Halotolerance of Phytoplankton and Invasion Success of Nostocalean Cyanobacteria Under Freshwater Salinization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cyanobacterial Isolation and Maintenance
2.2. Monocultures Experiment
2.3. Microcosm Experiment
2.4. Data Visualization and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
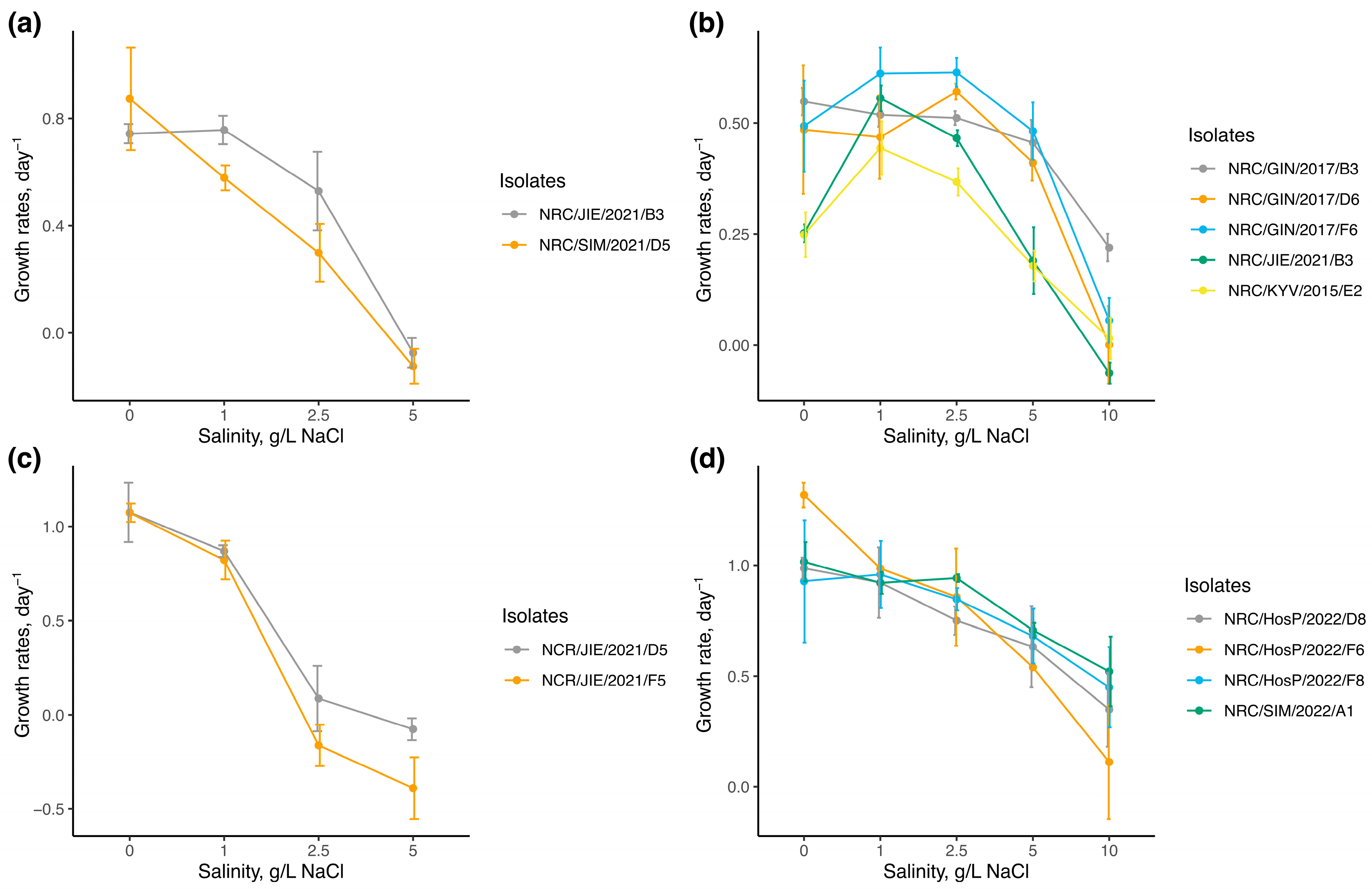
3.1. Monocultures Experiment
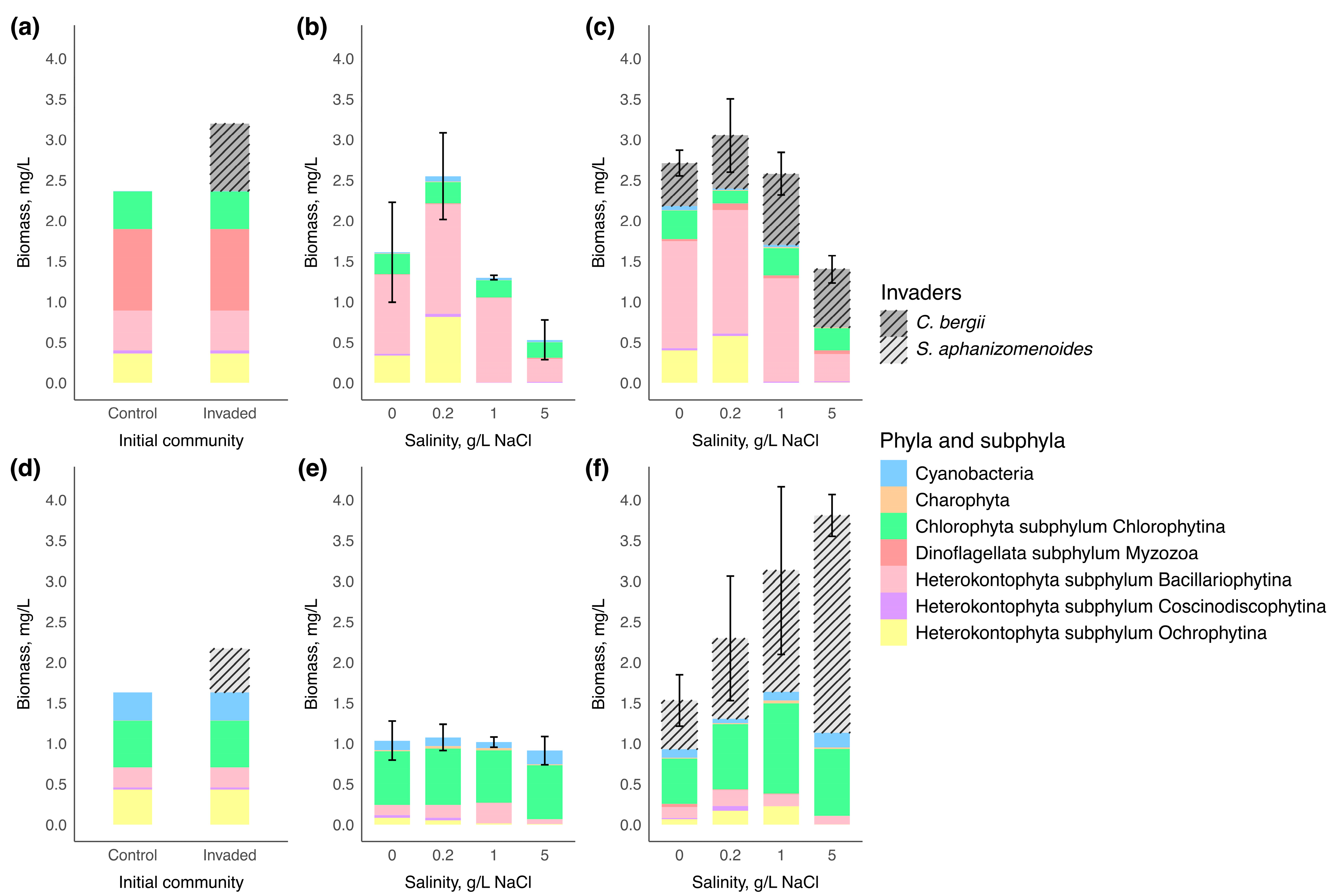
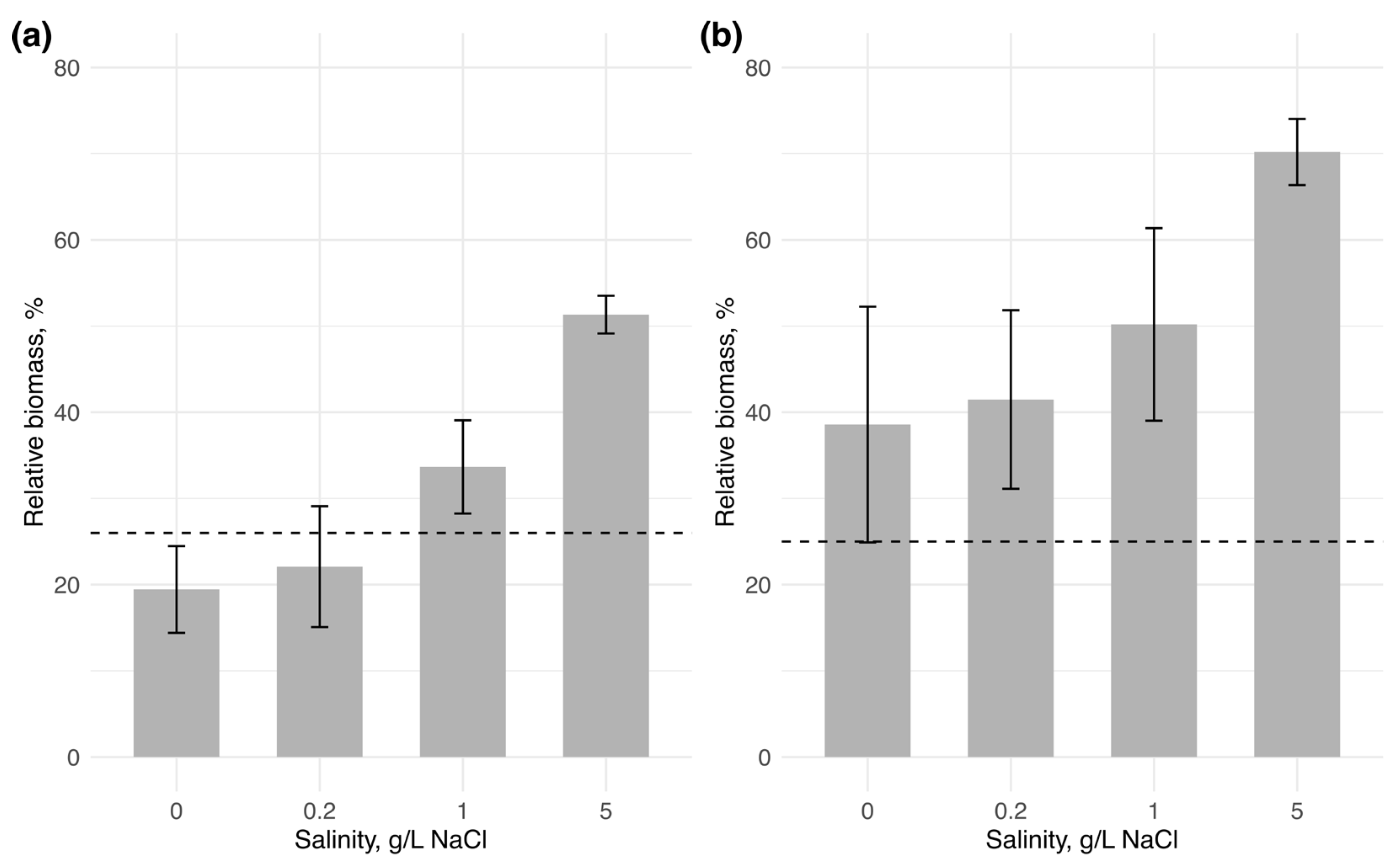
3.2. Microcosm Experiment
4. Discussion
4.1. Halotolerance of Nostocalean Cyanobacteria
4.2. Effects of Salinization on Phytoplankton Community Composition
4.3. Invasion Success of Halotolerant Cyanobacteria
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seebens, H.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Capinha, C.; Dawson, W.; Dullinger, S.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; van Kleunen, M.; Kühn, I.; et al. Projecting the Continental Accumulation of Alien Species through to 2050. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essl, F.; Lenzner, B.; Bacher, S.; Bailey, S.; Capinha, C.; Daehler, C.; Dullinger, S.; Genovesi, P.; Hui, C.; Hulme, P.E.; et al. Drivers of Future Alien Species Impacts: An Expert-Based Assessment. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 4880–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elton, C.S. The Ecology of Invasion by Animals and Plants; Chapman & Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Huenneke, L.F. Disturbance, Diversity, and Invasion—Implications for Conservation. Conserv. Biol. 1992, 6, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaertner, M.; Wilson, J.R.U.; Cadotte, M.W.; MacIvor, J.S.; Zenni, R.D.; Richardson, D.M. Non-Native Species in Urban Environments: Patterns, Processes, Impacts and Challenges. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 3461–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana Marques, P.; Resende Manna, L.; Clara Frauendorf, T.; Zandonà, E.; Mazzoni, R.; El-Sabaawi, R. Urbanization Can Increase the Invasive Potential of Alien Species. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk-Woźniak, E.; Najberek, K. Towards Clarifying the Presence of Alien Algae in Inland Waters—Can We Predict Places of Their Occurrence? Biologia 2013, 68, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoka, J.; Bláha, M.; Kalous, L.; Kouba, A. Irresponsible Vendors: Non-native, Invasive and Threatened Animals Offered for Garden Pond Stocking. Aquat. Conserv. 2017, 27, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, B.C.; McIntosh, A.R.; O’Regan, R.P.; Brown, S.K.; Warburton, H.J. Invasion of a Non-Native Anuran Likely Disrupts Pond Ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2023, 68, 1194–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater Biodiversity: Importance, Threats, Status and Conservation Challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging Threats and Persistent Conservation Challenges for Freshwater Biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Beklioglu, M.; Özkan, K.; Akyürek, Z. Salinization Increase Due to Climate Change Will Have Substantial Negative Effects on Inland Waters and Freshwater Resources: A Call for Multifaceted Research at the Local and Global Scale. Innovation 2020, 1, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorslund, J.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Oude Essink, G.H.P.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; van Vliet, M.T.H. Common Irrigation Drivers of Freshwater Salinisation in River Basins Worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugan, H.A.; Bartlett, S.L.; Burke, S.M.; Doubek, J.P.; Krivak-Tetley, F.E.; Skaff, N.K.; Summers, J.C.; Farrell, K.J.; McCullough, I.M.; Morales-Williams, A.M.; et al. Salting Our Freshwater Lakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunillera-Montcusí, D.; Beklioğlu, M.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Jeppesen, E.; Ptacnik, R.; Amorim, C.A.; Arnott, S.E.; Berger, S.A.; Brucet, S.; Dugan, H.A.; et al. Freshwater Salinisation: A Research Agenda for a Saltier World. Trends. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 37, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz, W.D.; Relyea, R.A. A Review of the Species, Community, and Ecosystem Impacts of Road Salt Salinisation in Fresh Waters. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, S.E.; Celis-Salgado, M.P.; Valleau, R.E.; DeSellas, A.M.; Paterson, A.M.; Yan, N.D.; Smol, J.P.; Rusak, J.A. Road Salt Impacts Freshwater Zooplankton at Concentrations below Current Water Quality Guidelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9398–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz, W.D.; Fay, L.; Relyea, R.A. Road Salts, Human Safety, and the Rising Salinity of Our Fresh Waters. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 20, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, D.A.; Arnott, S.E.; Fournier, I.B.; Schamp, B.S. Effects of Chloride and Nutrients on Freshwater Plankton Communities. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2023, 8, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukenik, A.; Hadas, O.; Kaplan, A.; Quesada, A. Invasion of Nostocales (Cyanobacteria) to Subtropical and Temperate Freshwater Lakes–Physiological, Regional, and Global Driving Forces. Front. Microbio. 2012, 3, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisander, P.H.; McClinton, E.; Paerl, H.W. Salinity Effects on Growth, Photosynthetic Parameters, and Nitrogenase Activity in Estuarine Planktonic Cyanobacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 43, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, P.; Jones, G.; Douglas, G. Response of Cultured Microcystis Aeruginosa from the Swan River, Australia, to Elevated Salt Concentration and Consequences for Bloom and Toxin Management in Estuaries. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2004, 55, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flöder, S.; Jaschinski, S.; Wells, G.; Burns, C.W. Dominance and Compensatory Growth in Phytoplankton Communities under Salinity Stress. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2010, 395, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, C.; Thomazeau, S.; Drelin, Y.; Yéprémian, C.; Bouvy, M.; Couloux, A.; Troussellier, M.; Rousseau, F.; Bernard, C. Phylogeny and Salt-Tolerance of Freshwater Nostocales Strains: Contribution to Their Systematics and Evolution. Harmful Algae 2018, 73, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballot, A.; Kotut, K.; Novelo, E.; Krienitz, L. Changes of Phytoplankton Communities in Lakes Naivasha and Oloidien, Examples of Degradation and Salinization of Lakes in the Kenyan Rift Valley. Hydrobiologia 2009, 632, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomati, F.; Rossetti, C.; Manarolla, G.; Burns, B.P.; Neilan, B.A. Interactions between Intracellular Na+ Levels and Saxitoxin Production in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii T3. Microbiology 2004, 150 Pt 2, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, F.S.; Wagner, N.D.; Taylor, R.B.; Chambliss, C.K.; Brooks, B.W.; Scott, J.T. The Effects of Salinity and N:P on N-Rich Toxins by Both an N-Fixing and Non-N-Fixing Cyanobacteria. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2023, 8, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J. Cyanoprokaryota 3. Teil/Part 3: Heterocytous Genera. In Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Büdel, B., Gärtner, G., Krienitz, L., Schagerl, M., Eds.; Springer Spektrum: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, R.R.L. Division Rates. In Handbook of Phycological Methods: Culture Methods and Growth Measurement; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1973; pp. 289–311. [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider, R.; Kerekes, J. Eutrophication of Waters: Monitoring, Assessment and Control; Report of the Cooperative Program on Eutrophication; OECD: Paris, France, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- The Venice System for the Classification of Marine Waters According to Salinity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1958, 3, 346–347. [CrossRef]
- LeGresley, M.; McDermott, G. Counting Chamber Methods for Quantitative Phytoplankton Analysis: Haemocytometer, Palmer-Maloney Cell and Sedgewick-Rafter Cell. In Microscopic and Molecular Methods for Quantitative Phytoplankton Analysis; Karlson, B., Cusack, C., Bresnan, E., Eds.; IOC Manuals and Guides; Ocean Best Practices System: Oostende, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Olenina, I.; Hajdu, S.; Edler, L.; Andersson, A.; Wasmund, N.; Busch, S.; Göbel, J.; Gromisz, S.; Huseby, S.; Huttunen, M.; et al. Biovolumes and Size-Classes of Phytoplankton in the Baltic Sea. HELCOM. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2006, 106, 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Abakumova, B.A. Rukovodstvo po metodam gidrobiologičeskogo analiza poverkhnostnykh vod i donnykh otloženij; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae 2. Teil: Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae. In Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Pascher, A., Ed.; Gustaw Fischer: Stuttgart, Germany, 1988; pp. 1–596. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae 1. Teil: Naviculaceae. In Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Pascher, A., Ed.; Gustaw Fischer: Jena, Germany, 1986; pp. 1–876. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. 3. Teil: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae. In Susswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fisher: Stuttgart, Germany, 1991; pp. 1–576. [Google Scholar]
- Starmach, K. Chrysophyceae und Haptophyceae. In Susswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fisher: Stuttgart, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Ettl, H. Chlorophyta I: Phytomonadina. In Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, 3rd ed.; Spektrum Akademischer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Focke-Casper, R.; Ettl, H.; Gärtner, G. Chlorophyta II–Tetrusporales, Chlorococcales, Gloeodendrales. In Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Gustav Fisher: Stuttgart, Germany, 1988; ISBN 3-334-00264-0. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota. 2. Teil/2nd Part, Oscillatoriales. In Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Elsevier GmbH: München, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Huber-Pestalozzi, G. Das phytoplankton des Süβwassers. Systematik und Biologie. 7 Teil, 1 Häfte: Chlorophyceae (Grünalgen) Ordnung Chlorococcales. In Die Binnengewässer Einzeldarstellungen aus der Limnologie und Ihren Nachbargebieten; Thienemann, A., Ed.; Schweizerbart’sche Verlasbuchhandlung: Stuttgart, Germany, 1983; pp. 1–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M.; AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication, University of Galway. 2025. Available online: https://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Kaštovský, J.; Hauer, T.; Mareš, J.; Krautová, M.; Bešta, T.; Komárek, J.; Desortová, B.; Heteša, J.; Hindáková, A.; Houk, V.; et al. A Review of the Alien and Expansive Species of Freshwater Cyanobacteria and Algae in the Czech Republic. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 3599–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuikaitė, I.; Koreiviene, J. An Overview of the Distribution and Ecology of the Alien Cyanobacteria Species Raphidiopsis Raciborskii, Sphaerospermopsis Aphanizomenoides and Chrysosporum Bergii in Europe. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2023, 52, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geitler, L. Cyanophyceae. In Rabenhorst’s Kryptogamen-Flora von Deutschland, Osterreich und der Schweiz; Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft: Leipzig, Germany, 1932; p. 1196. [Google Scholar]
- Sabour, B.; Loudiki, M.; Oudra, B.; Vasconcelos, V.; Oubraim, S.; Fawzi, B. Dynamics and Toxicity of Anabaena Aphanizomenoides (Cyanobacteria) Waterblooms in the Shallow Brackish Oued Mellah Lake (Morocco). Aquat. Ecosyst. Heal. Manag. 2005, 8, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hällfors, G.; Checklist of Baltic Sea Phytoplankton Species (Including Some Heterotrophic Protistan Groups). BSEP 2004, 95. Available online: https://www.helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/BSEP95.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Palińska, K.A.; Surosz, W. Population of Aphanizomenon from the Gulf of Gdańsk (Southern Baltic Sea): Differences in Phenotypic and Genotypic Characteristics. Hydrobiologia 2008, 607, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-J.; Yoon, S.-R.; Choi, H.J.; Ki, J.-S.; Lee, O.-M. Aphanizomenon gracile (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria), a Korean Newly Recorded Species from Brackish Water. Korean J. Microbiol. 2020, 56, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napiórkowska-Krzebietke, A.; Dunalska, J.A.; Bogacka-Kapusta, E. Ecological Implications in a Human-Impacted Lake-A Case Study of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Recreationally Used Water Body. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo, D.R.; Lopes, A.R.; Pereira, M.J.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Castro, B.B.; Gonçalves, F.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Cleary, D.F.R. Bacterioplankton Community Shifts during a Spring Bloom of Aphanizomenon gracile and Sphaerospermopsis aphanizomenoides at a Temperate Shallow Lake. Hydrobiology 2022, 1, 499–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokociński, M.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J.; Jurczak, T.; Spoof, L.; Meriluoto, J.; Rejmonczyk, E.; Hautala, H.; Vehniäinen, M.; Pawełczyk, J.; Soininen, J. Aphanizomenon gracile (Nostocales), a Cylindrospermopsin-Producing Cyanobacterium in Polish Lakes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5243–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houliez, E.; Briand, E.; Malo, F.; Rovillon, G.-A.; Hervé, F.; Robert, E.; Marchand, L.; Zykwinska, A.; Caruana, A.M.N. Physiological Changes Induced by Sodium Chloride Stress in Aphanizomenon gracile, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Dolichospermum sp. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarek, S.; Górecka, A.; Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A. The Effects of Road Salt on Freshwater Ecosystems and Solutions for Mitigating Chloride Pollution - A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachi, S.; Loreau, M. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Productivity in a Fluctuating Environment: The Insurance Hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thessen, A.E.; Dortch, Q.; Parsons, M.L.; Morrison, W. Effect of Salinity on Pseudo-Nitzschia Species (Bacillariophyceae) Growth and Distribution. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, A.; Pap, B.; Zsíros, O.; Patai, R.; Shetty, P.; Garab, G.; Bíró, T.; Ördög, V.; Maróti, G. Salinity Stress Provokes Diverse Physiological Responses of Eukaryotic Unicellular Microalgae. Algal Res. 2023, 73, 103155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, Y.; Xue, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, X. Freshwater Salinization Impacts the Interspecific Competition between Microcystis and Scenedesmus. Water 2023, 15, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.S.; Nguyen, D.A.K.; Nguyen, V.T.; Huu, H.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Pham, T.L.; Tran, P.Y.N.; Luu, T.T.N. Salinity Tolerance and Nutrient Uptake of the Freshwater Microalga Scenedesmus protuberans. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astorg, L.; Gagnon, J.-C.; Lazar, C.S.; Derry, A.M. Effects of Freshwater Salinization on a Salt-Naïve Planktonic Eukaryote Community. Limnol. Oceanog. Lett. 2023, 8, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Peng, F.; Gao, X.; Xiao, P.; Logares, R.; Jeppesen, E.; Ren, K.; Xue, Y.; Yang, J. Low Shifts in Salinity Determined Assembly Processes and Network Stability of Microeukaryotic Plankton Communities in a Subtropical Urban Reservoir. Microbiome 2021, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligorini, V.; Garrido, M.; Malet, N.; Simon, L.; Alonso, L.; Bastien, R.; Aiello, A.; Cecchi, P.; Pasqualini, V. Response of Phytoplankton Communities to Variation in Salinity in a Small Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon: Future Management and Foreseen Climate Change Consequences. Water 2023, 15, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Acharyya, T.; Raghunadh Babu, P.V.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Impact of Salinity and pH on Phytoplankton Communities in a Tropical Freshwater System: An Investigation with Pigment Analysis by HPLC. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, I.; Gligora Udovič, M.; Žutinić, P.; Hanžek, N.; Plenković-Moraj, A. Is Salinity a Driving Factor for the Phytoplankton Community Structure of a Brackish Shallow Mediterranean Lake? Hydrobiologia 2024, 851, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Langvall, O.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Hylander, S.; Lundgren, M.; Papadopoulou, S.; Striebel, M.; Lind, L.; Langenheder, S. Cyanobacteria Can Benefit from Freshwater Salinization Following the Collapse of Dominant Phytoplankton Competitors and Zooplankton Herbivores. Freshw. Biol. 2024, 69, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, E.R.; Baker, H.K.; Bonadonna, C.C.; Shurin, J.B.; Symons, C.C. Cascading Effects of Freshwater Salinization on Plankton Communities in the Sierra Nevada. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2023, 8, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourisseau, M.; Le Guennec, V.; Le Gland, G.; Plus, M.; Chapelle, A. Resource Competition Affects Plankton Community Structure; Evidence from Trait-Based Modeling. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 211510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weithoff, G.; Taube, A.; Bolius, S. The Invasion Success of the Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Experimental Mesocosms: Genetic Identity, Grazing Loss, Competition and Biotic Resistance. Aquat. Invasions 2017, 12, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchberger, F.; Stockenreiter, M. Unsuccessful Invaders Structure a Natural Freshwater Phytoplankton Community. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulleri, F.; Marzinelli, E.M.; Voerman, S.E.; Gribben, P.E. Propagule Composition Regulates the Success of an Invasive Seaweed across a Heterogeneous Seascape. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukenik, A.; Quesada, A.; Salmaso, N. Global Expansion of Toxic and Non-Toxic Cyanobacteria: Effect on Ecosystem Functioning. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 889–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Isolate | Water Body | Country | Year of Isolation |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. gracile | |||
| NRC/SIM/2022/D5 | Lake Simnas | Lithuania | 2022 |
| NRC/JIE/2022/B3 | Lake Jieznas | Lithuania | 2022 |
| C. bergii | |||
| NRC/KYV/2015/E2 | Lake Rėkyva | Lithuania | 2015 |
| NRC/GIN/2017/B3 | Lake Gineitiškės | Lithuania | 2017 |
| NRC/GIN/2017/D6 | Lake Gineitiškės | Lithuania | 2017 |
| NRC/GIN/2017/F6 | Lake Gineitiškės | Lithuania | 2017 |
| NRC/JIE/2021/B3 | Lake Jieznas | Lithuania | 2021 |
| C. issatschenkoi | |||
| NRC/JIE/2021/D5 | Lake Jieznas | Lithuania | 2021 |
| NRC/JIE/2021/F5 | Lake Jieznas | Lithuania | 2021 |
| S. aphanizomenoides | |||
| NRC/SIM/2022/A1 | Lake Simnas | Lithuania | 2022 |
| NRC/HosP/2022/D8 | Reservoir Hostivař | The Czech Republic | 2022 |
| NRC/HosP/2022/F6 | Reservoir Hostivař | The Czech Republic | 2022 |
| NRC/HosP/2022/F8 | Reservoir Hostivař | The Czech Republic | 2022 |
| Species | Factor | df | Test Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. gracile | Strain | 1 | W = 89 | 0.347 |
| Salinity | 3 | F = 59.3 | <0.001 | |
| C. bergii | Strain | 4 | χ2 = 15.18 | 0.004 |
| Salinity | 4 | F = 40.13 | <0.001 | |
| C. issatschenkoi | Strain | 1 | W = 87 | 0.410 |
| Salinity | 3 | F = 106.5 | <0.001 | |
| S. aphanizomenoides | Strain | 3 | F = 0.39 | 0.759 |
| Salinity | 4 | F = 33.97 | <0.001 |
| Taxonomic Group | Test Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Water body 1 | ||
| Bacillariophytina | F = 16.74 | <0.001 |
| Charophytina | χ2 = 2.02 | 0.569 |
| Chlorophyta | F = 0.95 | 0.439 |
| Coscinodiscophytina | F = 5.24 | 0.008 |
| Cyanobacteria | F = 1.53 | 0.239 |
| Myzozoa | χ2 = 2.37 | 0.499 |
| Ochrophytina | χ2 = 19.45 | <0.001 |
| Water body 1 | ||
| Bacillariophytina | F = 5.27 | 0.009 |
| Charophyta | χ2 = 5.42 | 0.144 |
| Chlorophytina | χ2 = 1.92 | 0.590 |
| Coscinodiscophytina | χ2 = 16.64 | <0.001 |
| Cyanobacteria | F = 9.17 | <0.001 |
| Myzozoa | χ2 = 2.05 | 0.563 |
| Ochrophytina | χ2 = 11.15 | 0.011 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šuikaitė, I.; Šiurkutė, G.; Ptacnik, R.; Koreivienė, J. Halotolerance of Phytoplankton and Invasion Success of Nostocalean Cyanobacteria Under Freshwater Salinization. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061378
Šuikaitė I, Šiurkutė G, Ptacnik R, Koreivienė J. Halotolerance of Phytoplankton and Invasion Success of Nostocalean Cyanobacteria Under Freshwater Salinization. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061378
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠuikaitė, Izabelė, Gabrielė Šiurkutė, Robert Ptacnik, and Judita Koreivienė. 2025. "Halotolerance of Phytoplankton and Invasion Success of Nostocalean Cyanobacteria Under Freshwater Salinization" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061378
APA StyleŠuikaitė, I., Šiurkutė, G., Ptacnik, R., & Koreivienė, J. (2025). Halotolerance of Phytoplankton and Invasion Success of Nostocalean Cyanobacteria Under Freshwater Salinization. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061378







