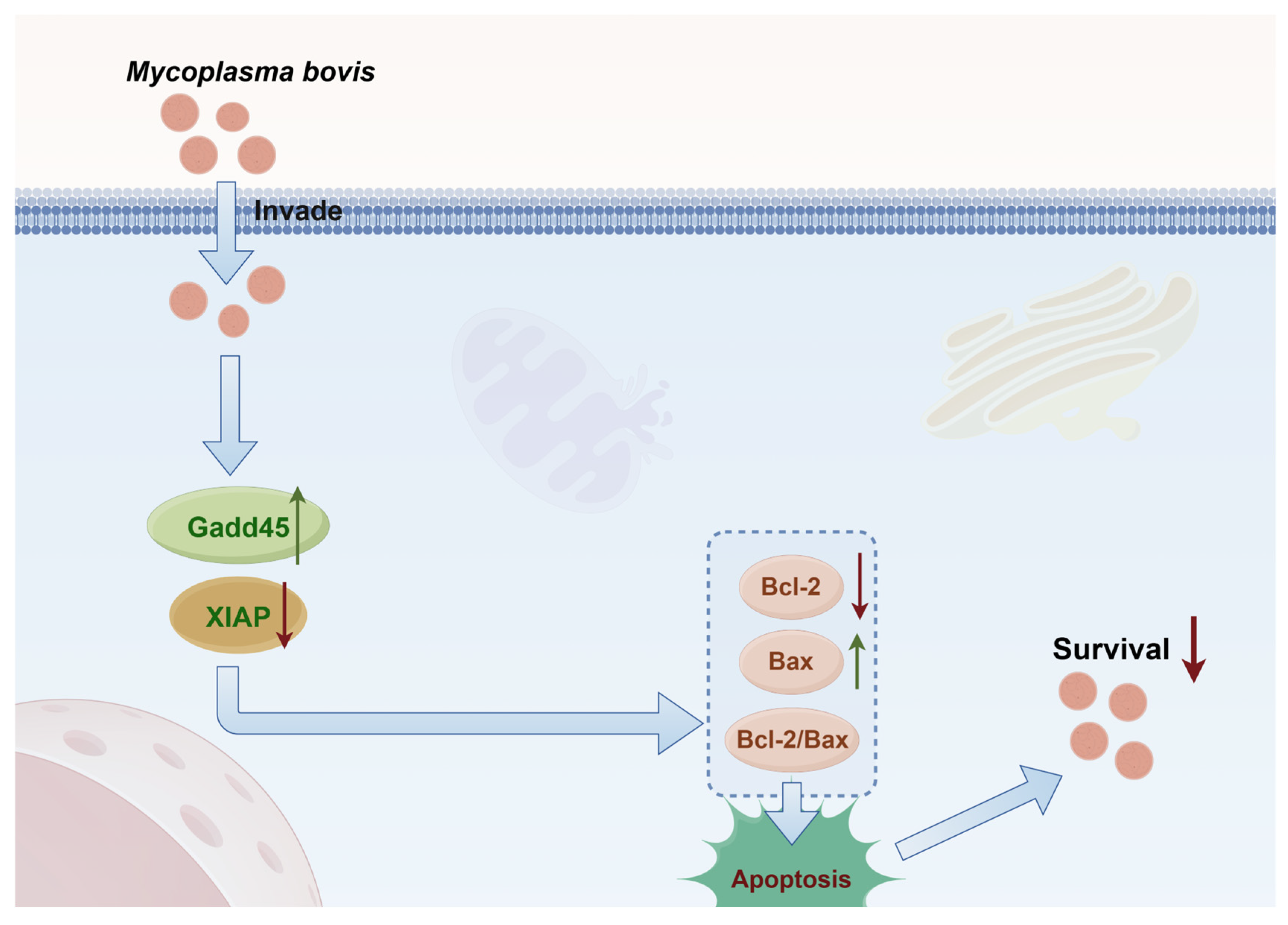
Mycoplasma bovis Infection Induces Apoptosis Through Gadd45/XIAP in Bovine Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture of Cells and M. bovis
2.2. Isolation and Identification of M. bovis
2.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing of M. bovis Isolate XJ01
2.4. Comparative Genomics Analysis of M. bovis Isolate XJ01
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assessment and Condition Optimization of M. bovis Infection in BoMac Cells
2.6. CCK8 Assay for Cell Viability
2.7. Detection of Cell Apoptosis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.9. Western Blot
2.10. Transcriptome Sequencing and Analysis of M. bovis -Infected BoMac Cells
2.11. Construction and Transfection of Gadd45 and XIAP Gene Overexpression Plasmids and siRNAs
2.12. Three siRNA Fragments Targeting Gadd45 mRNA (GenBank: NM_001034247.1) and XIAP mRNA (GenBank: NM_001205592.1) Were Designed and Synthesized by Sangon Biotech (China)
2.13. Quantitative Detection of Intracellular M. bovis
2.14. Quantitative and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation, Identification and Characterization of M. bovis Xinjiang Isolate XJ01
3.2. Genomic Features of M. bovis Strain XJ01 Reveal High Coding Density and Metabolic Diversity
3.3. Comparative Genomics and Evolutionary Analysis of M. bovis Strain XJ01
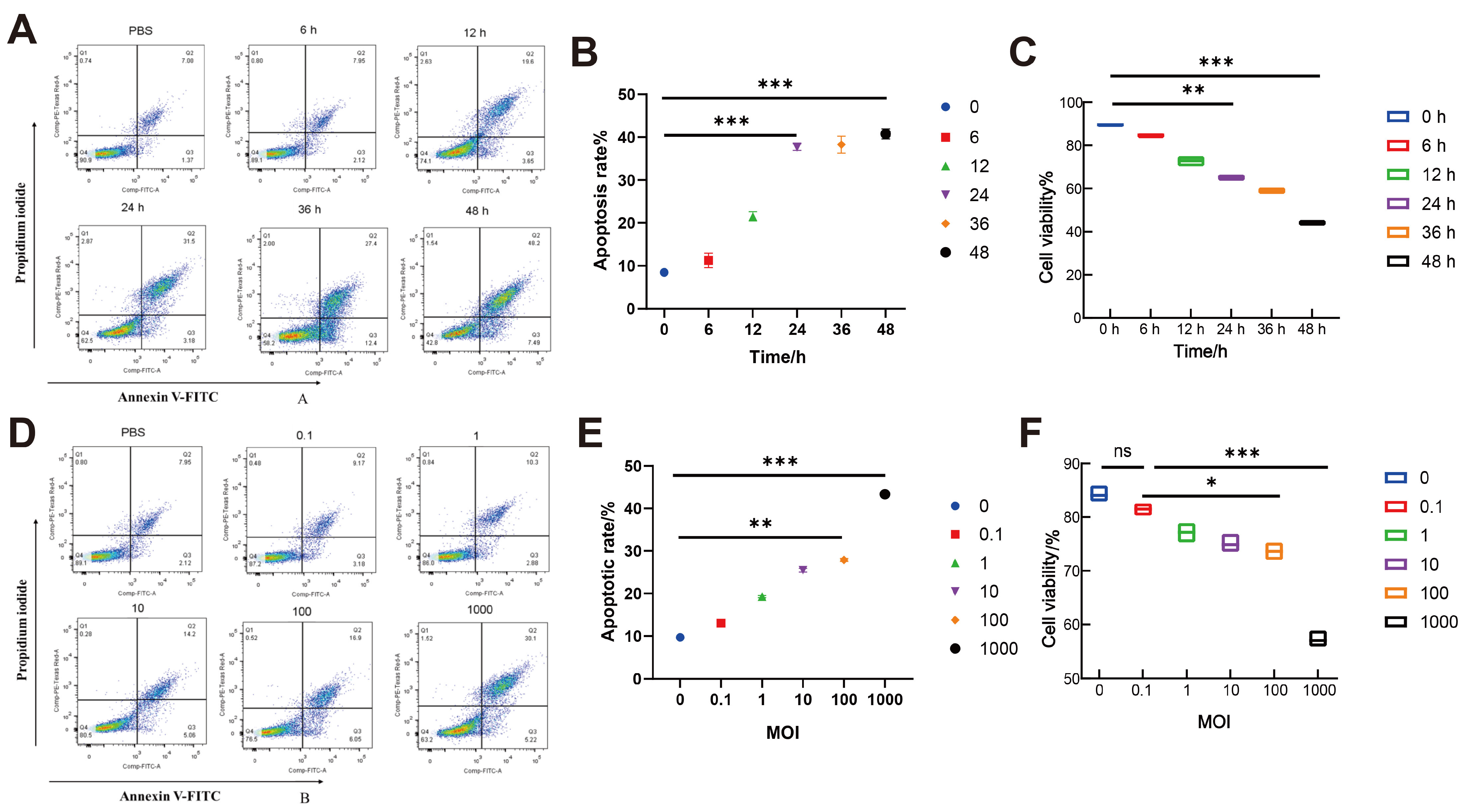
3.4. Establishment of an Apoptosis Model in BoMac Cells Induced by M. bovis Strain XJ01
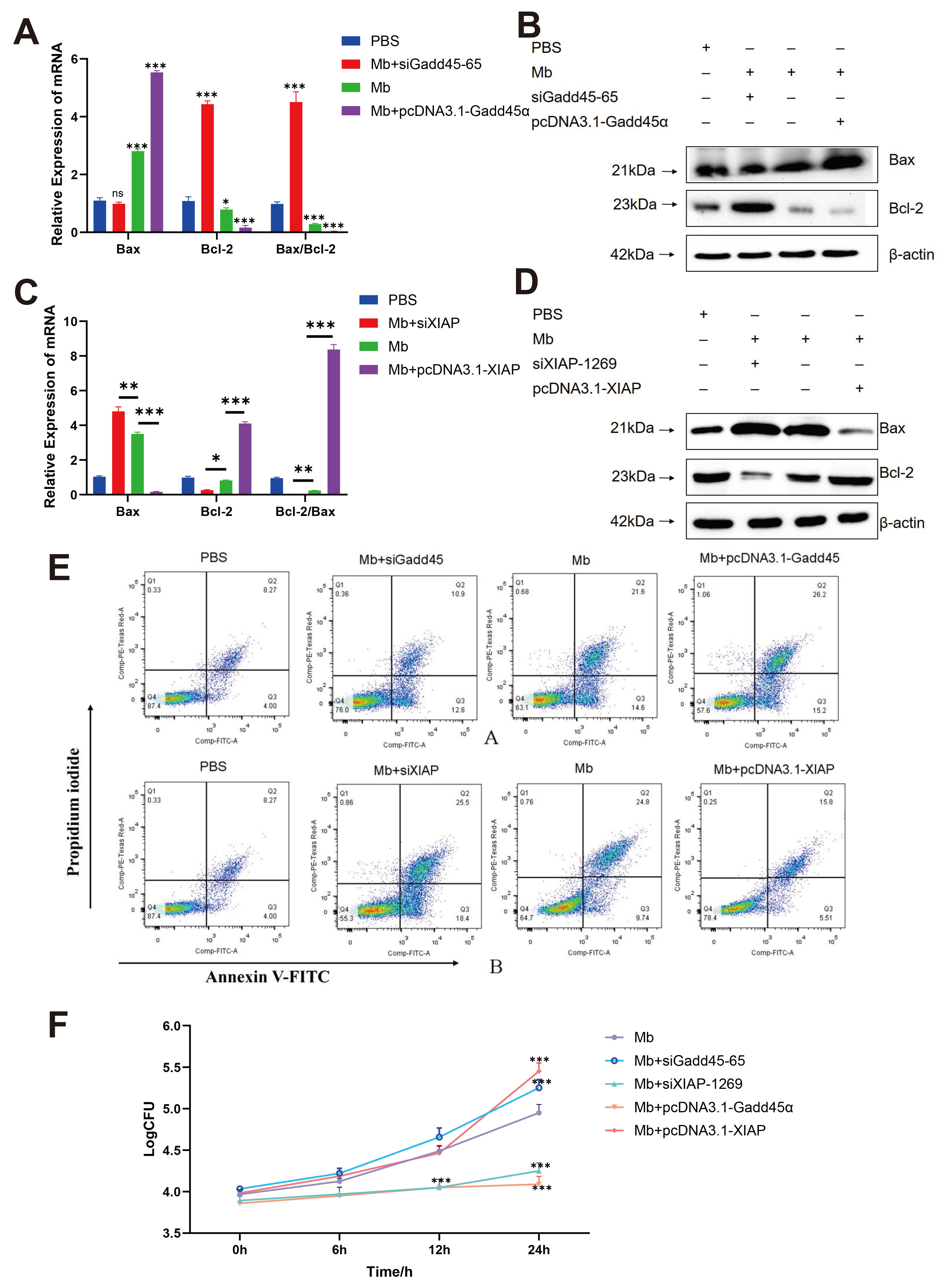
3.5. M. bovis XJ01 Induces Bax/Bcl-2-Mediated Apoptosis in BoMac Cells
3.6. M. bovis XJ01 Modulates Apoptosis-Associated Gene Networks in Infected BoMac Cells
3.7. M. bovis Targets Gadd45 and XIAP to Orchestrate Apoptotic Cascades in BoMac Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicholas, R.A.J.; Ayling, R.D. Mycoplasma bovis: Disease, diagnosis, and control. Res. Vet. Sci. 2003, 74, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Fu, P.; Wei, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiang, F.; Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Wu, W. Identification of novel immunogenic proteins from Mycoplasma bovis and establishment of an indirect ELISA based on recombinant E1 beta subunit of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, R.; Qi, J.; Ba, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C. In vitro quinolones susceptibility analysis of chinese Mycoplasma bovis isolates and their phylogenetic scenarios based upon QRDRs of DNA topoisomerases revealing a unique transition in ParC. Pak. Vet. J. 2013, 33, 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Pholpunthin, P.; Fukuyo, Y.; Matsuoka, K.; Nimura, Y. Immunomodulatory effect of Mycoplasma bovis in experimentally infected calves. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2013, 57, 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, H.H.; Helmboldt, C.F.; Plastridge, W.N.; Stula, E.F. Bovine mastitis caused by a Mycoplasma species. Cornell Vet. 1962, 52, 582–591. [Google Scholar]
- Walz, P.H.; Mullaney, T.P.; Render, J.A.; Walker, R.D.; Mosser, T.; Baker, J.C. Otitis media in preweaned Holstein dairy calves in Michigan due to Mycoplasma bovis. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1997, 9, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, J.L.; Archambault, M. Mycoplasma bovis pneumonia in cattle. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2007, 8, 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfi, Y.; Lartigue, C.; Sirand-Pugnet, P.; Blanchard, A. Beware of Mycoplasma anti-immunoglobulin strategies. mBio 2021, 12, e0197421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottem, S. Interaction of Mycoplasmas With Host Cells. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GroHennig, S.; Ischebeck, T.; Gibhardt, J.; Busse, J.; Feussner, I.; Stülke, J. Hydrogen sulfide is a novel potential virulence factor of Mycoplasma pneumoniae: Characterization of the unusual cysteine desulfurase/desulfhydrase HapE. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 100, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blötz, C.; Stülke, J. Glycerol metabolism and its implication in virulence in Mycoplasma. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, J.Y.; Wawegama, N.K.; Condello, A.K.; Marenda, M.S.; Markham, P.F.; Browning, G.F.; Tivendale, K.A. Mycoplasma bovis membrane protein MilA is a multifunctional lipase with novel lipid and glycosaminoglycan binding activity. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00945-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.W.; Chiu, C.J.; Kanci, A.; Citti, C.; Markham, P.F. The oppD gene and putative peptidase genes may be required for virulence in Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00023-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, H.; Guo, S.; Lei, Y.; He, S. Multi-locus sequence typing of Mycoplasma bovis to assess its genetic diversity from 2009–2018 in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, T.J.V.; Rosenbusch, R.F. Mycoplasma bovis induces apoptosis of bovine lymphocytes. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 32, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulongo, M.; Prysliak, T.; Scruten, E.; Napper, S.; Perez-Casal, J. In vitro infection of bovine monocytes with Mycoplasma bovis delays apoptosis and suppresses production of gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha but not interleukin-10. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Tang, L.; Li, N.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, H.; Lian, Y.; Chu, Y. Mycoplasma bovis activates apoptotic caspases to suppress xenophagy for its intracellular survival. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 298, 110298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimbo, S.; Suleman, M.; Maina, T.; Prysliak, T.; Mulongo, M.; Perez-Casal, J. Effect of Mycoplasma bovis on bovine neutrophils. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 188, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, T.; Prysliak, T.; Perez-Casal, J. Mycoplasma bovis delay in apoptosis of macrophages is accompanied by increased expression of anti-apoptotic genes, reduced cytochrome C translocation and inhibition of DNA fragmentation. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2019, 208, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, K.; Nicholas, R.A.J.; Szacawa, E.; Bednarek, D. Mycoplasma bovis infections—Occurrence, diagnosis and control. Pathogens 2020, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeris-Chacin, R.; Powledge, S.; McAtee, T.; Morley, P.S.; Richeson, J. Mycoplasma bovis is associated with Mannheimia haemolytica during acute bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 946792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydock, L.A.; Fenton, R.K.; Sergejewich, L.; Veldhuizen, R.A.; Smerek, D.; Ojkic, D.; Caswell, J.L. Bronchopneumonia with interstitial pneumonia in beef feedlot cattle: Characterization and laboratory investigation. Vet. Pathol. 2023, 60, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelgie, A.E.; Desai, S.E.; Gelalcha, B.D.; Kerro Dego, O. Mycoplasma bovis mastitis in dairy cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1322267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürki, S.; Gaschen, V.; Stoffel, M.H.; Stojiljkovic, A.; Pilo, P. Invasion and persistence of Mycoplasma bovis in embryonic calf turbinate cells. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thézé, J.; Ambroset, C.; Barry, S.; Masseglia, S.; Colin, A.; Tricot, A.; Tardy, F.; Bailly, X. Genome-wide phylodynamic approach reveals the epidemic dynamics of the main Mycoplasma bovis subtype circulating in France. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 001067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Long, C.; An, Z.; Xing, X.; Wen, F.; Bao, S. Mycoplasmas bovis P48 induces apoptosis in EBL cells via an endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent signaling pathway. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 255, 109013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, A. Novel secreted protein of Mycoplasma bovis MbovP280 induces macrophage apoptosis through CRYAB. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 619362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, S.; Chao, J.; Lu, D.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Faisal, M.; Yang, L.; Hu, C.; et al. The attenuated Mycoplasma bovis strain promotes apoptosis of bovine macrophages by upregulation of CHOP expression. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 925209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Xu, S.; Khan, M.A.; Han, B. Mycoplasma bovis-generated reactive oxygen species and induced apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cell cultures. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 10429–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Mayinuer, T.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, D.; Kastelic, J.P.; Han, B. Mycoplasma bovis inhibits autophagy in bovine mammary epithelial cells via a PTEN/PI3K-Akt-mTOR-dependent pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 935547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Noh, S.G.; Kim, S.; Chung, H.Y.; Lee, H.; Moon, J.O. Integrative transcriptomic analysis reveals upregulated apoptotic signaling in wound-healing pathway in rat liver fibrosis models. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xie, J.; Li, K.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xiong, X. Mulberrin alleviates triclocarban induced hepatic apoptosis and inflammation by regulating the ROS/NF-κB pathway in grass carp. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 273, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; He, Z.; Wang, L.; Gaoyang, H.; Wang, D.; Luo, P. Alterations of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio contribute to NaAsO 2 induced thyrotoxicity in human thyroid follicular epithelial cells and SD rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, J.; You, Y.; Zhou, Z. Purine metabolism and pyrimidine metabolism alteration is a potential mechanism of BDE-47-induced apoptosis in marine rotifer brachionus plicatilis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. GADD45 proteins: Roles in cellular senescence and tumor development. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ETamura, R.; Fde Vasconcellos, J.; Sarkar, D.; Libermann, T.A.; Fisher, P.B.; Zerbini, L.F. GADD45 proteins: Central players in tumorigenesis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 634–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmi, T.; Alecci, C.; Aquila, M.; Montorsi, L.; Martello, A.; Guizzetti, F.; Volpi, N.; Parenti, S.; Ferrari, S.; Salomoni, P. ZFP36 stabilizes RIP1 via degradation of XIAP and cIAP2 thereby promoting ripoptosome assembly. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Juan, X.; Liang, C. GADD45 proteins inhibit HIV-1 replication through specific suppression of HIV-1 transcription. Virology 2016, 493, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Kohama, Y.; Kuge, A.; Kido, E.; Sakurai, H. GADD45 family proteins suppress JNK signaling by targeting MKK7. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 635, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
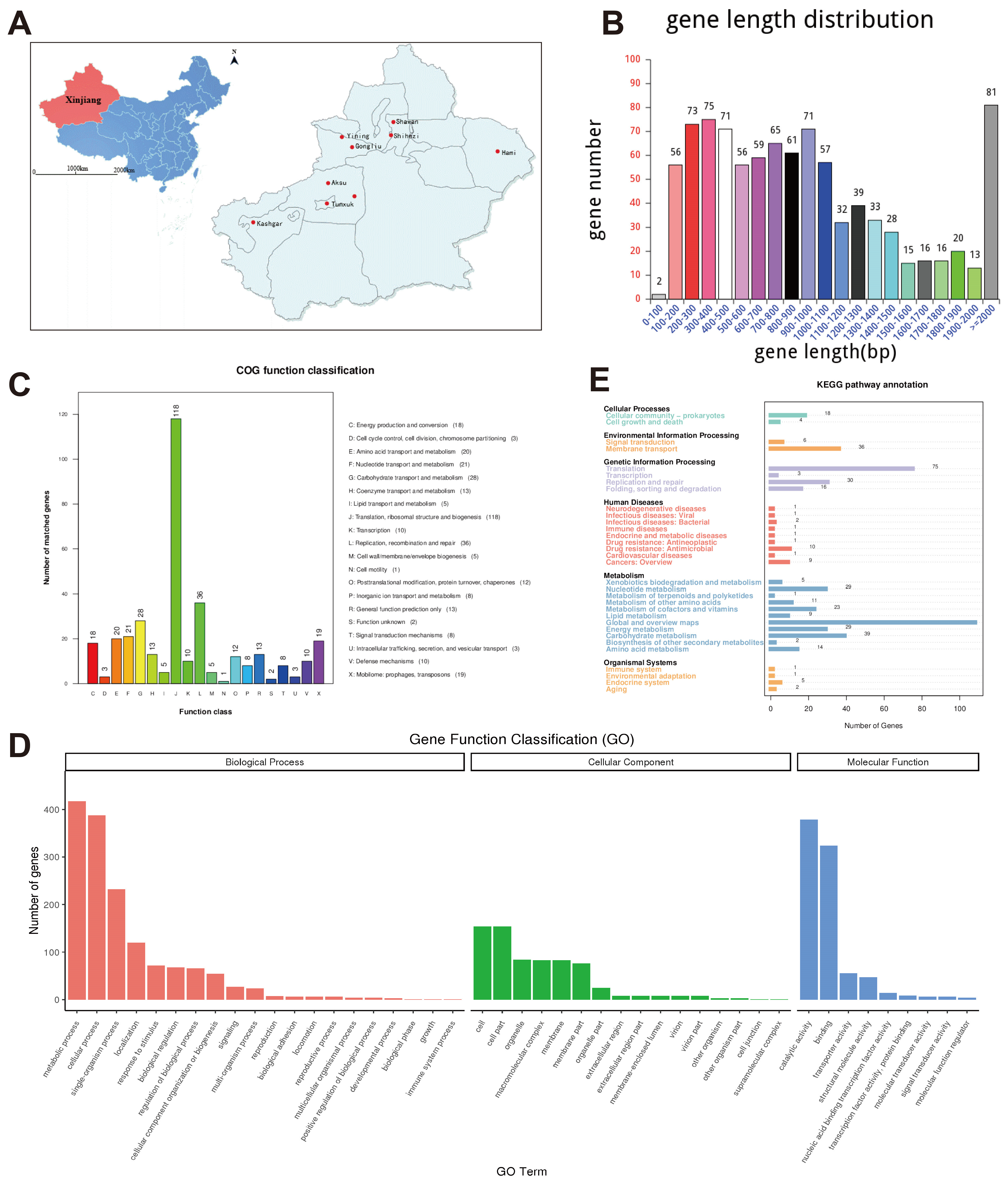
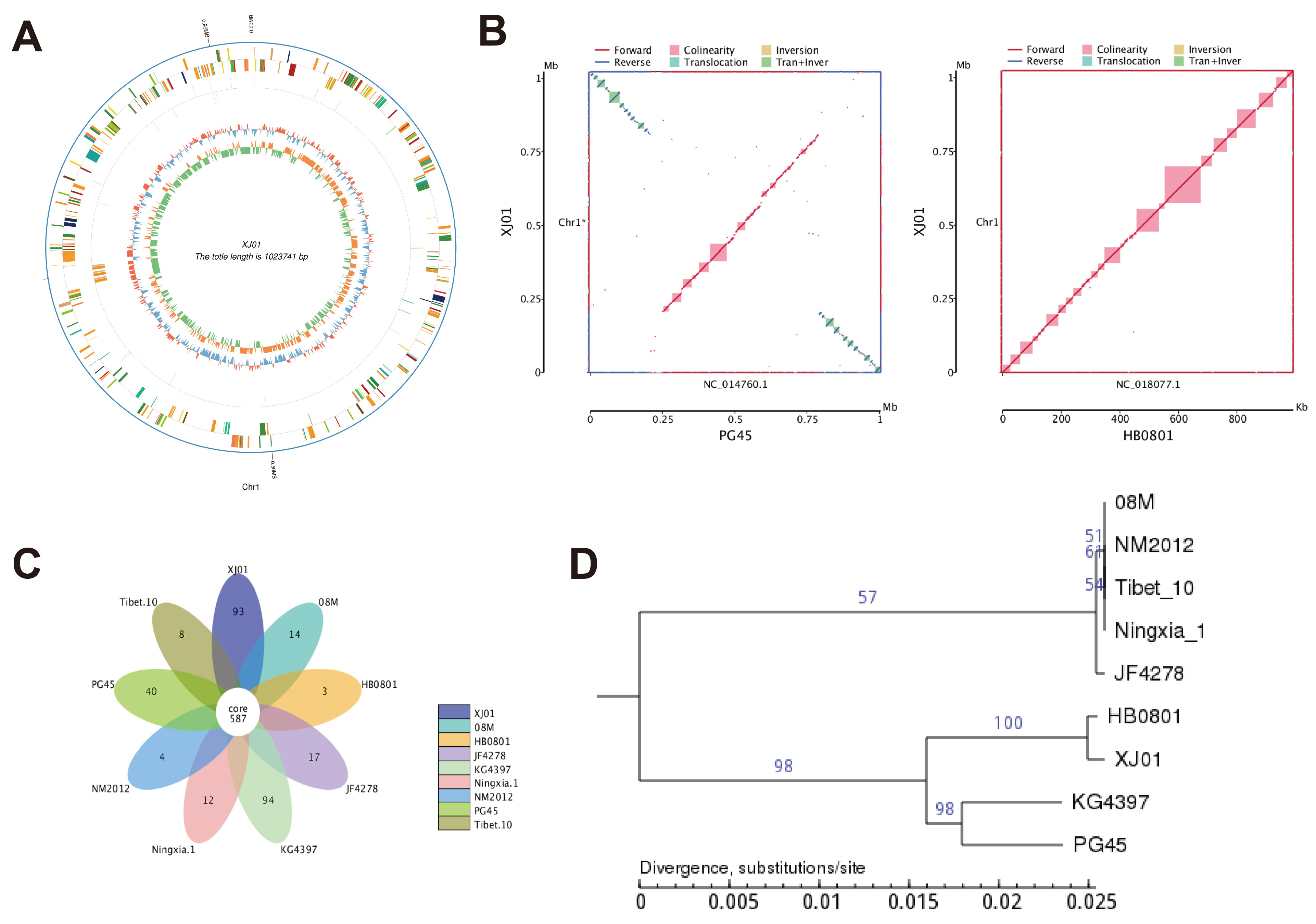


| Reference Strain Name | Reference Strain Genomic ID | Separated Area |
|---|---|---|
| PG45 | NC_014760 | MD, USA |
| HB0801 | NC_018077 | Hubei, China |
| Ningxia-1 | NZ_CP023663 | Ningxia, China |
| Tibet-10 | NZ_CP062195 | Qinghai, China |
| 08M | CP019639.1 | Gansu, China |
| NM2012 | CP011348.1 | Inner Mongolia, China |
| JF4278 | LT578453.1 | Bern, Switzerland |
| KG4397 | AP019558 | Tokyo, Japan |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Yu, X.; Tang, T.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z. Mycoplasma bovis Infection Induces Apoptosis Through Gadd45/XIAP in Bovine Macrophages. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092031
Li R, Yu X, Tang T, Sheng J, Zhang H, Chen C, Wang Y, Ma Z. Mycoplasma bovis Infection Induces Apoptosis Through Gadd45/XIAP in Bovine Macrophages. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092031
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruirui, Xiaojiao Yu, Tian Tang, Jinliang Sheng, Hui Zhang, Chuangfu Chen, Yong Wang, and Zhongchen Ma. 2025. "Mycoplasma bovis Infection Induces Apoptosis Through Gadd45/XIAP in Bovine Macrophages" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092031
APA StyleLi, R., Yu, X., Tang, T., Sheng, J., Zhang, H., Chen, C., Wang, Y., & Ma, Z. (2025). Mycoplasma bovis Infection Induces Apoptosis Through Gadd45/XIAP in Bovine Macrophages. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092031





