escherichia coli clinical isolates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, A.; Ambrosino, A.; Giugliano, R.; Palma, F.; Parimal, P.; Acunzo, M.; Monti, A.; Doti, N.; Zannella, C.; Galdiero, M.; et al. Frog Skin Peptides Hylin-a1, AR-23, and RV-23: Promising Tools Against Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, A.; Zannella, C.; Foglia, F.; Nastri, B.M.; Monti, A.; Doti, N.; Franci, G.; De Filippis, A.; Galdiero, M. Hylin-a1: A Host Defense Peptide with Antibacterial Potential against Staphylococcus aureus Multi-Resistant Strains. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, F.; Acunzo, M.; Della Marca, R.; Dell’Annunziata, F.; Folliero, V.; Chianese, A.; Zannella, C.; Franci, G.; De Filippis, A.; Galdiero, M. Evaluation of antifungal spectrum of Cupferron against Candida albicans. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 194, 106835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsari, C.; Luciani, R.; Pozzi, C.; Poehner, I.; Henrich, S.; Trande, M.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A.; Santarem, N.; Baptista, C.; Tait, A.; et al. Profiling of Flavonol Derivatives for the Development of Antitrypanosomatidic Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7598–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, F.; Heidrich, G.; Nordholt, N.; Schreiber, F. Prevalent Synergy and Antagonism Among Antibiotics and Biocides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 615618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, C.; Giugliano, R.; Della Sala, G.; Palma Esposito, F.; Tedesco, P.; Folliero, V.; Galdiero, M.; Franci, G.; de Pascale, D. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Properties and Potential Applications of Pseudomonas gessardii M15 Rhamnolipids towards Multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.; Della Sala, G.; Buonocore, C.; Zannella, C.; Tedesco, P.; Palma Esposito, F.; Ragozzino, C.; Chianese, A.; Morone, M.V.; Mazzella, V.; et al. New Imidazolium Alkaloids with Broad Spectrum of Action from the Marine Bacterium Shewanella aquimarina. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huarachi-Olivera, R.; Teresa Mata, M.; Ardiles-Candia, A.; Escobar-Mendez, V.; Gatica-Cortes, C.; Ahumada, M.; Orrego, J.; Vidal-Veuthey, B.; Cardenas, J.P.; Gonzalez, L.; et al. Modification of the Trizol Method for the Extraction of RNA from Prorocentrum triestinum ACIZ_LEM2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surekha, S.; Lamiyan, A.K.; Gupta, V. Antibiotic Resistant Biofilms and the Quest for Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Indian. J. Microbiol. 2024, 64, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakavan, M.; Gholami, M.; Ahanjan, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Salehian, M.; Roozbahani, F.; Goli, H.R. Expression of bap gene in multidrug-resistant and biofilm-producing Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.J.; Tu, I.F.; Tseng, T.S.; Tsai, Y.H.; Wu, S.H. The deficiency of poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-glucosamine deacetylase trigger A. baumannii to convert to biofilm-independent colistin-tolerant cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.; Doosti, A.; Kargar, M.; Bijanzadeh, M.; Jafarinya, M.J.J.J.o.M. Antimicrobial resistant determination and prokaryotic expression of smpA gene of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from admitted patients. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G. Natural peptides and their synthetic congeners acting against Acinetobacter baumannii through the membrane and cell wall: Latest progress. RSC Med. Chem. 2025, 16, 561–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, N.; Mishra, B.; Felix, L.; Mylonakis, E. Antimicrobial Peptides and Small Molecules Targeting the Cell Membrane of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2023, 87, e0003722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Tan, H.; Cheng, T.; Shen, H.; Shao, J.; Guo, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhang, X. Human beta-defensin 3 inhibits antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus biofilm formation. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 183, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, L.; Mishra, B.; Khader, R.; Ganesan, N.; Mylonakis, E. In Vitro and In Vivo Bactericidal and Antibiofilm Efficacy of Alpha Mangostin Against Staphylococcus aureus Persister Cells. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 898794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Forward Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Reverse Sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| bap | GTGGCTTAGACCGTTCACCA | CGAATCGAGCGCACAAGTTC |
| smpA | TGCAAAAACTCGTGCTGACG | GGGGATCAGTCACTGTTGGG |
| pgaA | TTGTCAGCAATTGTGTCGCA | ACCATCTTCCCCTGCATCAA |
| 16s | GGTAGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG | ATTACCGCGGCTGCTGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Capasso, C.; Zannella, C.; Giugliano, R.; Chianese, A.; Monti, A.; Donadio, F.; Esposito, E.; Marino, G.; Doti, N.; De Filippis, A.; et al. Scorpion Venom-Derived Peptides: A New Weapon Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microorganisms 2026, 14, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010068
Capasso C, Zannella C, Giugliano R, Chianese A, Monti A, Donadio F, Esposito E, Marino G, Doti N, De Filippis A, et al. Scorpion Venom-Derived Peptides: A New Weapon Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microorganisms. 2026; 14(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapasso, Carla, Carla Zannella, Rosa Giugliano, Annalisa Chianese, Alessandra Monti, Federica Donadio, Emanuela Esposito, Gerardo Marino, Nunzianna Doti, Anna De Filippis, and et al. 2026. "Scorpion Venom-Derived Peptides: A New Weapon Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii" Microorganisms 14, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010068
APA StyleCapasso, C., Zannella, C., Giugliano, R., Chianese, A., Monti, A., Donadio, F., Esposito, E., Marino, G., Doti, N., De Filippis, A., & Galdiero, M. (2026). Scorpion Venom-Derived Peptides: A New Weapon Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microorganisms, 14(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010068











