Hypomagnetic Field and Its Effect on the Growth and Survival of Microorganisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Organisms
2.2. Magnetic Field Induction
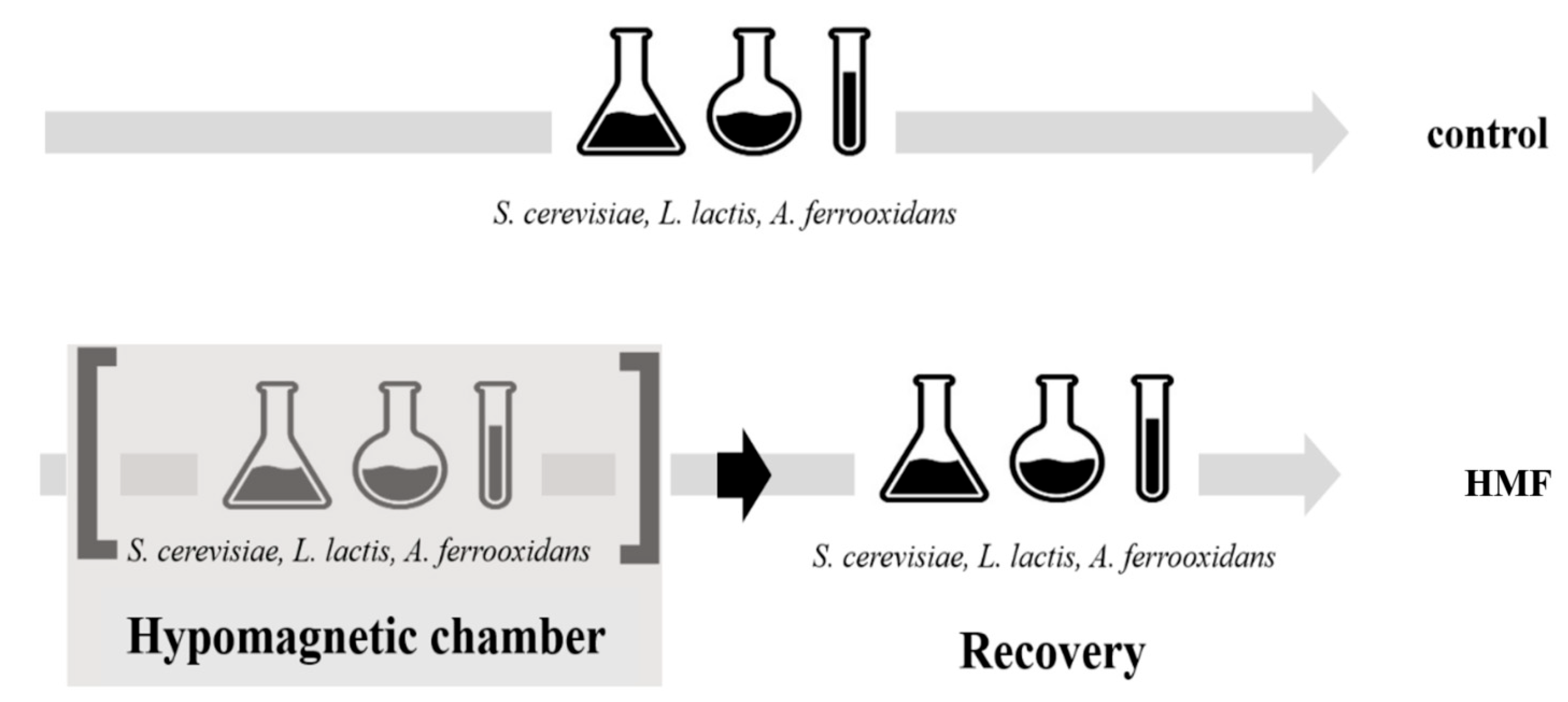
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Measured Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Organisms in Hypomagnetic Field
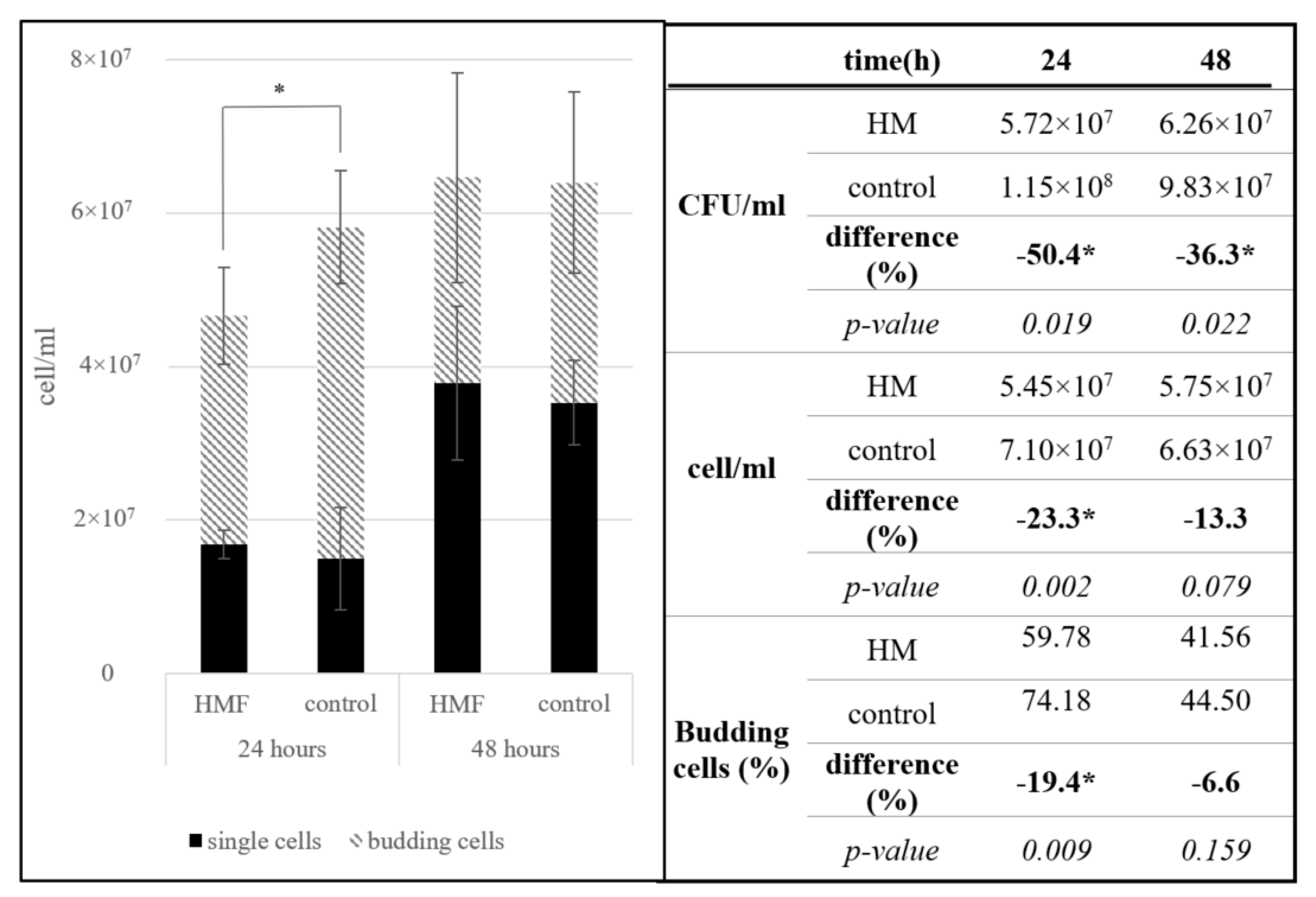
3.1.1. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
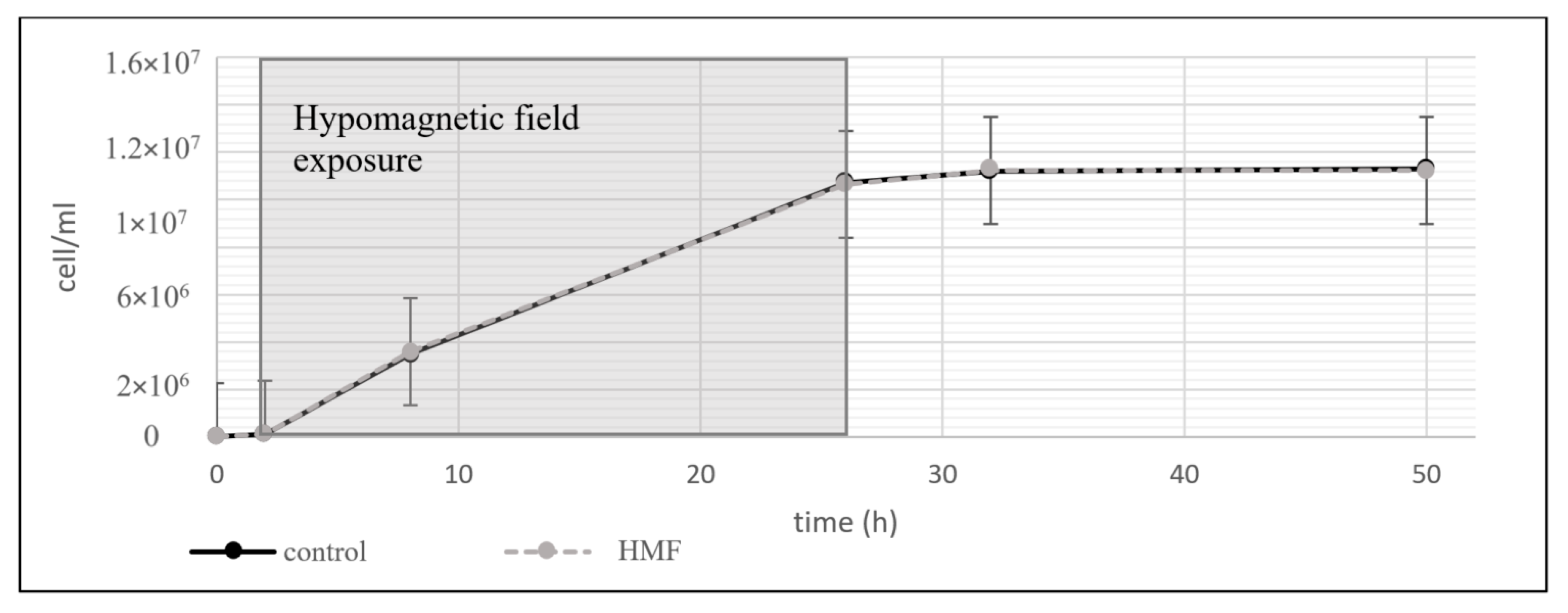
3.1.2. Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
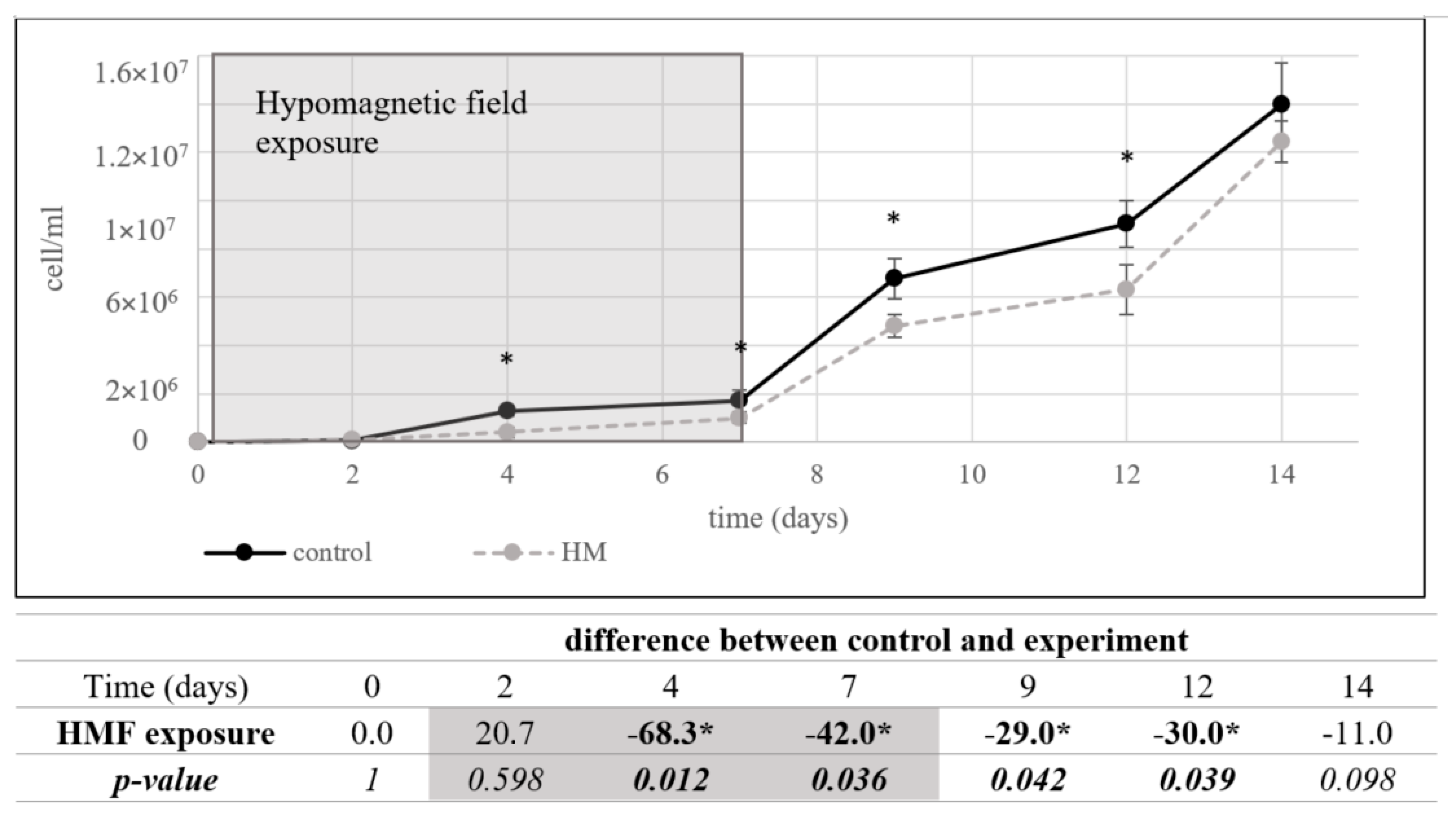
3.1.3. Lactobacillus plantarum
3.2. Comparison of Experimental Organisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saliev, T.; Begimbetova, D.; Masoud, A.-R.; Matkarimov, B. Biological effects of non-ionizing electromagnetic fields: Two sides of a coin. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2018, 141, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabros, M.; Schuler, M.M.; Marison, I.W. Simple control of specific growth rate in biotechnological fed-batch processes based on enhanced online measurements of biomass. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinčák, M.; Sedlakova-Kadukova, J. Hypomagnetic fields and their multilevel effects on living organisms. Processes 2023, 11, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Liu, Y.; He, R. Hypomagnetic field, an ignorable environmental factor in space. Sci. China Life Sci. 2014, 57, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Binhi, V.N.; Prato, F.S. Biological effects of the Hypomagnetic field: An analytical review of experiments and theories. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.P.; Mo, W.C.; Liu, Y.; Bartlett, P.F.; He, R.Q. Elimination of the geomagnetic field stimulates the proliferation of mouse neural progenitor and stem cells. Protein Cell 2016, 7, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogneva, I.V.; Usik, M.A.; Burtseva, M.V.; Biryukov, N.S.; Zhdankina, Y.S.; Sychev, V.N.; Orlov, O.I. Drosophila melanogaster sperm under simulated microgravity and a Hypomagnetic field: Motility and cell respiration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wei, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Song, T. Removal of the local geomagnetic field affects reproductive growth in Arabidopsis. Bioelectromagnetics 2013, 34, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Maffei, M.E.; Vigani, G. The geomagnetic field is a contributing factor for an efficient iron uptake in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, H.; Xi, W.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, A. Exposure to hypomagnetic field space for multiple generations causes amnesia in Drosophila melanogaster. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 371, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poiata, A.; Creanga, D.E.; Morariu, V.V. Life in zero magnetic field. E. coli resistance to antibiotics. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2003, 22, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.K.; Ma, Q.F.; Jiang, W.; Lv, J.; Pan, W.D.; Song, T.; Wu, L.F. Effects of hypomagnetic field on magnetosome formation of Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1. Geomicrobiol. J. 2008, 25, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Luo, Y.; Qin, H.; Lin, W.; Tian, L. Hypomagnetic field exposure affecting gut microbiota, reactive oxygen species levels, and colonic cell proliferation in mice. Bioelectromagnetics 2022, 43, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santomartino, R.; Zea, L.; Cockell, C.S. The smallest space miners: Principles of space biomining. Extremophiles 2022, 26, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, S.S.; Eaton, G.R. The world as viewed by and with unpaired electrons. J. Magn. Reson. 2012, 223, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerloch, M. Magnetism and Ligand-Field Analysis; CUP Archive: Cambridge, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, D.; Suturina, E.A.; Kuprov, I.; Chilton, N.F. How the ligand field in lanthanide coordination complexes determines magnetic susceptibility anisotropy, paramagnetic NMR shift, and relaxation behavior. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaka, M.; Ikehata, M.; Miyakoshi, J.; Ueno, S. Strong static magnetic field effects on yeast proliferation and distribution. Bioelectrochemistry 2004, 65, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Barcia, M.; Ristori-Bogajo, E.; Ruiz-Gómez, M.; Martínez-Morillo, M. Static and 50 Hz magnetic fields of 0.35 and 2.45 mT have no effect on the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioelectrochemistry 2004, 64, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Gómez, M.J.; Sendra-Portero, F.; Martínez-Morillo, M. Effect of 2.45 mT sinusoidal 50 Hz magnetic field on Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains deficient in DNA strand breaks repair. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2010, 86, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladko, D.V.; Zakharzhevskii, M.A.; Vinogradov, V.V. Magnetic field-mediated control of whole-cell biocatalysis. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 8989–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeira, C.Z.; de Carvalho Silvello, M.A.; Remedi, R.D.; Feltrin, A.C.P.; Santos, L.O.; Garda-Buffon, J. Mitigation of nivalenol using alcoholic fermentation and magnetic field application. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.O.; Alegre, R.M.; Garcia-Diego, C.; Cuellar, J. Effects of magnetic fields on biomass and glutathione production by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canli, O.; Kurbanoğlu, E.B. Application of low magnetic field on inulinase production by Geotrichum candidum under solid state fermentation using leek as substrate. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 28, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, V.H.; Reyes, A.F.; Justo, O.R.; Alvarez, D.C.; Alegre, R.M. Bioreactor Coupled with Electromagnetic Field Generator: Effects of Extremely Low Frequency Electromagnetic Fields on Ethanol Production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sincak, M.; Turker, M.; Derman, Ü.C.; Erdem, A.; Jandacka, P.; Luptak, M.; Luptakova, A.; Sedlakova-Kadukova, J. Exploring the impact of magnetic fields on biomass production efficiency under aerobic and anaerobic batch fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Motta, M.A.; Muniz, J.B.F.; Schuler, A.; Da Motta, M. Static magnetic fields enhancement of Saccharomyces cerevisae ethanolic fermentation. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajtos, M.; Radil, R.; Štefaňáková, M.; Janoušek, L.; Skurčák, Ľ. Bioimpact of Hypomagnetic Fields. Lékař A Tech.-Clin. Technol. 2024, 54, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchachenko, A.L.; Kuznetsov, D.A. Magnetic field affects enzymatic ATP synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12868–12869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, R.; Wu, L.; Wu, Y.; et al. Cellular ATP content was decreased by a homogeneous 8.5 T static magnetic field exposure: Role of reactive oxygen species. Bioelectromagnetics 2011, 32, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.W.; Wei, X.D.; Lu, L.L.; Jiang, J.L.; Liao, C.J.; Su, L. The effects of Static Magnetic Field in leaching Cadmium and Arsenic by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 675, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.G.; da Silva, M.T.; Dias, R.M.; Cardoso, V.L.; de Resende, M.M. Biolixiviation of metals from computer printed circuit boards by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and bioremoval of metals by mixed culture subjected to a magnetic field. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yan, L.; Xing, W.J.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.D. Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its potential application. Extremophiles 2018, 22, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Yang, J.; Zhang, G.; Lu, D.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Yan, L. Potential and whole-genome sequence-based mechanism of elongated-prismatic magnetite magnetosome formation in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans BYM. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, A.; Valenzuela, L.; Beard, S.; Mackey, A.J.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F.; Jerez, C.A. Periplasmic proteins of the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans: A high throughput proteomics analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisescu, C.; Ardelean, I.I.; Benning, L.G. The effect and role of environmental conditions on magnetosome synthesis. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadeh-Haghighi, H.; Simon, C. Magnetic field effects in biology from the perspective of the radical pair mechanism. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Tang, X.; Du, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, N.; Wu, Q.; Wei, W.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Ma, B.; et al. Optical/electrochemical methods for detecting mitochondrial energy metabolism. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 71–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, E.D. The Lactobacillus anomaly: Total iron abstinence. Perspect. Biol. Med. 1997, 40, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macklaim, J.M.; Gloor, G.B.; Anukam, K.C.; Cribby, S.; Reid, G. At the crossroads of vaginal health and disease, the genome sequence of Lactobacillus iners AB-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4688–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Pan, Y.; Guo, W.; Tian, L.; Zhan, A. Long-term exposure to a hypomagnetic field attenuates adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognition. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, O.; Ilyin, V.; Skedina, M.; Morozova, Y.; Artamonov, A.; Plotnikov, E.; Vladimirov, S. Prognostic model for bacterial drug resistance genes horizontal spread in space-crews. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 190, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlakova-Kadukova, J. Microorganisms in metal recovery—Tools or teachers? In Microbial Syntrophy-Mediated Eco-Enterprising; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biz, A.; Mahadevan, R. Overcoming challenges in expressing iron–sulfur enzymes in yeast. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| pH | Redox Potential (mV) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Hypomagnetic Field | Control | Hypomagnetic Field | |
| S. cerevisiae | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 92.3 ± 1.5 | 100.3 ± 1.2 |
| A. ferrooxidans | 2.3 ± 0.05 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 421.2 ± 3.1 | 408.0 ± 4.2 |
| L. plantarum | 3.8 ± 0.15 | 3.8 ± 0.1 | 101.9 ± 1.8 | 99.4 ± 2.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sincak, M.; Benediktová, K.; Adámková, J.; Sedlakova-Kadukova, J. Hypomagnetic Field and Its Effect on the Growth and Survival of Microorganisms. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061362
Sincak M, Benediktová K, Adámková J, Sedlakova-Kadukova J. Hypomagnetic Field and Its Effect on the Growth and Survival of Microorganisms. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061362
Chicago/Turabian StyleSincak, Miroslava, Kateřina Benediktová, Jana Adámková, and Jana Sedlakova-Kadukova. 2025. "Hypomagnetic Field and Its Effect on the Growth and Survival of Microorganisms" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061362
APA StyleSincak, M., Benediktová, K., Adámková, J., & Sedlakova-Kadukova, J. (2025). Hypomagnetic Field and Its Effect on the Growth and Survival of Microorganisms. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061362







