Profiling of Bacterial Communities of Hospital Wastewater Reveals Clinically Relevant Genera and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Consumption and HWW Discharge Points of HJM
2.2. HWW Sample Collection and In Situ Temperature Determination
2.3. Determination of Physicochemical Parameters of HWW
2.4. Metagenomic DNA Extraction and Quality Control
2.5. Targeted Amplicon Sequencing (V3-V4 Hypervariable Region) with the Illumina Platform
2.6. Quality Control of Sequencing Data
2.7. Assignment of Taxonomic Levels and Relative Abundance
2.8. Diversity Analysis
2.9. Influence of Physicochemical Factors on Bacterial Communities in HWW
2.10. Detection of Carbapenems and Polymyxin Resistance Genes
3. Results
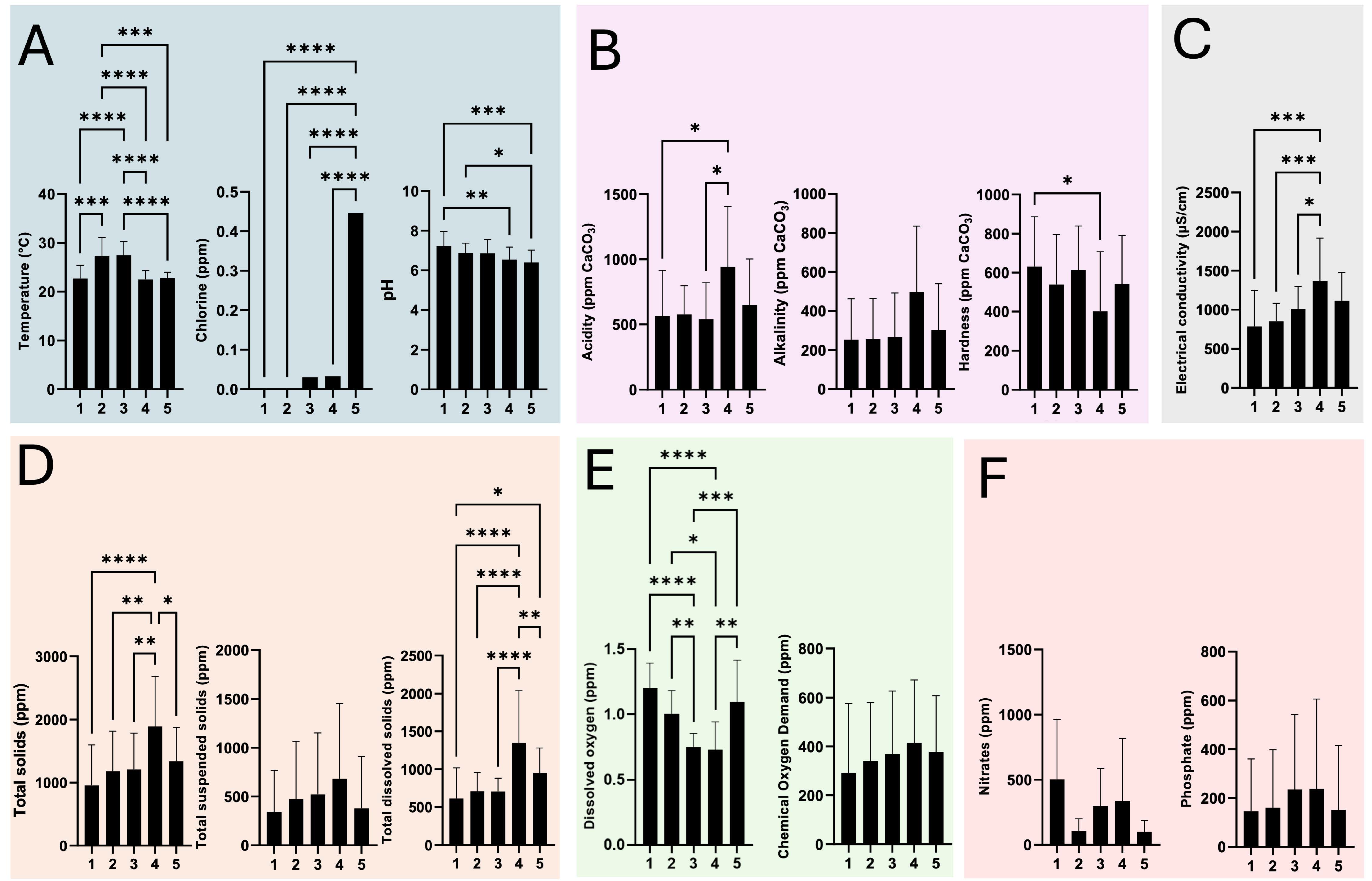
3.1. Evaluation of Physicochemical Parameters of HWW
3.2. Quality Control and Error Models in Sequencing Data
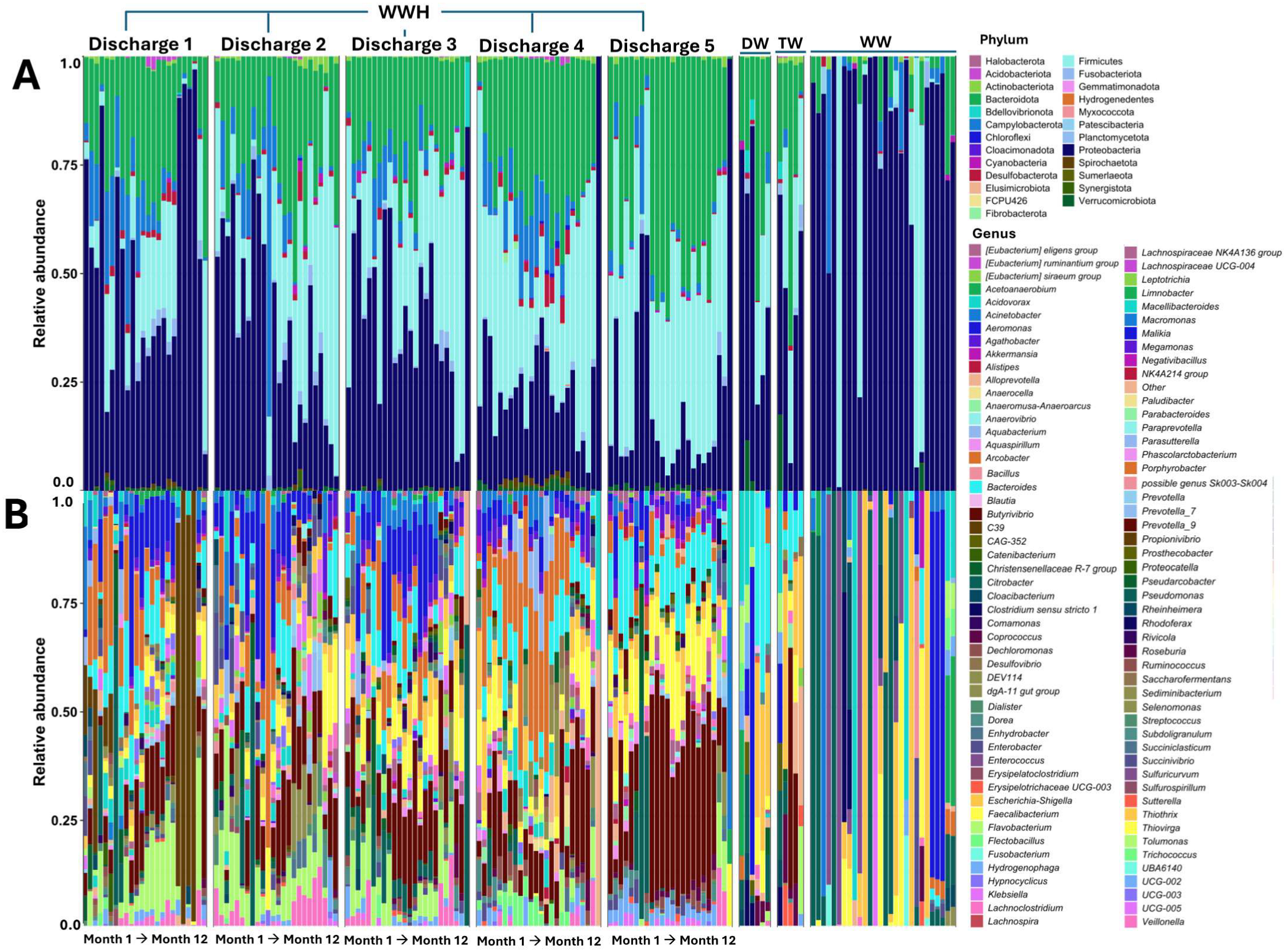
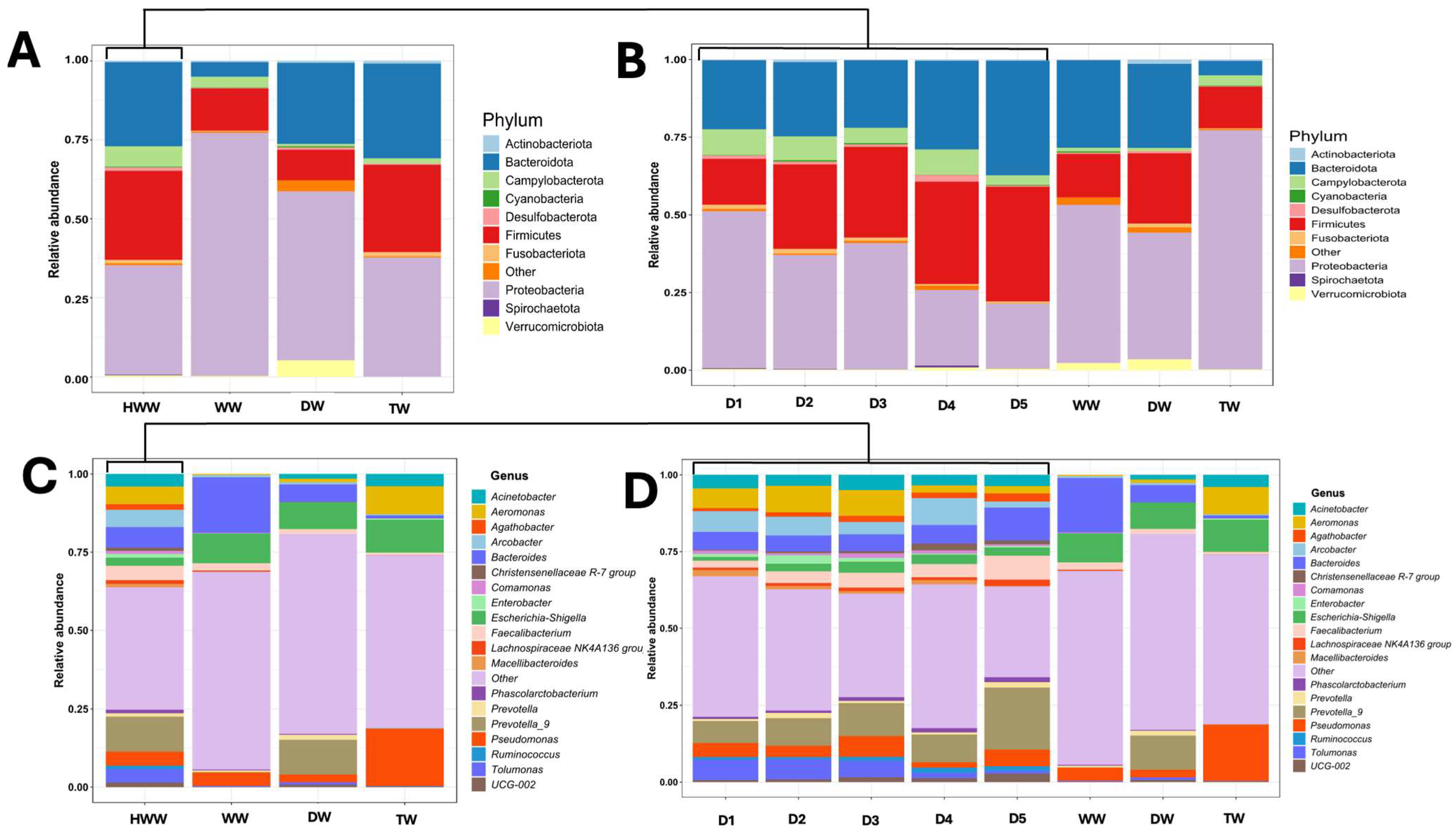
3.3. Characteristics of the Bacterial Communities of the HWW, DW, TW, and WW
3.4. The Taxonomic Diversity in HWW Reveals Clinically Relevant Bacteria
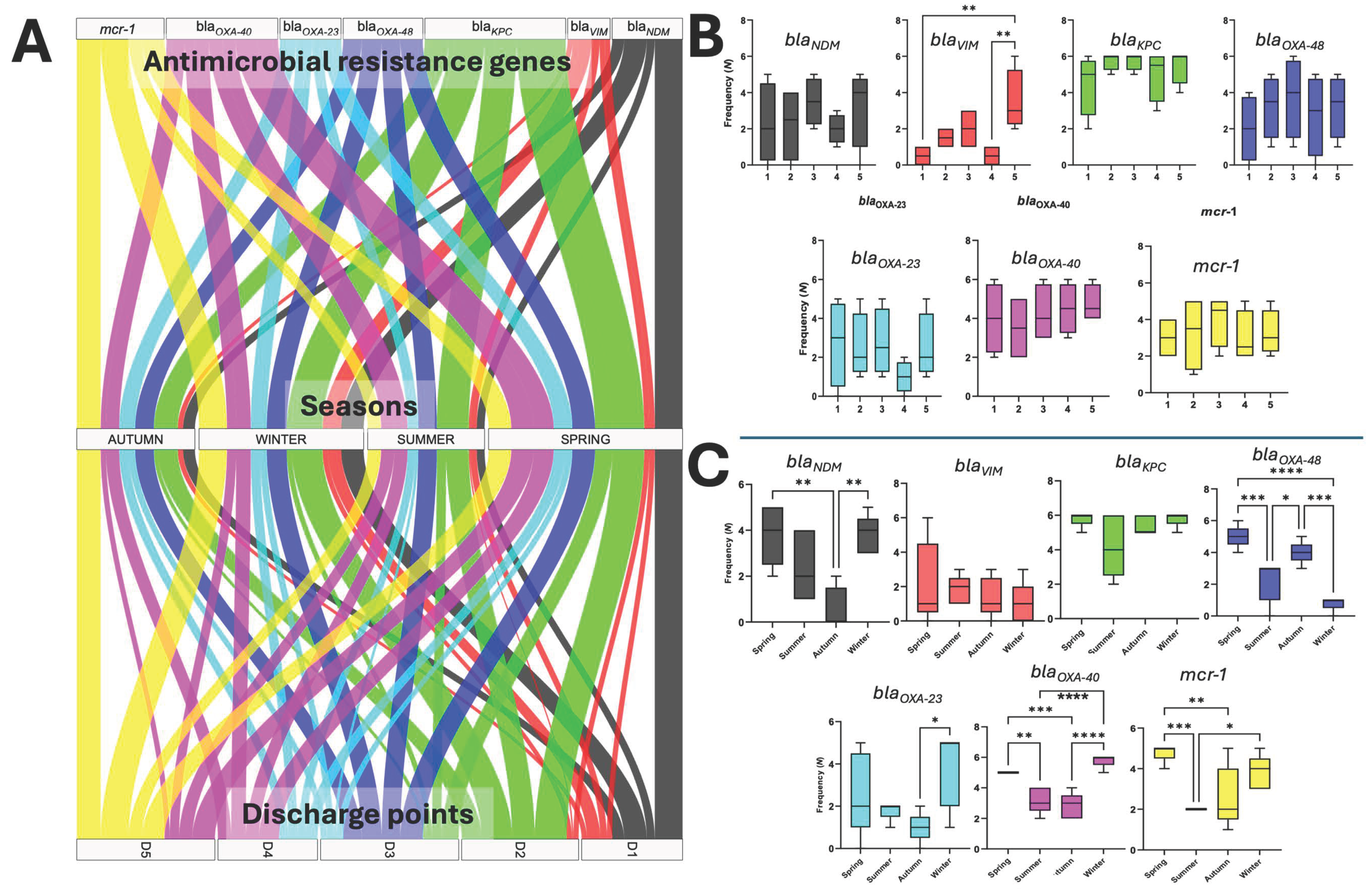
3.5. Seasonal Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in HWW
3.6. Taxonomic Diversity and Average Relative Abundance of HWW, DW, TW, and WW
3.7. Alpha Diversity
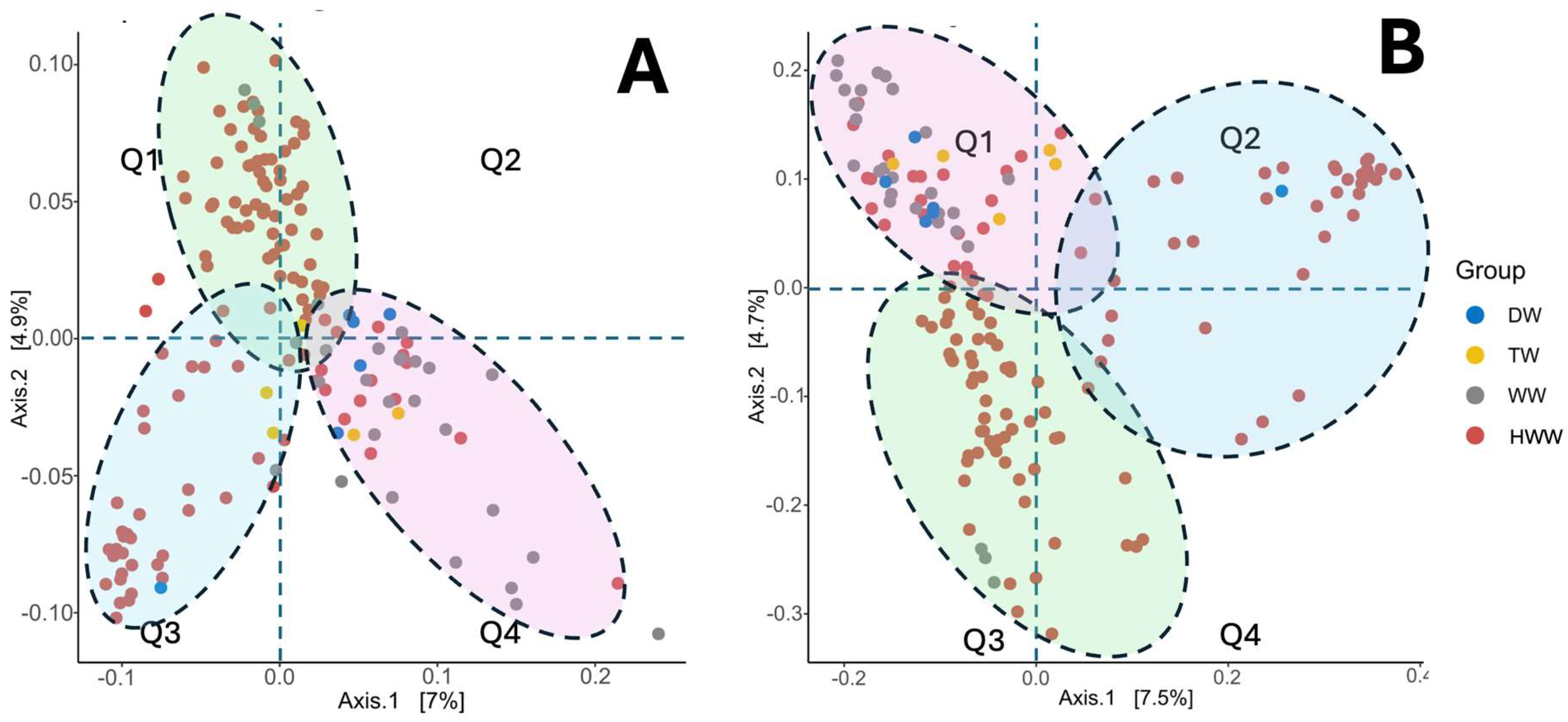
3.8. Beta Diversity
3.9. Influence of Physicochemical Factors on Bacterial Communities in HWW
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González, A.G.; García-Sanz-Calcedo, J.; Salgado, D.R.; Mena, A.A. Quantitative Analysis of Cold Water for Human Consumption in Hospitals in Spain. J. Healthc. Eng. 2016, 1, 6534823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Maraver, F.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Sáenz de Pipaon, M.; Vitoria, I.; Moreno, L.A. Importancia del consumo de agua en la salud y la prevención de la enfermedad: Situación actual. Nutr. Hosp. 2020, 37, 1072–1086. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hocaoglu, S.M.; Celebi, M.D.; Basturk, I.; Partal, R. Treatment-based hospital wastewater characterization and fractionation of pollutants. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, E.; Durán, J. WASH PRESS-Soluciones de Agua, Saneamiento e Higiene y Medidas de Prevención y Control de Infecciones Para la Preparación y Respuesta de los Establecimientos de Salud en Casos de Emergencias de Salud y Desastres; Pan American Health Organization: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 1–302. [Google Scholar]
- Sistema de Aguas de la Ciudad de México (SACMEX). Informe de Gestión Hídrica 2020–2021. Gobierno de la Ciudad de México. Available online: https://www.sacmex.cdmx.gob.mx/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Galarde-López, M.; Velazquez-Meza, M.E.; Bobadilla-Del-Valle, M.; Carrillo-Quiroz, B.A.; Cornejo-Juárez, P.; Ponce-de-León, A.; Sassoé-González, A.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M. Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Hospital Wastewater: Identification of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella spp. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urzua-Abad, M.M.; Aquino-Andrade, A.; Castelan-Vega, J.A.; Merida-Vieyra, J.; Ribas-Aparicio, R.M.; Belmont-Monroy, L.; Jimenez-Alberto, A.; Aparicio-Ozores, G. Detection of carbapenemases in Enterobacterales and other Gram-negative bacilli recovered from hospital and municipal wastewater in Mexico City. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, E.; Pierre, M.G.; Perrodin, Y. Groundwater contamination by microbiological and chemical substances released from hospital wastewater: Health risk assessment for drinking water consumers. Environ. Internat. 2009, 35, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, K.; Mahapatra, S.; Ali, M.H. Pharmaceutical wastewater as Emerging Contaminants (EC): Treatment technologies, impact on environment and human health. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Vambol, V.; Vambol, S.; Bolibrukh, B.; Sillanpaa, M.; Changani, F.; Yousefi, M. Hospital effluent guidelines and legislation scenario around the globe: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahrich, S.; Laghrib, F.; Farahi, A.; Bakasse, M.; Saqrane, S.; El Mhammedi, M.A. Review on the contamination of wastewater by COVID-19 virus: Impact and treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 142325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Ghosal, P.S.; Varma, M. A review on hospital wastewater treatment: A special emphasis on occurrence and removal of pharmaceutically active compounds, resistant microorganisms, and SARS-CoV-2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, V.K.; Sikarwar, D.; Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K. An assessment of hospital wastewater and biomedical waste generation, existing legislations, risk assessment, treatment processes, and scenario during COVID-19. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galarde-López, M.; Velazquez-Meza, M.E.; Godoy-Lozano, E.E.; Carrillo-Quiroz, B.A.; Cornejo-Juárez, P.; Sassoé-González, A.; Ponce-de-León, A.; Saturno-Hernández, P.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M. Presence and Persistence of ESKAPEE Bacteria before and after Hospital Wastewater Treatment. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Meza, M.E.; Galarde-López, M.; Cornejo-Juárez, P.; Carrillo-Quiroz, B.A.; Velázquez-Acosta, C.; Bobadilla-Del-Valle, M.; Ponce-de-León, A.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M. Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus sp. and Enterococcus sp. in Municipal and Hospital Wastewater: A Longitudinal Study. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siri, Y.; Bumyut, A.; Precha, N.; Sirikanchana, K.; Haramoto, E.; Makkaew, P. Multidrug antibiotic resistance in hospital wastewater as a reflection of antibiotic prescription and infection cases. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-003-1980. Aguas Residuales-Muestreo. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 1980. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-003-1980/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-007-SCFI-2013. Medición de la Temperatura en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas–Método de Prueba. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2013. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-007-scfi-2013/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Nolasco-Rojas, A.E.; Cruz-Del-Agua, E.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Ayil-Gutiérrez, B.A.; Tamayo-Ordóñez, M.C.; Tamayo-Ordoñez, Y.d.J.; Rojas-Bernabé, A.; Tamayo-Ordoñez, F.A.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; et al. Microbiological Risks to Health Associated with the Release of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and β-Lactam Antibiotics Through Hospital Wastewater. Pathogens 2025, 14, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-008-SCFI-2016. Análisis de Agua-Medición del pH en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. Método de Prueba. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2016. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-008-scfi-2016/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-108-SCFI-2001a. Método Para la Determinación de Cloro Libre y Cloro Total en Aguas Naturales y Residuales. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2001. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-108-scfi-2001/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-036-SCFI-2001. Análisis de Agua—Determinación de Acidez y Alcalinidad en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2001. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-036-scfi-2001/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-072-SCFI-2001. Análisis de Agua—Determinación de Dureza Total en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2001. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-072-scfi-2001/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-093-SCFI-2018. Análisis de Agua-Determinación de la Conductividad Electrolítica. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2000. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-093-scfi-2018/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-034-SCFI-2015. Análisis de Agua—Medición de Sólidos y Sales Disueltas en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2015. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-034-scfi-2015/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-012-SCFI-2001. Análisis de Agua—Determinación de Oxígeno Disuelto en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2001. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-012-scfi-2001/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-030-SCFI-2011. Análisis de Agua-Determinación de la Demanda Química de Oxígeno en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. -Método de Prueba- Parte 2—Determinación del Índice de la Demanda Química de Oxígeno—Método de Tubo Sellado a Pequeña Escala. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2011. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-030-2-scfi-2011/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-079-SCFI-2001. Análisis de Análisis de Aguas-Determinación de Nitratos en Aguas Naturales, Potables, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2001. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-079-scfi-2001/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana NMX-AA-029-SCFI-2001 Análisis de Aguas-Determinación de Fósforo Total en Aguas Naturales, Residuales y Residuales Tratadas. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial (SCFI). Secretaría de Economía. 2001. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-aa-029-scfi-2001/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Chung, M.; de Lencastre, H.; Matthews, P.; Tomasz, A.; Adamsson, I.; Aires de Sousa, M.; Camou, T.; Cocuzza, C.; Corso, A.; Couto, I.; et al. Multilaboratory Project Collaborators. Molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: Comparison of results obtained in a multilaboratory effort using identical protocols and MRSA strains. Microbe. Drug Resist. 2000, 6, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Brodie, E.L.; Moberg, J.P.; Zubieta, I.K.; Piceno, Y.M.; Andersen, G.L. High-density universal 16S rRNA microarray analysis reveals broader diversity than typical clone library when sampling the environment. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 53, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews Simon FASTQC. A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2020. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, P.S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, M.; Elli, T.; Caviglia, G.; Uboldi, G.; Azzi, M. RAWGraphs: RAWGraphs: A visualisation platform to create open outputs. In Proceedings of the 12th Biannual Conference on Italian SIGCHI, Chapter, Cagliari, Italy, 18–20 September 2017; Volume 28, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés-Ortíz, I.A.; Juárez-Gómez, J.C.; Cu-Quijano, C.; Flores-Paz, R.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Gutiérrez-Muñoz, V.H.; Sosa-Hernández, O.; Escobar-Escamilla, N.; Bravata-Alcántara, J.C.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae blaNDM-1 carrying a class 1 integron causing a hospital outbreak in a Mexican attention center. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyola-Cruz, M.A.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Márquez-Valdelamar, L.M.; Bravata-Alcántara, J.C.; Cortés-Ortíz, I.A.; Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Fernández-Sánchez, V.; Castro-Escarpulli, G.; et al. ESKAPE bacteria characterization reveals the presence of Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa outbreaks in COVID-19/VAP patients. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2013, 51, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Plascencia-Nieto, E.S.; Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Nolasco-Rojas, A.E.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Gómez-Zamora, E.; Tamayo-Ordóñez, M.C.; Tamayo-Ordóñez, Y.J.; et al. Gram-Negative ESKAPE Bacteria Surveillance in COVID-19 Pandemic Exposes High-Risk Sequence Types of Acinetobacter baumannii MDR in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Pathogens. 2024, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallenne, C.; Da Costa, A.; Decré, O.; Favier, C.; Arlet, G. Development of a set of multiplex PCR assays for the detection of genes encoding important β-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L.; Carrër, A.; Toleman, M.; Walsh, T. How to detect NDM-1 producers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 718–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Salazar, A.; Martínez-Vázquez, A.V.; Aguilera-Arreola, G.; de Jesus de Luna-Santillana, E.; Cruz-Hernández, M.A.; Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M.; Bocanegra-Garcia, V. Prevalence of ESKAPE bacteria in surface water and wastewater sources: Multidrug resistance and molecular characterization, an updated review. Water 2023, 15, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Bravata-Alcantará, J.C.; Sosa-Hernández, O.; Delgado-Balbuena, L.; León-García, G.; Cortés-Ortíz, I.A.; Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Castro-Escarpulli, G.; et al. Clonal dispersion of Acinetobacter baumannii in an intensive care unit designed to patients COVID-19. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Rojo-Gutiérrez, M.I.; Moncayo-Coello, C.V.; Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Castro-Escarpulli, G.; Hernández, D.M.R.B.; Bello-López, J.M. Impact of the modification of a cleaning and disinfection method of mechanical ventilators of COVID-19 patients and ventilator-associated pneumonia: One year of experience. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2021, 49, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Manuel, E.M.; Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Gaytán-Cervantes, J.; González-Torres, C.; Quiroga-Vargas, E.; Calzada-Mendoza, C.C.; Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Fernández-Sánchez, V.; et al. Massive sequencing of the V3-V4 hypervariable region of bronchoalveolar lavage from patients with COVID-19 and VAP reveals the collapse of the pulmonary microbiota. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 71, 001634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvarajan, R.; Sibanda, T.; Venkatachalam, S.; Kamika, I.; Nel, W.A. Industrial wastewaters harbor a unique diversity of bacterial communities revealed by high-throughput amplicon analysis. Ann. Microbiol. 2018, 6, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelow, E.; Rico, A.; Gaschet, M.; Lourenço, J.; Kennedy, S.P.; Wiest, L.; Ploy, M.C.; Dagot, C. Hospital discharges in urban sanitation systems: Long-term monitoring of wastewater resistome and microbiota in relationship to their eco-exposome. Water Res. X 2020, 7, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buelow, E.; Bayjanov, J.R.; Majoor, E.; Willems, R.J.; Bonten, M.J.; Schmitt, H.; van Schaik, W. Limited influence of hospital wastewater on the microbiome and resistome of wastewater in a community sewerage system. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelow, E.; Dauga, C.; Carrion, C.; Mathé-Hubert, H.; Achaibou, S.; Gaschet, M.; Jové, T.; Chesneau, O.; Kennedy, S.P.; Ploy, M.C.; et al. Hospital and urban wastewaters shape the matrix and active resistome of environmental biofilms. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, B.; Lourenço, A.B.; Monteiro, S.; Santos, R.; Cunha, M.V. Metagenomic profiling of raw wastewater in Portugal highlights microbiota and resistome signatures of public health interest beyond the usual suspects. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Meta-analysis addressing the characterization of antibiotic resistome in global hospital wastewater. J. Hazard Mater. 2024, 466, 133577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J.; Liang, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Cai, H.; Yao, S.; Chen, X.; Liang, B.; Gao, F.; Huang, Z.; et al. Fecal carriage and molecular epidemiology of mcr-1-harboring Escherichia coli from children in southern China. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Liu, M.; Katayama, H.; Takemura, T.; Kasuga, I. Association of the colistin resistance gene mcr-1 with faecal pollution in water environments in Hanoi, Vietnam. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Primer | Molecular Target | Sequence (5′→3′) | Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMP-F | blaIMP | TTGACACTCCATTTACDG | 139 | [43] |
| IMP-R | GATYGAGAATTAAGCCACYCT | |||
| VIM-F | blaVIM | GATGGTGTTTGGTCGCATA | 390 | |
| VIM-R | CGAATGCGCAGCACCAG | |||
| KPC-F | blaKPC | CATTCAAGGGCTTTCTTGCTGC | 538 | |
| KPC-R | ACGACGGCATAGTCATTTGC | |||
| OXA-48F | blaOXA-48 | GCACTTCTTTTGTGATGGC | 281 | |
| OXA-48R | GAGCACTTCTTTTGTGATGGC | |||
| SHV-F | blaSHV | AGCCGCTTGAGCAAATTAAAC | 713 | |
| SHV-R | ATCCCGCAGATAAATCACCAC | |||
| CTX-M-1-F | blaCTX | TTAGGAARTGTGCCGCTGYA | 688 | |
| CTX-M-1-R | CGATATCGTTGGTGGTRCCAT | |||
| NDM-F | blaNDM | GGTTTGGCGAT CTGGTTTTC | 621 | [44] |
| NDM-R | CGGAATGGCTCATCACGATC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz-Cruz, C.; Gaytán-Cervantes, J.; González-Torres, C.; Nolasco-Rojas, A.E.; Loyola-Cruz, M.Á.; Delgado-Balbuena, L.; Delgado-Balbuena, J.; Paredes-Mendoza, M.; Tamayo-Ordóñez, M.C.; Tamayo-Ordoñez, Y.d.J.; et al. Profiling of Bacterial Communities of Hospital Wastewater Reveals Clinically Relevant Genera and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061316
Cruz-Cruz C, Gaytán-Cervantes J, González-Torres C, Nolasco-Rojas AE, Loyola-Cruz MÁ, Delgado-Balbuena L, Delgado-Balbuena J, Paredes-Mendoza M, Tamayo-Ordóñez MC, Tamayo-Ordoñez YdJ, et al. Profiling of Bacterial Communities of Hospital Wastewater Reveals Clinically Relevant Genera and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061316
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz-Cruz, Clemente, Javier Gaytán-Cervantes, Carolina González-Torres, Andres Emmanuel Nolasco-Rojas, Miguel Ángel Loyola-Cruz, Laura Delgado-Balbuena, Josué Delgado-Balbuena, Marianela Paredes-Mendoza, María Concepción Tamayo-Ordóñez, Yahaira de Jesús Tamayo-Ordoñez, and et al. 2025. "Profiling of Bacterial Communities of Hospital Wastewater Reveals Clinically Relevant Genera and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061316
APA StyleCruz-Cruz, C., Gaytán-Cervantes, J., González-Torres, C., Nolasco-Rojas, A. E., Loyola-Cruz, M. Á., Delgado-Balbuena, L., Delgado-Balbuena, J., Paredes-Mendoza, M., Tamayo-Ordóñez, M. C., Tamayo-Ordoñez, Y. d. J., Durán-Manuel, E. M., Rojas-Bernabé, A., Jiménez-Zamarripa, C. A., Sosa-Hernández, O., García-Hernández, O. A., Ocharan-Hernández, E., Zárate-Segura, P. B., González-Terreros, E., Ramírez-Villanueva, D. A., ... Bello-López, J. M. (2025). Profiling of Bacterial Communities of Hospital Wastewater Reveals Clinically Relevant Genera and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061316












