Salinity Gradients Override Hydraulic Connectivity in Shaping Bacterial Community Assembly and Network Stability at a Coastal Aquifer–Reservoir Interface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Sampling Collection and Environmental Parameters Determination
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Analysis of Environmental Variables
2.4.2. Microbiota Statistical Analyses
3. Results
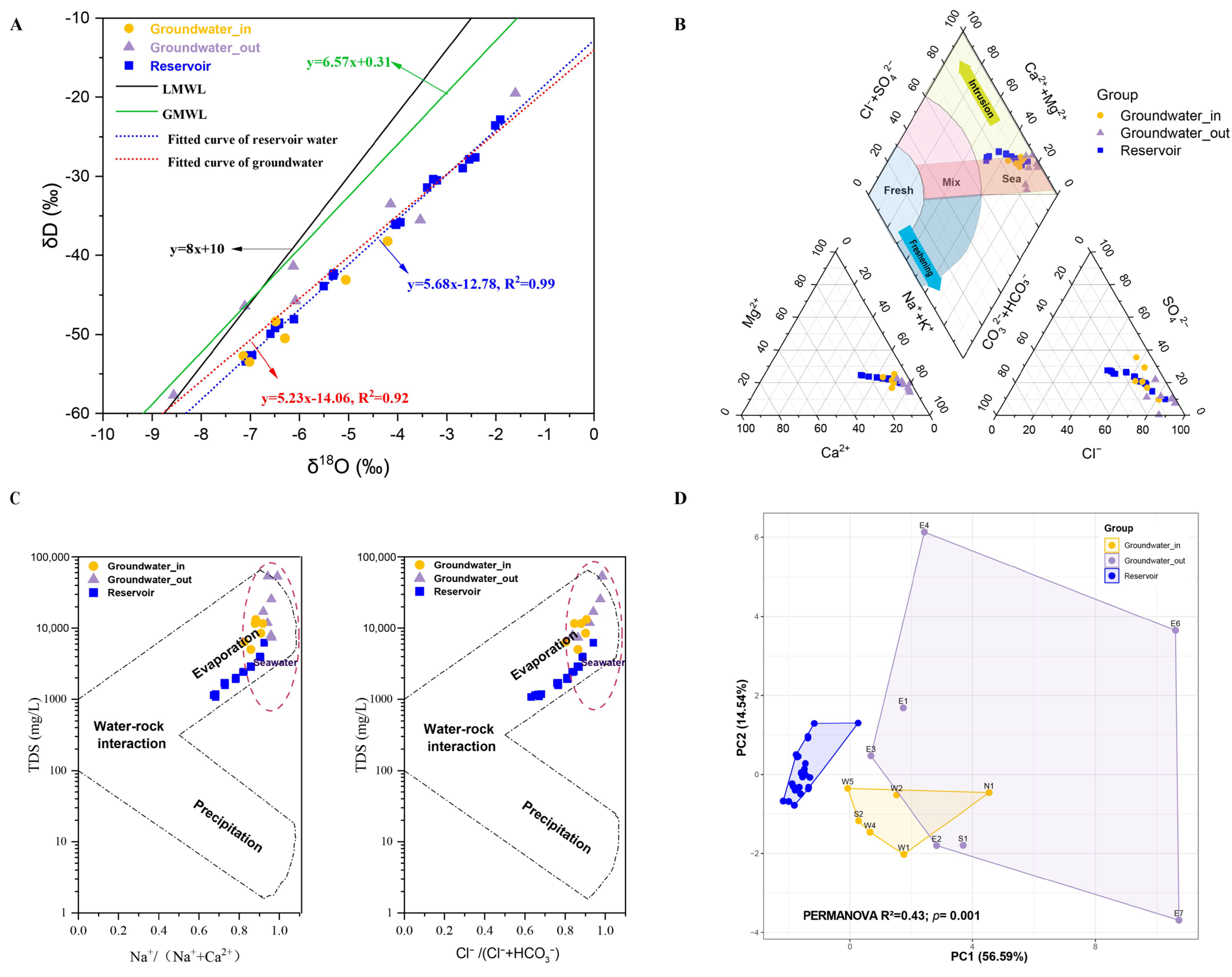
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Stable Isotope Profiles of Groundwater and Reservoir Water
3.2. Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity Across the Reservoir–Aquifer Interface
3.3. Environmental Factors Influencing Bacterial Community and Assembly Mechanisms
3.4. Co-Occurrence Networks of Bacterial Community in the Groundwater and Reservoir
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications of Isotopic and Hydrochemical Characteristics for Reservoir–Aquifer Connectivity and Salinity
4.2. Environmental Gradients and Connectivity Drive Bacterial Community Divergence
4.3. Drivers and Assembly Mechanisms of Bacterial Communities at the Reservoir–Aquifer Interface
4.4. Network Structure and Stability in Groundwater and Reservoir Bacteria
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| Eh | Oxidation-reduction potential |
| TDS | Total dissolved solids |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| NH4+ | Ammonia nitrogen |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| ASV | Amplicon sequence variant |
| LEfSe | Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| β-MNTD | β-mean nearest taxon distance |
| βNTI | β-nearest taxon index |
| RCbray | Bray-Curtis-based Raup-Crick |
| SIMPER | Similarity percentage |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PCoA | Principal coordinates analysis |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| NCM | Neutral community model |
| CCA | Canonical correspondence analysis |
| DCA | Detrended correspondence analysis |
| DESeq2 | Sequence count data 2 |
| GMWL | Global Meteoric Water Line |
| LMWL | Local Meteoric Water Line |
References
- Boyd, E.S.; Cummings, D.E.; Geesey, G.G. Mineralogy influences structure and diversity of ba communities associated with geological substrata in a pristine aquifer. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 54, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, E.B.; Crump, A.R.; Resch, C.T.; Fansler, S.; Arntzen, E.; Kennedy, D.W.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Stegen, J.C. Deterministic influences exceed dispersal effects on hydrologically-connected microbiomes. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griebler, C.; Lueders, T. Microbial biodiversity in groundwater ecosystems. Freshwater Biol. 2009, 54, 649–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küsel, K.; Totsche, K.; Trumbore, S.; Lehmann, R.; Steinhäuser, C.; Herrmann, M. How Deep Can Surface Signals Be Traced in the Critical Zone? Merging Biodiversity with Biogeochemistry Research in a Central German Muschelkalk Landscape. Front. Earth Sci. 2016, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Hermans, S.M.; Totsche, K.U.; Lehmann, R.; Herrmann, M.; Kuesel, K. Groundwater bacterial communities evolve over time in response to recharge. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.Q.; Mo, Y.M.; Li, M.D.; Tang, H.W.; Qi, Y.Z.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A. Desalinization and salinization: A review of major challenges for coastal reservoirs. J. Coastal Res. 2019, 35, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.M.; Jin, G.Q.; Zhang, C.M.; Xu, J.; Tang, H.W.; Shen, C.J.; Scheuermann, A.; Li, L. Combined effect of inland groundwater input and tides on flow and salinization in the coastal reservoir and adjacent aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitharam, T.G.; Kolathayar, S. Challenges and opportunities for coastal reservoir development in India. In Sustainable Water Resource Development Using Coastal Reservoirs; Sitharam, T.G., Yang, S.-Q., Falconer, R., Sivakumar, M., Jones, B., Kolathayar, S., Sinpoh, L., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007, 104, 11436–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Thermodynamic limits to microbial life at high salt concentrations. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1908–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.A.; Achenbach, L.A.; Coates, J.D. Microorganisms pumping iron: Anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; Stams, A.J.M. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.T.; Robeson, M.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J. 2009, 3, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daims, H.; Lebedeva, E.V.; Pjevac, P.; Han, P.; Herbold, C.; Albertsen, M.; Jehmlich, N.; Palatinszky, M.; Vierheilig, J.; Bulaev, A.; et al. Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 2015, 528, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Jia, C.; Wang, Y. Identification of groundwater microbial communities and their connection to the hydrochemical environment in southern Laizhou Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 14263–14278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, B.X.; Dai, H.; Zhang, X.; Xia, C.A.; Zhang, J. Characterizing microbial diversity and community composition of groundwater in a salt-freshwater transition zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Dai, H.; Hu, B.X.; Tong, J.; Gui, D.; Zhang, X.; Xia, C. Comparison of the groundwater microbial community in a salt-freshwater mixing zone during the dry and wet seasons. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, F.; Vargas-García, M.d.C.; Vallejos, A. Interrelation prokaryotic community-aquifer in a carbonate coastal environment. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 82, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, C.; Hu, X.; Yang, F.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, G.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S. Unraveling microbial community variation along a salinity gradient and indicative significance to groundwater salinization in the coastal aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2024, 642, 131893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Gao, Z.; Wan, L.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Desalination of saline groundwater by a weakly permeable clay stratum: A case study in the North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Yi, L.; Ren, H.; Li, S.; Liu, N.; Ren, L.; Liu, J.; Li, R.; Dong, Y. Hydrochemical fingerprints and health risk assessment of groundwater contamination in the Bohai Sea region, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 212, 117559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xiong, G.; Chen, G.; Fu, T.; Yu, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Su, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Characteristics of coastal aquifer contamination by seawater intrusion and anthropogenic activities in the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea, eastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 217, 104830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Leakage recharge from pores saline groundwater to deep fresh groundwater on the condition of pumping in Huabei plain: A case of Tianjing plain. Hydrol. Eng. Geol. 2002, 6, 235–237. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yue, F.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Lang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ding, H.; Liu, C. Spatial variations in water chemical components in a coastal zone of northern China: Insights from environmental isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liang, H.; Gong, S.; Qiao, J.; Peng, X.; Li, W. Hydrochemical characteristics and oxygen isotope tracing study of shallow groundwater seawater—Intrusion in Tianjin. J. Capital Norm. Univ. 2019, 40, 66–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Xiao, M.; Yue, F.; Yi, Y.; Mostofa, K. Seasonal Variations of Dissolved Organic Matter by Fluorescent Analysis in a Typical River Catchment in Northern China. Water 2021, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.G.; Free, G.; Kolada, A.; Phillips, G.; Warner, S.; Wolfram, G.; Poikane, S. Warding off freshwater salinization: Do current criteria measure up? WIREs Water 2024, 11, e1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DZ/T 0064-2021; Methods for Analysis of Water Quality of Groundwater. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Liu, Z.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. Accurate taxonomy assignments from 16S rRNA sequences produced by highly parallel pyrosequencers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossa, C.W.; Oberdorf, W.E.; Yang, L.; Aas, J.A.; Paster, B.J.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Brodie, E.L.; Malamud, D.; Poles, M.A.; Pei, Z. Design of 16S rRNA gene primers for 454 pyrosequencing of the human foregut microbiome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 4135–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Shi, X.; Jia, K.; Sun, B.; Zhao, S.; Fu, C. Determining the Discharge and Recharge Relationships between Lake and Groundwater in Lake Hulun Using Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes and Chloride Ions. Water 2019, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y. Stable isotope characteristics of different water bodies in the Lhasa River Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yue, S.; Wu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, D.; Zhu, R. Effects of flood inundation on biogeochemical processes in groundwater during riverbank filtration. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Han, J.; Song, X. Isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics of salinization water in Beidagang Reservoir, Tianjin. J. China Hydrol. 2017, 37, 44–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J. Development of Seawater Intrusion Protection regulations. In Proceedings of the 1st SWIM-SWICA Joint Saltwater Intrusion Conference, Cagliari-Chia Laguna, Italy, 24–29 September 2006; Volume Session 6. [Google Scholar]
- Marandi, A.; Shand, P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 97, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z. Complex heatmap visualization. iMeta 2022, 1, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, L.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Tian, C.; Lan, P.; Zhu, L.; Loomba, R.; Zhu, R. Targeting keystone species helps restore the dysbiosis of butyrate-producing bacteria in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. iMeta 2022, 1, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ren, K.; Isabwe, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, J. Stochastic processes shape microeukaryotic community assembly in a subtropical river across wet and dry seasons. Microbiome 2019, 7, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Venkataraman, A.; Bassis, C.M.; Beck, J.M.; Young, V.B.; Curtis, J.L.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Schmidt, T.M. Application of a Neutral Community Model to Assess Structuring of the Human Lung Microbiome. MBio 2015, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Ning, D.L. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev 2017, 81, e00002–00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lian, C.; Wan, W.; Qiu, Z.; Luo, X.; Huang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yu, K. Salinity-triggered homogeneous selection constrains the microbial function and stability in lakes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 6591–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layeghifard, M.; Hwang, D.M.; Guttman, D.S. Disentangling Interactions in the Microbiome: A Network Perspective. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Xie, P.; Yang, S.; Niu, G.; Liu, X.; Ding, Z.; Xue, C.; Liu, Y.-X.; Shen, Q.; Yuan, J. ggClusterNet: An R package for microbiome network analysis and modularity-based multiple network layouts. iMeta 2022, 1, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimerà, R.; Amaral, L.A.N. Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature 2005, 433, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The modularity of pollination networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Nuccio, E.E.; Shi, Z.J.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; Firestone, M.K. The interconnected rhizosphere: High network complexity dominates rhizosphere assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röttjers, L.; Faust, K. Can we predict keystones? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Ning, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Navarro, A.; Hiraldo, F.; Tella, J.L.; Blanco, G. Network structure embracing mutualism-antagonism continuums increases community robustness. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.-S.; Wu, J. Optimal network topology for structural robustness based on natural connectivity. Physical A 2016, 443, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, K.P.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; He, J.S.; Chu, H.Y. Interannual climate variability and altered precipitation influence the soil microbial community structure in a Tibetan Plateau grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapelle, F.H. Dissolved Organic Carbon in Groundwater Systems; The Groundwater Project: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, N.; Baker, A.; Reynolds, D. Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste and polluted waters—A review. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Besemer, K.; Bengtsson, M.M.; Romani, A.M.; Packmann, A.I. The ecology and biogeochemistry of stream biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.J.; Hokajarvi, A.M.; Ikonen, J.; Kauppinen, A.; Miettinen, I.T.; Pitkanen, T.; Rossi, P.M.; Kujala, K. Surface Water Intrusion, Land Use Impacts, and Bacterial Community Composition in Shallow Groundwater Wells Supplying Potable Water in Sparsely Populated Areas of a Boreal Region. Microbiol Spectr. 2021, 9, e0017921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, R.; Kazpard, V.; El Samrani, A.G.; Amacha, N.; Saad, Z.; Chou, L. Hydrodynamic influence on reservoir sustainability in semi-arid climate: A physicochemical and environmental isotopic study. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Pang, Z. The role of deuterium excess in determining the water salinisation mechanism: A case study of the arid Tarim River Basin, NW China. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Develle, A.-L.; Herreros, J.; Vidal, L.; Sursock, A.; Gasse, F. Controlling factors on a paleo-lake oxygen isotope record (Yammoûneh, Lebanon) since the Last Glacial Maximum. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 865–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. Isotope Hydrology; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, X.; Michael, H.A. Preferential flow enhances pumping-induced saltwater intrusion in volcanic aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Zhang, X.; Dai, H.; Hu, B.X.; Ou, H.; Sun, L. Diversity and predictive metabolic pathways of the prokaryotic microbial community along a groundwater salinity gradient of the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Garcia, M.d.C.; Sola, F.; Vallejos, A. Comparative Study of Microbial Diversity in Different Coastal Aquifers: Determining Factors. Water 2023, 15, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.J.; Yapiyev, V.; Lehosmaa, K.; Ronkanen, A.K.; Rossi, P.M.; Kujala, K. Physicochemical and isotopic similarity between well water and intruding surface water is not synonymous with similarity in prokaryotic diversity and community composition. Water Res. 2025, 269, 122812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, E.W.; Lanclos, V.C.; Kojima, C.Y.; Cheng, C.; Henson, M.W.; Schon, M.E.; Ettema, T.J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Thrash, J.C. The AEGEAN-169 clade of bacterioplankton is synonymous with SAR11 subclade V (HIMB59) and metabolically distinct. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, F.; Eiler, A.; Bertilsson, S. Seasonality and environmental control of freshwater SAR11 (LD12) in a temperate lake (Lake Erken, Sweden). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 70, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, M.W.; Lanclos, V.C.; Thrash, J.C. Insights on the importance of salinity from the first cultured freshwater SAR11 (LD12) representative. bioRxiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillinger, L.; Hug, K.; Griebler, C. Aquifer recharge viewed through the lens of microbial community ecology: Initial disturbance response, and impacts of species sorting versus mass effects on microbial community assembly in groundwater during riverbank filtration. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Ning, K. Determining the primary sources of groundwater bacterial communities in a large-scale plain area: Microbial source tracking and interpretation for different land use patterns. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 338, 108092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Ning, K. High biodiversity and distinct assembly patterns of microbial communities in groundwater compared with surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Herrmann, M.; Kampe, B.; Lehmann, R.; Totsche, K.U.; Kusel, K. Environmental selection shapes the formation of near-surface groundwater microbiomes. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adyasari, D.; Hassenrück, C.; Oehler, T.; Sabdaningsih, A.; Moosdorf, N. Microbial community structure associated with submarine groundwater discharge in northern Java (Indonesia). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hery, M.; Volant, A.; Garing, C.; Luquot, L.; Poulichet, F.E.; Gouze, P. Diversity and geochemical structuring of bacterial communities along a salinity gradient in a carbonate aquifer subject to seawater intrusion. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Dai, H.; Hu, B.X.; Hao, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. The Study of Hydrogeochemical Environments and Microbial Communities along a Groundwater Salinity Gradient in the Pearl River Delta, China. Water 2019, 11, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.; Wu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Rocha, C.; Ibánhez, J.S.P.; Zhang, J. Organic carbon in a seepage face of a subterranean estuary: Turnover and microbial interrelations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Gao, H.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Ju, F. Hydrodynamic and anthropogenic disturbances co-shape microbiota rhythmicity and community assembly within intertidal groundwater-surface water continuum. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Li, W.; Bi, L.; Li, W.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y. Divergent Driving Mechanisms Shape the Temporal Dynamics of Benthic Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Communities in Coastal Subtidal Zones. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Niu, L.; Zheng, J. Hydrodynamic disturbance and nutrient accumulation co-shape the depth-dependent prokaryotic community assembly in intertidal sediments of a mountainous river estuary. J. Hydrol. 2025, 651, 132580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, J.B.H.; Eisen, J.A.; Penn, K.; Allison, S.D.; Horner-Devine, M.C. Drivers of bacterial β-diversity depend on spatial scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7850–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Xue, D.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Rui, J.; Feng, K.; Wang, Z.-l. The responses and adaptations of microbial communities to salinity in farmland soils: A molecular ecological network analysis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 120, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial interactions: From networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J. Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.-Y.; Hwang, C.; Ling, F.; Andersen, G.L.; LeChevallier, M.W.; Liu, W.-T. Pyrosequencing Analysis of Bacterial Biofilm Communities in Water Meters of a Drinking Water Distribution System. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5631–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yue, Z.; Ma, D.; Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Mechanisms and responses of nitrogen transformations mediated by microbial communities in constructed tailwater wetlands to salinity stress. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Kan, J.; Yang, M.; Yu, X.; Guo, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; et al. Assembly and Network Stability of Planktonic Microorganisms under the Influence of Salinity Gradient: An Arctic Case Study from the Lena River Estuary to the Laptev Sea. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02115-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.; Widder, S. Deciphering microbial interactions and detecting keystone species with co-occurrence networks. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Su, S.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, H. Salinity Gradients Override Hydraulic Connectivity in Shaping Bacterial Community Assembly and Network Stability at a Coastal Aquifer–Reservoir Interface. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071611
Zhang C, Li H, Li M, Zhang Q, Su S, Zhang X, Xiao H. Salinity Gradients Override Hydraulic Connectivity in Shaping Bacterial Community Assembly and Network Stability at a Coastal Aquifer–Reservoir Interface. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071611
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Cuixia, Haiming Li, Mengdi Li, Qian Zhang, Sihui Su, Xiaodong Zhang, and Han Xiao. 2025. "Salinity Gradients Override Hydraulic Connectivity in Shaping Bacterial Community Assembly and Network Stability at a Coastal Aquifer–Reservoir Interface" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071611
APA StyleZhang, C., Li, H., Li, M., Zhang, Q., Su, S., Zhang, X., & Xiao, H. (2025). Salinity Gradients Override Hydraulic Connectivity in Shaping Bacterial Community Assembly and Network Stability at a Coastal Aquifer–Reservoir Interface. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071611





