Impact of Tetracycline Stress on Water Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities of Eichhornia crassipes: Implications for Bioremediation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Experimental Materials
2.2. Tet Stress of E. crassipes
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. Biomass and Root Exudates
2.5. Rhizosphere Microbial Sampling and Sequencing
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in E. crassipes Growth and Physicochemical Indicators in Rhizospheric Water Under Tet Stress
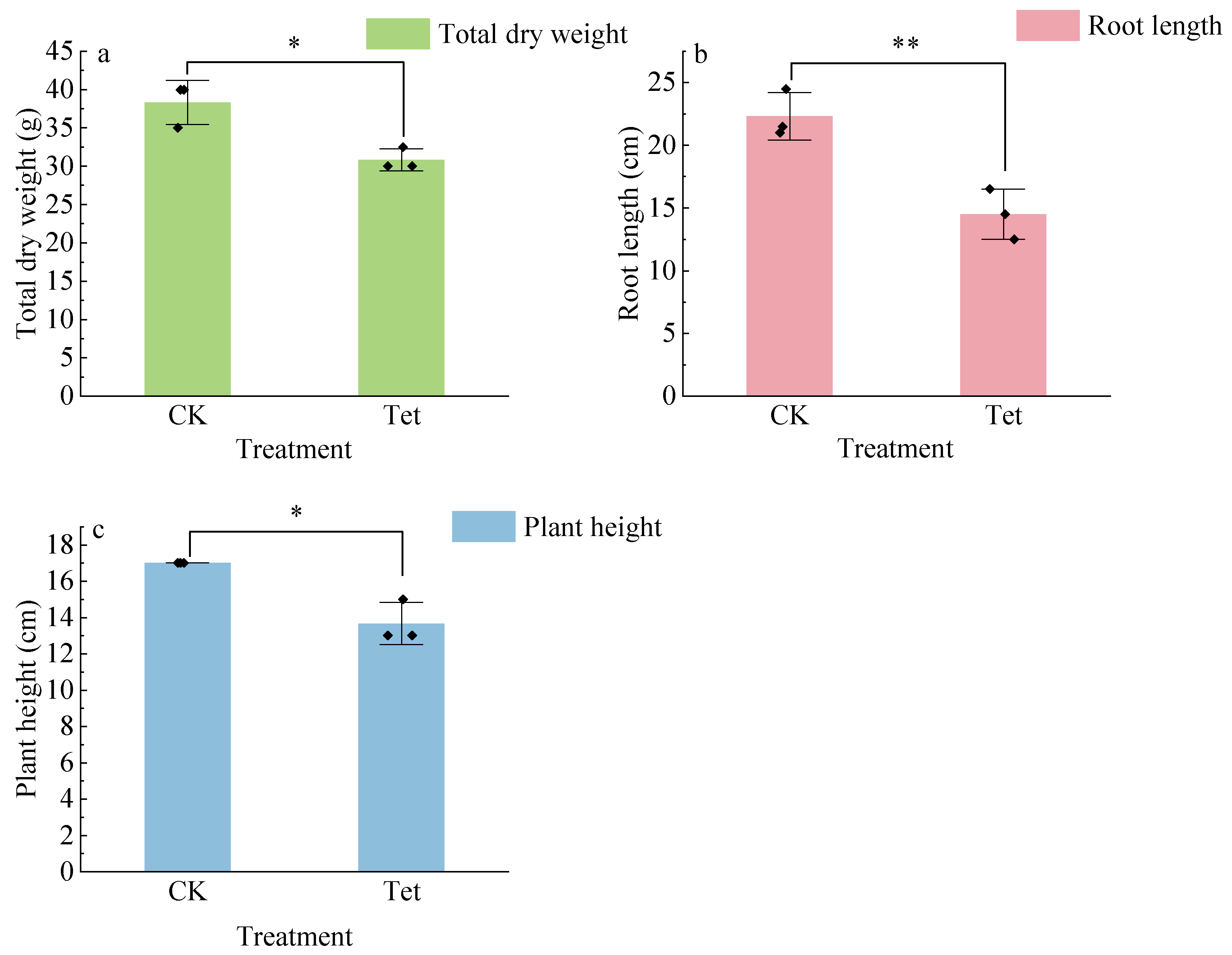
3.1.1. Growth of E. crassipes Under Tet Stress
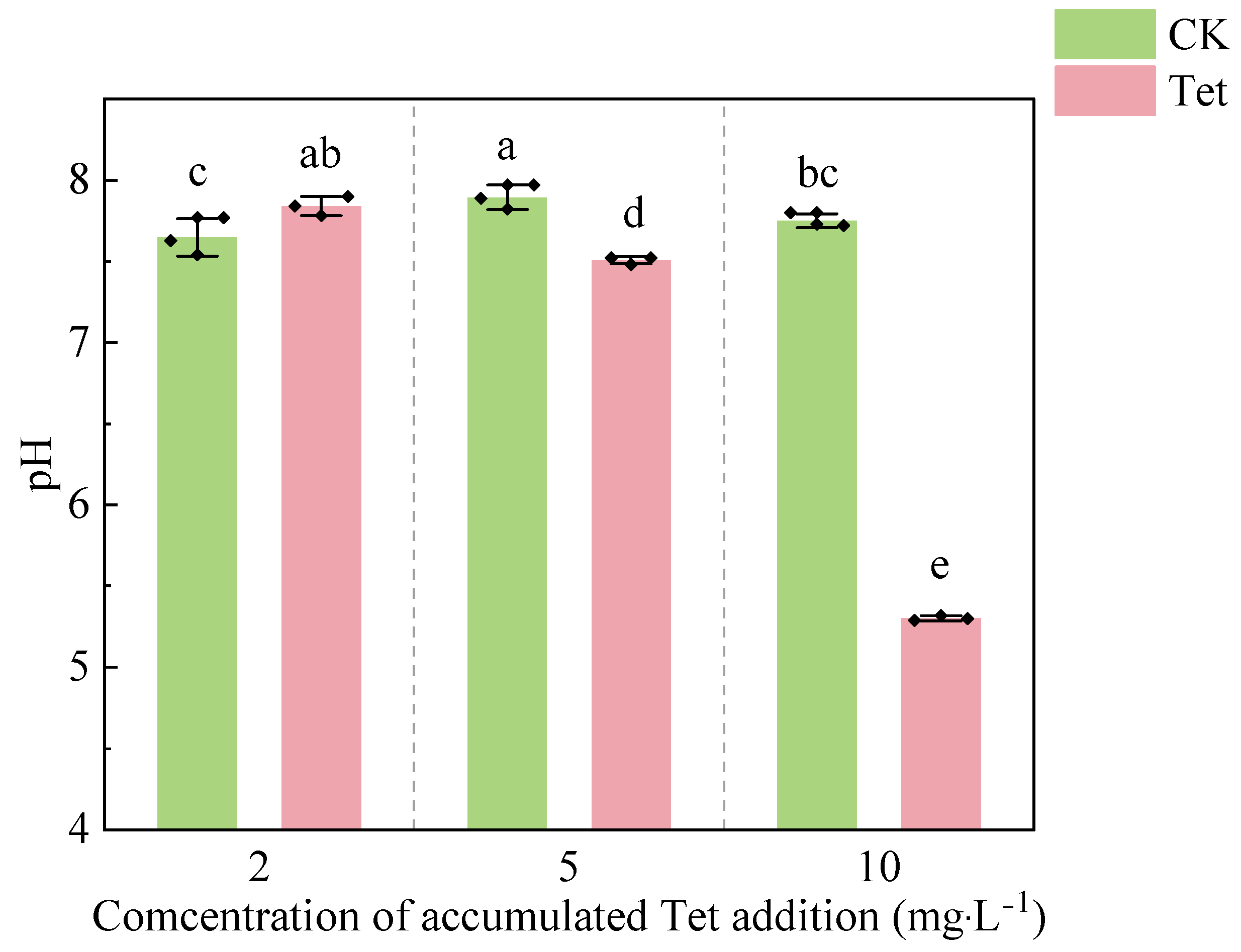
3.1.2. Changes in pH in the Rhizospheric Water
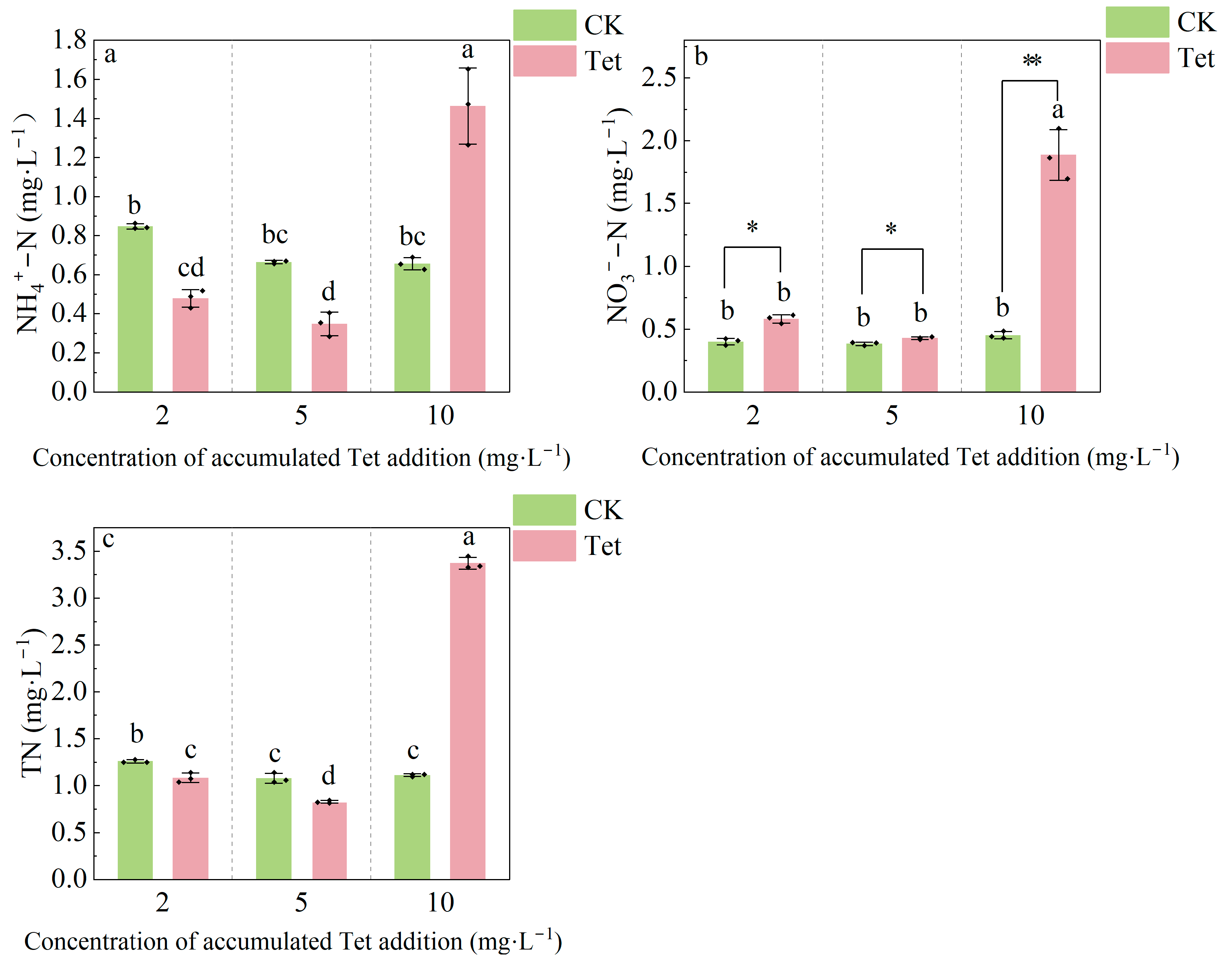
3.1.3. Changes in NH4+-N, NO3−-N and TN in the Rhizospheric Water
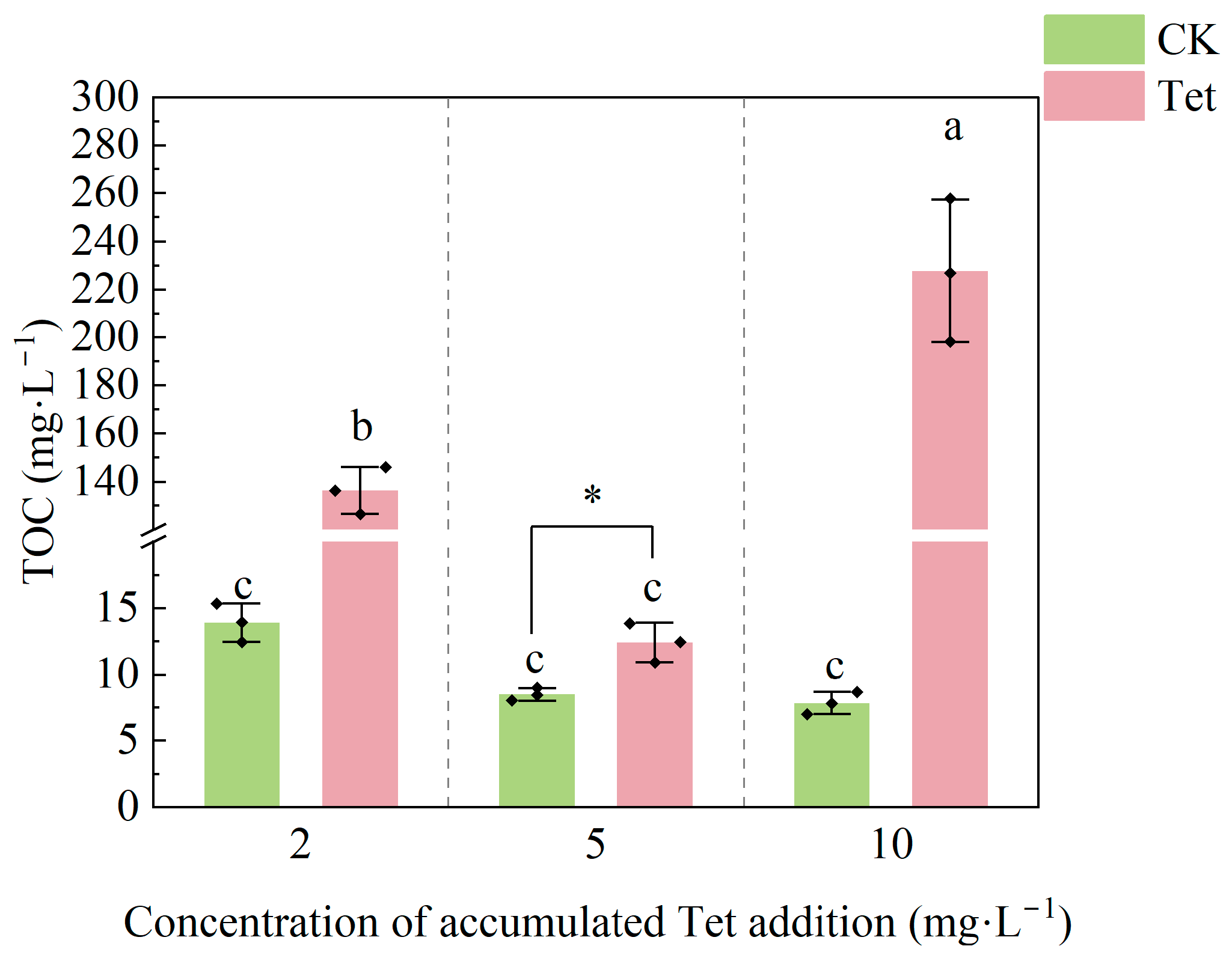
3.1.4. Changes in TOC in the Rhizospheric Water
3.1.5. Changes in LMWOAs in the Rhizospheric Water
3.2. Changes in Microbial Communities in the Root and Rhizospheric Water of E. crassipes Under Tet Stress
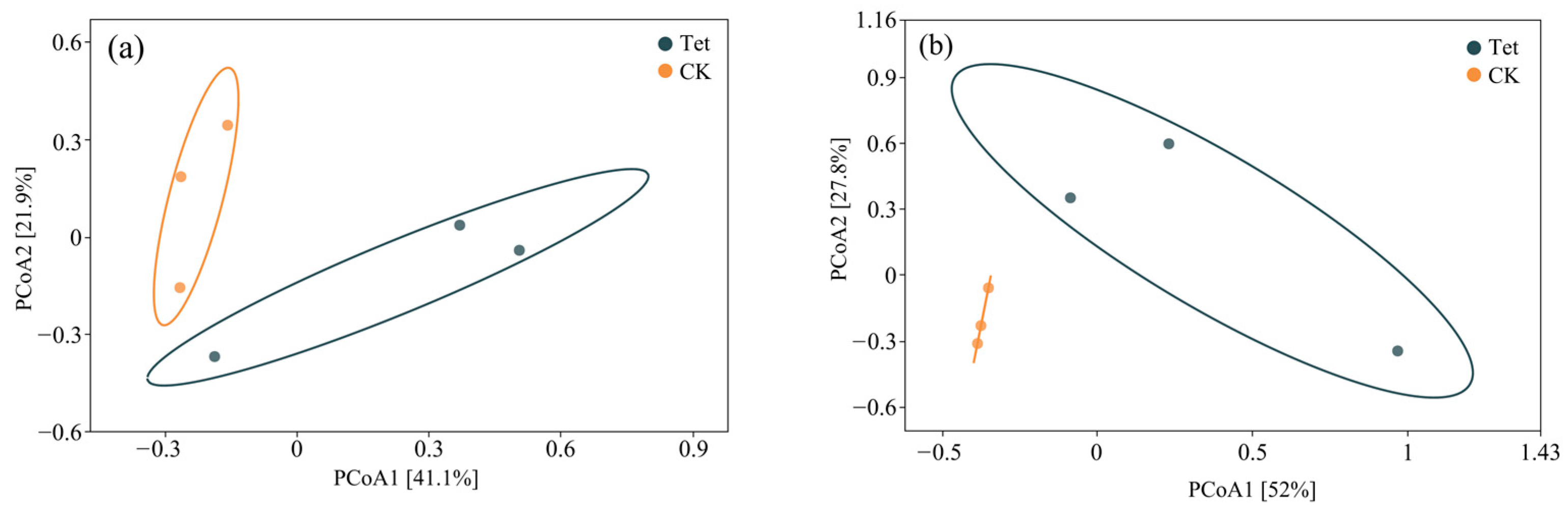
3.2.1. Principal Coordinate Analysis
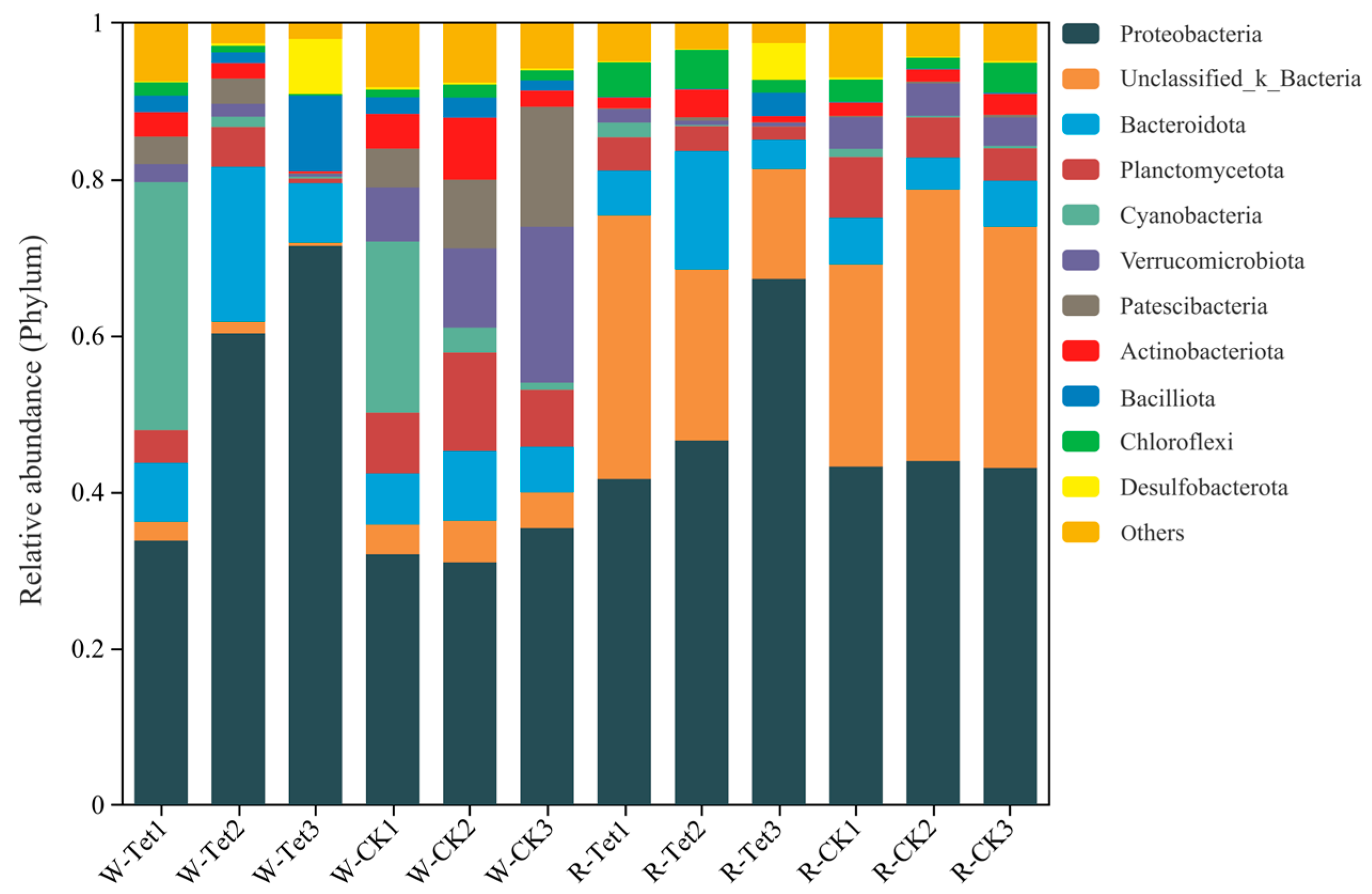
3.2.2. Relative Abundances at the Phylum Level
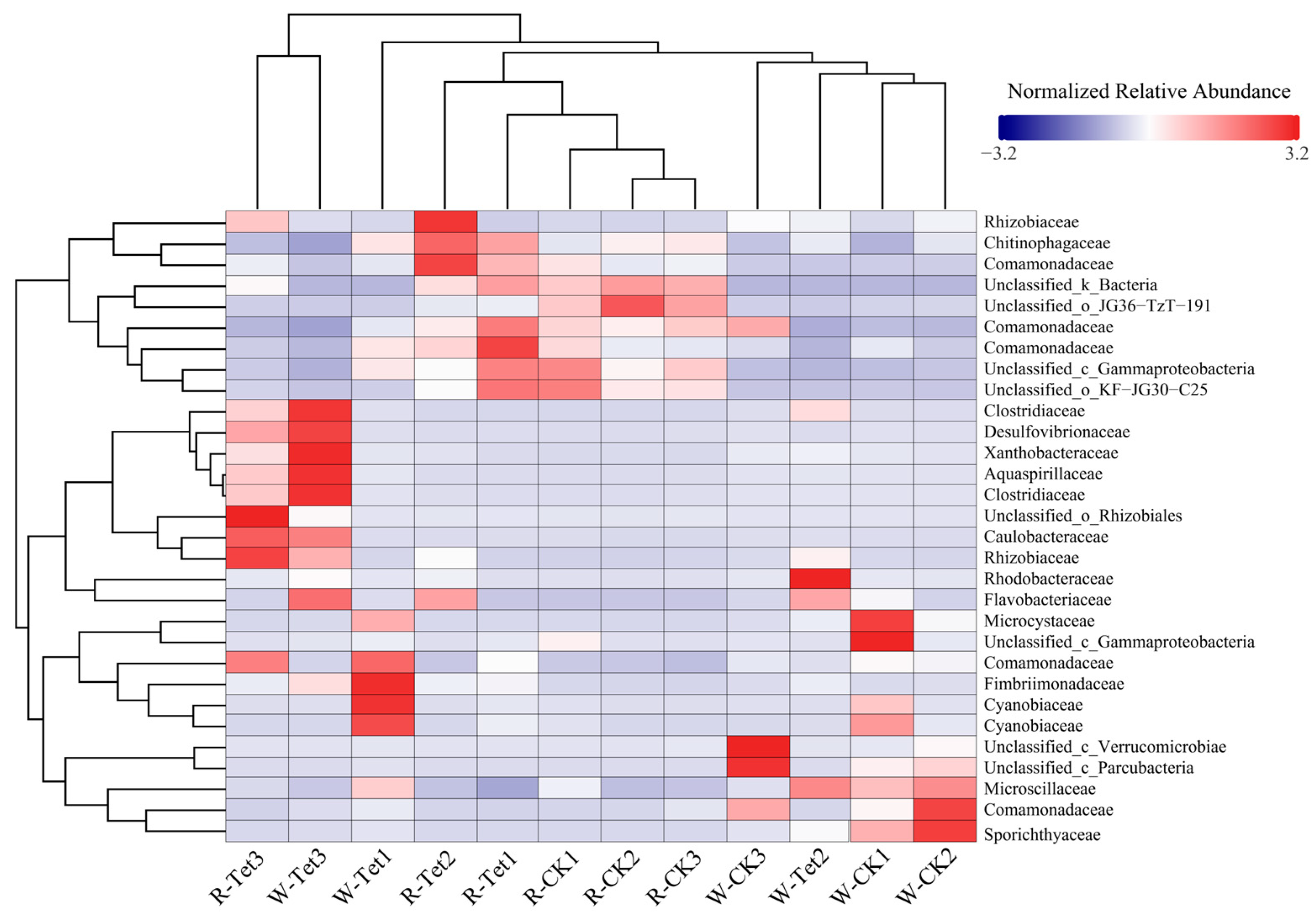
3.2.3. Microbial Community Shifts Under Tet Stress
Water Sample Analysis
Root Sample Analysis
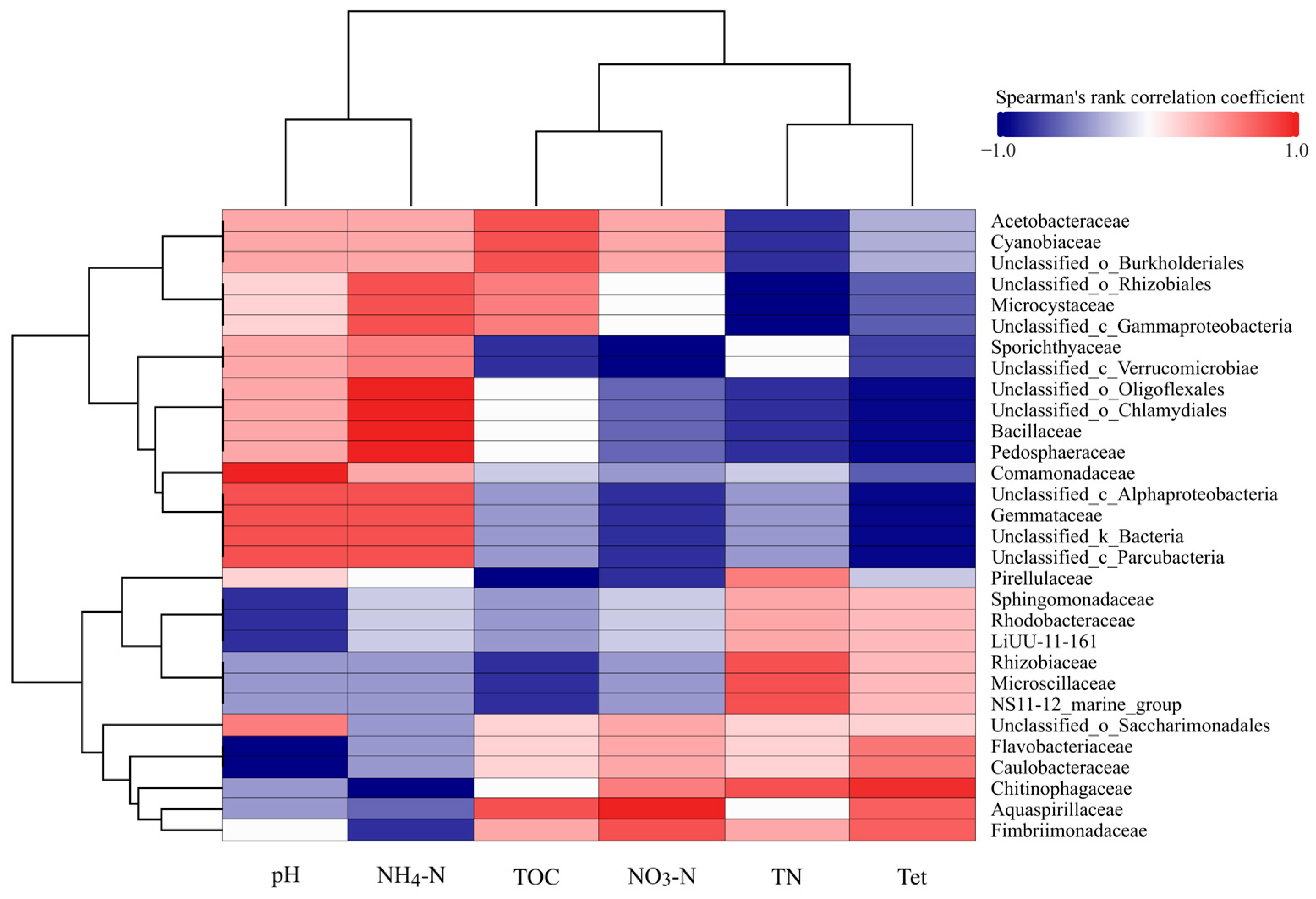
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Microbial Taxa and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Tet | Tetracycline |
| NH4+-N | Ammonium nitrogen |
| NO3−-N | Nitrate nitrogen |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| LMWOAs | Low-molecular-weight organic acids |
| ARGs | Antibiotic resistance genes |
| OTUS | Operational taxonomic units |
References
- Kunhikannan, S.; Thomas, C.J.; Franks, A.E.; Mahadevaiah, S.; Kumar, S.; Petrovski, S. Environmental hotspots for antibiotic resistance genes. MicrobiologyOpen 2021, 10, e1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Chang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, L.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, W. The Safety of Consuming Water Dropwort Used to Purify Livestock Wastewater Considering Accumulated Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Gu, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, A.; Jiang, X.; Deng, M.; Zeng, J.; et al. Metagenomic assembly insight into the antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotic resistant bacteria in packaged drinking water system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Suyamud, B.; Yuan, Y.; Ghosh, S.; Xu, X.; Hu, J. Effect of non-antibiotic factors on conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in aquaculture water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 483, 136701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Hu, Y.; Tang, L.; Tian, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wei, D.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y. New hydrolysis products of oxytetracycline and their contribution to hard COD in biological effluents of antibiotic production wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, M.; Ben, W.; Qiang, Z. Potential of solar photodegradation of antibiotics in shallow ditches: Kinetics, the role of dissolved organic matter and prediction models. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, S.; Niu, J.; Dong, X.; Leong, Y.K.; Chang, J.-S. Dissecting the ecological risks of sulfadiazine degradation intermediates under different advanced oxidation systems: From toxicity to the fate of antibiotic resistance genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 941, 173678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J. Environmental fate of tetracycline antibiotics: Degradation pathway mechanisms, challenges, and perspectives. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhuang, R.; Liu, J.; Guo, G.; Chen, J.; Yao, Y. Bioremediation of tetracycline antibiotics-contaminated soil by bioaugmentation. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 33086–33102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, M.S.; Kumar, A.; Javed, M.A.; Dubey, A.; de Medeiros, F.H.V.; Santoyo, G. Harnessing root exudates for plant microbiome engineering and stress resistance in plants. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 279, 127564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Leach, J.E.; Tringe, S.G.; Sa, T.; Singh, B.K. Plant–microbiome interactions: From community assembly to plant health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.M.; Aranda, B. Microbial Growth under Limiting Conditions-Future Perspectives. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Lee, H.-S. Interplay between Plants and Microbial Communities: Insights from Holobionts and Environmental Interactions. Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 93, 2519–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Ortega-Villaizán, A.; King, E.; Patel, M.K.; Pérez-Alonso, M.-M.; Scholz, S.S.; Sakakibara, H.; Kiba, T.; Kojima, M.; Takebayashi, Y.; Ramos, P.; et al. The endophytic fungus Serendipita indica affects auxin distribution in Arabidopsis thaliana roots through alteration of auxin transport and conjugation to promote plant growth. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 3899–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo, G. How plants recruit their microbiome? New insights into beneficial interactions. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 40, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Gao, Y.; Luo, J.; Yan, S.; Rengel, Z.; Zhang, Z. Interaction of veterinary antibiotic tetracyclines and copper on their fates in water and water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Sodhi, K.K.; Singh, D.K. Understanding the bacterial community structure associated with the Eichhornia crassipes rootzone. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 51, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Qian, X.; Wu, Y.; Ma, T.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Yan, Y. Effects of ciprofloxacin on Eichhornia crassipes phytoremediation performance and physiology under hydroponic conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2022, 29, 47363–47372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G. Effects and Removal of the Antibiotic Sulfadiazine by Eichhornia crassipes: Potential Use for Phytoremediation. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Arabacı, D.N.; Shahi, A.; Fakhri, H.; Ovez, S. Enhanced removal of antibiotics using Eichhornia crassipes root biomass in an aerobic hollow-fiber membrane bioreactor. Biofouling 2022, 38, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, W.; Du, W.; Gu, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, X. Phytoremediation of antibiotic-contaminated wastewater: Insight into the comparison of ciprofloxacin absorption, migration, and transformation process at different growth stages of E. crassipes. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ke, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, C.; Xie, S. Enrichment of tetracycline-degrading bacterial consortia: Microbial community succession and degradation characteristics and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Liang, D. Effect of tetracycline on nitrogen removal in Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) System. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Feng, J.; Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Li, X.; Li, B. Deciphering of microbial community and antibiotic resistance genes in activated sludge reactors under high selective pressure of different antibiotics. Water Res. 2019, 151, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-Q.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.-H.; Zhang, H.-C.; Sheng, G.-P. Tetracycline exposure shifted microbial communities and enriched antibiotic resistance genes in the aerobic granular sludge. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Environmental Protection Administration; The Water and Wastewater Monitoring Analysis Method Editorial Board. Water and Wastewater Monitoring Analysis Method, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 254–284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Yang, S.K.; Han, C.; Xu, D.; Wang, Z.D.; Ke, F.; Shen, Q.S. Effects of environmental stress on characteristics of low molecular weight organic acids secreted by macrophyte roots. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.; berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.; Wagner, H. R Package, Version 2.2-1; Vegan: Community Ecology Package; 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2011, 174, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R. Pretty Heatmaps, version 1.0.12; 2019. Available online: https://raivokolde.r-universe.dev/pheatmap (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Taiyun, W.; Viliam, S.; Michael, L.; Yihui, X.; Yan, J.; Jeff, Z.; Moritz, F.; Jun, C.P.T. Package ‘corrplot’, version 0.95; Visualization of a Correlation Matrix; 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/corrplot/index.html (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J. Effect of antibiotics on diverse aquatic plants in aquatic ecosystems. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 281, 107289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Yu, F. Sensing and regulation of plant extracellular pH. Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 1422–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-G.; Johnson, T.A.; Su, J.-Q.; Qiao, M.; Guo, G.-X.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Hashsham, S.A.; Tiedje, J.M. Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes in Chinese swine farms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3435–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, J.C.; Harvey, R.W.; Metge, D.W.; Repert, D.A.; Baumgartner, L.K.; Smith, R.L.; Roane, T.M.; Barber, L.B. Effects of the Antimicrobial Sulfamethoxazole on Groundwater Bacterial Enrichment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3096–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Kong, Q.; Li, W.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Release of dissolved organic matter from wetland plants and its interaction with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Xu, Y. Microbial-mediated conversion of soil organic carbon co-regulates the evolution of antibiotic resistance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, A. A comprehensive review of recent research concerning the role of low molecular weight organic acids on the fate of organic pollutants in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.L.; Dennis, P.G.; Owen, A.G.; van Hees, P.A.W. Organic acid behavior in soils—Misconceptions and knowledge gaps. Plant Soil 2003, 248, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haichar, F.e.Z.; Santaella, C.; Heulin, T.; Achouak, W. Root exudates mediated interactions belowground. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 77, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mithöfer, A.; Schulze, B.; Boland, W. Biotic and heavy metal stress response in plants: Evidence for common signals. FEBS Lett. 2004, 566, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudrappa, T.; Czymmek, K.J.; Paré, P.W.; Bais, H.P. Root-Secreted Malic Acid Recruits Beneficial Soil Bacteria. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.-L.; Cantón, R. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.L. Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11436–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.L. Natural antibiotic resistance and contamination by antibiotic resistance determinants: The two ages in the evolution of resistance to antimicrobials. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; He, Y.; Li, R.; Mu, C.; Wang, C.; Shi, C.; Ye, Y. Adaptive changes of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) associated bacteria helping host against dibutyl phthalate toxification. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Cao, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, N. The organophosphorus pesticides in soil was degradated by Rhodobacter sphaeroides after wastewater treatment. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 141, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Chen, W.; Wei, D.; Li, X.; Tang, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Anaerobic fermentation for hydrogen production and tetracycline degradation: Biodegradation mechanism and microbial community succession. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, G.; Smalla, K. Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.-H.; He, M.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Lü, H. Root-associated bacterial communities of vegetable Brassica parachinensis enrich pollutant-degrading taxa and functions for enhancing phthalate dissipation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, I.; Roberts, M. Tetracycline antibiotics: Mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, S.; Wyrsch Ethan, R.; Drigo, B.; Baker Dave, J.; Charles Ian, G.; Donner, E.; Jarocki Veronica, M.; Djordjevic Steven, P. Genomic Analysis of Carbapenem-Resistant Comamonas in Water Matrices: Implications for Public Health and Wastewater Treatments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e00646-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, K.J.; Reyes, A.; Wang, B.; Selleck, E.M.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Dantas, G. The Shared Antibiotic Resistome of Soil Bacteria and Human Pathogens. Science 2012, 337, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Su, J.-Q.; Guo, Y.; Wilkinson, D.M.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Yang, J. Large-scale biogeographical patterns of bacterial antibiotic resistome in the waterbodies of China. Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Miguel, A.B.; Smith, G.J.; Cremers, G.; van Alen, T.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Op den Camp, H.J.M.; Welte, C.U. Microbial paracetamol degradation involves a high diversity of novel amidase enzyme candidates. Water Res. X 2022, 16, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zheng, X.; Long, M.; Chen, Y. Inorganic carbon metabolism enhanced hydrogen-driven denitrification: Evaluation of carbon fixation pathways and microbial traits. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, D.; Zhang, H.; Pan, G.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, J.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Lu, X. Impact of Tetracycline Stress on Water Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities of Eichhornia crassipes: Implications for Bioremediation. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040893
Sun D, Zhang H, Pan G, Zhang Z, Xing J, Li J, Gao Y, Chen W, Lu X. Impact of Tetracycline Stress on Water Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities of Eichhornia crassipes: Implications for Bioremediation. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040893
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Dandan, Huan Zhang, Guojun Pan, Zhenhua Zhang, Jincheng Xing, Jiangye Li, Yan Gao, Wei Chen, and Xin Lu. 2025. "Impact of Tetracycline Stress on Water Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities of Eichhornia crassipes: Implications for Bioremediation" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040893
APA StyleSun, D., Zhang, H., Pan, G., Zhang, Z., Xing, J., Li, J., Gao, Y., Chen, W., & Lu, X. (2025). Impact of Tetracycline Stress on Water Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities of Eichhornia crassipes: Implications for Bioremediation. Microorganisms, 13(4), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040893





