Control of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using Photodynamic Therapy in Synergy with Staphylococcus epidermidis: Role of Mixed Cultures in Developing Strategies to Inhibit Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Pre-Inoculum Preparation
2.2. Light Source—Biotable
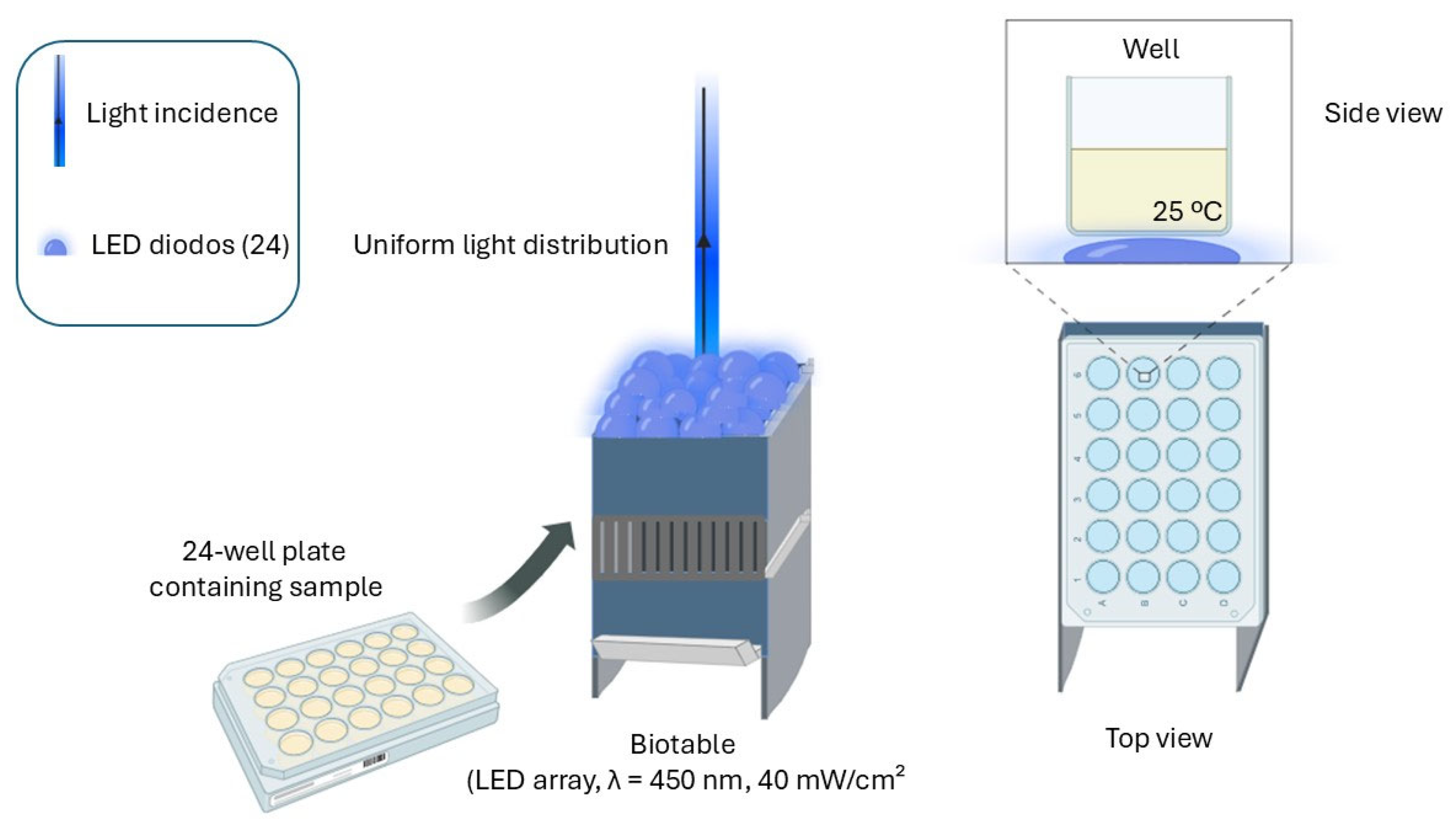
2.3. Photodynamic Inactivation (PDI)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of Photodynamic Inactivation Standardization for Bacteria
3.2. Survival Curve
4. Discussion
4.1. About Standardization of Photodynamic Inactivation
4.2. About Survival Curve
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bromfield, J.I.; Hugenholtz, P.; Frazer, I.H.; Khosrotehrani, K.; Chandra, J. Targeting Staphylococcus aureus dominated skin dysbiosis in actinic keratosis to prevent the onset of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Outlook for future therapies? Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1091379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowron, K.; Bauza-Kaszewska, J.; Kraszewska, Z.; Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N.; Grudlewska-Buda, K.; Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Radtke, L.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Human skin microbiome: Impact of intrinsic and extrinsic factors on skin microbiota. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Hata, T. Dysbiosis of the skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. In Skin Microbiome Handbook: From Basic Research to Product Development; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 185–201. [Google Scholar]
- Min, Z.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Huang, R. Oral microbiota dysbiosis accelerates the development and onset of mucositis and oral ulcers. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1061032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.E.; Bäumler, A.J. Gut dysbiosis: Ecological causes and causative effects on human disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2316579120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation: A bright new technique to kill resistant microbes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 33, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; El-Gendy, A.O.; Radi, N.A.M.; Mohamed, T. The bactericidal efficacy of femtosecond laser-based therapy on the most common infectious bacterial pathogens in chronic wounds: An in vitro study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2021, 36, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Li, X.; Pan, Q.; Wang, K.; Liu, N.; Yutao, W.; Zhang, Y. Nanotechnology-based approaches for antibacterial therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 279, 116798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gendy, A.O.; Ezzat, S.; Samad, F.A.; Dabbous, O.A.; Dahm, J.; Hamblin, M.R.; Mohamed, T. Studying the viability and growth kinetics of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis V583 following femtosecond laser irradiation (420–465 nm). Lasers Med. Sci. 2024, 39, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gendy, A.O.; Obaid, Y.; Ahmed, E.; Enwemeka, C.S.; Hassan, M.; Mohamed, T. The antimicrobial effect of gold quantum dots and femtosecond laser irradiation on the growth kinetics of common infectious eye pathogens: An in vitro study. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; El-Gendy, A.O.; Hamblin, M.R.; Mohamed, T. The effect of femtosecond laser irradiation on the growth kinetics of Staphylococcus aureus: An in vitro study. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2021, 221, 112240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.A.; Cheburkanov, V.; Chen, S.; Soares, J.M.; Kassab, G.; Blanco, K.C.; Bagnato, V.S.; de Figueiredo, P.; Yakovlev, V.V. Breaking down antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Combining antimicrobial photodynamic and antibiotic treatments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2208378119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebisher, D.; Serafin, I.; Batóg-Szczęch, K.; Dynarowicz, K.; Chodurek, E.; Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Bartusik-Aebisher, D. Photodynamic Therapy in the Treatment of Cancer—The Selection of Synthetic Photosensitizers. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Shi, T.; Long, S.; Chen, P.; Sun, W.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Enhanced photodynamic therapy for overcoming tumor hypoxia: From microenvironment regulation to photosensitizer innovation. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simplicio, F.I.; Maionchi, F.; Hioka, N. Terapia fotodinâmica: Aspectos farmacológicos, aplicações e avanços recentes no desenvolvimento de medicamentos. Quím. Nova 2002, 25, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.M.; Guimarães, F.E.G.; Yakovlev, V.V.; Bagnato, V.S.; Blanco, K.C. Physicochemical mechanisms of bacterial response in the photodynamic potentiation of antibiotic effects. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.D.; Blanco, K.C.; Mfouo-Tynga, I.S.; Inada, N.M.; Bagnato, V.S. Curcumin as a photosensitizer: From molecular structure to recent advances in antimicrobial photodynamic therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2020, 45, 100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, T.Q.; Blanco, K.C.; Soares, J.M.; Inada, N.M.; Kurachi, C.; Golim, M.d.A.; Deffune, E.; Bagnato, V.S. Photodynamic inactivation for in vitro decontamination of Staphylococcus aureus in whole blood. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 28, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci Donato, H.A.; Pratavieira, S.; Grecco, C.; Brugnera-Júnior, A.; Bagnato, V.S.; Kurachi, C. Clinical comparison of two photosensitizers for oral cavity decontamination. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2017, 35, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odunitan, T.T.; Apanisile, B.T.; Akinboade, M.W.; Abdulazeez, W.O.; Oyaronbi, A.O.; Ajayi, T.M.; Oyekola, S.A.; Ibrahim, N.O.; Nafiu, T.; Afolabi, H.O.; et al. Microbial mysteries: Staphylococcus aureus and the enigma of carcinogenesis. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 194, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullander, J.; Forslund, O.; Dillner, J. Staphylococcus aureus and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, N.; Pausan, M.R.; Halwachs, B.; Durdević, M.; Windisch, M.; Kehrmann, J.; Patra, V.; Wolf, P.; Boukamp, P.; Moissl-Eichinger, C.; et al. Molecular profiling of keratinocyte skin tumors links Staphylococcus aureus overabundance and increased human β-defensin-2 expression to growth promotion of squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Lv, Z.; Liang, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Tao, A.; et al. Exploring the role of Staphylococcus aureus in inflammatory diseases. Toxins 2022, 14, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J.; Jackson, M.S.; Bagg, J. The ecology of Staphylococcus species in the oral cavity. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, B.T.; Sumida, W.K.; Taira, D.A.; Davis, J.W.; Seto, T.B. Hospital-Acquired Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Related to Medicare Antibiotic Prescriptions: A State-Level Analysis. Hawaii J. Med. Public Health 2016, 75, 303. [Google Scholar]
- Okello, C.; Achieng, L.; Mwachari, C.; Otieno, D.; Otieno, F.; Omonge, E. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical specimens at the Mater Hospital Nairobi, Kenya. Preprint 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chen, T.H.; Butcher, A.M.; Trzoss, L.L.; Nam, S.-J.; Shirakawa, K.T.; Zhou, W.; Oh, J.; Otto, M.; Fenical, W.; et al. A commensal strain of Staphylococcus aureus protects against skin neoplasia. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottery, M.J.; Pitchford, J.W.; Friman, V.-P. Ecology and evolution of antimicrobial resistance in bacterial communities. ISME J. 2021, 15, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, R.M.; Dourado, M.N.; Araújo, W.L. Microbial interactions: Ecology in a molecular perspective. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.P.J.; Wucher, B.R.; Nadell, C.D.; Foster, K.R. Bacterial defences: Mechanisms, evolution and antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Zuo, J.; Wang, H.; Grenier, D.; Yi, L.; Wang, Y. Contribution of quorum sensing to virulence and antibiotic resistance in zoonotic bacteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 59, 107965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muteeb, G.; Rehman, T.; Shahwan, M.; Aatif, M. Origin of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance, and their impacts on drug development: A narrative review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynarczyk-Bonikowska, B.; Kowalewski, C.; Krolak-Ulinska, A.; Marusza, W. Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo, N.J.; Tovar, J.S.D.; Dovigo, L.N.; Dias, L.D.; Bagnato, V.S.; Inada, N.M. Natural versus synthetic curcuminoids as photosensitizers: Photobleaching and antimicrobial photodynamic therapy evaluation. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2023, 42, 103495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, K.C.; Inada, N.M.; Carbinatto, F.M.; Bagnato, V.S. Antimicrobial efficacy of curcumin formulations by photodynamic therapy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 5, 506–511. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, P.; Soares, J.M.; Martins, G.M.; Cocca, L.H.Z.; De Boni, L.; de Oliveira, K.T.; Bagnato, V.S.; Blanco, K.C. Improving the efficacy of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy through curcumin modifications. Photochem. Photobiol. 2024, 101, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, G.C.; Schito, A.M.; Zuccari, G. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated antibacterial oxidative therapies: Available methods to generate ROS and a novel option proposal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilaberte, Y.; Rezusta, A.; Juarranz, A.; Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy: A new paradigm in the fight against infections. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 788888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.M.; Yakovlev, V.V.; Blanco, K.C.; Bagnato, V.S. Photodynamic inactivation and its effects on the heterogeneity of bacterial resistance. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Liao, B.; Cheng, L.; Ren, B. Reactive oxygen species in pathogen clearance: The killing mechanisms, the adaption response, and the side effects. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 622534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.M.; Yakovlev, V.V.; Blanco, K.C.; Bagnato, V.S. Recovering the susceptibility of antibiotic-resistant bacteria using photooxidative damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2311667120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, R.V.; Soares, J.M.; Blanco, K.C.; Bagnato, V.S. Influence of photodynamic action on pure and mixed cultures of gram-negative bacteria: Related to growth mechanisms. Laser Phys. Lett. 2023, 21, 015601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira de Lima, R.; Blanco, K.C.; Bagnato, V.S. Control of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using Photodynamic Therapy in Synergy with Staphylococcus epidermidis: Role of Mixed Cultures in Developing Strategies to Inhibit Infections. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061196
Vieira de Lima R, Blanco KC, Bagnato VS. Control of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using Photodynamic Therapy in Synergy with Staphylococcus epidermidis: Role of Mixed Cultures in Developing Strategies to Inhibit Infections. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061196
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira de Lima, Rebeca, Kate Cristina Blanco, and Vanderlei Salvador Bagnato. 2025. "Control of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using Photodynamic Therapy in Synergy with Staphylococcus epidermidis: Role of Mixed Cultures in Developing Strategies to Inhibit Infections" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061196
APA StyleVieira de Lima, R., Blanco, K. C., & Bagnato, V. S. (2025). Control of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using Photodynamic Therapy in Synergy with Staphylococcus epidermidis: Role of Mixed Cultures in Developing Strategies to Inhibit Infections. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061196






