Sorption–Biological Treatment of Coastal Substrates of the Barents Sea in Low Temperature Using the Rhodococcus erythropolis Strain HO-KS22
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Objects
2.2. Water–Oil Emulsion
2.3. Sorbents
- -
- Granular activated carbon (GAC VSK, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia) with granule sizes of 2–3 mm consists of 87–97% carbon and exhibits a sorption capacity for hydrocarbons up to 980 mg·g−1 [36].
- -
- Thermally activated vermiculite (JSC “Mica Factory”, St. Petersburg, Russia) is a mineral of the aluminosilicate group with a layered structure. When heated, vermiculite swells and increases in volume several fold; it has a high absorption coefficient, with a sorption capacity for hydrocarbons up to 5400 mg·g−1 [37].
- -
- Highmoor milled peat with a low degree of decomposition (not exceeding 35%), with a hydrocarbon sorption capacity ranging from 1560 to 1825 mg·g−1 [38].
2.4. Hydrocarbon-Oxidizing Strain Rhodococcus Erythropolis HO-KS22
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Total Petroleum Hydrocarbon Content
2.7. The Number of Hydrocarbon-Oxidizing Bacteria
2.8. Assessment of Dehydrogenase Activity
2.9. Measuring pH Value
2.10. Statistical Processing
3. Results
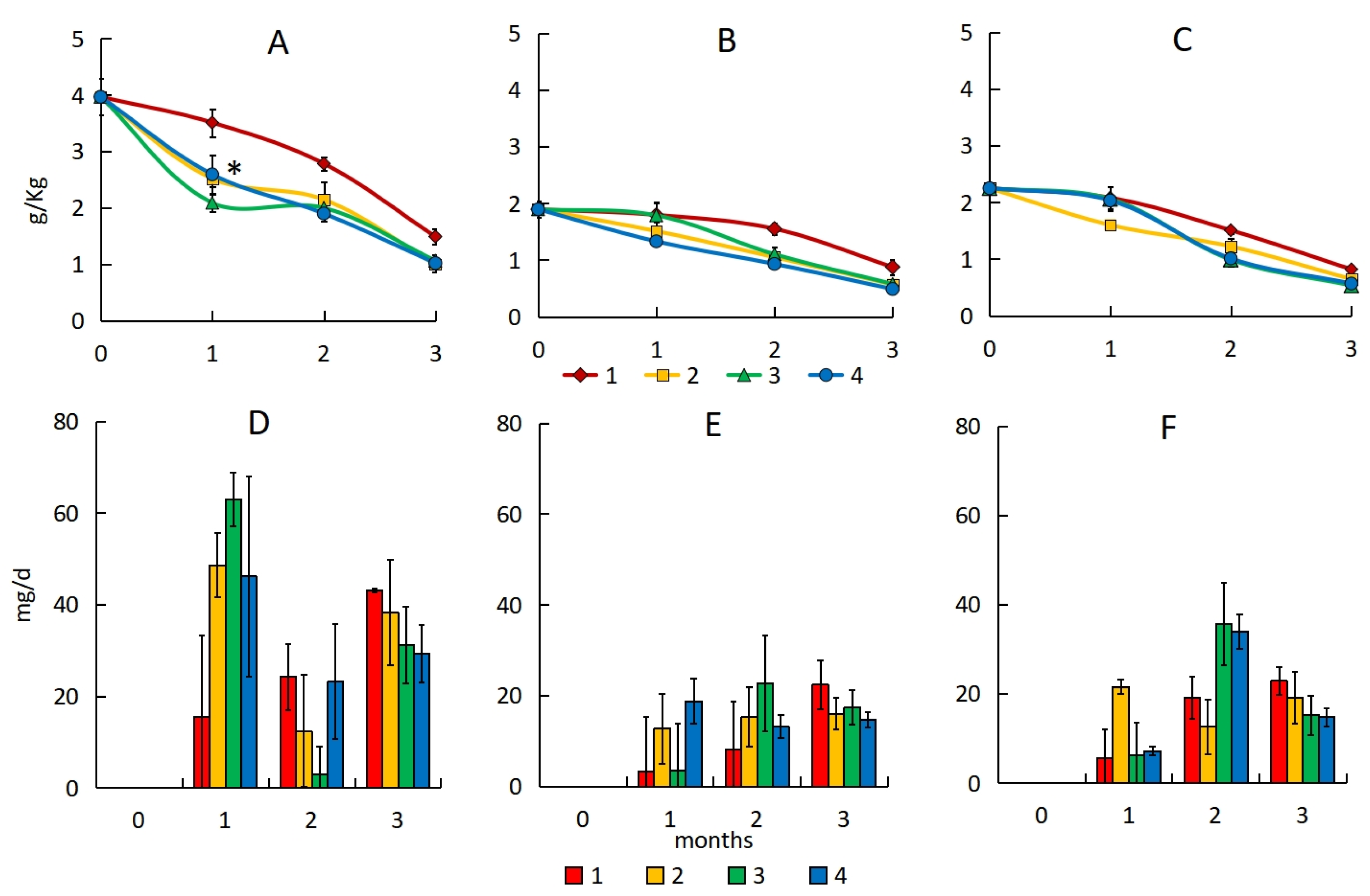
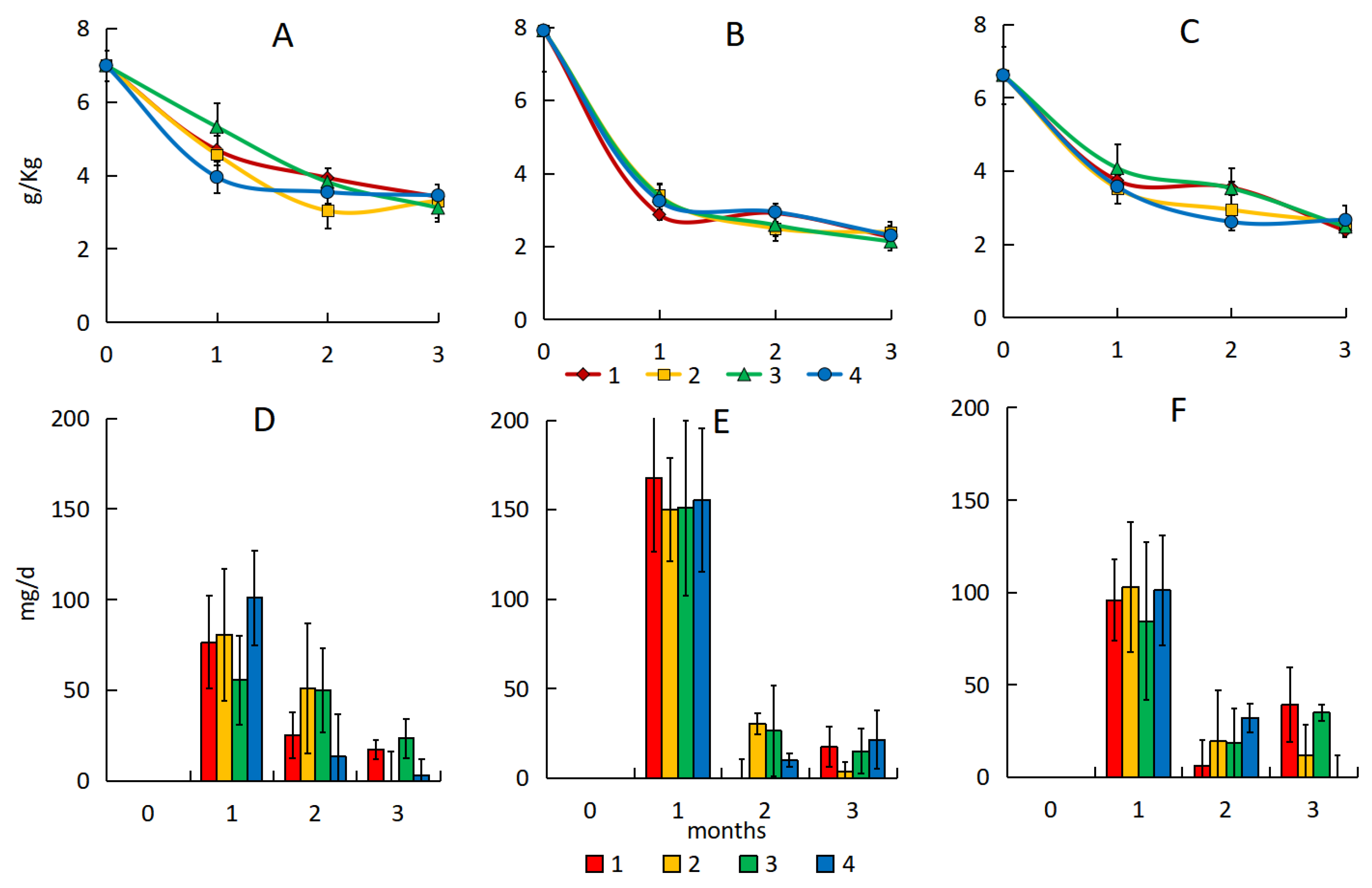
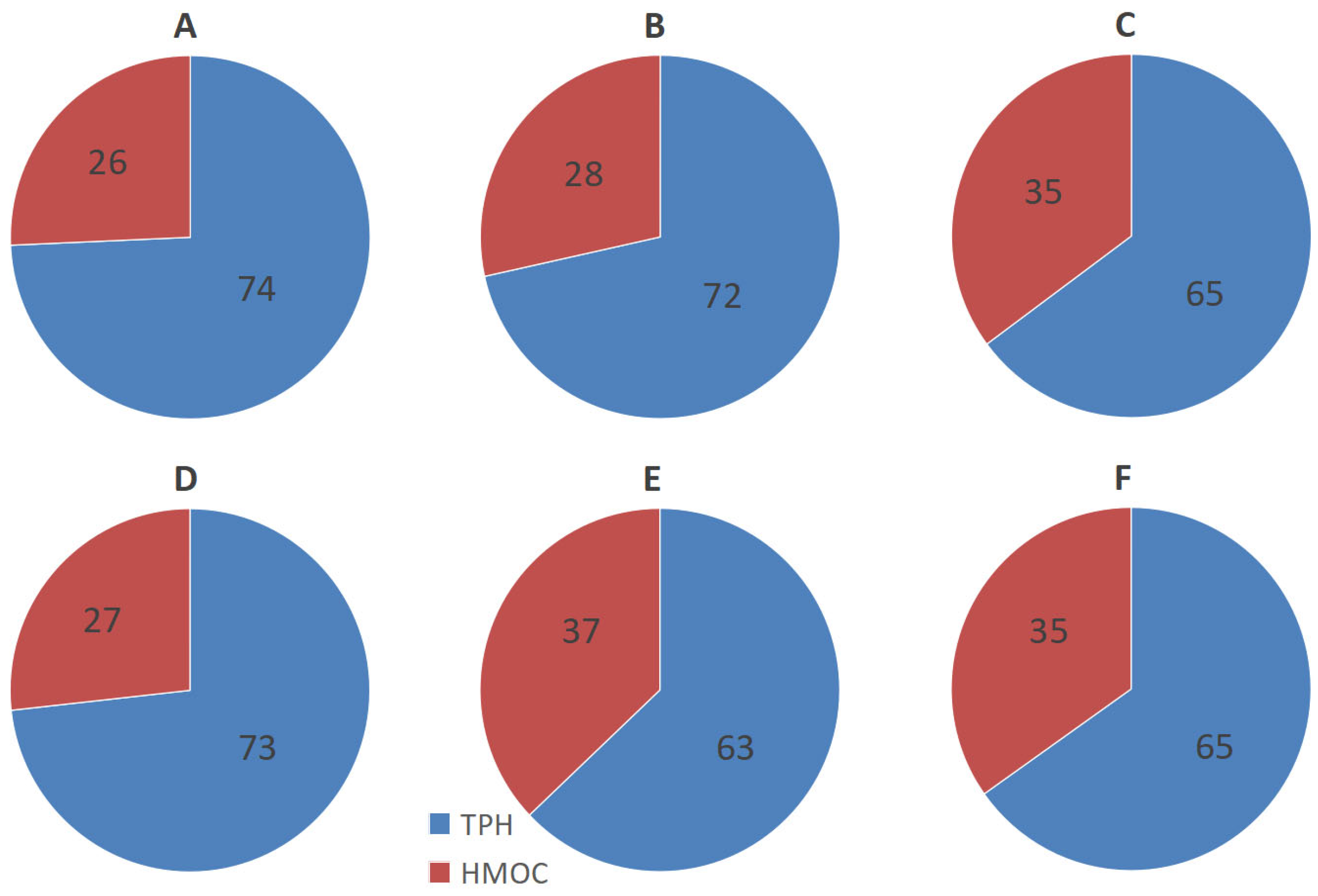
3.1. Content of Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons
3.2. Content of High-Molecular Organic Compounds
3.3. Number of Hydrocarbon-Oxidizing Bacteria
3.4. Dehydrogenase Activity
3.5. pH Value
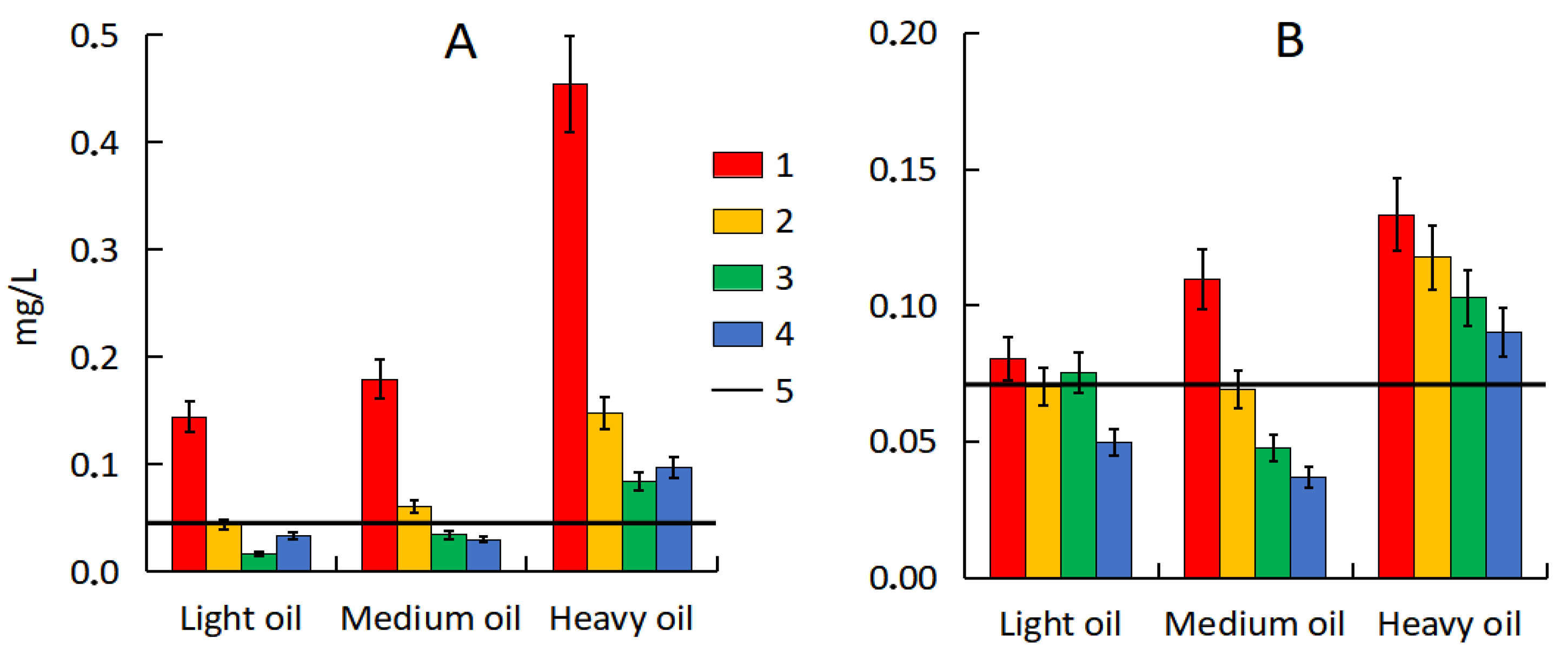
3.6. Desorption of Hydrocarbons from Polluted Soil and Sand
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi, H.; Wang, Z.; Yue, R.; Sui, J.; Mulligan, C.N.; Lee, K.; Pegau, S.; Chen, Z.; An, C. Oil spills in coastal regions of the Arctic and Subarctic: Environmental impacts, response tactics, and preparedness. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, P.M.; Smith, C.; Walsh, T.; Lamb, W.F.; Lamboll, R.; Hall, B.; Hauser, M.; Ribes, A.; Rosen, D.; Gillett, N.P.; et al. Indicators of Global Climate Change 2023: Annual update of key indicators of the state of the climate system and human influence. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 2625–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongora, E.; Chen, Y.; Ellis, M.; Okshevsky, M.; White, L. Hydrocarbon bioremediation on Arctic shorelines: Historic perspective and roadway to the future. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Babanin, A.V.; Zieger, S.I.; Young, R.; Guan, C. Wind and wave climate in the arctic ocean as observed by altimeters. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 7957–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, A.R.; Boe, U.S.; Henriksen, P.; Malmquist, L.M.V.; Christensen, J.H. Full-scale bioremediation of diesel-polluted soil in an Arctic landfarm. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verasoundarapandian, G.; Wong, C.Y.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Gomez-Fuentes, C.; Zulkharnain, A.; Ahmad, S.A. A review and bibliometric analysis on applications of microbial degradation of hydrocarbon contaminants in Arctic marine environment at metagenomic and enzymatic levels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.S.; Zakaria, N.N.; Zulkharnain, A.; Sabri, S.; Gomez-Fuentes, C.; Ahmad, S.A. Bibliometric analysis of hydrocarbon bioremediation in cold regions and a review on enhanced soil bioremediation. Biology 2021, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Christensen, J.H.; Gründger, F.; Kjeldsen, K.U.; Rysgaard, S.; Vergeynst, L. Biodegradation of water-accommodated aromatic oil compounds in Arctic seawater at 0 °C. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergeynst, L.; Greer, C.W.; Mosbech, A.; Gustavson, K.; Meire, L.; Poulsen, K.G.; Christensen, J.H. Biodegradation, photo-oxidation, and dissolution of petroleum compounds in an Arctic Fjord during summer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12197–12206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeberg, M.R.; Maselko, J.; Heintz, R.A.; Fugate, C.J.; Holland, L. Conditions of persistent oil on beaches in Prince William Sound 26 years after the Exxon Valdez spill. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2018, 147, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, M.; Barabadi, A.; Barabady, J. Bioremediation treatment of hydrocarbon-contaminated Arctic soils: Influencing parameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 11250–11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavykin, A.A. (Ed.) Kola Bay and Oil: Biota, Vulnerability Maps, Pollution; MMBI KSC RAS: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 2018; 520p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment and Climate Change Canada. A Field Guide to Oil Spill Response on Marine Shorelines, Prepared and Provided by Polaris Applied Sciences and S3; Environmental Inc.: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Preparedness for Oil-Polluted Shoreline Cleanup and Olied Wildlife Intervention (POSOW). The Olied Shorline Cleanup Manual; Progress Press Co., Ltd.: B’Kara, Malta, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.; Boufadel, M.; Zhao, L.; Robinson, B.; King, T.; Lee, K. Formation of oil-particle aggregates: Particle penetration and impact of particle properties and particle-to-oil concentration ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppuswami, S.; Raju, M.N.; Mallavarapu, M.; Kadiyala, V. Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons. Environmental Fate, Toxicity, and Remediation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfumo, A.; Banat, I.M.; Marchant, R. Going green and cold: Biosurfactants from low-temperature environments to biotechnology applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiewer, S.; Iverson, A.; Sharma, P. Biodegradation and Transport of Crude Oil in Sand and Gravel Beaches of Arctic Alaska; U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Ocean Energy Management: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, D.K.; Li, C.; Jiang, C.; Chakraborty, A.; Grasby, S.E.; Hubert, C.R.J. Natural attenuation of spilled crude oil by cold-adapted soil bacterial communities at a decommissioned High Arctic oil well site. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlas, R.M. Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons: An Environmental Perspective. Microbiol. Rev. 1981, 45, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, N.; Chandran, P. Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contaminants: An Overview. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 941810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.; Sharma, S.; Sibi, G. Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons and Factors Influencing the Degradation Process. Bioprocess Eng. 2019, 3, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawniczak, L.; Wozniak-Karczewska, M.; Loibner, A.P.; Heipieper, H.J.; Chrzanowski, L. Microbial Degradation of Hydrocarbons—Basic Principles for Bioremediation: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, T.; Sabo, I.A.; Lambu, Z.N.; Danlami, D.; Shehu, A.A. Hydrocarbon Degradation Potentials of Fungi: A Review. J. Environ. Bioremediat. Toxicol. 2022, 5, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; García-Sánchez, M. Microbial Dynamics During the Bioremediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Soils Through Biostimulation: An Overview. In Approaches in Bioremediation, Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences; Prasad, R., Aranda, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdel, F.; Knittel, K.; Galushko, A. Anaerobic Hydrocarbon-Degrading Microorganisms: An Overview. In Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology; Timmis, K.N., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bi, H.; Yue, R.; Chen, Z.; An, C. Effects of oil characteristics on the performance of shoreline response operations: A review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1033909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Li, N.; Han, X.; Wang, C.; Yue, J.; Yu, H. Synergistic low-temperature petroleum remediation via surfactant-modified biochar and cold-tolerant microorganisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 434, 132769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, G.K.; Strijakova, E.R.; Ortega-Calvo, J.J. Remediation of Soils Polluted by Oil Industries. In Soil Remediation Science and Technology: The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Ortega-Calvo, J.J., Coulon, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, G.; Mikhedova, E.; Zinnatshina, L.; Strijakova, E.; Akhmetov, L.; Sushkova, S.; Ortega-Calvo, J.J. Use of natural sorbents for accelerated bioremediation of grey forest soil contaminated with crude oil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myazin, V.A.; Korneykova, M.V.; Chaporgina, A.A.; Fokina, N.V.; Vasilyeva, G.K. The Effectiveness of Biostimulation, Bioaugmentation and Sorption-Biological Treatment of Soil Contaminated with Petroleum Products in the Russian Subarctic. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilyeva, G.; Kondrashina, V.; Strijakova, E.; Ortega-Calvo, J.J. Adsorptive bioremediation of soil highly contaminated with crude oil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneykova, M.V.; Myazin, V.A.; Fokina, N.V.; Chaporgina, A.A. Bioremediation of Soil of the Kola Peninsula (Murmansk Region) Contaminated With Diesel Fuel. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 14, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkina, T.; Vasilyeva, G.; Popileshko, Y.; Bauer, T.; Sushkova, S.; Fedorenko, A.; Antonenko, E.; Pinskii, D.; Mazarji, M.; Ferreira, C.S.S. Sorption of benzo[a]pyrene by Chernozem and carbonaceous sorbents: Comparison of kinetics and interaction mechanisms. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myazin, V.A.; Isakova, E.A.; Vasilyeva, G.K. The effect of activated carbon on the bioremediation rate of soils of the historically contaminated with oil products in the Murmansk region. Probl. Reg. Ecol. 2020, 2, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenyuk, N.N.; Yatsenko, V.S.; Strijakova, E.R.; Filonov, A.E.; Petrikov, K.V.; Zavgorodnyaya, Y.A.; Vasilyeva, G.K. Effect of Activated Charcoal on Bioremediationof Diesel Fuel Contaminated Soil. Microbiology 2014, 83, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubkina, T.G.; Belyaevsky, A.T.; Masloboev, V.A. Methods for obtaining hydrophobic oil sorbents by modifying the surface of vermiculite with organosiloxanes. Bull. Mosc. State Technol. Univ. 2011, 4, 767–773. [Google Scholar]
- Chukhareva, N.V.; Shishmina, L.V. Low-moor and moor peat sorption properties comparison relative to commercial oil and stable gas condensate. Chem. Plant Raw Mater. 2012, 4, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Nazina, T.; Sokolova, D.; Grouzdev, D.; Semenova, E.; Babich, T.; Bidzhieva, S.; Serdukov, D.; Volkov, D.; Bugaev, K.; Ershov, A.; et al. The Potential Application of Microorganisms for Sustainable Petroleum Recovery from Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Sustainability 2020, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazina, T.N.; Sokolova, D.S.; Babich, T.L.; Semenova, E.M.; Ershov, A.P.; Bidzhieva, S.K.; Borzenkov, I.A.; Poltaraus, A.B.; Khisametdinov, M.R.; Tourova, T.P. Microorganisms of low-temperature heavy oil reservoirs (Russia) and their possible application for enhanced oil recovery. Microbiology 2017, 86, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzenkov, I.A.; Semenova, E.M.; Sokolova, D.S.; Babich, T.L.; Ershov, A.P.; Bidzhieva, A.K.; Nazina, T.N. Strain Rhodococcus erythropolis ho-ks22, having high urease activity, capable of generation of an oil-displacing agent bio-surfactant in an oil reservoir. RU 2717025C1, 17 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- GOST R 57447-2017; Reclamation of Lands Contaminated with Oil and Oil Products; Reclamation of Lands Contaminated with Oil and Oil Products. Standartinform: Moscow, Russia, 2017; 32p.
- Gennadiev, A.N.; Pikovsky, Y.I.; Tsibart, A.S.; Smirnova, M.A. Hydrocarbons in soils: Origin, composition, behavior (review). Soil Sci. 2015, 10, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, E.R. Aseptic laboratory techniques: Plating methods. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 63, e3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineev, V.G. Practical Training in Agrochemistry: Textbook, 2nd ed.; Moscow State University Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 2001; 689p. [Google Scholar]
- GOST 26423-85; Methods for Determination of Specific Electric Conductivity, pH and Solid Residue of Water Extract. Standartinform: Moscow, Russia, 2011.
- Lifshits, S.; Glyaznetsova, Y.; Erofeevskaya, L.; Chalaya, O.; Zueva, I. Effect of oil pollution on the ecological condition of soils and bottom sediments of the arctic region (Yakutia). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlin, K.M.; Perkins, M.J.; Field, J.A.; Leigh, M.B. Biodegradation of Crude Oil and Corexit 9500 in Arctic Seawater. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarlin, K.M.; Prince, R.C.; Perkins, R.; Leigh, M.B. Biodegradation of dispersed oil in arctic seawater at −1 °C. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, R.C.; Butler, J.D.; Redman, A.D. The rate of crude oil biodegradation in the sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribicic, D.; McFarlin, K.M.; Netzer, R.; Brakstad, O.G.; Winkler, A.; Throne-Holst, M.; Størseth, T.R. Oil type and temperature dependent biodegradation dynamics—Combining chemical and microbial community data through multivariate analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustitus, S.A.; Clement, T.P. Formation, fate, and impacts of microscopic and macroscopic oil-sediment residues in nearshore marine environments: A critical review. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 1130–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, R.C. Petroleum spill bioremediation in marine environments. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1993, 19, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlas, R.M. Biodegradation of Hydrocarbons in the Environment; Environmental Biotechnology, Omenn, G.S., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.M.C.; Bautista, M.A.; Cramm, M.A.; Hubert, C.R.J. Diesel and crude oil biodegradation by cold-adapted microbial communities in the Labrador Sea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e00800–e00821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M. Microbial hydrocarbon degradation—Bioremediation of oil spills. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1991, 52, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Altshuler, I.; Freyria, N.J.; Lirette, A.; Góngora, E.; Greer, C.W.; Whyte, L.G. Arctic’s hidden hydrocarbon degradation microbes: Investigating the effects of hydrocarbon contamination, biostimulation, and a surface washing agent on microbial communities and hydrocarbon biodegradation pathways in high-Arctic beaches. Environ. Microbiome 2024, 19, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delille, D.; Delille, B.; Pelletier, E. Effectiveness of bioremediation of crude oil contaminated subantarctic intertidal sediment: The microbial response. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 44, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røberg, S.; Østerhus, J.I.; Landfald, B. Dynamics of bacterial community exposed to hydrocarbons and oleophilic fertilizer in high-Arctic intertidal beach. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vasilyeva, Z.V.; Vasekha, M.V.; Tyulyaev, V.S. Evaluation of the efficiency of sorbents for accidental oil spill response in the Arctic waters. J. Min. Inst. 2023, 264, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Substrates | TOC, % | pH | Dehydrogenase Activity, mg TPP·10 g−1 | TPH, mg·kg−1 | Description of the Site |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | 0.10 | 6.25 | 0.01 | 41 | Sandy beach |
| Soil | 4.74 | 3.85 | 0.17 | 85 | Meadow shores: 0–2 cm—organogenic, deeper than 2 cm—loam |
| Variants * | Sorbents, g | Mineral Fertilizers, g | Bacterial Suspension, mL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peat | GAC | VER | |||
| 1 (Natural attenuation) | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 (HO-KS22 + Peat) | 10 | - | - | 0.36 | 4 |
| 3 (HO-KS22 + GAC) | - | 2 | - | 0.36 | 4 |
| 4 (HO-KS22 + vermiculite) | - | - | 1 | 0.36 | 4 |
| Sand | Soil | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light Oil | Medium Oil | Heavy Oil | Light Oil | Medium Oil | Heavy Oil | |
| Natural attenuation | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.011 |
| R. erythropolis and peat | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.008 | 0.013 | 0.010 |
| R. erythropolis and activated carbon | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.009 | 0.015 | 0.011 |
| R. erythropolis and vermiculite | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Myazin, V.; Korneykova, M.; Fokina, N.; Semenova, E.; Babich, T.; Murzaeva, M. Sorption–Biological Treatment of Coastal Substrates of the Barents Sea in Low Temperature Using the Rhodococcus erythropolis Strain HO-KS22. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092181
Myazin V, Korneykova M, Fokina N, Semenova E, Babich T, Murzaeva M. Sorption–Biological Treatment of Coastal Substrates of the Barents Sea in Low Temperature Using the Rhodococcus erythropolis Strain HO-KS22. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092181
Chicago/Turabian StyleMyazin, Vladimir, Maria Korneykova, Nadezhda Fokina, Ekaterina Semenova, Tamara Babich, and Milana Murzaeva. 2025. "Sorption–Biological Treatment of Coastal Substrates of the Barents Sea in Low Temperature Using the Rhodococcus erythropolis Strain HO-KS22" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092181
APA StyleMyazin, V., Korneykova, M., Fokina, N., Semenova, E., Babich, T., & Murzaeva, M. (2025). Sorption–Biological Treatment of Coastal Substrates of the Barents Sea in Low Temperature Using the Rhodococcus erythropolis Strain HO-KS22. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092181






