Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Vibrio harveyi Strains from Larimichthys crocea with Divergent Virulence Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Virulence Assays
2.3. Genomic DNA Extraction
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.5. Genome Assembly
2.6. Genome Annotation
2.7. Identification and Analysis of Mobile Genetic Elements and CRISPR-Cas Systems
2.8. Phylogenetic Analysis and Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI)
2.9. Genomic Collinearity Analysis Between V. harveyi Strains N8T11 and 45T2
2.10. Pan-Genome Analysis
2.11. Identification of Virulence Factors, Resistance Genes, and Secreted Proteins
2.12. Plasmid Conjugation Assay
3. Results
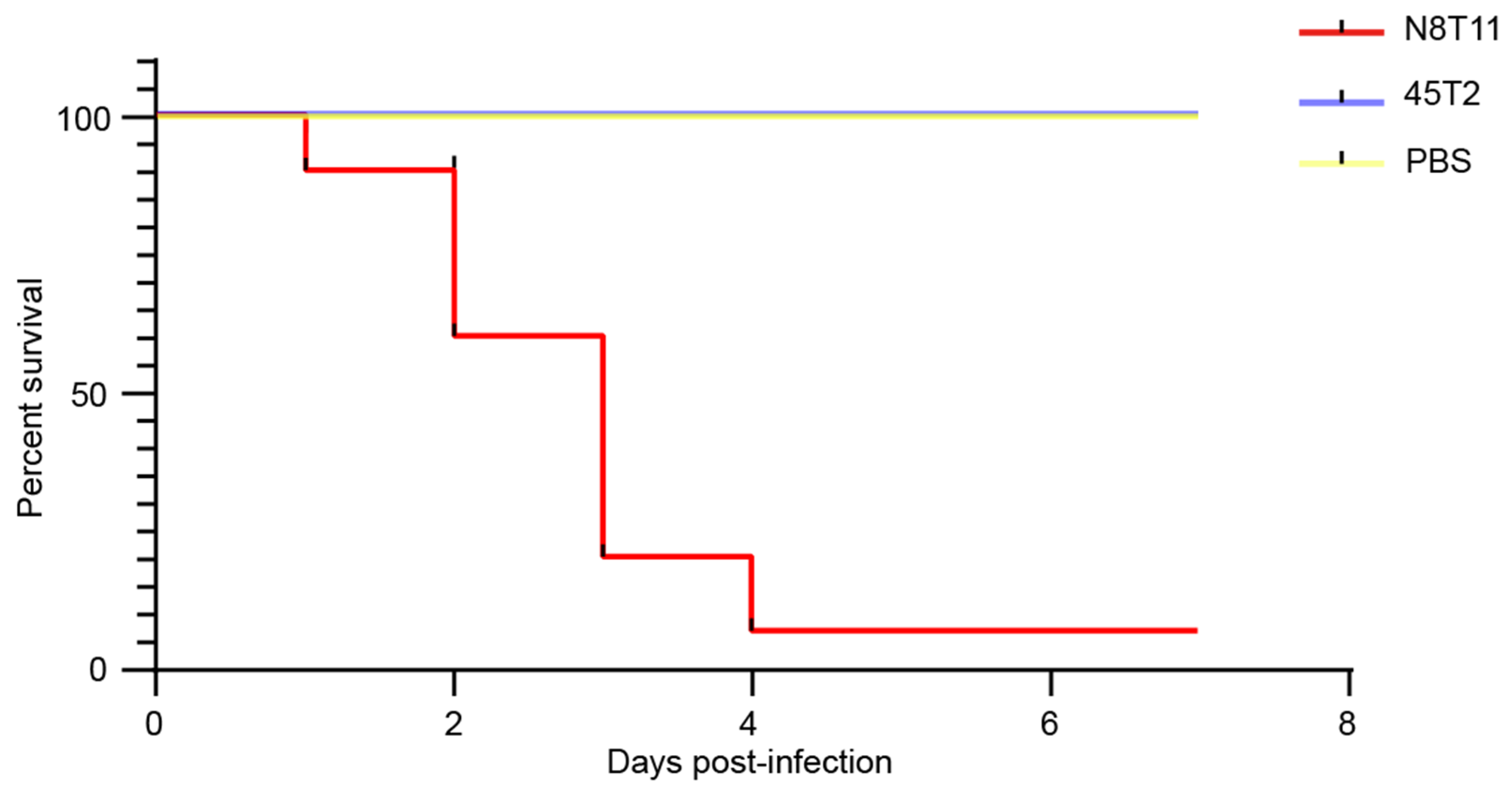
3.1. Virulence Assessment in Large Yellow Croaker
3.2. Genome Sequencing Quality Control and Coverage Analysis
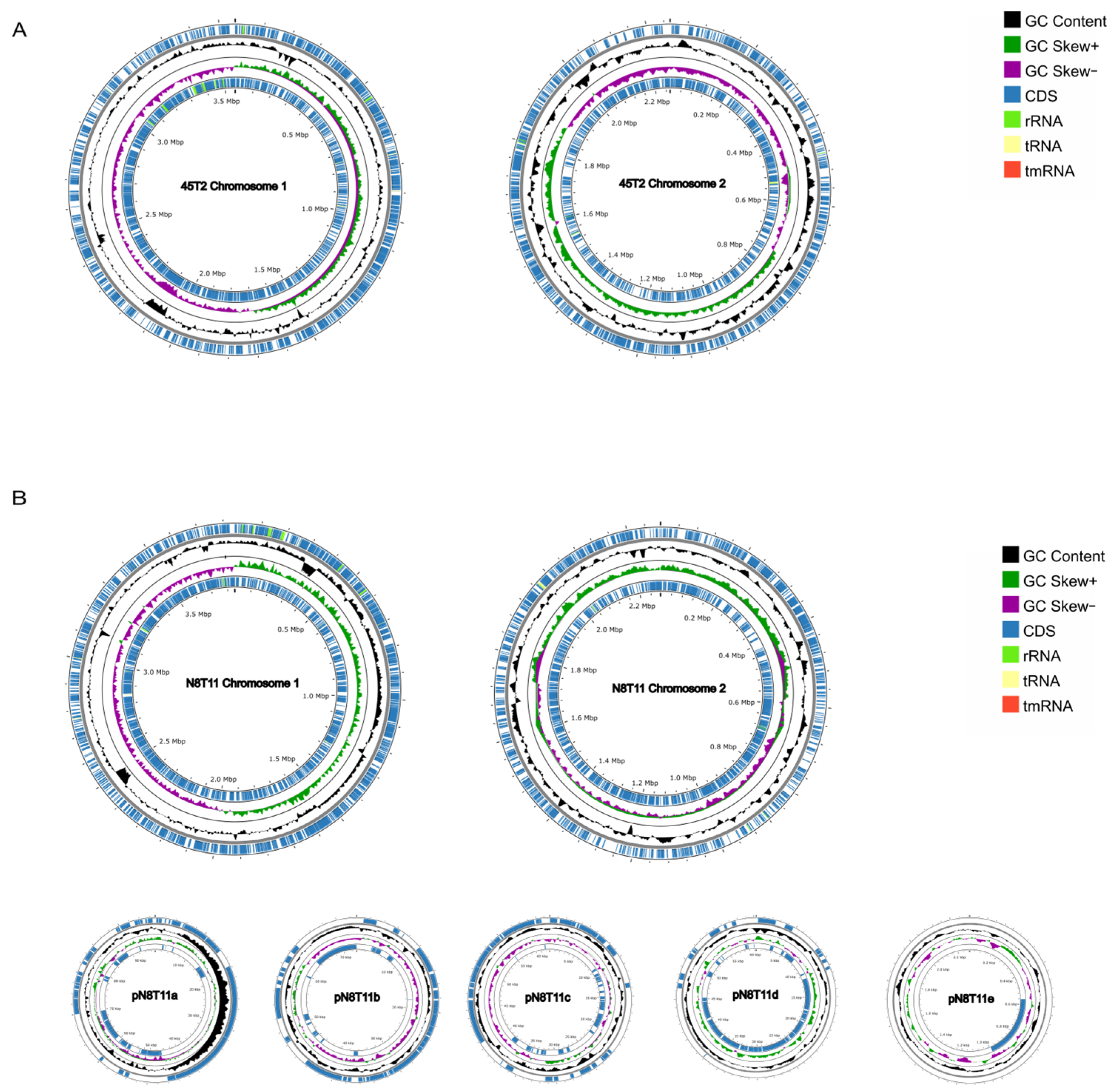
3.3. Genomic Features and Annotation of V. harveyi Strains 45T2 and N8T11
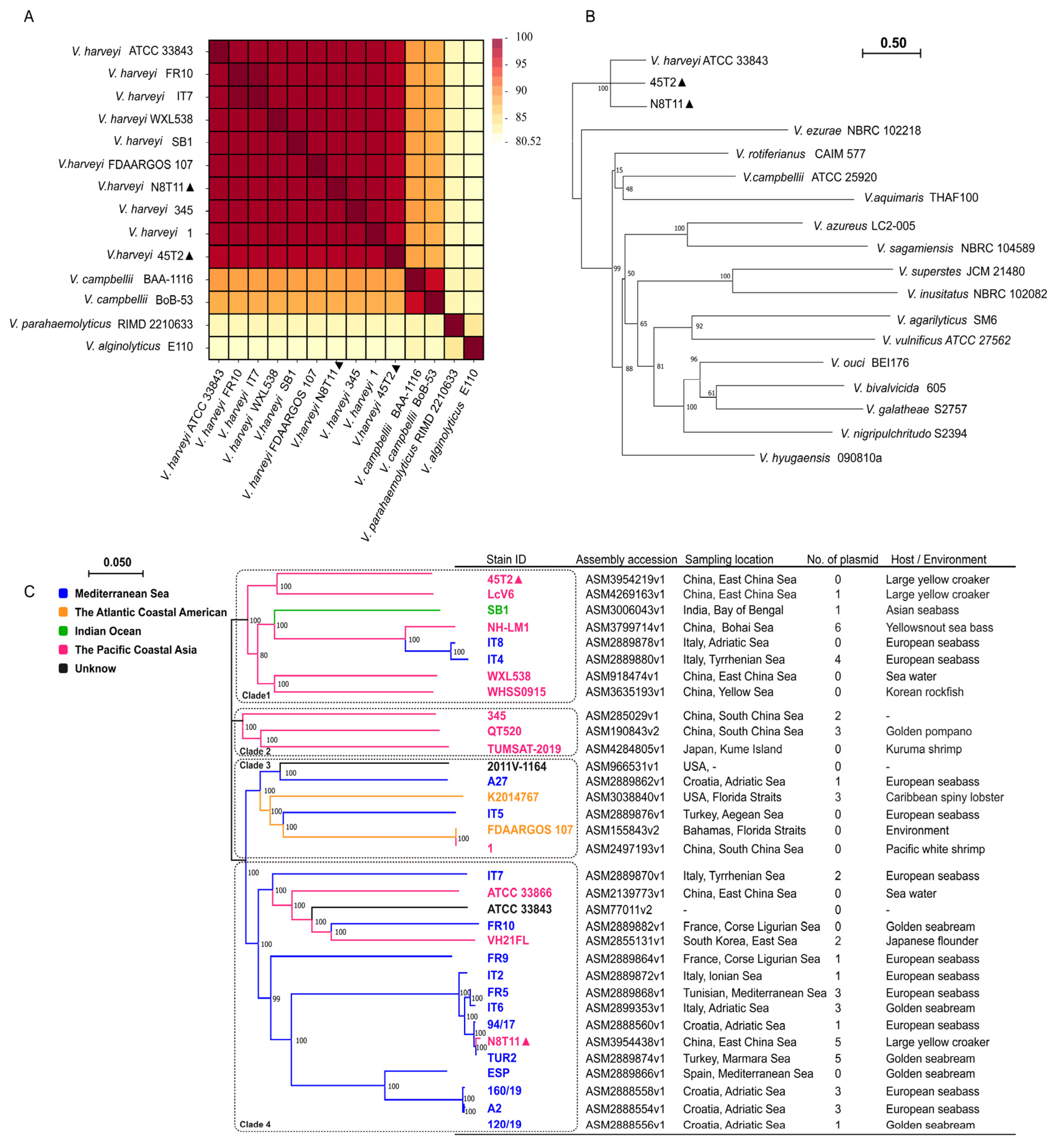
3.4. ANI and Phylogenetic Analysis
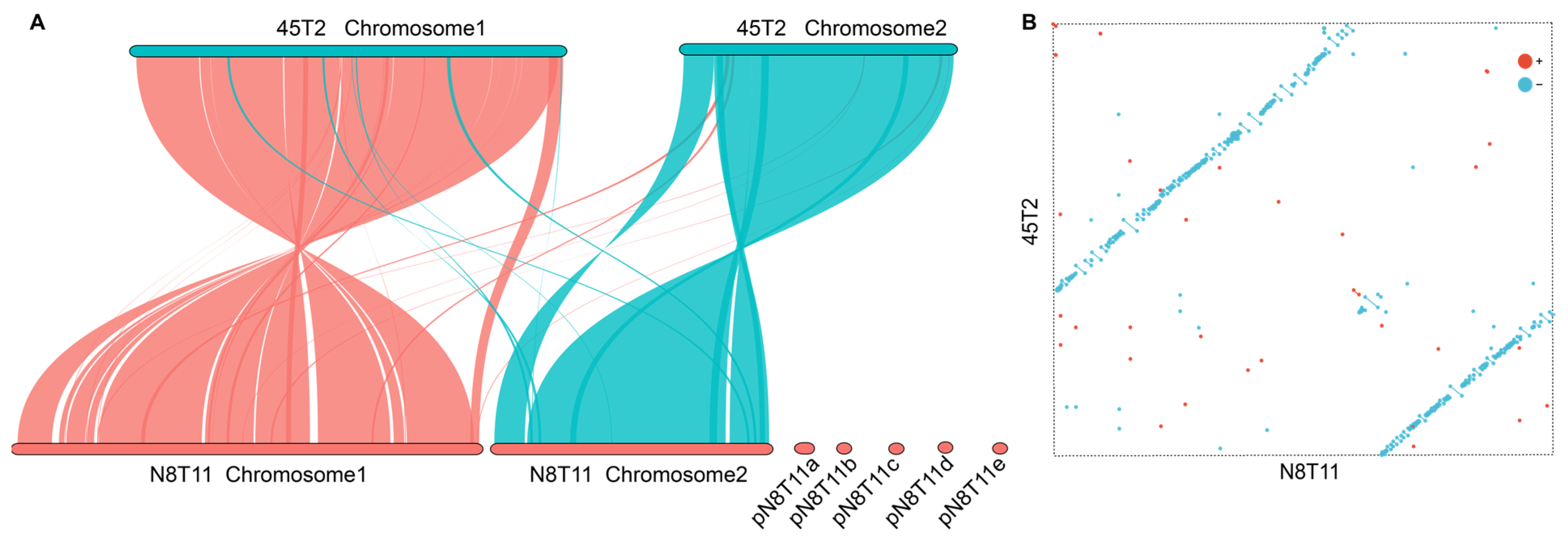
3.5. Genomic Collinearity Between V. harveyi Strains N8T11 and 45T2
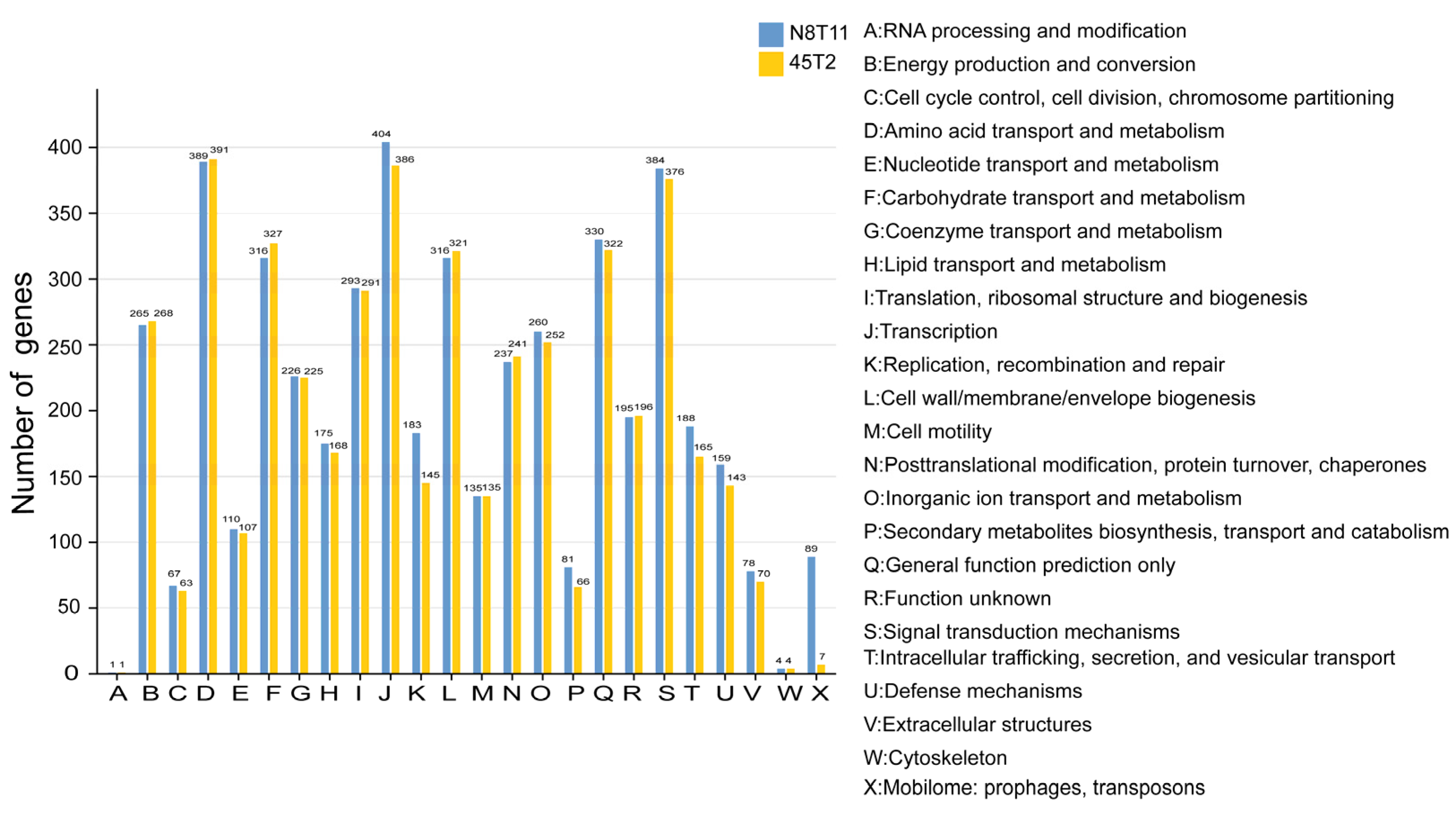
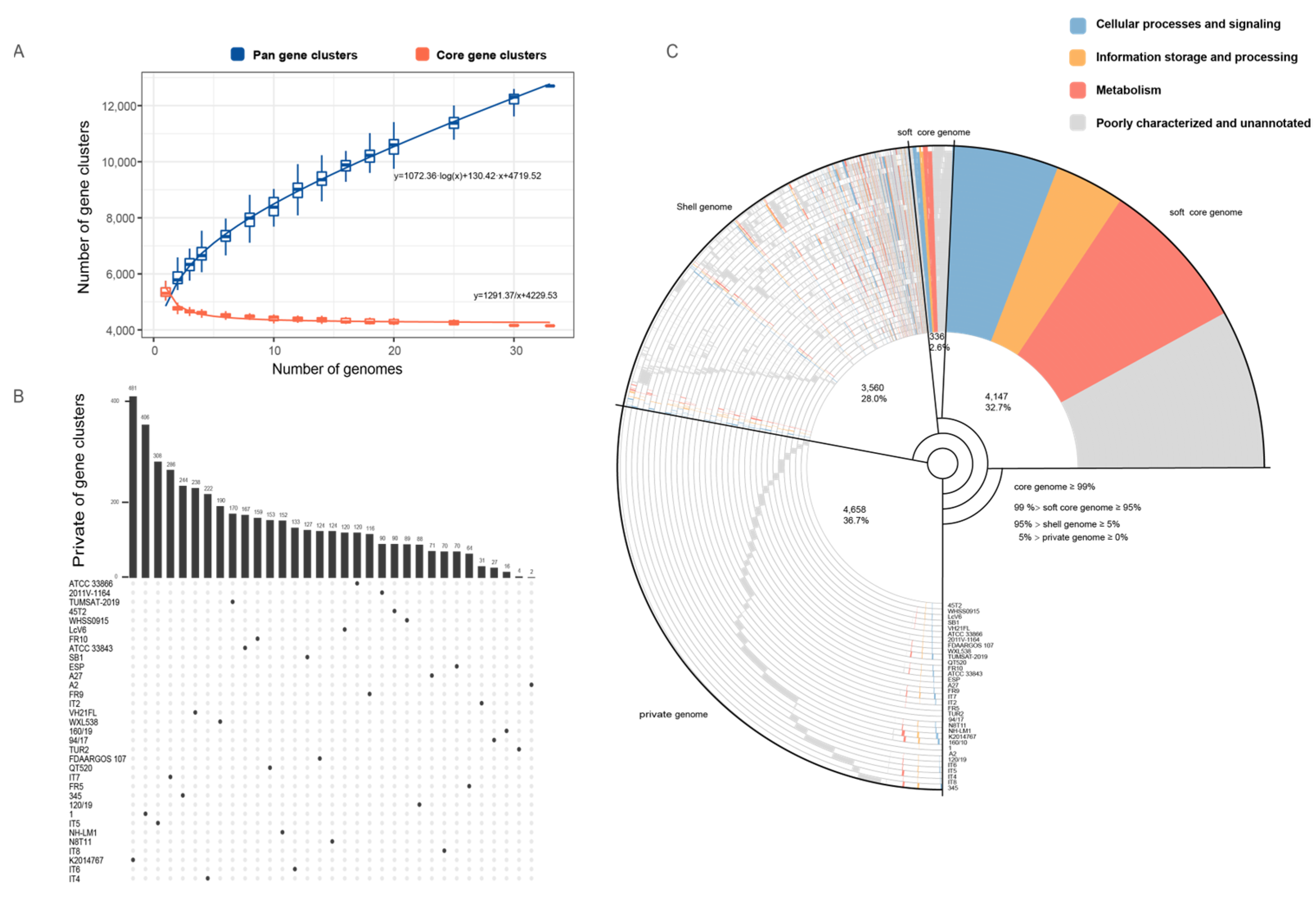
3.6. Pan-Genome and Accessory Gene Variability in V. harveyi Strains
3.7. Predicted Secretion Systems and Secreted Proteins
3.8. Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors
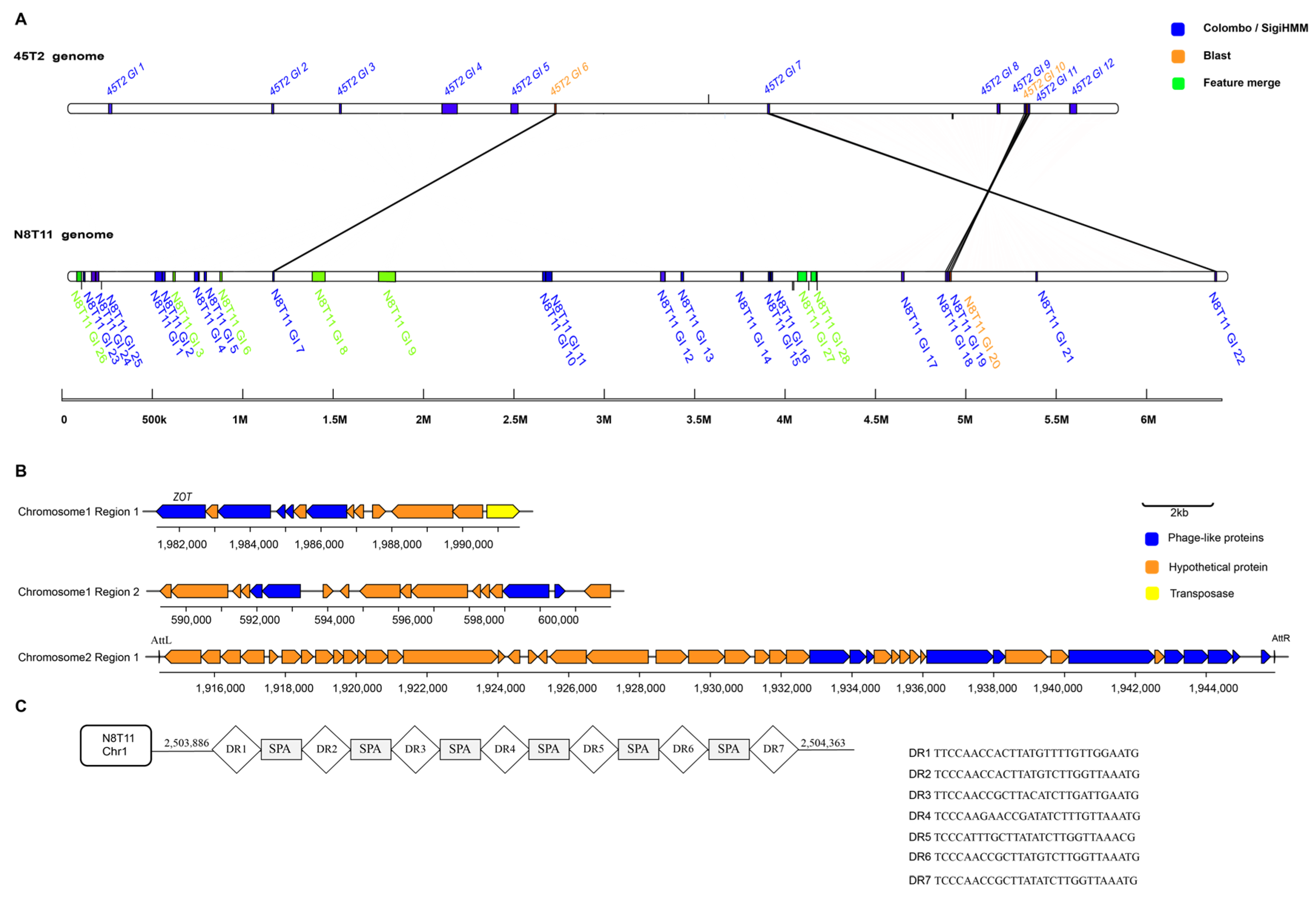
3.9. Genomic Islands, Prophages, Insertion Sequences, and CRISPR-Cas Systems
3.10. Plasmid Characterization in V. harveyi Strain N8T11
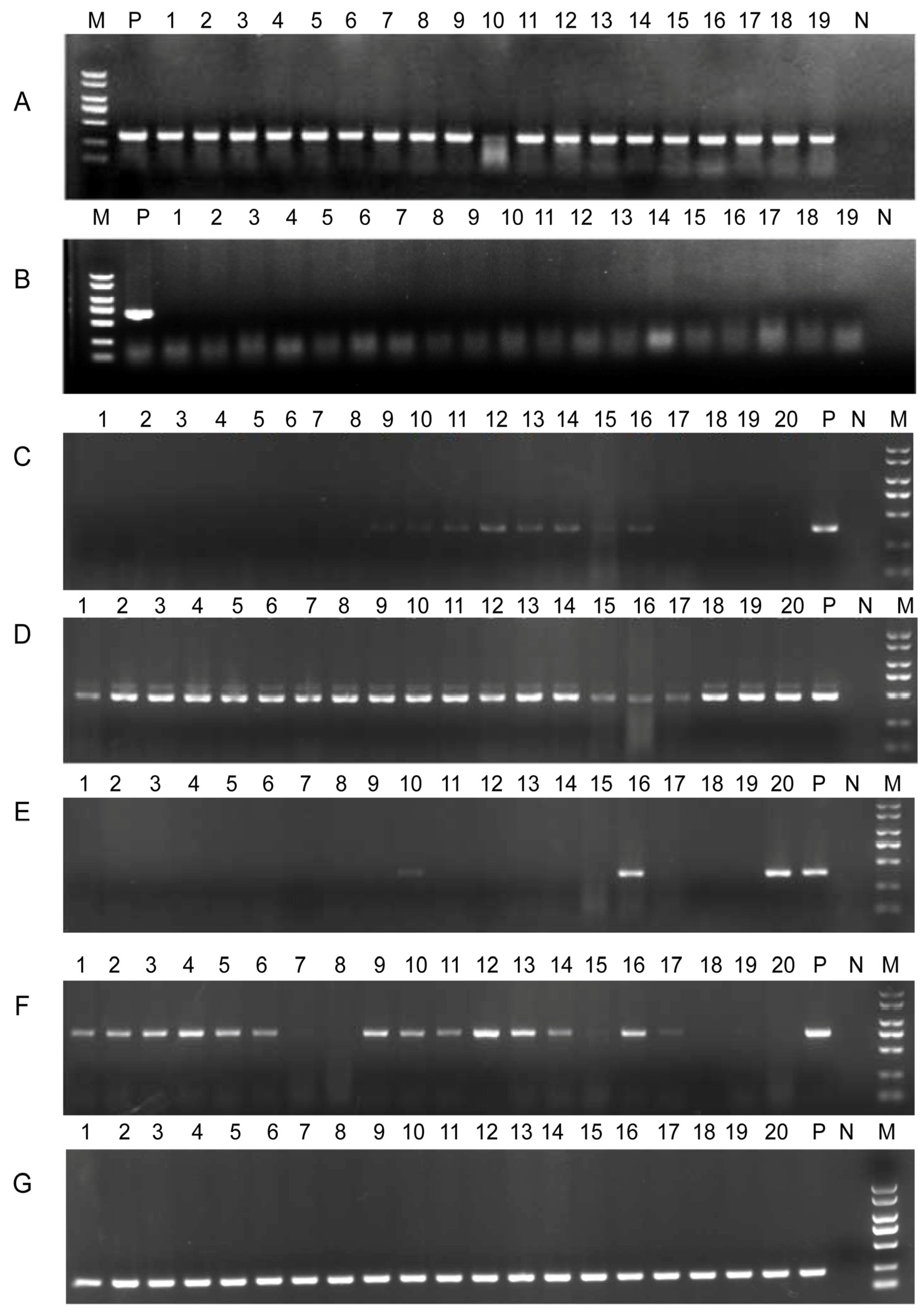
3.11. Conjugation and Stability of N8T11 Plasmids in 45T2
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANI | Average Nucleotide Identity |
| HGT | Horizontal Gene Transfer |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| GIs | Genomic Islands |
| RND | Resistance Nodulation Division. |
References
- Zhang, X.H.; He, X.; Austin, B. Vibrio harveyi: A serious pathogen of fish and invertebrates in mariculture. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruwandeepika, H.A.D.; Jayaweera, T.S.P.; Bhowmick, P.P.; Karunasagar, I.; Bossier, P.; Defoirdt, T. Pathogenesis, virulence factors and virulence regulation of vibrios belonging to the Harveyi clade. Rev. Aquac. 2012, 4, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Zhang, X.H. Vibrio harveyi: A significant pathogen of marine vertebrates and invertebrates. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L. Strategies for Prevention and Control of Vibriosis in Asian Fish Culture. Vaccines 2023, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanchez, I.; Kaberdin, V.R. Vibrio harveyi: A brief survey of general characteristics and recent epidemiological traits associated with climate change. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 154, 104850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natrah, F.M.; Ruwandeepika, H.A.; Pawar, S.; Karunasagar, I.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P.; Defoirdt, T. Regulation of virulence factors by quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 154, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Wolf, Y.I. Evolution of microbes and viruses: A paradigm shift in evolutionary biology? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, A.; Oren, Y.; Kelly, D.; Pascoe, B.; Dunn, S.; Sreecharan, T.; Vehkala, M.; Valimaki, N.; Prentice, M.B.; Ashour, A.; et al. Combined Analysis of Variation in Core, Accessory and Regulatory Genome Regions Provides a Super-Resolution View into the Evolution of Bacterial Populations. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, F.; Wegner, K.M.; Baker-Austin, C.; Vezzulli, L.; Osorio, C.R.; Amaro, C.; Ritchie, J.M.; Defoirdt, T.; Destoumieux-Garzon, D.; Blokesch, M.; et al. The emergence of Vibrio pathogens in Europe: Ecology, evolution, and pathogenesis (Paris, 11–12th March 2015). Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucy, S.M.; Huang, J.; Gogarten, J.P. Horizontal gene transfer: Building the web of life. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, H.; Su, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, L.; Guo, Z.; Wu, J.; Cheng, C.; Feng, J. Horizontal gene transfer contributes to virulence and antibiotic resistance of Vibrio harveyi 345 based on complete genome sequence analysis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, S.; Guttman, D.; Fitzgerald, J. Population genomics of bacterial host adaptation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, P.; Li, C.; Segev, O.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Yue, L.; Jiang, X.; Sheng, Y.; Levy, A.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis reveals differential genomic characteristics and featured genes between rapid- and slow-growing non-tuberculous mycobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1243371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, C.; Turner, S.; Riley, M.; Petri, W.; Hewlett, E. Whole-genome sequencing in outbreak analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Gu, C.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, S.Y. Current status of pan-genome analysis for pathogenic bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 63, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, K.; Chan, B.K.W.; Ye, L.; Yang, X.; Xie, M.; Liu, X.; Ni, H.; Chan, E.W.C. A siderophore-encoding plasmid encodes high-level virulence in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02528-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Mendez, G.; Zermeno-Cervantes, L.A.; Venancio-Landeros, A.A.; Diaz, S.F.; Cardona-Felix, C.S. Natural genetic transformation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus via pVA1 plasmid acquisition as a potential mechanism causing AHPND. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2019, 137, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wei, D.; Yang, Q.; Xie, G.; Pang, B.; Wang, Y.; Lan, R.; Wang, Q.; Dong, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Horizontal plasmid transfer promotes the dissemination of Asian acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease and provides a novel mechanism for genetic exchange and environmental adaptation. mSystems 2020, 5, e00799-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-T.; Amaro, C.; Wu, K.-M.; Valiente, E.; Chang, Y.-F.; Tsai, S.-F.; Chang, C.-H.; Hor Lien, I. A common virulence plasmid in biotype 2 Vibrio vulnificus and its dissemination aided by a conjugal plasmid. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1638–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Li, W.; Tao, Z.; Ye, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yan, X. Vibrio harveyi isolated from marine aquaculture species in eastern China and virulence to the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Schweizer, H.P. mini-Tn7 insertion in bacteria with single attTn7 sites: Example Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, M.A.; Kozarewa, I.; Smith, F.; Scally, A.; Stephens, P.J.; Durbin, R.; Swerdlow, H.; Turner, D.J. A large genome center’s improvements to the Illumina sequencing system. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.-y.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Szklarczyk, D.; Heller, D.; Hernandez-Plaza, A.; Forslund, S.K.; Cook, H.; Mende, D.R.; Letunic, I.; Rattei, T.; Jensen, L.J.; et al. eggNOG 5.0: A hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D309–D314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, P.S.; Lipinski, L.; Dziembowski, A. PlasFlow: Predicting plasmid sequences in metagenomic data using genome signatures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galata, V.; Fehlmann, T.; Backes, C.; Keller, A. PLSDB: A resource of complete bacterial plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D195–D202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siguier, P.; Perochon, J.; Lestrade, L.; Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. ISfinder: The reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, C.; Gray, K.L.; Woods, N.; Lim, A.C.; Tilley, K.E.; Winsor, G.L.; Hoad, G.R.; Roudgar, A.; Spencer, A.; Peltier, J.; et al. Enabling genomic island prediction and comparison in multiple genomes to investigate bacterial evolution and outbreaks. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, mgen000818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, D.; Grant, J.R.; Marcu, A.; Sajed, T.; Pon, A.; Liang, Y.; Wishart, D.S. PHASTER: A better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W16–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourcel, C.; Touchon, M.; Villeriot, N.; Vernadet, J.P.; Couvin, D.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Vergnaud, G. CRISPRCasdb a successor of CRISPRdb containing CRISPR arrays and cas genes from complete genome sequences, and tools to download and query lists of repeats and spacers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D535–D544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.N.; Slezak, T.; Hall, B.G. kSNP3. 0: SNP detection and phylogenetic analysis of genomes without genome alignment or reference genome. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2877–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Ha, S.-m.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, J. A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van. Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G.; Sun, D.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Shi, W.; Ma, J. IPGA: A handy integrated prokaryotes genome and pan-genome analysis web service. iMeta 2022, 1, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenberg, C.B.; Kahlke, T.; Haugen, P. Vibrionaceae core, shell and cloud genes are non-randomly distributed on Chr 1: An hypothesis that links the genomic location of genes with their intracellular placement. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z.; Sun, L.; Shen, Y.; Jin, Q. VFDB: A reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33 (Suppl. S1), D325–D328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2022: A general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D912–D917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcock, B.P.; Huynh, W.; Chalil, R.; Smith, K.W.; Raphenya, A.R.; Wlodarski, M.A.; Edalatmand, A.; Petkau, A.; Syed, S.A.; Tsang, K.K.; et al. CARD 2023: Expanded curation, support for machine learning, and resistome prediction at the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D690–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H. Predicting Secretory Proteins with SignalP. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1611, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Ye, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, S.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Xie, J.; Munang’andu, H.M.; Xu, C.; Wang, P.; et al. PvgAS: A novel two-component system that controls type III and type VI secretion systems and virulence in the fish pathogen Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. Aquaculture 2024, 578, 740102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupičić, I.G.; Oraić, D.; Križanović, K.; Zrnčić, S. Whole genome sequencing of Vibrio harveyi from different sites in the Mediterranean Sea providing data on virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes. Aquaculture 2024, 581, 740439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-López, J.M.; Cabrero-Martínez, O.A.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Hernández-Cortez, C.; Pelcastre-Rodríguez, L.I.; Gonzalez-Avila, L.U.; Castro-Escarpulli, G. Horizontal Gene Transfer and Its Association with Antibiotic Resistance in the Genus Aeromonas spp. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lery, L.M.; Frangeul, L.; Tomas, A.; Passet, V.; Almeida, A.S.; Bialek-Davenet, S.; Barbe, V.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Sansonetti, P.; Brisse, S. Comparative analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae genomes identifies a phospholipase D family protein as a novel virulence factor. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mesa, C.A.; Mendoza, R.M.; Penir, S.M.U.; de la Pena, L.D.; Amar, E.C.; Saloma, C.P. Genomic analysis of Vibrio harveyi strain PH1009, a potential multi-drug resistant pathogen due to acquisition of toxin genes. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Pei, X.; Wu, Y.; Yan, L.; Yan, Y.; Song, Y.; Coyle, N.M.; Martinez-Urtaza, J.; Quince, C.; Hu, Q.; et al. Recent mixing of Vibrio parahaemolyticus populations. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2578–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.; Goh, S.; Saeidi, N.; Gerhard, W.; Gunsch, C.; Gin, K. Occurrence of Vibrio species, beta-lactam resistant Vibrio species, and indicator bacteria in ballast and port waters of a tropical harbor. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.M.; Rawlings, T.K.; Dobbs, F.C.; Drake, L.A.; Mullady, T.; Huq, A.; Colwell, R.R. Global spread of microorganisms by ships. Nature 2000, 408, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strains/ Plasmids | Species/ Vector Strain | Description | References or Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| N8T11 | V. harveyi | Wild-type strain isolated from LYC liver | Yang et al. [20] |
| 45T2 | V. harveyi | Wild-type strain isolated from LYC kidney | Yang et al. [20] |
| 45T2-KanR | V. harveyi | V. harveyi 45T2 strain carrying a kanamycin resistance marker via transposition | This work |
| DH5α | E. coli | Strain for general cloning | Vazyme |
| pUC18T-mini-Tn7T-Km | E. coli | Mini-Tn7 vector for chromosomal DNA integration; confers Ampicillin and Kanamycin resistance | Choi et al. [21] |
| pTNS2 | E. coli | Helper plasmid, providing the Tn7 transposition function; confers Ampicillin resistance | Choi et al. [21] |
| Strain | Chromosome/Plasmid | Size (bp) | GC Content (%) | GenBank Accession No. | No. of Genes | No. of tRNA | No. of rRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N8T11 | Chromosome 1 | 3,842,609 | 44.61 | CP154266 | 3610 | 109 | 31 |
| Chromosome 2 | 2,274,153 | 44.93 | CP154267 | 2063 | 16 | 3 | |
| pN8T11a | 97,019 | 41.97 | CP154268 | 72 | 0 | 0 | |
| pN8T11b | 72,910 | 41.49 | CP154269 | 66 | 0 | 0 | |
| pN8T11c | 61,668 | 43.86 | CP154270 | 72 | 0 | 0 | |
| pN8T11d | 60,275 | 44.13 | CP154271 | 59 | 0 | 0 | |
| pN8T11e | 2285 | 44.96 | CP154272 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 45T2 | Chromosome 1 | 3,555,107 | 45.05 | CP154264 | 3298 | 110 | 34 |
| Chromosome 2 | 2,254,156 | 44.89 | CP154265 | 1988 | 16 | 3 |
| Gene Locus | Antibiotic Resistance Ontology Term | Detection Criteria | AMR Gene Family | Drug Class | Resistance Mechanism | Identity (%) | Reference Length (%) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shared resistance genes (present in both N8T11 and 45T2) | ||||||||
| AAIA70_01850/ AAIA71_15865 | Fluoroquinolone-resistant parE | Protein variant | ParE | Fluoroquinolone antibiotics | Antibiotic target alteration | 78.98 | 99.37 | Chr 1 |
| AAIA70_14670/ AAIA71_01910 | Glycopeptide resistance gene cluster vanT | Protein homolog | VanT | Glycopeptide antibiotics | Altered cell wall precursor targets | 32.5 | 50.7 | Chr 1 |
| AAIA70_14950/ AAIA71_01350 | RND antibiotic efflux pump | Protein homolog | RND 1 family | Macrolide, fluoroquinolone, penam antibiotics | Antibiotic efflux | 95.24 | 100 | Chr 1 |
| AAIA70_16780/ AAIA71_18920 | RND antibiotic efflux pump | Protein homolog | AdeF | Fluoroquinolone, tetracycline antibiotics | Antibiotic efflux | 43.25 | 99.15 | Chr 2 |
| AAIA70_06905/ AAIA71_10245 | SMR antibiotic efflux pump | Protein homolog | QacG | Disinfecting agent antiseptics | Efflux pump for disinfectants | 35.64 | 109.35 | Chr 1 |
| 45T2-specific resistance genes | ||||||||
| AAIA70_05875 | Tetracycline resistance ABC efflux pump | ABC model | TxR | Tetracycline antibiotics | Antibiotic efflux | 85.76 | 99.37 | Chr 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Munang’andu, H.M.; Xu, C.; Cai, W.; Yan, X.; Tao, Z. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Vibrio harveyi Strains from Larimichthys crocea with Divergent Virulence Profiles. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051129
Wang K, Zhang C, Munang’andu HM, Xu C, Cai W, Yan X, Tao Z. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Vibrio harveyi Strains from Larimichthys crocea with Divergent Virulence Profiles. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051129
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kequan, Chaozheng Zhang, Hetron Mweemba Munang’andu, Cheng Xu, Wenlong Cai, Xiaojun Yan, and Zhen Tao. 2025. "Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Vibrio harveyi Strains from Larimichthys crocea with Divergent Virulence Profiles" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051129
APA StyleWang, K., Zhang, C., Munang’andu, H. M., Xu, C., Cai, W., Yan, X., & Tao, Z. (2025). Comparative Genomic Analysis of Two Vibrio harveyi Strains from Larimichthys crocea with Divergent Virulence Profiles. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051129






