Unraveling Pediatric Group A Streptococcus Meningitis: Lessons from Two Case Reports and a Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- highlight the key clinical features, common complications, and outcomes of GAS meningitis;
- -
- identify factors associated with a complicated course of disease.
2. Case Reports
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GAS | Group A streptococcus |
| iGAS | Invasive GAS |
| SPE | Secreted pyogenic exotoxins |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| AOM | Acute Otitis Media |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| WBC | White blood cell |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PICU | Pediatric Intensive Care Unit |
References
- Brouwer, S.; Rivera-Hernandez, T.; Curren, B.F.; Harbison-Price, N.; De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Jespersen, M.G.; Davies, M.R.; Walker, M.J. Pathogenesis, epidemiology and control of Group A Streptococcus infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.W. Pathogenesis of group a streptococcal infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 470–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carapetis, J.R.; Steer, A.C.; Mulholland, E.K.; Weber, M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddington, C.S.; Snelling, T.L.; Carapetis, J.R. Management of invasive group A streptococcal infections. J. Infect. 2014, 69 (Suppl. S1), S63–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link-Gelles, R.; Toews, K.-A.; Schaffner, W.; Edwards, K.M.; Wright, C.; Beall, B.; Barnes, B.; Jewell, B.; Harrison, L.H.; Kirley, P.D.; et al. Characteristics of Intracranial Group A Streptococcal Infections in US Children, 1997–2014. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2020, 9, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Disease Outbreak News; Increased Incidence of Scarlet Fever and Invasive Group A Streptococcus Infection—Multi-Country. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2022-DON429 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Schlapbach, L.J.; Watson, R.S.; Sorce, L.R.; Argent, A.C.; Menon, K.; Hall, M.W.; Akech, S.; Albers, D.J.; Alpern, E.R.; Balamuth, F.; et al. International Consensus Criteria for Pediatric Sepsis and Septic Shock. JAMA 2024, 331, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhammour, W.; Hasan, R.A.; Unuvar, E. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal bacteremia. Indian J. Pediatr. 2004, 71, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoni, M.V.; Berezin, E.N.; Sáfadi, M.A.; Almeida, F.J.; Lopes, C.R. Streptococcus pyogenes meningitis in children: Report of two cases and literature review. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Givner, L.B. Invasive disease due to group A beta-hemolytic streptococci: Continued occurrence in children in North Carolina. South. Med. J. 1998, 91, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnden, A.; Lennon, D. Serious suppurative group A streptococcal infections in previously well children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1988, 7, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, B.A.; Blackburn, J.; Pham-Huy, A.; Muir, K. High-dose steroid and heparin: A novel therapy for cerebral vasculitis associated with presumed group A Streptococcus meningitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e239618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Blackburn, J.; Pham-Huy, A. Uncommon clinical presentation of a common bug: Group A Streptococcus meningitis. Paediatr. Child Health 2020, 26, e129–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, E.N.; Griffith, J.A.; Carvajal, H.F. Localized meningoencephalitis and group A streptococcal bacteremia. Clin. Pediatr. 1992, 31, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, G.S.; Patel, C.C.; Buck, G. Meningitis caused by toxigenic group a beta-hemolytic streptococcus in a pediatric patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1991, 10, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.P.; Jerwood, S. Group A streptococcal septicemia, meningitis and cerebral abscess: Case report and literature review. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2012, 54, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, G.; Ovetchkine, P.; Tapiero, B. Group a streptococcal meningitis in a pediatric patient following cochlear implantation: Report of the first case and review of the literature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5816–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ruvinsky, R.O.; Schindler, Y.; Urman, G.; Lopera, L.C.; Carrano, J.; Paolillo, A.L.; Grosman, A. Meningitis por Streptococcus pyogenes: Informe de un caso pediátrico. [Streptococcus pyogenes meningitis: A pediatric case report]. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2020, 118, e309–e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M.; Yager, J.Y.; Hartfield, D.S. Group A streptococcal meningitis as a complication of an infected capillary haemangioma. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2004, 163, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K.; Frankel, L.R.; Maldonado, Y.; Falco, D.A.; Lewis, D.B. Group A streptococcal meningitis: Report of a case and review of literature since 1976. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2001, 17, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zitteren, L.M.; Arents, N.L.; Halbertsma, F. Group-A-streptococcal meningitis in a 7-year-old child—A rare pathogen in a non-immune compromised patient. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011, bcr1020114896corr1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.; Chodock, R.; Quinn, C.; Peglow, S. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal meningitis associated with uncomplicated varicella. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1994, 12, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berner, R.; Herdeg, S.; Gordjani, N.; Brandis, M. Streptococcus pyogenes meningitis: Report of a case and review of the literature. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2000, 159, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.J.; Gutiérrez, P.B.; Villán, E.A.; Aguado, I.C. Meningitis y Streptococcus pyogenes: Un cruce de caminos poco frecuente [Meningitis and Streptococcus pyogenes: A rare cross-roads]. An. Pediatr. 2013, 80, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.M.; Kitz, R.; Lütticken, R.; Brade, V. Streptococcus pyogenes meningitis complicating varicella in a 3-month-old child. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 35, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez Ramiro, A.G.; Adell Sales, A.; Calderón Fernández, R.J.; Frasquet, J.; Pérez Tamarit, A. Meningitis bacteriana aguda por Streptococcus pyogenes [Acute bacterial meningitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes]. An. Pediatr. 2013, 78, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppberger, K.; Adams, I.; Deutscher, J.; Müller, H.; Kiess, W. Meningitis in a girl with recurrent otitis media caused by Streptococcus pyogenes—Otitis media has to be treated appropriately. Infection 2001, 29, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouhadi, Z.; Sadiki, H.; Lehlimi, M.; Honsali, Z.; Najib, J.; Zerouali, K.; Belabess, H.; Mdaghri, N. Meningites à streptocoque du groupe A. Med. Mal. Infect. 2012, 42, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, N.; Abulhoul, L.; Green, M.; Swann, R. Group A streptococcal meningitis: Case report and review of the literature. J. Infect. 2005, 51, E1–E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, A.; Beeri, M.; Engelhard, D. Group A streptococcal meningitis: Report of two cases. J. Infect. 1998, 36, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busetti, M.; Marchetti, F.; Croci, E.; L’Erario, I.; Creti, R.; D’Agaro, P. Group A streptococcal meningitis: A case report. New Microbiol. 2013, 36, 419–422. [Google Scholar]
- Fanella, S.; Embree, J. Group A Streptococcal Meningitis in a Pediatric Patient. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 19, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.C.; Pickering, L.K.; Baker, C.J. Group A streptococcal meningitis without predisposing factors. South. Med. J. 1981, 74, 1029–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevon, G.P.; Dunne, W.M.; Hawkins, H.K.; Armstrong, D.L.; Musser, J.M. Fatal group a streptococcal meningitis and toxic shock-like syndrome: Case report. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, T.; Kittang, B.R.; Mylvaganam, H.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Skrede, S. Clinical, microbiological and molecular characteristics of six cases of group A streptococcal meningitis in western Norway. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 42, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.A.; Peñaranda, N.A.D.; Fernández, J.M.R.; Alonso, J.M.C. Post-infective transverse myelitis following Streptococcus pyogenes meningitis. An. Pediatr. 2024, 101, 224–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, D.; Kameda-Smith, M.; Afshari, F.T.; Elawadly, A.; Hogg, F.; Mehta, S.; Samarasekara, J.; Aquilina, K.; Jeelani, N.U.O.; Tahir, M.Z.; et al. Intracranial invasive group A Streptococcus: A neurosurgical emergency in children. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2023, 32, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Francisco, C.; Santos, S.; Carvalho, P. Streptococcus pyogenes Meningitis in a Pediatric Patient: Case Report. Acta Medica Port. 2024, 37, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, V.L.J.; Chieffi, L.N.; Ceccon, M.E.J.R.; Diniz, E.M.D.A.; Feferbaum, R.; Takeuchi, C.A.; Marques-Dias, M.J.; Carneiro, J.D.A.; Vaz, F.A.C. Meningite neonatal por Streptococcus pyogenes e trombose de seio sagital: Relato de caso. [Neonatal Streptococcus pyogenes meningitis and sagittal sinus thrombosis: Case report]. Arq. Neuro Psiquiatr. 1998, 56, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacalhau, S.; Zarcos, M.M.; Rezende, T. Meningite bacteriana. Uma etiologia pouco frequente [Bacterial meningitis. A rare cause]. Acta Med. Port. 2011, 24 (Suppl. S3), 627–630. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.; Jain, S. Meningitis with bilateral acute suppurative otitis media caused by Group A Streptococcus. Indian Pediatr. 2005, 42, 79–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hmami, F.; Oulmaati, A.; Mahmoud, M.; Boubou, M.; Tizniti, S.; Bouharrou, A. Méningite néonatale à streptocoque A et thrombose porte: Une association fortuite ? [Neonatal group A streptococcal meningitis and portal vein thrombosis: A casual association? Arch. Pediatr. 2014, 21, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertner, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Barnett, S.H.; Shah, K. Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus and Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1992, 11, 595–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutman, J.; Henig, E.; Wilunsky, E.; Reisner, S.H. Acute necrotising fasciitis due to streptococcal infection in a newborn infant. Arch. Dis. Child. 1979, 54, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagupsky, P.; Giladi, Y. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal septicemia complicating infected hemangioma in children. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1987, 4, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Z.-Z.; Li, W.; Hu, H.-L.; Guo, X.; Hu, B.; Chen, T.-M.; Chen, H.-Y.; Guo, L.-Y.; Liu, G. Group A Streptococcal meningitis in children: A short case series and systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 43, 1517–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S. Acute bacterial meningitis in infants and children. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gier, B.; Marchal, N.; de Beer-Schuurman, I.; Wierik, M.T.; Hooiveld, M.; ISIS-AR Study Group; GAS Study group; de Melker, H.E.; van Sorge, N.M. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal (Streptococcus pyogenes) infections (iGAS) in young children in The Netherlands, 2022. Euro. Surveill. 2023, 28, 2200941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, R.; Henderson, K.L.; Coelho, J.; Hughes, H.; Mason, E.L.; Gerver, S.M.; Demirjian, A.; Watson, C.; Sharp, A.; Brown, C.S.; et al. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal infection notifications, England, 2022. Euro. Surveill. 2023, 28, 2200942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, Y.; Assad, Z.; Ouldali, N.; Caseris, M.; Mariani, P.; Birgy, A.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bidet, P.; Faye, A. Unexpected Increase in Invasive Group A Streptococcal Infections in Children After Respiratory Viruses Outbreak in France: A 15-Year Time-Series Analysis. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo-Vázquez, E.; Aguilera-Alonso, D.; Carrasco-Colom, J.; Calvo, C.; Saavedra-Lozano, J.; Mellado, I.; Grandioso, D.; Rincón, E.; Jové, A.; Cercenado, E.; et al. Increasing incidence and severity of invasive Group A streptococcal disease in Spanish children in 2019–2022. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2023, 27, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kempen, E.B.; Bruijning-Verhagen, P.C.J.; Borensztajn, D.M.; Vermont, C.L.; Quaak, M.S.W.; Janson, J.-A.; Maat, I.; Stol, K.; Vlaminckx, B.J.M.; Wieringa, J.W.; et al. Increase in Invasive Group a Streptococcal Infections in Children in the Netherlands, A Survey Among 7 Hospitals in 2022. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, e122–e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercadante, S.; Ficari, A.; Romani, L.; De Luca, M.; Tripiciano, C.; Chiurchiù, S.; Carducci, F.I.C.; Cursi, L.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Krzysztofiak, A.; et al. The Thousand Faces of Invasive Group A Streptococcal Infections: Update on Epidemiology, Symptoms, and Therapy. Children 2024, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, S.L.; Martinez, C.V.; Fonz, R.B.; Lobera, I.B.; Alonso, M.B. Mastoiditis aguda con complicación intracraneal. Reporte de un caso pediátrico. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2020, 118, e166–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, L.; Andreoni, F.; Boumasmoud, M.; Schweizer, T.A.; Heuberger, D.M.; Parietti, E.; Hertegonne, S.; Epprecht, J.; Mattle, D.; Raez, A.K.; et al. Group A Streptococcus strains causing meningitis without distinct invasive phenotype. Microbiologyopen 2024, 13, e1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Torres, R.S.; Fedalto, L.E.; Steer, A.C.; Smeesters, P.R. Group A Streptococcus meningitis in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, M.J.; McGill, F.; Solomon, T. Management of acute meningitis. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alamarat, Z.; Hasbun, R. Management of Acute Bacterial Meningitis in Children. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 4077–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Trujillo-Gómez, J.; Tsokani, S.; Arango-Ferreira, C.; Atehortúa-Muñoz, S.; Jimenez-Villegas, M.J.; Serrano-Tabares, C.; Veroniki, A.-A.; Florez, I.D. Biofire FilmArray Meningitis/Encephalitis panel for the aetiological diagnosis of central nervous system infections: A systematic review and diagnostic test accuracy meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2022, 44, 101275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Amor, L.; García-Prieto, E.; Fernández-Suárez, J.; Escudero, D.; Vázquez, F.; Fernández, J. Evaluation of a commercial multiplex PCR for diagnosis of central nervous system (CNS) nosocomial infections. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 171, 105865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, E.; Hoenigl, M.; Wagner, B.; Krause, R.; Feierl, G.; Grisold, A.J. Performance of the FilmArray Blood culture identification panel in positive blood culture bottles and cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of sepsis and meningitis. GMS Infect. Dis. 2016, 4, Doc06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezahosseini, O.; Roed, C.; Holler, J.G.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Harboe, Z.B. Adjunctive antibiotic therapy with clindamycin or linezolid in patients with group A streptococcus (GAS) meningitis. Infect. Dis. 2023, 55, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsten, H.; Medina, L.M.P.; Morgan, M.; Moll, K.; Skutlaberg, D.H.; Skrede, S.; Wajima, T.; Svensson, M.; Norrby-Teglund, A. Adjunctive Rifampicin Increases Antibiotic Efficacy in Group A Streptococcal Tissue Infection Models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0065821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, A.; De Luca, M.; Simeoli, R.; Goffredo, B.M.; Cursi, L.; Tripiciano, C.; Romani, L.; Mercadante, S.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Carducci, F.I.C.; et al. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring-Guided Linezolid Therapy for the Treatment of Multiple Staphylococcal Brain Abscesses in a 3-Month-Old Infant. Pathogens 2024, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesters, K.; Alemayehu, T.; Benou, S.; Buonsenso, D.; Decloedt, E.H.; Lorente, V.P.-F.; Downes, K.J.; Allegaert, K. Pharmacokinetics of Antimicrobials in Children with Emphasis on Challenges Faced by Low and Middle Income Countries, a Clinical Review. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullins, A.K.; Abdel-Rahman, S.M. Pharmacokinetics of Antibacterial Agents in the CSF of Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Drugs 2013, 15, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, E.A. Targeting Bacterial Virulence: The role of protein synthesis inhibitors in severe infections. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2003, 23, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreoni, F.; Zürcher, C.; Tarnutzer, A.; Schilcher, K.; Neff, A.; Keller, N.; Maggio, E.M.; Poyart, C.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Zinkernagel, A.S. Clindamycin Affects Group A Streptococcus Virulence Factors and Improves Clinical Outcome. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 215, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brouwer, M.C.; McIntyre, P.; Prasad, K.; van de Beek, D. Corticosteroids for acute bacterial meningitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2018, CD004405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaad, U.; Wedgwood, J.; Lips, U.; Gnehm, H.; Heinzer, I.; Blumberg, A. Dexamethasone therapy for bacterial meningitis in children. Lancet 1993, 342, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, N.I.; Farid, Z.; Mikhail, I.A.; Farrag, I.; Sultan, Y.; Kilpatrick, M.E. Dexamethasone treatment for bacterial meningitis in children and adults. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1989, 8, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, P.B.; MacIntyre, C.R.; Gilmour, R.; Wang, H. A population based study of the impact of corticosteroid therapy and delayed diagnosis on the outcome of childhood pneumococcal meningitis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliano, P.; Fusco, U.; Attanasio, V.; Rossi, M.; Pantosti, A.; Conte, M.; Faella, F.S. Pneumococcal meningitis in childhood: A longitudinal prospective study. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelton, S.I.; Yogev, R. Improving the outcome of pneumococcal meningitis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Putten, B.C.L.; Vlaminckx, B.J.M.; de Gier, B.; Graaf, W.F.-D.; van Sorge, N.M. Group A Streptococcal Meningitis With the M1UK Variant in the Netherlands. JAMA 2023, 329, 1791–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergova, R.; Boyanov, V.; Muhtarova, A.; Alexandrova, A. A Review of the Impact of Streptococcal Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance on Human Health. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-López, V.; Valdezate, S.; Álvarez, D.; Villalón, P.; Medina, M.J.; Salcedo, C.; Sáez-Nieto, J.-A. Molecular epidemiology, antimicrobial susceptibilities and resistance mechanisms of Streptococcus pyogenes isolates resistant to erythromycin and tetracycline in Spain (1994–2006). BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbel, D.; González-Díaz, A.; de Egea, G.L.; Càmara, J.; Ardanuy, C. An Overview of Macrolide Resistance in Streptococci: Prevalence, Mobile Elements and Dynamics. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.A.; Dorfmueller, H.C. Update on the development of Group A Streptococcus vaccines. npj Vaccines 2023, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case One | Case Two | |
|---|---|---|
| Age Sex | 4 years and 8 months Female | 5 years and 9 months Female |
| Comorbidities | No | No |
| Local infection | AOM | No |
| Blood exams | ||
| White blood cells | 32,280/m3 | 18,370/m3 |
| Neutrophils | 95.54% | 94% |
| Lymphocytes | 1.1% | 3.0% |
| Hemoglobin | 11.5 g/dL | 9.7 g/dL |
| Platelets | 450,000/m3 | 137,000/m3 |
| CRP | 16.76 mg/dL | 26.74 mg/dL |
| Procalcitonin | 28.6 ng/mL | 24.3 ng/mL |
| Glucose | 95 mg/dL | 140 mg/dL |
| Cerebrospinal fluid | ||
| Appearance | turbid | turbid |
| Color | xanthochrome | xanthochrome |
| White blood cells | 296/m3 | 49/m3 |
| Glucose | 2 mg/dL | 58 mg/dL |
| Proteins | 511 mg/dL | 125 mg/dL |
| Treatment and Outcome | ||
| Therapy | Ceftriaxone, Linezolid | Ceftriaxone, Vancomycin, Linezolid, Immunoglobulins |
| Surgery | Craniectomy | Craniectomy |
| Length of stay | 2 days | 21 days |
| Outcome | Death | Full recovery |
| Variable | Variable Subclassification | Results | Variable | Variable Subclassification | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predisposing conditions | HIV VPS Cochlear implant Prematurity | 1.75% (1/57) 1.75% (1/57) 1.75% (1/57) 1.75% (1/57) | Cerebral TC/RMN findings | Cerebral collection Hydrocephalus Cerebral edema Vasculopathy Necrosis Ventriculitis Myelitis | 21.04% (12/57) 5.26% (3/57) 8.77% (12/57) 21.04% (12/57) 8.77% (5/57) 7.01% (4/57) 1.75% (1/57) |
| Empiric antibiotic therapy | Cephalosporin Cephalosporin plus glycopeptides Other regimes Overall use of protein-synthesis inhibitors | 66.66% (38/57) 17.54% (10/57) 15.78 (9/57) 26.31% (15/57) | Additional treatment/ therapies | Steroids Immunoglobulins Surgery | 33.33% (19/57) 5.26% (3/57) 22.80% (13/57) |
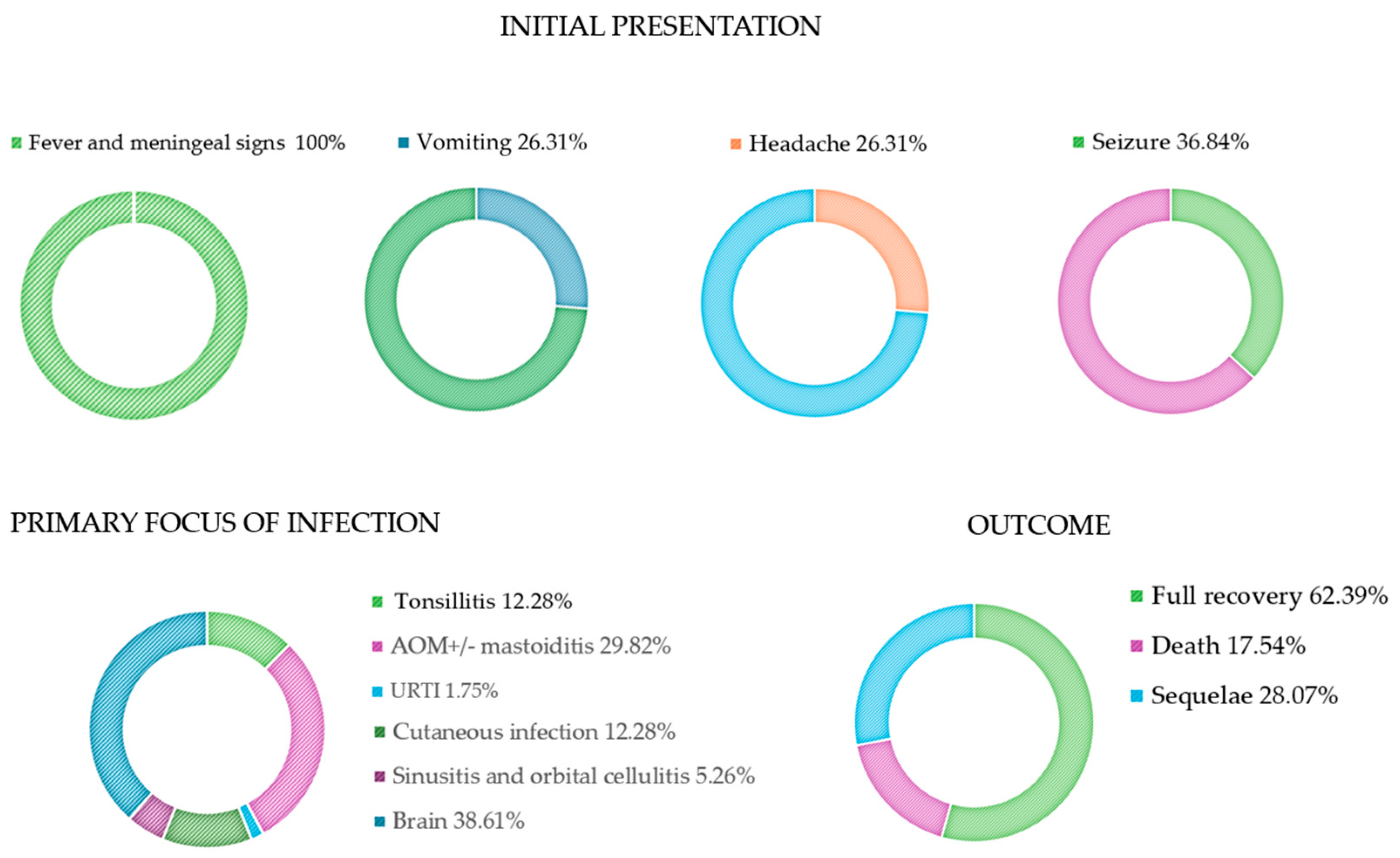
| Overall complications | Status epilepticus Nerve involvement Hydrocephalus Brain collection Vasculopathy Hygroma Cerebral edema Coma Phoenix Sepsis Score ≥ 2 | 21.04% (12/57) 7.01% (4/57) 5.26% (3/57) 21.04% (12/57) 12.28% (7/57) 7.01% (4/57) 24.56% (14/57) 33.33% (19/57) 45.61% (26/57) | Outcome | Full recovery Death Sequelae: -NSHL -Third nerve palsy -Moderate disability -Severe disability | 62.39% (31/57) 17.54% (10/57) 28.07% (16/57) 5.26% (3/57) 1.75% (1/57) 5.26% (3/57) 15.80% (9/57) |
| Variable | Uneventful Course N = 22 | Complicated Course N = 35 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 5.5 | 5.21 | 0.41 |
| Age below 1 y | 4/22 | 11/35 | 0.26 |
| Female sex | 12/22 | 19/35 | 0.98 |
| Predisposing conditions | 2/22 | 2/35 | 0.62 |
| Other focus of infection beside the brain | 13/22 | 22/35 | 0.77 |
| CSF WBC (mg/dL) | 1350.3 | 2586 | 0.03 |
| CSF proteins (mg/dL) | 126.26 | 252.42 | 0.02 |
| CSF glucose (mg/dL) | 29.25 | 20.33 | 0.12 |
| WBC on blood (mmc) | 18,836.36 | 20,216.4 | 0.35 |
| S. pyogenes on blood | 3/22 | 18/35 | <0.01 |
| Phoenix Sepsis Score ≥ 2 | 1/22 | 25/35 | <0.01 |
| Use of protein-synthesis inhibitors | 3/22 | 12/35 | 0.064 |
| Dexamethasone therapy | 4/22 | 15/35 | 0.054 |
| Length of stay (d) | 17 | 24 | 0.02 |
| Variable | p-Value | Odds Ratio | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predisposing conditions | 0.618 | 0.595 | 0.0771–4.59 |
| Other focus of infection beside the brain | 0.712 | 1.247 | 0.386–4.02 |
| S. pyogenes on blood | 0.01 | 6.101 | 1.512–24.62 |
| Phoenix Sepsis Score ≥ 2 | <0.001 | 68.570 | 7.3733–637.68 |
| Use of protein-synthesis inhibitors | 0.06 | 3.846 | 0.915–16.16 |
| Dexamethasone therapy | 0.05 | 3.763 | 0.999–14.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Meglio, L.; De Luca, M.; Cursi, L.; Romani, L.; Pisani, M.; Musolino, A.M.; Mercadante, S.; Cortazzo, V.; Vrenna, G.; Bernaschi, P.; et al. Unraveling Pediatric Group A Streptococcus Meningitis: Lessons from Two Case Reports and a Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051100
Di Meglio L, De Luca M, Cursi L, Romani L, Pisani M, Musolino AM, Mercadante S, Cortazzo V, Vrenna G, Bernaschi P, et al. Unraveling Pediatric Group A Streptococcus Meningitis: Lessons from Two Case Reports and a Systematic Review. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051100
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Meglio, Lavinia, Maia De Luca, Laura Cursi, Lorenza Romani, Mara Pisani, Anna Maria Musolino, Stefania Mercadante, Venere Cortazzo, Gianluca Vrenna, Paola Bernaschi, and et al. 2025. "Unraveling Pediatric Group A Streptococcus Meningitis: Lessons from Two Case Reports and a Systematic Review" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051100
APA StyleDi Meglio, L., De Luca, M., Cursi, L., Romani, L., Pisani, M., Musolino, A. M., Mercadante, S., Cortazzo, V., Vrenna, G., Bernaschi, P., Bianchi, R., & Lancella, L. (2025). Unraveling Pediatric Group A Streptococcus Meningitis: Lessons from Two Case Reports and a Systematic Review. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051100






