Cyanobacterial Bloom in Urban Rivers: Resource Use Efficiency Perspectives for Water Ecological Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
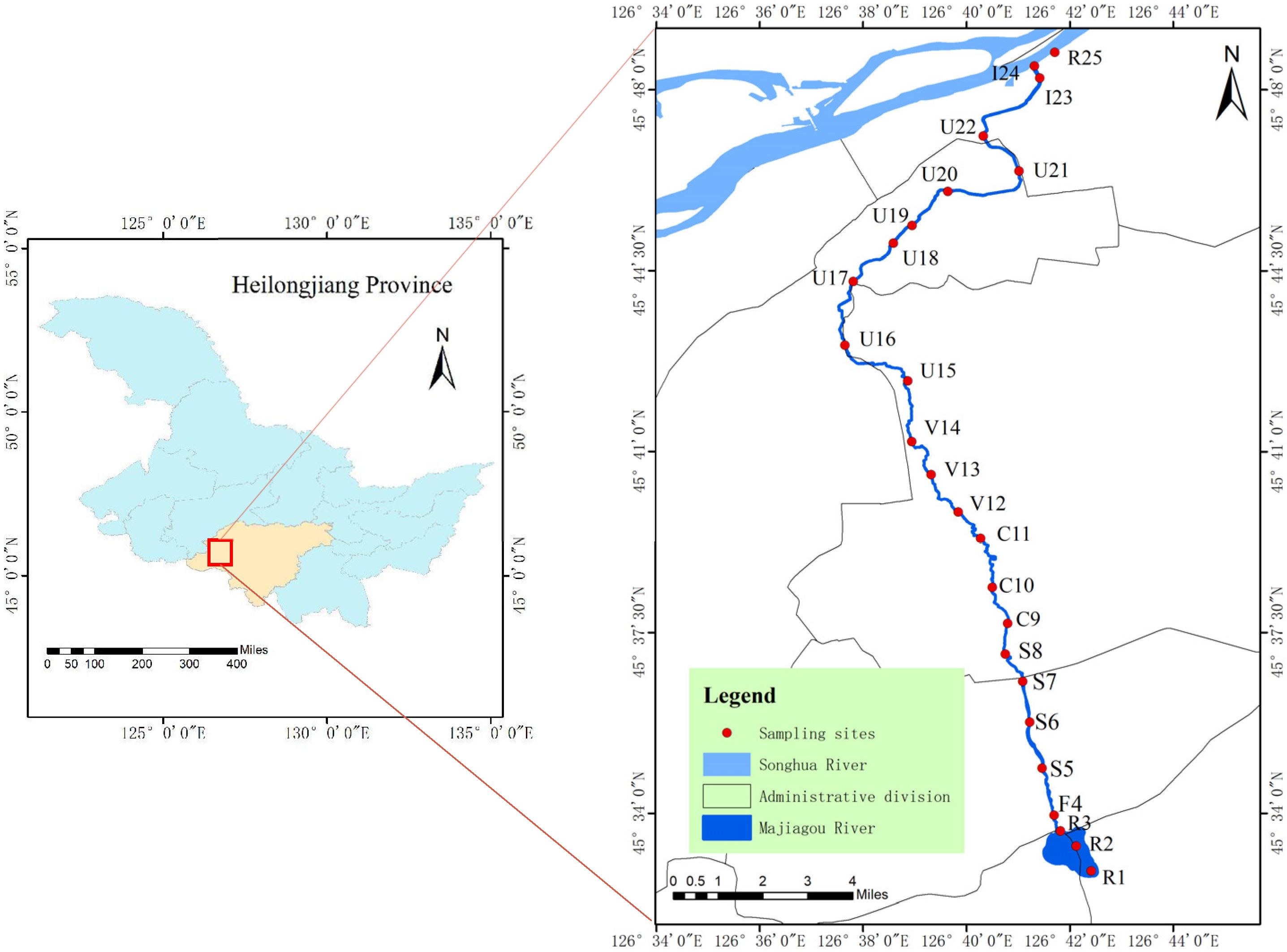
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
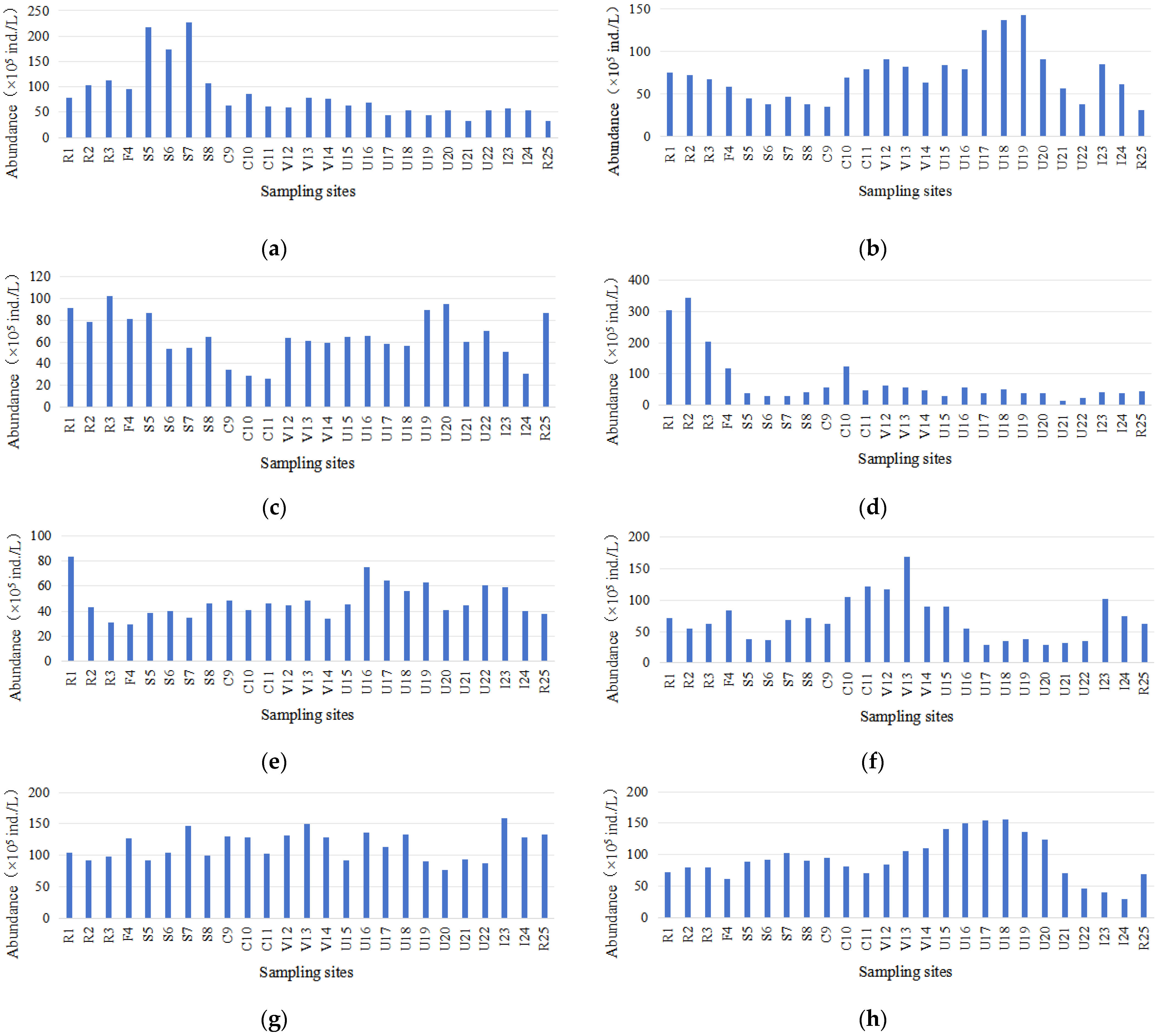
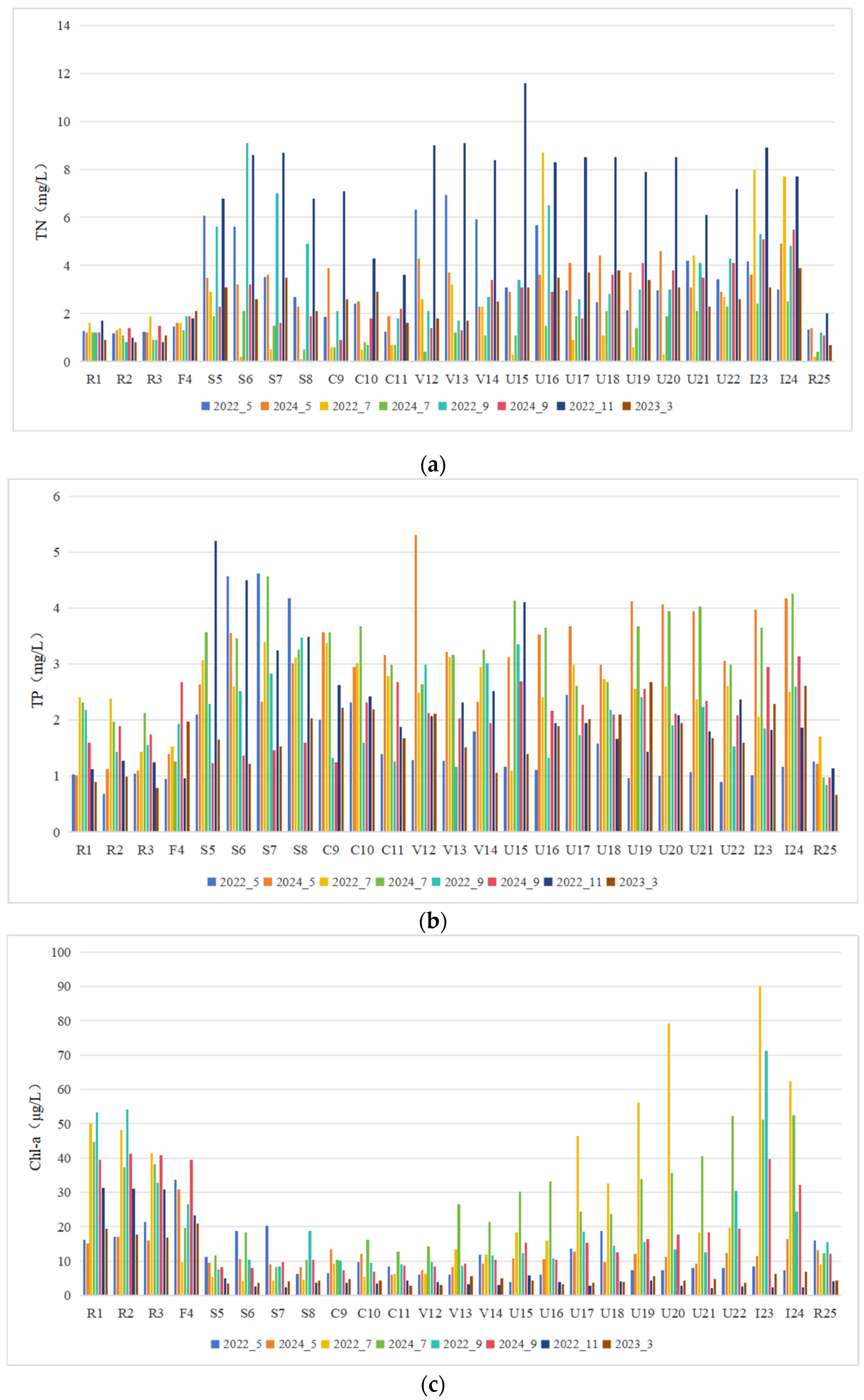
3.1. Algal Communities and Water Quality
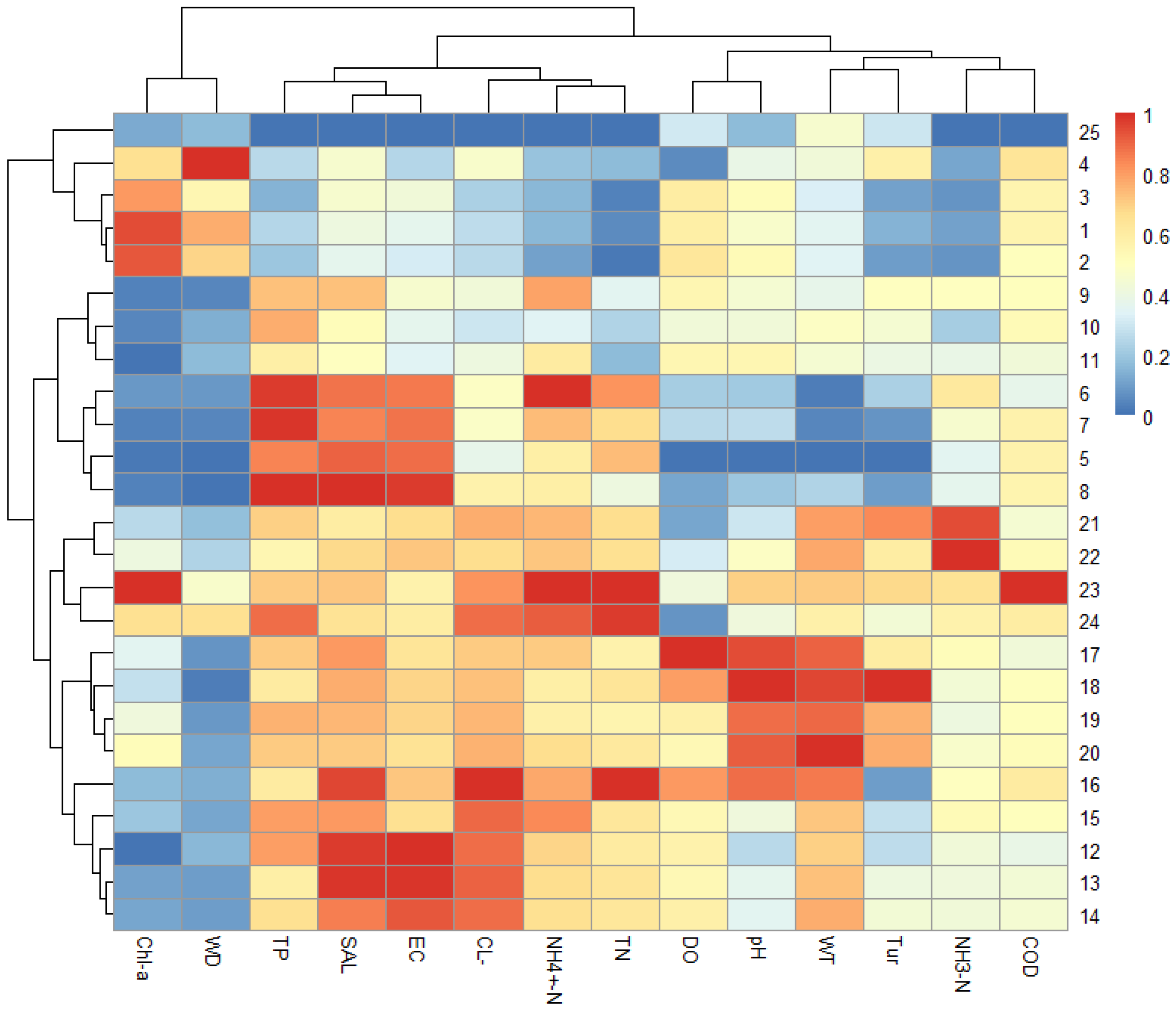
3.2. River Section Division Based on Hierarchical Clustering
3.3. Spatiotemporal Variations in the Relative Abundance of Cyanobacteria
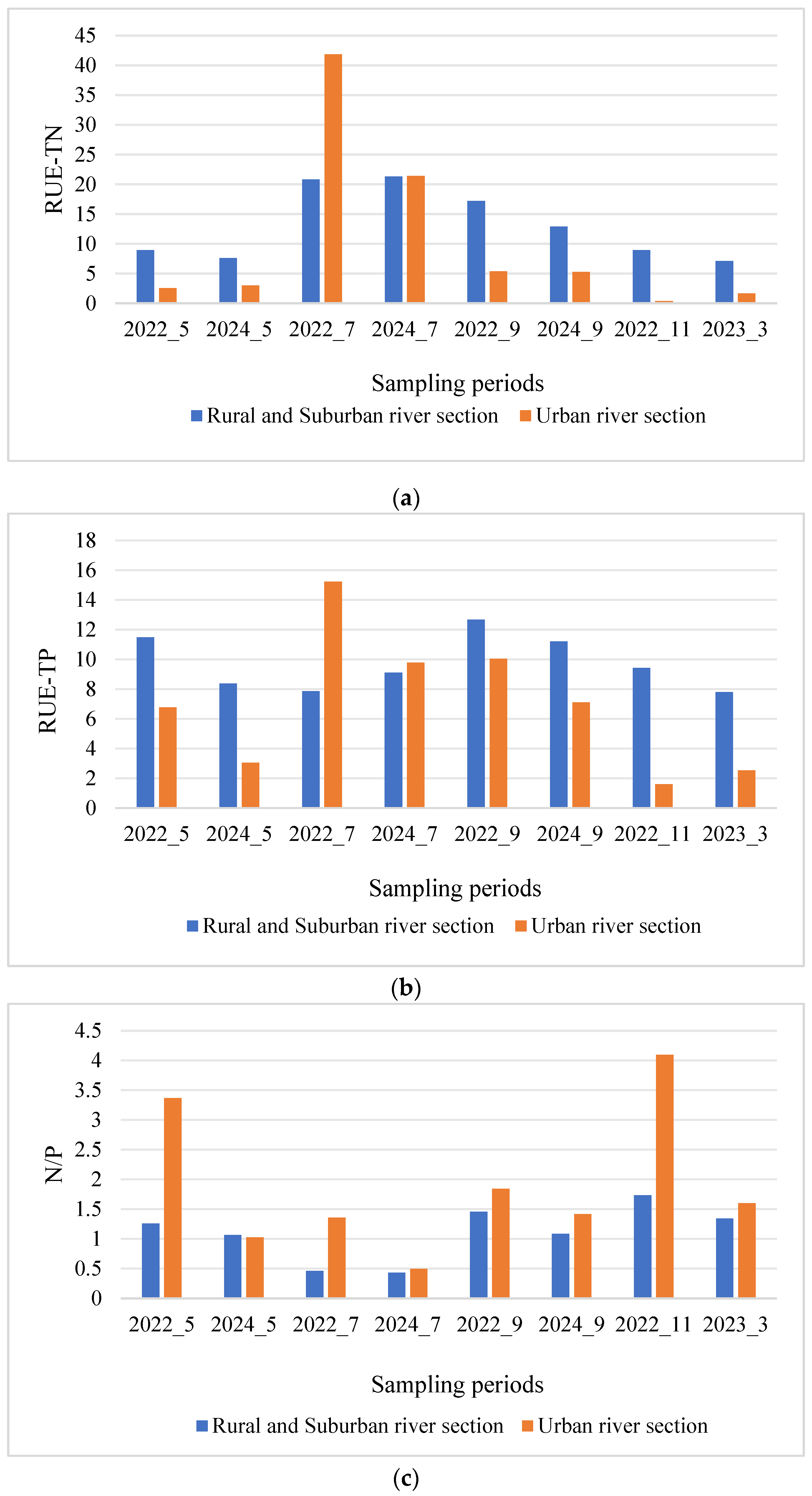
3.4. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Resource Use Efficiency
3.5. Analysis of Cyanobacterial Impact Mechanisms Based on Resource Use Efficiency
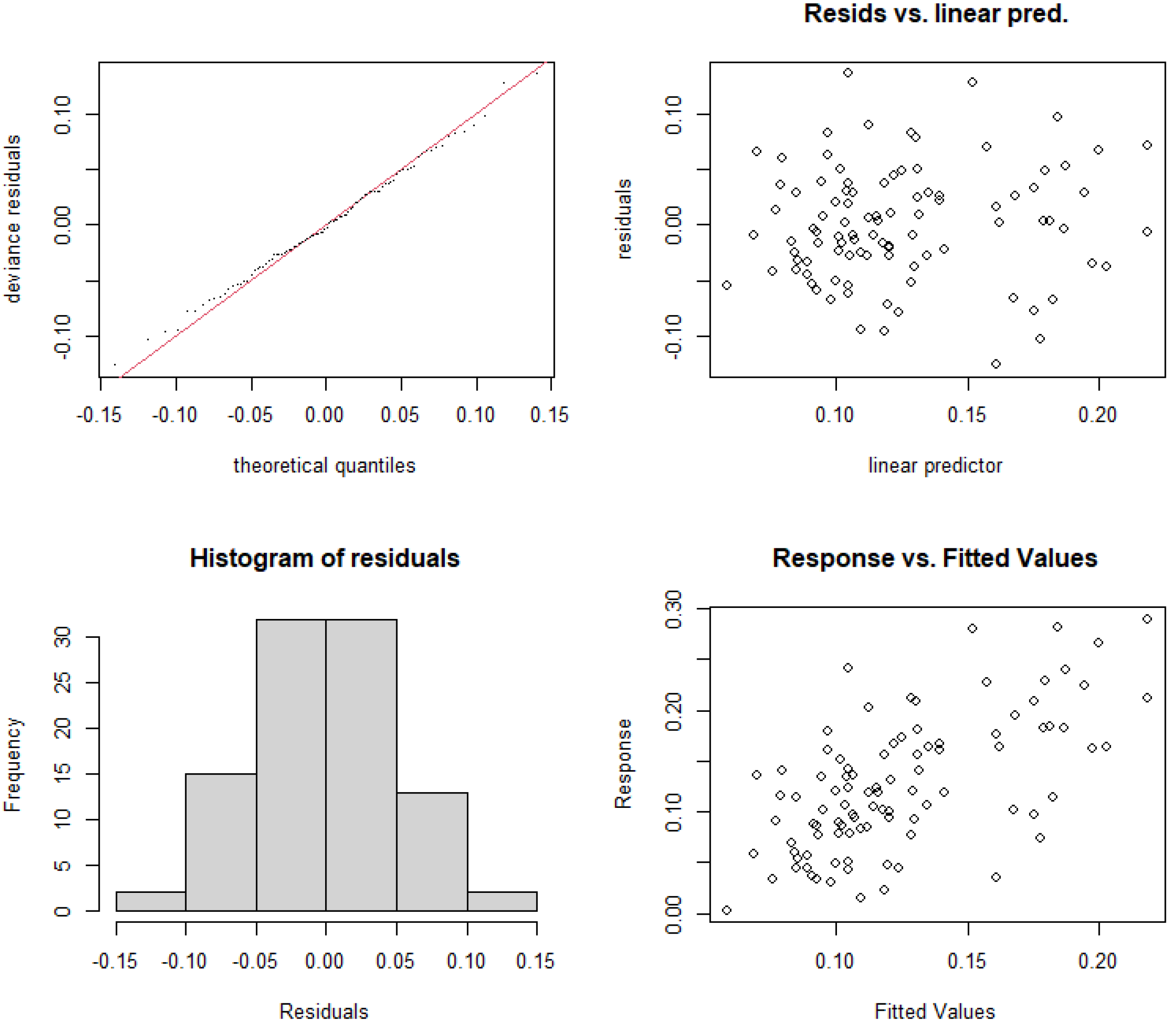
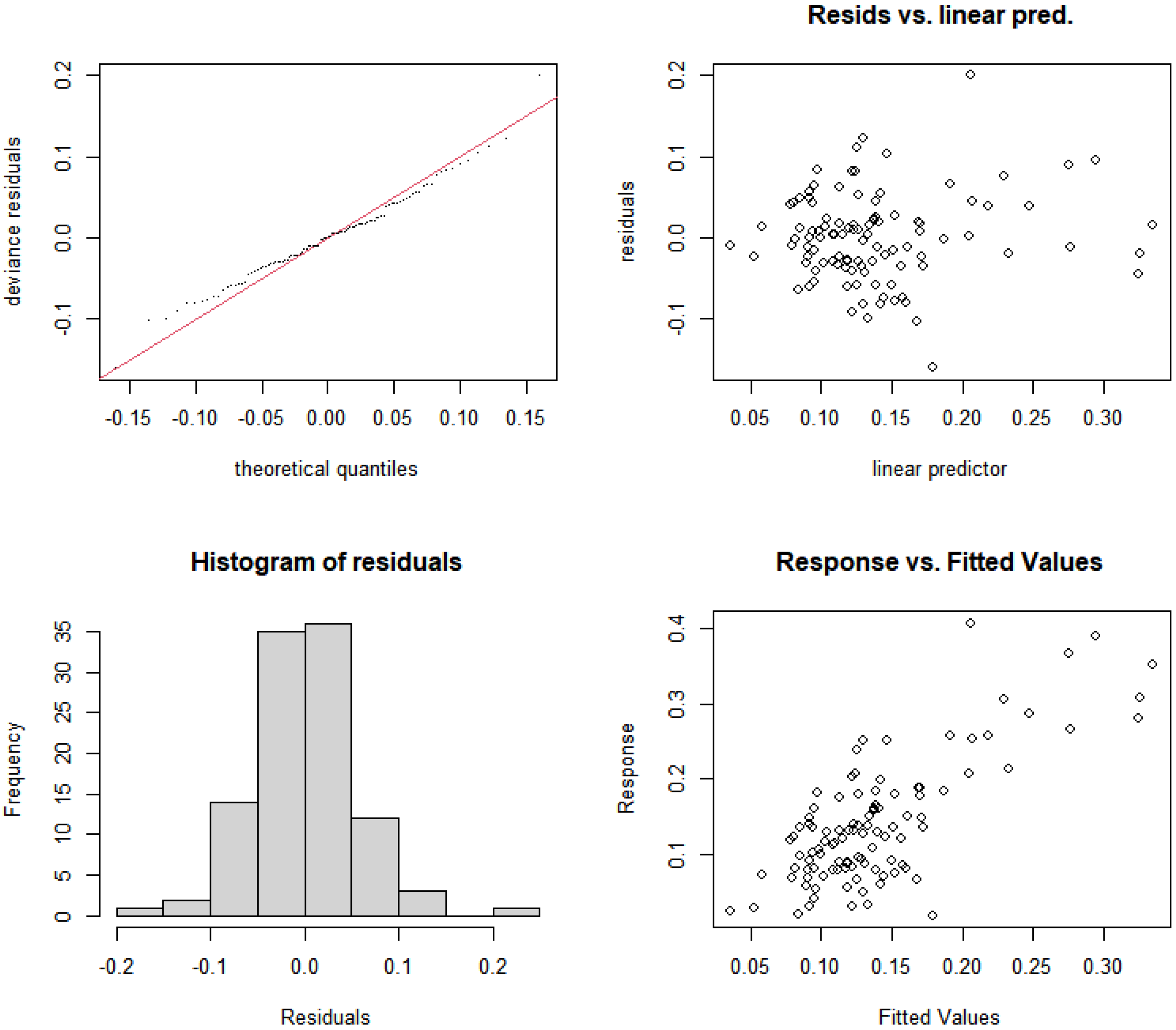
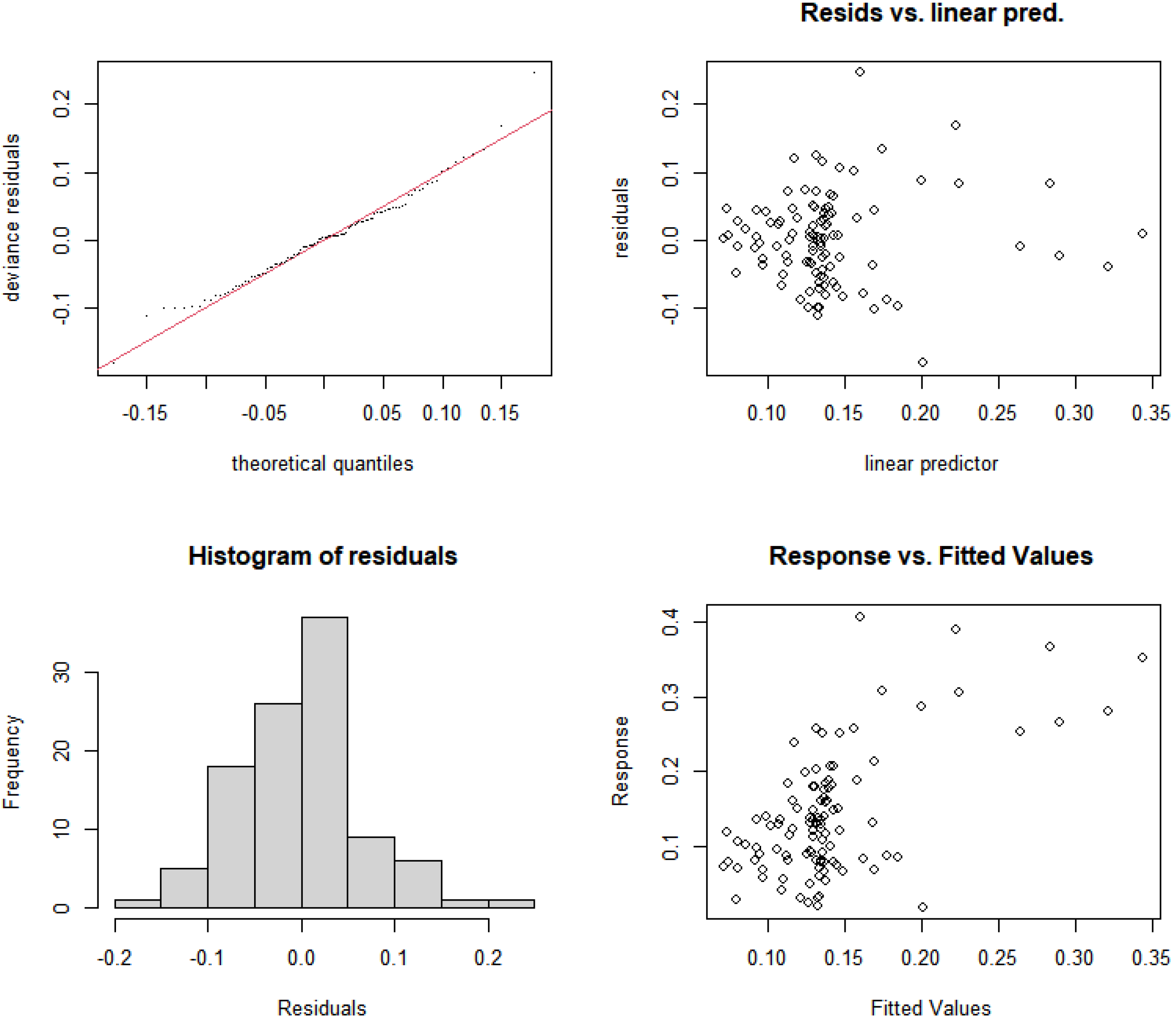
3.5.1. Construction and Selection of GAMs for Rural and Suburban River Sections
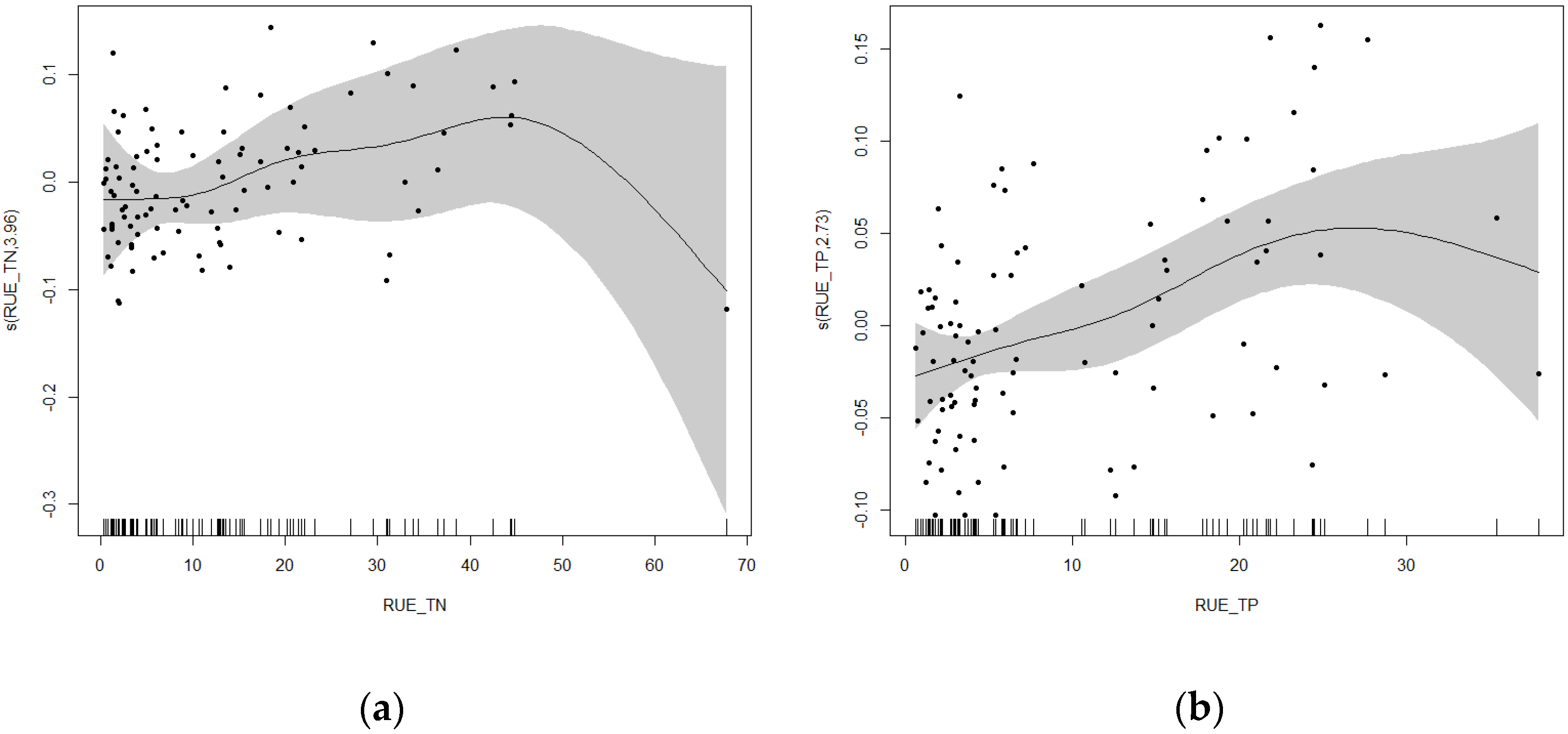
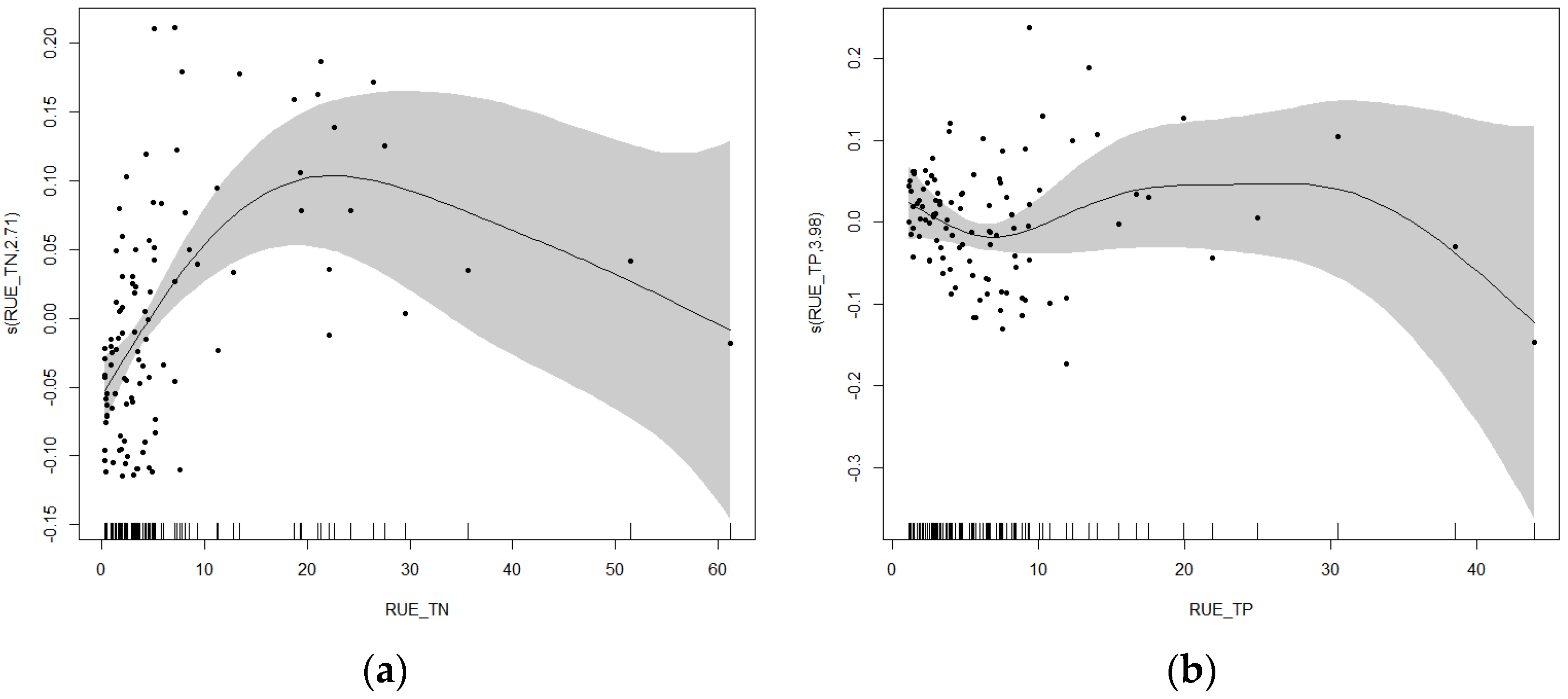
3.5.2. Nonlinear Analysis of Cyanobacteria Relative Abundance and Resource Use Efficiency in Rural and Suburban River Sections
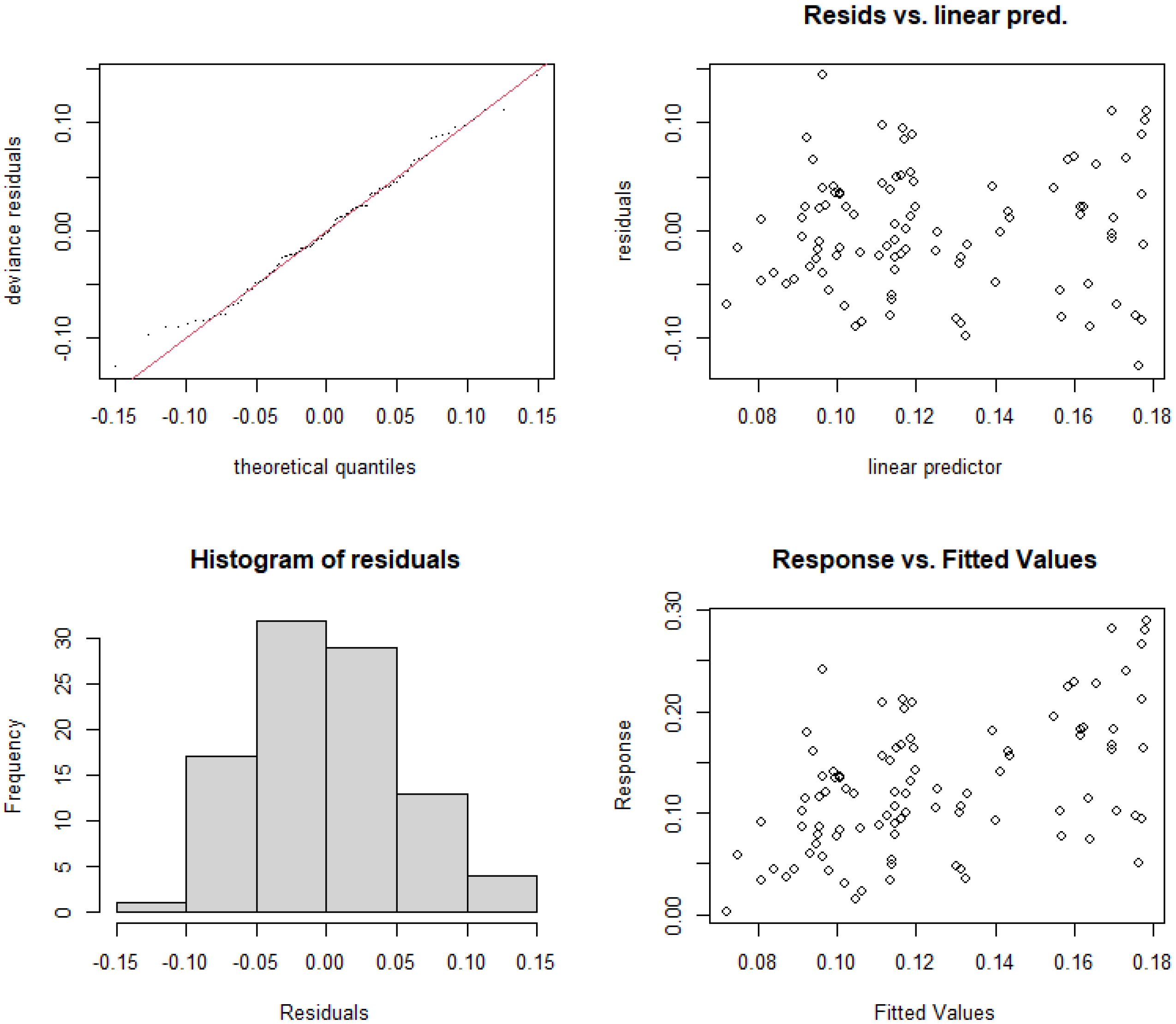
3.5.3. Construction and Selection of GAMs for Urban River Sections
3.5.4. Nonlinear Analysis of Cyanobacteria Relative Abundance and Resource Use Efficiency in Urban River Sections
4. Discussion
4.1. The Driving Effects of Environmental Factors on Phytoplankton Resource Use Efficiency
4.2. Mechanistic Analysis of Factors Driving Cyanobacterial Blooms
4.3. Seasonal and Sectional Nonlinear Responses of Cyanobacterial Abundance to Resource Use Efficiency
4.4. Ecological Management and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pitois, F.; Thoraval, I.; Baurès, E.; Thomas, O. Geographical Patterns in Cyanobacteria Distribution: Climate Influence at Regional Scale. Toxins 2014, 6, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, C.; Segura, A.; Piñeiro, G.; Baldassini, P.; Pérez-Becoña, L.; García-Rodríguez, F.; Perera, G.; Piccini, C. Rise of toxic cyanobacterial blooms is promoted by agricultural intensification in the basin of a large subtropical river of South America. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 1774–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathokleous, E.; Peñuelas, J.; Azevedo, R.A.; Rillig, M.C.; Sun, H.Y.; Calabrese, E.J. Low Levels of Contaminants Stimulate Harmful Algal Organisms and Enrich Their Toxins. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 11991–12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, V.; Arockiaraj, J. Unveiling the trifecta of cyanobacterial quorum sensing: LuxI, LuxR and LuxS as the intricate machinery for harmful algal bloom formation in freshwater ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.S.; Shao, N.F.; Yang, S.T.; Ren, H.; Ge, Y.R.; Zhang, Z.S.; Feng, P.; Liu, W.L. Quantitative assessment of the effects of human activities on phytoplankton communities in lakes and reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manica, A.N.; Isaac, R.D. Seasonal dynamics and diversity of cyanobacteria in a eutrophied Urban River in Brazil. Water Supply 2023, 23, 3868–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Brewton, R.A.; McFarland, M.N.; Stockley, N. Nutrient availability in a freshwater-to-marine continuum: Cyanobacterial blooms along the Lake Okeechobee Waterway. Harmful Algae 2024, 139, 102710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Bian, W.B.; Qi, X.M.; He, D.; Lu, H.; Yang, L.Y. Cycles of solar ultraviolet radiation favor periodic expansions of cyanobacterial blooms in global lakes. Water Res. 2024, 255, 121471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, A.; Ikeda, S.; Tsushima, R.; Ishikawa, Y.; Hidaka, S. Spatial and temporal variations in nutrients in water and riverbed sediments at the mouths of rivers that enter Lake Hachiro, a shallow eutrophic lake in Japan. Catena 2015, 133, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phlips, E.J.; Badylak, S.; Milbrandt, E.C.; Stelling, B.; Arias, M.; Armstrong, C.; Behlmer, T.; Chappel, A.; Foss, A.; Kaplan, D.; et al. Fate of a toxic Microcystis aeruginosa bloom introduced into a subtropical estuary from a flow-managed canal and management implications. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.Q.; Li, W.; Zhu, G.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, T.F.; Gao, G. Cyanobacterial bloom management through integrated monitoring and forecasting in large shallow eutrophic Lake Taihu (China). J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Xu, H.; Kang, L.J.; Zhao, X.C. Spatial and seasonal change in algal community structure and its interaction with nutrient dynamics in a gravel-bed urban river. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Determan, R.T.; White, J.D.; McKenna, L.W. Quantile regression illuminates the successes and shortcomings of long-term eutrophication remediation efforts in an urban river system. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboim, I.L.; Gomes, D.F.; Mafalda, P.O. Phytoplankton response to water quality seasonality in a Brazilian neotropical river. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, T.L.; Dahedl, E.K.; Kratz, M.A.; Urakawa, H. The synchronicity of bloom-forming cyanobacteria transcription patterns and hydrogen peroxide dynamics. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 348, 123812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, R.; Zheng, B.H.; Jia, H.F. Effects of dissolved organic matter from sediment and soil samples on the growth and physiology of four bloom-forming algal species. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2023, 263, 115266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savadova-Ratkus, K.; Grendaite, D.; Karosiene, J.; Stonevicius, E.; Kasperoviciene, J.; Koreiviene, J. Modelling harmful algal blooms in a mono- and a polydominant eutrophic lake under temperature and nutrient changes. Water Res. 2025, 275, 123138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwinska-Wilczewska, S.; Felpeto, A.B.; Mozdzen, K.; Vasconcelos, V.; Latala, A. Physiological Effects on Coexisting Microalgae of the Allelochemicals Produced by the Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Synechococcus sp. and Nodularia Spumigena. Toxins 2019, 11, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, R.; Christensen, V.G.; Graham, J.L.; Rogosch, J.S.; Rosen, B.H. Toxic Algae in Inland Waters of the Conterminous United States-A Review and Synthesis. Water 2023, 15, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughrey, Z.R.; Christensen, V.G.; Dusek, R.J.; Senegal, S.; Lankton, J.S.; Ziegler, T.A.; Jones, L.C.; Jones, D.K.; Williams, B.M.; Gordon, S.; et al. A review of algal toxin exposures on reserved federal lands and among trust species in the United States. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 4284–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Singh, S.; Ahn, C.Y.; Oh, H.M.; Asthana, R.K. Monitoring Approaches for a Toxic Cyanobacterial Bloom. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8999–9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhou, B.T. Remote sensing of cyanobacterial blooms in inland waters: Present knowledge and future challenges. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1540–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, J.S.; Yan, X.; Fang, S.Z.; Du, Y.C.; Xue, B.; Yu, K.; Wang, C. Monitoring Cyanobacteria Bloom in Dianchi Lake Based on Ground-Based Multispectral Remote-Sensing Imaging: Preliminary Results. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, A.; Almanza, V.; Haakonsson, S.; Palacio, H.; Rodas, G.; Barros, M.; Capelo-Neto, J.; Urrutia, R.; Aubriot, L.; Bonilla, S. Cyanobacterial bloom monitoring and assessment in Latin America. Harmful Algae 2023, 125, 102429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukhele, T.; Msagati, T. Eutrophication of Inland Surface Waters in South Africa: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 18, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibuye, F.A.; Zamyadi, A.; Wert, E.C. A critical review on operation and performance of source water control strategies for cyanobacterial blooms: Part I-chemical control methods. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibuye, F.A.; Zamyadi, A.; Wert, E.C. A critical review on operation and performance of source water control strategies for cyanobacterial blooms: Part II-mechanical and biological control methods. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, G. Eutrophication control of large shallow lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulne, D.; Fotopoulos, G. Development of an algal bloom satellite and in situ metadata hub with case studies in Canada. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 79, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-López, L.; González-Rodríguez, L.; Duran-Llacer, I.; Cardenas, R.; Urrutia, R. Spatio-temporal analysis of chlorophyll in six Araucanian lakes of Central-South Chile from Landsat imagery. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 65, 101431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Cho, K.H.; Recknagel, F. Bibliometric network analysis of scientific research on early warning signals for cyanobacterial blooms in lakes and rivers. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; You, L.H. Coupled effects of environmental conditions on the spatio-temporal variability of phytoplankton in canyon-shaped reservoirs. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 386, 135797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, M.G.; Nixdorf, B. Low disturbances favor steady state: Case of cyanobacterial monodominance in a Brazilian coastal lagoon. Inland Waters 2014, 4, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.F.; Gan, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, Z.W.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y.; Liao, Y.P.; Ding, R.; Liu, G.Q.; Wu, J.X.; et al. A novel indicator for defining plain urban river network cyanobacterial blooms: Resource use efficiency. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalas, A.; Catherine, A.; Maloufi, S.; Cellamare, M.; Hamlaoui, S.; Yéprémian, C.; Louvard, C.; Troussellier, M.; Bernard, C. Drivers and ecological consequences of dominance in periurban phytoplankton communities using networks approaches. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, J.M.; Li, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Zhang, M.; Chen, F.Z. Nitrogen Reduction Causes Shifts in Winter and Spring Phytoplankton Composition and Resource Use Efficiency in a Large Subtropical Lake in China. Ecosystems 2023, 26, 1640–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, L.Z.; You, Q.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Pang, W.T.; Wang, Q.X. Impact of cyanobacterial bloom intensity on plankton ecosystem functioning measured by eukaryotic phytoplankton and zooplankton indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 109028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.A.; Moura, A.D. Ecological impacts of freshwater algal blooms on water quality, plankton biodiversity, structure, and ecosystem functioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Chen, H.H.; Al, M.A.; Ndayishimiye, J.C.; Yang, J.R.; Isabwe, A.; Luo, A.Q.; Yang, J. Urbanization reduces resource use efficiency of phytoplankton community by altering the environment and decreasing biodiversity. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 112, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.P.; Wang, L.; Tang, Q.H.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Jeppesen, E.; Han, B.P. The Relationship Between Phytoplankton Diversity and Ecosystem Functioning Changes with Disturbance Regimes in Tropical Reservoirs. Ecosystems 2023, 26, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.R.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Shi, K.; Chang, J.J.; Pan, M.; Song, L.R.; Jeppesen, E.; Zhou, Q.C. Urbanization shifts long-term phenology and severity of phytoplankton blooms in an urban lake through different pathways. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 4983–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; He, K.; Li, Y.Y.; Qin, M.Q.; Cui, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.L.; Chen, X.N.; Deng, M.J.; Gray, A.; et al. Driving Factors of Total Organic Carbon in Danjiangkou Reservoir Using Generalized Additive Model. Water 2022, 14, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pärn, J.; Verhoeven, J.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Dise, N.B.; Ullah, S.; Aasa, A.; Egorov, S.; Espenberg, M.; Järveoja, J.; Jauhiainen, J.; et al. Nitrogen-rich organic soils under warm well-drained conditions are global nitrous oxide emission hotspots. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lu, A.R.; Li, J.X.; Ma, M.D.; Meng, G.; Chen, Q.; Liu, G.; Yin, X.W. Effects of Aquatic Plant Coverage on Diversity and Resource Use Efficiency of Phytoplankton in Urban Wetlands: A Case Study in Jinan, China. Biology 2024, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Guan, M.X.; Tian, Y.L. Hydrological conditions can change the effects of major nutrients and dissolved organic matter on phytoplankton community dynamics in a eutrophic river. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, X.F.; Chen, J. Do submerged macrophyte species influence crustacean zooplankton functional group richness and their resource use efficiency in the low-light environment? Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1185947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchasov, Y.; Porat, R.; Zur, B.; Dubinsky, Z. Photoacoustics: A novel tool for the determination of photosynthetic energy storage efficiency in phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 2007, 579, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Hu, H.J.; Gao, X.; Kan, J.J.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, J. Phytoplankton Diversity, Spatial Patterns, and Photosynthetic Characteristics Under Environmental Gradients and Anthropogenic Influence in the Pearl River Estuary. Biology 2024, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, W. The impact of environmental parameters on phytoplankton functional groups in northeastern China. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 164, 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.M.; Guo, Y.; Yu, H.X.; Liu, M.H. The Driving Mechanism of Phytoplankton Resource Utilization Efficiency Variation on the Occurrence Risk of Cyanobacterial Blooms. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockenreiter, M.; Navarro, J.I.; Buchberger, F.; Stibor, H. Community shifts from eukaryote to cyanobacteria dominated phytoplankton: The role of mixing depth and light quality. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 2145–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Period | Phylum | Family | Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Cyanophyta | Pseudanabaenaceae | Raphidiopsis sinensis |
| Chlorellaceae | Chlorella vulgaris | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscaceae | Cyclotella meneghiniana | |
| Fragilariaceae | Synedra acusvar | ||
| Synedra ulna | |||
| Fragilaria intermedia | |||
| Stauroneidaceae | Stauroneis anceps | ||
| Chlorophyta | Polyblepharidaceae | Platymonas subcordiformis | |
| Summer | Cyanophyta | Oscillatoriaceae | Oscillatoria tenuis |
| Phormidiaceae | Phormidium tenue | ||
| Chlorophyta | Scenedesmaceae | Scenedesmus bicaudatus | |
| Chlorellaceae | Chlorella vulgaris | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscaceae | Cyclotella meneghiniana | |
| Fragilariaceae | Synedra ulna | ||
| Synedra acusvar | |||
| Stauroneidaceae | Stauroneis anceps | ||
| Autumn | Cyanophyta | Pseudanabaenaceae | Raphidiopsis sinensis |
| Chlorophyta | Scenedesmaceae | Scenedesmus bicaudatus | |
| Bacillariophyta | Naviculaceae | Navicula radiosa | |
| Coscinodiscaceae | Cyclotella meneghiniana | ||
| Fragilariaceae | Synedra acusvar | ||
| Synedra ulna | |||
| Ice Formation Period | Cyanophyta | Phormidiaceae | Phormidium tenue |
| Pseudanabaenaceae | Raphidiopsis sinensis | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscaceae | Cyclotella meneghiniana | |
| Fragilariaceae | Synedra acusvar | ||
| Synedra ulna | |||
| Thawing Period | Cyanophyta | Pseudanabaenaceae | Raphidiopsis sinensis |
| Microcystaceae | Microcystis wesenbergii | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Fragilariaceae | Synedra acusvar |
| River Sections | Significance Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rural and Suburban River Section | Urban River Section | p-Value | |
| RUE-TN | 13.11 ± 1.37 | 10.19 ± 2.78 | 0.685 |
| RUE-TP | 9.74 ± 0.93 | 7.02 ± 0.69 | <0.05 |
| N/P | 1.11 ± 0.07 | 1.9 ± 0.14 | <0.05 |
| Seasons | Significance Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Freezing Period | Thawing Period | Statistics | p-Value | |
| RUE-TN | 5.41 ± 0.733 | 26.56 ± 5.42 | 9.99 ± 1.79 | 4.49 ± 2.02 | 4.29 ± 1.23 | F = 9.142 | <0.05 |
| RUE-TP | 7.33 ± 0.967 | 10.58 ± 1.26 | 10.19 ± 1.18 | 5.36 ± 1.79 | 5.07 ± 1.22 | F = 3.48 | <0.05 |
| N/P | 1.7 ± 0.18 | 0.7 ± 0.12 | 1.46 ± 0.12 | 2.96 ± 0.28 | 1.48 ± 0.09 | F = 21.957 | <0.05 |
| GAMs | p-Value | GCV | Variance Explanation | AIC | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model1 RAC~s (TN, k = 3) | 0.0736 | 0.00412 | 8.56% | −252.85 | × |
| Model2 RAC~s (TP, k = 3) | 0.0815 | 0.00415 | 8.51% | −252.16 | × |
| Model3 RAC~s (RUE_TN, k = 3) | p < 0.001 | 0.00373 | 25.4% | −270.47 | √ |
| Model4 RAC~s (RUE_TP, k = 3) | p < 0.001 | 0.00364 | 20.3% | −264.93 | √ |
| Model5 RAC~s (N/P, k = 3) | p < 0.001 | 0.00436 | 0.532% | −247.31 | √ |
| Model6 RAC~s(RUE_TN) + te(TP,TN) + te(NP,RUE_TP) | 0.00355 | 39.5% | −269.60 | ||
| Model7 RAC~s(RUE_TP) + te(TP,TN) | 0.00354 | 36.4% | −263.66 |
| GAMs | p-Value | GCV | Variance Explanation | AIC | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1: RAC~s (TN, k = 3) | p < 0.01 | 0.00603 | 25.5% | −235.26 | √ |
| Model 2: RAC~s (TP, k = 3) | p < 0.05 | 0.00656 | 5.95% | −225.70 | √ |
| Model 3: RAC~s (RUE_TN, k = 3) | p < 0.01 | 0.00607 | 16.6% | −233.85 | √ |
| Model 4: RAC~s (RUE_TP, k = 3) | p < 0.001 | 0.00571 | 18.2% | −240.16 | √ |
| Model 5: RAC~s (N/P, k = 3) | 0.149 | 0.00673 | 4.99% | −223.03 | × |
| Model 6: RAC~s(RUE_TN) + te(TP,TN) | 0.00536 | 56% | −247.78 | ||
| Model 7: RAC~s(RUE_TP) + te(TP,TN) | 0.00514 | 54.7% | −251.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H. Cyanobacterial Bloom in Urban Rivers: Resource Use Efficiency Perspectives for Water Ecological Management. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091981
Chai Q, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Yu H. Cyanobacterial Bloom in Urban Rivers: Resource Use Efficiency Perspectives for Water Ecological Management. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091981
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Qingyu, Yongxin Zhang, Yuxi Zhao, and Hongxian Yu. 2025. "Cyanobacterial Bloom in Urban Rivers: Resource Use Efficiency Perspectives for Water Ecological Management" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091981
APA StyleChai, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhao, Y., & Yu, H. (2025). Cyanobacterial Bloom in Urban Rivers: Resource Use Efficiency Perspectives for Water Ecological Management. Microorganisms, 13(9), 1981. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091981





