Antimicrobial and Anti-Efflux Machinery of FDA-Approved Proton Pump Inhibitors and Vitamins Against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PCR Confirmation for Efflux Pump Genes
2.2. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of the Tested Compounds Against the Gram-Negative Standard Strains
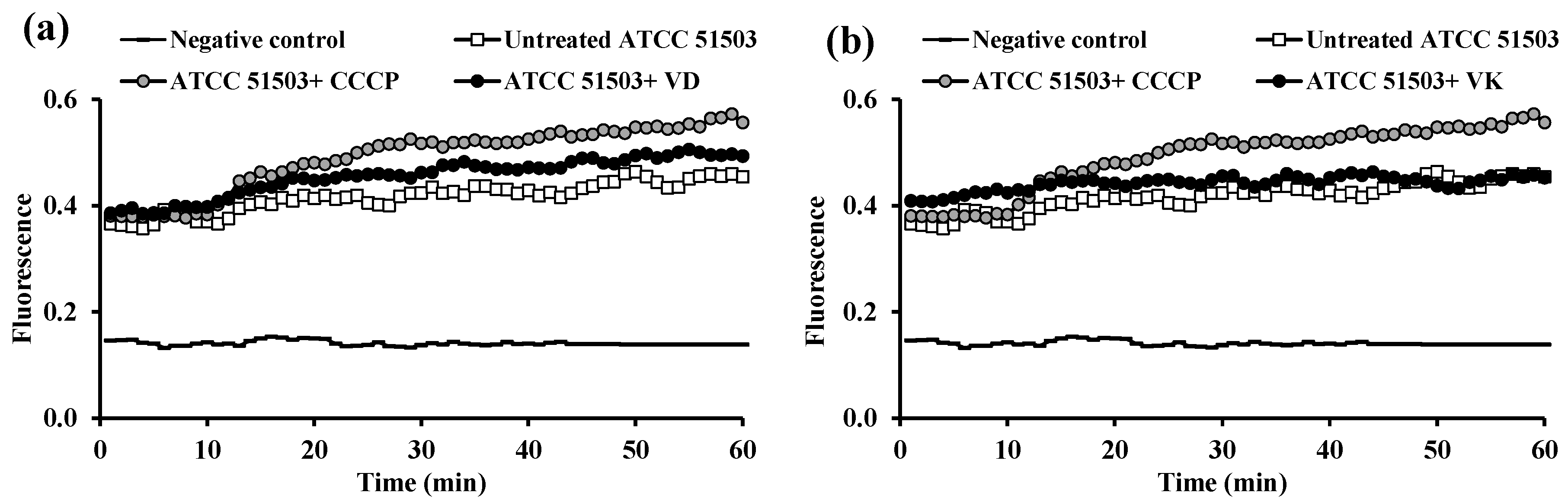
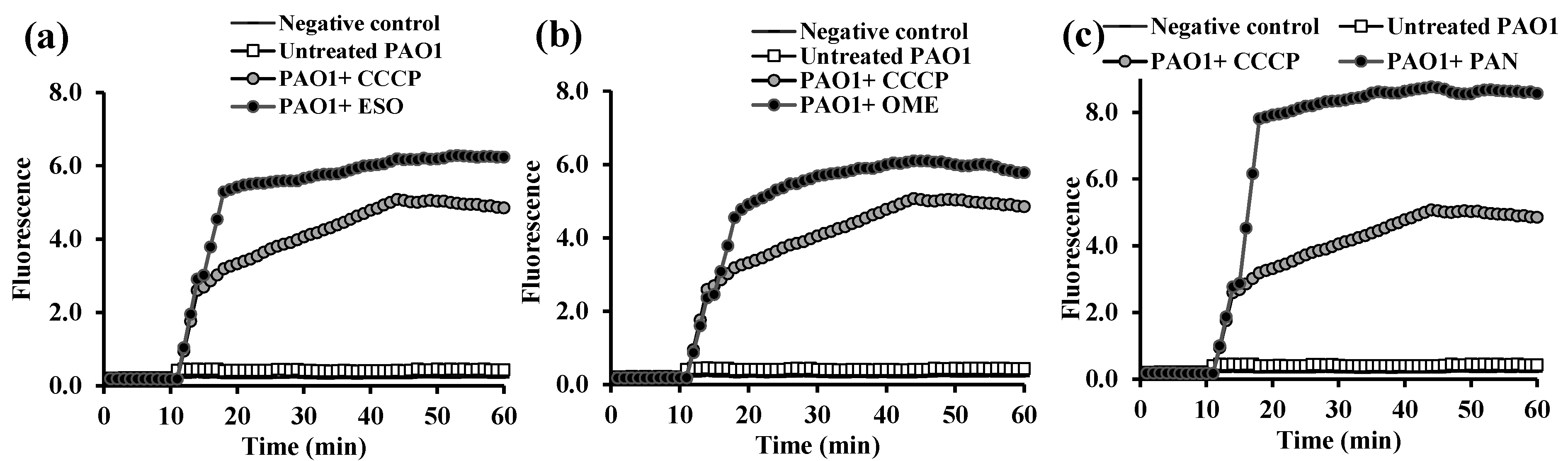
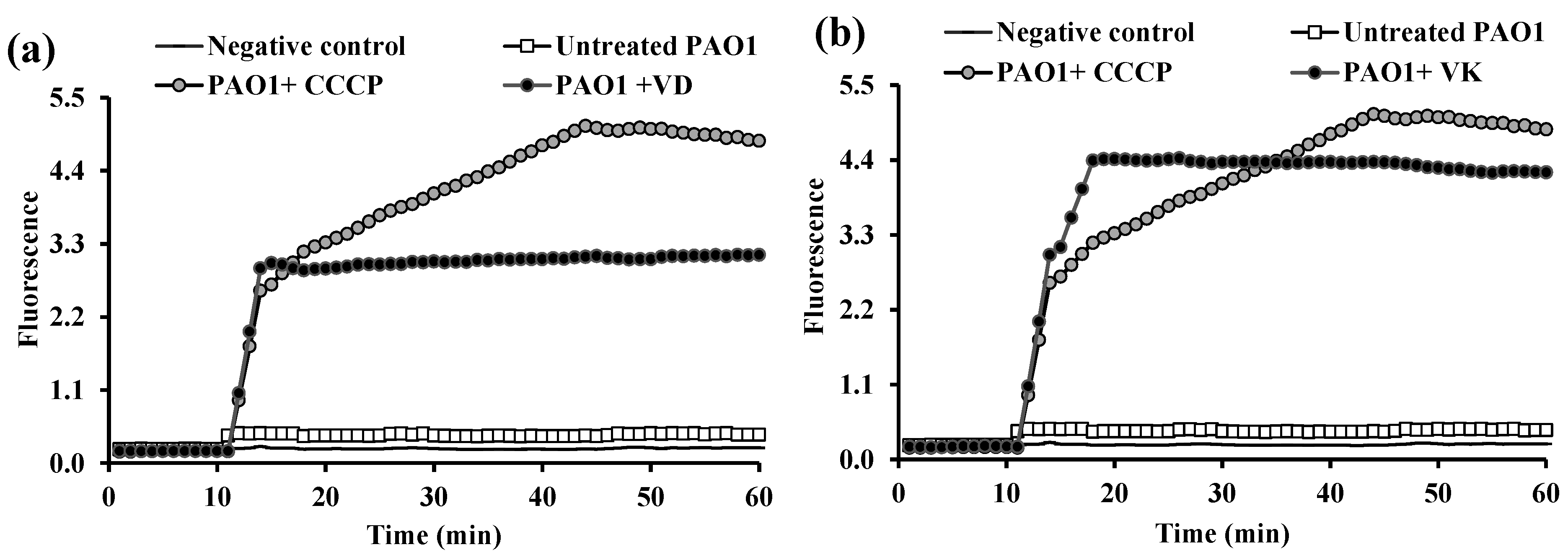
2.3. Fluorometric Real-Time Estimation of Efflux Activity
2.3.1. EB Accumulation Assay
2.3.2. Evaluation of EPI Activities of the Tested PPIs and Vitamins
2.4. The MIC of Ciprofloxacin Alone and in Combination with the Tested Compounds
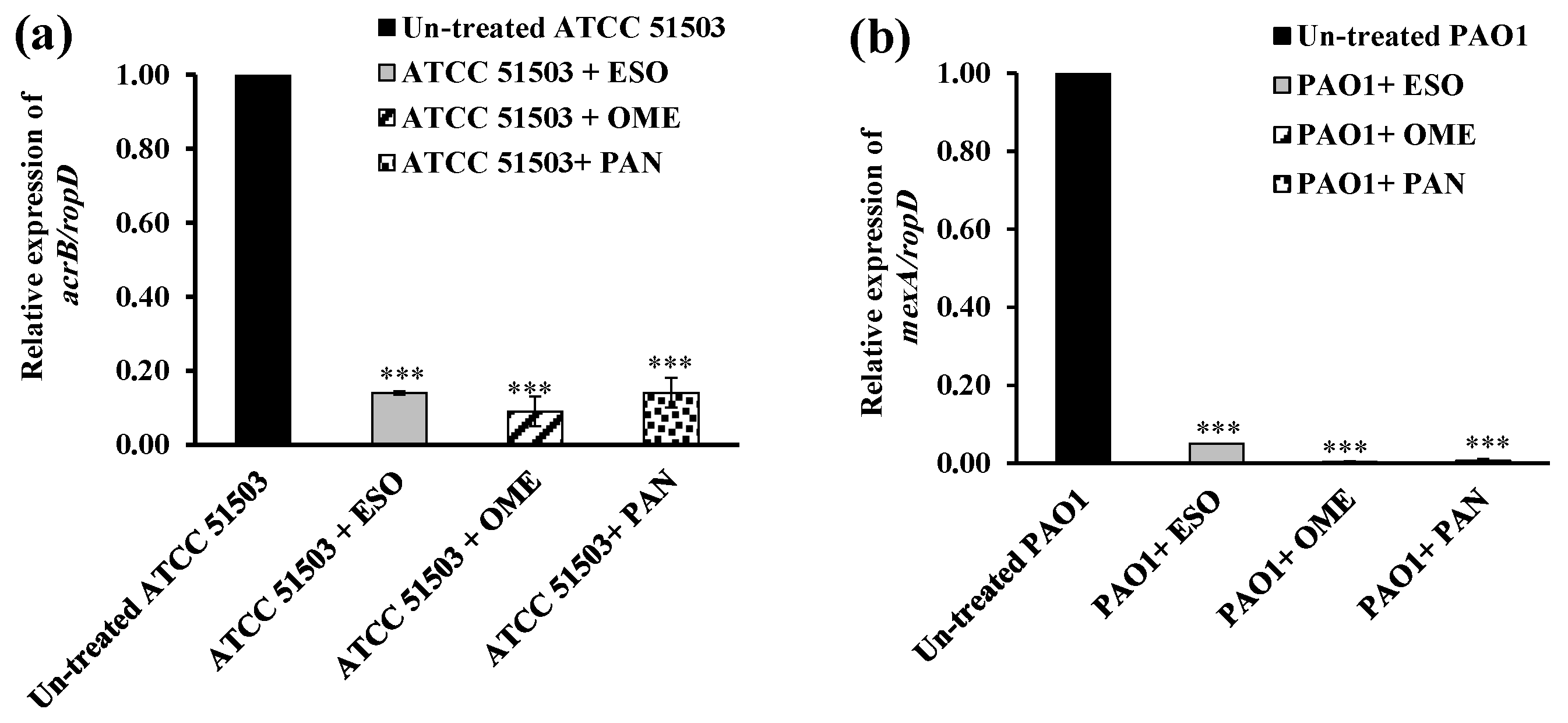
2.5. RT-PCR Assessment for Efflux Gene Quantification
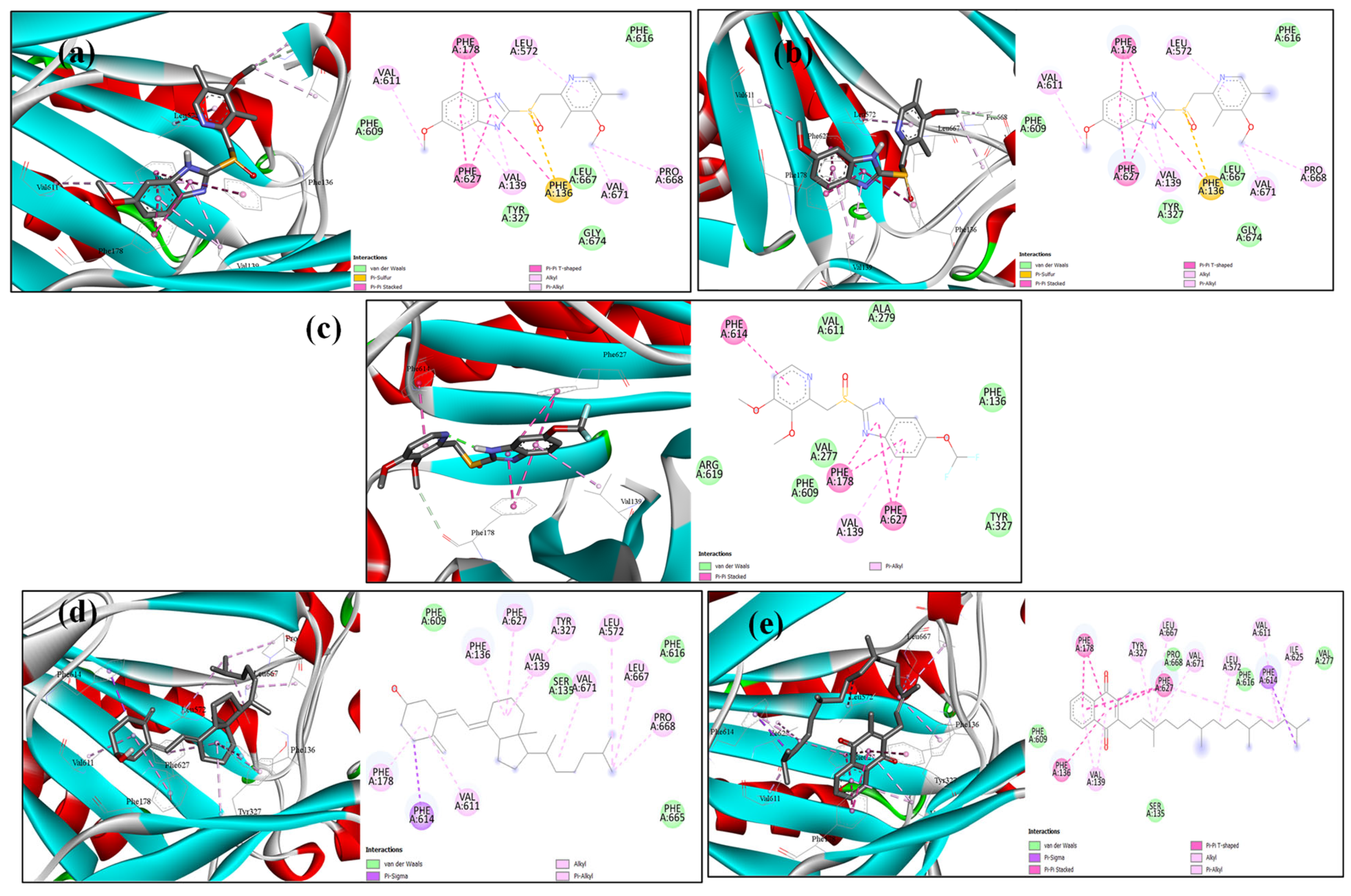
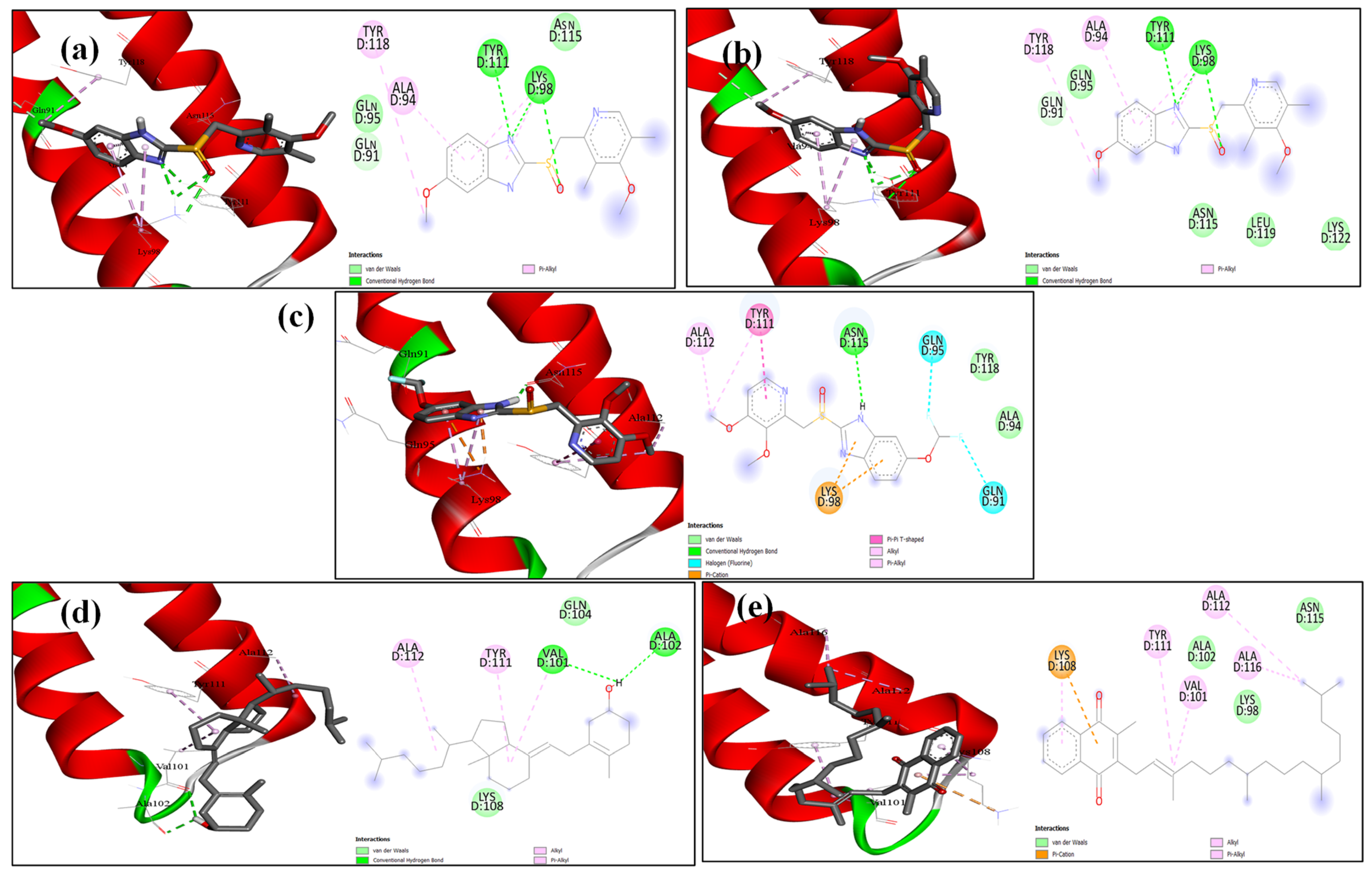
2.6. Docking Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Cultivation Media
4.2. Chemicals and FDA-Approved Pharmaceutical Medications
4.3. Confirmation of Efflux Pump-Mediated Resistance
4.4. Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs) of the Tested Compounds
4.5. Quantitative Determination of Efflux Pump Inhibitory Effect of Some FDA-Approved Drugs and Supplements by Semi-Automated Fluorometric System
4.6. Real-Time EB Accumulation Assay
4.7. Demonstration of the Activity of the Tested Compounds on Real-Time EB Accumulation
4.8. Effect of Vitamins and PPIs on MIC of Ciprofloxacin
4.9. RT-qPCR Assay
4.10. Molecular Modelling Docking
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| K. pneumoniae | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| P. aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| MDR | Multidrug resistance |
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| RND | Resistance–nodulation–cell division |
| SMR | Small multidrug resistance |
| MFS | Major facilitator superfamily |
| MATE | Multidrug and toxins extrusion |
| PACE | Proteo-bacterial antimicrobial complex efflux family |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| EPIs | Efflux pump inhibitors |
| CCCP | Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazine |
| LB broth | Luria–Bertani broth |
| EB | Ethidium bromide |
| PPIs | Proton pump inhibitors |
| ESO | Esomeprazole |
| OME | Omeprazole |
| PAN | Pantoprazole |
| VD | Vitamin D |
| VK | Vitamin K |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| CLSI | Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute |
| MHB | Mueller–Hinton broth |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| RF | Relative final fluorescence |
| RT-qPCR | Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| CT | Threshold cycle |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
References
- Duval, R.E.; Grare, M.; Demore, B. Fight Against Antimicrobial Resistance: We Always Need New Antibacterials but for Right Bacteria. Molecules 2019, 24, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E. Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development. 2017. Available online: https://remed.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/lobal-priority-list-of-antibiotic-resistant-bacteria-2017.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- Saleh, N.M.; Ezzat, H.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Zedan, H. Regulation of overexpressed efflux pump encoding genes by cinnamon oil and trimethoprim to abolish carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbuTaha, S.A.; Al-Kharraz, T.; Belkebir, S.; Abu Taha, A.; Zyoud, S.E.H. Patterns of microbial resistance in bloodstream infections of hemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional study from Palestine. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, M.; Jin, P.; Rahman, K.M. Efflux pumps in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and their inhibition to tackle antimicrobial resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelsen, V.; Kumar, A. Update on Multidrug Resistance Efflux Pumps in Acinetobacter spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0051421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, S.; Sutton, J.M.; Rahman, K.M. An overview of bacterial efflux pumps and computational approaches to study efflux pump inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang-Kan, X.; Neuberger, A.; van Veen, H.W.; Pos, K.M.; Piddock, L.J.V.; Luisi, B.F. Multidrug efflux pumps: Structure, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bina, X.R.; Weng, Y.; Budnick, J.; Van Allen Mia, E.; Bina James, E. Klebsiella pneumoniae TolC contributes to antimicrobial resistance, exopolysaccharide production, and virulence. Infect. Immun. 2023, 91, e00303-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Blanco, P.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Corona, F.; Reales-Calderón, J.A.; Sánchez, M.B.; Martínez, J.L. Multidrug efflux pumps as main players in intrinsic and acquired resistance to antimicrobials. Drug Resist. Updates 2016, 28, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi Bialvaei, A.; Rahbar, M.; Hamidi-Farahani, R.; Asgari, A.; Esmailkhani, A.; Mardani Dashti, Y.; Soleiman-Meigooni, S. Expression of RND efflux pumps mediated antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 153, 104789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.A.; Al-Kubaisy, S.H.; Al-Ouqaili, M.T.S. The influence of efflux pump, outer membrane permeability and β-lactamase production on the resistance profile of multi, extensively and pandrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 102544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardebili, A.; Talebi, M.; Azimi, L.; Rastegar Lari, A. Effect of Efflux Pump Inhibitor Carbonyl Cyanide 3-Chlorophenylhydrazone on the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Ciprofloxacin in Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, e8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Ye, X.G.; He, L.T.; Zhang, S.R.; Wang, R.L.; Zhou, J.; He, Z.S. In vitro characterization and inhibition of the interaction between ciprofloxacin and berberine against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Tripathi, A. Quercetin inhibits carbapenemase and efflux pump activities among carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Apmis 2020, 128, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Nie, T.; Zhang, Y.; You, X. A Novel Tigecycline Adjuvant ML-7 Reverses the Susceptibility of Tigecycline-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 809542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaratnam, R.; Sheikh, R.; Alharbi, F.; Kwon, D.H. An efflux pump (MexAB-OprM) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with antibacterial activity of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2017, 36, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazlett, L.D.; Ekanayaka, S.A.; McClellan, S.A.; Francis, R. Glycyrrhizin use for multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: In vitro and in vivo studies. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 2978–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambat, R.; Mahey, N.; Chandal, N.; Verma, D.K.; Jangra, M.; Thakur, K.G.; Nandanwar, H. A Microbe-Derived Efflux Pump Inhibitor of the Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Protein Restores Antibiotic Susceptibility in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Rosado-Lugo, J.D.; Zhang, Y.; Datta, P.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Banerjee, A.; Parhi, A.K. Evaluation of Heterocyclic Carboxamides as Potential Efflux Pump Inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2021, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rosado-Lugo, J.D.; Datta, P.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Banerjee, A.; Yuan, Y.; Parhi, A.K. Evaluation of a Conformationally Constrained Indole Carboxamide as a Potential Efflux Pump Inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Ahn, J. Advances in the Discovery of Efflux Pump Inhibitors as Novel Potentiators to Control Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh Chauhan, S.; Pandey, P.; Manickam, S.; Parthasarathi, R. Bac-EPIC: A web interface for developing novel efflux pump inhibitor compounds targeting Escherichia coli. Med. Drug Discov. 2023, 20, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahey, N.; Tambat, R.; Chandal, N.; Verma Dipesh, K.; Thakur Krishan, G.; Nandanwar, H. Repurposing Approved Drugs as Fluoroquinolone Potentiators to Overcome Efflux Pump Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00951-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Karim, S.A.M.; El-Ganiny, A.M.A.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Abbas, H.A.A. Promising FDA-approved drugs with efflux pump inhibitory activities against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.H.; He, H.L.; Zheng, Z.J.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Ren, H.; Zhou, Y.F.; Zhao, D.H.; Fang, L.X.; et al. Phentolamine Significantly Enhances Macrolide Antibiotic Antibacterial Activity against MDR Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputo, S.; Faustoferri, R.C.; Quivey, R.G., Jr. Vitamin D Compounds Are Bactericidal against Streptococcus mutans and Target the Bacitracin-Associated Efflux System. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01675-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintino, S.R.; Souza, V.C.A.; Silva, J.M.A.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.D.M.; Pereira, P.S.; Leal-Balbino, T.C.; Pereira-Neves, A.; Siqueira-Junior, J.P.; da Costa, J.G.M.; Rodrigues, F.F.G.; et al. Effect of Vitamin K3 Inhibiting the Function of NorA Efflux Pump and Its Gene Expression on Staphylococcus aureus. Membranes 2020, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramatla, T.; Mokgokong, P.; Lekota, K.; Thekisoe, O. Antimicrobial resistance profiles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from broiler chickens. Food Microbiol. 2024, 120, 104476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ouqaili, M.T.; Khalaf, E.A.; Al-Kubaisy, S.H. DNA Sequence Analysis of BlaVEB Gene Encoding Multi-drug Resistant and Extended-spectrum β-lactamases Producer Isolates of Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Open Microbiol. J. 2020, 14, 1874285802014010040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, T.-J.; Lalla, U.; Taljaard, J.; John, K.; Slabbert, J.; Koegelenberg, C. An outbreak of community-acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in a setting of high water stress. QJM Int. J. Med. 2017, 110, 855–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denissen, J.; Reyneke, B.; Waso-Reyneke, M.; Havenga, B.; Barnard, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, W. Prevalence of ESKAPE pathogens in the environment: Antibiotic resistance status, community-acquired infection and risk to human health. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 244, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, M.; Bolla, J.M. RND Efflux Pump Induction: A Crucial Network Unveiling Adaptive Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms of Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auda, I.G.; Salman, I.M.A.; Odah, J.G. Efflux pumps of Gram-negative bacteria in brief. Gene Rep. 2020, 20, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, A.; Du, D.; Luisi, B.F. Structure and mechanism of bacterial tripartite efflux pumps. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybenkov, V.V.; Zgurskaya, H.I.; Ganguly, C.; Leus, I.V.; Zhang, Z.; Moniruzzaman, M. The Whole Is Bigger than the Sum of Its Parts: Drug Transport in the Context of Two Membranes with Active Efflux. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 5597–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H.; Pagès, J.-M. Broad-specificity efflux pumps and their role in multidrug resistance of Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 340–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.; Fernandes, L.; Costa, S.S.; Cannalire, R.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; Couto, I.; Sabatini, S.; Viveiros, M. Mode of action of the 2-phenylquinoline efflux inhibitor PQQ4R against Escherichia coli. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Sheng, Z.; Hao, M.; Jiang, J.; Ye, M.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, M. RamA upregulates multidrug resistance efflux pumps AcrAB and OqxAB in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.; Richmond, G.E.; Piddock, L.J. Multidrug efflux pumps in Gram-negative bacteria and their role in antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamut, A.; Peterlin Masic, L.; Kikelj, D.; Tomasic, T. Efflux pump inhibitors of clinically relevant multidrug resistant bacteria. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2460–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.; Barnett, P.; Perlmutter, J.; Dunman, P.M. Identification of Acinetobacter baumannii serum-associated antibiotic efflux pump inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6360–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. M100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; Clinical Laboratory and Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2021; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Charpiat, B.; Bleyzac, N.; Tod, M. Proton Pump Inhibitors are Risk Factors for Viral Infections: Even for COVID-19? Clin. Drug Investig. 2020, 40, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Ha, E.K.; Yeniova, A.O.; Moon, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Koh, H.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Jeong, S.J.; Moon, S.J.; Cho, J.Y.; et al. Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: A nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching. Gut 2021, 70, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, I.; James, S. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 2022. Available online: https://clsi.org/shop/standards/m100/ (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- Abdulaal, W.H.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Asseri, A.H.; Radwan, M.F.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Okbazghi, S.Z.; Abbas, H.A.; Mansour, B.; Shoun, A.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; et al. Redirecting pantoprazole as a metallo-beta-lactamase inhibitor in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1366459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Hang, X.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, D.; Bi, H. Armeniaspirol A: A novel anti-Helicobacter pylori agent. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Huang, Y.; Hang, X.; Tong, Q.; Zeng, L.; Jia, J.; Zhang, G.; Bi, H. Dihydrotanshinone I Is Effective against Drug-Resistant Helicobacter pylori In Vitro and In Vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e01921-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, S.; Rana, N.F.; Zahid, M.A.; Zargaham, M.K.; Tanweer, T.; Batool, A.; Naeem, A.; Nawaz, A.; Rizwan Ur, R.; Muneer, Z.; et al. Virtual Screening of FDA-Approved Drugs against LasR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for Antibiofilm Potential. Molecules 2020, 25, 3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mdanda, S.; Baijnath, S.; Shobo, A.; Singh, S.D.; Maguire, G.E.M.; Kruger, H.G.; Arvidsson, P.I.; Naicker, T.; Govender, T. Lansoprazole-sulfide, pharmacokinetics of this promising anti-tuberculous agent. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2017, 31, e4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidaillac, C.; Guillon, J.; Arpin, C.; Forfar-Bares, I.; Ba, B.B.; Grellet, J.; Moreau, S.; Caignard, D.H.; Jarry, C.; Quentin, C. Synthesis of omeprazole analogues and evaluation of these as potential inhibitors of the multidrug efflux pump NorA of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, S.; Ashraf, M.A.; Sajid, M.; Shahzad, A.; Rafique, A.; Mahmood, M.S. Evaluation of synergistic antimicrobial effect of vitamins (A, B1, B2, B6, B12, C, D, E and K) with antibiotics against resistant bacterial strains. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 13, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.S.; Mousavi, S.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Vitamin E as promising adjunct treatment option in the combat of infectious diseases caused by bacterial including multi-drug resistant pathogens—Results from a comprehensive literature survey. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 10, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patti, G.; Pellegrino, C.; Ricciardi, A.; Novara, R.; Cotugno, S.; Papagni, R.; Guido, G.; Totaro, V.; De Iaco, G.; Romanelli, F.; et al. Potential Role of Vitamins A, B, C, D and E in TB Treatment and Prevention: A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golpour, A.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Antimicrobial and Immune-Modulatory Effects of Vitamin D Provide Promising Antibiotics-Independent Approaches to Tackle Bacterial Infections—Lessons Learnt from a Literature Survey. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 9, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Najjar, M.A.A.; Abdulrazzaq, S.B.; Al-Shaer, S.; Barakat, M.; Omar, A.; Zrieq, R.; Hasen, E.; Abu Samak, M. The Antimicrobial Activity of Combination of Vitamin D3 and Omega-3 against Pathogenic Microorganisms. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2024, 28, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feindt, E.; Stroder, J. Studies on the antimicrobial effect of vitamin D (author’s trans.). Klin. Wochenschr. 1977, 55, 507–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.C.; Morais Braga, M.F.; Guedes, G.M.; Tintino, S.R.; Freitas, M.A.; Quintans, L.J., Jr.; Menezes, I.R.; Coutinho, H.D. Menadione (vitamin K) enhances the antibiotic activity of drugs by cell membrane permeabilization mechanism. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Cho, Y.; Woo, H.J.; Kwon, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Park, M.; Moon, C.; Yeon, M.J.; Kim, H.W.; et al. Inhibitory Effects of Menadione on Helicobacter pylori Growth and Helicobacter pylori-Induced Inflammation via NF-κB Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.A.; Miller, C.W.; El-Abbassi, A.M.; Cutchins, D.C.; Cutchins, C.; Grant, W.B.; Peiris, A.N. Antimicrobial implications of vitamin D. Derm. Endocrinol. 2011, 3, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.W.; Teles, R.M.B.; Haile, S.; Liu, P.T.; Modlin, R.L. Vitamin D status contributes to the antimicrobial activity of macrophages against Mycobacterium leprae. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, N.; Chin, V.K.; Chong, P.P.; Lim, W.F.; Lim, C.W.; Basir, R.; Chang, S.K.; Lee, T.Y. Riboflavin as a promising antimicrobial agent? A multi-perspective review. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassuna, N.A.; Rabie, E.M.; Mahd, W.K.M.; Refaie, M.M.M.; Yousef, R.K.M.; Abdelraheem, W.M. Antibacterial effect of vitamin C against uropathogenic E. coli in vitro and in vivo. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebi, O.; Celebi, D.; Baser, S.; Yilmaz, A.; Yildirim, S. Vitamins Can Increase Antibiotic Effects Against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii in an In Vitro Infection Model. Eurasian J. Med. 2024, 56, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proton Pump Inhibitors. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Dia-betes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012.
- Sugandhi, V.V.; Pangeni, R.; Vora, L.K.; Poudel, S.; Nangare, S.; Jagwani, S.; Gadhave, D.; Qin, C.; Pandya, A.; Shah, P.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of vitamin dosage forms: A complete overview. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 48–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.; Farooq, N. Vitamin D Toxicity; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Mladenka, P.; Macakova, K.; Kujovska Krcmova, L.; Javorska, L.; Mrstna, K.; Carazo, A.; Protti, M.; Remiao, F.; Novakova, L.; OEMONOM Researchers and Collaborators. Vitamin K—Sources, physiological role, kinetics, deficiency, detection, therapeutic use, and toxicity. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 677–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, L.; Rodrigues, L.; Couto, I.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, P.; de Carvalho, C.C.; Monteiro, G.A.; Sansonetty, F.; Amaral, L.; Viveiros, M. Fluorometric determination of ethidium bromide efflux kinetics in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Eng. 2009, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, M.A.; Diederichs, K.; Eicher, T.; Brandstätter, L.; Schiefner, A.; Verrey, F.; Pos, K.M. The AcrB efflux pump: Conformational cycling and peristalsis lead to multidrug resistance. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffey, M.; Jumde, R.P.; da Costa, R.M.A.; Ropponen, H.K.; Blasco, B.; Piddock, L.J.V. Extending the Potency and Lifespan of Antibiotics: Inhibitors of Gram-Negative Bacterial Efflux Pumps. ACS Infect Dis 2024, 10, 1458–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullié, C.; Bouharkat, B.; Guiheneuf, R.; Serra, C.; Touil-Meddah, A.T.; Sonnet, P. Efflux Pumps in Acinetobacter Baumannii: Role in Antibiotic Resistance and Interest of Efflux Pump Inhibitors as Additional Therapeutic Weapons. In Antimicrobial Research: Novel Bioknowledge and Educational Programs; Microbiology Book Series #6; Formatex Research Center: Norristown, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lake, M.A.; Adams, K.N.; Nie, F.; Fowler, E.; Verma, A.K.; Dei, S.; Teodori, E.; Sherman, D.R.; Edelstein, P.H.; Spring, D.R.; et al. The human proton pump inhibitors inhibit Mycobacterium tuberculosis rifampicin efflux and macrophage-induced rifampicin tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2215512120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Yan, H.; Yu, C.; Yuan, L.; Sun, S. Proton pump inhibitors act synergistically with fluconazole against resistant Candida albicans. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ganiny, A.M.; Kamel, H.A.; Yossef, N.E.; Mansour, B.; El-Baz, A.M. Repurposing pantoprazole and haloperidol as efflux pump inhibitors in azole resistant clinical Candida albicans and non-albicans isolates. Saudi Pharm. J. SPJ Off. Publ. Saudi Pharm. Soc. 2022, 30, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Effects of domperidone in combination with omeprazole in the treatment of chronic superficial gastritis. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, N.; Suhani, S.; Purkaystha, A.; Begum, M.K.; Raihan, T.; Alam, M.J.; Islam, K.; Azad, A.K. Identification of AcrAB-TolC Efflux Pump Genes and Detection of Mutation in Efflux Repressor AcrR from Omeprazole Responsive Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates Causing Urinary Tract Infections. Microbiol. Insights 2019, 12, 1178636119889629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, B.V.; Babu, T.M.; Reddy, N.V.; Rajendra, W. Homology modeling, molecular dynamics, and virtual screening of NorA efflux pump inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 3237–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Pathania, R. Efflux pump inhibitors for bacterial pathogens: From bench to bedside. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacios, O.; Fernández-García, L.; Bleriot, I.; Blasco, L.; Ambroa, A.; López, M.; Ortiz-Cartagena, C.; González de Aledo, M.; Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Oteo-Iglesias, J.; et al. Adaptation of clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae to the combination of niclosamide with the efflux pump inhibitor phenyl-arginine-β-naphthylamide (PaβN): Co-resistance to antimicrobials. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.K.; Mohanty, P. Bacterial efflux pumps involved in multidrug resistance and their inhibitors: Rejuvinating the antimicrobial chemotherapy. Recent Pat. Anti-Infect. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomovskaya, O.; Warren, M.S.; Lee, A.; Galazzo, J.; Fronko, R.; Lee, M.; Blais, J.; Cho, D.; Chamberland, S.; Renau, T.; et al. Identification and characterization of inhibitors of multidrug resistance efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Novel agents for combination therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdali, N.; Parks, J.M.; Haynes, K.M.; Chaney, J.L.; Green, A.T.; Wolloscheck, D.; Walker, J.K.; Rybenkov, V.V.; Baudry, J.; Smith, J.C. Reviving antibiotics: Efflux pump inhibitors that interact with AcrA, a membrane fusion protein of the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump. ACS Infect. Dis. 2017, 3, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, M.; Shaaban, A.; Rahman, K.M. Antibiotic resistance breakers: Current approaches and future directions. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2019, 43, 490–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang, Z.; James, N.R.; Voss, J.E.; Klimont, E.; Ohene-Agyei, T.; Venter, H.; Chiu, W.; Luisi, B.F. Structure of the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump. Nature 2014, 509, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, E.; Llobet, E.; Domenech-Sanchez, A.; Martinez-Martinez, L.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Alberti, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae AcrAB efflux pump contributes to antimicrobial resistance and virulence. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, R.; Liu, G.; Xu, Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H. AcrAB Efflux Pump Plays a Crucial Role in Bile Salts Resistance and Pathogenesis of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, Y.; Tomida, J.; Kawamura, Y. MexXY multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, H.R.; Nahaei, M.R.; Rezaee, M.A.; Hasani, A.; Kafil, H.S.; Aghazadeh, M.; Nikbakht, M.; Khalili, Y. Role of MexAB-OprM and MexXY-OprM efflux pumps and class 1 integrons in resistance to antibiotics in burn and Intensive Care Unit isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassuna, N.A.; Darwish, M.K.; Sayed, M.; Ibrahem, R.A. Molecular Epidemiology and Mechanisms of High-Level Resistance to Meropenem and Imipenem in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, A.B.; Carrara, J.A.; Barroso, C.D.N.; Tuon, F.F.; Faoro, H. Role of Efflux Pumps on Antimicrobial Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kello, E.; Greenberg, R.; Li, W.; Polansky, S.; Maldonado, R.; Peter, Y.; Basu, P. The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment and Gene Expression of Mex B Efflux Transporters on the Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisuria, V.B.; Hosseinidoust, Z.; Tufenkji, N. Polyphenolic extract from maple syrup potentiates antibiotic susceptibility and reduces biofilm formation of pathogenic bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3782–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Guo, M.; Fei, B.; Ren, Y.; You, X.; Li, Y. Effect of piperine on the inhibitory potential of MexAB-OprM efflux pump and imipenem resistance in carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 185, 106397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjuts, H.; Vargiu, A.V.; Kwasny, S.M.; Nguyen, S.T.; Kim, H.-S.; Ding, X.; Ornik, A.R.; Ruggerone, P.; Bowlin, T.L.; Nikaido, H.J.P.; et al. Molecular basis for inhibition of AcrB multidrug efflux pump by novel and powerful pyranopyridine derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3509–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, W.; Allen, S.; Janda, W. Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Iranpour, D.; Hassanpour, M.; Ansari, H.; Tajbakhsh, S.; Khamisipour, G.; Najafi, A.J.B. Phylogenetic groups of Escherichia coli strains from patients with urinary tract infection in Iran based on the new Clermont phylotyping method. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 846219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratu, S.; Landman, D.; George, A.; Salvani, J.; Quale, J. Correlation of the expression of acrB and the regulatory genes marA, soxS and ramA with antimicrobial resistance in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae endemic to New York City. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutfi, L.L.; Shaaban, M.I.; Elshaer, S.L. Vitamin D and vitamin K1 as novel inhibitors of biofilm in Gram-negative bacteria. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboelenin, A.M.; Hassan, R.; Abdelmegeed, E.S. The effect of EDTA in combination with some antibiotics against clinical isolates of gram negative bacteria in Mansoura, Egypt. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 154, 104840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mowafy, S.A.; Abd El Galil, K.H.; El-Messery, S.M.; Shaaban, M.I. Aspirin is an efficient inhibitor of quorum sensing, virulence and toxins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 74, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveiros, M.; Martins, A.; Paixão, L.; Rodrigues, L.; Martins, M.; Couto, I.; Fähnrich, E.; Kern, W.V.; Amaral, L. Demonstration of intrinsic efflux activity of Escherichia coli K-12 AG100 by an automated ethidium bromide method. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveiros, M.; Rodrigues, L.; Martins, M.; Couto, I.; Spengler, G.; Martins, A.; Amaral, L. Evaluation of Efflux Activity of Bacteria by a Semi-automated Fluorometric System. In Antibiotic Resistance Protocols, 2nd ed.; Gillespie, S.H., McHugh, T.D., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 159–172. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, L.; Viveiros, M.; Aínsa, J.A. Measuring Efflux and Permeability in Mycobacteria. In Mycobacteria Protocols; Parish, T., Roberts, D.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 227–239. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, S.S.; Lopes, E.; Azzali, E.; Machado, D.; Coelho, T.; Da Silva, P.E.A.; Viveiros, M.; Pieroni, M.; Couto, I.J.A.; Technologies, D.D. An experimental model for the rapid screening of compounds with potential use against mycobacteria. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2016, 14, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, L.; Spengler, G.; Evaristo, M.; Handzlik, J.; Molnar, J.; Viveiros, M.; Kiec-Kononowicz, K.; Amaral, L.J. Biological activity of twenty-three hydantoin derivatives on intrinsic efflux pump system of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis NCTC 13349. In Vivo 2011, 25, 769–772. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, L.; Villellas, C.; Bailo, R.; Viveiros, M.; Aínsa, J.A. Role of the Mmr efflux pump in drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.; Coelho, T.S.; Perdigao, J.; Pereira, C.; Couto, I.; Portugal, I.; Maschmann, R.D.A.; Ramos, D.F.; von Groll, A.; Rossetti, M.L.J.F. Interplay between mutations and efflux in drug resistant clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.; Perdigão, J.; Portugal, I.; Pieroni, M.; Silva, P.A.; Couto, I.; Viveiros, M.J.A. Efflux activity differentially modulates the levels of isoniazid and rifampicin resistance among multidrug resistant and monoresistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D.J. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Morgan, C.E.; Bonomo, R.A.; Yu, E.W. Cryo-EM Structures of the Klebsiella pneumoniae AcrB Multidrug Efflux Pump. mBio 2023, 14, e00659-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavier, M.; Puvanendran, D.; Salvador, D.; Decossas, M.; Phan, G.; Garnier, C.; Frezza, E.; Cece, Q.; Schoehn, G.; Picard, M.; et al. Antibiotic export by MexB multidrug efflux transporter is allosterically controlled by a MexA-OprM chaperone-like complex. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
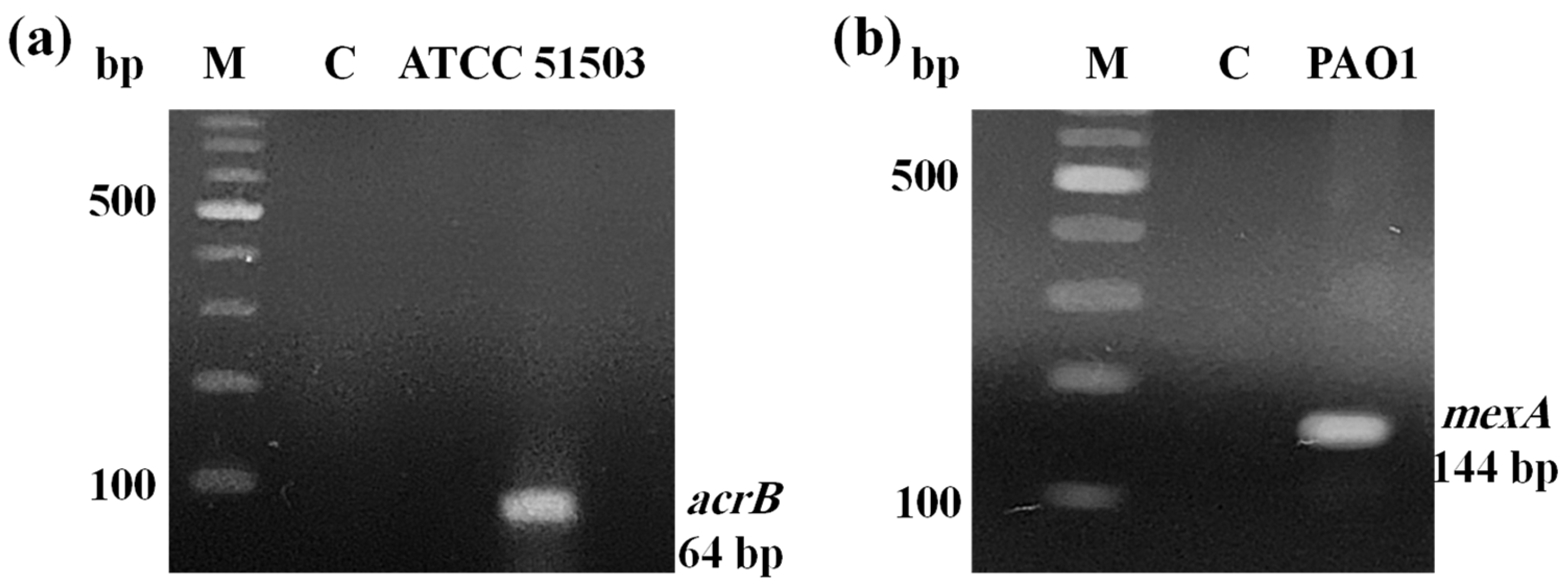
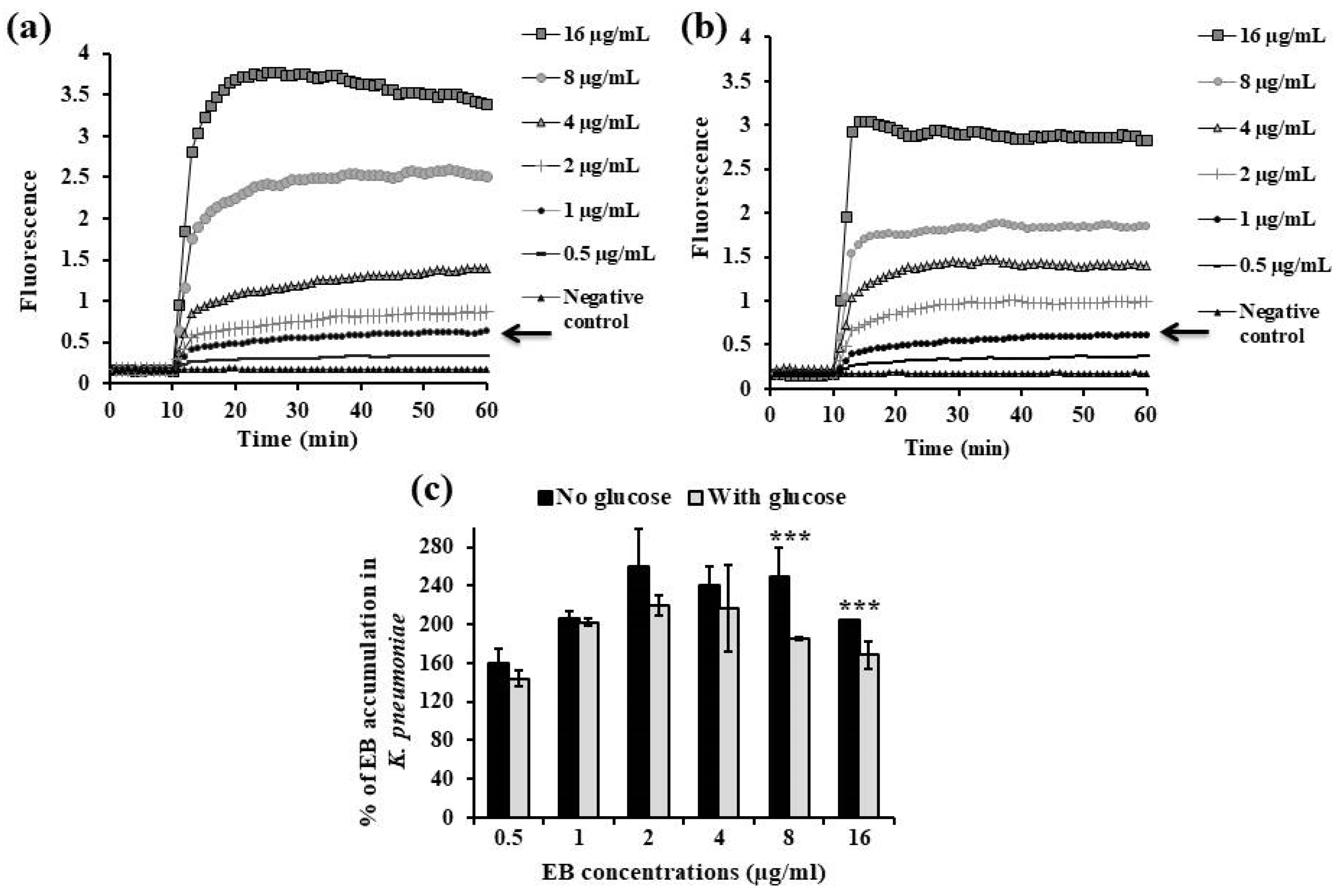
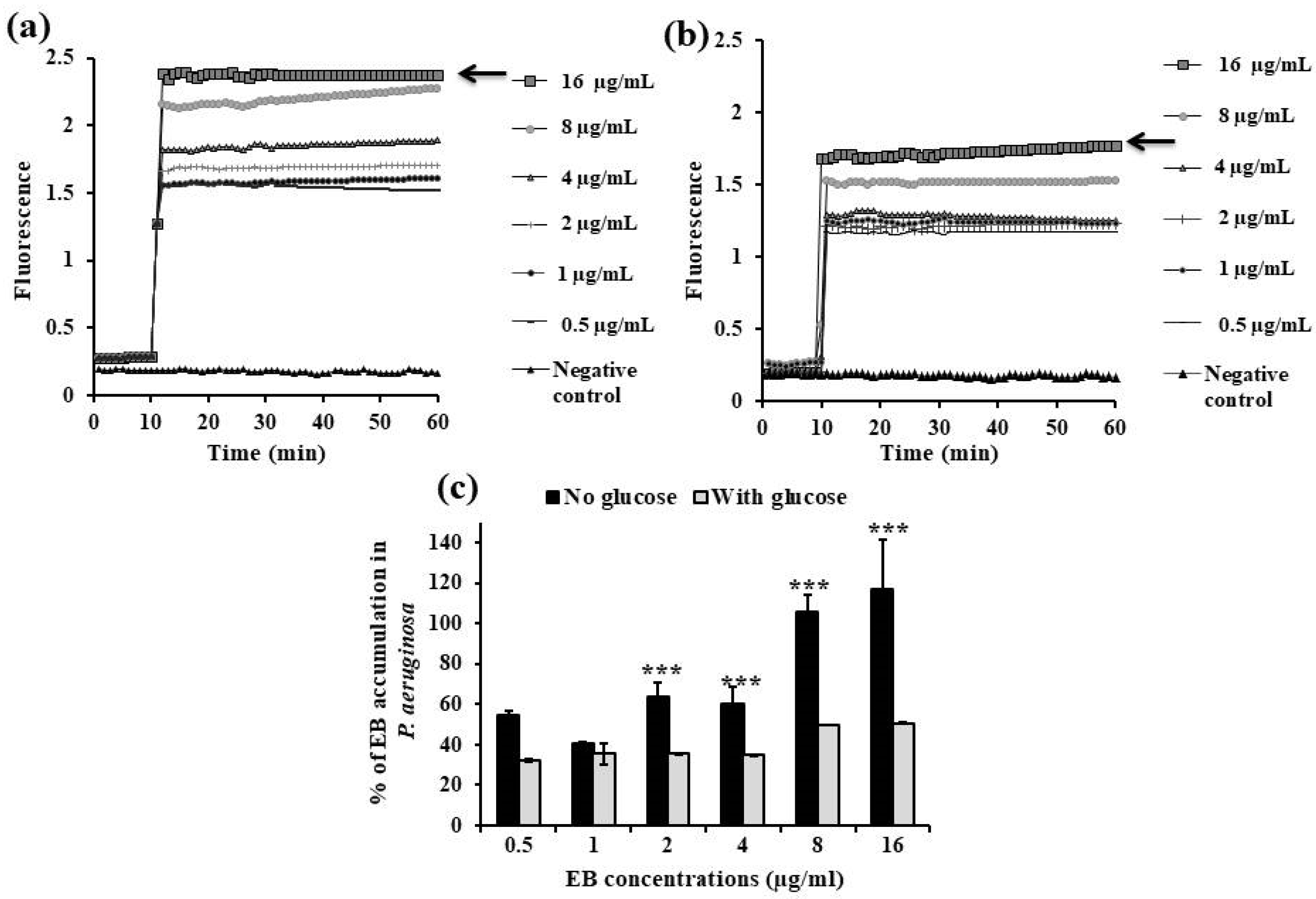
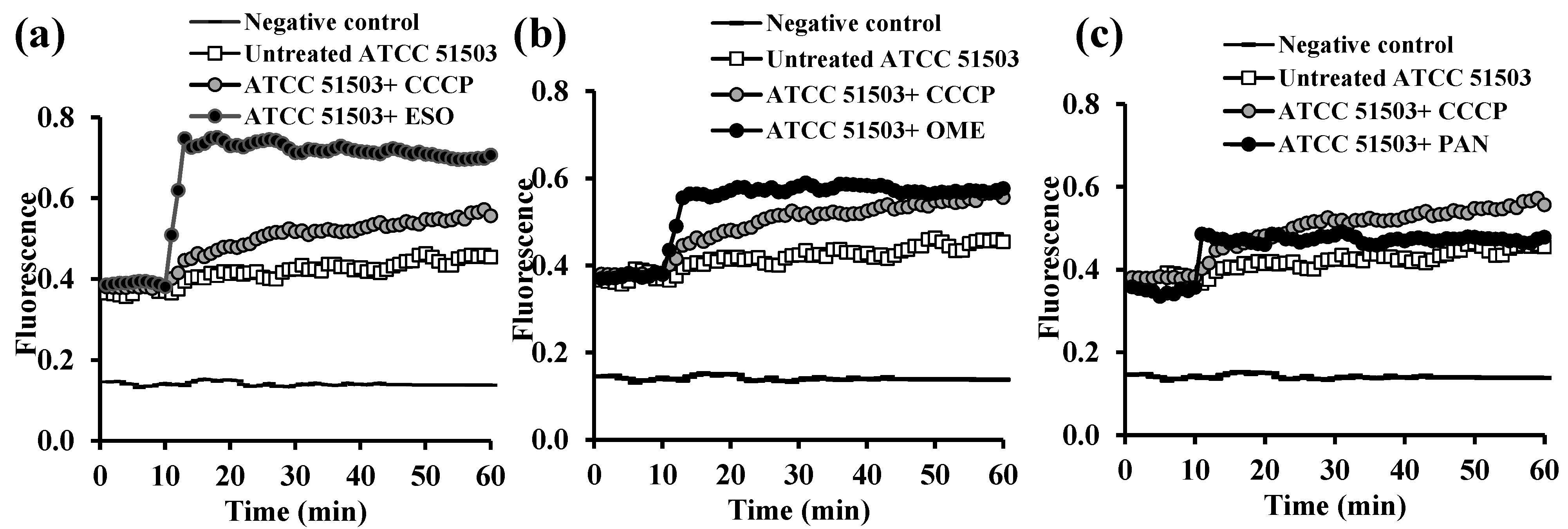
| Category | Chemical/Pharmaceutical Medications | Bacterial Strains | MIC (µg/mL) | 0.5× MIC (µg/mL) | 0.25× MIC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference efflux substrate | EB | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 32 | 16 | 8 | ||
| Reference efflux inhibitor | CCCP | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 16,000 | 8000 | 4000 |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 16,000 | 8000 | 4000 | ||
| Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) | ESO | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 16,000 | 8000 | 4000 |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 32,000 | 16,000 | 8000 | ||
| OME | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 16,000 | 8000 | 4000 | |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 16,000 | 8000 | 4000 | ||
| PAN | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 16,000 | 8000 | 4000 | |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 32,000 | 16,000 | 8000 | ||
| Vitamins | VD | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 625 | 312.5 | 156.25 |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 1250 | 625 | 312.5 | ||
| VK | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 2500 | 1250 | 625 | |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 5000 | 2500 | 1250 |
| CEq= 1 µg/ml | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compounds | RFF ± SD | |
| Standard EPI | CCCP | 0.18 ± 0.09 *** |
| Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) | Esomeprazole (ESO) | 0.58 ± 0.06 *** |
| Omeprazole (OME) | 0.29 ± 0.13 *** | |
| Pantoprazole (PAN) | 0.14 ± 0.14 *** | |
| Vitamins | Vitamin D (VD) | 0.092 ± 0.04 *** |
| Vitamin K (VK) | 0.06 ± 0.04 *** | |
| CEq = 16 µg/mL | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compounds | RFF ± SD | |
| Standard EPI | CCCP | 15.6 ± 1.8 *** |
| Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) | Esomeprazole (ESO) | 21.03 ± 2.2 *** |
| Omeprazole (OME) | 19.70 ± 1.3 *** | |
| Pantoprazole (PAN) | 29.9 ± 2.8 *** | |
| Vitamins | Vitamin D (VD) | 10.8 ± 1.4 *** |
| Vitamin K (VK) | 15.10 ± 1.3 *** | |
| Category | Antibiotic/Utilized Medications and Supplements | Bacterial Strains | MIC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic alone | CIP alone | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 62.5 |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | |||
| Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) | CIP/ESO | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | ˂0.98 |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | |||
| CIP/OME | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 15.6 | |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | ˂0.98 | ||
| CIP/PAN | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 7.8 | |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | ˂0.98 | ||
| Vitamins | CIP/VD | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 3.9 |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 0.98 | ||
| CIP/VK | K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | 7.8 | |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 1.95 |
| Organism | Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) | AT (°C) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K. pneumoniae ATCC 51503 | acrB | AcrB F | CAATACGGAAGAGTTTGGCA | 56 | 64 | [99] |
| AcrB R | CAGACGAACCTGGGAACC | |||||
| rpoD | RpoD F | AAGACGAAGATGAAGACGCC | 57 | 129 | [100] | |
| RpoD R | CTTTGGCTTTGATGGTGTCG | |||||
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | mexA | MexA F | GTGACCCTGAATACCGAGC | 60 | 144 | [101] |
| MexA R | GTCGATCTGGTAGAGCTGC | |||||
| ropD | RopD F | CGAACTGCTTGCCGACTT | 56 | 131 | [102] | |
| RopD R | GCGAGAGCCTCAAGGATAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lutfi, L.L.; Shaldam, M.A.; Shaaban, M.I.; Elshaer, S.L. Antimicrobial and Anti-Efflux Machinery of FDA-Approved Proton Pump Inhibitors and Vitamins Against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061227
Lutfi LL, Shaldam MA, Shaaban MI, Elshaer SL. Antimicrobial and Anti-Efflux Machinery of FDA-Approved Proton Pump Inhibitors and Vitamins Against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061227
Chicago/Turabian StyleLutfi, Lekaa L., Moataz A. Shaldam, Mona I. Shaaban, and Soha Lotfy Elshaer. 2025. "Antimicrobial and Anti-Efflux Machinery of FDA-Approved Proton Pump Inhibitors and Vitamins Against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061227
APA StyleLutfi, L. L., Shaldam, M. A., Shaaban, M. I., & Elshaer, S. L. (2025). Antimicrobial and Anti-Efflux Machinery of FDA-Approved Proton Pump Inhibitors and Vitamins Against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061227





