The Improvement Effects of Intercropping Systems on Saline-Alkali Soils and Their Impact on Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment Site
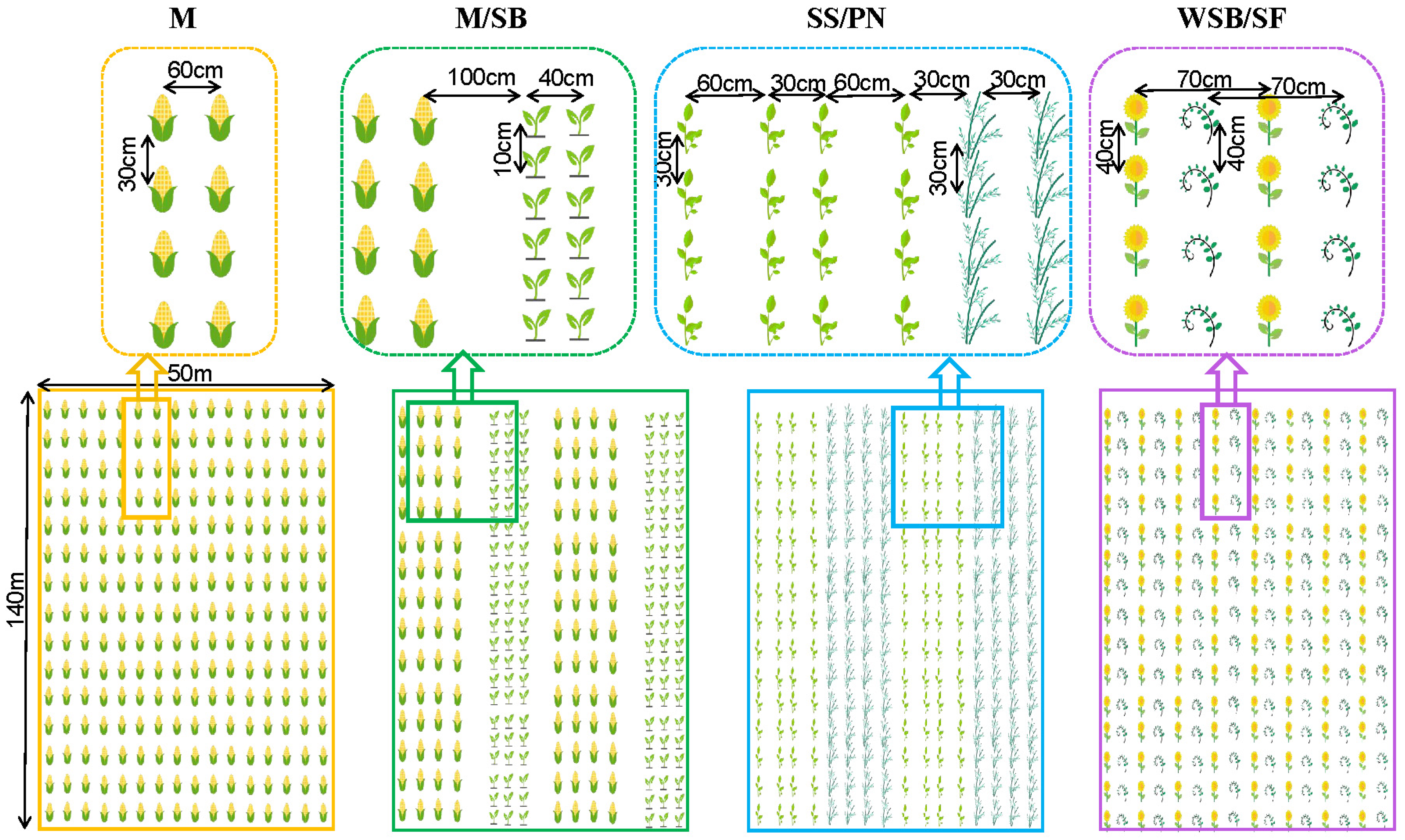
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sampling and Soil Chemical Property Analysis
2.4. Analysis Methods for Soil Microbial Community Structure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
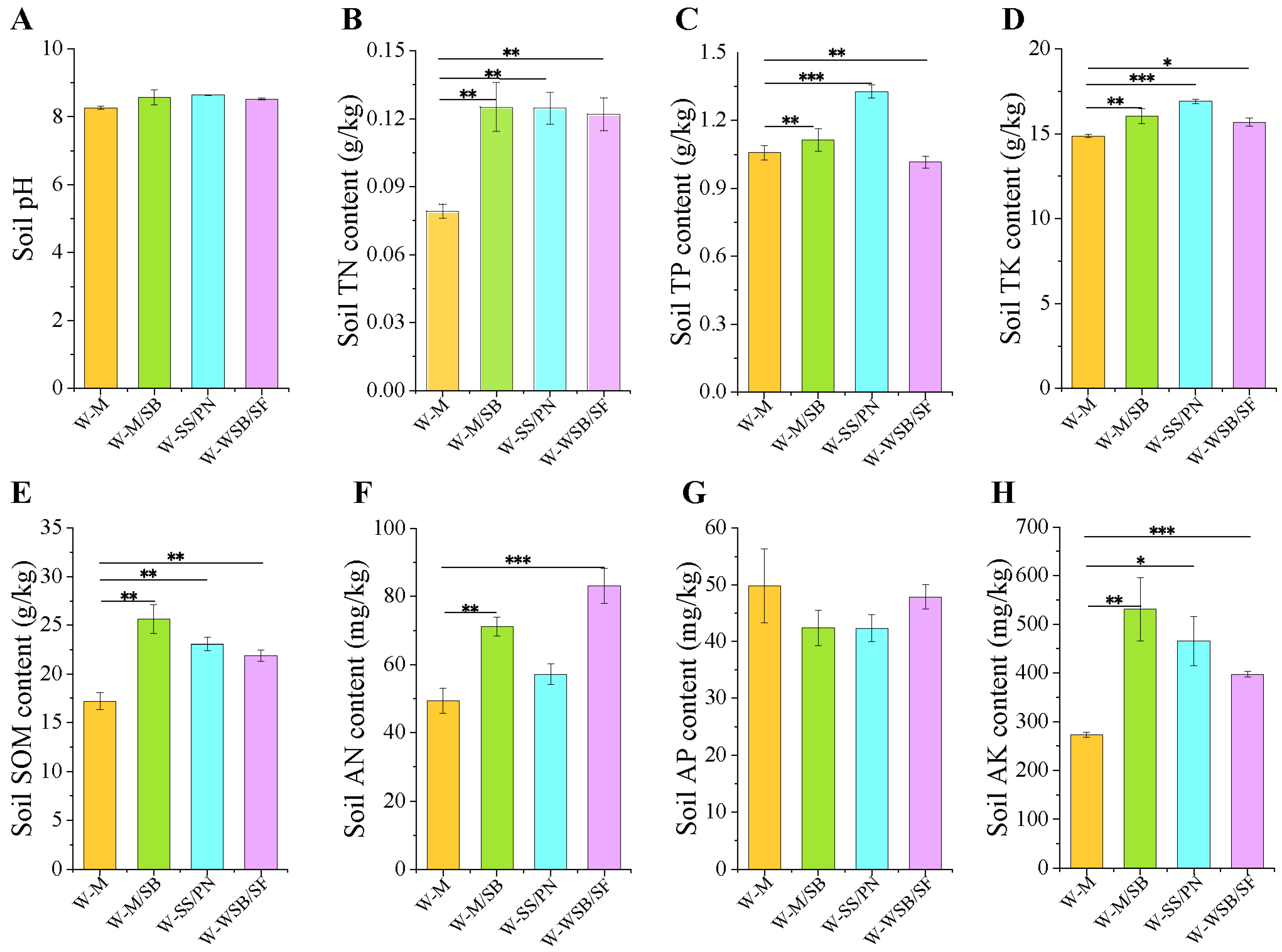
3.1. The Impact of Intercropping Systems on Soil Chemical Properties
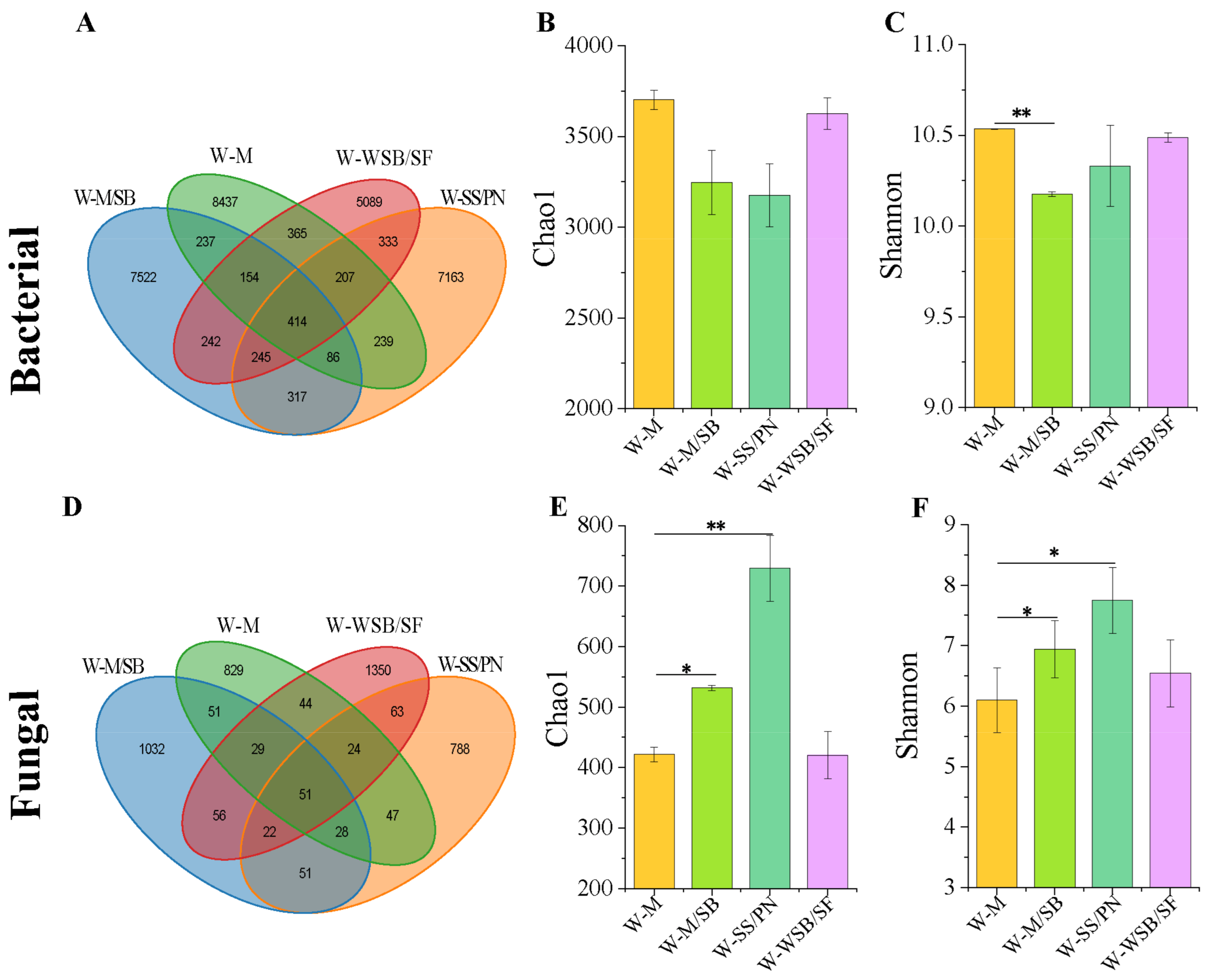
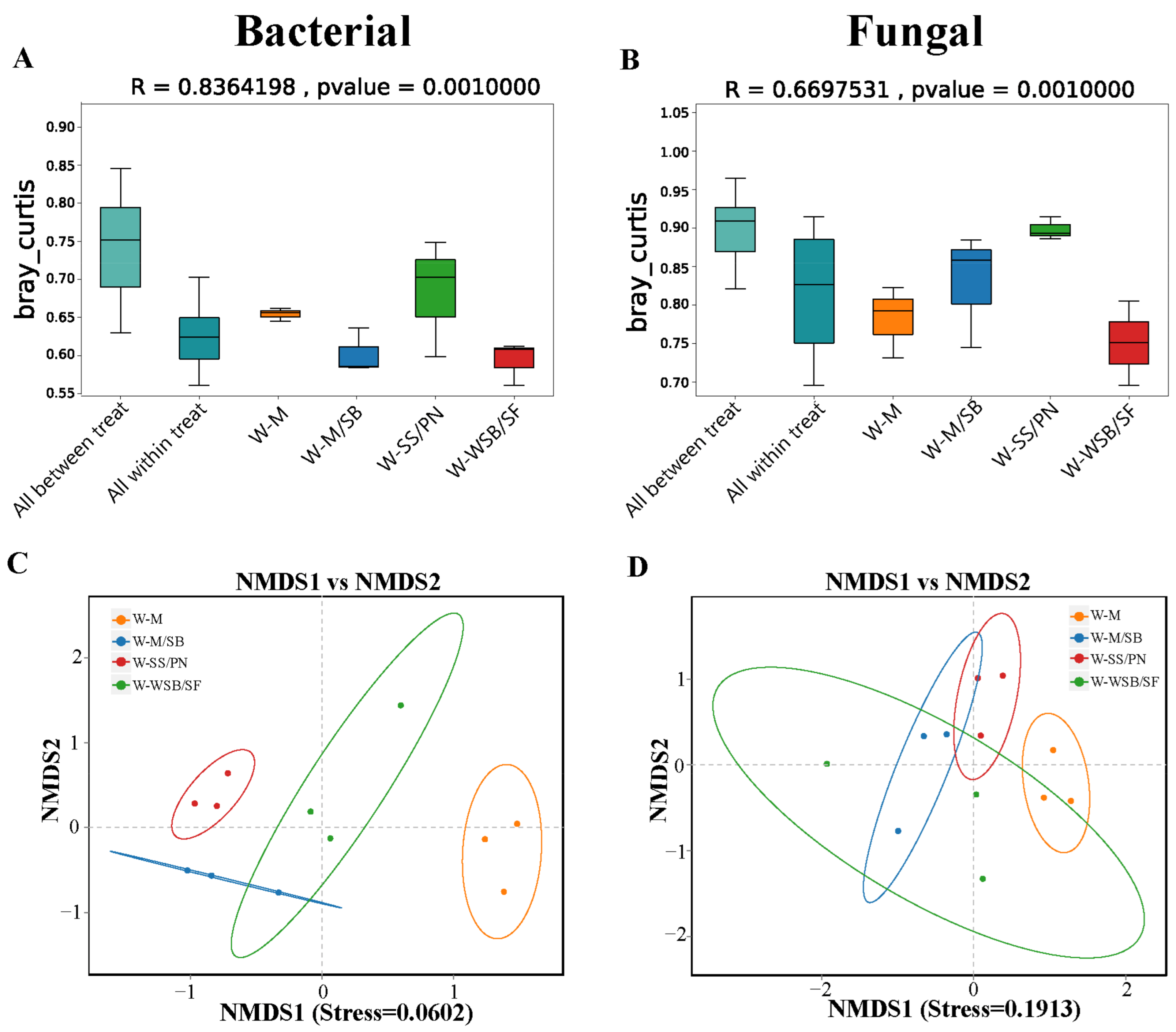
3.2. Diversity and Structure of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities
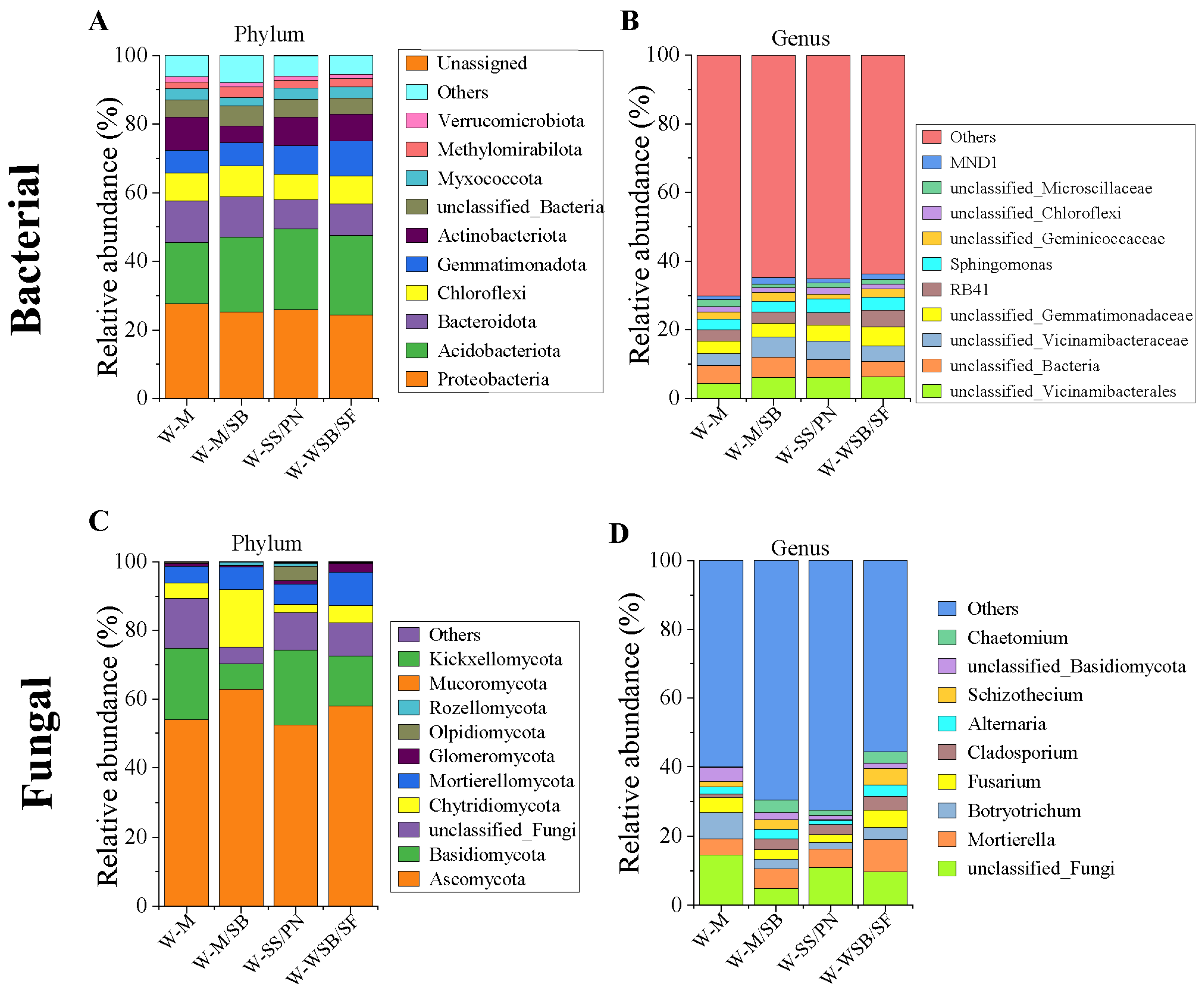
3.3. Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Compositions
3.4. Differences in the Soil Bacterial and Fungal Networks Under Different Cropping Systems
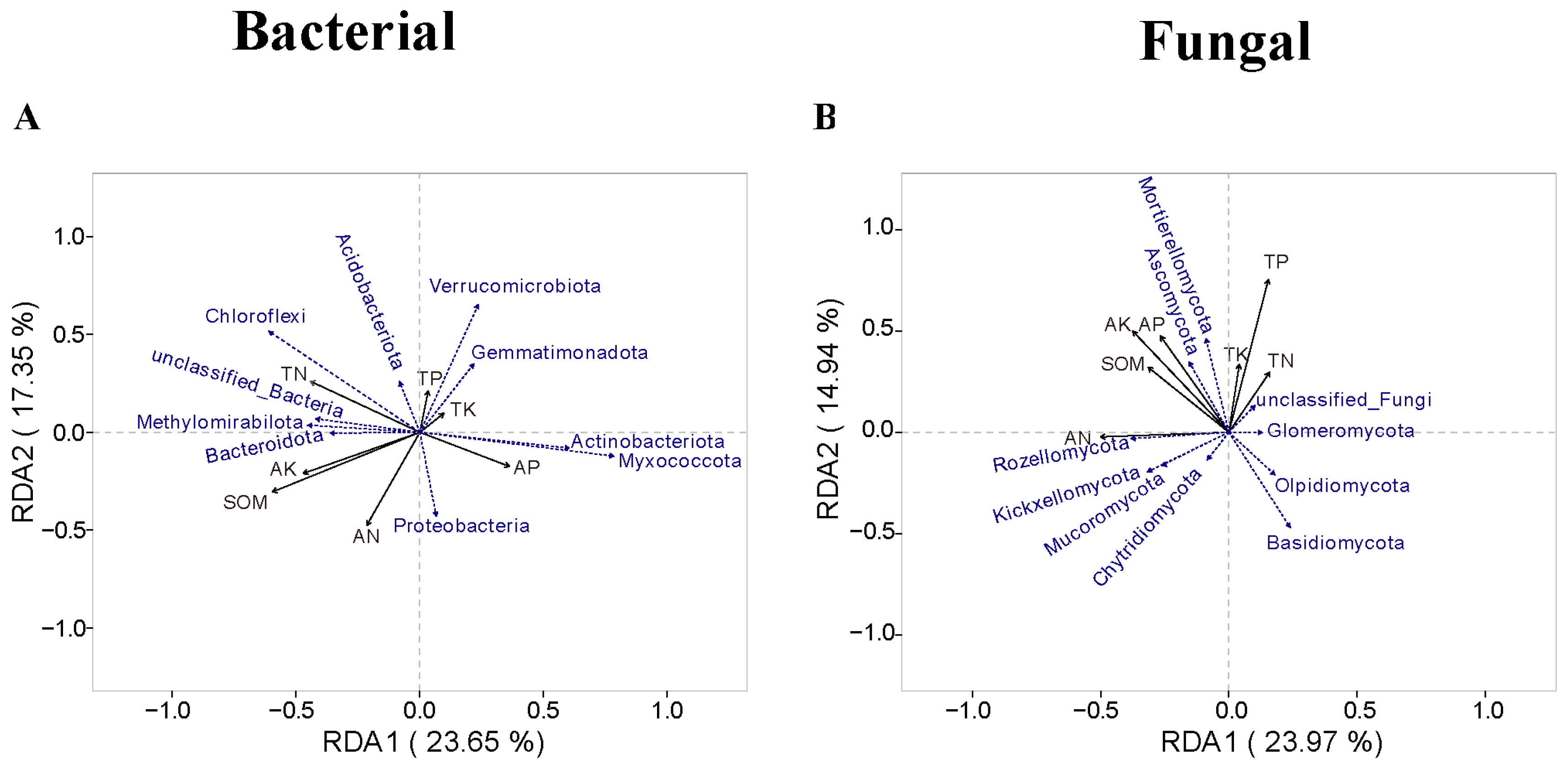
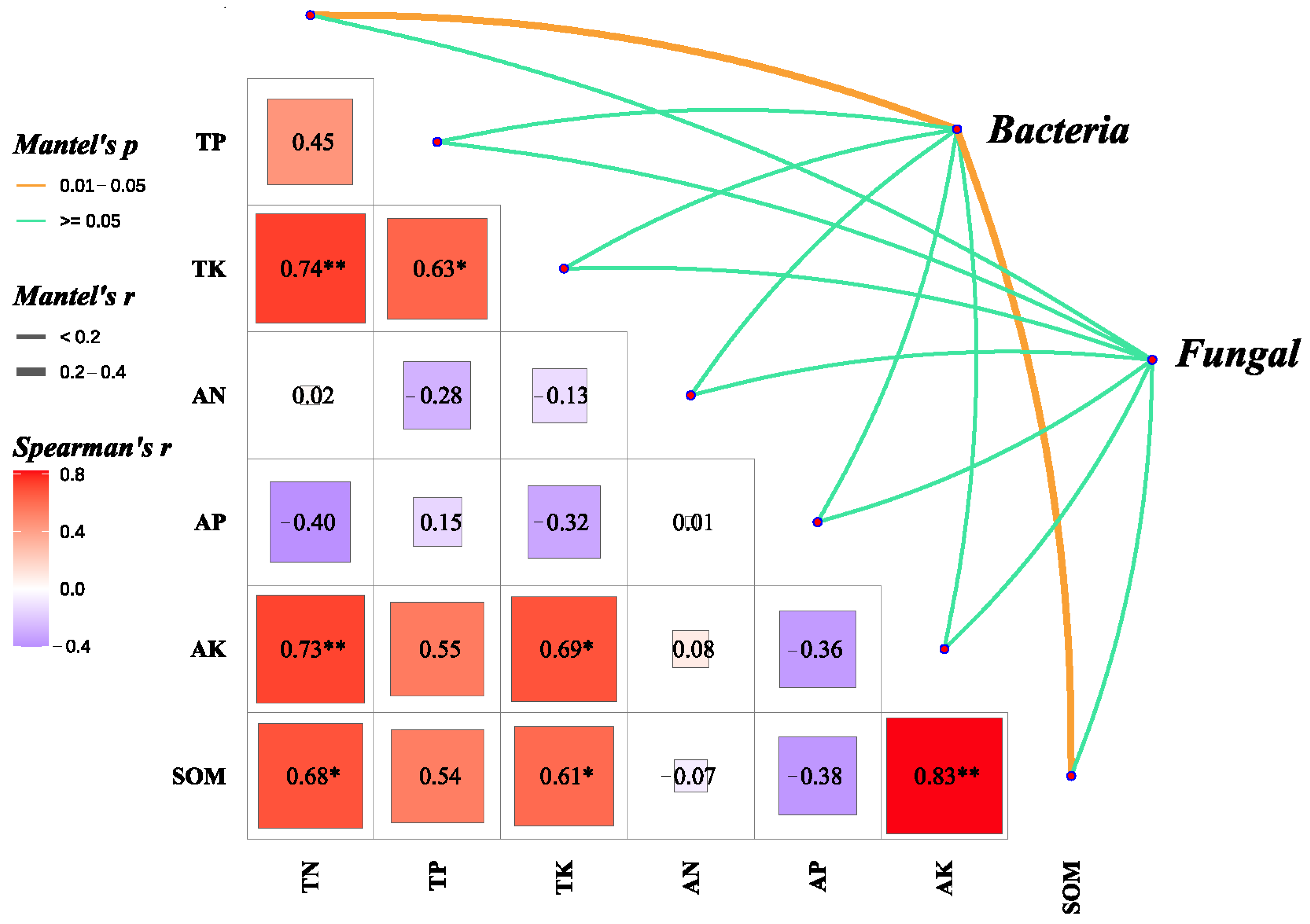
3.5. The Relationship Between Microbial Communities and Soil Chemical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Intercropping System Can Effectively Enhance Soil Nutrient Content in Saline-Alkali Soil
4.2. Intercropping System Effects on Microbial Community Structures
4.3. Intercropping System Effects on Microbial Community Network
4.4. Importance of Enhancing SOM in Saline-Alkali Soils
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| M/SB. | Maize/soybeans |
| SS/PN | Sesame/peanuts |
| WSB/SF | Soybeans/sunflowers |
| M | Maize |
| W-M | The maize monoculture system |
| W-M/SB | The maize and soybean intercropping system |
| W-SS/PN | The sesame and peanut intercropping system |
| W-WSB/SF | The sunflower and wild soybean intercropping system |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| AN | Available nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| AP | Available phosphorus |
| TK | Total potassium |
| AK | Available potassium |
References
- Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Han, G.; Zhou, D.; Fu, Y. The spatial distribution characteristics of soil salinity in coastal zone of the Yellow River Delta. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 72, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litalien, A.; Zeeb, B. Curing the earth: A review of anthropogenic soil salinization and plant-based strategies for sustainable mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yao, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shen, T.; Ding, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Cui, J.; et al. Effects of different amendments on aggregate stability and microbial communities of coastal saline-alkali soil in the Yellow River Delta. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hou, X.; Yang, M.; Cheng, F.; Coxixo, G. Factors driving the relationships between vegetation and soil properties in the Yellow River Delta, China. CATENA 2018, 165, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Xin, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, F.; Tang, Z.; Ci, D. Peanut production in saline-alkali land of Yellow River Delta: Influence of spatiotemporal changes of meteorological conditions and soil properties. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Geng, J.; Su, F. Estimation of the Ecosystem Service Value of the Yellow River Delta-Laizhou Bay Coastal Zone Considering Regional Differences and Social Development. Environ. Manag. 2024, 74, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, C. Characterization of the Microstructural Properties of Saline-Alkali Soils in the Yellow River Delta, China. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2021, 52, 1527–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, S.; Zhang, K.; Tian, C.; Mai, W. The Effects of Suaeda salsa/Zea mays L. Intercropping on Plant Growth and Soil Chemical Characteristics in Saline Soil. Agriculture 2022, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Biswas, A.; Chau, H.W.; Liang, J.; Zhang, F.; Bai, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Targeted biochar application alters physical, chemical, hydrological and thermal properties of salt-affected soils under cotton-sugarbeet intercropping. CATENA 2022, 216, 106414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Li, X.; Simunek, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Hu, Q. Evaluation of soil salt dynamics in a tomato-corn intercropping system with various spatial arrangements: Experiment and modeling. Soil Till. Res. 2025, 247, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Lachouani, P.; Knudsen, M.T.; Ambus, P.; Boelt, B.; Gislum, R. Productivity and carbon footprint of perennial grass-forage legume intercropping strategies with high or low nitrogen fertilizer input. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Mu, L.; Zhou, T.; Yang, H. Quantifying spatiotemporal transfer of soil water and salt between intercrop root zones under alfalfa/spring wheat strip intercropping based on HYDRUS-2D. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 375, 109172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.L.; Duan, H.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, H.J.; Xu, S.X. Complementarity and competitive trade-offs enhance forage productivity, nutritive balance, land and water use, and economics in legume-grass intercropping. Field Crop. Res. 2024, 319, 109642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Duan, Y.; Lei, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, L.; Shang, X.; Wang, M.; Lv, C.; Ma, Y.; Fang, W.; et al. Tea Plantation Intercropping Legume Improves Soil Ecosystem Multi-functionality and Tea Quality by Regulating Rare Bacterial Taxa. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Carlsson, G.; Englund, J.-E.; Flöhr, A.; Pelzer, E.; Jeuffroy, M.-H.; Makowski, D.; Jensen, E.S. Grain legume-cereal intercropping enhances the use of soil-derived and biologically fixed nitrogen in temperate agroecosystems. A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 118, 126077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Hina, K.; Hussain, Q.; Qiu, T.; Zhu, J. Revitalizing coastal saline-alkali soil with biochar application for improved crop growth. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 179, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Ruan, X.; Mao, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, P. Analysis of the effect of modified biochar on saline-alkali soil remediation and crop growth. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lv, J. The impact of land-use change on the soil bacterial community in the Loess Plateau, China. J. Agric. Environ. 2021, 188, 104469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alori, E.T.; Osemwegie, O.O.; Ibaba, A.L.; Daramola, F.Y.; Olaniyan, F.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Babalola, O.O. The Importance of Soil Microorganisms in Regulating Soil Health. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2024, 55, 2636–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lv, C.; Tang, B.; Wang, M.; Cao, B.; Wu, K. Dynamics of Soil N and P Nutrient Heterogeneity in Mixed Forest of Populus x Euramercana ’Neva’ and Robinia pseucdoacacia in Coastal Saline-Alkali Land. Forests 2024, 15, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Analysis on Soil and Agricultural Chemistry, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, K.M.; Espey, M.G.; Wink, D.A. A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric. Oxide 2001, 5, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, D.; Peterson, G.A.; Pratt, P.F. Lithium, sodium, and potassium. In Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 225–246. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus Methods of Soil Analysis. Methods 1982, 9, 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.I.; Miletto, M.; Taylor, J.W.; Bruns, T.D. Dispersal in microbes: Fungi in indoor air are dominated by outdoor air and show dispersal limitation at short distances. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Qian, W.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, Z.; Gao, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, X. Effects of acid mine drainage and sediment contamination on soil bacterial communities, interaction patterns, and functions in alkaline desert grassland. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ali, F.; Amjad, N.; Ouyang, Q.; Almutairi, M.H.; Wang, D. Microbiome analysis reveals the differences in gut fungal community between Dutch Warmblood and Mongolian horses. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 188, 106566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.F.; He, Z.L.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J.Z. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinforma 2012, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Alm, E.J. Inferring correlation networks from genomic survey data. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Kuai, J.; Jing, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; You, Y.; Zhu, W. Effects of understory intercropping with salt-tolerant legumes on soil organic carbon pool in coastal saline-alkali land. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Yang, Y. Phylogenetic Molecular Ecological Network of Soil Microbial Communities in Response to Elevated CO2. ASM J. 2011, 2, e00122-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W. Effect of interspecific root interaction on soil nutrition, enzymatic activity and rhizosphere biology in maize/peanut intercropping system. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 51, 405–416. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.-Y.; Surigaoge, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.-C.; Christie, P.; Zhang, W.P.; Li, L. Responses of soil microbial community diversity and co-occurrence networks to interspecific interactions in soybean/maize and peanut/maize intercropping systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 203, 105613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtright, A.J.; Tiemann, L.K. Intercropping increases soil extracellular enzyme activity: A meta-analysis. Environment 2021, 319, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilas, R.D.; Bretman, A.; Bennett, T.J. Friends, neighbours and enemies: An overview of the communal and social biology of plants. Friends, neighbours and enemies: An overview of the communal and social biology of plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-P.; Li, Z.-X.; Gao, S.-N.; Yang, H.; Xu, H.-S.; Yang, X.; Fan, H.-X.; Su, Y.; Surigaoge; Weiner, J.; et al. Resistance vs. surrender: Different responses of functional traits of soybean and peanut to intercropping with maize. Field Crop. Res. 2023, 291, 108779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, X.; Jia, Z.; Li, C.; Leng, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Keystone Microbial Species Drive the Responses of Saline-Alkali Soil to Three-Year Amendment Measures. Forests 2023, 14, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Bian, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Gai, X.; Zhong, Z. Microorganisms facilitated the saline-alkali soil remediation by biochar: Soil properties, microbial communities, and plant responses. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 3567–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Huang, P.; Huang, Z. The response of soil microbial community to application of organic amendment to saline land. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1481156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Yu, R.; Chen, S.; Hu, A.; Dong, Z.; Tang, L.; Lu, L.; Yang, W.; Dong, R. Intercropping in Coconut Plantations Regulate Soil Characteristics by Microbial Communities. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lin, X.; Lin, W. Effects of intercropping with legume forage on the rhizosphere microbial community structure of tea plants. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1474941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Xu, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Soil microbial composition, diversity, and network stability in intercropping versus monoculture responded differently to drought. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 365, 108915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Van Treuren, W.; Lozupone, C.; Faust, K.; Friedman, J.; Deng, Y.; Xia, L.C.; Xu, Z.Z.; Ursell, L.; Alm, E.J.; et al. Correlation detection strategies in microbial data sets vary widely in sensitivity and precision. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yuan, W.; Shi, L. Strong priming of soil organic matter induced by frequent input of labile carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 152, 108069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tian, J.; Liu, S.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Y. The complexity of the bacterial community in response to fertilization determines forage production in a semiarid grassland. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Qiao, Y.; Song, Q. Practice of Improving Saline-Alkali Soil with Bio-Humic Acid. Processes 2024, 12, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-H.; Fu, S.-L.; Zhang, X.-P.; Zhao, K.; Chen, H.Y. Intercropping improves soil nutrient availability, soil enzyme activity and tea quantity and quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 119, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
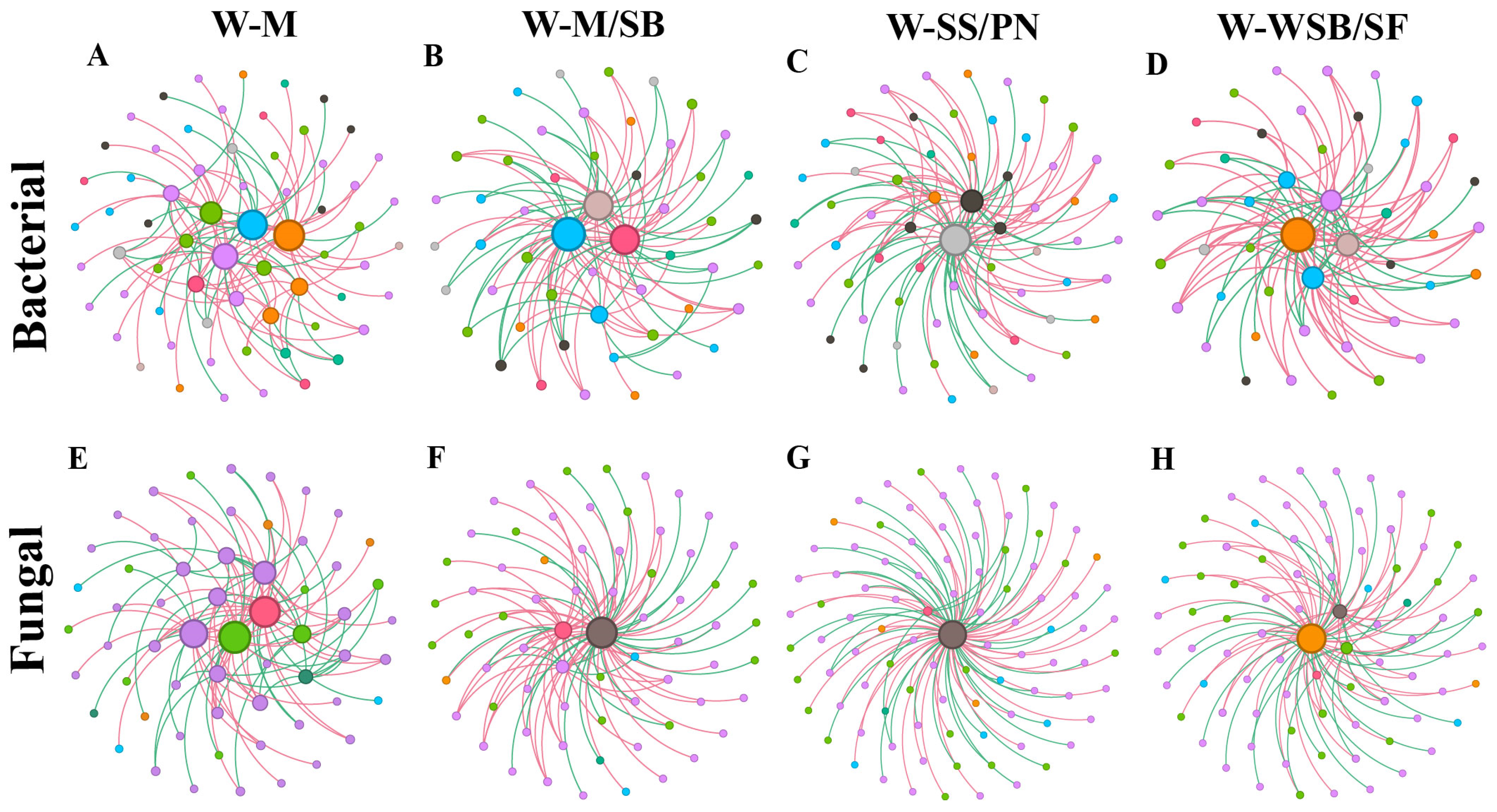
| Network Indexes | Bacterial | Fungal | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-M | W-M/SB | W-SS/PN | W-WSB/SF | W-M | W-M/SB | W-SS/PN | W-WSB/SF | |
| nodes_num | 65 | 52 | 63 | 49 | 59 | 68 | 94 | 82 |
| edges_num | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| average_degree | 3.077 | 3.846 | 3.175 | 4.082 | 3.390 | 2.941 | 2.128 | 2.439 |
| nodes_connectivity | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| edges_connectivity | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| average_path_length | 3.588 | 2.523 | 2.424 | 2.300 | 2.961 | 2.059 | 1.996 | 2.557 |
| graph_diameter | 36 | 36 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 18 | 18 | 24 |
| graph_density | 0.048 | 0.075 | 0.051 | 0.085 | 0.058 | 0.044 | 0.023 | 0.030 |
| clustering_coefficient | 0.058 | 0.005 | 0.027 | 0.086 | 0.052 | 0.039 | 0.005 | 0.004 |
| betweenness_centralization | 0.503 | 0.512 | 0.724 | 0.523 | 0.381 | 0.868 | 0.994 | 0.873 |
| degree_centralization | 0.264 | 0.552 | 0.691 | 0.644 | 0.286 | 0.867 | 0.966 | 0.748 |
| modularity | 0.529 | 0.295 | 0.360 | 0.247 | 0.439 | 0.280 | 0.131 | 0.400 |
| Module Hubs | Network Hubs | Connectors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Num. | Plylum | Num. | Num. | |||
| Bacterial Taxa | ||||||
| W-M | 3 | Acidobacteriota; Chloroflexi; Bacteroidota | 1 | Proteobacteria | 5 | Proteobacteria (2); Bacteroidota; Gemmatimonadota |
| W-M/SB | 3 | Acidobacteriota; Gemmatimonadota; unclassified bacteria | 0 | 0 | ||
| W-SS/PN | 2 | Acidobacteriota; unclassified bacteria | 2 | Patescibacteria; Bacteroidota | 0 | |
| W-WSB/SF | 2 | Proteobacteria; unclassified bacteria | 2 | Acidobacteriota; Gemmatimonadota | 9 | Proteobacteria (4); Bacteroidota; Actinobacteriota (3); Myxococcota |
| Fungal Taxa | ||||||
| W-M | 3 | Ascomycota; Basidiomycota; unclassified fungi | 0 | 5 | Ascomycota (5) | |
| W-M/SB | 3 | Ascomycota; Mortierellomycota; unclassified fungi | 0 | 3 | Ascomycota; Mortierellomycota; unclassified fungi | |
| W-SS/PN | 2 | Mortierellomycota; unclassified fungi | 0 | 0 | ||
| W-WSB/SF | 2 | Mortierellomycota; unclassified fungi | 1 | Basidiomycota | 2 | Ascomycota; Basidiomycota |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-J.; Qi, G.-X.; Wang, N.-N.; Dong, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.-C.; Li, X.-H.; Liu, H.-Y. The Improvement Effects of Intercropping Systems on Saline-Alkali Soils and Their Impact on Microbial Communities. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071436
Wang Y-J, Qi G-X, Wang N-N, Dong H-Y, Zhang Y, Lu H, Li Y, Wang H-C, Li X-H, Liu H-Y. The Improvement Effects of Intercropping Systems on Saline-Alkali Soils and Their Impact on Microbial Communities. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071436
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yan-Jun, Gao-Xiang Qi, Na-Na Wang, Hong-Yun Dong, Yan Zhang, Han Lu, Ying Li, Hong-Cheng Wang, Xin-Hua Li, and Hong-Yuan Liu. 2025. "The Improvement Effects of Intercropping Systems on Saline-Alkali Soils and Their Impact on Microbial Communities" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071436
APA StyleWang, Y.-J., Qi, G.-X., Wang, N.-N., Dong, H.-Y., Zhang, Y., Lu, H., Li, Y., Wang, H.-C., Li, X.-H., & Liu, H.-Y. (2025). The Improvement Effects of Intercropping Systems on Saline-Alkali Soils and Their Impact on Microbial Communities. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071436






