Microbiological Profiles, Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns and the Role of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Patients Diagnosed with Periprosthetic Joint Infection over 8 Years: Results from a Single-Center Observational Cohort Study from Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Laboratory Studies
2.4. Study Definitions and Classification
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
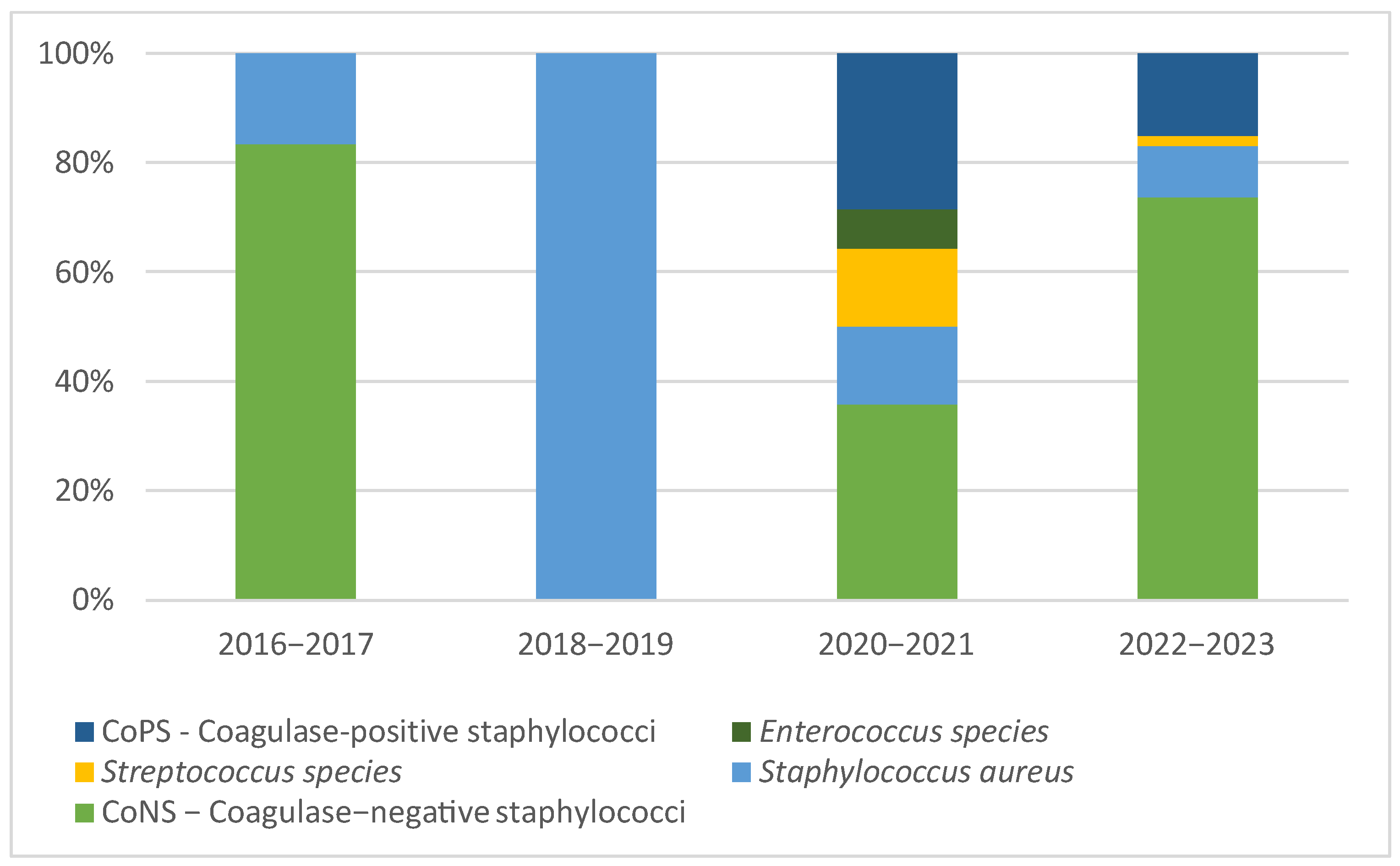
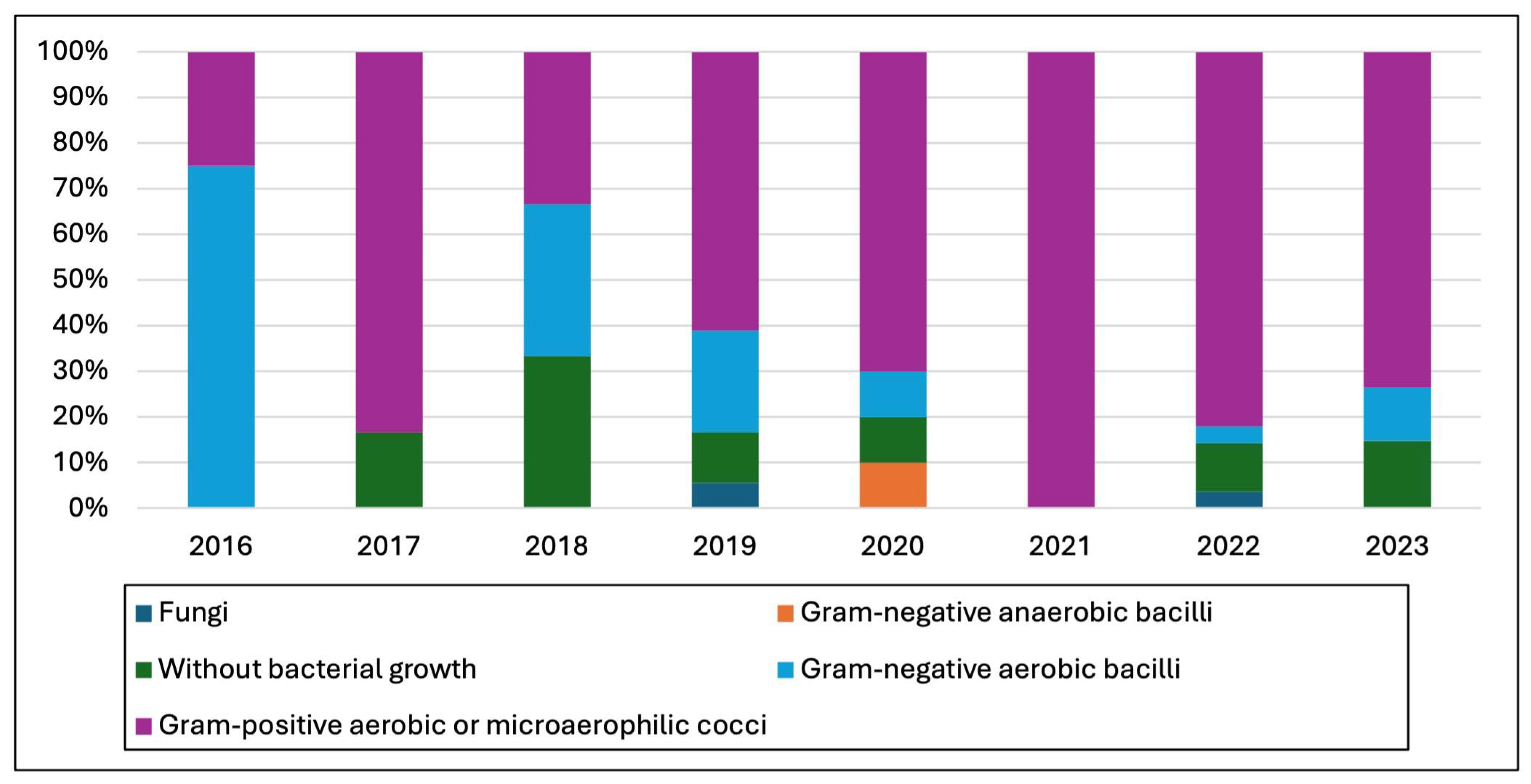
3.2. Microbiological Studies and Patterns
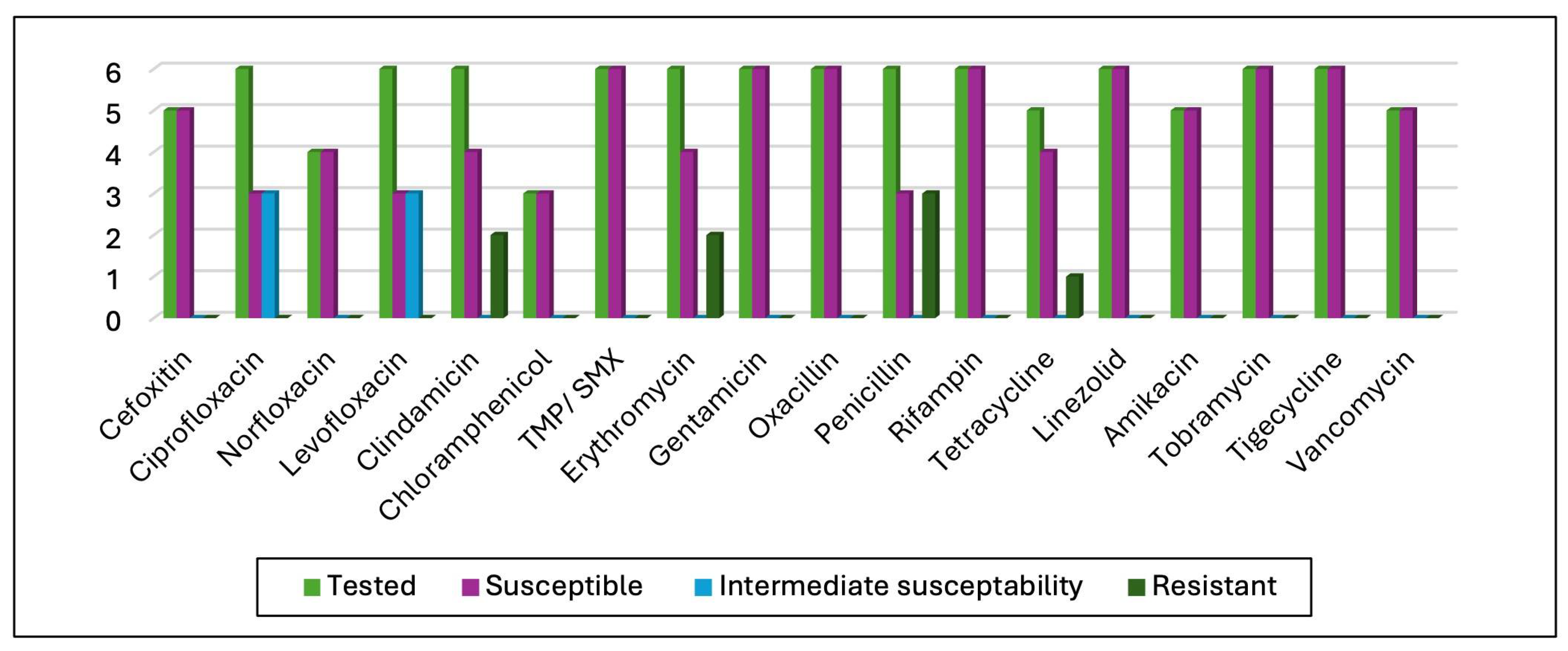
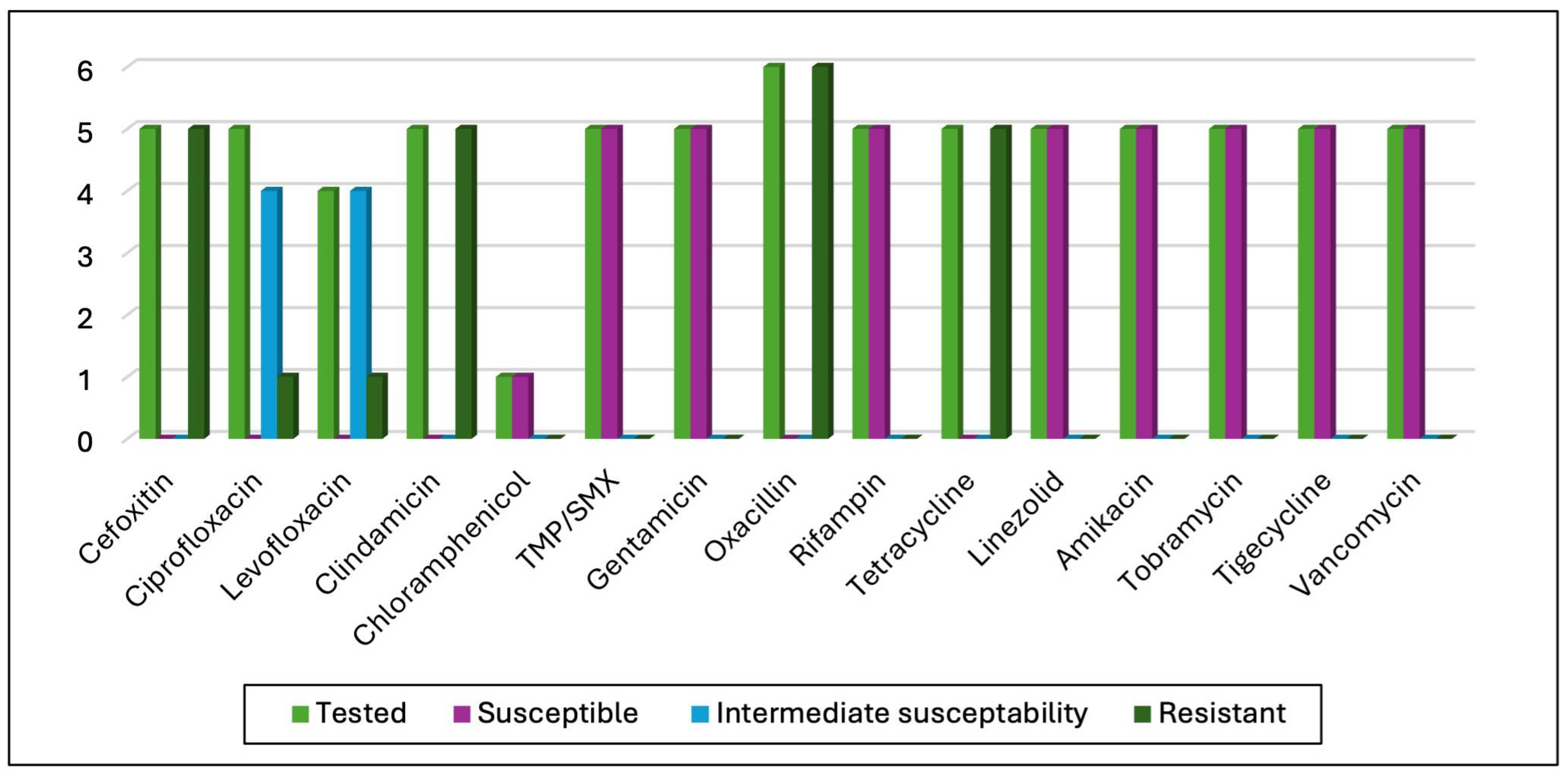
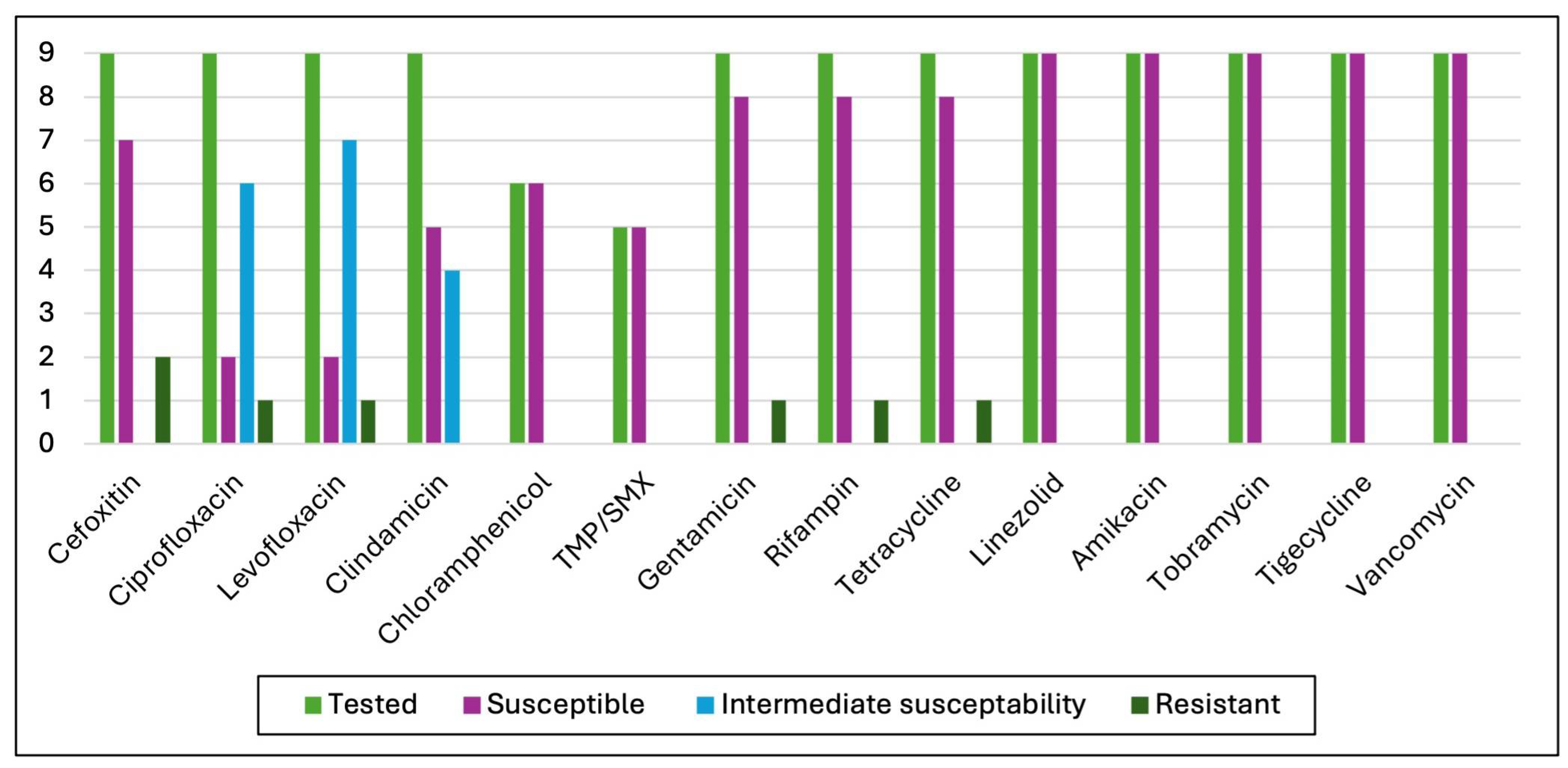
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test (AST) Results
3.4. Multidrug-Resistant Periprosthetic Joint Infections
4. Discussion
4.1. Pathogen Distribution and Epidemiological Patterns
4.2. Multi-Drug Resistant Strains
4.3. Polymicrobial Infections
4.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test Results
4.5. Patterns in Epidemiology or MDR-Isolated Strains
4.6. Implications for Antimicrobial Stewardship and Surveillance
4.7. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PJI | Prosthetic joint infection |
| ASA score | American Society of Anesthesiologists score |
| MDR | Multidrug-resistant |
| CoPS CoNS | Coagulase-positive staphylococci Coagulase-negative staphylococci |
Appendix A
| Microorganisms × Type of Infection × Year Crosstabulation | Pearson Chi-Square Value | p = | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Type of Infection | Total | |||||
| Acute | Chronic | ||||||
| 2016 | Microorganisms | Enterobacter aerogenes | 0 | 1 | 1 | - | - |
| Proteus spp. | 0 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Coagulase-negative staphylococci | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Total | 0 | 4 | 4 | ||||
| 2017 | Microorganisms | Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2.626 | 0.269 |
| Without bacterial growth | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 1 | 3 | 4 | ||||
| Total | 2 | 4 | 6 | ||||
| 2018 | Microorganisms | Enterobacter spp. | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3.000 | 0.223 |
| Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Without bacterial growth | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Total | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 2019 | Microorganisms | Candida tropicalis | 0 | 1 | 1 | 9.775 | 0.369 |
| E. coli | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Enterococcus avium | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Proteus mirabilis | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus hominis | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Coagulase-positive staphylococci | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Without bacterial growth | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 0 | 5 | 5 | ||||
| Total | 5 | 12 | 17 | ||||
| 2020 | Microorganisms | Enterococcus faecium | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6.875 | 0.442 |
| Gram-negative anaerobic bacilli | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Group B Streptococcus | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Streptococcus viridans | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Proteus mirabilis | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Coagulase-positive staphylococci | 0 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Without bacterial growth | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Total | 2 | 8 | 10 | ||||
| 2021 | Microorganisms | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2.917 | 0.405 |
| Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Coagulase-positive staphylococci | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 0 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| Total | 1 | 6 | 7 | ||||
| 2022 | Microorganisms | Candida albicans | 1 | 0 | 1 | 17.395 | 0.097 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus capitis | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus simulans | 0 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| Coagulase-negative staphylococci | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus hominis | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Coagulase-positive staphylococci | 0 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| Without bacterial growth | 0 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 1 | 8 | 9 | ||||
| Total | 5 | 23 | 28 | ||||
| 2023 | Microorganisms | Citrobacter braakii | 0 | 1 | 1 | 22.120 | 0.076 |
| Citrobacter freundii | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Enterobacter cloacae | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus auricularis | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Streptococcus viridans | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Staphylococcus capitis | 2 | 0 | 2 | ||||
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Staphylococcus simulans | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Coagulase-negative staphylococci | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Staphylococcus hominis | 0 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Without bacterial growth | 0 | 5 | 5 | ||||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 3 | 7 | 10 | ||||
| Total | 11 | 23 | 34 | ||||

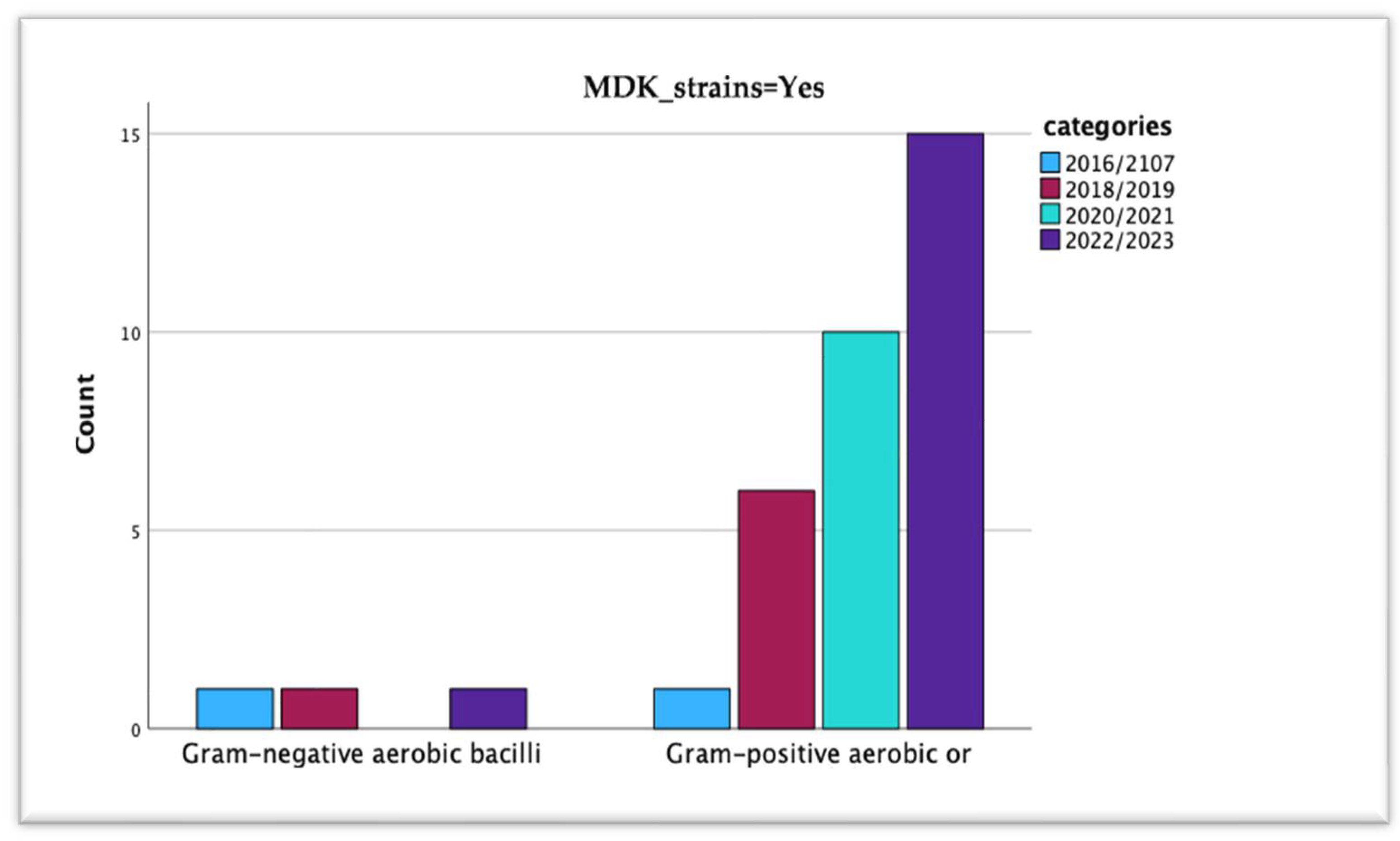
| MDR Strains | Years | Total | Pearson Chi-Square Value | p = | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016/2107 | 2018/2019 | 2020/2021 | 2022/2023 | ||||||
| No | Type of strain | Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 1.490 | 0.685 |
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 4 | 6 | 3 | 28 | 41 | ||||
| Total | 5 | 7 | 3 | 30 | 45 | ||||
| Yes | Type of strain | Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 5.719 | 0.126 |
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 1 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 32 | ||||
| Total | 2 | 7 | 10 | 16 | 35 | ||||
| Without bacterial growth | Type of strain | Without bacterial growth | 1 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 13 | - | - |
| Total | 1 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 13 | ||||
| Total | Type of strain | Without bacterial growth | 1 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 13 | 6.427 | 0.377 |
| Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 2 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 7 | ||||
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 5 | 12 | 13 | 43 | 73 | ||||
| Total | 8 | 17 | 14 | 54 | 93 | ||||
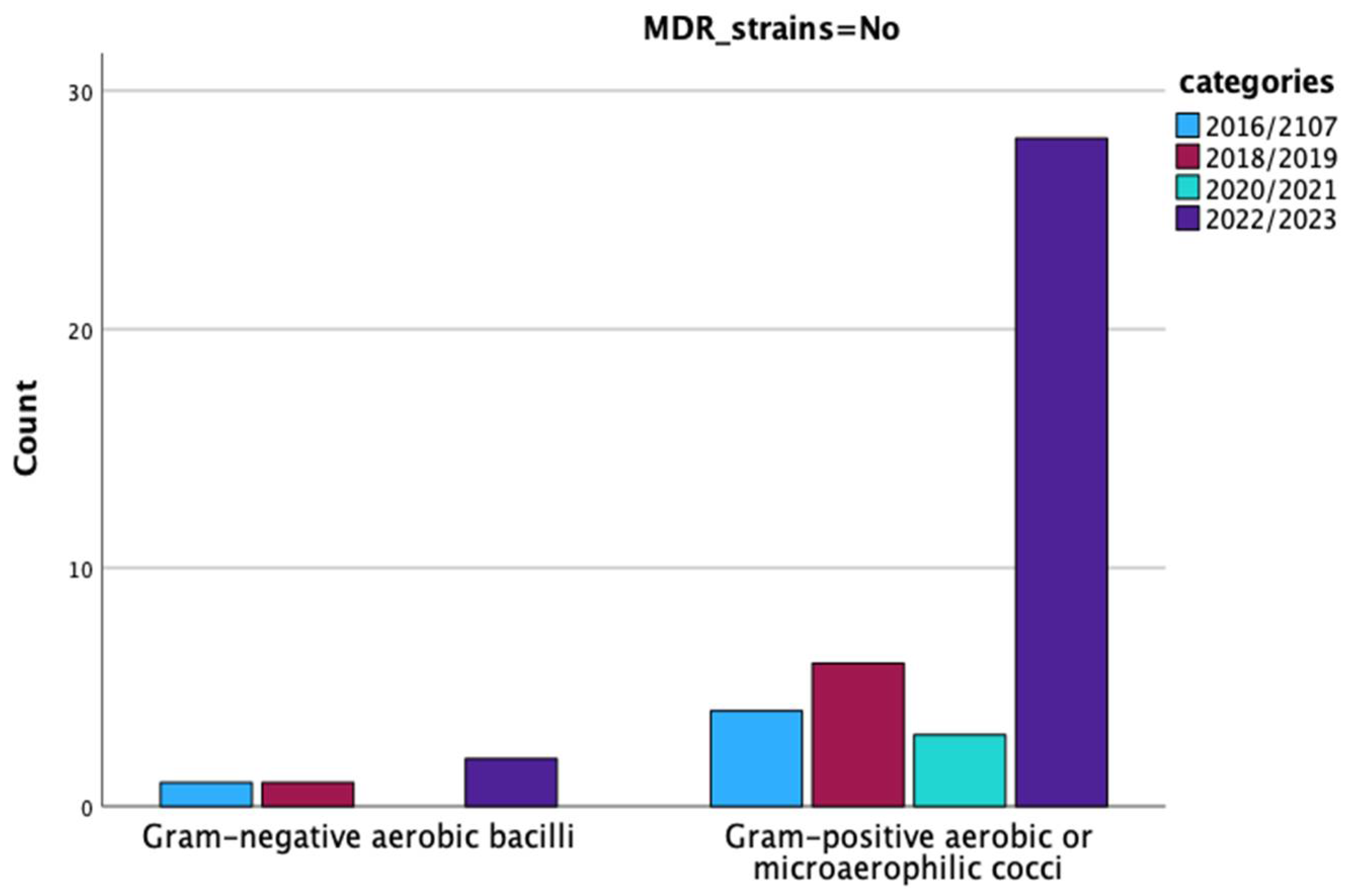
| MDR Strains | Type of Infection | Total | Pearson Chi-Square Value | p = | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute | Chronic | ||||||
| No | Type_Gram_Fungi | Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0.006 | 0.937 |
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 11 | 30 | 41 | ||||
| Total | 12 | 33 | 45 | ||||
| Yes | Type of microorganism | Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0.365 | 0.546 |
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 6 | 26 | 32 | ||||
| Total | 7 | 28 | 35 | ||||
| Total | Type of microorganism | Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 2 | 5 | 7 | 0.098 | 0.754 |
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 17 | 56 | 73 | ||||
| Total | 19 | 61 | 80 | ||||
| MDR Strains | Site | Total | Pearson Chi-Square Value | p = | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip | Knee | ||||||
| No | Type of microorganism | Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 4 | 0 | 4 | 1.784 | 0.182 |
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 28 | 13 | 41 | ||||
| Total | 32 | 13 | 45 | ||||
| Yes | Type of microorganism | Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0.122 | 0.727 |
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 14 | 18 | 32 | ||||
| Total | 15 | 20 | 35 | ||||
| Without bacterial growth | Type of microorganism | Without bacterial growth | 5 | 8 | 13 | - | - |
| Total | 5 | 8 | 13 | ||||
| Total | Type of microorganism | Without bacterial growth | 5 | 8 | 13 | 2.368 | 0.306 |
| Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 5 | 2 | 7 | ||||
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 42 | 31 | 73 | ||||
| Total | 52 | 41 | 93 | ||||
References
- Zhao, A.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Understanding bacterial biofilms: From definition to treatment strategies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1137947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birlutiu, V.; Birlutiu, R.M. Endocarditis due to Abiotrophia defectiva, a biofilm-related infection associated with the presence of fixed braces. Medicine 2017, 96, e8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlutiu, V.; Birlutiu, R.M.; Costache, V.S. Viridans streptococcal infective endocarditis associated with fixed orthodontic appliance managed surgically by mitral valve plasty. Medicine 2018, 97, e11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.D.; Bocea, B.-A.; Ion, N.-I.; Vorovenci, A.E.; Dragomirescu, D.; Birlutiu, R.-M.; Birlutiu, V.; Fleaca, S.R. Are There Any Changes in the Causative Microorganisms Isolated in the Last Years from Hip and Knee Periprosthetic Joint Infections? Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Results Analysis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmølle, M.; Thomsen, T.R.; Fazli, M.; Dige, I.; Christensen, L.; Homøe, P.; Tvede, M.; Nyvad, B.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Givskov, M.; et al. Biofilms in chronic infections—A matter of opportunity—Monospecies biofilms in multispecies infections. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpen, M.; Kragh, K.N.; Enciso, J.B.; Faurholt-Jepsen, D.; Lindegaard, B.; Egelund, G.B.; Jensen, A.V.; Ravn, P.; Mathiesen, I.H.M.; Gheorge, A.G.; et al. Bacterial biofilms predominate in both acute and chronic human lung infections. Thorax 2022, 77, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendi, P.; Zimmerli, W. Antimicrobial treatment concepts for orthopaedic device-related infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, P.F.; Lichstein, P.M.; Shen, C.; Tokarski, A.T.; Parvizi, J. Why Are Total Knee Arthroplasties Failing Today—Has Anything Changed After 10 Years? J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 1774–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitta, M.; Esposito, C.I.; Li, Z.; Lee, Y.; Wright, T.M.; Padgett, D.E. Failure After Modern Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Study of 18,065 Knees. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerli, W.; Sendi, P. Orthopaedic biofilm infections. APMIS 2017, 125, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymski, D.; Walter, N.; Alt, V.; Rupp, M. Evaluation of Comorbidities as Risk Factors for Fracture-Related Infection and Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Germany. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of Primary and Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragosloveanu, S.; Petre, M.-A.; Cretu, B.; Mihailescu, A.A.; Cergan, R.; Scheau, C. Etiology of Total Knee Arthroplasty Revisions: A Two-Decade Institutional Perspective. Cureus 2024, 16, e55263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tande, A.J.; Patel, R. Prosthetic Joint Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 302–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, J.; Baraia-Etxaburu, J.; de Benito, N.; Bori, G.; Cabo, J.; Corona, P.; Esteban, J.; Horcajada, J.P.; Lora-Tamayo, J.; Murillo, O.; et al. Executive summary of management of prosthetic joint infections. Clinical practice guidelines by the Spanish Society of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology (SEIMC). Enfermedade Infecc. Y Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2017, 35, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tande, A.J.; Gomez-Urena, E.O.; Berbari, E.F.; Osmon, D.R. Management of Prosthetic Joint Infection. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlutiu, R.M.; Roman, M.D.; Cismasiu, R.S.; Fleaca, S.R.; Popa, C.M.; Mihalache, M.; Birlutiu, V. Sonication contribution to identifying prosthetic joint infection with Ralstonia pickettii: A case report and review of the literature. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlutiu, R.M.; Birlutiu, V.; Mihalache, M.; Mihalache, C.; Cismasiu, R.S. Diagnosis and management of orthopedic implant-associated infection: A comprehensive review of the literature. Biomed. Res. 2017, 28, 5063–5073. [Google Scholar]
- Birlutiu, R.M.; Stoica, C.I.; Russu, O.; Cismasiu, R.S.; Birlutiu, V. Positivity Trends of Bacterial Cultures from Cases of Acute and Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periferakis, A.; Periferakis, A.-T.; Troumpata, L.; Dragosloveanu, S.; Timofticiuc, I.-A.; Georgatos-Garcia, S.; Scheau, A.-E.; Periferakis, K.; Caruntu, A.; Badarau, I.A.; et al. Use of Biomaterials in 3D Printing as a Solution to Microbial Infections in Arthroplasty and Osseous Reconstruction. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leekha, S.; Terrell, C.L.; Edson, R.S. General Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peel, T.N.; Cheng, A.C.; Choong, P.F.M.; Buising, K.L. Early onset prosthetic hip and knee joint infection: Treatment and outcomes in Victoria, Australia. J. Hosp. Infect. 2012, 82, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Zhu, M.; Coleman, B.; Munro, J.T.; Young, S.W. Differing Microorganism Profile in Early and Late Prosthetic Joint Infections Following Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty—Implications for Empiric Antibiotic Treatment. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 1858–1864.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, N.; Franco, M.; Ribera, A.; Soriano, A.; Rodriguez-Pardo, D.; Sorlí, L.; Fresco, G.; Fernández-Sampedro, M.; Dolores del Toro, M.; Guío, L.; et al. Time trends in the aetiology of prosthetic joint infections: A multicentre cohort study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, e1–e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, N.; Mur, I.; Ribera, A.; Soriano, A.; Rodríguez-Pardo, D.; Sorlí, L.; Cobo, J.; Fernández-Sampedro, M.; del Toro, M.D.; Guío, L.; et al. The Different Microbial Etiology of Prosthetic Joint Infections according to Route of Acquisition and Time after Prosthesis Implantation, Including the Role of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebše, R. The EBJIS definition of periprosthetic joint infection. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103-B, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Higuera, C.; Della Valle, C.; Chen, A.F.; Shohat, N. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1309–1314.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A.; Ochsner, P.E. Prosthetic-Joint Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Bassi, G.L.; Coenye, T.; Donelli, G.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Holá, V.; Imbert, C.; Kirketerp-Møller, K.; et al. ESCMID∗ guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of biofilm infections 2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, S1–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Zmistowski, B.; Berbari, E.F.; Bauer, T.W.; Springer, B.D.; Della Valle, C.J.; Garvin, K.L.; Mont, M.A.; Wongworawat, M.D.; Zalavras, C.G. New Definition for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: From the Workgroup of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2992–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, R.A.; Martin, A.; Young, B.C.; Kendrick, B.J.; Alvand, A.; Jeys, L.; Stevenson, J.; Palmer, A.J. Frequent microbiological profile changes are seen in subsequent-revision hip and knee arthroplasty for prosthetic joint infection. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2023, 8, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, V.; Kerroumi, Y.; Meyssonnier, V.; Heym, B.; Metten, M.-A.; Desplaces, N.; Marmor, S. Analysis of postoperative and hematogenous prosthetic joint-infection microbiological patterns in a large cohort. J. Infect. 2018, 76, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwik, C.A.M.; Zijlstra, W.P.; Knobben, B.A.S.; Ploegmakers, J.J.W.; Dijkstra, B.; de Vries, A.J.; Kampinga, G.A.; Mithoe, G.; Al Moujahid, A.; Jutte, P.C.; et al. Obese patients have higher rates of polymicrobial and Gram-negative early periprosthetic joint infections of the hip than non-obese patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussa, M.; Manciulli, T.; Corbella, M.; Mariani, B.; Cambieri, P.; Gipsz, N.; Scudeller, L.; Abbott, D.M.; Brunetti, E.; Mosconi, M.; et al. Epidemiology and microbiology of prosthetic joint infections: A nine-year, single-center experience in Pavia, Northern Italy. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2021, 105, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triffault-Fillit, C.; Ferry, T.; Laurent, F.; Pradat, P.; Dupieux, C.; Conrad, A.; Becker, A.; Lustig, S.; Chidiac, C.; Valour, F.; et al. Microbiologic epidemiology depending on time to occurrence of prosthetic joint infection: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröschen, F.S.; Randau, T.M.; Franz, A.; Molitor, E.; Hoerauf, A.; Hischebeth, G.T.R. Microbiological Trends and Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns in Patients with Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip or Knee over 6 Years. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Chang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Chang, Y. Different microbiological profiles between hip and knee prosthetic joint infections. J. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 230949901984776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröschen, F.S.; Randau, T.M.; Franz, A.; Molitor, E.; Hischebeth, G.T.R. Microbiological Profiles of Patients with Periprosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip or Knee. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.M.; Wang, L.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.X.; Tian, H.; Lin, J.H.; Guo, W.S.; Lin, Y.; Qu, T.B.; Guo, A.; et al. Microbiology analysis of periprothetic joint infection post total hip and knee arthroplasty of 9 centers in Beijing between 2014 and 2016. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 2019, 57, 596–600. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Lyu, J.; Ma, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Wei, Y.; Shi, J.; Xia, J.; Zhao, G.; et al. Comparative analysis of pathogen distribution in patients with fracture-related infection and periprosthetic joint infection: A retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Staphylococcus aureus Infections: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, B.C.; Becker, K.; Löffler, B. Clinical Significance and Pathogenesis of Staphylococcal Small Colony Variants in Persistent Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 401–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Sebillotte, M.; Huotari, K.; Sánchez, R.E.; Benavent, E.; Parvizi, J.; Fernandez-Sampedro, M.; Barbero, J.M.; Garcia-Cañete, J.; Trebse, R.; et al. Lower Success Rate of Débridement and Implant Retention in Late Acute versus Early Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection Caused by Staphylococcus spp. Results from a Matched Cohort Study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevoska, S.; Himmelbauer, F.; Stiftinger, J.; Stadler, C.; Pisecky, L.; Gotterbarm, T.; Klasan, A. Significant Difference in Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacteria in Septic Revision between Total Knee Arthroplasty and Total Hip Arthroplasty. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chai, W.; Zhang, G.; Hao, L.; Chen, J. Trends in microbiological profiles and antibiotic resistance in periprosthetic joint infections. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 030006052110027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondaan, C.; Maso, A.; Birlutiu, R.-M.; Sampedro, M.F.; Soriano, A.; de Brito, V.D.; Junyent, J.G.; Del Toro, M.D.; Hofstaetter, J.G.; Salles, M.J.; et al. Is an isolated positive sonication fluid culture in revision arthroplasties clinically relevant? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, J.; Miguel, L.G.S.; Euba, G.; Rodríguez, D.; García-Lechuz, J.; Riera, M.; Falgueras, L.; Palomino, J.; Benito, N.; Toro, d.; et al. Early prosthetic joint infection: Outcomes with debridement and implant retention followed by antibiotic therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornero, E.; Martínez-Pastor, J.C.; Bori, G.; García-Ramiro, S.; Morata, L.; Bosch, J.; Mensa, J.; Soriano, A. Risk Factors for Failure in Early Prosthetic Joint Infection Treated with Debridement. Influence of Etiology and Antibiotic Treatment. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2014, 12, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Bakhshi, H.; Ecker, N.; Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T.; Kendoff, D. Organism Profile in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Pathogens Differ at Two Arthroplasty Infection Referral Centers in Europe and in the United States. J. Knee Surg. 2014, 27, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casenaz, A.; Piroth, L.; Labattut, L.; Sixt, T.; Magallon, A.; Guilloteau, A.; Neuwirth, C.; Amoureux, L. Epidemiology and antibiotic resistance of prosthetic joint infections according to time of occurrence, a 10-year study. J. Infect. 2022, 85, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhkova, S.; Tikhilov, R.; Labutin, D.; Denisov, A.; Shubnyakov, I.; Razorenov, V.; Artyukh, V.; Rukina, A. Failure of the first step of two-stage revision due to polymicrobial prosthetic joint infection of the hip. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2016, 17, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, M.D.; Friedrich, M.J.; Randau, T.M.; Ploeger, M.M.; Schmolders, J.; Strauss, A.A.; Hischebeth, G.T.R.; Pennekamp, P.H.; Vavken, P.; Gravius, S. Polymicrobial infections reduce the cure rate in prosthetic joint infections: Outcome analysis with two-stage exchange and follow-up ≥two years. Int. Orthop. 2016, 40, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, M.; Baertl, S.; Walter, N.; Hitzenbichler, F.; Ehrenschwender, M.; Alt, V. Is There a Difference in Microbiological Epidemiology and Effective Empiric Antimicrobial Therapy Comparing Fracture-Related Infection and Periprosthetic Joint Infection? A Retrospective Comparative Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefánsdóttir, A.; Johansson, D.; Knutson, K.; Lidgren, L.; Robertsson, O. Microbiology of the infected knee arthroplasty: Report from the Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register on 426 surgically revised cases. Scand J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 41, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, S.; Sezgin, E.A.; Stučinskas, J.; Tarasevičius, Š.; Liu, Y.; Raina, D.B.; Tägil, M.; Lidgren, L.; W-Dahl, A. Different microbial and resistance patterns in primary total knee arthroplasty infections—A report on 283 patients from Lithuania and Sweden. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Zhu, M.; Luey, C.; Young, S.W. Antibiotic resistance in early periprosthetic joint infection. ANZ J. Surg. 2016, 86, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic joint infection: Current concepts and outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, N.; Franco, M.; Coll, P.; Gálvez, M.L.; Jordán, M.; López-Contreras, J.; Pomar, V.; Monllau, J.C.; Mirelis, B.; Gurguí, M. Etiology of surgical site infections after primary total joint arthroplasties. J. Orthop. Res. 2014, 32, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pardo, D.; Pigrau, C.; Lora-Tamayo, J.; Soriano, A.; Toro, d.; Cobo, J.; Palomino, J.; Euba, G.; Riera, M.; Sánchez-Somolinos, M.; et al. Gram-negative prosthetic joint infection: Outcome of a debridement, antibiotics and implant retention approach, A large multicentre study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O911–O919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vecchi, E.; George, D.; Romanò, C.L.; Pregliasco, F.; Mattina, R.; Drago, L. Antibiotic sensitivities of coagulase-negative staphylococci and Staphylococcus aureus in hip and knee periprosthetic joint infections: Does this differ if patients meet the International Consensus Meeting Criteria? Infect Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalambous, L.T.; Kim, B.I.; Schwartz, A.M.; Case, A.; Seidelman, J.L.; Hendershot, E.F.; Bolognesi, M.P.; Seyler, T.M.; Jiranek, W.A. Prosthetic Knee Infection with Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus: A Harbinger of Poor Outcomes. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, S313–S320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, M.D.; Hischebeth, G.T.; Randau, T.M.; Gathen, M.; Schildberg, F.A.; Fröschen, F.S.; Kohlhof, H.; Gravius, S. Difficult-to-treat pathogens significantly reduce infection resolution in periprosthetic joint infections. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 115114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, N.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A. Management periprothetischer Infektionen des Kniegelenks. Orthopade 2016, 45, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourtet-Hascoët, J.; Félicé, M.P.; Bicart-See, A.; Bouige, A.; Giordano, G.; Bonnet, E. Species and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of coagulase-negative staphylococci in periprosthetic joint infections. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlutiu, V.; Birlutiu, R.-M.; Ene, R.; Rusu, D. Experience in Implementing Colonization Screening in a Multidisciplinary County Clinical Hospital in Romania. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codru, I.R.; Vintilă, B.I.; Sava, M.; Bereanu, A.S.; Neamțu, S.I.; Bădilă, R.M.; Bîrluțiu, V. Optimizing Diagnosis and Management of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Systematic Evaluation of Biofilm Detection Methods and Bacterial Colonization on Endotracheal Tubes. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M. Cultures in periprosthetic joint infections, the imperfect gold standard? EFORT Open Rev. 2023, 8, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlutiu, R.M.; Birlutiu, V.; Cismasiu, R.S.; Mihalache, M. bbFISH-ing in the sonication fluid. Medicine 2019, 98, e16501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, M.R.; Kildow, B.J.; Hartman, C.W.; Lyden, E.R.; Springer, B.D.; Fehring, T.K.; Garvin, K.L. Increased Incidence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Knee and Hip Prosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, S326–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerke-Kroll, B.T.; Christ, A.B.; McLawhorn, A.S.; Sculco, P.K.; Jules-Elysée, K.M.; Sculco, T.P. Periprosthetic Joint Infections Treated with Two-Stage Revision over 14Years: An Evolving Microbiology Profile. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
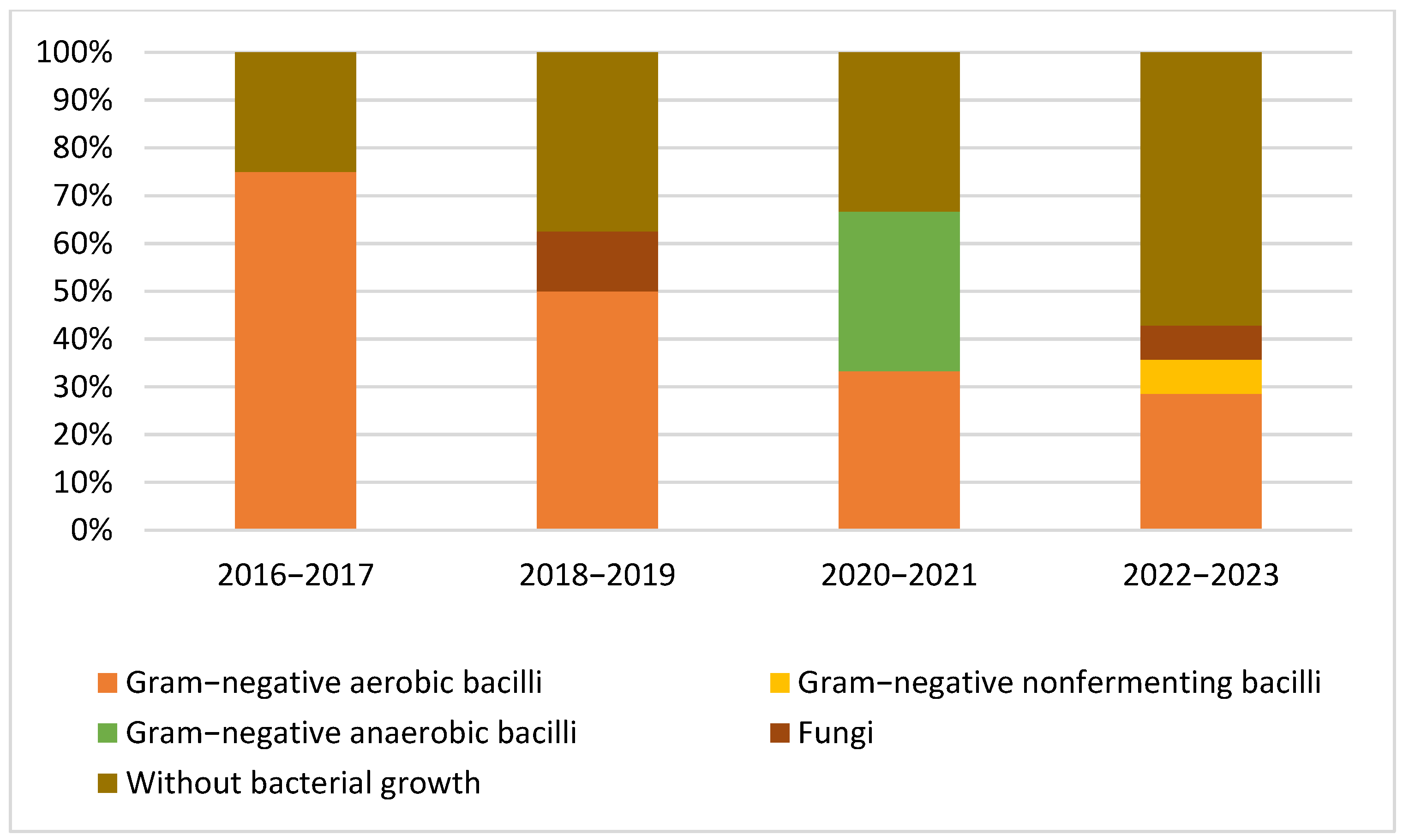
| Characteristic | No. of Cases (n = 102) |
|---|---|
| Median age (interquartile range, standard deviation), years | 67.08 (11, ±8.848) |
| Male gender | 53 (51.96) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index, median (interquartile range) | 3 (2) |
| Index arthroplasty site | |
| Hip | 55 |
| Knee | 47 |
| ASA score, median (interquartile range) | 2 (1) |
| Indication for index arthroplasty | |
| Osteoarthritis | 60 (58.82) |
| Avascular necrosis | 9 (8.82) |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 4 (3.92) |
| Femoral neck fracture | 12 (11.76) |
| other | 17 (16.66) |
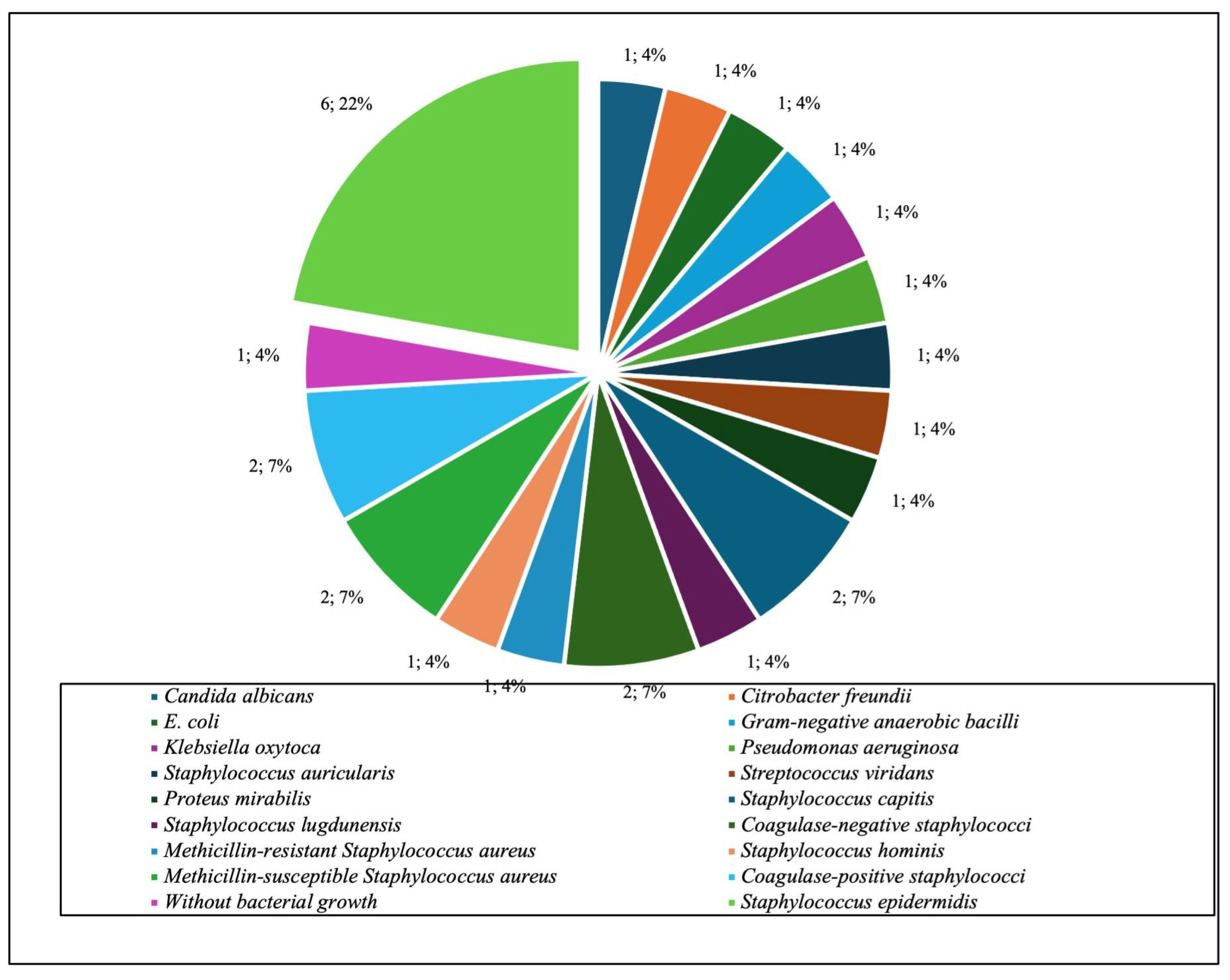
| Microorganism or Group | Total no. of Positive Cultures n (%; 95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 80 (73.4; 65.1–81.7) |
| CoNS—Coagulase-negative staphylococci | 55 (50.5; 42.2–59.6) |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 33 (30.3; 22.0–39.4) |
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | 3 (2.8; 0.0–6.4) |
| Staphylococcus simulans | 4 (3.7; 0.9–7.3) |
| Staphylococcus hominis | 5 (4.6; 0.9–9.2) |
| Staphylococcus capitis | 3 (2.8; 0.0–6.4) |
| Staphylococcus auricularis | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Unidentified CoNS | 5 (4.6; 0.9–9.2) |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 11 (10.1; 4.6–16.5) |
| Methicillin-resistant S. aureus | 5 (4.6; 0.9–9.2) |
| Methicillin-susceptible S. aureus | 6 (5.5; 1.8–10.1) |
| Streptococcus species | 3 (2.8; 0.0–6.4) |
| Group B Streptococcus | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Streptococcus viridans | 2 (1.8; 0.0–4.6) |
| Enterococcus species | 2 (1.8; 0.0–4.6) |
| Enterococcus faecium | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Enterococcus avium | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| CoPS—Coagulase-positive staphylococci | 9 (8.3; 3.7–13.8) |
| Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 14 (11.9; 7.2–19.3) |
| Enterobacteriaceae | 12 (11.0; 3.7–15.5) |
| Escherichia coli | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Enterobacter spp. | 3 (2.8; 0.0–6.4) |
| Enterobacter cloacae complex | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Enterobacter spp. | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Proteus spp. | 2 (1.8; 0.0–4.6) |
| Proteus mirabilis | 3 (2.8; 0.0–6.4) |
| Citrobacter braakii | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Citrobacter freundii | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Gram-negative nonfermenting bacilli | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Gram-negative anaerobic bacilli | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Fungi | 2 (1.8; 0.0–4.6) |
| Candida spp. | 2 (1.8; 0.0–4.6) |
| Candida albicans | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Candida tropicalis | 1 (0.9; 0.0–2.8) |
| Without bacterial growth | 13 (11.9; 5.5–18.3) |
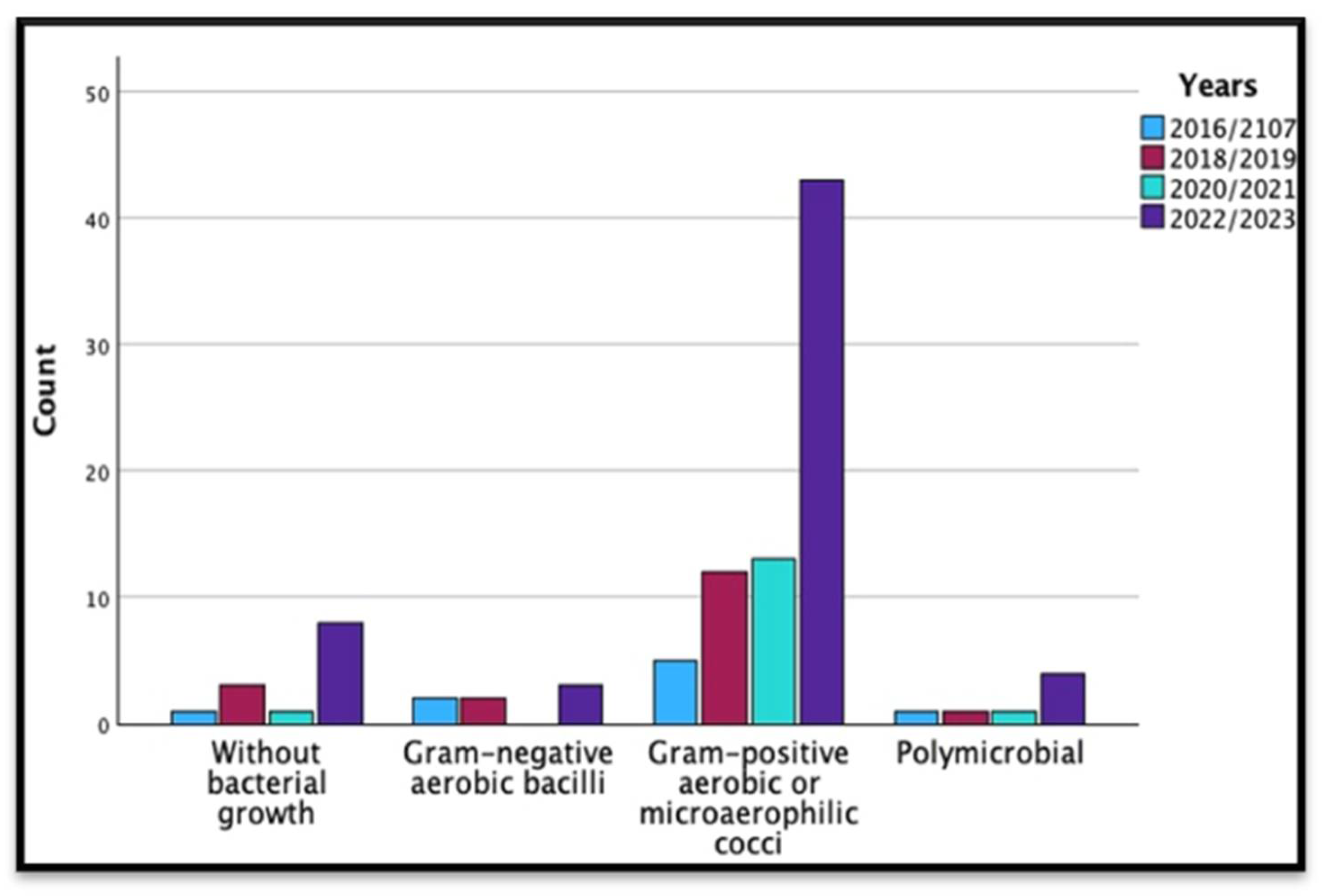
| Years | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016/2107 | 2018/2019 | 2020/2021 | 2022/2023 | |||
| Type of bacteria | Without bacterial growth | 1 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 13 |
| Gram-negative aerobic bacilli | 2 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 7 | |
| Gram-positive aerobic or microaerophilic cocci | 5 | 12 | 13 | 43 | 73 | |
| Polymicrobial | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 7 | |
| Total | 9 | 18 | 15 | 58 | 100 | |
| Type of Infection * | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute | Chronic | |||
| Microorganisms | Candida albicans | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Candida tropicalis | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Citrobacter braakii | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Citrobacter freundii | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| E. coli | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Enterobacter spp. | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Enterococcus avium | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Enterococcus faecium | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Gram-negative anaerobic bacilli | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Group B Streptococcus | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Staphylococcus auricularis | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Proteus spp. | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Streptococcus viridans | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Proteus mirabilis | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Staphylococcus capitis | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Staphylococcus simulans | 0 | 4 | 4 | |
| Coagulase-negative staphylococci | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | 1 | 4 | 5 | |
| Staphylococcus hominis | 1 | 4 | 5 | |
| Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus | 2 | 4 | 6 | |
| Coagulase-positive staphylococci | 2 | 7 | 9 | |
| Without bacterial growth culture | 1 | 12 | 13 | |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 6 | 27 | 33 | |
| Total | 27 | 82 | 109 | |
| Bacterial Strain/Antibiotic (MIC/Result) | GEN | AMI | TOB | TMP/SMX | CRX | IMI | MEM | CIP | LFX | PPT | CTZ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterobacter cloacae | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | ||
| Enterobacter spp. | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | ||
| Enterobacter aerogenes | S | S | R | S | R | I | S | S | R | R | R | ||
| GEN | AMI | TOB | TMP/SMX | CRX | IMI | MEM | CIP | LFX | PPT | CTZ | CTR | ||
| Citrobacter braakii | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | |
| Citrobacter freundii | S | S | S | S | - | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| GEN | AMI | TOB | TMP/SMX | CRX | IMI | MEM | CIP | LFX | NOR | PPT | CTZ | AMC | |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | R | R | R | S | R | R |
| GEN | AMI | TOB | TMP/SMX | CRX | IMI | MEM | CIP | LFX | NOR | PPT | CTZ | AMC | |
| Proteus mirabilis | R | S | R | R | R | I | S | R | R | R | I | R | R |
| Proteus mirabilis | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Proteus mirabilis | S | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Proteus spp. | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R |
| Proteus spp. | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | R | R | R | S | S | S |
| GEN | AMI | TOB | TMP/SMX | CRX | IMI | MEM | CIP | LFX | NOR | PPT | CTZ | AMC | |
| E. coli | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| GEN | AMI | TOB | AZT | IMI | MEM | CIP | LFX | PPT | CTZ | COL | |||
| Psuedomonas aeruginosa | S | S | S | I | I | S | I | R | I | I | S | ||
| Candida strain/Antimycotics | 5-FX | AmpB | FCZ | ITZ | VOR | ||||||||
| Candida albicans | S | S | R | R | R | ||||||||
| Candida tropicalis | S | S | R | R | R | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dragosloveanu, S.; Birlutiu, R.-M.; Neamtu, B.; Birlutiu, V. Microbiological Profiles, Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns and the Role of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Patients Diagnosed with Periprosthetic Joint Infection over 8 Years: Results from a Single-Center Observational Cohort Study from Romania. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051168
Dragosloveanu S, Birlutiu R-M, Neamtu B, Birlutiu V. Microbiological Profiles, Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns and the Role of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Patients Diagnosed with Periprosthetic Joint Infection over 8 Years: Results from a Single-Center Observational Cohort Study from Romania. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051168
Chicago/Turabian StyleDragosloveanu, Serban, Rares-Mircea Birlutiu, Bogdan Neamtu, and Victoria Birlutiu. 2025. "Microbiological Profiles, Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns and the Role of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Patients Diagnosed with Periprosthetic Joint Infection over 8 Years: Results from a Single-Center Observational Cohort Study from Romania" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051168
APA StyleDragosloveanu, S., Birlutiu, R.-M., Neamtu, B., & Birlutiu, V. (2025). Microbiological Profiles, Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns and the Role of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Patients Diagnosed with Periprosthetic Joint Infection over 8 Years: Results from a Single-Center Observational Cohort Study from Romania. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051168









