The Aerobic Denitrification Characteristics of a Halophilic Marinobacter sp. Strain and Its Application in a Full-Scale Fly Ash-Washing Wastewater Treatment Plant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Screening and Isolation
2.2. Strain Morphology and Species Identification
2.3. Genomic Sequencing
2.4. Denitrification Characteristics of the Strain
2.5. Application in Full-Scale Fly Ash Leachate Treatment System
2.6. Analysis of the Microbial Community Structure
2.7. Data Processing Methods
3. Results
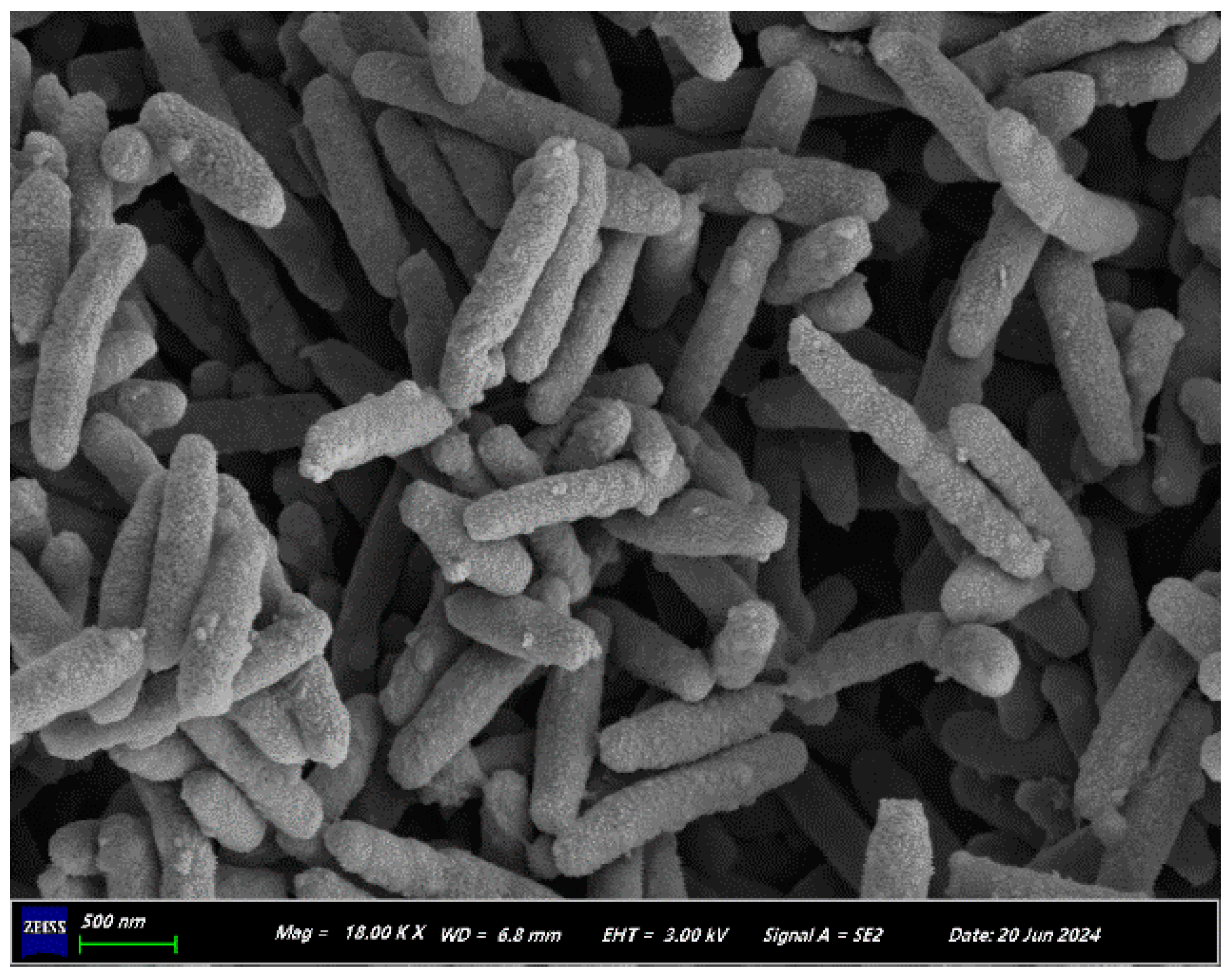
3.1. Strain Identification
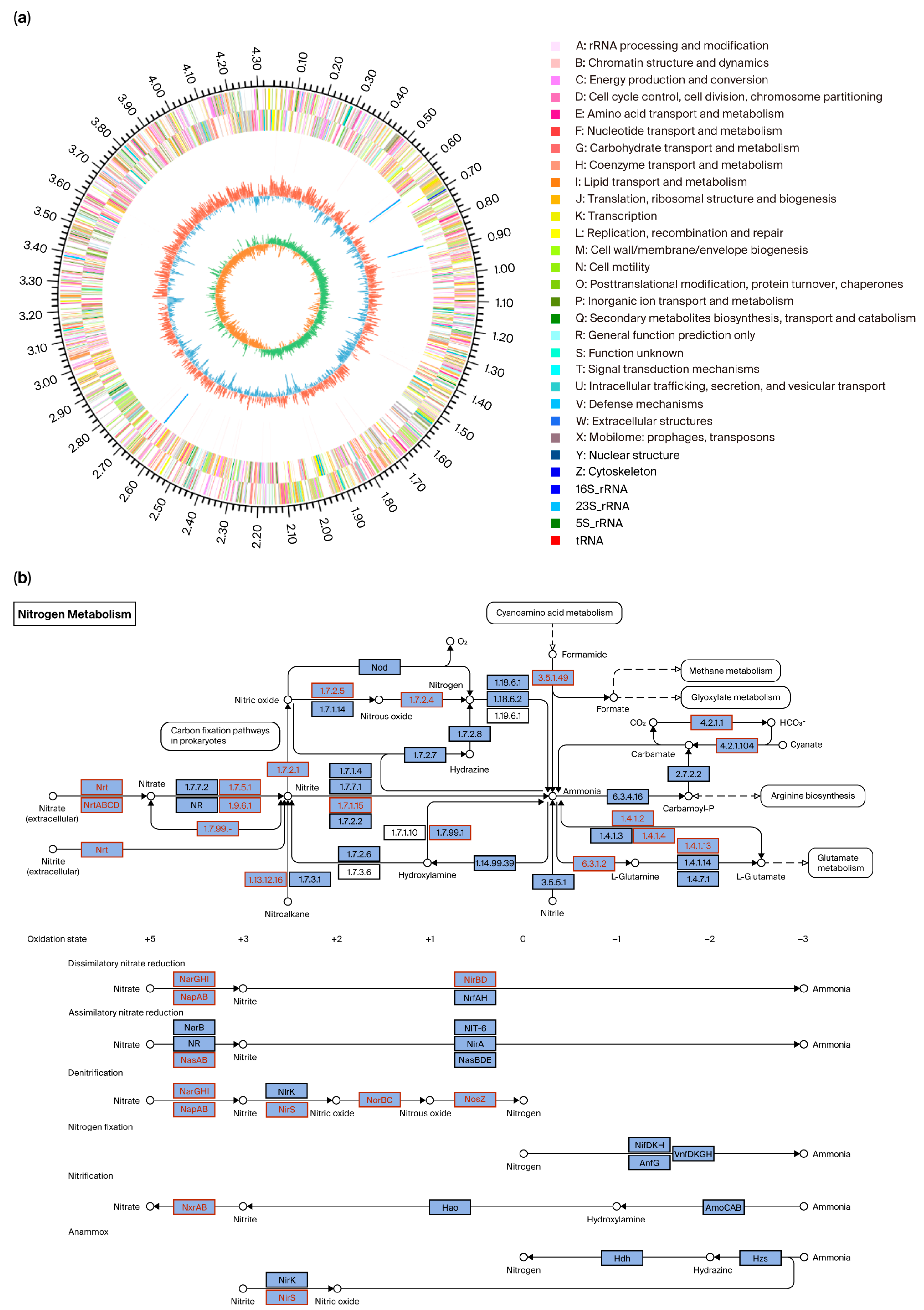
3.2. Whole-Genome Information and Functional Gene Annotation
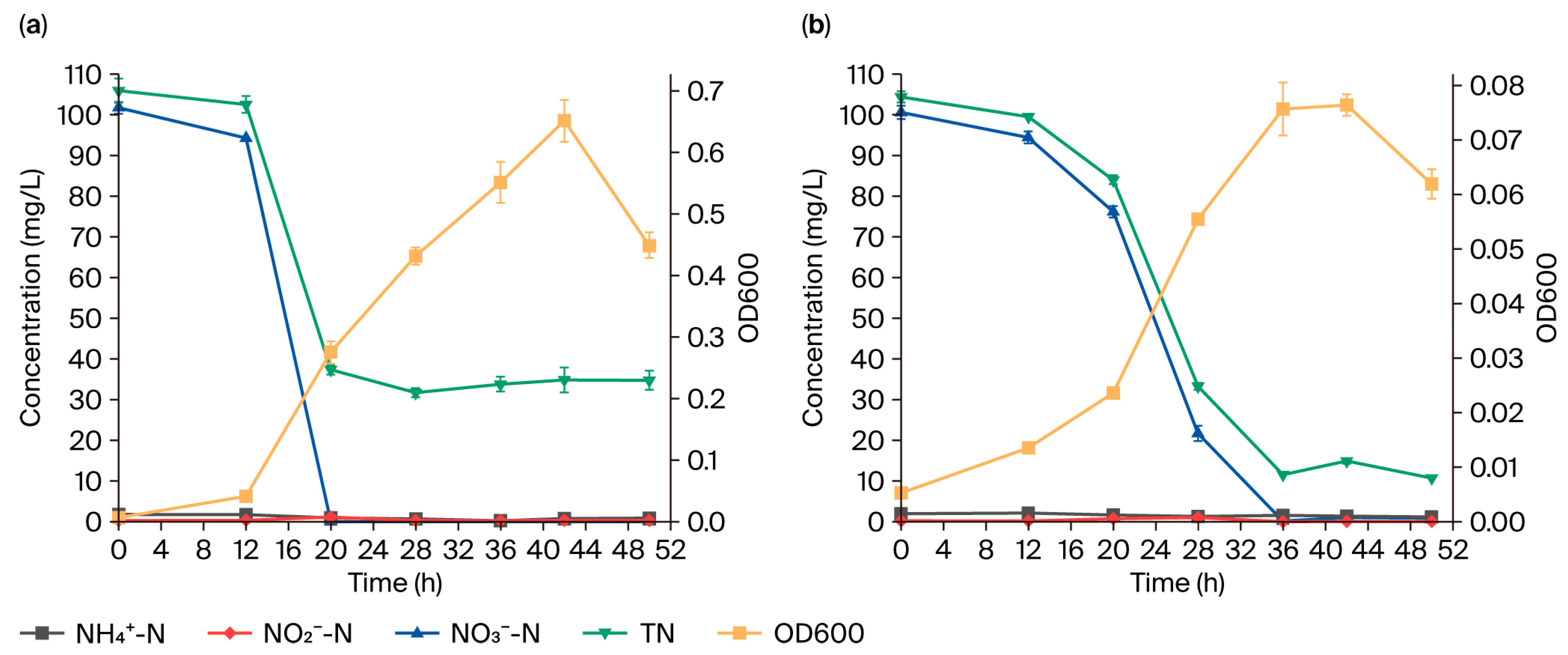
3.3. Oxygen and Salinity Effects on Nitrogen Removal Efficiency of Strain GH-1
3.3.1. Oxygen Effects
3.3.2. Salinity Effects
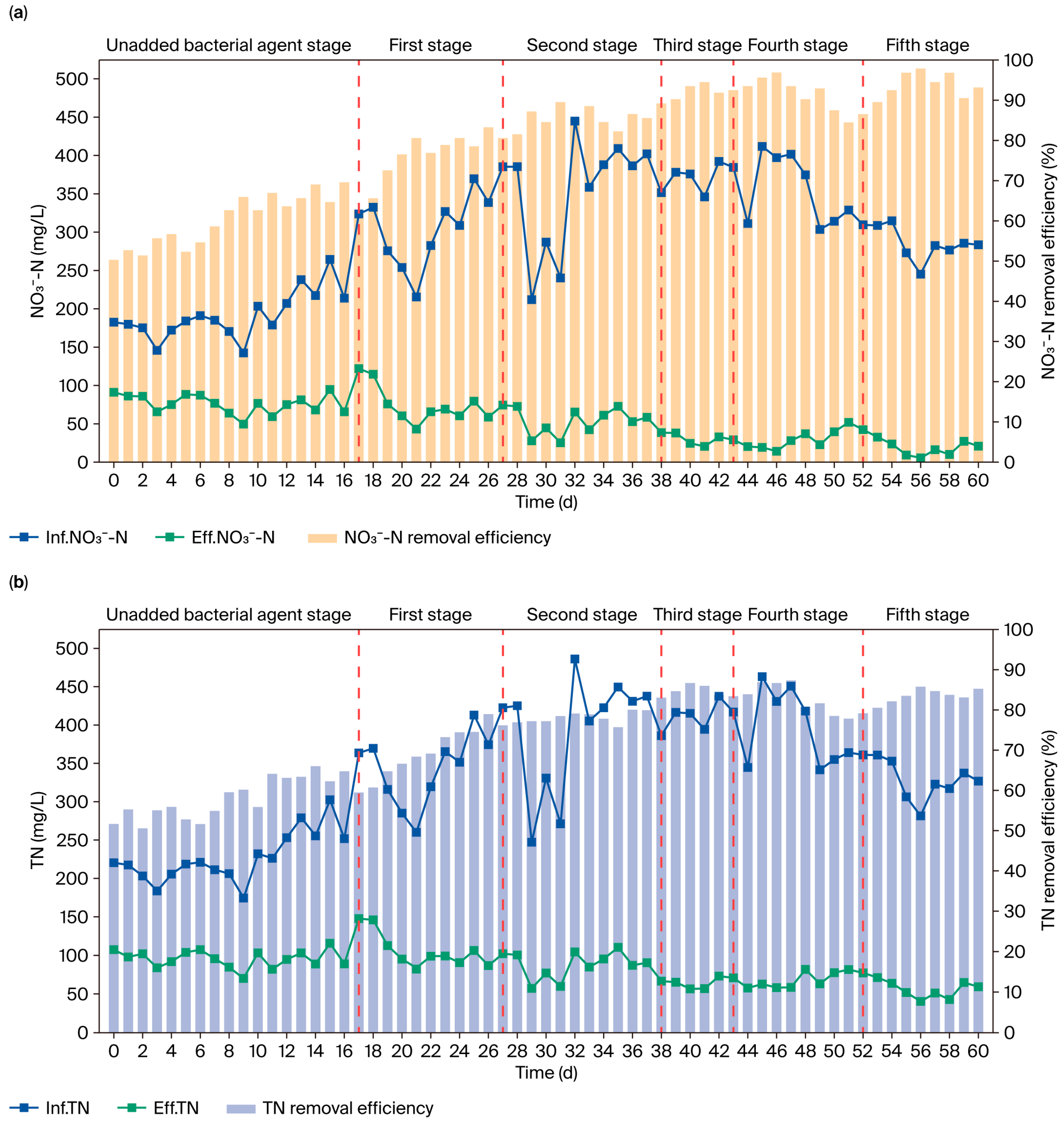
3.4. Bioaugmentation Effects of Strain GH-1 at Full Scale
3.4.1. Enhancement of Treatment Efficiency
3.4.2. Impact of Bioaugmentation on Microbial Community Structure
4. Discussion
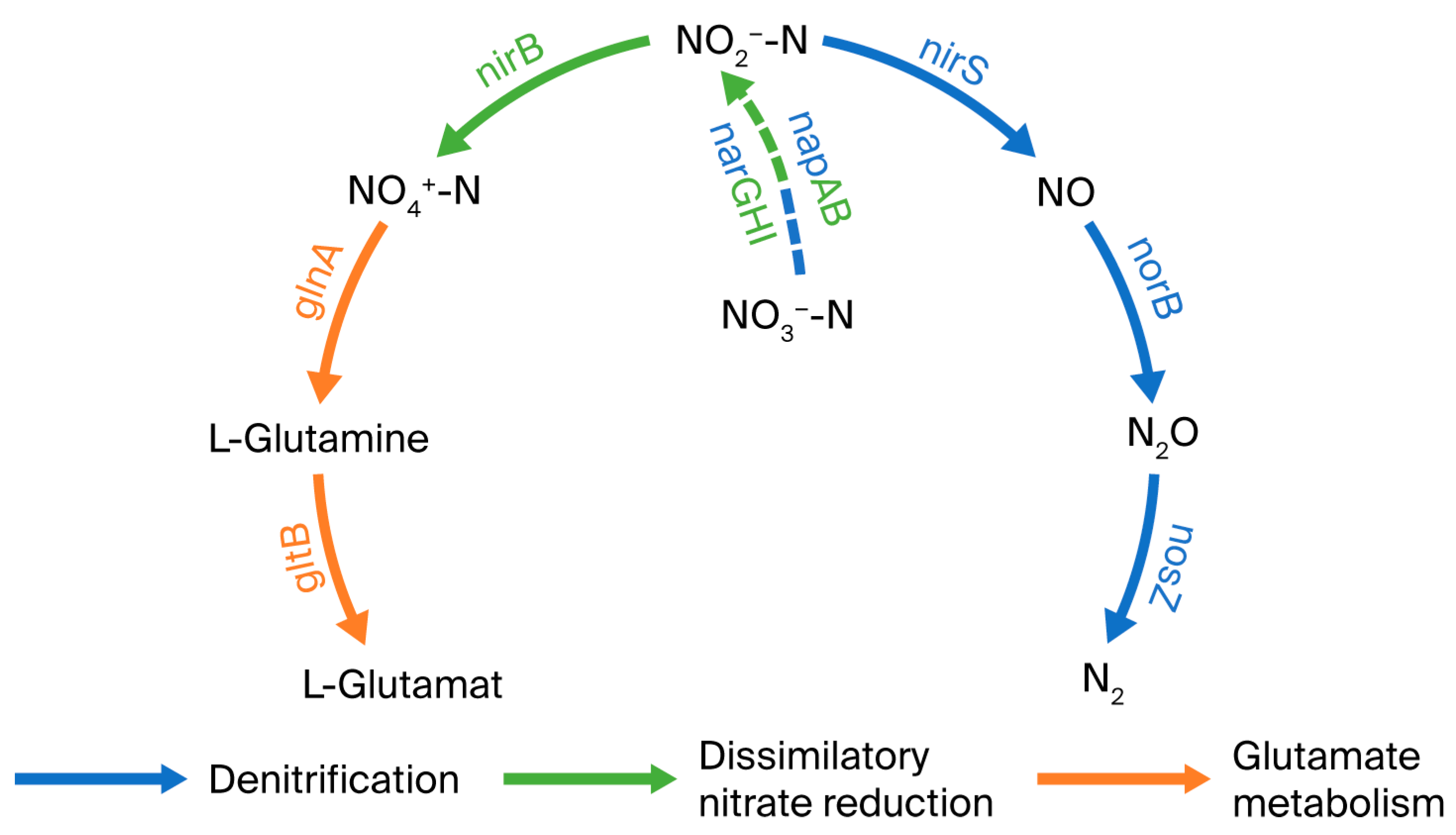
4.1. Nitrogen Metabolic Pathways and Halophilic Mechanisms of Strain GH-1
4.2. Impacts of Different Culture Conditions on Nitrogen Removal Efficiency of Strain GH-1
4.3. Bioaugmentation of Strain GH-1 in Full-Scale Systems and Microbial Community Dynamics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norgaard, K.P.; Hyks, J.; Mulvad, J.K.; Frederiksen, J.O.; Hjelmar, O. Optimizing large-scale ageing of municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash prior to the advanced metal recovery: Phase I: Monitoring of temperature, moisture content, and CO2 level. Waste Manag. 2019, 85, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, F.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ren, K.; Liu, S.J.; Ding, H. Analysis of composition characteristics and treatment techniques of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 357, 120783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Crespo, J.G.; Afonso, C.A.M. Dioxins sources and current remediation technologies—A review. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Inoue, K.; Harada, H.; Kawakita, H.; Ohto, K. Leaching behavior of heavy metals with hydrochloric acid from fly ash generated in municipal waste incineration plants. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L.; Yi, Y.L. Acid washing of incineration bottom ash of municipal solid waste: Effects of pH on removal and leaching of heavy metals. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.J.; Wu, G.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Tian, Z.J.; Li, B.; Cheng, J.M.; Yang, G.F. Improving denitrification performance of biofilm technology with salt-tolerant denitrifying bacteria agent for treating high-strength nitrate and sulfate wastewater from lab-scale to pilot-scale. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, M.R.; Liu, Z.; Shang, H.G.; Li, Q.; Zhou, W.Z. Dynamic characteristics of microbial community and soluble microbial products in partial nitrification biofilm system developed from marine sediments treating high salinity wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Lv, Y.K. Biological nitrogen removal characteristics and mechanisms of a novel salt-tolerant strain Vibrio sp. LV-Q1 and its application capacity for high-salinity nitrogen-containing wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 105098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ren, Y.X.; Liang, X.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wang, J.P.; Xia, Z.H. Nitrogen removal characteristics of a heterotrophic nitrifier Acinetobacter junii YB and its potential application for the treatment of high-strength nitrogenous wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.M.; Fang, H.D.; Su, B.; Chen, J.F.; Lin, J.M. Characterization of a halophilic heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium and its application on treatment of saline wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.P.; Zhao, L.; Huangshen, L.K.; Wu, J.F. Isolation and identification of a salt-tolerant aerobic denitrifying bacterial strain and its application to saline wastewater treatment in constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 290, 121725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, G.D.; Gao, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.L.; Liu, Z.P. Denitrification characteristics of a marine origin psychrophilic aerobic denitrifying bacterium. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Shi, Q.; Hou, B.X.; Yang, Q.B. Identification of bacteria associated with periapical abscesses of primary teeth by sequence analysis of 16S rDNA clone libraries. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 141, 103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilcreas, F.W. Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1966, 56, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, D.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Jin, Y.P.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Q.X. Intra-tumoral microbial community profiling and associated metabolites alterations of TNBC. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1143163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Che, H.; Cui, H.; Zhang, Y. Elemental sulfur-driven autotrophic denitrification process for effective removal of nitrate in mariculture wastewater: Performance, kinetics and microbial community. Chemosphere 2023, 337, 139354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Tang, T.; Liu, L. Nitrogen removal characteristics and mechanism of the aerobic denitrifying bacterium Stutzerimonas stutzeri os3 isolated from shrimp aquaculture sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 214, 117711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Goebel, B.M. Taxonomic Note: A Place for DNA-DNA Reassociation and 16S rRNA Sequence Analysis in the Present Species Definition in Bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1994, 44, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, S.; Terada, A. Complete genome sequence of Marinobacter shengliensis D49 harboring ectABC genes for ectoine synthesis. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2023, 12, e00414-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkassas, S.M.; Serres, M.H.; Navarro, M.; Patterson, A.; Zhivkova, T.; Petersen, M.; Weeks, K.; Lang, S.; Seewald, J.; Wheat, G.; et al. Draft genome sequences of six high pH adapted Marinobacter shengliensis strains isolated from Mariana forearc serpentinite mud volcanoes. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2025, 14, e01045-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.L.; Jiang, J.S.; Liu, S.; Yin, M.Y.; Yang, M.Y.; Zhang, X.Q. Performance and mechanism of nitrate removal by the aerobic denitrifying bacterium JI-2 with a strong autoaggregation capacity. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 365, 128111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, L.C.; Richardson, D.J.; Ferguson, S.J. Periplasmic and membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductases in Thiosphaera pantotropha. The periplasmic enzyme catalyzes the first step in aerobic denitrification. FEBS Lett. 1990, 265, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braker, G.; Zhou, J.; Wu, L.; Devol, A.H.; Tiedje, J.M. Nitrite reductase genes (nirK and nirS) as functional markers to investigate diversity of denitrifying bacteria in pacific northwest marine sediment communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubrie, A.; Gemeinhardt, S.; Field, S.; Marritt, S.; Thomson, A.J.; Saraste, M.; Richardson, D.J. Properties of a soluble domain of subunit C of a bacterial nitric oxide reductase. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 10858–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.P.; Duo, Y.K.; He, J.J.; Yao, J.C.; Qian, H.F.; Hrynsphan, D.; Tatsiana, S.; Chen, J. A newly isolated and rapid denitrifier Pseudomonas citronellolis WXP-4: Difference in N2O emissions under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 43, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.J.; Luoluo; Xie, D.T.; Li, Z.L. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in four Pseudomonas spp. under aerobic conditions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, O.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, S. Insights into the Nitrogen Removal Mechanism of Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification Bacterium Delfitia sp. B7. Water 2024, 16, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, J.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Roles of osmoprotectants in improving salinity and drought tolerance in plants: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio-Technol. 2015, 14, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriyama, W.; Honma, K.; Hiratsuka, T.; Takahashi, I.; Nomizu, T.; Takashima, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Takahashi, D.; Moriyama, K.; Mori, S.; et al. Diversities and similarities in pH dependency among bacterial NhaB-like Na+/H+ antiporters. Microbiology 2013, 159, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, R.; Aroca, R.; Azcon, R.; Ruiz-Lozano, J.M. Regulation of cation transporter genes by the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in rice plants subjected to salinity suggests improved salt tolerance due to reduced Na+ root-to-shoot distribution. Mycorrhiza 2016, 26, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunte, H.J. Osmoregulation in bacteria: Compatible solute accumulation and osmosensing. Environ. Chem. 2006, 3, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.L.; Ross, T.; Mcmeekin, T.A.; Nichols, P.D. Acid habituation of Escherichia coli and the potential role of cyclopropane fatty acids in low pH tolerance. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1997, 37, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevarech, M.; Frolow, F.; Gloss, L.M. Halophilic enzymes: Proteins with a grain of salt. Biophys. Chem. 2000, 86, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleator, R.D.; Hill, C. Bacterial osmoadaptation: The role of osmolytes in bacterial stress and virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durell, S.R.; Hao, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Bakker, E.P.; Guy, H.R. Evolutionary Relationship between K+ Channels and Symporters. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, H.A.; Hampton, E.; Lesley, S.A. The Thermotoga maritima Trk Potassium Transporter-from Frameshift to Function. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zheng, P.; Ding, A.Q.; Zhang, M.; Ghulam, A.; Yang, C.; Zhao, H.P. Effects of inorganic salts on denitrifying granular sludge: The acute toxicity and working mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 204, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygur, A.; Kargi, F. Salt inhibition on biological nutrient removal from saline wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2004, 34, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.A.; Hontoria, E.; González-López, J. Effect of dissolved oxygen concentration on nitrate removal from groundwater using a denitrifying submerged filter. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 90, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.L.; Ali, A.; Ren, Y.; Su, J.F.; Wang, Z. A mechanistic review on aerobic denitrification for nitrogen removal in water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojean, A.N.Y.; Zopfi, J.; Gerster, A.; Frey, C.; Lepori, F.; Lehmann, M.F. Direct O2 control on the partitioning between denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in lake sediments. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 4705–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.B.; Banks, D.D.; Lohman, J.R.; Hilsenbeck, J.L.; Gloss, L.M. The Effect of Salts on the Activity and Stability of Escherichia coli and Haloferax volcanii Dihydrofolate Reductases. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 323, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.A.C.B.; Okamoto, D.N.; Ruiz, D.M.; Oliveira, L.C.G.; Kondo, M.Y.; Tersario, I.L.S.; Juliano, L.; Castro, R.E.D.; Gouvea, I.E.; Murakami, M.T. Correlation between catalysis and tertiary structure arrangement in an archaeal halophilic subtilase. Biochimie 2012, 94, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowitzka, M.A.; Borowitzka, L.J.; Kessly, D. Effects of salinity increase on carotenoid accumulation in the green alga Dunaliella salina. J. Appl. Phycol. 1990, 2, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Cao, G.; Li, K.; Huang, J. Effect of salinity on biological nitrogen removal from wastewater and its mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 24713–24723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.C.; She, D.L.; Shi, Z.Q.; Cao, T.H.; Xia, Y.Q.; Shan, J. Salinity and high pH reduce denitrification rates by inhibiting denitrifying gene abundance in a saline-alkali soil. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurczy, M.E.; Forsberg, E.M.; Thorgersen, M.P.; Poole, F.L.; Siuzdak, G. Global Isotope Metabolomics Reveals Adaptive Strategies for Nitrogen Assimilation in Pseudomonas. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, M.C.; Jakobs-Schoenwandt, D.; Persicke, M.; Gómez, M.I.; Ruppel, S.; Patel, A.V. Anhydrobiotic engineering for the endophyte bacterium Kosakonia radicincitans by osmoadaptation and providing exogenously hydroxyectoine. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenström, F.; la Cour Jansen, J. Promotion of nitrifiers through side-stream bioaugmentation: A full-scale study. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2016, 74, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raper, E.; Stephenson, T.; Anderson, D.R.; Fisher, R.; Soares, A. Industrial wastewater treatment through bioaugmentation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 118, S0957582018303999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riisgaard-Jensen, M.; Dottorini, G.; Nierychlo, M.; Nielsen, P.H. Primary settling changes the microbial community of influent wastewater to wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2023, 244, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Q.; Ng, K.K.; Li, X.R.; Ng, H.Y. Investigation of Intertidal Wetland Sediment as a Novel Inoculation Source for Anaerobic Saline Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6231–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Tanong, K.; Xu, J.; Shon, H. Microbial community analysis of an aerobic nitrifying-denitrifying MBR treating ABS resin wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5337–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.J.; Nerurkar, A.S. Thauera sp. for efficient nitrate removal in continuous denitrifying moving bed biofilm reactor. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 47, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.K.; He, J.Z. Complete nitrogen removal via simultaneous nitrification and denitrification by a novel phosphate accumulating Thauera sp. strain SND5. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ni, J.; Ma, T.; Liu, T.; Zheng, M. Bioaugmentation treatment of municipal wastewater with heterotrophic-aerobic nitrogen removal bacteria in a pilot-scale SBR. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 183, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Bai, S.; Ma, F.; Wang, L. Microbial population dynamics in response to bioaugmentation in a constructed wetland system under 10 °C. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 205, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, W.J.; Kim, I.S.; Ekpeghere, K.I.; Song, B.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, J.T.; Koh, S.C. Metagenomic insight of nitrogen metabolism in a tannery wastewater treatment plant bioaugmented with the microbial consortium BM-S-1. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Toxic Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2016, 51, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Xie, J.Z.; Song, M.L.; Gao, Z.L.; Zheng, D.X.; Liu, X.; Ning, G.H.; Cheng, X.; Bruning, H. Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community changes in subsurface wastewater infiltration systems (SWISs) at low temperature with different bioaugmentation strategies. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Tang, Q.; Wu, M.; Qu, Y. Performance and microbial community analysis of bioaugmented activated sludge for nitrogen-containing organic pollutants removal. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.L.; Zhao, Y.X.; Yang, K.C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.G.; Ji, M. Application oriented bioaugmentation processes: Mechanism, performance improvement and scale-up. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Stage | Inoculation Time (d) | Inoculation Dosage (m3) |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-inoculation | / | 0 |
| Batch 1 | 17 | 5 |
| Batch 2 | 27, 29, 31 | 6 |
| Batch 3 | 38 | 3 |
| Batch 4 | 43 | 5 |
| Batch 5 | 55 | 2 |
| Category | Gene(s) | Halophilic Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane Regulation Mechanism | cfa (cyclopropane fatty acid synthase) | Catalysis of unsaturated fatty acid cyclopropanation to improve membrane stress resistance [33]. |
| Sodium–Potassium Pump | nhaB (Na+/H+ antiporter), kdpA/B/C/D/E (high-affinity ATP-driven K+ transport system), trkA/H (potassium transporter) | Transportation of Na+, K+, and H+ to maintain intracellular pH and ion balance [30,36,37]. |
| Compatible Solutes | betA/B (betaine–aldehyde dehydrogenase), ectA/B/C/D (ectoine synthase), proA/B/C (proline synthesis) | Compatible solutes (e.g., sugars, amino acids, and their derivatives) regulate cellular osmotic balance [32]. |
| Halophilic Enzymes | phoD (alkaline phosphatase), maeB (malate dehydrogenase) | Alkaline phosphatase and malate dehydrogenase can maintain activity under high-salinity conditions [38,39]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Liao, M. The Aerobic Denitrification Characteristics of a Halophilic Marinobacter sp. Strain and Its Application in a Full-Scale Fly Ash-Washing Wastewater Treatment Plant. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061274
Guo M, Liu K, Wang H, Song Y, Li Y, Zhang W, Gao J, Liao M. The Aerobic Denitrification Characteristics of a Halophilic Marinobacter sp. Strain and Its Application in a Full-Scale Fly Ash-Washing Wastewater Treatment Plant. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061274
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Mengyang, Kai Liu, Hongfei Wang, Yilin Song, Yingying Li, Weijin Zhang, Jian Gao, and Mingjun Liao. 2025. "The Aerobic Denitrification Characteristics of a Halophilic Marinobacter sp. Strain and Its Application in a Full-Scale Fly Ash-Washing Wastewater Treatment Plant" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061274
APA StyleGuo, M., Liu, K., Wang, H., Song, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, W., Gao, J., & Liao, M. (2025). The Aerobic Denitrification Characteristics of a Halophilic Marinobacter sp. Strain and Its Application in a Full-Scale Fly Ash-Washing Wastewater Treatment Plant. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061274






