CGRP Suppresses Protective SiglecFhi Neutrophil Development in Neonatal Group B Streptococcus Pneumonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animal Housing
2.3. Bacterial Strains and Culture
2.4. Neonatal Mouse Model of GBS Pneumonia
2.5. Clinical Evaluation
2.6. Tissue Collection
2.7. Bacterial Load Analysis
2.8. Histological Analysis
2.9. Cell Isolation
2.10. Flow Cytometry
2.11. Intracellular Staining
2.12. RNA Extraction
2.13. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.14. Bacterial Killing Assays
2.15. Neutrophil Stimulation with CGRP In Vitro
2.16. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
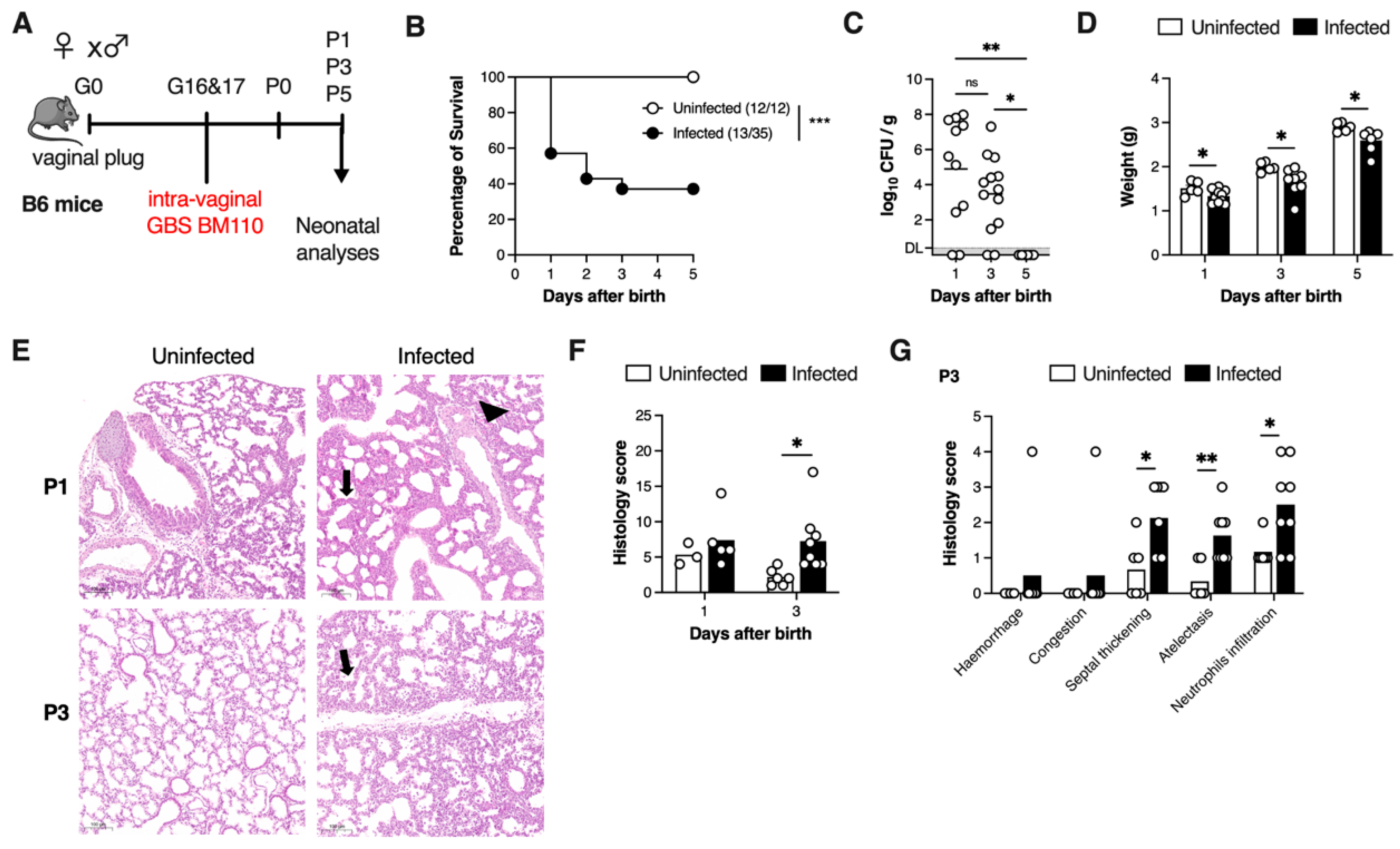
3.1. Vertical Transmission of GBS Leads to Lung Pathology
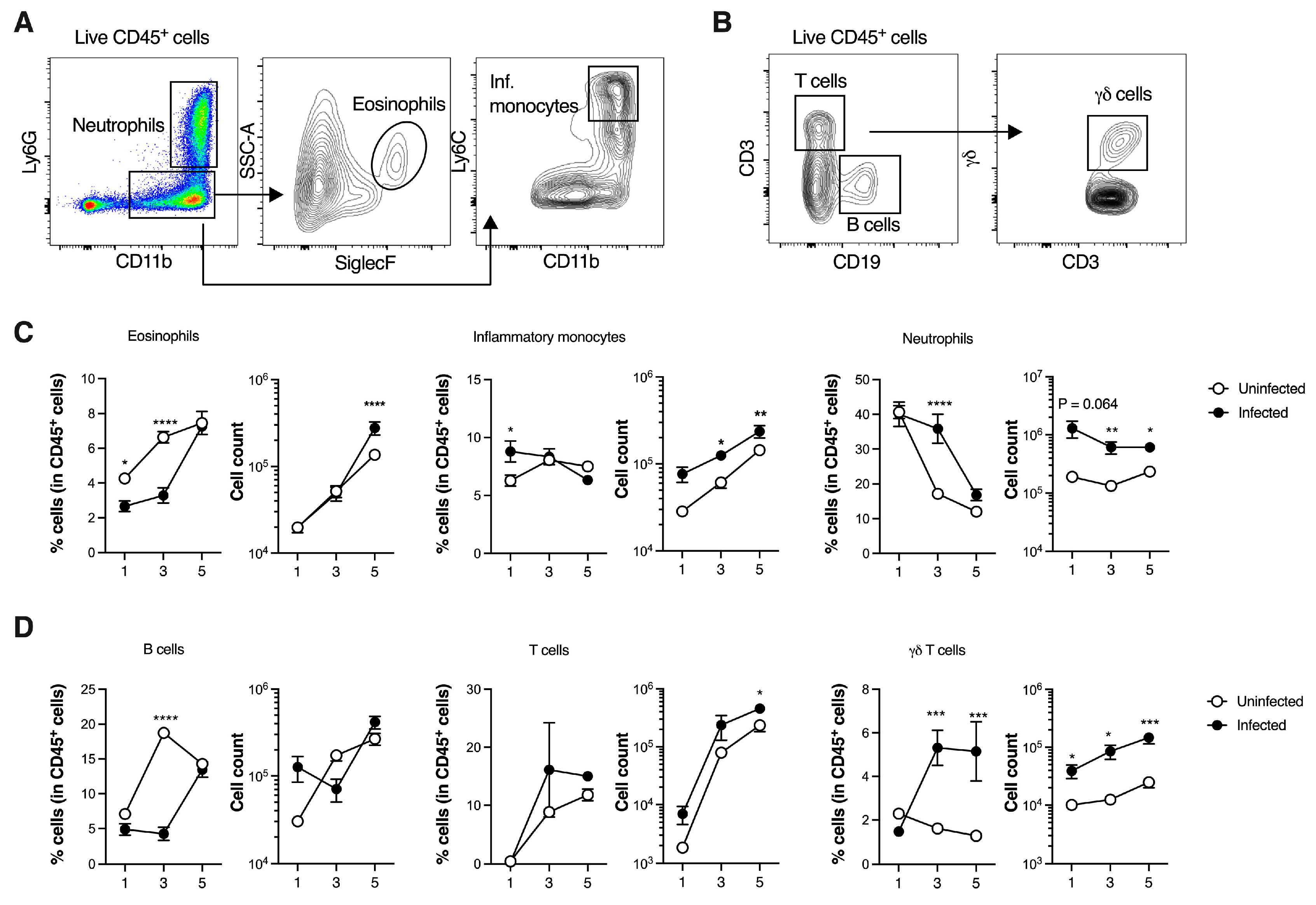
3.2. GBS Neonatal Pneumonia Does Not Impair Neutrophil Recruitment to the Lungs
3.3. SiglecFhi Neutrophils Accumulate in the Neonatal Lungs During Moderate Disease
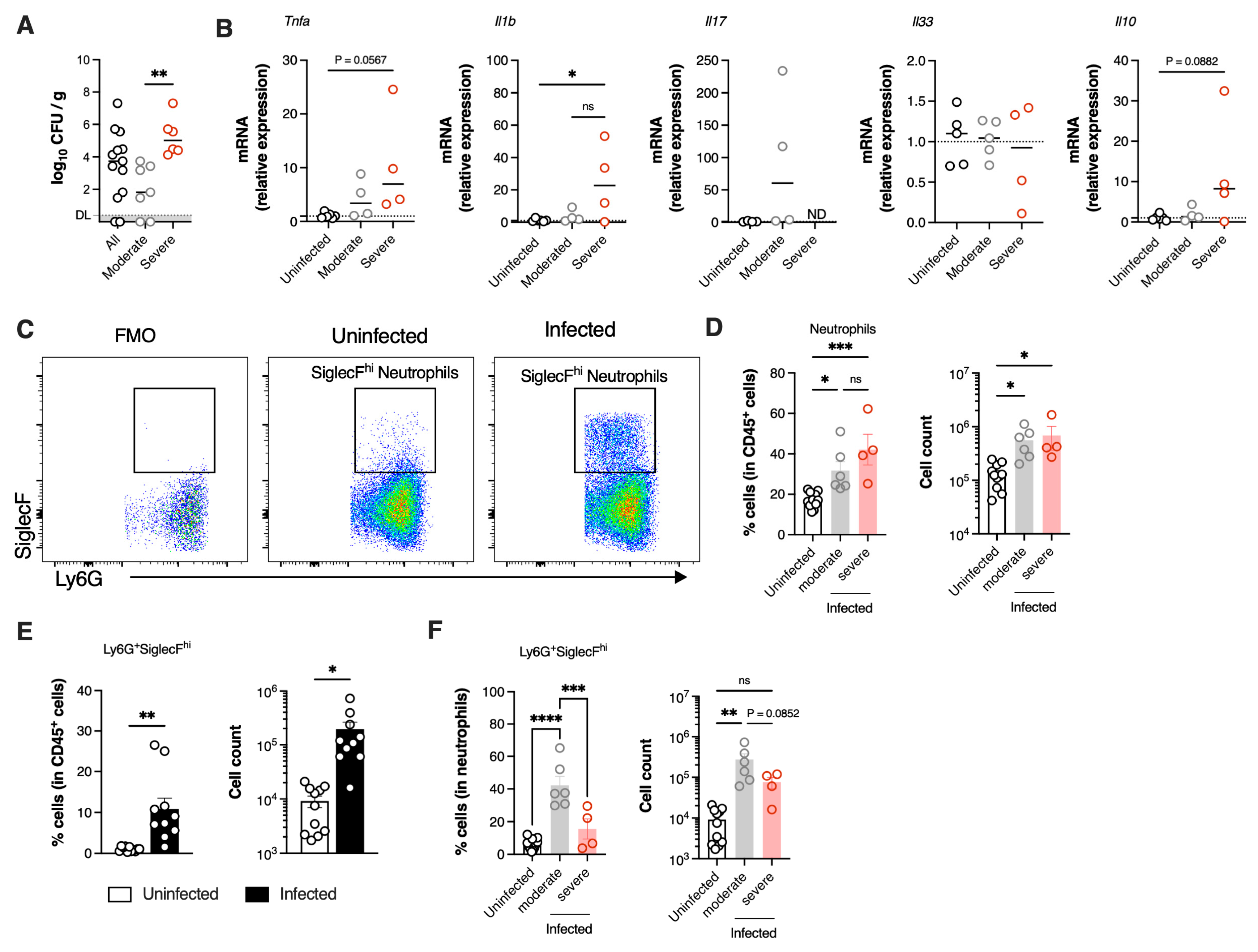
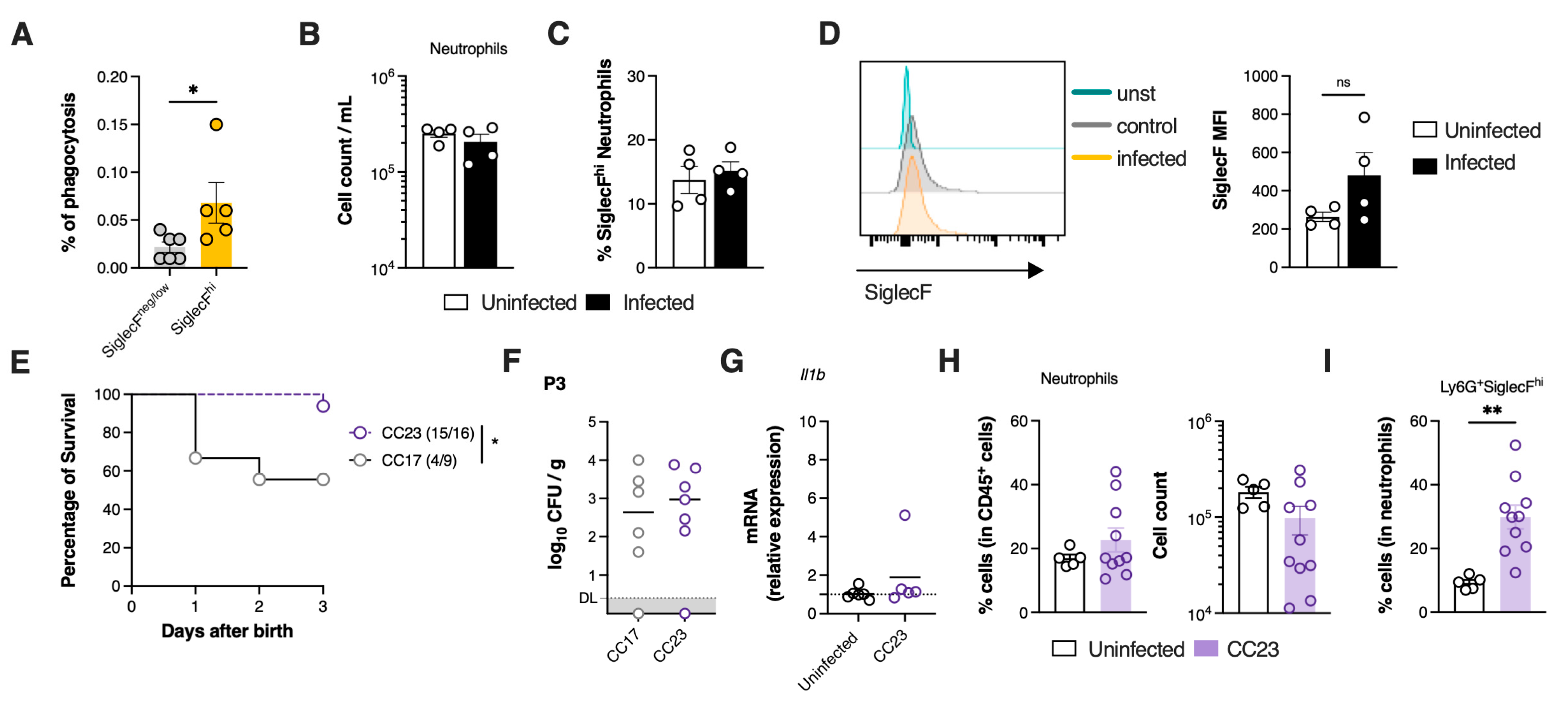
3.4. SiglecFhi Neutrophils Exhibit Enhanced Phagocytic Capacity and Contribute to Bacterial Clearance
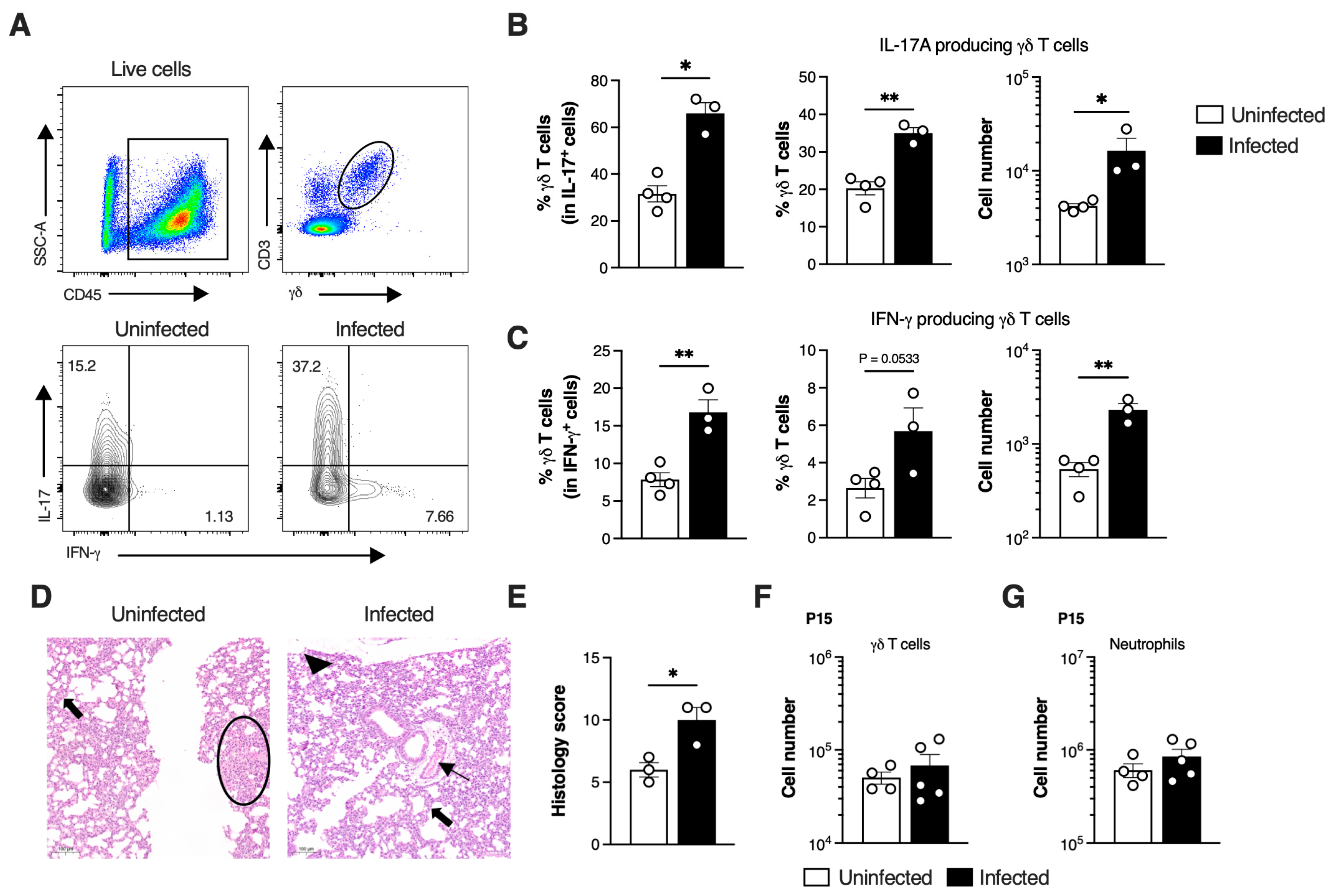
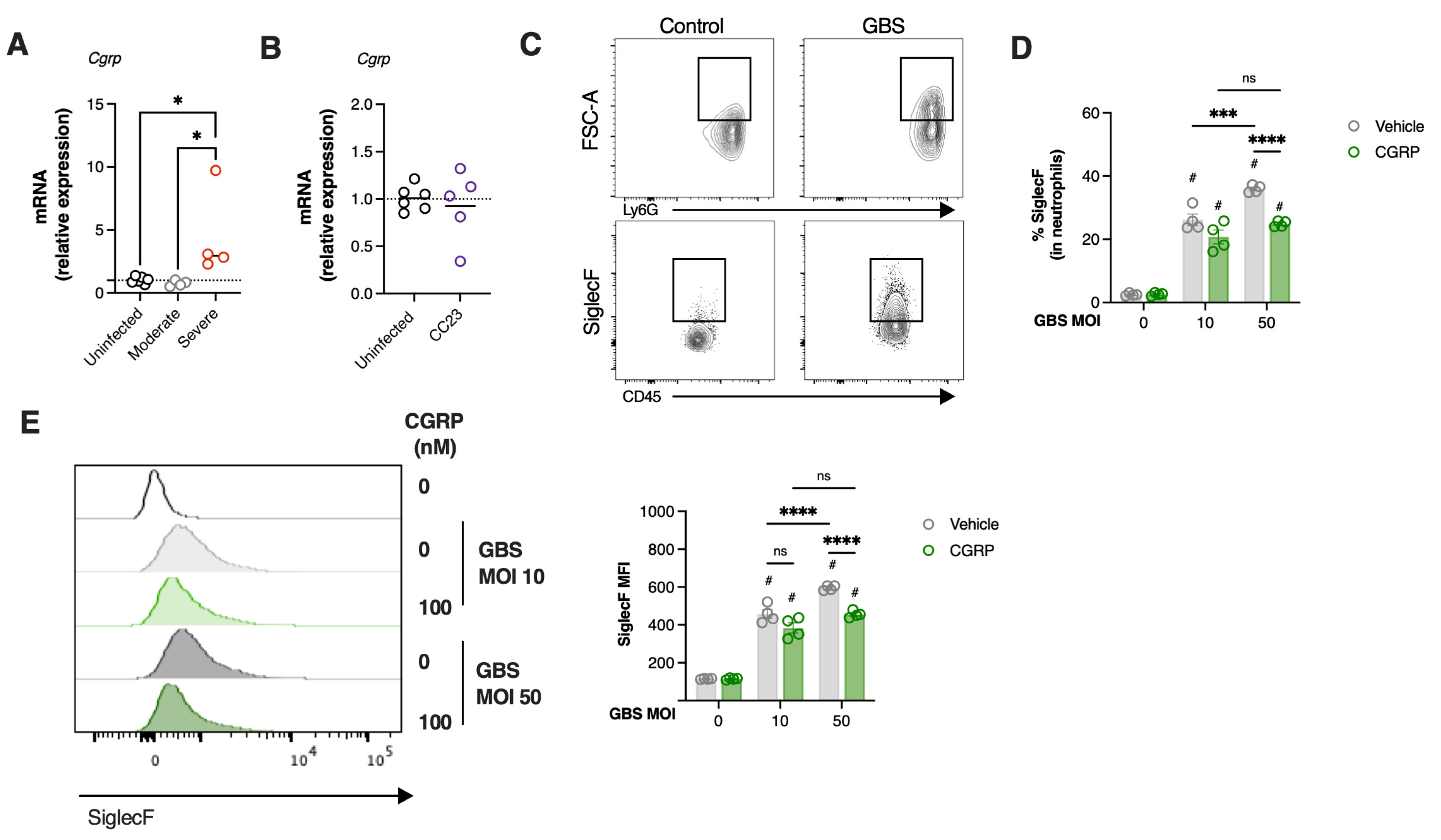
3.5. Severe GBS Pneumonia Induces CGRP Expression in the Lungs Dampening SiglecFhi Neutrophil Development
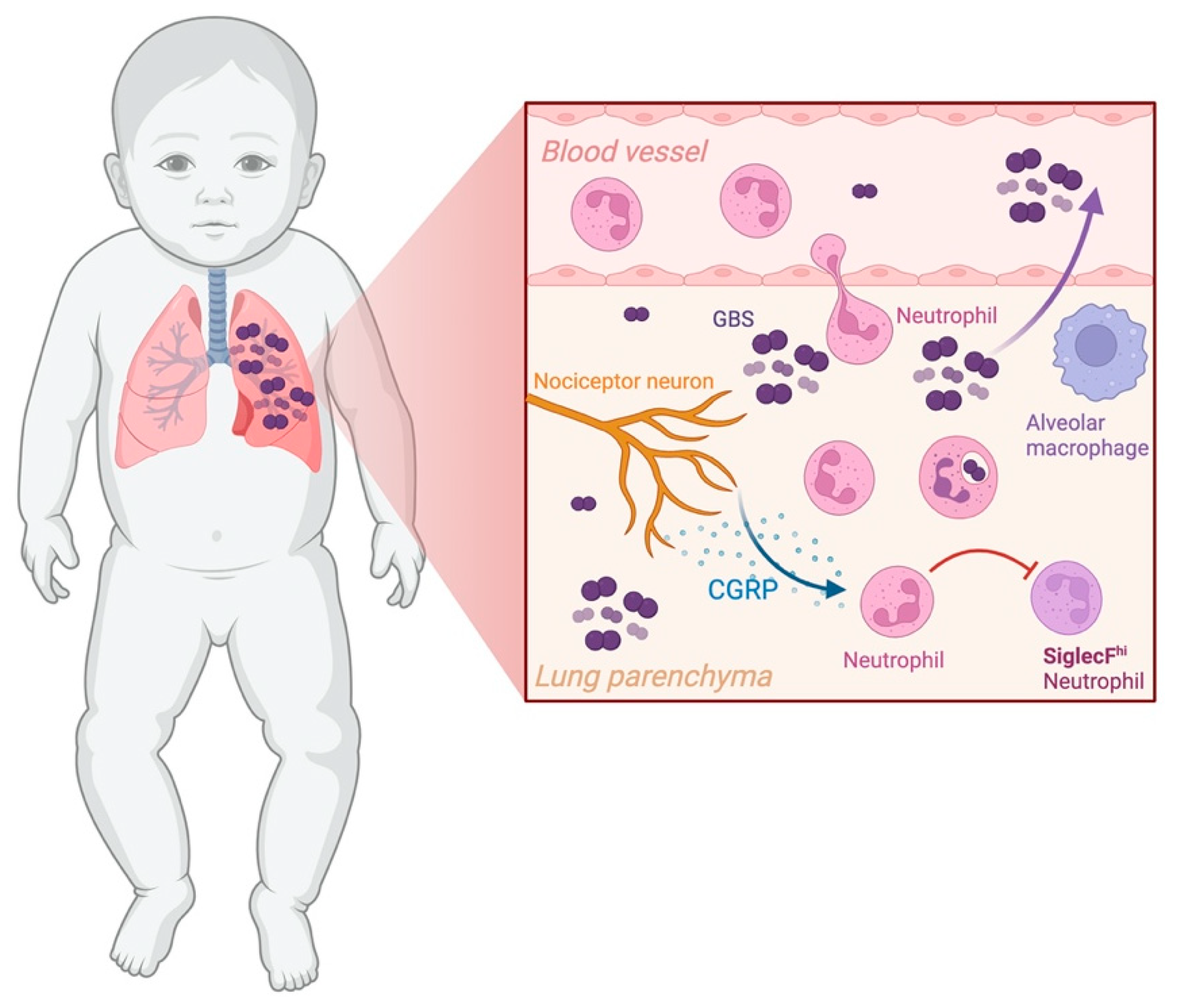
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hooven, T.A.; Polin, R.A. Pneumonia. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 22, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.U.-M. Global, regional, and national progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 3.2 for neonatal and child health: All-cause and cause-specific mortality findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2021, 398, 870–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, Y.; Nizet, V.; Barnett, E.D.; Edwards, K.M.; Malley, R. Remington and Klein’s Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant; Elsevier/Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, T.; Pinho, L.; Bonifacio Andrade, E. Group B Streptococcal Neonatal Meningitis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e0007921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randis, T.M.; Baker, J.A.; Ratner, A.J. Group B streptococcal infections. Pediatr. Rev. 2017, 38, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, P.; Umans, B.D.; Li, L.; Wallrapp, A.; Bist, M.; Kirschbaum, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Burkett, P.R.; et al. Nociceptor sensory neurons suppress neutrophil and gammadelta T cell responses in bacterial lung infections and lethal pneumonia. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, V.G.; McCloskey, D.W.; Hill, H.R. Pneumonia in the neonate associated with group B streptococcal septicemia. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1976, 130, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsafaras, G.P.; Ntontsi, P.; Xanthou, G. Advantages and Limitations of the Neonatal Immune System. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollmann, T.R.; Kampmann, B.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Marchant, A.; Levy, O. Protecting the Newborn and Young Infant from Infectious Diseases: Lessons from Immune Ontogeny. Immunity 2017, 46, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burn, G.L.; Foti, A.; Marsman, G.; Patel, D.F.; Zychlinsky, A. The Neutrophil. Immunity 2021, 54, 1377–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, O.; Martin, S.; Eichenwald, E.; Ganz, T.; Valore, E.; Carroll, S.F.; Lee, K.; Goldmann, D.; Thorne, G.M. Impaired innate immunity in the newborn: Newborn neutrophils are deficient in bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. Pediatrics 1999, 104, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmen, M.; Satar, M.; Atici, A. Neutrophil chemotaxis and random migration in preterm and term infants with sepsis. Am. J. Perinatol. 2000, 17, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, C.C.; Cody, M.J.; Harris, E.S.; Thornton, N.L.; McInturff, A.M.; Martinez, M.L.; Chandler, N.B.; Rodesch, C.K.; Albertine, K.H.; Petti, C.A.; et al. Impaired neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation: A novel innate immune deficiency of human neonates. Blood 2009, 113, 6419–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfirschke, C.; Engblom, C.; Gungabeesoon, J.; Lin, Y.; Rickelt, S.; Zilionis, R.; Messemaker, M.; Siwicki, M.; Gerhard, G.M.; Kohl, A.; et al. Tumor-Promoting Ly-6G(+) SiglecF(high) Cells Are Mature and Long-Lived Neutrophils. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, M.; Nagakubo, D.; Satooka, H.; Hirata, T. A novel Siglec-F(+) neutrophil subset in the mouse nasal mucosa exhibits an activated phenotype and is increased in an allergic rhinitis model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroki, C.H.; Hassanabad, M.F.; Defaye, M.; Sarden, N.; Bartlett, A.; Farias, R.; Nguyen, A.P.; Guerrero-Fonseca, I.M.; Yoon, G.; Brown, L.; et al. Nociceptor neurons suppress alveolar macrophage-induced Siglec-F(+) neutrophil-mediated inflammation to protect against pulmonary fibrosis. Immunity 2025, 58, 2054–2068.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, K.J.; Jiang, X.R.; Chiu, I.M. Neuronal Regulation of Immunity in the Skin and Lungs. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, I.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Woolf, C.J. Pain and infection: Pathogen detection by nociceptors. Pain 2016, 157, 1192–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trankner, D.; Hahne, N.; Sugino, K.; Hoon, M.A.; Zuker, C. Population of sensory neurons essential for asthmatic hyperreactivity of inflamed airways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11515–11520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baral, P.; Udit, S.; Chiu, I.M. Pain and immunity: Implications for host defence. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Baddal, B.; Haarsma, R.; O’Seaghdha, M.; Yang, N.J.; Blake, K.J.; Portley, M.; Verri, W.A.; Dale, J.B.; Wessels, M.R. Blocking neuronal signaling to immune cells treats streptococcal invasive infection. Cell 2018, 173, 1083–1097.E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Deng, L.; Neel, D.V.; Erdogan, O.; Basu, H.; Yang, D.; Choi, S.; Walker, A.J.; Carneiro-Nascimento, S.; He, K.; et al. Bacteria hijack a meningeal neuroimmune axis to facilitate brain invasion. Nature 2023, 615, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.-Y.C.; Whiting, A.; Adderson, E.; Takahashi, S.; Dunn, D.M.; Weiss, R.; Azimi, P.H.; Philips III, J.B.; Weisman, L.E.; Regan, J. Phylogenetic lineages of invasive and colonizing strains of serotype III group B streptococci from neonates: A multicenter prospective study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jones, N.; Bohnsack, J.F.; Takahashi, S.; Oliver, K.A.; Chan, M.-S.; Kunst, F.; Glaser, P.; Rusniok, C.; Crook, D.W.; Harding, R.M. Multilocus sequence typing system for group B streptococcus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2530–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlhaber, B.; Heinemann, A.S.; Rubensam, K.; Willers, M.; Vollger, L.; Pfeifer, S.; von Kockritz-Blickwede, M.; Viemann, D. A sensitive scoring system for the longitudinal clinical evaluation and prediction of lethal disease outcomes in newborn mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubags, N.D.; Suratt, B.T. Isolation and characterization of mouse neutrophils. In Lung Innate Immunity and Inflammation: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, E.B.; Magalhaes, A.; Puga, A.; Costa, M.; Bravo, J.; Portugal, C.C.; Ribeiro, A.; Correia-Neves, M.; Faustino, A.; Firon, A.; et al. A mouse model reproducing the pathophysiology of neonatal group B streptococcal infection. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Doare, K.; Heath, P.T. An overview of global GBS epidemiology. Vaccine 2013, 31, D7–D12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Cilloniz, C.; Niederman, M.S.; Menendez, R.; Chalmers, J.D.; Wunderink, R.G.; van der Poll, T. Pneumonia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, F.T.; Traber, K.E. Innate immune responses in pneumonia. Pneumonia 2023, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi-zhi, J.G.; Dash, P.; Crawford, J.C.; Allen, E.K.; Zamora, A.E.; Boyd, D.F.; Duan, S.; Bajracharya, R.; Awad, W.A.; Apiwattanakul, N. Lung γδ T cells mediate protective responses during neonatal influenza infection that are associated with type 2 immunity. Immunity 2018, 49, 531–544.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairallah, C.; Chu, T.H.; Sheridan, B.S. Tissue adaptations of memory and tissue-resident gamma delta T cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittny, J.C.; Mund, S.I.; Stampanoni, M. Evidence and structural mechanism for late lung alveolarization. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L246–L254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kleer, I.M.; Kool, M.; de Bruijn, M.J.; Willart, M.; van Moorleghem, J.; Schuijs, M.J.; Plantinga, M.; Beyaert, R.; Hams, E.; Fallon, P.G.; et al. Perinatal Activation of the Interleukin-33 Pathway Promotes Type 2 Immunity in the Developing Lung. Immunity 2016, 45, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilliams, M.; De Kleer, I.; Henri, S.; Post, S.; Vanhoutte, L.; De Prijck, S.; Deswarte, K.; Malissen, B.; Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. Alveolar macrophages develop from fetal monocytes that differentiate into long-lived cells in the first week of life via GM-CSF. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1977–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, P.; Rusniok, C.; Buchrieser, C.; Chevalier, F.; Frangeul, L.; Msadek, T.; Zouine, M.; Couve, E.; Lalioui, L.; Poyart, C.; et al. Genome sequence of Streptococcus agalactiae, a pathogen causing invasive neonatal disease. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 1499–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollman, J.H.; Smith, W.L.; Ballard, E.T.; Light, I.J. Early onset group B streptococcal disease: Clinical, roentgenographic, and pathologic features. J. Pediatr. 1976, 89, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, D.J.; Levy, O. Ontogeny of early life immunity. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamim, C.F.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q. Role of nitric oxide in the failure of neutrophil migration in sepsis. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Filho, J.C.; Spiller, F.; Cunha, F.Q. Neutrophil paralysis in sepsis. Shock 2010, 34 (Suppl. 1), 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosara-Alberto, D.P.; Darini, A.L.; Inoue, R.Y.; Silva, J.S.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q. Involvement of NO in the failure of neutrophil migration in sepsis induced by Staphylococcus aureus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, H.M.; Calhoun, D.A.; Christensen, R.D. Use of myeloid colony-stimulating factors in neonates with septicemia. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2002, 14, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessler, P.; Kirchmann, N.; Kientsch-Engel, R.; Haas, N.; Lasch, P.; Kachel, W. Serum concentrations of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in healthy term and preterm neonates and in those with various diseases including bacterial infections. Blood 1993, 82, 3177–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, E.B.; Alves, J.; Madureira, P.; Oliveira, L.; Ribeiro, A.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A.; Correia-Neves, M.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Ferreira, P. TLR2-induced IL-10 production impairs neutrophil recruitment to infected tissues during neonatal bacterial sepsis. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4759–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madureira, P.; Andrade, E.B.; Gama, B.; Oliveira, L.; Moreira, S.; Ribeiro, A.; Correia-Neves, M.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Vilanova, M.; Ferreira, P. Inhibition of IL-10 production by maternal antibodies against Group B Streptococcus GAPDH confers immunity to offspring by favoring neutrophil recruitment. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, N.H.; Kallapur, S.G.; Jobe, A.H. Physiology of transition from intrauterine to extrauterine life. Clin. Perinatol. 2012, 39, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, L.; Eaton, D.C. Physiology of fetal lung fluid clearance and the effect of labor. Semin. Perinatol. 2006, 30, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engblom, C.; Pfirschke, C.; Zilionis, R.; Da Silva Martins, J.; Bos, S.A.; Courties, G.; Rickelt, S.; Severe, N.; Baryawno, N.; Faget, J.; et al. Osteoblasts remotely supply lung tumors with cancer-promoting SiglecF(high) neutrophils. Science 2017, 358, eaal5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagno, D.M.; Zhang, C.; Toomu, A.; Huang, K.; Ninh, V.K.; Miyamoto, S.; Aguirre, A.D.; Fu, Z.; Heller Brown, J.; King, K.R. SiglecF(HI) Marks Late-Stage Neutrophils of the Infarcted Heart: A Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Neutrophil Diversification. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafadarnejad, E.; Rizzo, G.; Krampert, L.; Arampatzi, P.; Arias-Loza, A.P.; Nazzal, Y.; Rizakou, A.; Knochenhauer, T.; Bandi, S.R.; Nugroho, V.A.; et al. Dynamics of Cardiac Neutrophil Diversity in Murine Myocardial Infarction. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, e232–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.W.; Kim, J.; Ham, S.; Choi, S.M.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.H.; Kang, H.R.; Kim, Y.M.; et al. A unique population of neutrophils generated by air pollutant-induced lung damage exacerbates airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1253–1269.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Shin, J.W.; Kwon, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.C.; Bae, Y.S.; Bae, Y.S.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Yang, S.H.; et al. Siglec-F-expressing neutrophils are essential for creating a profibrotic microenvironment in renal fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e156876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkner, L.; Curham, L.M.; Wilk, M.M.; Moran, B.; Mills, K.H.G. IL-17 mediates protective immunity against nasal infection with Bordetella pertussis by mobilizing neutrophils, especially Siglec-F(+) neutrophils. Mucosal Immunol. 2021, 14, 1183–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, M.; Ben-Shaanan, T.L.; Rolls, A. Neuronal regulation of immunity: Why, how and where? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.R.; Veiga-Fernandes, H. Neuroimmune circuits in inter-organ communication. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkless, K.; Argunhan, F.; Brain, S.D. CGRP Discovery and Timeline. In Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Mechanisms; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 255, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assas, B.M.; Pennock, J.I.; Miyan, J.A. Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a key neurotransmitter in the neuro-immune axis. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusek, G.; Reim, D.; Tsujikawa, K.; Holzmann, B. Deficiency of the CGRP receptor component RAMP1 attenuates immunosuppression during the early phase of septic peritonitis. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, E.; Green, A.M.; Flynn, J.L. IL-17 production is dominated by gammadelta T cells rather than CD4 T cells during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4662–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Yamada, H.; Hara, H.; Kishihara, K.; Yoshikai, Y. Resident Vdelta1+ gammadelta T cells control early infiltration of neutrophils after Escherichia coli infection via IL-17 production. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4466–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, A.; Wilk, M.M.; Raverdeau, M.; Mills, K.H. IL-17-Producing Innate and Pathogen-Specific Tissue Resident Memory gammadelta T Cells Expand in the Lungs of Bordetella pertussis-Infected Mice. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, C.E.; Lalor, S.J.; Sweeney, C.M.; Brereton, C.F.; Lavelle, E.C.; Mills, K.H. Interleukin-1 and IL-23 induce innate IL-17 production from gammadelta T cells, amplifying Th17 responses and autoimmunity. Immunity 2009, 31, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffelt, S.B.; Kersten, K.; Doornebal, C.W.; Weiden, J.; Vrijland, K.; Hau, C.S.; Verstegen, N.J.M.; Ciampricotti, M.; Hawinkels, L.; Jonkers, J.; et al. IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2015, 522, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Score | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Absence of histological changes |
| 1 | Parenchymal alterations in 1 to 25% of the tissue examined |
| 2 | Parenchymal alterations in 26 to 50% of the tissue examined |
| 3 | Parenchymal alterations in 51 to 75% of the tissue examined |
| 4 | Parenchymal alterations in 76 to 100% of the tissue examined |
| Primer ID | Oligonucleotide Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| Tnfa sense | GTGGAACTGGCAGAAGAG |
| Tnfa anti-sense | ATGAGAAGAGGCTGAGACA |
| Il1b sense | CAACCAACAAGTGATATTCTCCATG |
| Il1b anti-sense | GATCCACACTCTCCAGCTGCA |
| Il17a sense | CTCAGACTACCTCAACCGTTCCA |
| Il17a anti-sense | TTCCCTCCGCATTGACACA |
| Il33 sense | TCCAACTCCAAGATTTCCCCG |
| Il33 anti-sense | CATGCAGTAGACATGGCAGAA |
| Il10 sense | ATTTGAATTCCCTGGGTGAGAAG |
| Il10 anti-sense | CACAGGGGAGAAATCGATGACA |
| Cgrp sense | CCTGCAACACTGCCACCTGCG |
| Cgrp anti-sense | GAAGGCTTCAGAGCCCACATTG |
| Hprt1 sense | TCAGTCAACGGGGGACATAAA |
| Hprt1 anti-sense | GGGGCTGTACTGCTTAACCAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorga, I.; Teixeira, A.S.; Carvalho, B.; Soares, J.; Ribeiro, N.; Cardoso, M.S.; Cunha, J.; Santos, J.; Silva, R.A.; Vilanova, M.; et al. CGRP Suppresses Protective SiglecFhi Neutrophil Development in Neonatal Group B Streptococcus Pneumonia. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092119
Lorga I, Teixeira AS, Carvalho B, Soares J, Ribeiro N, Cardoso MS, Cunha J, Santos J, Silva RA, Vilanova M, et al. CGRP Suppresses Protective SiglecFhi Neutrophil Development in Neonatal Group B Streptococcus Pneumonia. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092119
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorga, Inês, Ana Sofia Teixeira, Bárbara Carvalho, Joana Soares, Nuno Ribeiro, Marcos S. Cardoso, Joana Cunha, Joana Santos, Regina A. Silva, Manuel Vilanova, and et al. 2025. "CGRP Suppresses Protective SiglecFhi Neutrophil Development in Neonatal Group B Streptococcus Pneumonia" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092119
APA StyleLorga, I., Teixeira, A. S., Carvalho, B., Soares, J., Ribeiro, N., Cardoso, M. S., Cunha, J., Santos, J., Silva, R. A., Vilanova, M., & Bonifácio Andrade, E. (2025). CGRP Suppresses Protective SiglecFhi Neutrophil Development in Neonatal Group B Streptococcus Pneumonia. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092119








