Magnetite-Assisted Capture Affinity, Concentration Dependence, and Magnetic Extraction Rate of Bacillus cereus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterisation of IONPs (Fe3O4)
2.3. Bacterial Capture/Affinity Studies with IONPs
2.4. In Vitro Evaluation of IONPs on the Viability of Bacillus cereus
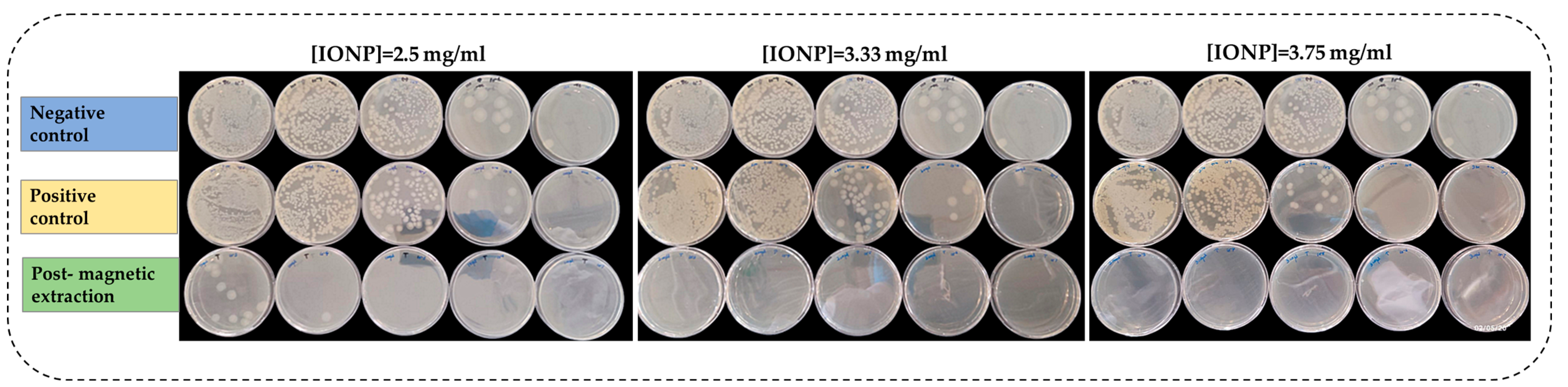
2.4.1. Comparison of Magnetic Extraction of Bacillus cereus with Controls
2.4.2. Colony-Forming Unit (CFU) Assay
2.4.3. Growth Kinetics for Bacillus cereus
2.4.4. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5. Influence of Time on Magnetic Decantation of Bacillus cereus
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of the Fe3O4 @ Citrate Nanoparticles
3.2. Bacterial Capture/Affinity Studies
3.3. Viability of Bacillus cereus Under IONP Exposure
3.3.1. Magnetic Extraction of Bacillus cereus with Controls Using Plate Assay
3.3.2. CFU Assay for Viability of B. cereus
3.4. Time-Dependent Magnetic Decantation of Bacillus cereus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MNP | Magnetic nanoparticle |
| IONP | Iron oxide nanoparticle |
| Fe3O4 | Magnetite |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| Fe2O3 | Maghemite |
| MHB | Mueller–Hinton broth |
| MHA | Mueller–Hinton agar |
| NB | Nutrient broth |
| TSA | Tryptic soy agar |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| OD | Optical density |
| CFU | Colony-forming units |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| DI | Dispersity index |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| IAA | Indole acetic acid |
References
- Vaezi-Kakhki, A.; Asoodeh, A. Comparison of Different Methods for Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Investigation of Their Cellular Properties, and Antioxidant Potential. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 645, 123417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapa-González, C.; Sosa, K.V.; Roacho-Pérez, J.A.; García-Casillas, P.E. Adsorption of Serum Protein in Chitosan-Coated and Polyethyleneimine-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles. MRS Adv. 2021, 6, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhong, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Design, Preparation, and Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Food Safety Analysis: A Review of Recent Advances. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhoo, A.; Sillanpää, M. Magnetic Nanoadsorbents for Micropollutant Removal in Real Water Treatment: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4393–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.; Ibrahim, H.; Rashid, F.L.; Hadi, A. Synthesis and Augmented Morphological and Optical Properties of Si3N4-TiN Inorganic Nanostructures Doped PVP for Promising Optoelectronics Applications. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024, 35, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzensteiner, A.; Rosalie, J.M.; Pippan, R.; Bachmaier, A. Synthesis of Nanodiamond Reinforced Silver Matrix Nanocomposites: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 782, 139254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.M.; El-Safty, S.; Tounsi, A.; Shenashen, M. A Review of Magnetic Nanoparticles Used in Nanomedicine. APL Mater. 2024, 12, 10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiao, F.; Bai, X.; Xu, H. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Food Hazard Factors Sensing: Synthesis, Modification and Application. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.; Ramalho, P.S.F.; Moreira, N.F.F.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Nunes, O.C.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P. Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Water Purification. Environ. Adv. 2020, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Ahamad, L.; Chaudhary, A.; Kumar, G.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, S. Nanoparticle-Mediated Bioremediation as a Powerful Weapon in the Removal of Environmental Pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabagh, S.; Haris, S.A.; Isfahani, B.K.; Ertas, Y.N. Silver-Decorated and Silica-Capped Magnetite Nanoparticles with Effective Antibacterial Activity and Reusability. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 2266–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowska, A.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Lendzion-Bieluń, Z. TiO2-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles (Fe3O4) with Antibacterial Properties. Materials 2022, 15, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, S.; Singh, I.K.; Singh, A. Microbial Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Plant Science and Agriculture. Plant Nano Biol. 2023, 4, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Tiwari, S.; Kumawat, K.C.; Cardinale, M. Nano-Biofertilizers as Bio-Emerging Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture Development: Potentiality and Their Limitations. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feris, K.; Otto, C.; Tinker, J.; Wingett, D.; Punnoose, A.; Thurber, A.; Kongara, M.; Sabetian, M.; Quinn, B.; Hanna, C.; et al. Electrostatic Interactions Affect Nanoparticle-Mediated Toxicity to Gram-Negative Bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4429–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Ruan, J.; Zhuang, X. Using Positively Charged Magnetic Nanoparticles to Capture Bacteria at Ultralow Concentration. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Sánchez, S.; Barrios-Gumiel, A.; Sánchez-Nieves, J.; Copa-Patiño, J.L.; de la Mata, F.J.; Gómez, R. Bacteria Capture with Magnetic Nanoparticles Modified with Cationic Carbosilane Dendritic Systems. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 133, 112622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.D.; Kim, U.; Oh, S.W. Simultaneous Capture of Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella typhimurium Using Arginine-Modified Chitosan-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles in Fresh-Cut Salad. Food Control 2025, 171, 111122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dester, E.; Alocilja, E. Current Methods for Extraction and Concentration of Foodborne Bacteria with Glycan-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jian, X.; Xing, X.-H.; Zhang, C. Highly Efficient Capture of Marine Microbial Strains in Seawater Using Bare Fe3O4 Magnetic Beads. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Deng, J.; Liang, J.; Shan, C.; Tong, M. Efficient Bacteria Capture and Inactivation by Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoudho, K.N.; Uddin, S.; Rumon, M.M.H.; Shakil, M.S. Influence of Physicochemical Properties of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles on Their Antibacterial Activity. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 33303–33334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranmadugala, D.; Ebrahiminezhad, A.; Manley-Harris, M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Berenjian, A. The Effect of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles on Bacillus subtilis Biofilm, Growth and Viability. Process Biochem. 2017, 62, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Dobara, M.I.; Kamel, M.A.; El-Sayed, A.K.A.; El-Zahed, M.M. Antibacterial Activity of Extracellular Biosynthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles against Locally Isolated β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Egypt. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, F.; BaniHani, W.; BaniHani, R.; Al-Khateeb, H.; Al-Qadi, M.; Bataineh, Q. Al Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag), Magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4), and Magnetite/Silver Core-Shell (Fe3O4/Ag) Nanoparticles, and Their Application against Drug-Resistant Bacteria. J. Clust. Sci. 2024, 35, 2979–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, R.; Nguyen, N.D.; Fathima, H.A.; Devanesan, S.; Farhat, K.; Liu, X. In Vitro Analysis of Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoparticle Mediated Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Their Antimicrobial Activity. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leareng, S.K.; Ubomba-Jaswa, E.; Musee, N. Toxicity of Zinc Oxide and Iron Oxide Engineered Nanoparticles to Bacillus subtilis in River Water Systems. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Cheng, J. Effects of Water Chemistry and Surface Contact on the Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles to Bacillus subtilis. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzepiłko, A.; Matyszczuk, K.M.; Święciło, A. Effect of Sublethal Concentrations of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Bacillus cereus. Pathogens 2023, 12, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamuni-Badiger, P.P.; Patil, P.M.; Badiger, M.V.; Patel, P.R.; Thorat-Gadgil, B.S.; Pandit, A.; Bohara, R.A. Biofilm Formation to Inhibition: Role of Zinc Oxide-Based Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. ZnO Nanoparticles Inhibit Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factor Production. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.; Rabbi, M.A.; Ara, T.; Hossain, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Elaissari, A.; Ahmad, H.; Rahman, M.M. Vancomycin Conjugated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Magnetic Targeting and Efficient Capture of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36319–36328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Hong, M.; Miao, Z.; Miao, Z.; Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Immobilized with Sugar-Containing Poly(Ionic Liquid) Brushes for Efficient Trapping and Killing of Bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 3664–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daramola, O.B.; Torimiro, N.; George, R.C.; Daramola, I.V.; Omole, R.K. Affinity Capture Using Ligand and Polymer-Functionalized Iron Oxide, Gold and Iron-Gold Nanocomposites to Target Enteric Bacteria. Bionanoscience 2025, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Smith, G.; Javed, B.; Dee, G.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Curtin, J.; Byrne, H.J.; O’Connor, C.; Tian, F. Design and Development of Magnetic Iron Core Gold Nanoparticle-Based Fluorescent Multiplex Assay to Detect Salmonella. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atapattu, G.; Obeng, S.A.; Battersby, T.; Giltrap, M.; Tian, F. Effect of ‘Peatland-Use’ Type on Culturable Microbial Groups in Irish Peatlands in the Midlands. Land 2023, 12, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakha, M.; Pal, S.; Samantarrai, D.; Panigrahi, T.K.; Mallick, B.C.; Pramanik, K.; Mallick, B.; Jha, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Iron Oxide Nanoparticle upon Modulation of Nanoparticle-Bacteria Interface. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, G.; Chandra, G.K.; Elayaraja, K.; Mahapatra, D.R.; Subramania, A.; Guo, Z.; Umapathy, S.; Manikandan, E. Nanoparticles and Bacterial Interaction of Host-Pathogens and the Detection Enhancement of Biomolecules by Fluorescence Raman Spectroscopic Investigation. Eng. Sci. 2022, 20, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A. A Comparative Study of Physical Properties in Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Prepared by Coprecipitation and Citrate Methods. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 3577–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu Zhou, K.; Ionescu, A.; Wan, E.; Ho, Y.N.; Barnes, C.H.W.; Christie, G.; Wilson, D.I. Paramagnetism in Bacillus Spores: Opportunities for Novel Biotechnological Applications. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 115, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleanthous, C.; Armitage, J.P. The Bacterial Cell Envelope. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20150019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Carretero, M.; Rodríguez-López, J.; Ropero-Moreno, C.; Granada, J.; Delgado-Martín, J.; Martinez-Bueno, M.; Fernandez-Vivas, A.; Jimenez-Lopez, C. Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles for Bacterial Magnetic Concentration in Liquids and QPCR-Detection. Food Control 2023, 147, 109623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenmaier, C.; Peschel, A. Teichoic Acids and Related Cell-Wall Glycopolymers in Gram-Positive Physiology and Host Interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chwalibog, A.; Sawosz, E.; Hotowy, A.; Szeliga, J.; Mitura, S.; Mitura, K.; Grodzik, M.; Orlowski, P.; Sokolowska, A. Visualization of Interaction between Inorganic Nanoparticles and Bacteria or Fungi. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Sun, B.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L. Self-Defense Mechanisms of Microorganisms from the Antimicrobial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles: Highlight the Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindedahl, A.M.; Strehlau, J.H.; Arnold, W.A.; Penn, R.L. Organic Matter and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Aggregation, Interactions, and Reactivity. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Jiang, W.; McClements, J.D.; Xing, B. Colloidal Stability of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Influence of Natural Organic Matter and Synthetic Polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 2011, 27, 8036–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elechalawar, C.K.; Hossen, M.N.; McNally, L.; Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Analysing the Nanoparticle-Protein Corona for Potential Molecular Target Identification. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Khan, S.; Rehman, S.U.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ur, Z.; Mashwani, R.; Rha, E.S.; Jamil, M. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Enhance the Tolerance and Remediation Potential of Bacillus spp. against Heavy Metal Stress. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.; Rashad, E.; Elgarahy, A.; Elwakeel, K. Effect of Green Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles on Bacterial Microbiome for Clean up the Crude Oil. Aswan Univ. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 4, 49–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcherding, J.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Chen, H.; Stebounova, L.; Wu, C.M.; Rubasinghege, G.; Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Caraballo, J.C.; Zabner, J.; Grassian, V.H.; et al. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Growth, Induce Biofilm Formation, and Inhibit Antimicrobial Peptide Function. Environ. Sci. Nano 2014, 1, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, Z.L.; Daneshjou, S. Bacterial Nano-Factories as a Tool for the Biosynthesis of TiO2 Nanoparticles: Characterization and Potential Application in Wastewater Treatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 5656–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.; Pandey, A.; Neogi, S. Bacterial Cell Permeability Study by Metal Oxide and Mixed Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Analysis of the Factors Contributing to the Antibacterial Activity of Nanoparticles. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.A.; Oves, M.; Satar, R.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, S.I.; Jafri, M.A.; Zaidi, S.K.; Alqahtani, M.H. Antibacterial Activity of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Technology against And Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2017, 19, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; El-Tohamy, M.F.; Moubayed, N.M.S. Impact of Metal Nanoparticles Biosynthesized Using Camel Milk on Bacterial Growth and Copper Removal from Wastewater. Green Process. Synth. 2025, 14, 20240192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atapattu, G.N.; Battersby, T.; Giltrap, M.; Tian, F. Do the Culturable Microbial Groups Present in Cutaway Bogs Change According to Temporal Variation? Pilot Study Based on the Midlands in the Republic of Ireland. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atapattu, G.N.; Giltrap, M.; Tian, F. Magnetite-Assisted Capture Affinity, Concentration Dependence, and Magnetic Extraction Rate of Bacillus cereus. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061176
Atapattu GN, Giltrap M, Tian F. Magnetite-Assisted Capture Affinity, Concentration Dependence, and Magnetic Extraction Rate of Bacillus cereus. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061176
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtapattu, Gouri Nilakshika, Michelle Giltrap, and Furong Tian. 2025. "Magnetite-Assisted Capture Affinity, Concentration Dependence, and Magnetic Extraction Rate of Bacillus cereus" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061176
APA StyleAtapattu, G. N., Giltrap, M., & Tian, F. (2025). Magnetite-Assisted Capture Affinity, Concentration Dependence, and Magnetic Extraction Rate of Bacillus cereus. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061176






