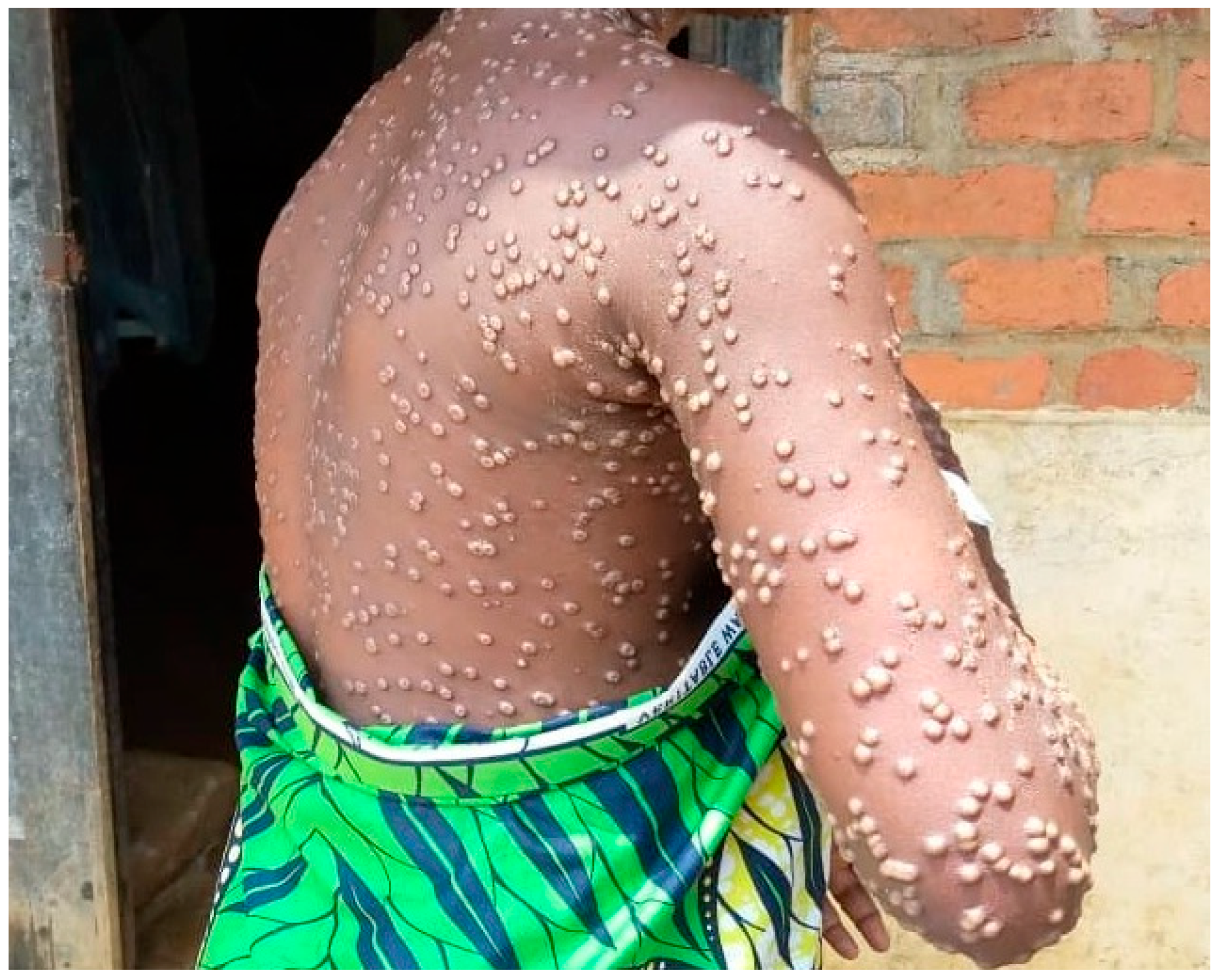
The Trans-Kingdom Spectrum of Mpox-like Lesion Pustules of Suspect Patients in the Mpox Clade Ib Outbreak in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample Collection
2.2. Metagenomics Sequencing Methodology
2.3. Taxonomic Annotation
3. Results
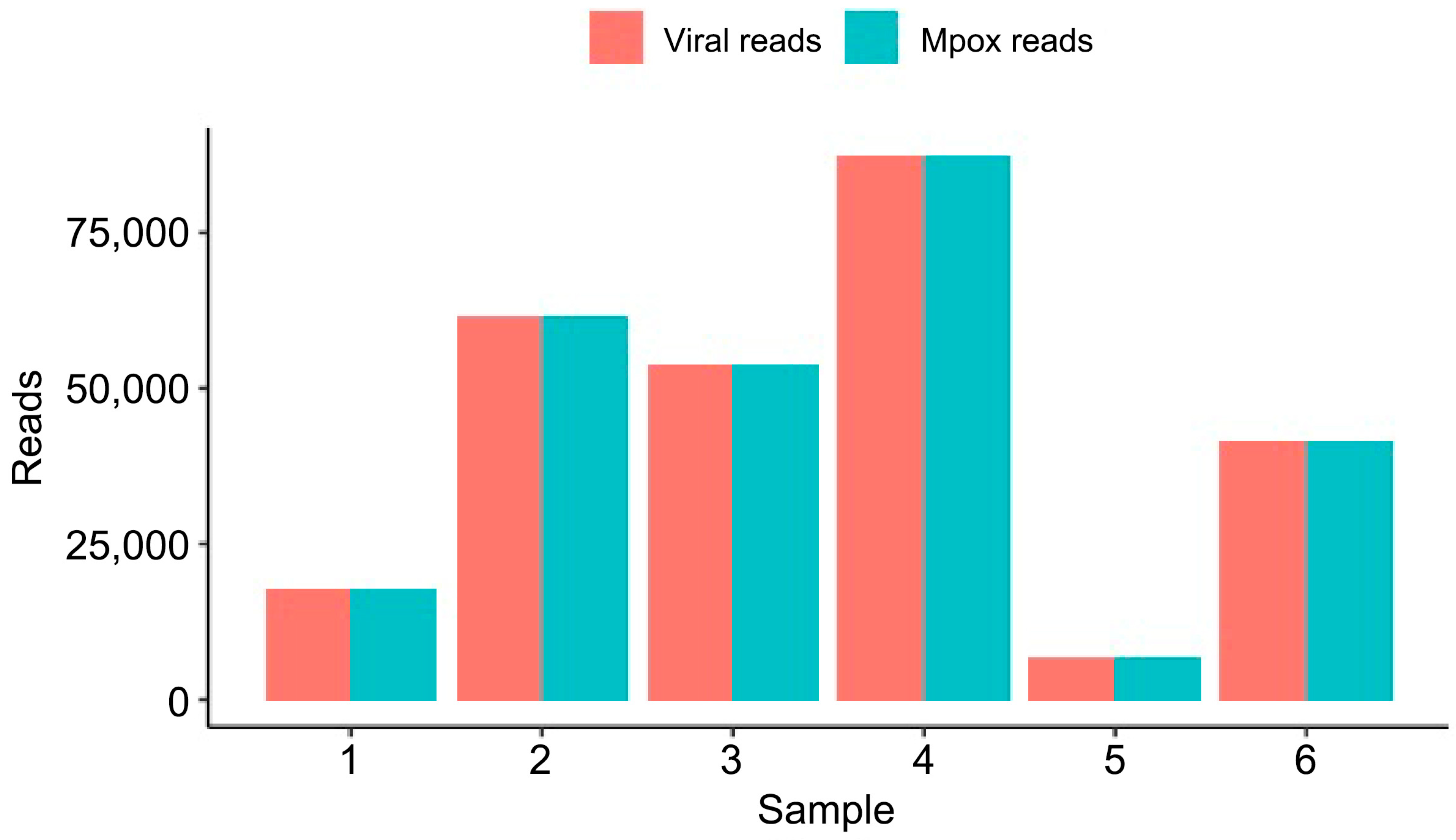
3.1. Metagenomics Sequencing
3.2. Trans-Kingdom Taxonomic Annotation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ladnyj, I.D.; Ziegler, P.; Kima, E. A Human Infection Caused by Monkeypox Virus in Basankusu Territory, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Bull. World Health Organ. 1972, 46, 593. [Google Scholar]
- von Magnus, P.; Andersen, E.K.; Petersen, K.B.; Birch-Andersen, A. A Pox-like Disease in Cynomolgus Monkeys. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1959, 46, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetifa, I.; Muyembe, J.J.; Bausch, D.G.; Heymann, D.L. Mpox Neglect and the Smallpox Niche: A Problem for Africa, a Problem for the World. Lancet 2023, 401, 1822–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C. Mpox—Is There a More Dangerous New Clade? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, e667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzón, S.; Varona, S.; Negredo, A.; Vidal-Freire, S.; Patiño-Galindo, J.A.; Ferressini-Gerpe, N.; Zaballos, A.; Orviz, E.; Ayerdi, O.; Muñoz-Gómez, A.; et al. Monkeypox Virus Genomic Accordion Strategies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutt, M.; Kumar, A.; Rout, M.; Dehury, B.; Martinez, G.; Ndishimye, P.; Kelvin, A.A.; Kelvin, D.J. Drug Repurposing for Mpox: Discovery of Small Molecules as Potential Inhibitors against DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Using Molecular Modeling Approach. J. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 124, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkevich, T.G.; Yutin, N.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V.; Moss, B. Ancient Gene Capture and Recent Gene Loss Shape the Evolution of Orthopoxvirus-Host Interaction Genes. mBio 2021, 12, e01495-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittek, R.; Moss, B. Tandem Repeats within the Inverted Terminal Repetition of Vaccinia Virus DNA. Cell 1980, 21, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchelkunov, S.N.; Totmenin, A.V.; Safronov, P.F.; Mikheev, M.V.; Gutorov, V.V.; Ryazankina, O.I.; Petrov, N.A.; Babkin, I.V.; Uvarova, E.A.; Sandakhchiev, L.S.; et al. Analysis of the Monkeypox Virus Genome. Virology 2002, 297, 172–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakaniaki, E.H.; Kacita, C.; Kinganda-Lusamaki, E.; O’Toole, Á.; Wawina-Bokalanga, T.; Mukadi-Bamuleka, D.; Amuri-Aziza, A.; Malyamungu-Bubala, N.; Mweshi-Kumbana, F.; Mutimbwa-Mambo, L.; et al. Sustained Human Outbreak of a New MPXV Clade I Lineage in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2791–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masirika, L.M.; Kumar, A.; Dutt, M.; Ostadgavahi, A.T.; Hewins, B.; Nadine, M.B.; Steeven, B.K.; Mweshi, F.K.; Mambo, L.M.; Mbiribindi, J.B.; et al. Complete Genome Sequencing, Annotation, and Mutational Profiling of the Novel Clade I Human Mpox Virus, Kamituga Strain. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2024, 18, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adepoju, P. Mpox Declared a Public Health Emergency. Lancet 2024, 404, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masirika, L.M.; Udahemuka, J.C.; Ndishimye, P.; Martinez, G.S.; Kelvin, P.; Nadine, M.B.; Steeven, B.K.; Mweshi, F.K.; Mambo, L.M.; Munnink, B.B.O.; et al. Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics, and Transmission Patterns of a Novel Mpox (Monkeypox) Outbreak in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC): An Observational, Cross-Sectional Cohort Study. medRxiv 2024. 2024.03.05.24303395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masirika, L.M.; Udahemuka, J.C.; Schuele, L.; Ndishimye, P.; Otani, S.; Mbiribindi, J.B.; Marekani, J.M.; Mambo, L.M.; Bubala, N.M.; Boter, M.; et al. Ongoing Mpox Outbreak in Kamituga, South Kivu Province, Associated with Monkeypox Virus of a Novel Clade I Sub-Lineage, Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2024. Eurosurveill 2024, 29, 2400106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Mpox Trends. Available online: https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/mpx_global/ (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Nolen, L.D.; Osadebe, L.; Katomba, J.; Likofata, J.; Mukadi, D.; Monroe, B.; Doty, J.; Hughes, C.M.; Kabamba, J.; Malekani, J.; et al. Extended Human-to-Human Transmission during a Monkeypox Outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibungu, E.M.; Vakaniaki, E.H.; Kinganda-Lusamaki, E.; Kalonji-Mukendi, T.; Pukuta, E.; Hoff, N.A.; Bogoch, I.I.; Cevik, M.; Gonsalves, G.S.; Hensley, L.E.; et al. Clade I–Associated Mpox Cases Associated with Sexual Contact, the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, A.; Makambo, M.T.; Ramazani, P.; Zahiga, I.; Mbika, B.; Safari, O.; Bachunguye, R.; Mirindi, J.; Glass, N. A Congolese Community-Based Health Program for Survivors of Sexual Violence. Confl. Health 2012, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Saavedra, B.; Montes-Madariaga, E.S.; Cabanillas-Ramirez, C.; Alva, N.; Ricardo-Martínez, A.; León-Figueroa, D.A.; Barboza, J.J.; Mohanty, A.; Padhi, B.K.; Sah, R. Epidemiologic Situation of HIV and Monkeypox Coinfection: A Systematic Review. Vaccines 2023, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpox: Treating Severe Lesions. Available online: https://www.aad.org/member/clinical-quality/clinical-care/mpox/severe-lesions (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Ortiz-Martínez, Y.; Rodríguez-Morales, A.J.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Chastain, D.B.; Gharamti, A.A.; Vargas Barahona, L.; Henao-Martínez, A.F. Monkeypox—A Description of the Clinical Progression of Skin Lesions: A Case Report from Colorado, USA. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, 20499361221117726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Pozza, G.; Salari, F.; Giacomelli, A.; Mileto, D.; Cossu, M.V.; Mancon, A.; Gagliardi, G.; Micol, B.; Micheli, V.; et al. Concomitant Diagnosis of Sexually Transmitted Infections and Human Monkeypox in Patients Attending a Sexual Health Clinic in Milan, Italy. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, N.A.; Morier, D.S.; Kisalu, N.K.; Johnston, S.C.; Doshi, R.H.; Hensley, L.E.; Okitolonda-Wemakoy, E.; Muyembe-Tamfum, J.J.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; Rimoin, A.W. Varicella Coinfection in Patients with Active Monkeypox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Ecohealth 2017, 14, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khallafallah, O.; Grose, C. Reassessment of Evidence about Coinfection of Chickenpox and Monkeypox (Mpox) in African Children. Viruses 2022, 14, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.M.; Liu, L.; Davidson, W.B.; Radford, K.W.; Wilkins, K.; Monroe, B.; Metcalfe, M.G.; Likafi, T.; Lushima, R.S.; Kabamba, J.; et al. A Tale of Two Viruses: Coinfections of Monkeypox and Varicella Zoster Virus in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 104, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Garberi, M.; Sarrio-Sanz, P.; Martinez-Cayuelas, L.; Delgado-Sanchez, E.; Bernabeu-Cabezas, S.; Peris-Garcia, J.; Sanchez-Caballero, L.; Nakdali-Kassab, B.; Egea-Sancho, C.; Olarte-Barragan, E.H.; et al. Genitourinary Lesions Due to Monkeypox. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ran, X.; Tang, J.; Pradhan, S.; Dai, Y.; Zhuang, K.; Ran, Y. Skin Microbiota in Non-Inflammatory and Inflammatory Lesions of Acne Vulgaris: The Underlying Changes within the Pilosebaceous Unit. Mycopathologia 2021, 186, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved Metagenomic Analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dropulic, L.K.; Lederman, H.M. Overview of Infections in the Immunocompromised Host. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharko, F.S.; Mazloum, A.; Krotova, A.O.; Byadovskaya, O.P.; Prokhvatilova, L.B.; Chvala, I.A.; Zolotikov, U.E.; Kozlova, A.D.; Krylova, A.S.; Grosfeld, E.V.; et al. Metagenomic Profiling of Viral and Microbial Communities from the Pox Lesions of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus and Sheeppox Virus-Infected Hosts. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1321202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewska, U.; Brzoza, P.; Kwiecień, K.; Kwitniewski, M.; Cichy, J. Metagenomic Studies in Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 3201–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, L.C.; Chai, Y.H.; Xu, J.F. Advantages and Challenges of Metagenomic Sequencing for the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Infectious Diseases. Clin. Respir. J. 2022, 16, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—The “accidental” Pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, S.; Gokon, Y. Migratory Cellulitis: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Infection of the Skin. BMJ Case Rep. CP 2021, 14, e239601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardnerella Vaginalis and Anaerobic Bacteria in the Etiology of Bacterial (Nonspecific) Vaginosis—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6607521/ (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Zhou, X.; Willems, R.J.L.; Friedrich, A.W.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Bathoorn, E. Enterococcus faecium: From Microbiological Insights to Practical Recommendations for Infection Control and Diagnostics. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.; Giron, M. Enterobacter Infections; StatPearls: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Davin-Regli, A.; Pagès, J.M. Enterobacter aerogenes and Enterobacter cloacae; Versatile Bacterial Pathogens Confronting Antibiotic Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| S. No | Virus Name | Accession Number | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hMpxV/DRC/CRSN-1/2023 | EPI_ISL_19004044 | 2 November 2023 |
| 2 | hMpxV/DRC/CRSN-2/2023 | EPI_ISL_19004045 | 15 November 2023 |
| 3 | hMpxV/DRC/CRSN-3/2023 | EPI_ISL_19004046 | 23 December 2023 |
| 4 | hMpxV/DRC/CRSN-4/2023 | EPI_ISL_19079342 | 23 December 2023 |
| 5 | hMpxV/DRC/CRSN-5/2024 | EPI_ISL_19079343 | 6 January 2024 |
| 6 | hMpxV/DRC/CRSN-6/2024 | EPI_ISL_19079344 | 14 January 2024 |
| Sequencing | Trans-Kingdom Composition | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Raw Reads (Million) | Total Bases (Gb) | Passed Bases (Gb) 1 | Mean Read Length, stdev, IQR | Bacteria/Archaea (Reads) | Fungi (Reads) | Viruses (Reads) |
| 1 | 0.964 | 3.18 | 2.43 | 3430.63, 1464.47, 1695-4112 | 5009 | 25 | 17,896 |
| 2 | 2.07 | 7.02 | 6.33 | 3910.66, 1593.1, 2316-3765 | 17,800 | 194 | 61,808 |
| 3 | 3 | 11.18 | 10.45 | 3159.89, 1413.37, 2825-4776 | 74 | 14 | 53,868 |
| 4 | 1.29 | 5.13 | 4.59 | 3741.09, 1302.62, 2863-4601 | 874 | 15 | 87,600 |
| 5 | 1.96 | 4.64 | 3.80 | 2715.25, 1119.55, 1922-3308 | 13 | 1 | 6821 |
| 6 | 1.58 | 5.23 | 4.63 | 3482.13, 1316.61, 2533, 4296 | 2820 | 11 | 41,620 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masirika, L.M.; Hewins, B.; Toloue Ostadgavahi, A.; Dutt, M.; Mambo, L.M.; Udahemuka, J.C.; Ndishimye, P.; Mbiribindi, J.B.; Siangoli, F.B.; Kelvin, P.; et al. The Trans-Kingdom Spectrum of Mpox-like Lesion Pustules of Suspect Patients in the Mpox Clade Ib Outbreak in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092025
Masirika LM, Hewins B, Toloue Ostadgavahi A, Dutt M, Mambo LM, Udahemuka JC, Ndishimye P, Mbiribindi JB, Siangoli FB, Kelvin P, et al. The Trans-Kingdom Spectrum of Mpox-like Lesion Pustules of Suspect Patients in the Mpox Clade Ib Outbreak in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092025
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasirika, Leandre Murhula, Benjamin Hewins, Ali Toloue Ostadgavahi, Mansi Dutt, Léandre Mutimbwa Mambo, Jean Claude Udahemuka, Pacifique Ndishimye, Justin Bengehya Mbiribindi, Freddy Belesi Siangoli, Patricia Kelvin, and et al. 2025. "The Trans-Kingdom Spectrum of Mpox-like Lesion Pustules of Suspect Patients in the Mpox Clade Ib Outbreak in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092025
APA StyleMasirika, L. M., Hewins, B., Toloue Ostadgavahi, A., Dutt, M., Mambo, L. M., Udahemuka, J. C., Ndishimye, P., Mbiribindi, J. B., Siangoli, F. B., Kelvin, P., Langille, M. G. I., Kelvin, D. J., Flores, L., Sganzerla Martinez, G., & Kumar, A. (2025). The Trans-Kingdom Spectrum of Mpox-like Lesion Pustules of Suspect Patients in the Mpox Clade Ib Outbreak in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092025







