Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov.: A Novel Selenium-Resistant Bacterium Isolated from the Rhizosphere of Galinsoga parviflora in a Selenium-Rich Region of Enshi, Hubei Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Isolation of Bacterial Strain
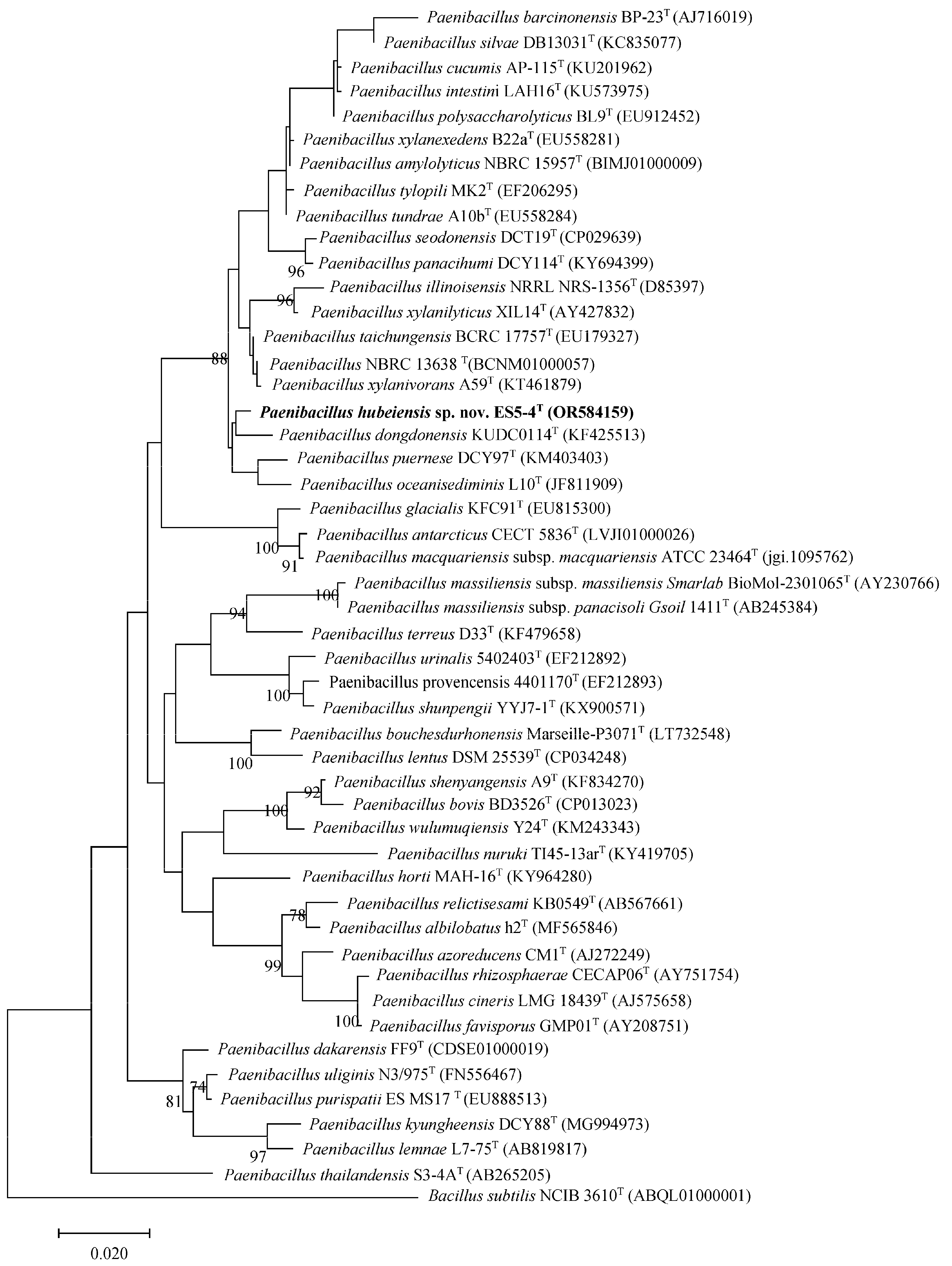
2.2. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
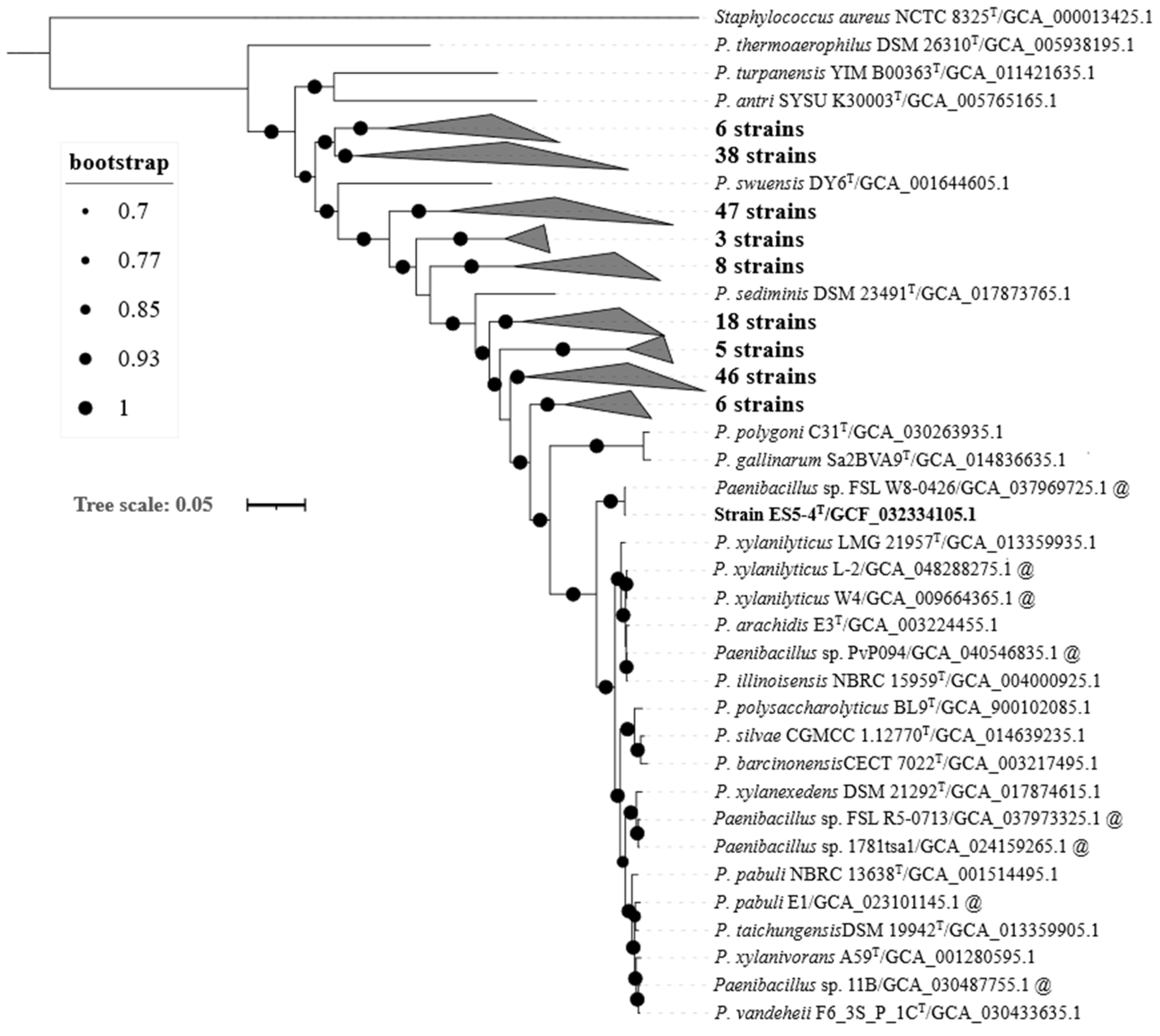
2.3. Genomic Characterization
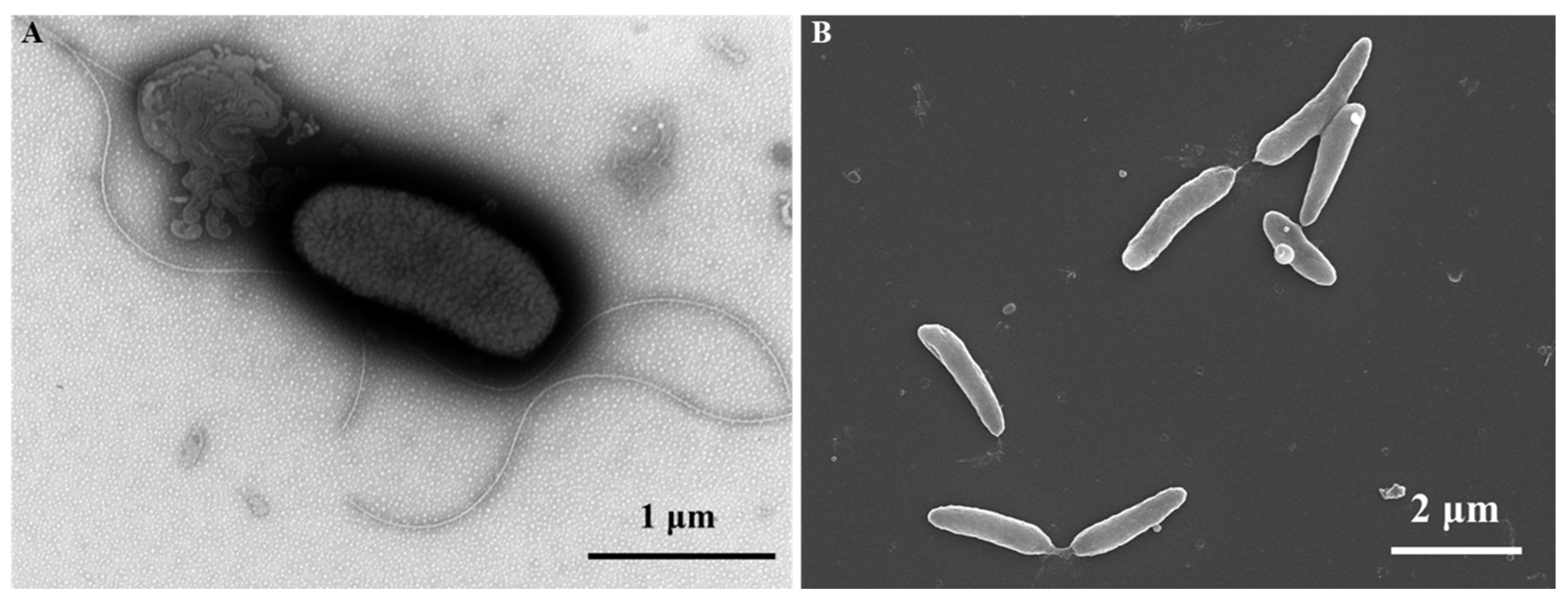
2.4. Phenotypic and Biochemical Characterization
2.5. Chemotaxonomic Analysis
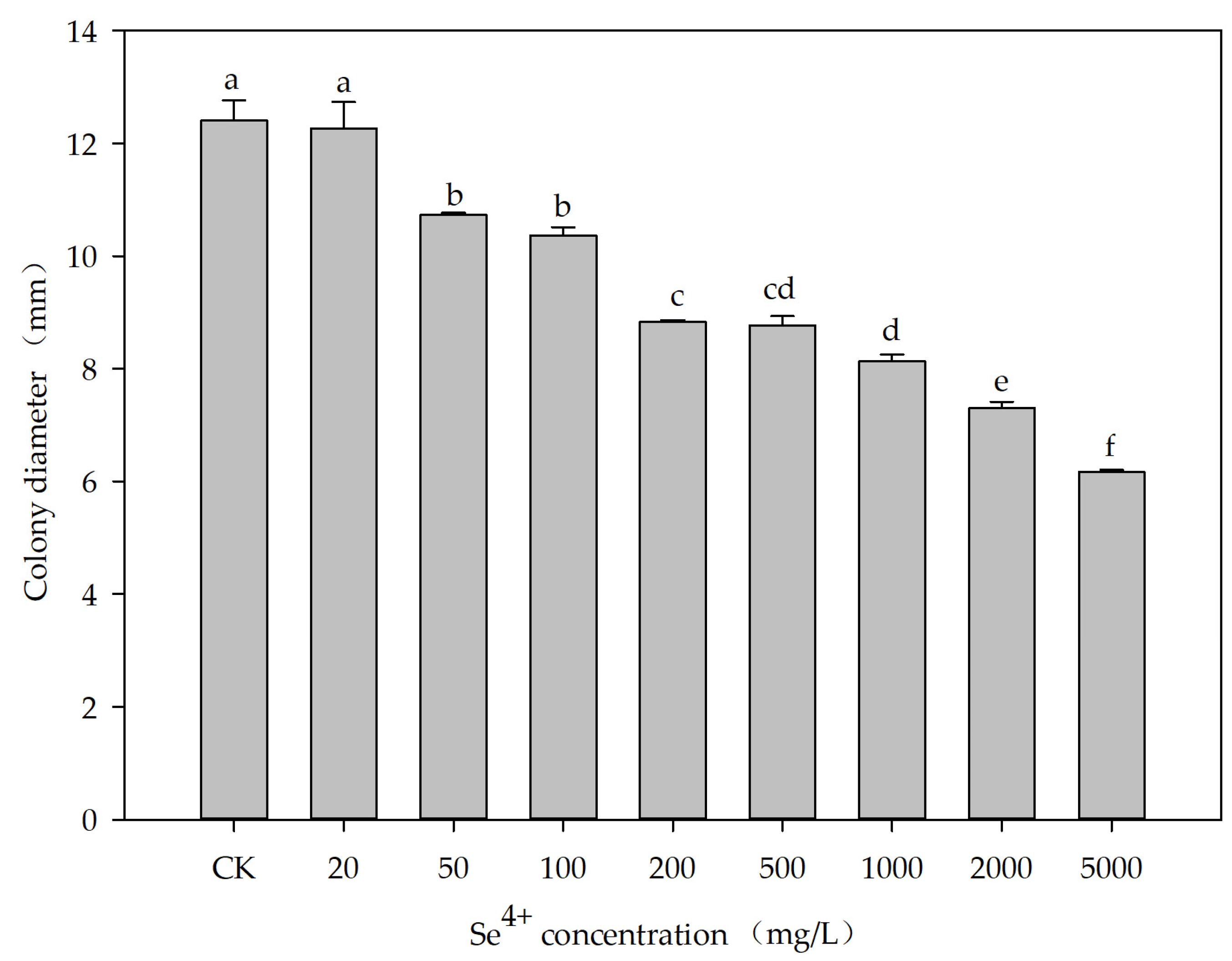
2.6. Effects of Se4+ Concentration on the Growth of the ES5-4T Strain
2.7. Identification of the Functional Gene for Selenocompound Metabolism
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of the 16S rRNA Gene
3.2. Genome-Based Characteristics
3.3. Phenotypic and Biochemical Characteristics
3.4. Effects of Se4+ Concentration on the Growth of the ES5-4T Strain
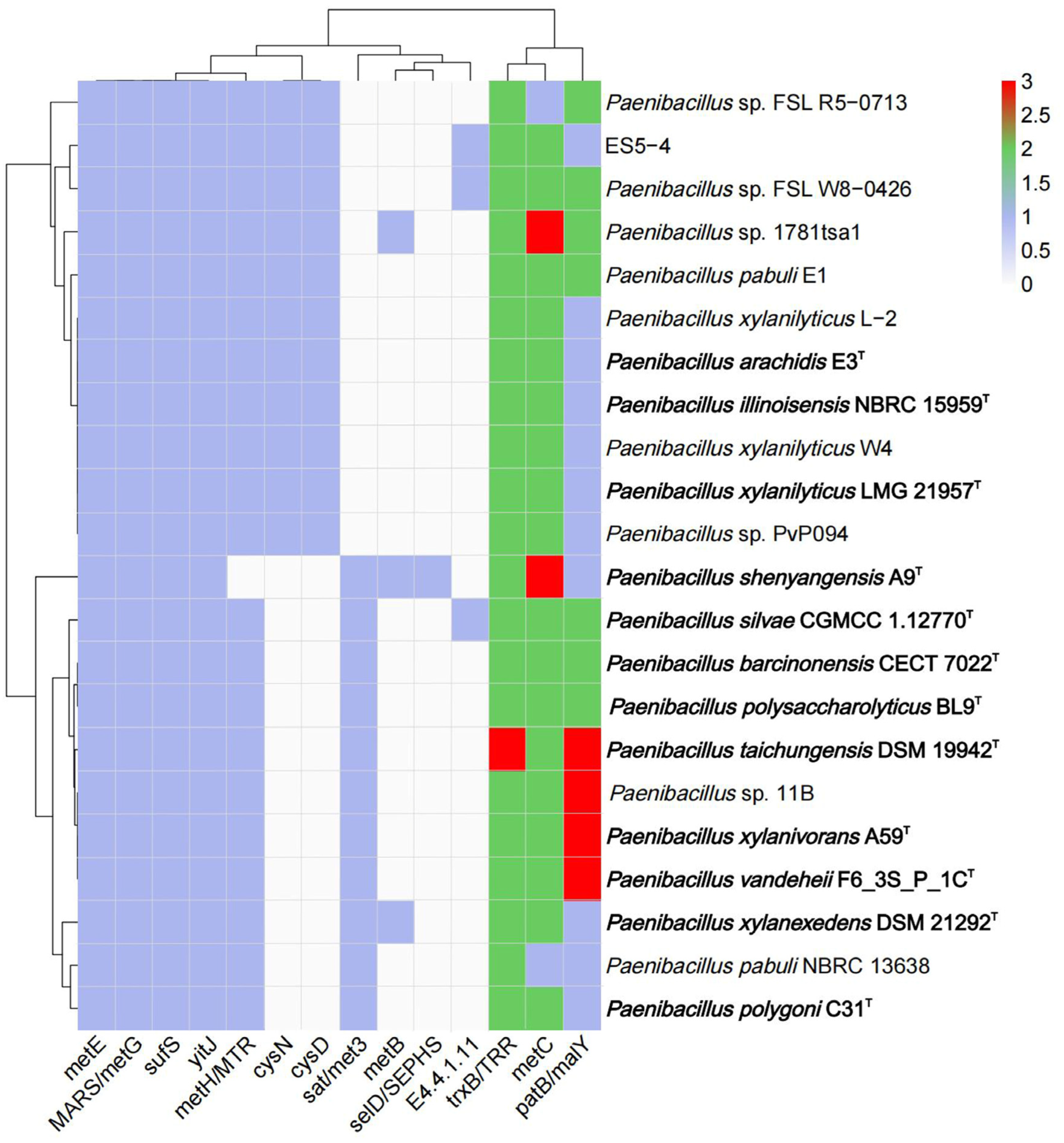
3.5. Genetic Features of Paenibacillus for Selenocompound Metabolism
3.6. Chemotaxonomic Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Description of Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANI | Average nucleotide identity |
| ANIb | Average nucleotide identity calculated by the alignment algorithms BLAST+ |
| APL | Unidentified aminophospholipid |
| bp | Base pairs |
| COG | Cluster of Orthologous Groups |
| dDDH | The digital DNA–DNA hybridization |
| DPG | Diphosphatidylglycerol |
| GGDC | Genome-to-Genome Distance Calculator |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| ICNP | International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| L | Unidentified lipid |
| MCCC | Marine Culture Collection of China |
| ME | Minimum evolution |
| MIDI | Microbial identification system |
| ML | Maximum likelihood |
| NCBI | National Center of Biotechnology Information |
| NJ | Neighbor-joining |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PG | Phosphatidylglycerol |
| PGPB | Plant growth-promoting bacteria |
| PGPR | Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria |
| PL | Unidentified phospholipid |
| Se | Selenium |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| sp. nov | Species novum |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| TSA | Trypticase Soy Agar |
| TSB | Trypticase soy broth |
References
- Ash, C.; Priest, F.G.; Collins, M.D. Molecular identification of rRNA group 3 bacilli (Ash, Farrow, Wallbanks and Collins) using a PCR probe test: Proposal for the creation of a new genus Paenibacillus. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. Microbiol. 1993, 64, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shida, O.; Takagi, H.; Kadowaki, K.; Nakamura, L.K.; Komagata, K. Transfer of Bacillus alginolyticus, Bacillus chondroitinus, Bacillus curdlanolyticus, Bacillus glucanolyticus, Bacillus kobensis, and Bacillus thiaminolyticus to the genus Paenibacillus and emended description of the genus Paenibacillus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.Y.; Ye, X.P.; Hu, Y.Y.; Tang, Z.X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, T.; Bai, X.L.; Pi, E.X.; Xie, B.H.; et al. Exopolysaccharides of Paenibacillus polymyxa: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. Paenibacillus sinensis sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing species isolated from plant rhizospheres. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 115, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, H.W.; Wang, Y.; Kou, Y.R.; Yin, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhao, G.F.; Zhu, W.Y.; Tang, S.K. Paenibacillus turpanensis sp. nov., isolated from a salt lake of Turpan city in Xinjiang province, north-west China. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, M.B.F.; Lemos, E.A.; Vollú, R.E.; Abreu, F.; Rosado, A.S.; Seldin, L. Paenibacillus piscarius sp. nov., a novel nitrogen-fixing species isolated from the gut of the armored catfish Parotocinclus maculicauda. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 9, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Reina, J.C.; Béjar, V.; Llamas, I. Paenibacillus lutrae sp. nov., a chitinolytic species isolated from a river otter in castril natural park, Granada, Spain. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Mo, K. Paenibacillus arenilitoris sp. nov., isolated from seashore sand and genome mining revealed the biosynthesis potential as antibiotic producer. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. Microbiol. 2022, 115, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.X.; Yin, M.; Zhang, D.Y.; Wang, J.; Miao, Y.M.; Cai, M.; Zhou, Y.G.; Miao, C.P.; Tang, S.K. Paenibacillus thermotolerans sp. nov., isolated from a hot spring in Yunnan Province, south-west China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, Z.T.L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G.Q.; Yin, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, W.Y.; Tang, S.K. Paenibacillus alkalitolerans sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from a salt lake of Turpan City in Xinjiang Province, north-west China. Folia Microbiol. 2023, 68, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, V.; Kirdat, K.; Tiwarekar, B.; Dhanavade, P.; Karodi, P.; Shouche, Y.; Sathe, S.; Lodha, T.; Yadav, A. Paenibacillus albicereus sp. nov. and Niallia alba sp. nov., isolated from digestive syrup. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpfer, P.; Lipski, A.; Lamothe, L.; Clermont, D.; Criscuolo, A.; Mclnroy, J.A.; Glaeser, S.P. Paenibacillus plantiphilus sp. nov. from the plant environment of Zea mays. Anto. Leeuw. Int. J. Microbiol. 2023, 116, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Chaudhary, D.K.; Lim, O.B.; Kim, D.U. Paenibacillus agricola sp. nov., isolated from agricultural soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, R.; Agrawal, L.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, M.; Yadav, S.; Chauhan, P.S.; Nautiyal, C.S. Southern blight disease of tomato control by 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase producing Paenibacillus lentimorbus B-30488. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016, 11, e1113363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Shi, H.; Du, Z.; Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. Comparative genomic and functional analysis reveal conservation of plant growth promoting traits in Paenibacillus polymyxa and its closely related species. Sci. Rep.-UK 2016, 6, 21329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, M.; Hua, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Dixon, R.; Li, J. Alanine synthesized by alanine dehydrogenase enables ammonium-tolerant nitrogen fixation in Paenibacillus sabinae T27. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2215855119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, S.K.; Ryu, C.M.; Park, S.H. Chronicle of a soil bacterium: Paenibacillus polymyxa E681 as a tiny guardian of plant and human health. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Q.M.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, X.J.; Yan, L.; Lv, J.; Sheng, J. Paenibacillus puerhi sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere soil of Pu-erh tea plants (Camellia sinensis var. assamica). Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Tu, Y.; Ma, T.; Jiang, N.; Piao, C.; Li, Y. Taxonomic study of three novel Paenibacillus species with cold-adapted plant growth-promoting capacities isolated from root of Larix gmelinii. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.; Jitaru, P.; Barbante, C. Selenium biochemistry and its role for human health. Metallomics 2014, 6, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Carocci, A. Biological activity of selenium and its impact on human health. Inter. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Lens, P.N.L. Ecology and biotechnology of selenium-respiring bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.R.; Chen, H.B.; Li, Y.X.; Zhou, Z.H.; Li, J.B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.H.; Wang, S.S. Priestia sp. LWS1 is a selenium-resistant plant growth-promoting bacterium that can enhance plant growth and selenium accumulation in Oryza sativa L. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 44971-2024; Soil Selenium Content Level. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- NY/T 1104-2006; Determination of Selenium in Soils. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Li, X.; Yan, Z.; Gu, D.; Li, D.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Su, L.; Ao, Y. Characterization of cadmium-resistant rhizobacteria and their promotion effects on Brassica napus growth and cadmium uptake. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.A.; Reich, C.I.; Sharma, S.; Weisbaum, J.S.; Wilson, B.A.; Olsen, G.J. Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2008, 74, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J. Spongiibacter thalassae sp. nov., a marine gammaproteobacterium isolated from seawater. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurk, S.; Bankevich, A.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Korobeynikov, A.; Lapidus, A.; Prjibelski, A.D.; Pyshkin, A.; Sirotkin, A.; Sirotkin, Y.; et al. Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products. J. Comput. Biol. 2013, 20, 714–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Golosova, O.; Fursov, M.; Team, U. Unipro UGENE: A unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Goker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-mapper v2: Functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Waite, D.W.; Rinke, C.; Skarshewski, A.; Chaumeil, P.A.; Hugenholtz, P. A standardized bacterial taxonomy based on genome phylogeny substantially revises the tree of life. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE v5 enables improved estimates of phylogenetic tree confidence by ensemble bootstrapping. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.F.; He, W.; Shao, Z.; Ahmed, I.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.J.; Zhao, Z. EasyCGTree: A pipeline for prokaryotic phylogenomic analysis based on core gene sets. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Yan, Z.; Ao, Y. Biosorption and bioaccumulation characteristics of cadmium by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 30902–30911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, Q.; He, N.; Kong, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, R.; Shao, Q. Potential application of Curtobacterium sp. GX_31 for efficient biosorption of Cadmium: Isotherm and kinetic evaluation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 30, 103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasser, M. Identification of Bacteria by Gas Chromatography of Cellular Fatty Acids; MIDI technical Note; MIDI Inc.: Newark, DE, USA, 1990; Volume 101. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, M.D.; Jones, D. Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implication. Microbiol. Rev. 1981, 45, 316–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnikin, D.E.; O’donnell, A.G.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G.; Athalye, M.; Schaal, A.; Parlett, J.H. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 1984, 2, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komagata, K.; Suzuki, K.I. 4 Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol. 1988, 19, 161–207. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Xue, H.P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, A.H.; Huang, J.K.; Zhang, D.F. Biomineralization of struvite induced by indigenous marine bacteria of the genus Alteromonas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1085345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramaki, T.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Endo, H.; Ohkubo, K.; Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Ogata, H. Kofam KOALA: KEGG Ortholog assignment based on profile HMM and adaptive score threshold. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2251–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.S.; Kang, H.U.; Ghim, S.Y. Paenibacillus dongdonensis sp. nov., isolated from rhizospheric soil of Elymus tsukushiensis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 2865–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.L.; Tien, C.J.; Tai, C.J.; Wang, L.T.; Liu, Y.C.; Chern, L.L. Paenibacillus taichungensis sp. nov., from soil in Taiwan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 2640–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, S.; Sauka, D.H.; Ferrari, A.E.; Piccini, F.E.; Ontañon, O.M.; Campos, E. Paenibacillus xylanivorans sp. nov., a xylan-degrading bacterium isolated from decaying forest soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3818–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goris, J.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Klappenbach, J.A.; Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; Tiedje, J.M. DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Shi, K.; Wang, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, R.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G. Paenibacillus flagellatus sp. nov., isolated from selenium mineral soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Llamosas, H.; Castro, L.; Blazquez, M.L.; Diaz, E.; Carmona, M. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles by Azoarcus sp. CIB. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.A., Jr.; Giddings, T.H.; DeBrine, P.; Fall, R. High incidence of selenite-resistant bacteria from a site polluted with selenium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Li, J.; Zan, S.; Zhou, S.; Yang, R. Two selenium tolerant Lysinibacillus sp. strains are capable of reducing selenite to elemental Se efficiently under aerobic conditions. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 77, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.; Su, J.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G. Paenibacillus selenitireducens sp. nov., a selenite-reducing bacterium isolated from a selenium mineral soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Cui, L.K.; He, S.B.; Sun, J.; Chen, Q.Z.; Bao, H.D.; Liang, T.Y.; Liang, B.Y.; Cui, L.Y. Preparation, characteristics and cytotoxicity of green synthesized selenium nanoparticles using Paenibacillus motobuensis LY5201 isolated from the local specialty food of longevity area. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Qiao, L.; Ma, L.; Yan, S.; Guo, Y.; Dou, X.; Zhang, B.H.; Roman, A. Biosynthesis of polysaccharides-capped selenium nanoparticles using Lactococcus lactis NZ9000 and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, G.B.; Iqbal, M.S.; Ghaith, M.M.S.; Haseeb, A.; Ahmed, B.; Qadir, M.I. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) from citrus fruit have anti-bacterial activities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, A.; Tekula, S.; Saifi, M.A.; Venkatesh, P.; Godugu, C. Therapeutic applications of selenium nanoparticles. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Tan, J.; Li, M.; Yuan, Z.; Zhou, H. The mechanism of Se(IV) multisystem resistance in Stenotrophomonas sp. EGS12 and its prospect in selenium-contaminated environment remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Yao, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, N.; Wei, H.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhao, C. Selenium nanoparticles: Enhanced nutrition and beyond. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 12360–12371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Kang, D.; Jung, J.; Yoo, T.J.; Shim, M.S.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Tsuji, P.A.; Hatfield, D.L.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, B.J. SEPHS1: Its evolution, function and roles in development and diseases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 730, 109426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, P.; Lan, Q.; Deng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Su, N.; He, F.; et al. High-coverage proteomics reveals methionine auxotrophy in Deinococcus radiodurans. Proteomics 2017, 17, 1700072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, T.M.; Gemoth, L.; Will, A.; Schwarz, M.; Ohse, V.A.; Kipp, A.P.; Steinbrenner, H.; Klotz, L.O. Selenium-binding protein 1 (SELENBP1) is a copper-dependent thiol oxidase. Redox Biol. 2023, 65, 102807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustacich, D.; Powis, G. Thioredoxin reductase. Biochem. J. 2000, 346, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarze, A.; Dauplais, M.; Grigoras, I.; Lazard, M.; Ha-Duong, N.T.; Barbier, F.; Blanquet, S.; Plateau, P. Extracellular production of hydrogen selenide accounts for thiol-assisted toxicity of selenite against Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8759–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Li, T.; Huang, X.; Zhu, K.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, J. Advances in the study of selenium-enriched probiotics: From the inorganic Se into Se nanoparticles. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, 2300432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; van Doesburg, W.; Rutten, G.A.; Marugg, J.D.; Alting, A.C.; van Kranenburg, R.; Kuipers, O.P. Molecular and functional analyses of the metC gene of Lactococcus lactis, encoding cystathionine β-lyase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Seeda, M.A.; Abou El-Nour, A.A.; El-Bassiouny, M.S.; Abdallah, M.S.; El-Monem, A.A.S. Supplementation of selenium and its nano on crop plant tolerance and physiological responses: A review. Middle East J. Agric. Res. 2025, 14, 213–283. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Whang, K.S. Paenibacillus pinistramenti sp. nov., isolated from pine litter. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 113, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Chaudhary, D.K.; Kim, D.U. Paenibacillus gyeongsangnamensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strain | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 76.4 | 76.2 | 76.3 | 76.8 |
| 2 | 21.2 | - | 88.6 | 88.4 | 80.5 |
| 3 | 20.9 | 36.3 | - | 91.8 | 80.4 |
| 4 | 20.6 | 35.9 | 45.6 | - | 80.5 |
| 5 | 21.6 | 23.8 | 29.9 | 23.6 | - |
| Characteristic | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motile | + | − | − |
| Optimal temperature (°C) | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| Optimal NaCl (%, w/v) | 0.5–1.0 | 0.5–2.0 | 0.5–1.0 |
| Optimal growth pH | 5.0–7.0 | 6.0–7.0 | 7.0–8.0 |
| H2S production | + | + | − |
| Starch hydrolysis | − | + | + |
| Cellulose hydrolysis | − | + | + |
| Tween 20/40/60 | −/+/+ | +/+/+ | −/+/− |
| API 50CH test | |||
| L-Arabinose | − | + | + |
| Mannose | − | − | + |
| D-Turanose | − | w | − |
| Assimilation of: | |||
| D-Maltose | − | + | + |
| D-Raffinose | − | − | + |
| L-Aspartic acid | − | + | − |
| Fusidic acid | + | − | − |
| D-Galacturonic acid | + | − | + |
| L-Glutamic acid | + | + | − |
| Polar lipids | DPG, PG, PE, PL | ND | L, DPG, PG, PE, APL, PL |
| Major fatty acids (>10%) | anteiso-C15:0, C16:0 | anteiso-C15:0, C16:0 | anteiso-C15:0, iso-C16:0, iso-C14:0 |
| DNA G + C content (%) | 50.5 | 44.3 | 44.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, J.; Fu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jin, C.; Peng, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Su, Y.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov.: A Novel Selenium-Resistant Bacterium Isolated from the Rhizosphere of Galinsoga parviflora in a Selenium-Rich Region of Enshi, Hubei Province. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071559
Kong J, Fu Z, Liu Y, Jin C, Peng X, Liu X, Gao Y, Xiao Q, Su Y, Zhao Z, et al. Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov.: A Novel Selenium-Resistant Bacterium Isolated from the Rhizosphere of Galinsoga parviflora in a Selenium-Rich Region of Enshi, Hubei Province. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071559
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Jiejie, Ziyue Fu, Yueyang Liu, Can Jin, Xiaobo Peng, Xiaolong Liu, Yang Gao, Qiusheng Xiao, Yuting Su, Zhigang Zhao, and et al. 2025. "Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov.: A Novel Selenium-Resistant Bacterium Isolated from the Rhizosphere of Galinsoga parviflora in a Selenium-Rich Region of Enshi, Hubei Province" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071559
APA StyleKong, J., Fu, Z., Liu, Y., Jin, C., Peng, X., Liu, X., Gao, Y., Xiao, Q., Su, Y., Zhao, Z., Song, Y., Li, X., & Zhang, D. (2025). Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov.: A Novel Selenium-Resistant Bacterium Isolated from the Rhizosphere of Galinsoga parviflora in a Selenium-Rich Region of Enshi, Hubei Province. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071559







