The Isolation and Construction of an Infectious Clone for a Duck Adenovirus Type 3 Strain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Plasmids, and Reagents
2.2. (RT)-PCR Detection for Common Duck Viruses
2.3. Virus Isolation and Viral Amplification
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
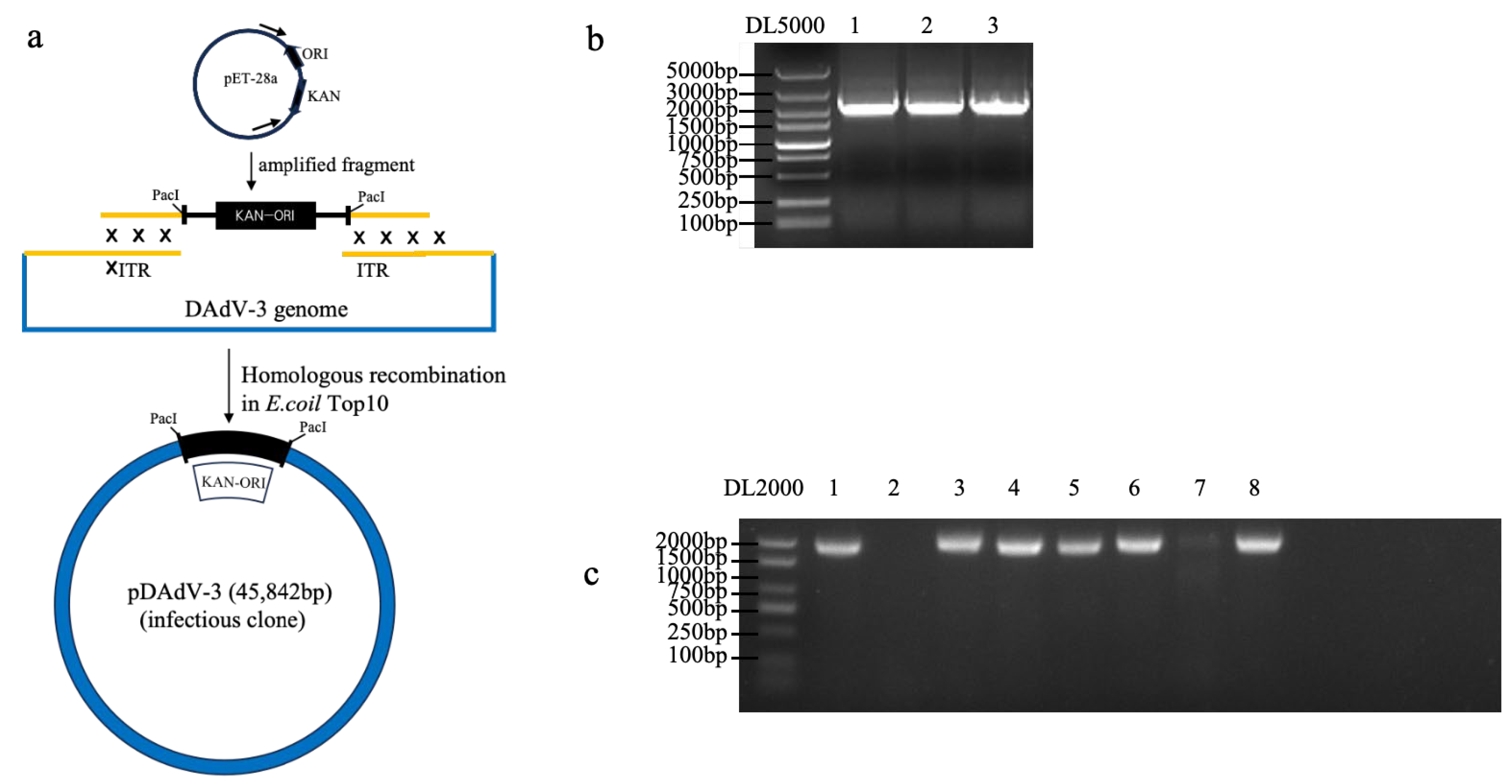
2.5. Construction of DAdV-3 Infectious Clone
2.6. Virus Rescue
2.7. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
2.8. Viral Growth Kinetics
2.9. Virus Titration
2.10. Duck Experiments
2.11. The qPCR Assay
2.12. Antibody Detection
2.13. Ethics Statement and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
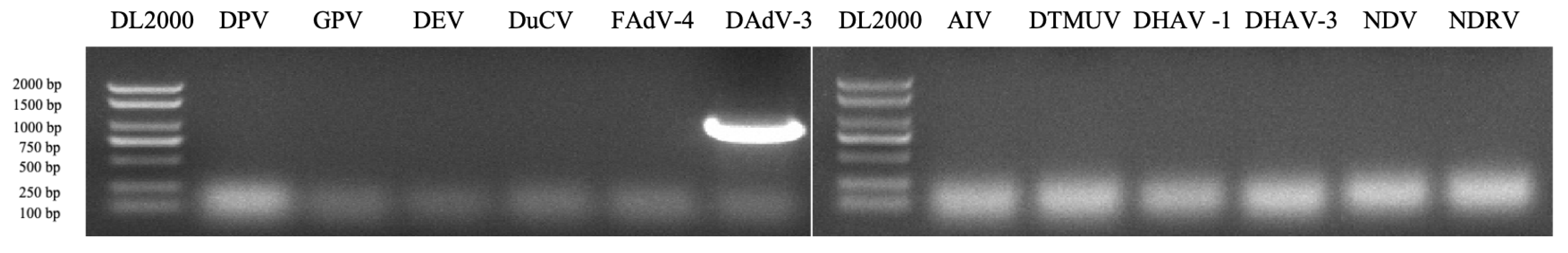
3.1. Virus Isolation and Identification
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Generation of DAdV-3 Infectious Clone
3.4. Virus Rescue
3.5. Growth Curves of rSD2019 and wtSD2019 in LMH Cells
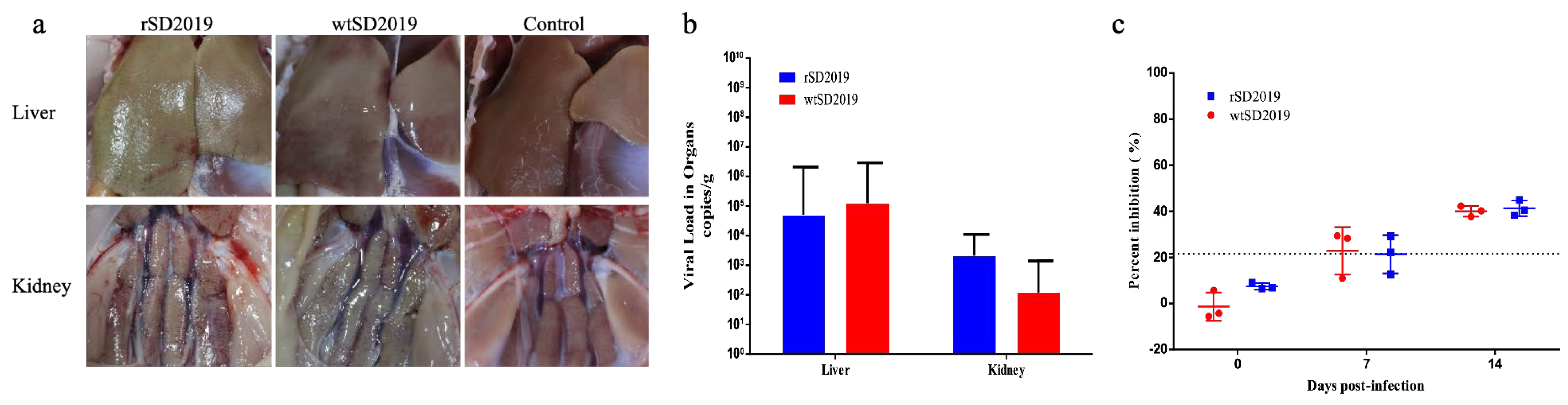
3.6. Pathogenicity of rSD2019 and wtSD2019 in Muscovy Ducks
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greber, U.F. Adenoviruses—Infection, pathogenesis and therapy. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, S.Y.; Kang, M.; Moon, O.K.; Park, C.K.; Jang, H.K. Respiratory disease due to current egg drop syndrome virus in Pekin ducks. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eck, J.H.; Davelaar, F.G.; Heuvel-Plesman, T.A.; Van Kol, N.; Kouwenhoven, B.; Guldie, F.H. Dropped egg production, soft shelled and shell-less eggs associated with appearance of precipitins to adenovirus in flocks of laying fowls. Avian Pathol. 1976, 5, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Raheem, M.A.; Xin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, X.; Dai, Y.; Ataya, F.S.; Chen, F. Isolation, characterization, evaluation of pathogenicity, and immunomodulation through interferon production of duck adenovirus type-3 (DAdV-3). Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Kang, H.; Dong, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, M. Isolation and partial genetic characterization of a new duck adenovirus in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 247, 108775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; Chen, W.; Xie, Q. Molecular characterization, phylogeny analysis and pathogenicity of a Muscovy duck adenovirus strain isolated in China in 2014. Virology 2016, 493, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Liu, R.; Wan, C.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Fu, G.; Chen, H.; Fu, Q.; Huang, Y. Isolation and characterization of duck adenovirus 3 circulating in China. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Wei, C.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H. Isolation and pathogenic characterization of duck adenovirus 3 mutant circulating in China. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhou, Q.; Mai, K.; Yan, Z.; Shen, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Q. Epidemiological investigation of duck adenovirus 3 in southern China, during 2018–2020. Avian Pathol. 2022, 51, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Chen, C.; Cheng, L.; Fu, G.; Shi, S.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.; Fu, Q.; Huang, Y. Development of a TaqMan-based real-time PCR for detecting duck adenovirus 3. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 261, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, A.; Eterradossi, N.; Delmas, B.; Payet, V.; Langlois, P. Construction of avian adenovirus CELO recombinants in cosmids. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5288–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Kong, J.; Shen, Y.; He, J.; Shao, G.; Feng, K.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, X. Construction and immune evaluation of the recombinant duck adenovirus type 3 delivering capsid protein VP1 of the type 1 duck hepatitis virus. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Corredor, J.C.; Griffin, B.D.; Krell, P.J.; Nagy, É. Fowl Adenovirus 4 (FAdV-4)-Based Infectious Clone for Vaccine Vector Development and Viral Gene Function Studies. Viruses 2018, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, A.; Cui, H.; Gao, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Gao, L.; et al. Development of a Novel Avian Vaccine Vector Derived from the Emerging Fowl Adenovirus 4. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 780978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Feng, D.; Fan, W.; Yan, L.; Song, S. Generation of an artificially attenuated fowl adenovirus 4 viral vector using the reverse genetics system based on full-length infectious clone. Vet. Res. 2025, 56, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.A.; Pooley, C.; Ignjatovic, J.; Tyack, S.G. A recombinant fowl adenovirus expressing the S1 gene of infectious bronchitis virus protects against challenge with infectious bronchitis virus. Vaccine 2003, 21, 2730–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Griffin, B.; de Jong, J.; Krell, P.J.; Nagy, É. Rapid generation of fowl adenovirus 9 vectors. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 223, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, G.; Teng, Q.; Yu, L.; Wu, X.; Li, Z. Development of a blocking ELISA for detection of serum neutralizing antibodies against newly emerged duck Tembusu virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e53026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M. Detection and differentiation of avian adenoviruses: A review. Avian Pathol. 2000, 29, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou, A.I.; Lehrmann, H.; Saltik, M.; Cotten, M. Mutational analysis of the avian adenovirus CELO, which provides a basis for gene delivery vectors. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Gao, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Gao, L.; et al. A Single Amino Acid at Residue 188 of the Hexon Protein Is Responsible for the Pathogenicity of the Emerging Novel Virus Fowl Adenovirus 4. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0060321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Tian, K.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Gao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J. Fiber2 and hexon genes are closely associated with the virulence of the emerging and highly pathogenic fowl adenovirus 4. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L. Intra-Molecular Homologous Recombination of Scarless Plasmid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Fan, Z.; Wan, Z.; Tian, X.; Chen, H.; Perez, D.R.; Qin, A.; Ye, J. An efficient and rapid influenza gene cloning strategy for reverse genetics system. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 222, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer Name | Sequence (5′→3′) | Target Gene | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAdV-3-F | GTACCGCCTTCGAGAACACA | Fiber 1 | 1014 bp |
| DAdV-3-1014R | GCTGTCTGATTCTGGTGATC | ||
| DPV-REP-F | CAAACGGGGAGGGCAAAATAAGA | VP 2 | 600 bp |
| DPV-REP-600R | GTGGTCGCAGGTCCGTAGAGC | ||
| GPV-F | CCAAGCTACAACAACCACATCTAC | VP 1 | 375 bp |
| GPV-375R | CTGCGGCAGGGCATAGACATCCGAC | ||
| DEV-F | GGACAGCGTACCACAGATAA | UL30 | 520 bp |
| DEV-520R | ACAAATCCCAAGCGTAG | ||
| DuCV-F | CGGCGCTTGTACTCCGTACTC | Rep | 619 bp |
| DuCV-619R | CCCGCGTGGTTTGTAATACTTG | ||
| FAdV-4-F | CAACTACATCGGGTTCAGGGATAACTTC | Hexon | 667 bp |
| FAdV-4-667R | CCAGTTTCTGTGGTGGTTGAAGGGGTT | ||
| AIV-F | TTCTAACCGAGGTCGAAAC | M | 229 bp |
| AIV-229R | AAGCGTCTACGCTGCAGTCC | ||
| DTMUV-F | CATAGGCTGGAATCTGGGAAC | E | 300 bp |
| DTMUV-300R | TCTGGATTCTGTCGTCACGTC | ||
| DHAV-1-F | CAGTTTACCGCCCCACTCTAT | VP 1 | 699 bp |
| DHAV-1-699R | TGGCTTCCACCTCCTCTTCAT | ||
| DHAV-3-F | GAAATCTGCACTCAATGGAGAG | VP 1 | 286 bp |
| DHAV-3-286R | CCCAGGAAATGATTGGTCAG | ||
| NDV-F | TGTAGTAACGGGAGACAAAGCAG | F | 350 bp |
| NDV-350R | GAATAAATACCAGGAGACATAGGGA | ||
| NDRV-F | GCATGAACATGCCAGTTGAG | S1 | 300 bp |
| NDRV-300R | AAGCCATAACGATGGCAGTC | ||
| DAdV-3-PacI-F | CAATTTACCGATGGTATATATATGATGATGTTAATTAATTTCCATAGGCTCCGC | 2200 bp | |
| DAdV-3-PacI-2000R | CAATTTACCGATGGTATATATATGATGATGTTAATTAAACGCGCCCTGTAGCGG | ||
| pDAdV-3 Kana F | AGCGTGGCGCTTTCTCATAG | 1800 bp | |
| pDAdV-3 Kana R | CTTTCGCTTTCTTCCCTTCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, H.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Yuan, C.; Pan, X.; Liu, Q.; Teng, Q.; Xu, B.; Yan, M.; et al. The Isolation and Construction of an Infectious Clone for a Duck Adenovirus Type 3 Strain. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061319
Lu H, Tang M, Zhang Z, Wu M, Yuan C, Pan X, Liu Q, Teng Q, Xu B, Yan M, et al. The Isolation and Construction of an Infectious Clone for a Duck Adenovirus Type 3 Strain. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061319
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Haipeng, Mei Tang, Zhifei Zhang, Mi Wu, Chunxiu Yuan, Xue Pan, Qinfang Liu, Qiaoyang Teng, Bangfeng Xu, Minghao Yan, and et al. 2025. "The Isolation and Construction of an Infectious Clone for a Duck Adenovirus Type 3 Strain" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061319
APA StyleLu, H., Tang, M., Zhang, Z., Wu, M., Yuan, C., Pan, X., Liu, Q., Teng, Q., Xu, B., Yan, M., Yan, D., Wang, F., & Li, Z. (2025). The Isolation and Construction of an Infectious Clone for a Duck Adenovirus Type 3 Strain. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061319








