Abstract
This study aimed to isolate and genetically characterize Arcobacter species from broiler chickens sampled at three slaughterhouses in Grenada, West Indies. A total of 126 samples—including cloacal swabs, intestinal contents, and meat—from 42 birds were cultured using a chromogenic agar medium. Arcobacter spp. were detected in 21.4% (9/42) of the birds. Among the sample types, meat exhibited the highest prevalence at 14.3% (6/42), followed by fecal samples at 7.1% (3/42) and cloacal swabs at 2.4% (1/42). Genus- and species-specific polymerase chain reaction assays on 33 isolates identified five Arcobacter species: A. butzleri, A. cryaerophilus, and A. skirrowii (each 18.2%), as well as A. cibarius and A. thereius (each 6.1%). Genetic diversity was further assessed via Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus–polymerase chain reaction, which revealed 13 distinct genotypic fingerprints forming six clusters, with a high discriminatory power (D = 0.96). This study represents the first documented isolation and molecular characterization of five Arcobacter species from broiler chickens in Grenada across multiple sample types. These findings underscore the zoonotic implications of isolating Arcobacter spp., particularly in contaminated poultry meat destined for human consumption. The presence of Arcobacter spp. in poultry carcasses poses a significant public health concern. To mitigate this public health risk, recommendations include surveillance for the presence of this pathogen in Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points plans or other tools used to identify pathogens compromising food safety and public health.
1. Introduction
The genus Arcobacter (synonym: Aliarcobacter) [1] comprises Gram-negative bacterial organisms that are non-spore-forming spiral rods and microaerophiles, measuring 0.2–0.9 μm wide and 0.5–3 μm long. Arcobacter cryaerophilus was the first species isolated from bovine and pig fetuses in 1977 in Belfast, UK [2]. However, at the time, it was classified within the genus Campylobacter and denoted as Campylobacter cryaerophila. The Arcobacter species were commonly referred to as “campylobacter-like” or “aerotolerant campylobacters” since these resembled Campylobacter. However, between 1991 and 1992, many of these “aerotolerant campylobacters” species were reclassified and placed under the new genus Arcobacter [3,4]. Since then, the genus Arcobacter has undergone multiple revisions and reclassifications [1,5,6,7,8,9]. Currently, there are 33 known species in this genus.
In recent years, Arcobacter has emerged as a significant foodborne pathogen, gaining considerable research attention [10]. Over the past decade, A. butzleri, A. cryaerophilus, and A. skirrowii have been linked to human illnesses. Specifically, A. butzleri has been associated with gastroenteritis and bacteremia in humans [11,12,13,14,15]. While diarrhea, akin to Campylobacter infections, is the primary symptom of Arcobacter species infections, A. butzleri typically causes persistent, watery diarrhea, in contrast to bloody diarrhea induced by C. jejuni [11]. Additional symptoms of A. butzleri infections include abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and fever, and in severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for patients [16]. Consequently, in 2002, the International Commission on Microbiological Specifications for Foods (ICMSF) classified A. butzleri as a significant threat to human health [17], likely due to the rising incidence of both individual cases and outbreaks associated with this pathogen [16,18,19,20,21,22]. Arcobacter butzleri and A. cryaerophilus have also been recognized as potential etiological agents for “Traveler’s Diarrhea” [23,24,25]. The most likely route of transmission of Arcobacter species to humans is through the consumption of contaminated or undercooked poultry meat [13,26,27,28].
In the Caribbean region, most people consume poultry meat since it is considered an efficient and cheap source of protein. Across the region, the annual per capita consumption of poultry meat varies from 74.7 kg in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines to 10.9 kg in Haiti, with Grenada at 37.4 kg [29]. Therefore, extensive research has focused on examining poultry meat for the presence of foodborne pathogens in the Caribbean region, with predominant infections attributed to pathogens from the Campylobacter and Salmonella genera [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. Conversely, Arcobacter species have been documented in poultry and poultry products across many countries [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47], but their presence has not been established in the Caribbean region, including Grenada. However, there was one report on an incidental finding of A. butzleri from pet tortoises in Grenada [48]. Arcobacter is categorized as an “emerging foodborne pathogen”; therefore, it is not included on the diagnostic list of known foodborne pathogens [49]. Consequently, the culture protocols primarily focus on detecting other well-established foodborne pathogens such as Campylobacter, Salmonella, and Shigella. Interestingly, other food items of animal origin like beef, pork, shellfish, cheese, and raw milk have been documented to exhibit contamination by Arcobacter species; however, poultry and poultry-derived products demonstrate the highest incidence of Arcobacter species [50,51,52,53,54].
In light of the above background, this study aimed at isolating and characterizing Arcobacter species from broiler chickens from three local farms in Grenada. A commercially available chromogenic agar medium was utilized for the accurate morphological identification of the bacterium. Further molecular characterization of the isolates was performed through the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Sample collection was performed per the approved Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee protocols (IACUC-20007-R) of Saint George’s University (SGU), Grenada, West Indies. Forty-two broiler chickens were sampled from three different slaughter farms in Grenada, West Indies. From each bird, a cloacal sample was collected using a sterile flocked swab (Puritan™ HydraFlock™, Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA, USA). Each swab was placed in a transport tube containing 3 mL of 1× Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS) and maintained in a cold storage box. After slaughter, meat samples were collected from the birds, including breast muscle (n = 3), gizzard (n = 11), heart (n = 9), and liver (n = 19). Additionally, fecal samples (n = 42), obtained from the intestinal contents, were collected from each bird. These samples were placed in a sterile container and transported on ice to the Microbiology Laboratory of the School of Veterinary Medicine, SGU, along with the swab samples, and processed within 4 h of collection.
2.2. Enrichment and Culture Isolation of Arcobacter
Samples in each category were enriched in Houf Broth (HB). Houf Broth was prepared by supplementing 5-fluorouracil (100 mg/L), amphotericin B (5 mg/L), cefoperazone (16 mg/L), novobiocin (32 mg/L), and trimethoprim (64 mg/L) in Arcobacter-Specific Broth (Oxoid, Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK) [55]. Each cloacal swab tip was pressed against the transport tube wall containing 1× PBS to squeeze out the sample. In total, 1 mL of the sample was added to 9 mL of HB. Approximately 1 g of each fecal sample was inoculated in 9 mL of HB and thoroughly mixed by vortexing. For the meat samples, approximately 1 g was placed in a stomacher bag containing 5 mL of 1× PBS. The sample was hand massaged for 1–2 min to expose the entire surface of the meat sample. In total, 1 mL of the sample was inoculated into 9 mL of HB and mixed by vortexing. All the samples were incubated at 30 °C for 48 h. After incubation, the samples were streaked onto Nguyen–Restaino–Juárez (NRJ)-Arcobacter Chromogenic Agar media plates (NRJ-M) (R & F® Products, Downers Grove, IL, USA). The agar plates were incubated aerobically at 30 °C for 48 to 72 h. Presumptive Arcobacter was identified by observing the bacterial growth on the NRJ-M plates. On NRJ-M plates, Arcobacter species appear as salmon flat to raised colonies, 0.5–1.5 mm in diameter, with or without a clear ring after 72 h at 30 °C under aerobic conditions [56,57]. Such colonies were sub-cultured for purification on another NRJ-M plate and incubated at 30 °C for 48 h. Presumptive Arcobacter isolates were subjected to Gram-staining, wet mounting, and biochemical tests.
2.3. Nucleic Acid Extraction from the Bacterial Isolates
Genomic Deoxyribonucleic Acid (gDNA) was extracted from the bacterial isolates using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The extraction protocols provided by the kit manufacturers were followed. American-Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA)-derived Arcobacter reference strains for A. butzleri (ATCC 49616), A. cryaerophilus (ATCC 43158), A. skirrowii (ATCC 51400), RM 4473 (A. butzleri), and RM 4598 (A. cryaerophilus) were used as positive controls. Genomic DNA from these reference strains was extracted separately using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The purity and concentrations of the gDNA were detected using the NanoDrop™ 2000 Spectrophotometer (Eppendorf, Hauppauge, NY, USA). The gDNA samples were then stored at −20 °C until further molecular and genetic characterizations were performed.
2.4. Molecular Characterization of the Arcobacter Species
The gDNA samples were subjected to Arcobacter genus-specific single-plex PCR. This PCR amplified a 16S rRNA gene fragment universally found in all Arcobacter species [58]. The samples that were PCR-positive for the genus-specific protocol were further subjected to a multiplex PCR that simultaneously amplified gene fragments from five Arcobacter species: butzleri, skirrowii, thereius, cibarius, and cryaerophilus [59]. Table 1 shows the sequences and origins of all primers used for gene amplification.

Table 1.
Oligonucleotide primers used to characterize the samples molecularly.
The PCR master mix preparation and cycling conditions for the single-plex assay were as follows: A total of 25 µL of reaction mixture was prepared that contained a final concentration of 1× Platinum PCR High Fidelity Supermix, 0.4 µM of the forward and reverse primers, and 1 μL (~10 ng to 30 ng) of DNA template. Samples were initially heated for 2 min at 94 °C, followed by 35 amplification cycles of 30 s. at 94 °C (denaturation), 30 s. at 56 °C (primer annealing), and 1 min at 68 °C (primer extension). A final elongation step (68 °C for 5 min) followed the final amplification cycle.
The PCR master mix preparation and cycling conditions for the multiplex assay were as follows: A total of 25 µL of reaction mixture was prepared that contained a final concentration of 1× High Fidelity PCR buffer, 0.2 mM of dNTPs, 1.5 mM of MgSO4, 0.5 µM of the forward and reverse primers for the five Arcobacter species, 1.5 U of the Taq DNA Polymerase, and 1 μL (~10 ng to 30 ng) of DNA template. Samples were initially heated for 3 min at 94 °C followed by 35 amplification cycles of 45 s. at 94 °C (denaturation), 45 s. at 58 °C (primer annealing), and 2 min at 68 °C (primer extension). A final elongation step (68 °C for 5 min) followed the final amplification cycle.
2.5. Sequencing of the Samples
For direct sequencing purposes, the positive samples were subjected to PCRs using the primers listed in Table 2 to amplify gene sequences for Arcobacter species. Twenty-five microliters of the PCR products were subjected to electrophoresis with a 1.5% agarose gel, stained with ethidium bromide, and photographed under a gel documentation system (LabNet International Inc., Edison, NJ, USA). Positively identified amplicons were purified using the QIAquick Gel Extract Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions and sent for direct sequencing to the sequencing facility provided by Molecular Cloning Laboratories (South San Francisco, CA, USA). The sequencing histograms were processed and compared to the GenBank® sequence database using the Standard Nucleotide Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLASTN) (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi; accessed on 23 June 2025) provided by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). The comparison was restricted to the RefSeq Reference Genome Database, specifically filtered to include only sequences belonging to the Arcobacter Group (taxonomic ID: 2808963).

Table 2.
Oligonucleotide primers used for direct sequencing.
2.6. Genetic Characterization of the Arcobacter Species
The Arcobacter species identified through the molecular assays and sequencing were subjected to genetic profiling. The Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus–PCR (ERIC-PCR) assay was performed on all Arcobacter species for the genetic fingerprinting of the bacterial genomes. The primers designed by Versalovic et al. [61] were used to perform the PCR: ERIC1R (5′-ATGTAAGCTCCTGGGGATTCAC-3′) and ERIC2 (5′-AAGTAAGTGACTGGGGTGAGCG-3′). These primers were used in a PCR protocol described by Houf et al. [62]. Briefly, a 50 μL reaction mixture containing a final concentration of 1× PCR reaction buffer, 0.5 μM of the forward primer and reverse primer, 0.2 mM of the dNTPs, 4 mM of MgCl2, 5 U of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase, and ~5–25 ng/μL of template DNA was used for each reaction. Nuclease-free water was used as a negative control, and the Arcobacter reference strains from ATCC were used as positive controls. The cycling conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, followed by 40 cycles of 1 min of denaturation at 94 °C, 1 min of annealing at 25 °C, and 2 min of extension at 72 °C, and a final 5 min extension at 72 °C after the last cycle.
Ten microliters of the ERIC-PCR products were size-separated by electrophoresis in ethidium bromide-stained 1.5% agarose gels with 1× Tris-acetate-EDTA buffer, run for 2.5 h at 100 Volts. The DNA profiles were visualized under a UV transilluminator and photographed using a gel documentation system (LabNet International Inc., Edison, New Jersey, USA). DNA patterns that differ in one or more DNA fragments were considered patterns that represent different types. To interpret the profiles of the isolates, the GelJ software program (version 2.0) [63] was used. GelJ uses the gel picture to generate a computer-based DNA band clustering matrix. Based on the presence or absence of a band, a binary matrix is marked with 1 (or +) or 0 (or −), respectively. This band clustering matrix is used to compute a similarity matrix using the Dice coefficient [64], which expresses the similarity level between two DNA patterns. Based on the similarity matrix, a dendrogram was constructed using the unweighted pair group linkage analysis method (UPGAM). The numerical index of discrimination for ERIC-PCR was calculated by Simpson’s index of diversity [65] using the following formula:
where D = index of discriminatory power; N = the total number of strains in the sample population; nj = the number of strains belonging to the jth type; and s = the total number of types defined.
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Culture
Culture protocols revealed that 21.4% of birds (9/42) had Arcobacter species in their fecal, giblet, and/or cloacal samples. Specifically, three birds had Arcobacter in fecal samples, five in giblet samples, and one in both giblet and cloacal swab samples. Out of 126 total samples, meat samples exhibited the highest prevalence of Arcobacter spp., with an isolation rate of 14.3% (6/42). Within the meat category, no Arcobacter spp. were cultured from breast (0/3) or gizzard (0/11) samples, while heart and liver samples showed isolation rates of 22.2% (2/9) and 21.1% (4/19), respectively. Fecal samples had a lower isolation rate of 7.1% (3/42), and Arcobacter spp. were detected in only 2.4% (1/42) of cloacal swab samples. The overall prevalence of Arcobacter spp. across all sample types was 7.9% (10/126) (Table 3). Thirty-three isolates were sub-cultured from these ten samples, and on NRJ-M plates, Arcobacter colonies appeared salmon-colored, 0.5–1.5 mm in diameter, and flat to raised, with or without a clear ring after 72 h at 30 °C under aerobic conditions (Figure 1). Gram-staining, wet mounting, and microscopy for these isolates showed that they were Gram-negative, curved rods with corkscrew motility. Biochemical tests revealed that the isolates were oxidase-positive, catalase-positive, and Hippurate hydrolysis-negative.

Table 3.
Occurrence of Arcobacter spp. in meat, cloacal swab, and feces samples and isolates.
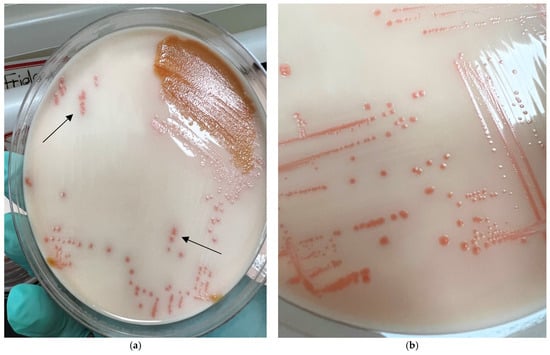
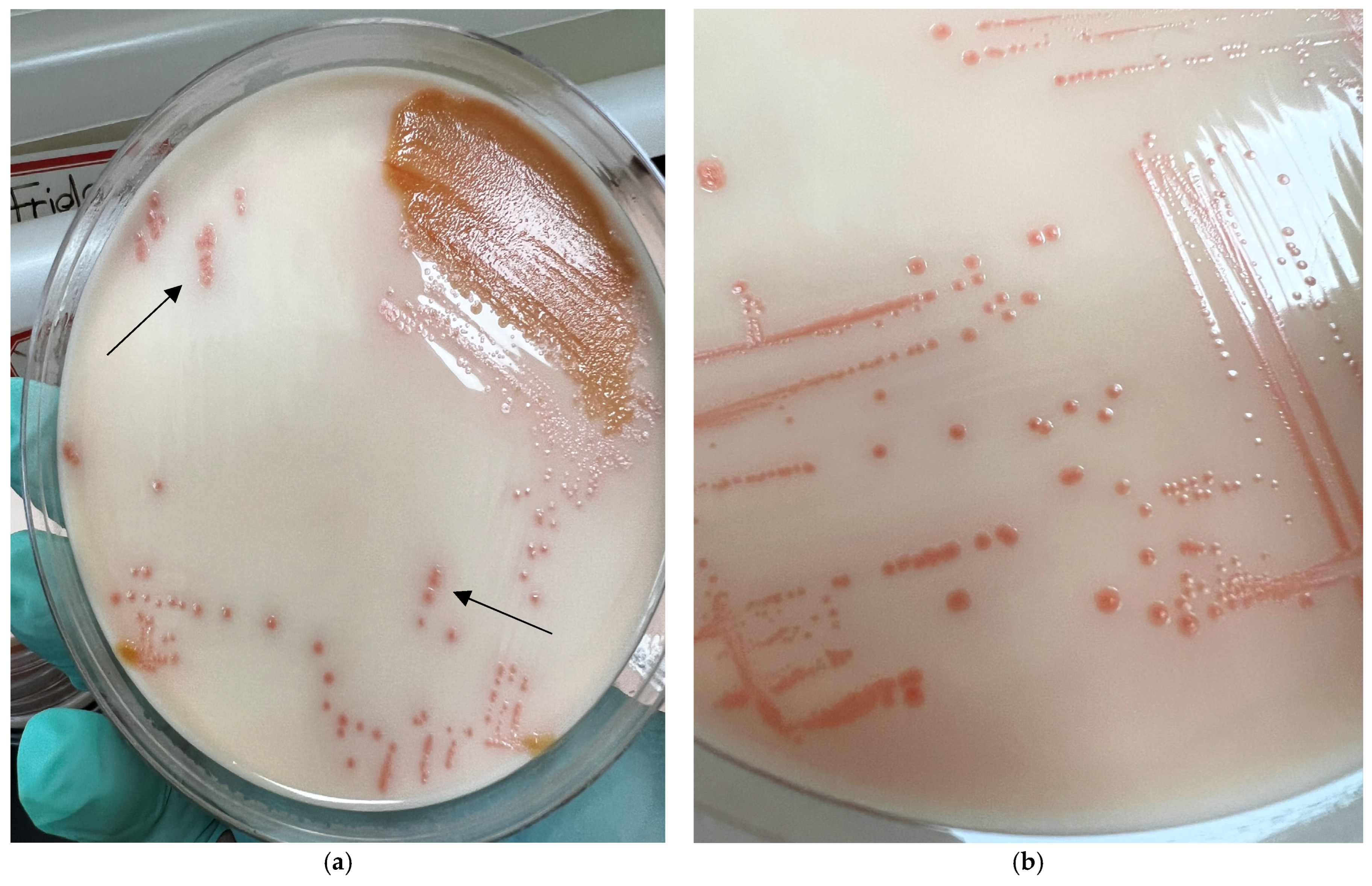
Figure 1.
Culture plates from sample M77 growing on the NRJ-chromogenic agar medium. (a) Mixed colonies (arrows showing salmon-pink colonies of Arcobacter); (b) pure isolate of Arcobacter.
3.2. Molecular Characterization and Sequence Analysis of the Isolates
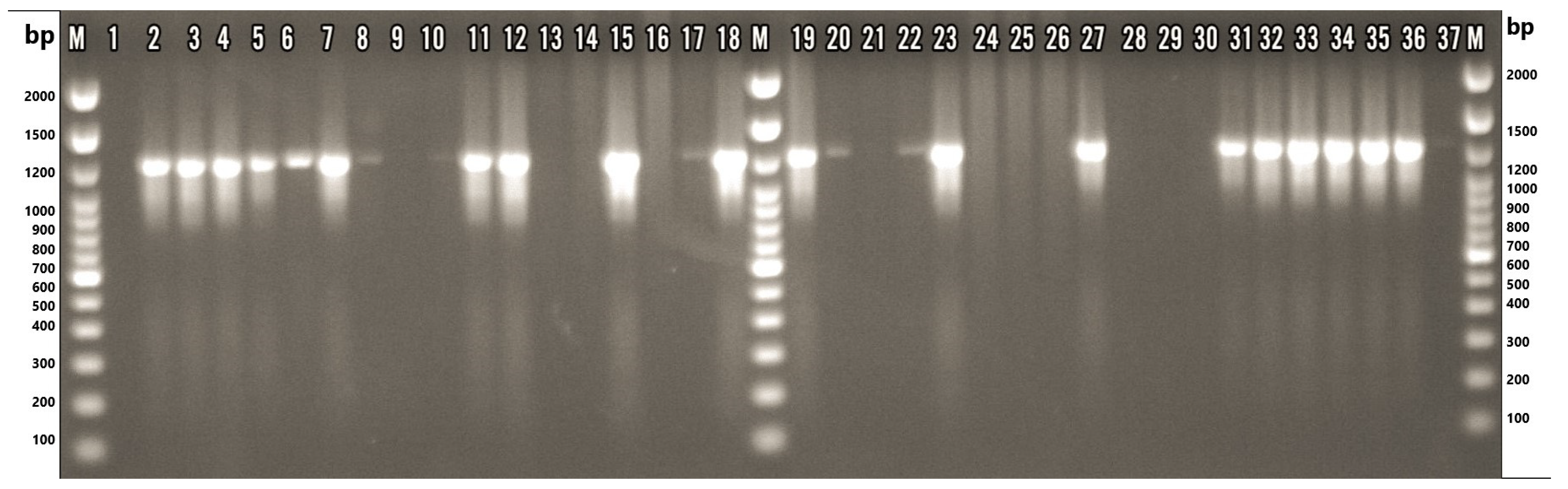
A genus-specific PCR assay targeting the 16S rRNA gene was performed on 33 presumptive Arcobacter isolates. Amplification of the expected 1223 bp fragment was observed in 22 isolates (66.7%), thereby confirming their classification within the Arcobacter genus (Figure 2). Distribution analysis of the confirmed isolates by sample type showed that 13 isolates (39.4%) originated from giblet samples, 10 (30.3%) from the liver, and three (9.1%) from heart tissue. Additionally, six isolates (18.2%) were obtained from fecal samples, and three (9.1%) from cloacal swabs (Table 3).

Figure 2.
Gel electrophoresis image of samples tested with Arcobacter genus-specific PCR. M: TrackIt™ 100 bp DNA Ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA); 1: nuclease-free water; 2: ATCC 49616 (A. butzleri); 3: ATCC 43158 (A. cryaerophilus); 4: ATCC 51400 (A. skirrowii); 5: F45.1; 6: F45.2; 7: F87.1; 8: F87.2; 9: F87.4; 10: F87.3; 11: F88.1; 12: M77.1; 13: M77.2; 14: M77.3; 15: M80.1; 16: M80.2; 17: M80.3; 18: M84.1; 19: M84.2; 20: M84.3; 21: M84.4; 22: M84.5; 23: M86.1; 24: M86.2; 25: M86.3; 26: M86.4; 27: M89.1; 28: M89.2; 29: M89.3; 30: M89.4; 31: M101.1; 32: M101.2; 33: M101.3; 34: M101.4; 35: S84.1; 36: S84.2; 37: S84.3. F: chicken feces; M: chicken meat; S: chicken cloacal swab.
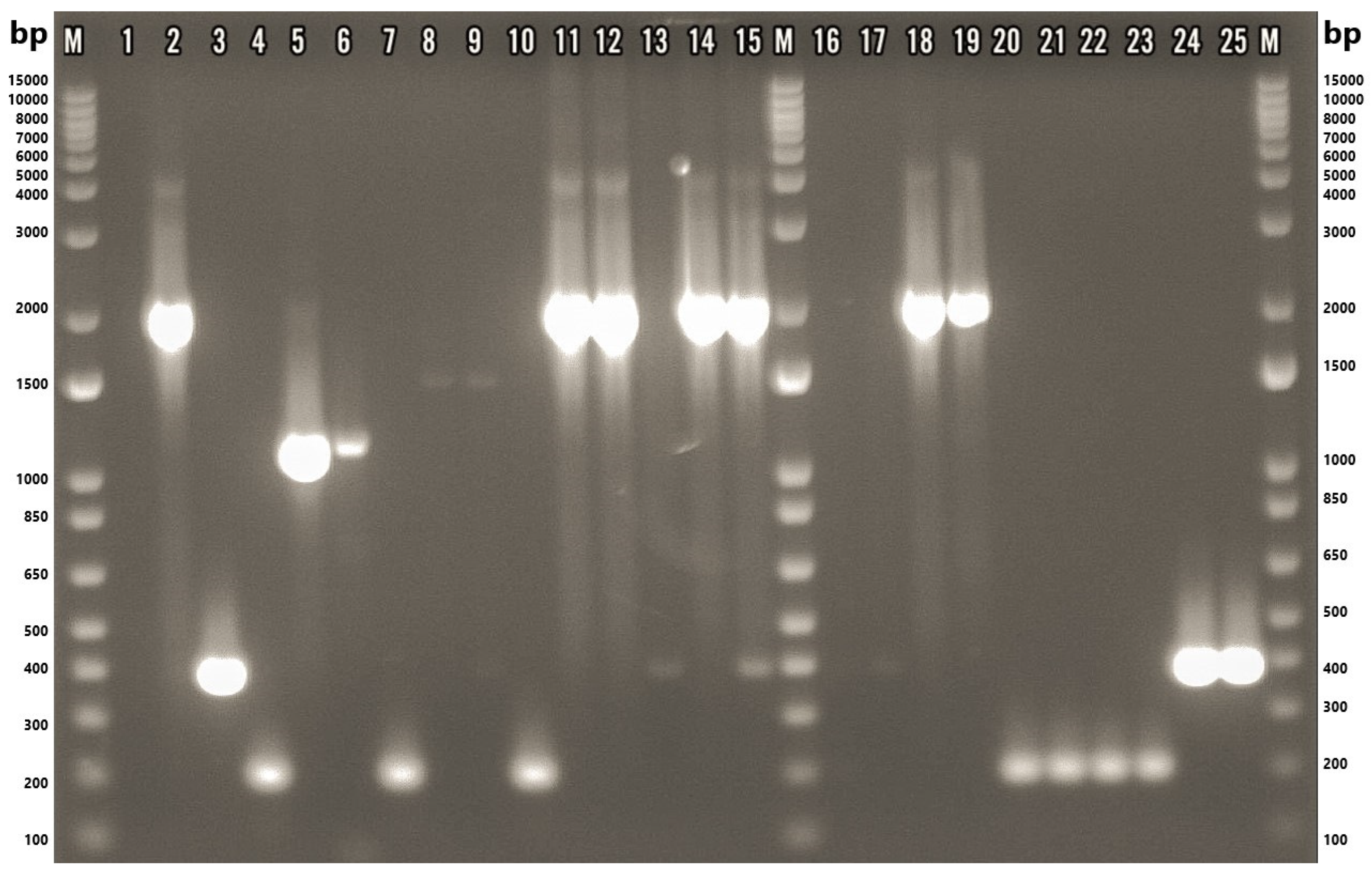
Species-level identification of the confirmed isolates was subsequently conducted using a multiplex PCR assay. Of the 22 Arcobacter-positive isolates, 17 (77.3%) yielded a single species-specific amplicon, indicating mono-species infections. Conversely, two isolates (9.1%) produced multiple bands, suggestive of mixed-species infections. Specifically, isolate F87.3 amplified fragments corresponding to both A. thereius (~1590 bp) and A. cryaerophilus (~395 bp), while isolate M84.2 showed bands indicative of A. butzleri (~2061 bp) and A. cryaerophilus (~395 bp) (Figure 3). Two isolates, M84.3 and S84.3 (9.1%), could not be identified at the species level despite sequencing the 16S rRNA gene fragment using the primer pair ArcoI and ArcoII. The resulting chromatograms exhibited poor resolution, which hindered accurate species-level identification. It should be noted that sample S84.3 was only subjected to a genus-specific PCR yielding an extremely faint band and therefore was not subjected to the multiplex PCR.
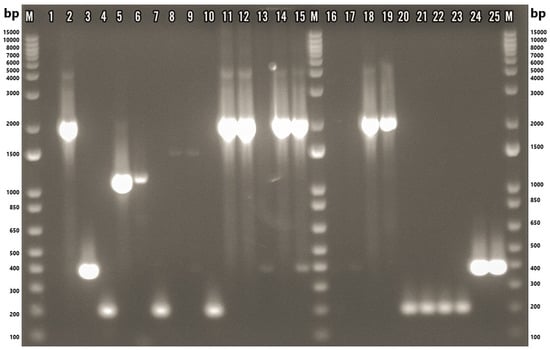
Figure 3.
Gel-electrophoresis image of samples tested via multiplex PCR. M: 1 Kb Plus DNA Ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA); 1: nuclease-free water; 2: ATCC 49616 (A. butzleri); 3: ATCC 43158 (A. cryaerophilus); 4: ATCC 51400 (A. skirrowii); 5: F45.1; 6: F45.2; 7: F87.1; 8: F87.2; 9: F87.3; 10: F88.1; 11: M77.1; 12: M80.1; 13: M80.3; 14: M84.1; 15: M84.2; 16: M84.3; 17: M84.5; 18: M86.1; 19: M89.1; 20: M101.1; 21: M101.2; 22: M101.3; 23: M101.4; 24: S84.1; 25: S84.2. F: chicken feces; M: chicken meat; S: chicken cloacal swab.
It is interesting to note that isolate F87.2 exhibited faint amplification products in both the genus- and species-specific PCR assays, which initially limited the ability to clearly identify the constituent species. Sequencing attempts using species-specific primers were unsuccessful due to the low band intensity. However, subsequent sequencing using genus-specific primers successfully identified Arcobacter cryaerophilus, and the sequence was deposited in GenBank (accession number PP937576). While the multiplex PCR (Figure 3) did not display a clear band corresponding to A. cryaerophilus, the genus-specific PCR (Figure 2) and sequencing results provided confirmatory evidence of its presence. Furthermore, the multiplex PCR revealed a distinct band for A. thereius in the same sample. Taken together, these molecular and sequencing results support that sample F87.2 contained both A. thereius and A. cryaerophilus, and it has, therefore, been classified as a mixed Arcobacter isolate.
Analysis of the species distribution by sample type (Table 3) revealed that giblet samples (liver and heart) harbored three Arcobacter species, with A. butzleri being the most prevalent (15.1%), followed by A. skirrowii (12.1%) and A. cryaerophilus (6.1%). Fecal samples contained four Arcobacter species—A. cibarius, A. cryaerophilus, A. thereius, and A. skirrowii—each at a frequency of 6.1%. The cloacal swab samples exclusively yielded A. skirrowii (6.1%).
Overall, A. skirrowii was the most frequently isolated species (18.2%), predominantly from liver (12.1%) and fecal (6.1%) samples. A. butzleri was detected in 15.1% of samples, exclusively in giblet tissue. A. cryaerophilus was recovered from both giblet and cloacal swab samples (12.1%), while A. cibarius was found only in fecal samples (6.1%).
3.3. Sequencing
Of the 20 isolates that tested positive via the multiplex PCR assay, 18 were sequenced using the primers listed in Table 2. Table 4 illustrates a further sample-wise breakdown of these isolates and the species identified via multiplex PCR and sequencing. The BLASTN (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi; accessed on 23 June 2025) analyses of the amplified gene sequences from these 18 isolates showed between 96 and 100% similarity with the described matches listed in Table 5. These sequences were subsequently deposited into the NCBI GenBank® ([Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; [1982]—[cited 23 June 2024]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/) and were assigned the accession numbers provided in Table 4. Notably, A. thereius amplified from samples F87.2 and F87.3 and A. cryaerophilus amplified from samples M80.3, M84.2, and M84.5 were not confirmed by direct sequencing since the band intensities were very low.

Table 4.
A sample-wise breakdown of the Arcobacter isolates and species identified via the multiplex PCR assay and sequencing.

Table 5.
BLAST analyses of the amplified Arcobacter gene sequences.
3.4. Genetic Characterization of the Arcobacter Species
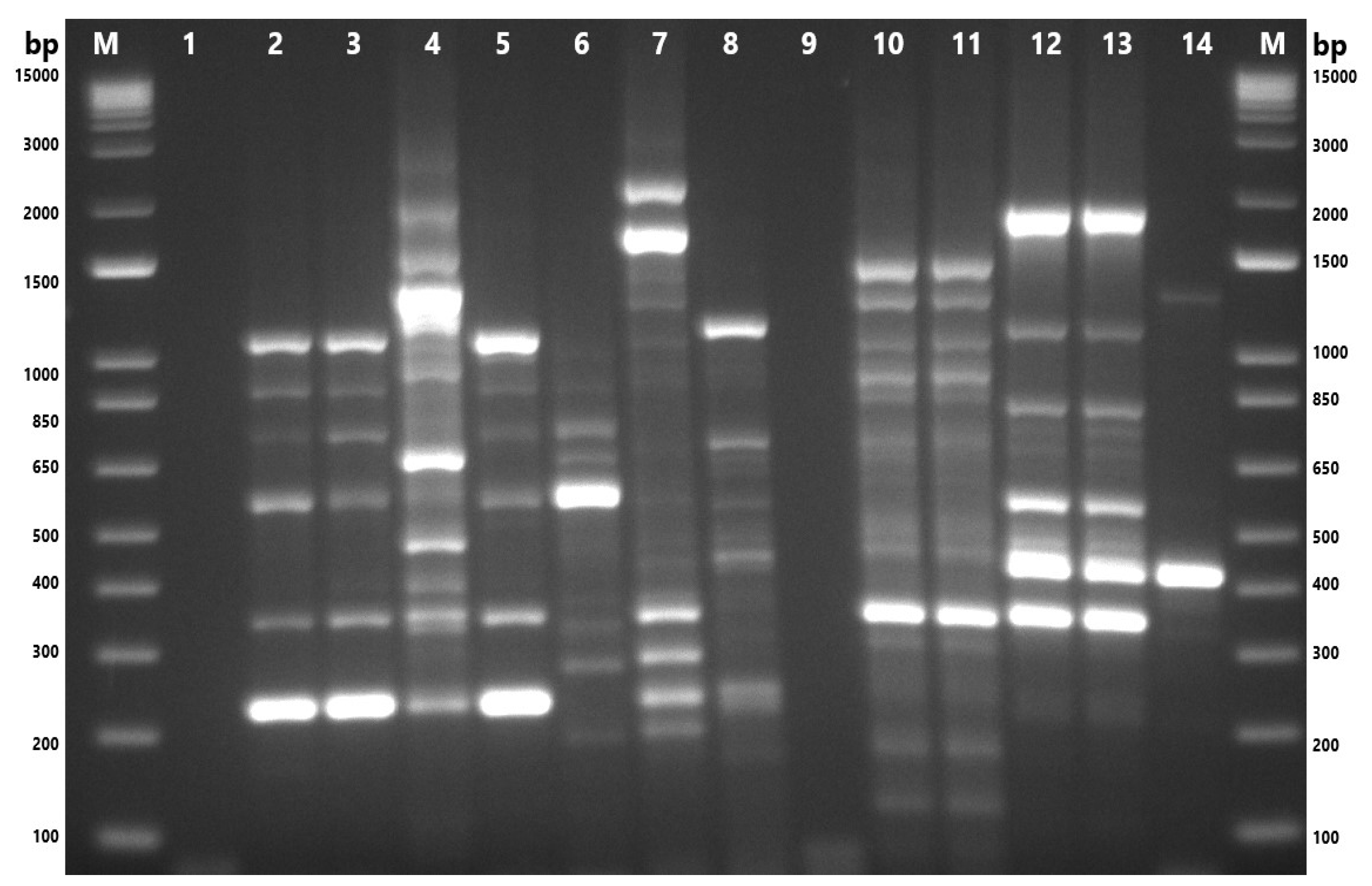
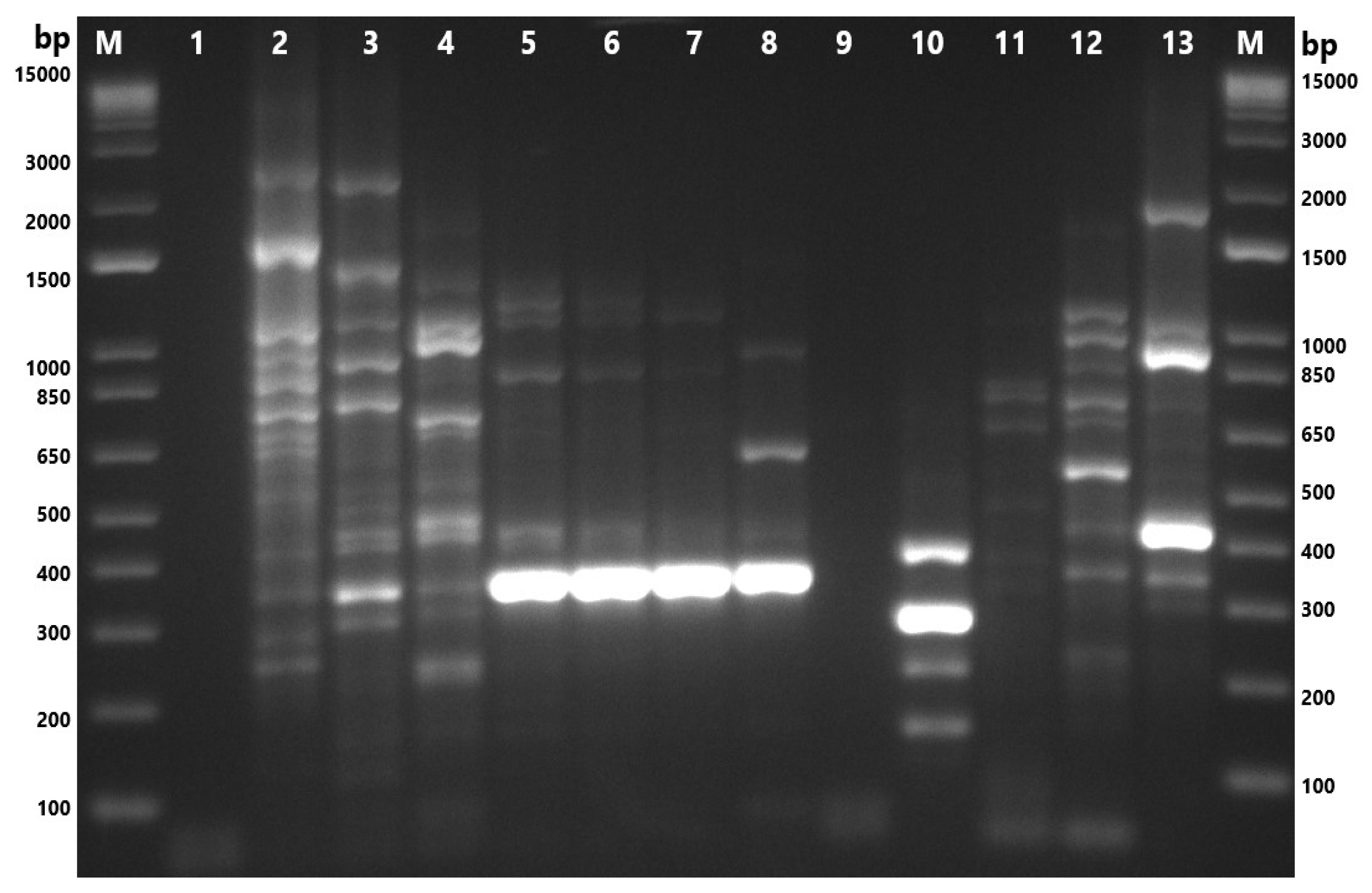
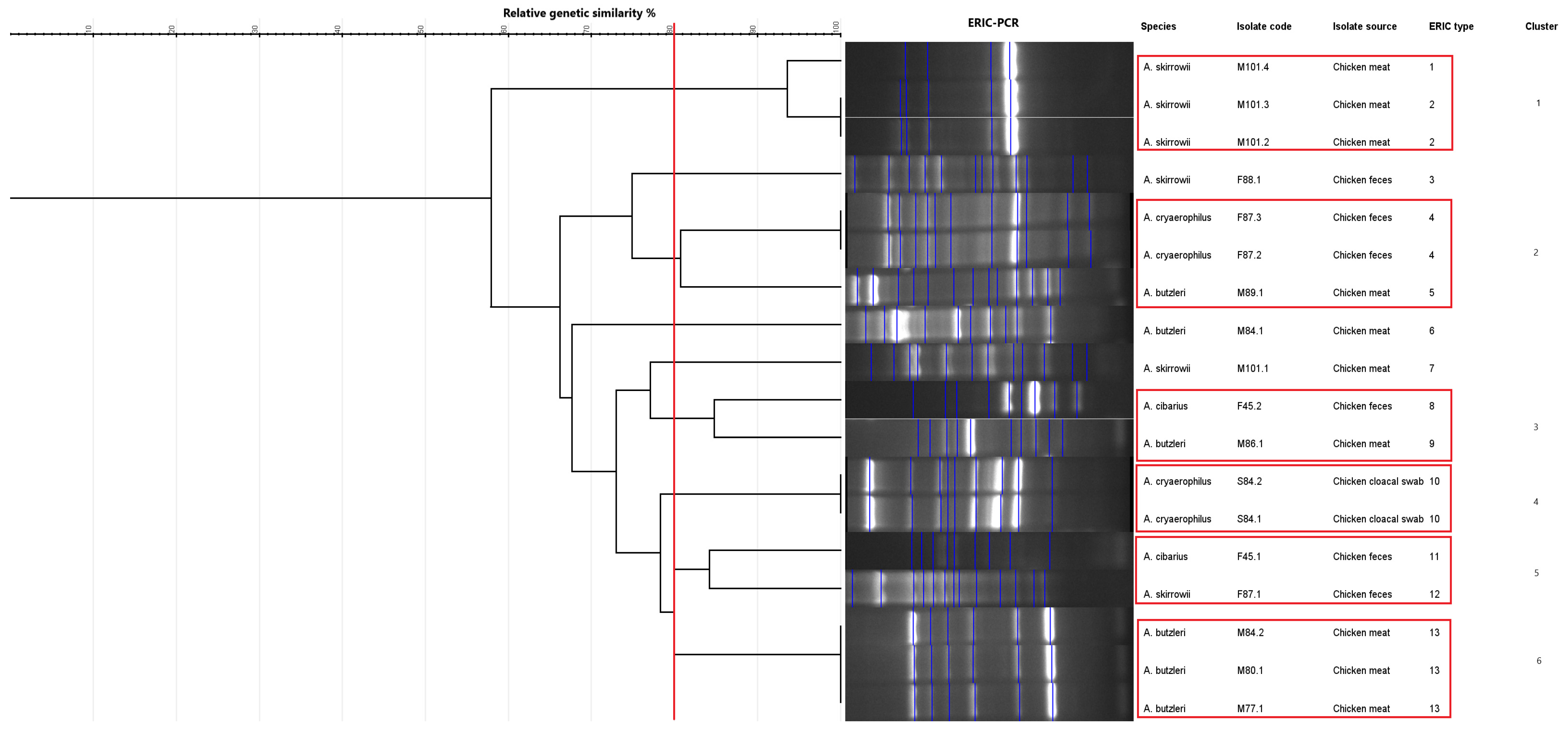
The genetic characterization of the 18 isolates was performed using ERIC-PCR, which generated banding patterns as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. The isolates exhibited 4–13 distinct bands, ranging from ~150 bp to ~2500 bp. These gels and the banding patterns were further analyzed using a software program called GelJ to create a dendrogram, which grouped the isolates into different “ERIC-Types” and “clusters,” providing information on the DNA fingerprints of these isolates (Figure 6). The dendrogram was constructed using the unweighted pair group linkage analysis method (UPGMA), with the cutoff value for clustering the isolates set at 80%. Applying this cutoff value, the isolates were clustered into six groups (each cluster containing 2–3 isolates), resulting in 13 ERIC-Types based on the banding patterns (Figure 6). The discriminatory power, calculated using Simpson’s Index of Diversity, was 0.96.
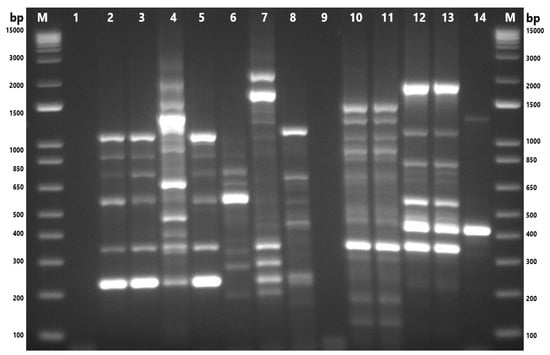
Figure 4.
Gel-electrophoresis analysis of Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus–polymerase chain reaction (ERIC-PCR) fingerprinting of A. butzleri and A. cryaerophilus isolates. M: 1 Kb Plus DNA Ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA); 1and 9: nuclease-free water; 2: M77.1; 3: M80.1; 4: M84.1; 5: M84.2; 6: M86.1; 7: M89.1; 8: ATCC 49616 (A. butzleri); 10: F87.2; 11: 87.3; 12: S84.1; 13: S84.2; 14: ATCC 43158 (A. cryaerophilus). F: chicken feces; M: chicken meat; S: chicken cloacal swab.
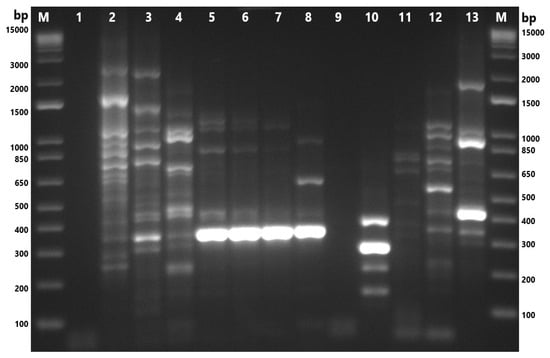
Figure 5.
Gel-electrophoresis analysis of Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus–polymerase chain reaction (ERIC-PCR) fingerprinting of A. skirrowii and A. cibarius isolates. M: 1 Kb Plus DNA Ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA); 1,9: nuclease-free water; 2: F87.1; 3: F88.1; 4: M101.1; 5: M101.2; 6: M101.3; 7: M101.4; 8: ATCC 51400 (A. skirrowii); 10: F45.2; 11: F45.1; 12: RM 4473 (A. butzleri); 13: RM 4598 (A. cryaerophilus). F: chicken feces; M: chicken meat; S: chicken cloacal swab.
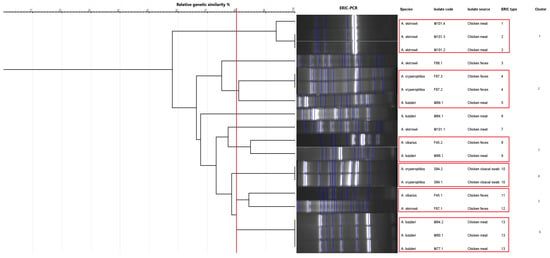
Figure 6.
Dendrogram generated from the Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus–polymerase chain reaction (ERIC-PCR) fingerprinting using the GelJ program. The dendrogram was generated by combining the gels of the two ERIC-PCRs (Figure 4 and Figure 5). The red vertical line represents the 80% similarity threshold used for clustering the isolates. Red frames denote groups of isolates that clustered together based on this cut-off.
4. Discussion
This is the first study conducted in Grenada, West Indies, to isolate and molecularly characterize Arcobacter species from chicken giblets and fecal samples. This study has established the presence of Arcobacter species in chickens from Grenada and emphasized the emerging status of Arcobacter as a foodborne pathogen. Since Arcobacters are closely related to Campylobacters, the latter being well-established as foodborne pathogens, the majority of the culture protocols available utilize enrichment media and temperature conditions that favor the growth of Campylobacters more than Arcobacters [66,67,68]. Although some Arcobacter-specific broths and enrichment media are commercially available, these products do not have high sensitivity for isolating Arcobacters from field samples (like meat and feces), as the growth of Arcobacters is suppressed due to the overgrowth of other species present in samples [69,70]. Therefore, we utilized a commercially available NRJ-chromogenic agar medium that allowed for the easy differentiation of Arcobacters based on the salmon-pink color of these colonies, even when present with other bacterial colonies (Figure 1a). Another advantage of using this chromogenic agar medium is that it does not support the growth of other related bacteria like Campylobacter and Helicobacter due to its composition [56,57,71].
In this study, Arcobacter species were cultured from 21% (9/42) of the birds, and all three sample types tested, the highest being the giblet samples (n = 6), followed by feces (n = 3) and a cloacal swab (n = 1). Five Arcobacter species were isolated from these samples. The six giblet samples harbored A. butzleri, A. cryaerophilus, and A. skirrowii. The three fecal samples harbored A. cibarius, A. cryaerophilus, A. skirrowii, and A. thereius, and one cloacal swab sample harbored A. cryaerophilus only. Arcobacter butzleri was predominantly present in giblet samples only. Arcobacter skirrowii was isolated from giblets and fecal samples. Arcobacter cibarius and A. thereius were only isolated from feces, and A. cryaerophilus was isolated from all three sample types. Of the 33 presumptive Arcobacter isolates tested via generic PCR, 22 (66.7%) belonged to the genus Arcobacter. Of these 22 isolates subjected to Arcobacter species-specific multiplex PCR, 20 isolates (91%) were successfully speciated. Among these, 17 isolates yielded amplification products corresponding to a single Arcobacter species (indicating pure isolates). However, three isolates showed amplification bands corresponding to two different Arcobacter species, indicating the presence of mixed cultures. This could potentially be attributed to manual error during colony selection, such as inadvertently picking more than one colony. Sanger sequencing of 18 multiplex PCR-positive isolates further confirmed the Arcobacter species, which were deposited in the NCBI GenBank database (Table 5).
Research on Arcobacter spp. within the Caribbean region remains limited. To date, only three published studies from Costa Rica—a Central American country geographically and ecologically proximal to the Caribbean—have reported on the isolation of Arcobacter from poultry products and retail meat sources [40,72,73]. These studies documented Arcobacter isolation rates ranging from 20% to 25%, which closely parallels the 21% isolation rate observed in the present study. In the Costa Rican investigations, Arcobacter spp. were recovered from various sample types, including poultry birds, retail meat, and fecal content. Among the isolated species, A. butzleri was the most prevalent, particularly in chicken meat, with detection rates between 30% and 60%. This was followed by A. cryaerophilus (19%) and A. skirrowii (4.3%). Comparative data from other geographic regions, such as Turkey, support the high prevalence of Arcobacter in poultry-derived products. Two studies, conducted in Turkey [74,75], which analyzed edible giblets and other meats from chickens, bovines, and lambs, reported that chicken giblet samples had the highest contamination levels (23.3% and 62%). In both studies, A. butzleri was the most frequently isolated species, with detection frequencies of 60.7% and 67.7%. Similarly, an Egyptian study [76] that focused on edible chicken giblets (livers, gizzards, and fillets) identified liver samples as having the highest contamination rate (30%), followed by fillets (22.5%) and gizzards (20%). In concordance with these findings, our study revealed that giblet samples exhibited the highest Arcobacter isolation rate (39.4%) compared to fecal samples (18.2%) and cloacal swabs (9.1%). Across all sample types, the overall isolation frequencies for A. butzleri, A. cryaerophilus, and A. skirrowii (both individually and in combination) were equal at 18.2%, followed by A. cibarius and A. thereius (6.1%). Notably, A. butzleri was isolated exclusively from giblet samples, at the highest individual frequency (15.1%), and was absent from fecal and cloacal swab samples. The observed differences in Arcobacter isolation rates across studies may be attributed to several factors, including geographic variability, seasonal influences, hygiene practices during animal product processing, sample size disparities, and methodological differences in bacterial isolation and detection [55,77,78].
Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus–polymerase chain reaction-based genotyping resulted in bands ranging between 4 and 13 (~150 bp to ~2500 bp); all 18 isolates were typable (100%), and a total of 13 ERIC-types and six clusters were observed. It was observed that isolates originating from the same bird or the same sample type clustered together (Figure 6). The ERIC-PCR discriminatory power, calculated using Simpson’s Index of Diversity, was 0.96, indicating ERIC-PCR to be a highly desirable genotyping method since discriminatory powers above 0.90 are considered highly significant [65].
Research shows that the intestinal tracts of live chickens sporadically harbor Arcobacter species. As an example, Schonknecht et al. (2020) [47] analyzed intestinal content from 157 samples collected at four stages of poultry slaughter. The authors (47) found that Arcobacter spp. are rarely isolated in the intestinal contents after bleeding (6.2%) and have not been isolated after scalding. However, detection increased significantly after defeathering (62%), peaking post-evisceration (90.6%). These findings indicate that the bacteria are not prominent colonizers of the chicken gut during poultry processing. Schonknecht et al. (2020) [47] also reported that the plucking fingers used for defeathering had high levels of Arcobacter contamination, suggesting that equipment surfaces serve as reservoirs for Arcobacter spp., leading to the cross-contamination of carcasses during processing [79]. These findings are supported by a more recent study [80]. Botta et al. (2024) [80] found a 31% prevalence of Arcobacter spp. in a poultry abattoir plucking sector, even after cleaning and sanitizing procedures. The study highlighted the persistence of Arcobacter spp. in specific environmental niches within the slaughterhouse, emphasizing that the lack of adequate sanitation and disinfection of slaughter equipment presents a risk of contamination of meat at the poultry plant. Although the present study did not focus on determining the primary sources of contamination in the analyzed sample types, the results support that Arcobacter colonizes the chicken gut occasionally and that the meat samples become contaminated during the slaughter process, most likely due to the environmental contamination of the equipment used for slaughter purposes. This “farm-to-fork” contamination route is further exacerbated by the physiological traits of Arcobacter, such as its resistance to cold temperatures [81] and aerotolerance, which can increase the probability of final contamination and persistence on broiler carcasses at the retail level [82].
From a public health perspective, the consumption of undercooked or raw poultry products, including their byproducts, presents a significant risk for foodborne illness from contaminated poultry meat. Poultry and related products have been identified as reservoirs for enteropathogenic microorganisms capable of causing gastrointestinal diseases in humans, particularly when proper cooking and hygienic handling practices are not followed [83,84]. Among these pathogens, Arcobacter butzleri, A. cryaerophilus, and A. skirrowii have been associated with human gastrointestinal disorders, such as diarrhea, and in more severe cases, bacteremia [15,28,85,86,87,88]. These species have been isolated from various food sources, including poultry giblets, underscoring their zoonotic potential [74,75]. In light of these findings, it is critical to inform consumers about the health risks associated with the consumption of contaminated chicken products, including the giblets. Preventive strategies should emphasize stringent hygienic handling and thorough cooking of these products to inactivate pathogenic organisms. Public health campaigns should prioritize education and awareness, particularly in regions where the consumption of giblets is common, to reduce the incidence of Arcobacter-associated infections. The documented presence of A. butzleri, A. cryaerophilus, and A. skirrowii in chicken giblet samples represents a noteworthy public health concern, especially considering the widespread use of giblets in Caribbean cuisine [89].
5. Conclusions
The findings of this study establish the presence of five Arcobacter spp. (A. butzleri, A. cryaerophilus, A. cibarius, A. skirrowii, and A. thereius) in chicken meat and feces from the Caribbean region of Grenada, West Indies. The successful isolation and genetic characterization of five Arcobacter species from broiler chickens in Grenada marks a significant advancement in understanding the presence and diversity of this emerging zoonotic pathogen in the region. The prevalence of Arcobacter in meat samples underscores the potential for foodborne transmission, emphasizing the need for improved biosecurity measures during poultry processing. Given the documented zoonotic potential of these species, particularly A. butzleri and A. cryaerophilus, this study highlights an urgent public health concern. Routine surveillance and strict hygienic practices are imperative to mitigate the risk of transmission to humans and to ensure food safety within both local and international markets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.S.; methodology, J.P.C. and B.S.; validation, J.P.C. and B.S.; investigation, J.P.C. and B.S.; resources, B.S.; data curation, J.P.C. and B.S.; writing—original draft preparation, B.S.; writing—review and editing, J.P.C., A.A., A.C., R.R. and B.S.; supervision, B.S.; project administration, B.S.; funding acquisition, J.P.C., A.A., A.C., R.R. and B.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by St. George’s University’s Graduate School Program (GSP) under the Small Research Grant Initiative (SRGI) (Application No. GSP\SRGI\21003) grant awarded to J.P.C., A.A., A.C., R.R., and B.S.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of St. George’s University (protocol #20007-R dated 6th October 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all the slaughterhouse owners of the animal subjects used in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The new nucleic acid sequences have been deposited in the database of GenBank. Accession numbers provided by GenBank ([Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; [1982]—[cited 23 June 2024]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/) have been included in the manuscript in Table 5.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge St. George’s University, Grenada, West Indies, for funding the project. We are grateful to Derek Thomas, Poultry and VEP Officer, Ministry of Agriculture, for his assistance in sample collection. We also thank Paul Nguyen for his guidance and for sharing his expertise on Arcobacter. During the preparation of this study, Chat GPT-3.5 was used to rewrite some text. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the study’s design; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ATCC | American-Type Culture Collection |
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| ERIC | Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus |
| gDNA | Genomic Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| HB | Houf broth |
| ICMSF | International Commission on Microbiological Specifications for Foods |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| NRJ-M | Nguyen–Restaino–Juárez-arcobacter chromogenic agar media plates |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| SGU | Saint George’s University |
| UPGAM | Unweighted pair group linkage analysis method |
References
- On, S.L.W.; Miller, W.G.; Biggs, P.J.; Cornelius, A.J.; Vandamme, P. Aliarcobacter, Halarcobacter, Malaciobacter, Pseudarcobacter and Poseidonibacter are later synonyms of Arcobacter: Transfer of Poseidonibacter parvus, Poseidonibacter antarcticus, ‘Halarcobacter arenosus’, and ‘Aliarcobacter vitoriensis’ to Arcobacter as Arcobacter parvus comb. nov., Arcobacter antarcticus comb. nov., Arcobacter arenosus comb. nov. and Arcobacter vitoriensis comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, W.A.; Neill, S.D.; O’Brien, J.J.; Ferguson, H.W.; Hanna, J. Isolation of Spirillum/Vibrio-like organisms from bovine fetuses. Vet. Rec. 1977, 100, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, P.; Falsen, E.; Rossau, R.; Hoste, B.; Segers, P.; Tytgat, R.; De Ley, J. Revision of Campylobacter, Helicobacter, and Wolinella taxonomy: Emendation of generic descriptions and proposal of Arcobacter gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1991, 41, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, P.; Vancanneyt, M.; Pot, B.; Mels, L.; Hoste, B.; Dewettinck, D.; Vlaes, L.; Borre, C.V.D.; Higgins, R.; Hommez, J.; et al. Polyphasic Taxonomic Study of the Emended Genus Arcobacter with Arcobacter butzleri comb. nov. and Arcobacter skirrowii sp. nov., an Aerotolerant Bacterium Isolated from Veterinary Specimens. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1992, 42, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- On, S.L.W.; Miller, W.G.; Houf, K.; Fox, J.G.; Vandamme, P. Minimal standards for describing new species belonging to the families Campylobacteraceae and Helicobacteraceae: Campylobacter, Arcobacter, Helicobacter and Wolinella spp. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 5296–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cataluña, A.; Salas-Massó, N.; Diéguez, A.L.; Balboa, S.; Lema, A.; Romalde, J.L.; Figueras, M.J. Corrigendum (2): Revisiting the Taxonomy of the Genus Arcobacter: Getting Order From the Chaos. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, S.L.W.; Miller, W.G.; Biggs, P.J.; Cornelius, A.J.; Vandamme, P. A critical rebuttal of the proposed division of the genus Arcobacter into six genera using comparative genomic, phylogenetic, and phenotypic criteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzanca, D.; Kerkhof, P.-J.; Alessandria, V.; Rantsiou, K.; Houf, K. Arcobacteraceae comparative genome analysis demonstrates genome heterogeneity and reduction in species isolated from animals and associated with human illness. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, S.L.W. International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes Subcommittee on the Taxonomy of Campylobacter and related bacteria: Minutes of the meetings, 21st August and 10th September 2019. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwu, C.D.; Ekundayo, T.C.; Okoh, A.I. A Systematic Analysis of Research on Arcobacter: Public Health Implications from a Food–Environment Interphase Perspective. Foods 2021, 10, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, O.; Dediste, A.; Houf, K.; Ibekwem, S.; Souayah, H.; Cadranel, S.; Douat, N.; Zissis, G.; Butzler, J.-P.; Vandamme, P. Arcobacter species in humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1863–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samie, A.; Obi, C.L.; Barrett, L.J.; Powell, S.M.; Guerrant, R.L. Prevalence of Campylobacter species, Helicobacter pylori and Arcobacter species in stool samples from the Venda region, Limpopo, South Africa: Studies using molecular diagnostic methods. J. Infect. 2007, 54, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappi, V.; Archer, J.R.; Cebelinski, E.; Leano, F.; Besser, J.M.; Klos, R.F.; Medus, C.; Smith, K.E.; Fitzgerald, C.; Davis, J.P. An outbreak of foodborne illness among attendees of a wedding reception in Wisconsin likely caused by Arcobacter butzleri. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kietsiri, P.; Muangnapoh, C.; Lurchachaiwong, W.; Lertsethtakarn, P.; Bodhidatta, L.; Suthienkul, O.; Waters, N.C.; Demons, S.T.; Vesely, B.A. Characterization of Arcobacter spp. Isolated from human diarrheal, non-diarrheal and food samples in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouzet-Mauléon, V.; Labadi, L.; Bouges, N.; Ménard, A.; Mégraud, F. Arcobacter butzleri: Underestimated enteropathogen. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, P.; Pugina, P.; Benzi, G.; Van Etterijck, R.; Vlaes, L.; Kersters, K.; Butzler, J.P.; Lior, H.; Lauwers, S. Outbreak of recurrent abdominal cramps associated with Arcobacter butzleri in an Italian school. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 2335–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkin, R.B. Microbiological Testing in Food Safety Management; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Burnens, A.; Schaad, U.; Nicolet, J. Isolation of Arcobacter butzleri from a girl with gastroenteritis on Yersinia selective agar. Med. Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 1, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Lerner, J.; Brumberger, V.; Preac-Mursic, V. Severe diarrhea associated with Arcobacter butzleri. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1994, 13, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, S.L.W.; Stacey, A.; Smyth, J. Isolation of Arcobacter butzleri from a neonate with bacteraemia. J. Infect. 1995, 31, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J.; Ko, W.C.; Huang, A.H.; Chen, H.M.; Jin, Y.T.; Wu, J.J. Arcobacter butzleri bacteremia in a patient with liver cirrhosis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2000, 99, 166–169. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Teng, J.L.L.; Leung, K.W.; Yuen, K.Y. Identification by 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing of Arcobacter butzleri bacteraemia in a patient with acute gangrenous appendicitis. Mol. Pathol. 2002, 55, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauche, J.D.L.C.; Dupont, H.L. New Developments in Traveler’s Diarrhea. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.-D.; DuPont, H.L.; Brown, E.L.; Nandy, R.K.; Ramamurthy, T.; Sinha, A.; Ghosh, S.; Guin, S.; Gurleen, K.; Rodrigues, S.; et al. Microbial Etiology of Travelers’ Diarrhea in Mexico, Guatemala, and India: Importance of Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis and Arcobacter Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1417–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vélez, R.; Lebens, M.; Bundy, L.; Barriga, J.; Steffen, R. Bacterial travellers’ diarrhoea: A narrative review of literature published over the past 10 years. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 47, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesley, I.V.; Miller, W.G. Arcobacter: An Opportunistic Human Food-Borne Pathogen? In Emerging Infections; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramees, T.P.; Dhama, K.; Karthik, K.; Rathore, R.S.; Kumar, A.; Saminathan, M.; Tiwari, R.; Malik, Y.S.; Singh, R.K. Arcobacter: An emerging food-borne zoonotic pathogen, its public health concerns and advances in diagnosis and control—A comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2017, 37, 136–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueras, M.J.; Levican, A.; Pujol, I.; Ballester, F.; Quilez, M.J.R.; Gomez-Bertomeu, F. A severe case of persistent diarrhoea associated with Arcobacter cryaerophilus but attributed to Campylobacter sp. and a review of the clinical incidence of Arcobacter spp. New Microbes New Infect. 2014, 2, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapped: Meat Consumption by Country and Type. Available online: https://www.visualcapitalist.com/cp/mapped-meat-consumption-by-country-and-type/#:~:text=The%20world’s%20largest%20consumers%20of,each%20type%20of%20meat%20below (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Amadi, V.A.; Hariharan, H.; Tiwari, K.; Matthew-Belmar, V.; Haan, J.S.; Singh, A.; Mor, S.K.; Goyal, S.M.; Sharma, R. Molecular Typing of Campylobacter Species Isolated from Healthy Indigenous Chickens in Grenada. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2018, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.M.M.; de Almeida, A.M.; Willingham, A.L. An overview of food safety and bacterial foodborne zoonoses in food production animals in the Caribbean region. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Georges, K.; Rahaman, S.; Abdela, W.; Adesiyun, A.A. Prevalence and serotypes of Salmonella spp. on chickens sold at retail outlets in Trinidad. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Georges, K.; Rahaman, S.; Abebe, W.; Adesiyun, A.A. Characterization of Salmonella Isolates Recovered from Stages of the Processing Lines at Four Broiler Processing Plants in Trinidad and Tobago. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.S.; Miller, W.G.; Behringer, M.; Hariharan, H.; Matthew, V.; Oyarzabal, O.A. DNA identification and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from caecal samples of chickens in Grenada. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.; Bianchini, A.; Chaves, B.D. A Review of Salmonella Prevalence and Salmonellosis Burden in the Caribbean Community Member Countries. Food Prot. Trends 2022, 42, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, S.; Adesiyun, A.; Asgarali, Z.; Swanston, W. Occurrence of Selected Foodborne Pathogens on Poultry and Poultry Giblets from Small Retail Processing Operations in Trinidad. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, S.; Adesiyun, A.; Asgarali, Z.; Swanston, W. Antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter spp. isolated from broilers in small poultry processing operations in Trinidad. Food Control. 2007, 18, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopnarine, R.; Stone, D.; Hariharan, H.; DeAllie, C.; Hand, C.; Hegamin-Younger, C.; Matthew, V.; Sharma, R. Fluoroquinolone and metronidazole resistance of Campylobacter spp from broiler chickens and antimicrobial use on farms in Grenada, West Indies. J. Anim. Res. 2012, 2, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Workman, S.N.; Mathison, G.E.; Lavoie, M.C. An investigation of sources of Campylobacter in a poultry production and packing operation in Barbados. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 121, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, K.; Angulo, I.; Zumbado, L.; Redondo-Solano, M.; Castro, E.; Arias, M.L. Isolation and Identification of Arcobacter Species from Costa Rican Poultry Production and Retail Sources. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jribi, H.; Sellami, H.; Amor, S.B.; Ducournau, A.; SifrÉ, E.; Benejat, L.; MÉgraud, F.; Gdoura, R. Occurrence and Antibiotic Resistance of Arcobacter Species Isolates from Poultry in Tunisia. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 2080–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodamoradi, S.; Abiri, R. The incidence and antimicrobial resistance of Arcobacter species in animal and poultry meat samples at slaughterhouses in Iran. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2020, 12, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, E.; Hotzel, H.; Ahlers, C.; Hänel, I.; Tomaso, H.; Abdel-Glil, M.Y. Genomic Analysis and Antimicrobial Resistance of Aliarcobacter cryaerophilus Strains From German Water Poultry. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourbakhsh, S.A.; Rahimi, E. The occurrence of some foodborne pathogens recovered from poultry meat in Shahrekord, Iran. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2023, 10, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, T.; Hara-Kudo, Y. Presence and quantification of pathogenic Arcobacter and Campylobacter species in retail meats available in Japan. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 73, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.G.X.; Gomes, V.T.d.M.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Moreno, L.Z.; Moreno, A.M.; Knöbl, T. Genotypic Characterization of Arcobacter spp. Isolated from Chicken Meat in Brazil. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönknecht, A.; Alter, T.; Gölz, G. Detection of Arcobacter species in different intestinal compartments of broiler chicken during slaughter and processing. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Thille, K.; Belmar, V.M.; Thomas, R.N.; Sharma, R.N. Molecular detection and genetic characterization of Arcobacter butzleri isolated from red-footed pet tortoises suspected for Campylobacter spp. from Grenada, West Indies. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switaj, T.L.; Winter, K.J.; Christensen, S.R. Diagnosis and Management of Foodborne Illness. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collado, L.; Figueras, M.J. Taxonomy, epidemiology, and clinical relevance of the genus Arcobacter. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molva, C.; Atabay, H.I. Prevalence and Diversity of Arcobacter spp. in Retail Chicken Meat in Turkey. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 7, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, A.M.D.; Sciortino, S.; Cardamone, C.; Ciravolo, C.; Napoli, C.; Alio, V.; Arculeo, P.; Oliveri, G.; Costa, A. Detection of Arcobacter spp. in food products collected from Sicilia region: A preliminary study. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2018, 7, 7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, L.; Fegan, N.; Vanderlinde, P. Isolation and characterisation of Arcobacter butzleri from meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 91, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Saleha, A.; Zunita, Z.; Murugaiyah, M. Arcobacter–An emerging threat to animals and animal origin food products? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houf, K.; Devriese, L.A.; De Zutter, L.; Van Hoof, J.; Vandamme, P. Development of a new protocol for the isolation and quantification of Arcobacter species from poultry products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 71, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Juárez, O.; Restaino, L. A New Method for Detection of Arcobacter butzleri, Arcobacter cryaerophilus, and Arcobacter skirrowii Using a Novel Chromogenic Agar. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Tuz, K.; Restaino, L.; Juárez, O. NRJ Media as the Gold-Standard Arcobacter-Specific Detection System: Applications in Poultry Testing. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 903079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, K.M.; Wesley, I.V. Identification of Arcobacter isolates by PCR. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 23, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douidah, L.; De Zutter, L.; Vandamme, P.; Houf, K. Identification of five human and mammal associated Arcobacter species by a novel multiplex-PCR assay. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 80, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houf, K.; Tutenel, A.; De Zutter, L.; Van Hoof, J.; Vandamme, P. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for the simultaneous detection and identification of Arcobacter butzleri, Arcobacter cryaerophilus and Arcobacter skirrowii. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 193, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versalovic, J.; Koeuth, T.; Lupski, R. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to finerpriting of bacterial enomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 6823–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houf, K.; De Zutter, L.; Van Hoof, J.; Vandamme, P. Assessment of the genetic diversity among arcobacters isolated from poultry products by using two PCR-based typing methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras, J.; Domínguez, C.; Mata, E.; Pascual, V.; Lozano, C.; Torres, C.; Zarazaga, M. GelJ--a tool for analyzing DNA fingerprint gel images. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P.R.; Gaston, M.A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: An application of Simpson’s index of diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 2465–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabay, H.I.; Corry, J.E.L. Evaluation of a new arcobacter enrichment medium and comparison with two media developed for enrichment of Campylobacter spp. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 41, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corry, J.E.L.; Atabay, H.I. Culture Media for the Isolation of Campylobacters, Helicobacters and Arcobacters. In Handbook of Culture Media for Food and Water Microbiology; Corry, J.E.L., Curtis, G.D.W., Baird, R.M., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F.U.; Andree, K.B.; Salas-Massó, N.; Fernandez-Tejedor, M.; Sanjuan, A.; Figueras, M.J.; Furones, M.D. Improved culture enrichment broth for isolation of Arcobacter-like species from the marine environment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, E.; Tilburg, J.J.; Woodward, D.L.; Lior, H.; Johnson, W.M. A selective medium for the isolation of Arcobacter from meats. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 23, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merga, J.Y.; Leatherbarrow, A.J.H.; Winstanley, C.; Bennett, M.; Hart, C.A.; Miller, W.G.; Williams, N.J. Comparison of Arcobacter Isolation Methods, and Diversity of Arcobacter spp. in Cheshire, United Kingdom. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Tuz, K.; Juárez, O.; Restaino, L. Comparison of Two Culture-Based Detection Systems for the Isolation of Arcobacter butzleri, Arcobacter cryaerophilus, and Arcobacter skirrowii in Raw Ground Poultry. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogantes, E.V.; Fallas-Padilla, K.L.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C.E.; Jaramillo, H.F.; Echandi, M.L.A. Zoonotic species of the genus Arcobacter in poultry from different regions of Costa Rica. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallas-Padilla, K.L.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C.E.; Jaramillo, H.F.; Echandi, M.L.A. Arcobacter: Comparison of isolation methods, diversity, and potential pathogenic factors in commercially retailed chicken breast meat from Costa Rica. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilmen, S.; Vural, A.; Erkan, M.E.; Yildirim, I.; Guran, H. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Arcobacter spp. isolates from meats, meat products, and giblets. Acta Vet. Eurasia 2022, 48, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, C.; Hizlisoy, H.; Onmaz, N.E.; Gundog, D.A.; Barel, M.; Disli, H.B.; Dishan, A.; Al, S.; Yildirim, Y.; Gonulalan, Z. Profile of Aliarcobacter spp. from edible giblets: Genetic diversity, antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 386, 110047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL-toukhy, E.I.; Dalia, A.S.; Samar, M.M.M. Molecular investigation of Arcobacter species isolated from some poultry products in Menofia governorate. Anim. Health Res. J. 2019, 7, 364–372. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, S.; Queiroz, J.A.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.C. Insights in the pathogenesis and resistance of Arcobacter: A review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.T.; Lipman, L.J.; Gaastra, W. Arcobacter, what is known and unknown about a potential foodborne zoonotic agent! Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 115, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkemik, Y.; Güner, A. Determination of the presence and antimicrobial resistance of Arcobacter species in broiler carcasses at different stages of slaughter line. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 3461–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, C.; Buzzanca, D.; Chiarini, E.; Chiesa, F.; Rubiola, S.; Ferrocino, I.; Fontanella, E.; Rantsiou, K.; Houf, K.; Alessandria, V. Microbial contamination pathways in a poultry abattoir provided clues on the distribution and persistence of Arcobacter spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0029624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldgaard, J.; Jørgensen, K.; Ingmer, H. Growth and survival at chiller temperatures of Arcobacter butzleri. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 131, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Joossens, M.; Houf, K. Analyses of the Bacterial Contamination on Belgian Broiler Carcasses at Retail Level. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 539540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouger, A.; Tresse, O.; Zagorec, M. Bacterial Contaminants of Poultry Meat: Sources, Species, and Dynamics. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves-Tenório, A.; Silva, B.N.; Rodrigues, V.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, U. Prevalence of Pathogens in Poultry Meat: A Meta-Analysis of European Published Surveys. Foods 2018, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayman, T.; Abay, S.; Hizlisoy, H.; Atabay, H.I.; Diker, K.S.; Aydin, F. Emerging pathogen Arcobacter spp. in acute gastroenteritis: Molecular identification, antibiotic susceptibilities and genotyping of the isolated arcobacters. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wybo, I.; Breynaert, J.; Lauwers, S.; Lindenburg, F.; Houf, K. Isolation of Arcobacter skirrowii from a Patient with Chronic Diarrhea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1851–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soelberg, K.K.; Danielsen, T.K.L.; Martin-Iguacel, R.; Justesen, U.S. Arcobacter butzleri is an opportunistic pathogen: Recurrent bacteraemia in an immunocompromised patient without diarrhoea. Access Microbiol. 2020, 2, acmi000145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyayesh, H.; Rahimi, E.; Shakerian, A.; Khamesipour, F. Arcobacter species isolated from human stool samples, animal products, ready-to-eat salad mixes, and ambient water: Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility, and virulence gene profiles. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, N.; Reyes, C.; Fernandez, Y.; Azevedo, V.; Francisco, L.E.D.; Ramos, R.T.; Maroto-Martín, L.O.; Franco, E.F. Bacterial Foodborne Diseases in Central America and the Caribbean: A Systematic Review. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).