Associations Between Candida and Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter Species as Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Isolates in 84 Cohorts of ICU Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Selection and Grouping of Cohorts
2.2. Outcomes of Interest
2.3. Regression Model
2.4. Sensitivity Tests
2.5. Missing Data
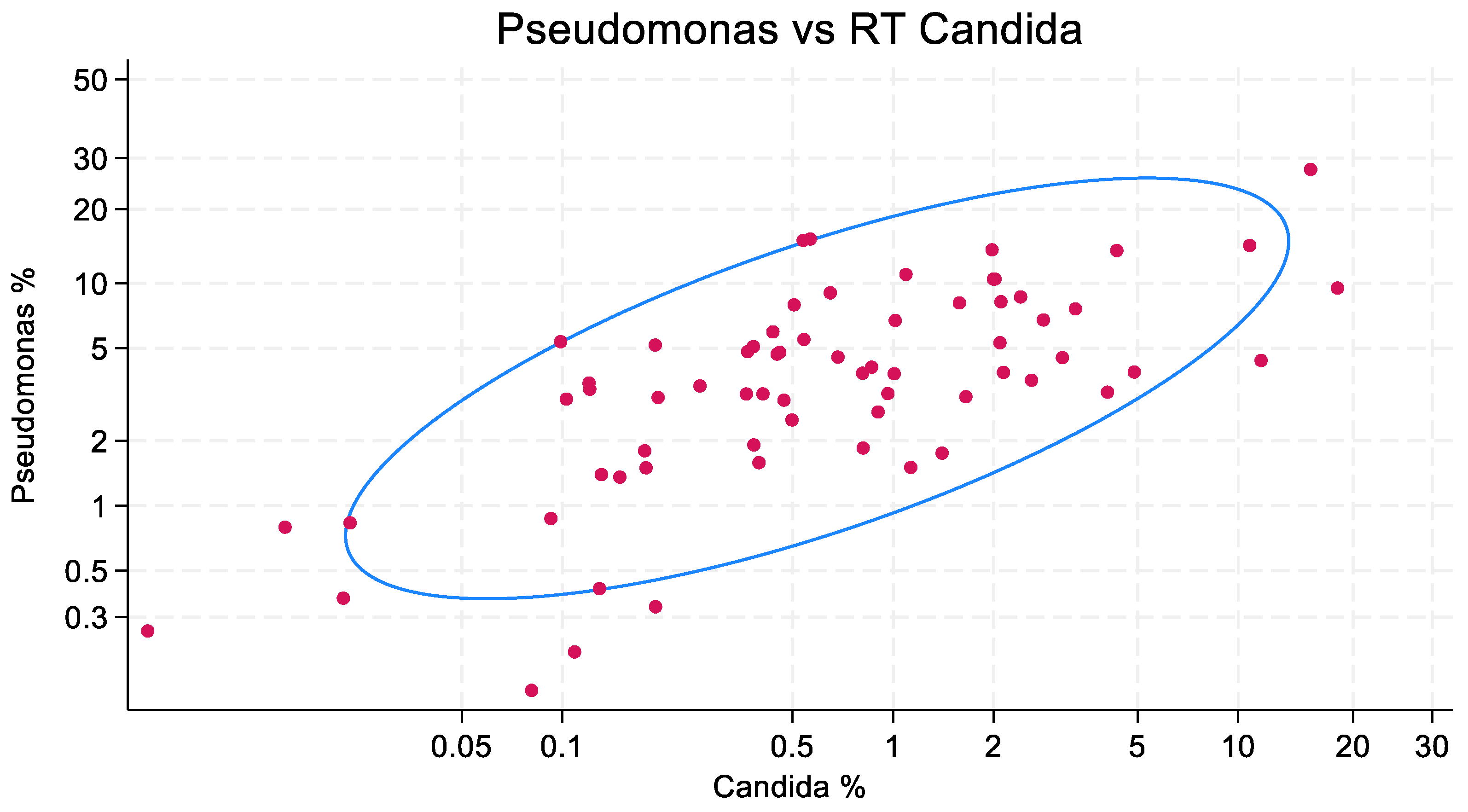
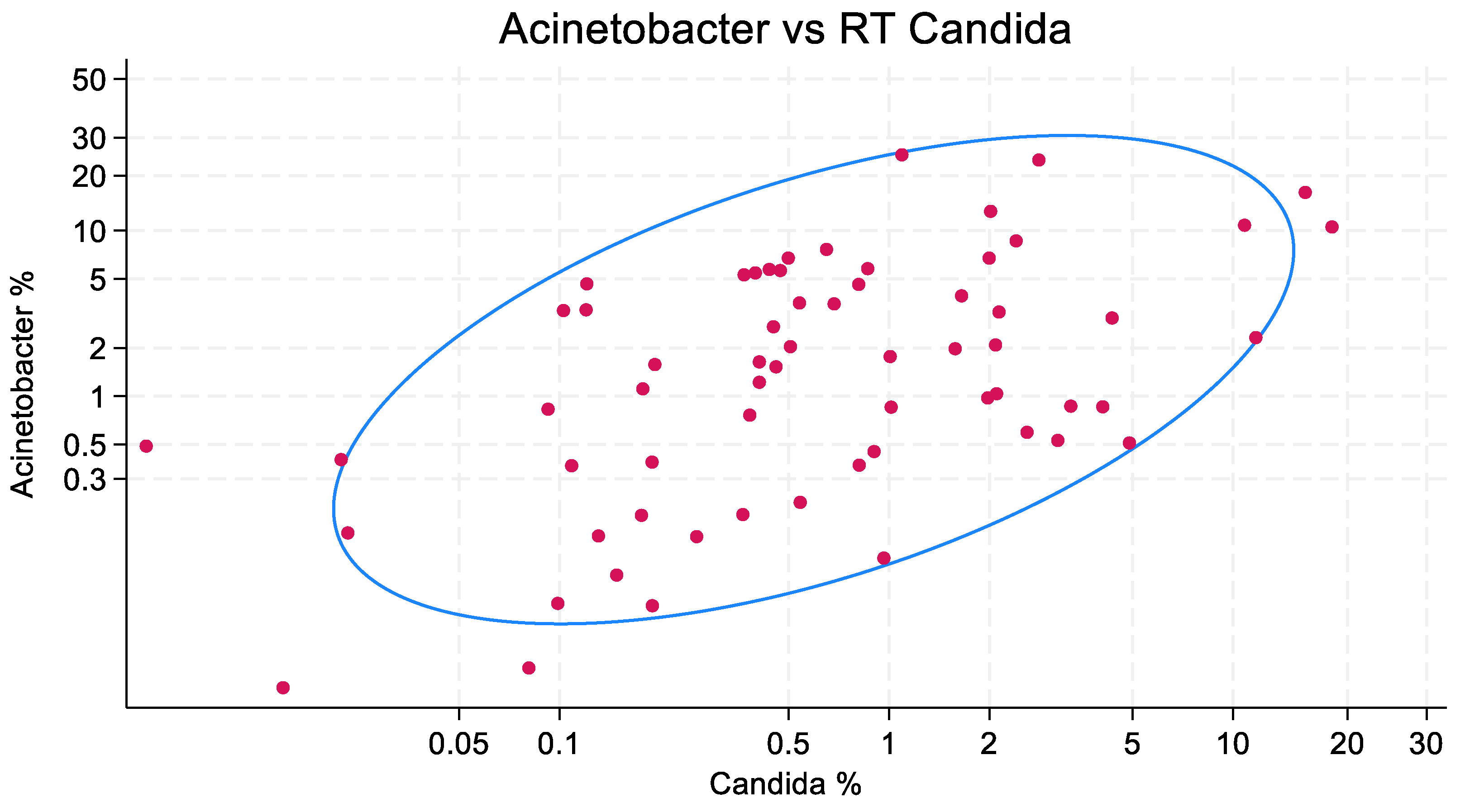
2.6. Bivariate Plots and Confidence Ellipses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Studies
3.2. Scatterplots
3.3. Regression Models and Sensitivity Tests
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Comparisons with Other Findings
5. Population Relevance
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IQR | Inter-quartile range |
| VAP | Ventilator-associated pneumonia |
| MV | Mechanical ventilation |
| LOS | Length of stay |
| RT | Respiratory tract |
References
- Antonelli, M.; Moro, M.L.; Capelli, O.; De Blasi, R.A.; D’errico, R.R.; Conti, G.; Bufi, M.; Gasparetto, A. Risk factors for early onset pneumonia in trauma patients. Chest 1994, 105, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercault, N.; Boulain, T. Mortality rate attributable to ventilator-associated nosocomial pneumonia in an adult intensive care unit: A prospective case-control study. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boots, R.J.; George, N.; Faoagali, J.L.; Druery, J.; Dean, K.; Heller, R.F. Double-heater-wire circuits and heat-and-moisture exchangers and the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregeon, F.; Papazian, L.; Visconti, A.; Gregoire, R.; Thirion, X.; Gouin, F. Relationship of microbiologic diagnostic criteria to morbidity and mortality in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia. JAMA 1997, 277, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, J.F.; McOwat, E.; Siganporia, R.; Keighley, C.; Presneill, J.; Sinickas, V. Uncertain relevance of gastric colonization in the seriously ill. Intensive Care Med. 1992, 18, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, M.; Ferrer, M.; Ferrer, R.; Morforte, R.; Garnacho, A.; Torres, A. Risk and prognostic factors of ventilator-associated pneumonia in trauma patients. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendrero, J.A.; Solé-Violán, J.; Benitez, A.B.; Catalán, J.N.; Fernández, J.A.; Santana, P.S.; de Castro, F.R. Role of different routes of tracheal colonization in the development of pneumonia in patients receiving mechanical ventilation. Chest 1999, 116, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastre, J.; Trouillet, J.L.; Vuagnat, A.; Joly-Guillou, M.L.; Clavier, H.; Dombret, M.C.; Gibert, C. Nosocomial pneumonia in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevret, S.; Hemmer, M.; Carlet, J. Incidence and risk factors of pneumonia acquired in intensive care units. Results from a multicenter prospective study on 996 patients. European Cooperative Group on Nosocomial Pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 1993, 19, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.; Norwood, S.; Berne, J. Ventilator-associated pneumonia is more common and of less consequence in trauma patients compared with other critically ill patients. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2010, 69, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, D.E.; Kunches, L.M.; Lichtenberg, D.A.; Kollisch, N.R.; Barry, M.A.; Heeren, T.C.; McCabe, W.R. Nosocomial infection and fatality in medical and surgical intensive care unit patients. Arch. Intern. Med. 1988, 148, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashner, F.D.; Frey, P.; Wolff, G.; Baumann, P.C.; Suter, P. Nosocomial infections in intensive care wards: A multicenter prospective study. Intensive Care Med. 1982, 8, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daschner, F.; Kappstein, I.; Schuster, F.; Scholz, R.; Bauer, E.; Jooβens, D.; Just, H. Influence of disposable (‘Conchapak’) and reusable humidifying systems on the incidence of ventilation pneumonia. J. Hosp. Infect. 1988, 11, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Rose, D.; Pezzotti, P.; Fortunato, E.; Sordillo, P.; Gini, S.; Boros, S.; Meledandri, M.; Gallo, M.T.; Prignano, G.; Caccese, R.; et al. Clinical predictors and microbiology of ventilator-associated pneumonia in the intensive care unit: A retrospective analysis in six Italian hospitals. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewig, S.; Torres, A.; El-Ebiary, M.; Fàbregas, N.; Hernandez, C.; Gonzalez, J.; Nicolas, J.M.; Soto, L. Bacterial colonization patterns in mechanically ventilated patients with traumatic and medical head injury. Incidence, risk factors, and association with ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagon, J.Y.; Chastre, J.; Domart, Y.; Trouillet, J.L.; Pierre, J.; Darne, C.; Gibert, C. Nosocomial pneumonia in patients receiving continuous mechanical ventilation. Prospective analysis of 52 episodes with use of a protected specimen brush and quantitative culture techniques. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, R.A.; Flavin, K.E.; Barr, J.; Weinacker, A.B.; Parsonnet, J.; Gould, M.K. Variability in antibiotic prescribing patterns and outcomes in patients with clinically suspected ventilator-associated pneumonia. Chest 2003, 123, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.L.; Falk, P.S.; Wunderink, R.G.; Leeper, K.V., Jr.; Meduri, G.U.; Steere, E.L.; Glen Mayhall, C. Epidemiology of ventilator-acquired pneumonia based on protected bronchoscopic sampling. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Bengmark, S.; Kanellakopoulou, K.; Kotzampassi, K. Pro- and synbiotics to control inflammation and infection in patients with multiple injuries. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2009, 67, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, C.; Girard, R.; Chemorin, C.; De Varax, R.; Fournier, G. Facial mask noninvasive mechanical ventilation reduces the incidence of nosocomial pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 1997, 23, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursel, G.; Aydogdu, M.; Nadir Ozis, T.; Tasyurek, S. Comparison of the value of initial and serial endotracheal aspirate surveillance cultures in predicting the causative pathogen of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 42, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyland, D.K.; Cook, D.J.; Schoenfeld, P.S.; Frietag, A.; Varon, J.; Wood, G. The effect of acidified enteral feeds on gastric colonization in critically ill patients: Results of a multicenter randomized trial. Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 27, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, L.; Chastang, C.; Demingeon, G.; Bohe, J.; Piralla, B.; Coupry, A. A randomized study assessing the systematic search for maxillary sinusitis in nasotracheally mechanically ventilated patients. Influence of nosocomial maxillary sinusitis on the occurrence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugonnet, S.; Uçkay, I.; Pittet, D. Staffing level: A determinant of late-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.H.; Ward, S.; Sherman, G.; Kollef, M.H. A comparative analysis of patients with early-onset vs. late-onset nosocomial pneumonia in the ICU setting. Chest 2000, 117, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, P.; Torres, A.; Rodríguez-Roisin, R.; de la Bellacasa, J.P.; Aznar, R.; Gatell, J.M.; Agustí-Vidal, A. Incidence and etiology of pneumonia acquired during mechanical ventilation. Crit. Care Med. 1989, 17, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Thomas, S.M.; Mathai, A.S.; Rajkumar, A. A prospective study on incidence and microbiological profile of ventilator associated pneumonia in the intensive care unit of a tertiary care centre. Int. J. Contemp. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 1840–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Kantorova, I.; Svoboda, P.; Scheer, P.; Doubek, J.; Rehorkova, D.; Bosakova, H.; Ochmann, J. Stress ulcer prophylaxis in critically ill patients: A randomized controlled trial. Hepato-Gastroenterology 2004, 51, 757–761. [Google Scholar]
- Kautzky, S.; Staudinger, T.; Presterl, E. Invasive Candida infections in patients of a medical intensive care unit. In Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 127, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kollef, M.H.; Prentice, D.; Shapiro, S.D.; Fraser, V.J.; Silver, P.; Trovillion, E.; Weilitz, P.; Von Harz, B.; John, R.S. Mechanical ventilation with or without daily changes of in-line suction catheters. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołpa, M.; Wałaszek, M.; Gniadek, A.; Wolak, Z.; Dobroś, W. Incidence, microbiological profile and risk factors of healthcare-associated infections in intensive care units: A 10 year observation in a provincial hospital in Southern Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koss, W.G.; Khalili, T.M.; Lemus, J.F.; Chelly, M.M.; Margulies, D.R.; Shabot, M.M. Nosocomial pneumonia is not prevented by protective contact isolation in the surgical intensive care unit. Am. Surg. 2001, 67, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laggner, A.N.; Lenz, K.; Base, W.; Druml, W.; Schneeweiss, B.; Grimm, G. Prevention of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in long-term ventilated patients: Sucralfate versus ranitidine. Am. J. Med. 1989, 86, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Dong, D.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Y.; Ni, Q.; Mao, E.; Peng, Y. The correlation between Candida colonization of distinct body sites and invasive candidiasis in emergency intensive care units: Statistical and molecular biological analysis. Mycopathologia 2016, 181, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, C.M.; Blanzaco, D.; Niederman, M.S.; Matarucco, W.; Baredes, N.C.; Desmery, P.; Palizas, F.; Menga, G.; Rios, F.; Apezteguia, C. Resolution of ventilator-associated pneumonia: Prospective evaluation of the clinical pulmonary infection score as an early clinical predictor of outcome. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnason, S.; Kristinsson, K.G.; Stefansson, T.; Erlendsdottir, H.; Jonsdottir, K.; Kristjansson, M.; Gudmundsson, S. Risk factors and outcome in ICU-acquired infections. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2008, 52, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahul, P.; Auboyer, C.; Jospe, R.; Ros, A.; Guerin, C.; El Khouri, Z.; Galliez, M.; Dumont, A.; Gaudin, O. Prevention of nosocomial pneumonia in intubated patients respective role of mechanical subglottic secretions drainage and stress ulcer prophylaxis. Intensive Care Med. 1992, 18, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memish, Z.A.; Cunningham, G.; Oni, G.A.; Djazmati, W. The incidence and risk factors of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a Riyadh hospital. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2000, 21, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moine, P.; Timsit, J.F.; De Lassence, A.; Troché, G.; Fosse, J.P.; Alberti, C.; Cohen, Y. Mortality associated with late-onset pneumonia in the intensive care unit: Results of a multi-center cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palabiyikoglu, I.; Oral, M.; Tulunay, M. Candida colonization in mechanically ventilated patients. J. Hosp. Infect. 2001, 47, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, P.D.; Linton, D.M.; Oliver, S.; Forder, A.A. Nosocomial infections in a respiratory intensive care unit. Crit. Care Med. 1987, 15, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, P.; Lopez-Ferraz, C.; Gordon, M.; Gimeno, A.; Villarreal, E.; Ruiz, J.; Menendez, R.; Torres, A. From starting mechanical ventilation to ventilator-associated pneumonia, choosing the right moment to start antibiotic treatment. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranes, J.L.; Gordon, S.M.; Chen, P.; Fatica, C.; Hammel, J.; Gonzales, J.P.; Arroliga, A.C. Predictors of long-term mortality in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 897.e13–897.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, J.; Lorente, C.; Diaz, E.; Bodi, M.; Boque, C.; Sandiumenge, A.; Santamaria, J.M. Incidence, etiology, and outcome of nosocomial pneumonia in ICU patients requiring percutaneous tracheotomy for mechanical ventilation. Chest 2003, 124, 2239–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rello, J.; Quintana, E.; Ausina, V.; Castella, J.; Luquin, M.; Net, A.; Prats, G. Incidence, etiology, and outcome of nosocomial pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients. Chest 1991, 100, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rello, J.; Ausino, V.; Ricart, M.; Castella, J.; Prats, G. Impact of previous antimicrobial therapy on the etiology and outcome of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Chest 1993, 104, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, M.M.; Monteiro, S.G.; Callegari, B.; Figueiredo, P.M.; Monteiro, C.R.; Monteiro-Neto, V. Epidemiology and outcomes of ventilator-associated pneumonia in northern Brazil: An analytical descriptive prospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.M.; Neto, C.; Santos, L.R.; Knibel, M.F. Ventilator-associated pneumonia: Epidemiology and impact on the clinical evolution of ICU patients. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2009, 35, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, V.D.; Rodrigues, C.; Madani, N.; Mitrev, Z.; Ye, G.; Salomao, R.; Ulger, F.; Guanche-Garcell, H.; Kanj, S.S.; Cuéllar, L.E.; et al. Effectiveness of a multidimensional approach for prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia in adult intensive care units from 14 developing countries of four continents: Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozaidi, S.W.; Sukro, J.; Dan, A. The incidence of nosocomial infection in the Intensive Care Unit, Hospital Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia: ICU-acquired nosocomial infection surveillance program 1998–1999. Med. J. Malays. 2001, 56, 207–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Santana, S.; Jimenez, A.G.; Esteban, A.; Guerra, L.; Alvarez, B.; Corcia, S.; Gudin, J.; Martinez, A.; Quintana, E.; Armengol, S.; et al. ICU pneumonias: A multi-institutional study. Crit. Care Med. 1987, 15, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salata, R.A.; Lederman, M.M.; Shlaes, D.M.; Jacobs, M.R.; Eckstein, E.; Tweardy, D.; Toossi, Z.; Chmielewski, R.; Marino, J.; King, C.H. Diagnosis of nosocomial pneumonia in intubated, intensive care unit patients. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987, 135, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shahin, J.; Bielinski, M.; Guichon, C.; Flemming, C.; Kristof, A.S. Suspected ventilator-associated respiratory infection in severely ill patients: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoclin, A.; Rotolo, F.; Hicheri, Y.; Mons, M.; Chachaty, E.; Gachot, B.; Pignon, J.P.; Wartelle, M.; Blot, F. Ventilator-associated pneumonia and bloodstream infections in intensive care unit cancer patients: A retrospective 12-year study on 3388 prospectively monitored patients. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, K.R.; Steinberg, K.P.; Maunder, R.J.; Milberg, J.A.; Allen, D.L.; Hudson, L.D. Pulmonary infection during the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terraneo, S.; Ferrer, M.; Martín-Loeches, I.; Esperatti, M.; Di Pasquale, M.; Giunta, V.; Rinaudo, M.; De Rosa, F.; Bassi, G.L.; Centanni, S.; et al. Impact of Candida spp. isolation in the respiratory tract in patients with intensive care unit-acquired pneumonia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 94.e1–94.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, J.F.; Cheval, C.; Gachot, B.; Bruneel, F.; Wolff, M.; Carlet, J.; Regnier, B. Usefulness of a strategy based on bronchoscopy with direct examination of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in the initial antibiotic therapy of suspected ventilator-associated pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 2001, 27, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urli, T.; Perone, G.; Acquarolo, A.; Zappa, S.; Antonini, B.; Ciani, A. Surveillance of infections acquired in intensive care: Usefulness in clinical practice. J. Hosp. Infect. 2002, 52, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhamme, K.M.; De Coster, W.; De Roo, L.; De Beenhouwer, H.; Nollet, G.; Verbeke, J.; Demeyer, I.; Jordens, P. Pathogens in early-onset and late-onset intensive care unit–acquired pneumonia. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2007, 28, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.S.; Xiong, W.; Lai, R.P.; Liu, L.; Gan, X.M.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, M.; Lou, Y.X.; Fu, X.Y.; Wang, H.F.; et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in intensive care units in Hubei Province, China: A multicentre prospective cohort survey. J. Hosp. Infect. 2011, 78, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlenberg, A.; Schwab, F.; Behnke, M.; Geffers, C.; Gastmeier, P. Pneumonia associated with invasive and noninvasive ventilation: An analysis of the German nosocomial infection surveillance system database. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Walker, V.; Chen, L.F.; Sexton, D.J.; Anderson, D.J. The epidemiology of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a network of community hospitals: A prospective multicenter study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2013, 34, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leblebicioglu, H.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Arıkan, Ö.A.; Özgültekin, A.; Yalcin, A.N.; Koksal, I.; Usluer, G.; Sardan, Y.C.; Ulusoy, S. Device-associated hospital-acquired infection rates in Turkish intensive care units. Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC). J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 65, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblebicioglu, H.; Yalcin, A.N.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Koksal, I.; Sirmatel, F.; Unal, S.; Turgut, H.; Ozdemir, D.; Ersoz, G.; Uzun, C.; et al. Effectiveness of a multidimensional approach for prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia in 11 adult intensive care units from 10 cities of Turkey: Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC). Infect 2013, 41, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, V.D.; Maki, D.G.; Salomao, R.; Moreno, C.A.; Mehta, Y.; Higuera, F.; Cuellar, L.E.; Arikan, O.A.; Abouqal, R.; Leblebicioglu, H. Device-associated nosocomial infections in 55 intensive care units of 8 developing countries. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Hu, B.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Gao, X.; He, L. Device-associated infection rates in 398 intensive care units in Shanghai, China: International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC) findings. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e774–e780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Hu, B.; Rosenthal, V.D.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; He, L. Impact of a multidimensional approach on ventilator-associated pneumonia rates in a hospital of Shanghai: Findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium. J. Crit. Care 2012, 27, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastre, J.; Fagon, J.Y. Ventilator-associated pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 867–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornely, O.A.; Bassetti, M.; Calandra, T.; Garbino, J.; Kullberg, B.J.; Lortholary, O.; Ullmann, A.J. ESCMID guideline for the diagnosis and management of Candida diseases 2012: Non-neutropenic adult patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Niederman, M.S.; Chastre, J.; Ewig, S.; Fernandez-Vandellos, P.; Hanberger, H.; Kollef, M.; Bassi, G.L.; Luna, C.M.; Martin-Loeches, I.; et al. Summary of the international clinical guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired and ventilator-acquired pneumonia. ERJ Open Res. 2018, 4, 00028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Qi, M.; Hu, Y.; Yu, M.; Liang, Z. The impact of Candida spp airway colonization on clinical outcomes in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2020, 48, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, T.; Tan, Q.; Xiong, L. Effects of Candida colonization on patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia and pathogenic microorganisms: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 111, 116580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenazy, H.; Alghamdi, A.; Pinto, R.; Daneman, N. Candida colonization as a predictor of invasive candidiasis in non-neutropenic ICU patients with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 102, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intra, J.; Sarto, C.; Beck, E.; Tiberti, N.; Leoni, V.; Brambilla, P. Bacterial and fungal colonization of the respiratory tract in COVID-19 patients should not be neglected. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2020, 48, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavaš Tahtler, J.; Cicvarić, A.; Koulenti, D.; Karvouniaris, M.; Bogdan, M.; Kralik, K.; Krajina Kmoniček, I.; Grbić Mlinarević, M.; Kvolik, S. Isolation of Candida Species is Associated with Comorbidities, Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation, and Treatment Outcomes in Surgical ICU Patients, a Cross-Sectional Study. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C. Structural equation modelling the impact of antimicrobials on the human microbiome. Colonization resistance versus colonization susceptibility as case studies. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C. Candida–Acinetobacter–Pseudomonas Interaction Modelled within 286 ICU Infection Prevention Studies. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, J.F.; Schwebel, C.; Styfalova, L.; Cornet, M.; Poirier, P.; Forrestier, C.; Ruckly, S.; Jacob, M.-C.; Souweine, B. Impact of bronchial colonization with Candida spp. on the risk of bacterial ventilator-associated pneumonia in the ICU: The FUNGIBACT prospective cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainha, T.; Jorge, P.; Alves, D.; Lopes, S.P.; Pereira, M.O. Unraveling Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans communication in coinfection scenarios: Insights through network analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 550505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlecht, L.M.; Peters, B.M.; Krom, B.P.; Freiberg, J.A.; Hänsch, G.M.; Filler, S.G.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A.; Shirtliff, M.E. Systemic Staphylococcus aureus infection mediated by Candida albicans hyphal invasion of mucosal tissue. Microbiology 2015, 161 Pt 1, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, K.; Viela, F.; Mathelié-Guinlet, M.; Demuyser, L.; Hauben, E.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A.; Velde, G.V.; Dufrêne, Y.F.; Krom, B.P.; Van Dijck, P. Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus to Candida albicans during co-infection promotes bacterial dissemination through the host immune response. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 624839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, A.K.; Hogan, D.A. Candida albicans: Molecular interactions with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2014, 28, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.; Williamson, D.; Muscedere, J.; Lauzier, F.; Rotstein, C.; Kanji, S.; Jiang, X.; Hall, M.; Heyland, D. Candida in the respiratory tract secretions of critically ill patients and the impact of antifungal treatment: A randomized placebo controlled pilot trial (CANTREAT study). Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.C. Candida and the Gram-positive trio: Testing the vibe in the ICU patient microbiome using structural equation modelling of literature derived data. Emerg. Themes Epidemiol. 2022, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C. Worldwide variation in Pseudomonas associated ventilator associated pneumonia. A meta-regression. J. Crit. Care 2019, 51, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C. World-Wide Variation in Incidence of Staphylococcus aureus Associated Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Meta-Regression. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C. Impact of selective digestive decontamination on respiratory tract Candida among patients with suspected ventilator-associated pneumonia. A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C. World-wide variation in incidence of Acinetobacter associated ventilator associated pneumonia: A meta-regression. BMC Infect Dis. 2016, 16, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata 18 Multiple-Imputation Reference Manual; Stata Press: College station, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersson, A. Graphing confidence ellipses: An update of ellip for Stata 8. Stata J. 2004, 4, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromentin, M.; Ricard, J.D.; Roux, D. Respiratory microbiome in mechanically ventilated patients: A narrative review. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajiei, A.; Liu, L.; Seinen, J.; Dieperink, W.; Hammerschmidt, S.; van Dijl, J.M.; Harmsen, H.J. Specific associations between fungi and bacteria in broncho-alveolar aspirates from mechanically ventilated intensive care unit patients. Virulence 2022, 13, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipiak, W.; Wenzel, M.; Ager, C.; Mayhew, C.A.; Bogiel, T.; Włodarski, R.; Nagl, M. Molecular Analysis of Volatile Metabolites Synthesized by Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus in In Vitro Cultures and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Specimens Reflecting Single-or Duo-Factor Pneumonia. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendleton, K.M.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Dickson, R.P. The significance of Candida in the human respiratory tract: Our evolving understanding. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, B.; Ola, M.; Rolling, T.; Tosini, N.L.; Joshowitz, S.; Littmann, E.R.; Amoretti, L.A.; Fontana, E.; Wright, R.J.; Miranda, E.; et al. High-resolution mycobiota analysis reveals dynamic intestinal translocation preceding invasive candidiasis. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, D.; Gaudry, S.; Dreyfuss, D.; El-Benna, J.; de Prost, N.; Denamur, E.; Saumon, G.; Ricard, J.-D. Candida albicans impairs macrophage function and facilitates Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in rat. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, D.; Gaudry, S.; Khoy-Ear, L.; Aloulou, M.; Phillips-Houlbracq, M.M.; Bex, J.; Skurnik, D.; Denamur, E.; Monteiro, R.C.; Dreyfuss, D.; et al. Airway fungal colonization compromises the immune system allowing bacterial pneumonia to prevail. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, e191–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nseir, S.; Jozefowicz, E.; Cavestri, B.; Sendid, B.; Di Pompeo, C.; Dewavrin, F.; Favory, R.; Roussel-Delvallez, M.; Durocher, A. Impact of antifungal treatment on Candida–Pseudomonas interaction: A preliminary retrospective case–control study. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 33, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Monge, R.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Román, E.; Hube, B.; Pla, J. Candida albicans colonization of the gastrointestinal tract: A double-edged sword. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, J.E.; Corti, M.; Lambert, P.; Ferris, M.; Xin, H. Horizontal transmission of Candida albicans and evidence of a vaccine response in mice colonized with the fungus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C.; Vadas, M.A. Eosinophilia and acquisition of resistance to Nematospiroides dubius in mice sensitized with adult worms. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 1983, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Y.T.; Xu, C.H.; Chen, D.C. Candida colonization in the respiratory tract: What is the significance? Front. Med. 2021, 7, 598037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C. Staphylococcus aureus hitchhiking from colonization to bacteremia via Candida within ICU infection prevention studies: A proof of concept modelling. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 42, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdar, N.; Maki, D.G. The commonality of risk factors for nosocomial colonization and infection with antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, enterococcus, Gram-negative bacilli, Clostridium difficile, and Candida. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Oliveira, J.; Sampaio, N.; Leite, G.S.; Pereira, M.A.; Fortaleza, C.M. Acquisition of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacilli among intensive care unit (ICU) patients with no previous use of carbapenems: Indirect population impact of antimicrobial use. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2022, 43, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, M.; Sahu, C.; Singh, P.; Bhaisora, K.S.; Tejan, N.; Patel, S.S.; Ghoshal, U. Prevalence of traumatic brain injury and associated infections in a trauma center in Northern India. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2023, 15, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J. Structural Equation Modelling as a Proof-of-Concept Tool for Mediation Mechanisms Between Topical Antibiotic Prophylaxis and Six Types of Blood Stream Infection Among ICU Patients. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J. Estimating the herd effects of anti-microbial-based decontamination (ABD) interventions on intensive care unit (ICU) acquired bloodstream infections: A deductive meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e092030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.S.; Tuttobene, M.R.; Montaña, S.; Subils, T.; Cantera, V.; Iriarte, A.; Tuchscherr, L.; Ramirez, M.S. Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin effect on Acinetobacter baumannii behavior. Biology 2022, 11, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wei, L.; Li, W.; Huang, B.; Liu, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; et al. Effect of nebulized amphotericin B in critically ill patients with respiratory Candida spp. de-colonization: A retrospective analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 723904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Su, S.; Yang, H.; Xie, H.B. Clinical outcomes of antifungal therapy on Candida pulmonary colonisation in immunocompetent patients with invasive ventilation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e083918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, P.; Vouidaski, A.; Spernovasilis, N.; Alexopoulou, C.; Papazachariou, A.; Paraschou, E.; Achyropoulou, A.; Maraki, S.; Samonis, G.; Kofteridis, D.P. Candida spp. isolation from critically ill patients’ respiratory tract. Does antifungal treatment affect survival? Germs 2021, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollef, M.H.; Chastre, J.; Fagon, J.Y.; François, B.; Niederman, M.S.; Rello, J.; Torres, A.; Vincent, J.L.; Wunderink, R.G.; Go, K.W.; et al. Global prospective epidemiologic and surveillance study of ventilator-associated pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- François, B.; Jafri, H.S.; Chastre, J.; Sánchez-García, M.; Eggimann, P.; Dequin, P.; Huberlant, V.; Soria, L.; Boulain, T.; Bretonnière, C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of suvratoxumab for prevention of Staphylococcus aureus ventilator-associated pneumonia (SAATELLITE): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase 2 pilot trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, H.; Saqib, M.; Khan, W.; Ismail, S.M.; Sohail, H.; Muneeb, M.; Sheikh, S.S. Ventilator associated pneumonia in intensive care unit patients: A systematic review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 2932–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nseir, S.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Povoa, P.; Metzelard, M.; Du Cheyron, D.; Lambiotte, F.; Tamion, F.; Labruyere, M.; Makris, D.; Geronimi, C.B.; et al. Relationship between ventilator-associated pneumonia and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A planned ancillary analysis of the coVAPid cohort. Crit. Care. 2021, 25, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, M.; Constantin, J.M.; Heming, N.; Camous, L.; Ferré, A.; Razazi, K.; Lapidus, N. COVID-ICU Investigators. Epidemiology, risk factors and prognosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia during severe COVID-19, Multicenter observational study across 149 European Intensive Care Units. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2023, 42, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.K.; Suh, J.W.; Kang, E.J.; Kim, J.Y. Efficacy and safety of fecal microbiota transplantation for decolonization of intestinal multidrug-resistant microorganism carriage: Beyond Clostridioides difficile infection. Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.K.; Lee, M.J.; Ju, Y.; Lee, S.E.; Yang, K.S.; Sohn, J.W.; Kim, M.J. Determining the clinical significance of co-colonization of vancomycin-resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the intestinal tracts of patients in intensive care units: A case–control study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2019, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C. Estimating the herd effects of antimicrobial prevention interventions on ventilator-associated pneumonia within ICU populations: A cluster randomized trial emulation using data from Cochrane reviews. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2025, 80, dkaf033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Lloréns-Villar, Y.; Solinís, M.Á.; Barrasa, H.; Canut-Blasco, A. Does selective digestive decontamination (SDD) increase antibiotic resistance? Long-term comparison of two intensive care units (with and without SDD) of the same tertiary hospital. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 43, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakopoulou, A.; Karakosta, P.; Vourli, S.; Tarpatzi, A.; Varda, P.; Kostoula, M.; Antoniadou, A.; Pournaras, S. Gastrointestinal carriage of vancomycin-resistant enterococci and carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in an endemic setting: Prevalence, risk factors, and outcomes. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reno, J.; Doshi, S.; Tunali, A.K.; Stein, B.; Farley, M.M.; Ray, S.M.; Jacob, J.T. Epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream coinfection among adults with candidemia in Atlanta, GA, 2008–2012. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2015, 36, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.T.; Leboucher, G.; Myard-Dury, A.F.; Girardo, P.; Luzzati, A.; Mary, M.; Sauzon, J.; Lafay, B.; Dauwalder, O.; Laurent, F.; et al. Metapopulation ecology links antibiotic resistance, consumption, and patient transfers in a network of hospital wards. Elife 2020, 9, e54795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.C. Fungi of the human gut microbiota: Roles and significance. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 311, 151490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibulková, I.; Řehořová, V.; Hajer, J.; Duška, F. Fecal microbial transplantation in critically ill patients—Structured review and perspectives. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Haku, A.; Bi, B.; Takahashi, H.; Kamada, N.; Yaguchi, T.; Saijo, S.; Yoneyama, M.; Goto, Y. Fecal microbiota transplantation prevents Candida albicans from colonizing the gastrointestinal tract. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 63, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.C. Endotoxemia and Gram-negative bacteremia as predictors of outcome in sepsis: A meta-analysis using ROC curves. J. Endotoxin. Res. 2003, 9, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patients | VAP Isolates (n) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Year | Ref. | LOS | (n) | Candida | Pseudomonas | Acinetobacter | Staph Aureus |
| Antonelli | 1994 | 1 | 16.8 | 124 | 1 | 5 | 6 | 10 |
| Bercault | 2001 | 2 | 26 | 1144 | 2 | · | · | · |
| Boots | 2008 | 3 | 12.6 | 412 | 0 | 15 | 14 | 32 |
| Bregeon | 1997 | 4 | 11 | 660 | 3 | 33 | 10 | 34 |
| Cade | 1993 | 5 | 16 | 98 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 13 |
| Cavalcanti | 2006 | 6 | 10 | 190 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 18 |
| Cenderero | 1999 | 7 | 6.5 | 123 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 9 |
| Chastre_ARDS | 1998 | 8 | 25 | 56 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 22 |
| Chastre_no_ARDS | 1998 | 8 | 15 | 187 | 1 | 28 | 7 | 22 |
| Chevret | 1993 | 9 | 5 | 255 | 4 | 21 | 5 | 23 |
| Cook_trauma | 2010 | 10 | 8 | 511 | 1 | 16 | 8 | 15 |
| Cook_non-trauma | 2010 | 10 | 13 | 2080 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 14 |
| Craven-surgical | 1988 | 11 | 5.7 | 521 | 5 | 17 | 0 | 12 |
| Craven-medical | 1988 | 11 | 6.4 | 277 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 9 |
| Daschner_Freiburg | 1982 | 12 | 5 | 5374 | 7 | 22 | · | 21 |
| Daschner_Switzerland | 1982 | 12 | 5 | 1578 | 6 | 30 | · | 20 |
| Daschner | 1988 | 13 | 6 | 142 | 22 | 39 | 23 | 55 |
| Daschner | 1988 | 13 | 6 | 116 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 13 |
| Delle Rose | 2016 | 14 | 5 | 1647 | 27 | 52 | 68 | 32 |
| Ewig | 1999 | 15 | 10 | 48 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 5 |
| Fagon’00_invasive | 2000 | 16 | 10.4 | 1 | 5 | 27 | 6 | 20 |
| Fagon’00_clinical | 2000 | 16 | 10.7 | 1 | 38 | 57 | 11 | 40 |
| Fowler | 2003 | 17 | 15 | 1 | 2 | 28 | 3 | 30 |
| George | 1998 | 18 | 8 | 223 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 8 |
| Giamarellos-Bourboulis | 2009 | 19 | 12 | 72 | 2 | 5 | 17 | · |
| Guérin | 1997 | 20 | 18.5 | 260 | 0 | 14 | 1 | 3 |
| Gursel | 2010 | 21 | 10 | 92 | 1 | 10 | 23 | 13 |
| Heyland | 1999 | 22 | 7 | 1014 | 26 | 38 | 6 | 64 |
| Holzapfel | 1999 | 23 | 16 | 399 | 4 | 16 | 7 | 28 |
| Hugonnet | 2007 | 24 | 6 | 936 | 40 | 31 | 8 | 55 |
| Ibrahim | 2000 | 25 | 4.8 | 1882 | 19 | 130 | 16 | 143 |
| Jimenez | 1989 | 26 | 10 | 77 | 0 | 7 | 6 | 2 |
| John | 2017 | 27 | 6 | 202 | 1 | 5 | 14 | · |
| Kantorova | 2004 | 28 | 9 | 287 | 4 | 5 | · | 5 |
| Kautzky | 2014 | 29 | 20 | 65 | 2 | · | · | · |
| Kollef ‘97_pre | 1997 | 30 | 4 | 353 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 5 |
| Kollef ‘97_post | 1997 | 30 | 4 | 327 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| Kolpa | 2018 | 31 | 19 | 1270 | 5 | 20 | 72 | 16 |
| Koss– N | 2001 | 32 | 14 | 87 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| Koss– P | 2001 | 32 | 11 | 66 | 3 | 9 | 2 | 4 |
| Laggner | 1989 | 33 | 10.1 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Li | 2016 | 34 | 15 | 131 | 11 | · | · | · |
| Luna | 2003 | 35 | 8 | 427 | 2 | 13 | 25 | 19 |
| Magnason | 2008 | 36 | 7.8 | 280 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 |
| Mahul | 1992 | 37 | 21.5 | 145 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 10 |
| Memish | 2000 | 38 | 11 | 202 | 4 | 21 | 14 | 16 |
| Moine | 2002 | 39 | 14.4 | 764 | 2 | 27 | 1 | 19 |
| Palabiyikoglu | 2001 | 40 | NA | 50 | 1 | · | · | · |
| Potgieter | 1987 | 41 | 9 | 250 | 5 | 26 | 32 | 23 |
| Ramirez | 2016 | 42 | 13 | 440 | 0 | · | · | 8 |
| Ranes | 2006 | 43 | NA | 1 | 10 | 236 | · | 79 |
| Rello’03 | 2003 | 44 | 20 | 99 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 2 |
| Rello’91 | 1991 | 45 | 7.9 | 264 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 15 |
| Rello’93 | 1993 | 46 | NA | 1 | 2 | 24 | 4 | 28 |
| Resende | 2013 | 47 | 22 | 126 | 3 | 11 | 11 | 5 |
| Rodrigues | 2009 | 48 | 10 | 233 | 2 | 10 | 14 | 11 |
| Rosenthal | 2012 | 49 | 6.9 | 3889 | 7 | 58 | 43 | 21 |
| Rosenthal | 2012 | 49 | 6.4 | 51,618 | 48 | 448 | 426 | 319 |
| Rozaidi | 2001 | 50 | 5 | 988 | 4 | · | 12 | 4 |
| Ruiz-Santana | 1987 | 51 | 7 | 1005 | 1 | 56 | 0 | 12 |
| Salata | 1987 | 52 | 11 | 51 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 2 |
| Shahin | 2013 | 53 | 10 | 267 | 3 | 4 | · | 6 |
| Stolcin | 2020 | 54 | 6 | 930 | 5 | 53 | 2 | 47 |
| Sutherland_ARDS | 1995 | 55 | 20 | 105 | 19 | 10 | 11 | 7 |
| Terraneo | 2016 | 56 | 22 | 1 | 21 | 69 | 1 | 65 |
| Timsit | 2001 | 57 | 30 | 1 | 2 | 21 | 4 | 10 |
| Urli | 2002 | 58 | 21 | 178 | 1 | 27 | · | 40 |
| Verhamme | 2007 | 59 | 8 | 4000 | 6 | 54 | 3 | 56 |
| Xie | 2011 | 60 | 7 | 4155 | 88 | 169 | 137 | 92 |
| Kohlenberg | 2010 | 61 | NA | 779,500 | 634 | 1067 | 152 | 1222 |
| Lee | 2013 | 62 | NA | 1 | 18 | 40 | 8 | 85 |
| Leblebicioglu | 2007 | 63 | NA | 3296 | 12 | 166 | 182 | 151 |
| Leblebicioglu | 2013 | 64 | 6 | 448 | 2 | 22 | 12 | 14 |
| Leblebicioglu | 2013 | 64 | 8 | 3864 | 4 | 119 | 130 | 51 |
| Rosenthal_D | 2006 | 65 | 5.3 | 3413 | 0 | 27 | 0 | 1 |
| Rosenthal_C | 2006 | 65 | 6.7 | 2172 | 0 | 18 | 3 | 25 |
| Rosenthal_E | 2006 | 65 | 6.3 | 1514 | 2 | 21 | 2 | 10 |
| Rosenthal_H | 2006 | 65 | 11.7 | 2305 | 10 | 142 | 137 | 118 |
| Rosenthal_G | 2006 | 65 | 5 | 1359 | 11 | 25 | 5 | 21 |
| Rosenthal_B | 2006 | 65 | 9.7 | 1029 | 7 | 49 | 38 | 19 |
| Rosenthal_A | 2006 | 65 | 5.5 | 8867 | 0 | 23 | 43 | 91 |
| Rosenthal_F | 2006 | 65 | 6.7 | 410 | 0 | 14 | 20 | 1 |
| Tao | 2011 | 66 | NA | 391,527 | 86 | 1446 | 1562 | 922 |
| Tao | 2012 | 67 | NA | 16,426 | 18 | 34 | 60 | 38 |
| Original Data | Accounting for Missing Data with MI 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Factor | Coefficient | 95% Confidence Interval | Coefficient | 95% Confidence Interval |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Candida2 | 0.53 | +0.37–+0.69 | 0.54 | +0.38–+0.71 |
| LOS 3 | 0.04 | −0.01–+0.08 | 0.04 | −0.01–+0.08 | |
| Year of study publication 4 | −0.02 | −0.05–+0.01 | −0.02 | −0.04–+0.01 | |
| Bronchoscopic sampling 5 | +0.14 | −0.37–+0.66 | +0.12 | −0.39–+0.64 | |
| Constant | −0.078 | −1.88–+0.38 | −0.071 | −1.85–+0.42 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Candida2 | 0.42 | +0.29–+0.54 | 0.42 | +0.28–+0.56 |
| LOS 3 | 0.04 | +0.01–+0.07 | 0.03 | −0.01–+0.07 | |
| Year of study publication 4 | −0.02 | −0.04–+0.01 | −0.02 | −0.04–+0.01 | |
| Bronchoscopic sampling 5 | −0.04 | −0.44–+0.37 | −0.05 | −0.5–+0.40 | |
| Constant | −1.09 | −2.0–−0.22 | −1.03 | −2.0–−0.10 | |
| Acinetobacter species | Candida2 | 0.57 | +0.30–+0.83 | 0.59 | +0.29–+0.88 |
| LOS 3 | 0.03 | −0.05–+0.10 | 0.03 | −0.06–+0.12 | |
| Year of study publication 4 | 0.02 | −0.03–+0.07 | 0.02 | −0.04–+0.08 | |
| Bronchoscopic sampling 5 | −0.35 | −1.23–+0.53 | −0.36 | −1.34–+0.62 | |
| Constant | −2.17 | −4.1–−0.26 | −2.16 | −4.53–−0.2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hurley, J. Associations Between Candida and Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter Species as Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Isolates in 84 Cohorts of ICU Patients. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061181
Hurley J. Associations Between Candida and Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter Species as Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Isolates in 84 Cohorts of ICU Patients. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061181
Chicago/Turabian StyleHurley, James. 2025. "Associations Between Candida and Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter Species as Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Isolates in 84 Cohorts of ICU Patients" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061181
APA StyleHurley, J. (2025). Associations Between Candida and Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter Species as Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Isolates in 84 Cohorts of ICU Patients. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061181






