Synergistic Potential of Contamination Remediation and Carbon Fixation: Functional Resilience of Carbon Fixation in Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Degrading Microbial Communities Under Enhanced Natural Attenuation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Physical and Chemical Parameter Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. Data Processing
- (1)
- Concentration–time curves were plotted using Origin software (2019b).
- (2)
- The apparent consumption concentrations of nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium were calculated by subtracting the detected concentrations from the added concentrations. Positive values indicated consumption, while negative values indicated production, i.e., apparent generation.
3. Results
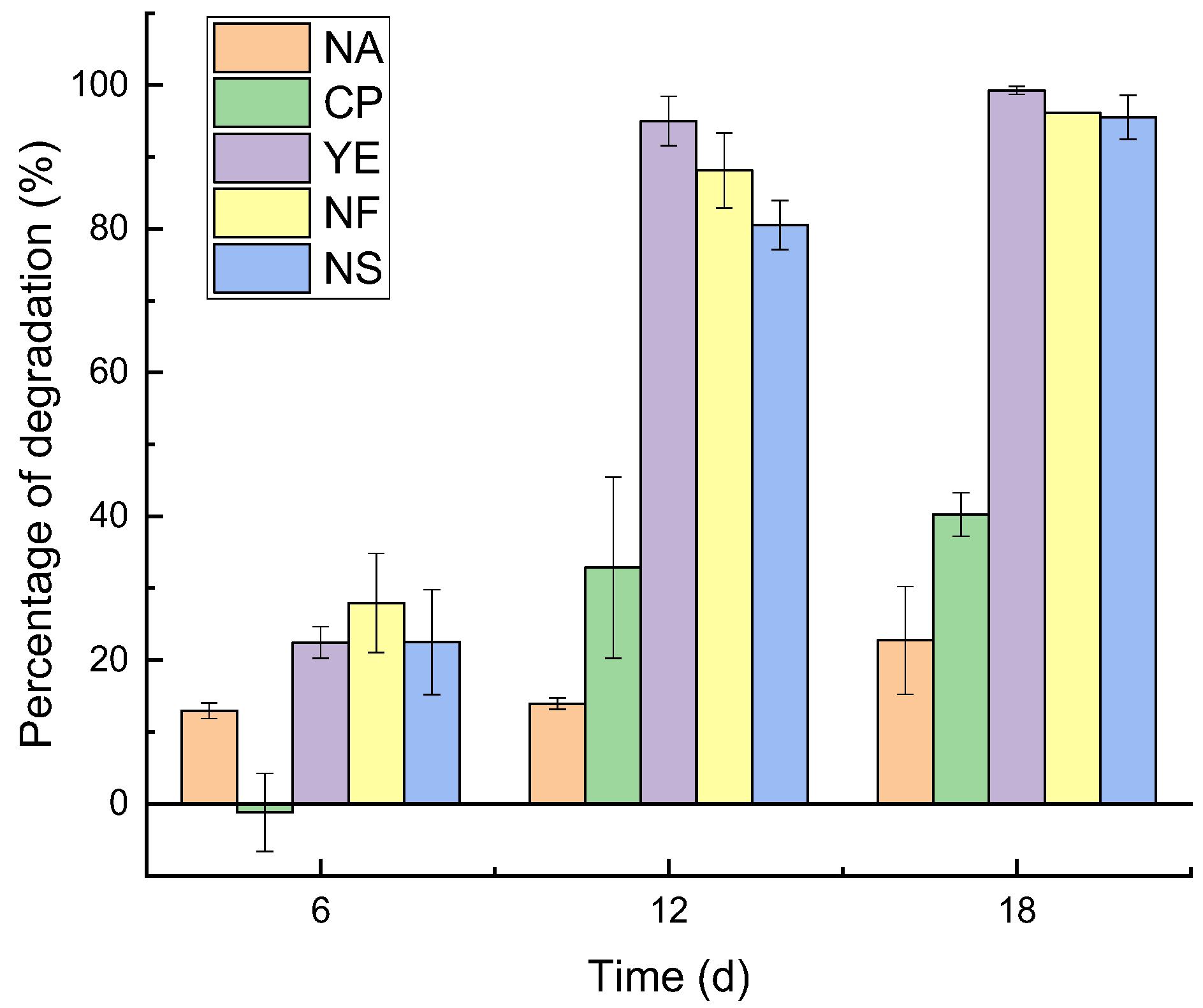
3.1. Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons and Evolutionary Characteristics of Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Evolution of Functional Abundance of Carbon-Fixing Microorganisms
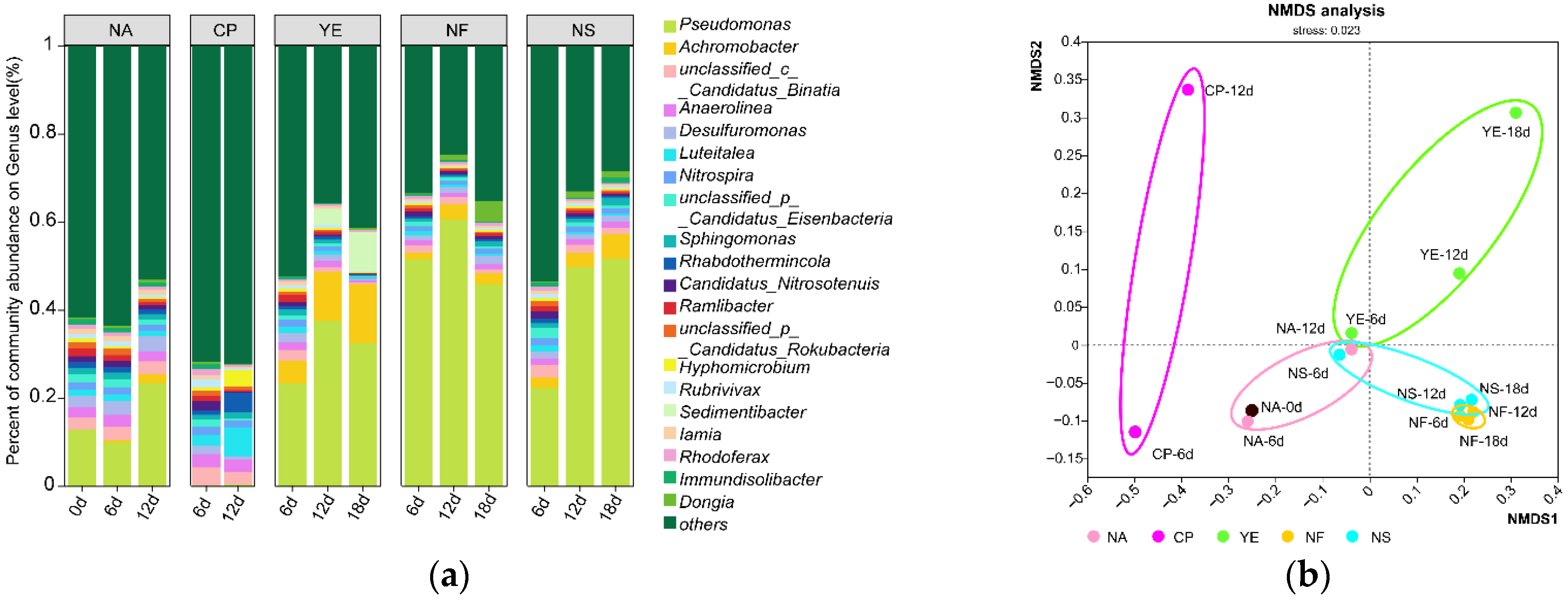
3.3. Evolution of Carbon-Fixing Microbial Species
4. Discussion
4.1. Petroleum Hydrocarbon Degradation Process
4.2. Carbon Fixation Gene Abundance
4.3. Species with Carbon Fixation Genes Annotated
4.4. Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lubi, S.P.; Akinluyi, F.O. Groundwater hydrocarbon contamination spatial pattern in opuama, western niger-delta, nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Ning, Z.; Zhang, M.; Guo, C.; Niu, M.; Shi, J. Autotrophic metabolism considered to extend the applicability of the carbon balances model for assessing biodegradation in petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifers with abnormally low dissolved inorganic carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 120738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Ning, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, M.; Guo, C.; Niu, M.; Shi, J. Insights into biodegradation related metabolism in an abnormally low dissolved inorganic carbon (dic) petroleum-contaminated aquifer by metagenomics analysis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Gan, S.; Guo, C.; Wang, S.; Cai, P.; Zhang, M. Metagenomic and isotopic insights into carbon fixation by autotrophic microorganisms in a petroleum hydrocarbon impacted red clay aquifer. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Cai, P.; Zhang, M. Metagenomic analysis revealed highly diverse carbon fixation microorganisms in a petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, S. Combining stable carbon isotope analysis and petroleum-fingerprinting to evaluate petroleum contamination in the yanchang oilfield located on loess plateau in china. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 2830–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; He, R.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Ping, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. The dominant microbial metabolic pathway of the petroleum hydrocarbons in the soil of shale gas field: Carbon fixation instead of CO2 emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponsin, V.; Coulomb, B.; Guelorget, Y.; Maier, J.; Hohener, P. In situ biostimulation of petroleum hydrocarbon degradation by nitrate and phosphate injection using a dipole well configuration. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2014, 171, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.T. An Approach for Evaluating the Progress of Natural Attenuation in Groundwater; US Environmental Protection Agency, National Risk Management Research Laboratory Office of Research and Development, Ada, Oklahoma Copyright of Shell International BV; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Ning, Z.; Liang, J.; Ti, J.; Zhang, M.; Cai, C. Enhanced natural attenuation of gasoline contaminants in groundwater: Applications and challenges of nitrate-stimulating substances. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhatkar, R.; Schnobrich, M. Land application of sulfate salts for enhanced natural attenuation of benzene in groundwater: A case study. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2017, 37, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, D.M.; Clark, K. Lessons learned from 20 years of molecular biological tools in petroleum hydrocarbon remediation. Remediat. J. 2021, 31, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Ning, Z.; Wang, S.; Sun, W.; Xu, Z.; Di, H.; Ti, J.; Guo, C.; Zhou, Y.; He, Z.; et al. Identification of carbon fixation microorganisms and pathways in an aquifer contaminated with long-chain petroleum hydrocarbons. Water Environ. Res. 2024, 96, e11078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Guzmán, C.L.; Muñoz-Páez, K.M.; Valdez-Vazquez, I. Effect of electron donors on CO2 fixation from a model cement industry flue gas by non-photosynthetic microbial communities in batch and continuous reactors. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 2387–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellermann, C.; Selesi, D.; Lee, N.; Hugler, M.; Esperschutz, J.; Hartmann, A.; Griebler, C. Microbial CO2 fixation potential in a tar-oil-contaminated porous aquifer. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 81, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Jin, F.; Fu, X.; Li, H. Universally improving effect of mixed electron donors on the CO2 fixing efficiency of non-photosynthetic microbial communities from marine environments. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.-J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.-P.; Fu, X.-H.; Le, Y.-Q.; Li, H.-R. Enhanced CO2 fixation by a non-photosynthetic microbial community under anaerobic conditions: Optimization of electron donors. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3220–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, B.R.; Barr, C.R.; Rowe, A.R.; Nealson, K.H. Differences in applied redox potential on cathodes enrich for diverse electrochemically active microbial isolates from a marine sediment. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Canstein, H.; Ogawa, J.; Shimizu, S.; Lloyd, J.R. Secretion of flavins byshewanellaspecies and their role in extracellular electron transfer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.A. Investigation of the Optimal Dissolved Carbon Dioxide Concentration and pH Combination for the Growth of Nitrifying Bacteria. Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Ning, Z.; Guo, C.; Shi, C.; Zhang, S.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, Z. Using compound specific isotope analysis to decipher the 1,2,3-trichloropropane-to-allyl chloride transformation by groundwater microbial communities. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiener, C.; Frimmel, F.H. Application of headspace gc/ms screening and general parameters for the analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in groundwater samples. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1998, 360, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Methods for Agrochemical Analysis of Soil; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vidyadharan, P.; Santhi, C.K.; Sethumadhavan, A.; Gopala, S.; Raghavan, C.; Urulangodi, M. Functional assessment of DNA extraction methods from frozen human blood samples for sanger sequencing analysis. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishii, K.; Möller, M.; Foster, R.G.; Forrest, L.L.; Kelso, N.; Barber, S.; Howard, C.; Hart, M.L. A high quality, high molecular weight DNA extraction method for pacbio hifi genome sequencing of recalcitrant plants. Plant Methods 2023, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hügler, M.; Sievert, S.M. Beyond the calvin cycle: Autotrophic carbon fixation in the ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 261–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, N.; Guo, C.; Hao, C.; Zhang, S.; Shi, C.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, Z. Metagenomic characterization of a novel enrichment culture responsible for dehalogenation of 1,2,3-trichloropropane to allyl chloride. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, J.A.; Gerritse, J.; Hartog, N.; Ertl, S.; Parsons, J.R.; Hassanizadeh, S.M. Anaerobic degradation of benzene and other aromatic hydrocarbons in a tar-derived plume: Nitrate versus iron reducing conditions. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 248, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, C.; Yang, S.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Ning, Z. The effects of toluene mineralization under denitrification conditions on carbonate dissolution and precipitation in water: Mechanism and model. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.R.; Tang, J.C.; Zhen, M.N.; Liu, X.M. Effect of rhamnolipids on enhanced anaerobic degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in nitrate and sulfate sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wu, S.X.; Yun, Z.C.; Xu, X.J.; Jiang, Y.H. Insights into the characteristics of changes in dissolved organic matter fluorescence components on the natural attenuation process of toluene. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhasz, A.L.; Smith, E.; Waller, N.; Stewart, R.; Weber, J. Bioavailability of residual polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons following enhanced natural attenuation of creosote-contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Bao, J.Q.; Liu, Q.; He, X.X.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wang, H.; Xing, J.M.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, J.F. Simultaneous natural attenuation of Cr(VI) and nitrate in the hyporheic zone sediments from an upstream tributary of the jinsha river in the sichuan basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Okabe, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Evaluation of the impact of bioaugmentation and biostimulation by in situ hybridization and microelectrode. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2206–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.T.; Wang, H. The negative effects of the excessive nitrite accumulation raised by anaerobic bioaugmentation on bioremediation of pah-contaminated soil. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 130090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, G.X.; An, Y.F.; Sun, J.; Yang, B.; Shen, Z.Y. Effects and driving mechanisms of bioremediation on groundwater after the neutral in situ leaching of uranium. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Qian, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. A critical review of solid peroxides in environmental remediation and water purification: From properties to field applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badger, M.R.; Bek, E.J. Multiple rubisco forms in proteobacteria: Their functional significance in relation to CO2 acquisition by the CBB cycle. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 1525–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.-C.; Hu, C. Carbon cycle in the microbial ecosystems of biological soil crusts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 171, 108729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Li, X.; Wang, N.; Lan, Z.; He, J.; Bai, Y. Contrasting effects of nitrogen forms and soil pH on ammonia oxidizing microorganisms and their responses to long-term nitrogen fertilization in a typical steppe ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 107, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheible, W.R.; Krapp, A.; Stitt, M. Reciprocal diurnal changes of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase expression and cytosolic pyruvate kinase, citrate synthase and nadp-isocitrate dehydrogenase expression regulate organic acid metabolism during nitrate assimilation in tobacco leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 2000, 23, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huergo, L.F.; Dixon, R. The emergence of 2-oxoglutarate as a master regulator metabolite. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfreider, A.; Grimus, V.; Luger, M.; Ekblad, A.; Salcher, M.M.; Summerer, M. Autotrophic carbon fixation strategies used by nitrifying prokaryotes in freshwater lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, L.; Liu, Q.; Sikder, M.M.; Vestergård, M.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y. Pseudomonas fluorescens promote photosynthesis, carbon fixation and cadmium phytoremediation of hyperaccumulator sedum alfredii. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donawa, A.; Ishaque, M.; Aleem, M. CO2 fixation and metabolic control in pseudomonas saccharophila. Can. J. Microbiol. 1973, 19, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bedics, A.; Tóth, E.; Kriszt, B.; Soares, A.R.; Bóka, K.; Táncsics, A. Isolation of Pseudomonas aromaticivorans sp. Nov from a hydrocarbon-contaminated groundwater capable of degrading benzene-, toluene-, m-and p-xylene under microaerobic conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masotti, F.; Barcarolo, M.V.; Zanor, M.I.; Burdisso, P.; Gottig, N.; Garavaglia, B.S.; Ottado, J. Efficient glyphosate removal from groundwater by biogenic manganese oxides produced by pseudomonas sagittaria. Microbe 2025, 7, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.-H.; Wang, Y.-N.; Du, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, B.; Bian, J.; Liu, S.-J.; Chen, G.-C. Pseudomonas linyingensis sp. Nov.: A novel bacterium isolated from wheat soil subjected to long-term herbicides application. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Megeed, A.; Suliman, A.-M.A.; Mueller, R. Genetics of alkane degrading enzymes by Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 8, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, B.Y.; Jung, I.L.L.; Park, D.H. Enrichment of CO2-fixing bacteria in cylinder-type electrochemical bioreactor with built-in anode compartment. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, K.; Jadhav, I. Sulfur oxidation by achromobacter xylosoxidans strain wsp05 reveals ecological widening over which thiotrophs are distributed. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, A.N.; Tolar, B.B.; Bargar, J.R.; Boye, K.; Francis, C.A. Diverse and unconventional methanogens, methanotrophs, and methylotrophs in metagenome-assembled genomes from subsurface sediments of the Slate River Floodplain, Crested Butte, CO, USA. mSystems 2024, 9, e00314–e00324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, M.J.; Finn, D.; Macedo-Tafur, F.; Tello-Espinoza, R.; Penaccio, C.; Bouskill, N.; Cadillo-Quiroz, H. Genes and genome-resolved metagenomics reveal the microbial functional make up of amazon peatlands under geochemical gradients. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 25, 2388–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermann, M.Y.; Wegener, G.; Elvert, M.; Yoshinaga, M.Y.; Lin, Y.-S.; Holler, T.; Mollar, X.P.; Knittel, K.; Hinrichs, K.-U. Autotrophy as a predominant mode of carbon fixation in anaerobic methane-oxidizing microbial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19321–19326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roslev, P.; Larsen, M.B.; Jørgensen, D.; Hesselsoe, M. Use of heterotrophic CO2 assimilation as a measure of metabolic activity in planktonic and sessile bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2004, 59, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Cycle (s) Involved | Enzyme Description | E.C. |
|---|---|---|
| Calvin–Benson–Bassham (CBB) | Ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase | 4.1.1.39 |
| Reductive tricarboxylic acid (rTCA) | Isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+) | 1.1.1.42 |
| 2-oxoglutarate synthase | 1.2.7.3 | |
| Reductive tricarboxylic acid (rTCA), Dicarboxylate/4-hydroxybutyrate (DH) | Pyruvate synthase | 1.2.7.1 |
| Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase | 4.1.1.31 | |
| Wood–Ljungdahl (WL) | Anaerobic carbon-monoxide dehydrogenase | 1.2.7.4 |
| 3-hydroxypropionate cycle (HP), 3-hydroxypropionate/4-hydroxybutyrate (HH) | Propionyl-CoA carboxylase | 6.4.1.3 |
| Acetyl-CoA carboxylase | 6.4.1.2 |
| Pathways | Enzyme | NA | CP | YE | NF | NS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6d | 12d | 6d | 12d | 6d | 12d | 18d | 6d | 12d | 18d | 6d | 12d | 18d | ||
| CBB | 4.1.1.39 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 1.30 | 0.36 | 0.67 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.54 | 0.38 | 0.30 |
| rTCA | 1.1.1.42 | 1.00 | 1.15 | 0.74 | 0.82 | 1.22 | 1.29 | 1.31 | 1.21 | 1.32 | 1.07 | 1.22 | 1.25 | 1.22 |
| 1.2.7.3 | 1.01 | 0.64 | 1.43 | 1.80 | 0.66 | 0.51 | 0.70 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.75 | 0.32 | 0.24 | |
| rTCA/DH | 1.2.7.1 | 0.96 | 0.54 | 1.41 | 1.09 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 1.47 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.73 | 0.30 | 0.21 |
| 4.1.1.31 | 1.01 | 1.21 | 0.69 | 1.29 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 0.98 | 1.53 | 1.58 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 1.41 | 1.20 | |
| HP/HH | 6.4.1.3 | 1.11 | 0.80 | 1.34 | 2.01 | 0.70 | 0.54 | 0.36 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| 6.4.1.2 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.07 | 1.04 | 1.09 | 1.15 | 1.12 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.97 | |
| Total | 1.01 | 0.90 | 1.11 | 1.28 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.80 | |
| Color scale | 0.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.50 | 2.00 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, P.; Gan, S.; Ning, Z.; Zhang, M. Synergistic Potential of Contamination Remediation and Carbon Fixation: Functional Resilience of Carbon Fixation in Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Degrading Microbial Communities Under Enhanced Natural Attenuation. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092205
Cai P, Gan S, Ning Z, Zhang M. Synergistic Potential of Contamination Remediation and Carbon Fixation: Functional Resilience of Carbon Fixation in Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Degrading Microbial Communities Under Enhanced Natural Attenuation. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092205
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Pingping, Shuang Gan, Zhuo Ning, and Min Zhang. 2025. "Synergistic Potential of Contamination Remediation and Carbon Fixation: Functional Resilience of Carbon Fixation in Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Degrading Microbial Communities Under Enhanced Natural Attenuation" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092205
APA StyleCai, P., Gan, S., Ning, Z., & Zhang, M. (2025). Synergistic Potential of Contamination Remediation and Carbon Fixation: Functional Resilience of Carbon Fixation in Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Degrading Microbial Communities Under Enhanced Natural Attenuation. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092205






