Isolation, Characterization and Growth-Promoting Properties of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (PSBs) Derived from Peach Tree Rhizosphere
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Isolation of PSBs
2.2. Assay of Phosphate-Solubilizing Capacity
2.3. Characterization of PSB Isolates
2.4. Determination of the Growth-Promoting Ability of PSBs
2.5. Determination of Biofilm Formation Ability of PSBs
2.6. Effect of PSBs on Growth of Peach Seedling
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
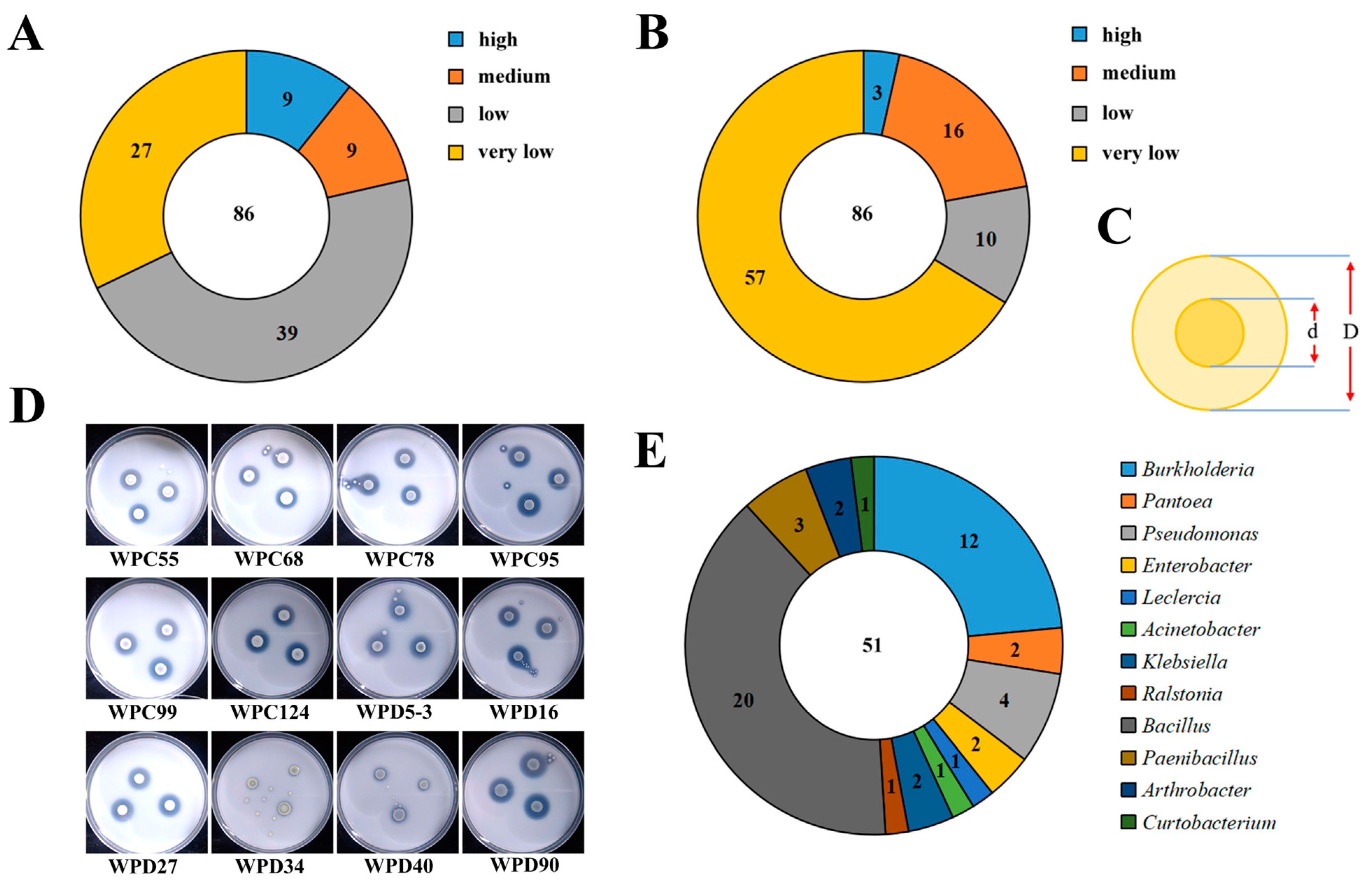
3.1. Isolation and Identification of PSBs
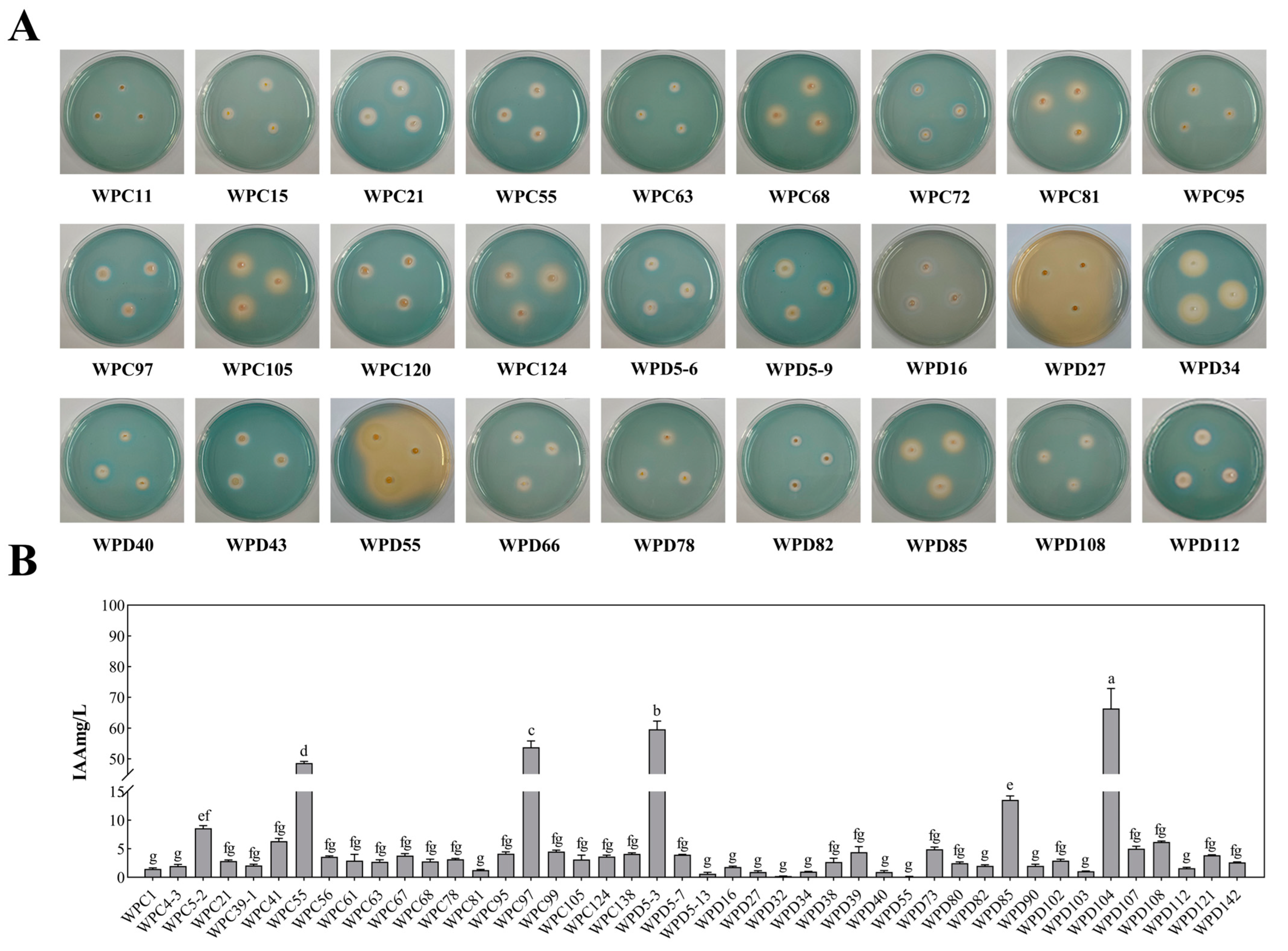
3.2. Determination of Growth-Promoting Ability of PSBs
3.3. Screening and Physiological and Biochemical Characterization of the Dominant Strains
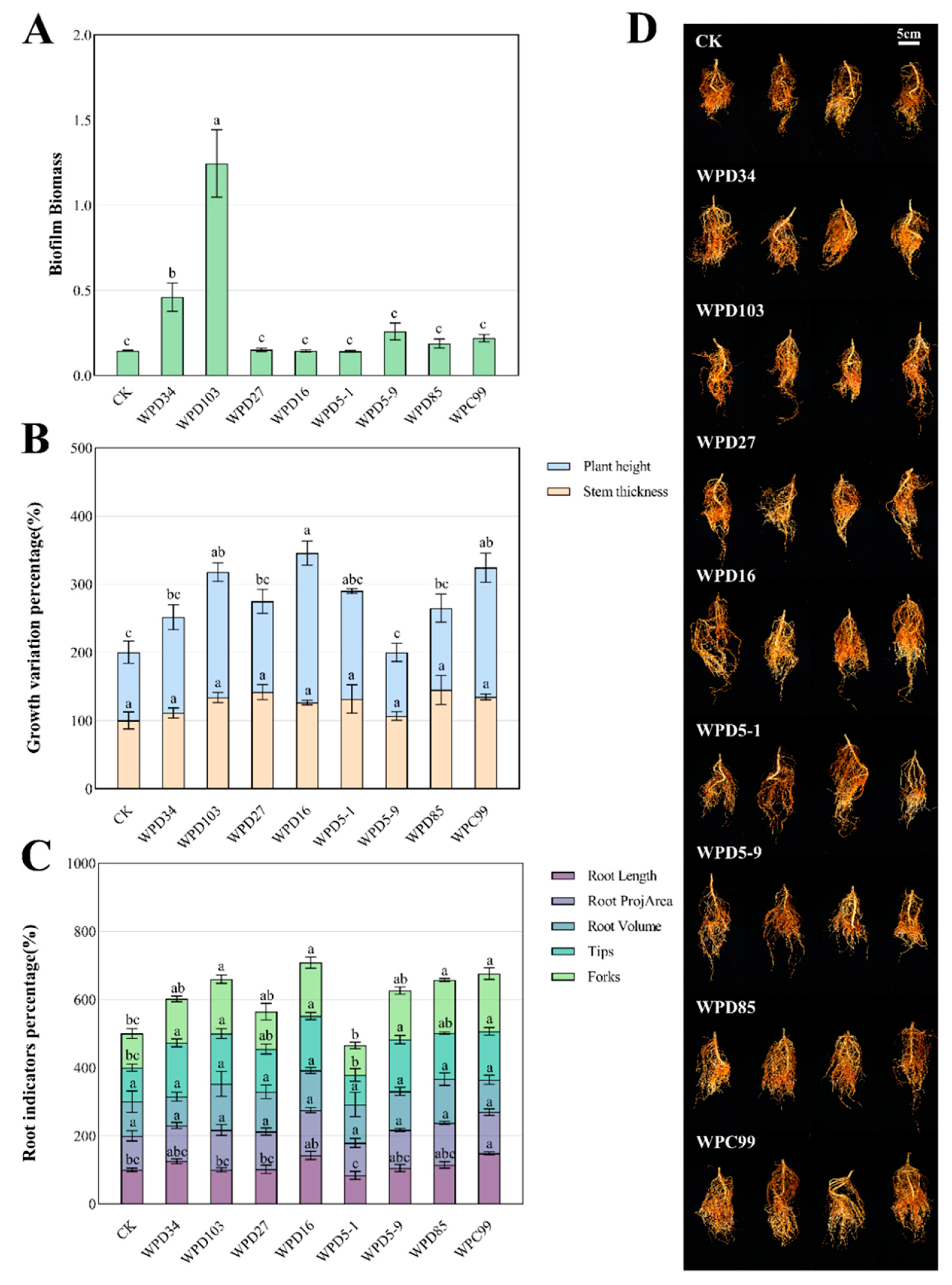
3.4. Biofilm Formation Capacity of Dominant Strains
3.5. Potting Trials
4. Discussion
4.1. Isolation of PSBs
4.2. Phosphate-Solubilizing Capacity of the Strains
4.3. Prospects for the Application of PSBs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vance, C.P.; Uhde-Stone, C.; Allan, D.L. Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol. 2003, 157, 423–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, H.; Fraga, R. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol. Adv. 1999, 17, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, V.; Kalagudi, G. Enhancing plant phosphorus use efficiency for sustainable cropping. Biotechnol. Adv. 2005, 23, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elhaissoufi, W.; Ghoulam, C.; Barakat, A.; Zeroual, Y.; Bargaz, A. Phosphate bacterial solubilization: A key rhizosphere driving force enabling higher P use efficiency and crop productivity. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 38, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Prisa, D.; Fresco, R.; Spagnuolo, D. Microbial Biofertilisers in Plant Production and Resistance: A Review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Hou, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L. Progress in Microbial Fertilizer Regulation of Crop Growth and Soil Remediation Research. Plants 2024, 13, 346. [Google Scholar]
- Kour, D.; Rana, K.L.; Kfaur, T.; Yadav, N.; Yadav, A.N.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, V.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Saxena, A.K. Biodiversity, current developments and potential biotechnological applications of phosphorus-solubilizing and -mobilizing microbes: A review. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 43–75. [Google Scholar]
- Tounsi-Hammami, S.; Hammami, Z.; Dhane-Fitouri, S.; Le Roux, C.; Ben Jeddi, F. A Mix of Agrobacterium Strains Reduces Nitrogen Fertilization While Enhancing Economic Returns in Field Trials with Durum Wheat in Contrasting Agroclimatic Regions. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 4816–4833. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, C.; Li, W.; Lin, L.; Liao, T.; Fan, X.; Peng, H.; An, Q.; Liang, Y. Phosphorus-, potassium-, and silicon-solubilizing bacteria from forest soils can mobilize soil minerals to promote the growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.; Islam, E.U.; Rasul, M.; Farooq, I.; Mahreen, N.; Tawab, A.; Irfan, M.; Rajput, L.; Amin, I.; Yasmin, S. Differential Root Exudation and Architecture for Improved Growth of Wheat Mediated by Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 744094. [Google Scholar]
- Karimzadeh, J.; Etesami, A.H.; Pourbabaei, H.; Ali, A. Improved Phosphorus Uptake by Wheat Plant (Triticum aestivum L.) with Rhizosphere Fluorescent Pseudomonads Strains Under Water-Deficit Stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 162–178. [Google Scholar]
- Rezakhani, L.; Motesharezadeh, B.; Tehrani, M.M.; Etesami, H.; Hosseini, M. Phosphate–solubilizing bacteria and silicon synergistically augment phosphorus (P) uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plant fertilized with soluble or insoluble P source. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 504–513. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, G.; Reddy, M.S. Effects of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria, Rock Phosphate and Chemical Fertilizers on Maize-Wheat Cropping Cycle and Economics. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 428–437. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhai, L.; Chai, X.; Liu, Y.; Lv, J.; Pi, Y.; Gao, B.; Wang, X.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; et al. Bacillus B2 promotes root growth and enhances phosphorus absorption in apple rootstocks by affecting MhMYB15. Plant J. 2024, 119, 1880–1899. [Google Scholar]
- Zenginbal, H.; Ztürk, A.; Faizi, Z.A. Bacterial strains effect on the nursery plants growth of ‘Granny Smith’ apple grafted on M-9, MM-106, and MM-111 rootstocks. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 50, 102747. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, R.; Huang, Q.; Gao, H.; Awasthi, M.K.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z. The spatio-temporal change in soil P and P-solubilizing bacteria under clover mulching in apple orchards of Loess Plateau. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiao, H.; Wang, R.; Qin, W.; Yang, J. Yang. Screening of rhizosphere nitrogen fixing, phosphorus and potassium solubilizing bacteria of Malus sieversii (Ldb.) Roem. and the effect on apple growth. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 292, 154142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fasusi, O.A.; Cruz, C.; Babalola, O.O. Agricultural Sustainability: Microbial Biofertilizers in Rhizosphere Management. Agriculture 2021, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xu, L. Economic situation and development countermeasures of Chinese peach. J. Fruit Sci. 2023, 40, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.L. Cultural methods for soil microorganisms. Agronomy Monographs. 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.A.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons, N.E.; Breed, E.S.; Murray, E.G.D. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. Williams & Wilkins Co. 1957.
- Monis, P.T.; Giglio, S.; Saint, C.P. Saint. Comparison of SYTO9 and SYBR Green I for real-time polymerase chain reaction and investigation of the effect of dye concentration on amplification and DNA melting curve analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 340, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.A.; Weber, R.P. Colorimetric Estimation Of Indoleacetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1951, 26, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shuaiqiang, W.; Yanhua, X.; Jiaqi, T.; Libo, S.; Yatian, L.; Liping, W.; Huicai, C.; Suna, W. Isolation and Plant Growth Promotion Effect of Endophytic Siderophore-Producing Bacteria: A Study on Halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum. Eco-Ind. Sci. Phosphorus Fluor. Eng. 2025, 40, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Luo, Y. Isolation and Plant Growth Promotion Effect of Endophytic Siderophore-Producing Bacteria: A Study on Halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum. Plants 2024, 13, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, O.S.; Mazumder, M.; Kini, S.; Hill, E.D.; Aow, J.S.B.; Phua, S.M.L.; Elejalde, U.; Kjelleberg, S.; Swarup, S. Volatile methyl jasmonate from roots triggers host-beneficial soil microbiome biofilms. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2024, 20, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, G.; Wei, Y.; Dong, Y.; Hou, L.; Jiao, R. Isolation and screening of multifunctional phosphate solubilizing bacteria and its growth-promoting effect on Chinese fir seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9081. [Google Scholar]
- Gaete, A.; Mandakovic, D.; González, M. Isolation and Identification of Soil Bacteria from Extreme Environments of Chile and Their Plant Beneficial Characteristics. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, S.A.; Marzouk, M.A.; Abbassy, M.A.; Abd-El-Haleem, D.A.; Shamseldin, A. Isolation and identification of efficient Egyptian malathion-degrading bacterial isolates. J. Basic Microbiol. 2013, 55, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Fan, X.; Patel, J.S.; Zhang, M. Characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from calcareous soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, Y.; Song, M.; Li, M. Isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from rhizosphere soils of the Yeyahu Wetland in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33976–33987. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, T.H.; Liu, G.H.; Mao, C. Isolation and characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from walnut and their effect on growth and phosphorus mobilization. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.C. Utilization of insoluble phosphates by soil fungi. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Xie, J.; Xue, X.; Jiang, Y. Screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and their abilities of phosphorus solubilization and wheat growth promotion. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Bolan, N.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Isolation of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their potential for lead immobilization in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 185, 829–836. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, G.; Frossard, E.; Mäder, P.; Nanzer, S.; Randall, D.G. Water soluble phosphate fertilizers for crops grown in calcareous soils—An outdated paradigm for recycled phosphorus fertilizers? Plant Soil 2017, 424, 367–388. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, M.; Kumar, S.; Babita, K. Biosolubilization of poorly soluble rock phosphates by Aspergillus tubingensis and Aspergillus niger. Bioresour Technol. 2002, 84, 187–189. [Google Scholar]
- Gyaneshwar, P.; Kumar, G.N.; Parekh, L.J.; Poole, P.S. Role of soil microorganisms in improving P nutrition of plants. Syst. Sci. Compr. Stud. Agric. 2002, 245, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Narayanan, M.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: Their agroecological function and optimistic application for enhancing agro-productivity. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 901, 166468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Shi, J.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhu, N.; Wang, Y. Consortium of Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria Promotes Maize Growth and Changes the Microbial Community Composition of Rhizosphere Soil. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Tao, X.; Zhang, L.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, J. Inoculation of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus) regulates microbial interaction to improve phosphorus fractions mobilization during kitchen waste composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Feng, K.; Hannula, S.E.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, H. Interkingdom plant-microbial ecological networks under selective and clear cutting of tropical rainforest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 491, 119182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Das, S.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Phosphate-Solubilizing Microorganisms: Mechanism and Their Role in Phosphate Solubilization and Uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 21, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, G.; Hu, Z.; Luo, W.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Ji, X.; Hu, W.; Li, M. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria improve the antioxidant enzyme activity of Potamogeton crispus L. and enhance the remediation effect on Cd-contaminated sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, D.; Tian, M.; Ruan, Y.; Han, H. Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria Enhance Cadmium Immobilization and Gene Expression in Wheat Roots to Reduce Cadmium Uptake. Plants 2024, 13, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, A.; Lee, K.-E.; Khan, M.A.; Kang, S.-M.; Adhikari, B.; Imran, M.; Jan, R.; Kim, K.-M.; Lee, I.-J. Effect of Silicate and Phosphate Solubilizing Rhizobacterium Enterobacter ludwigii GAK2 on Oryza sativa L. under Cadmium Stress. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.M.; Asaf, S.; Khan, A.L.; Lubna Khan, A.; Mun, B.G.; Lee, I.J. Complete Genome Sequence of Pseudomonas psychrotolerans CS51, a Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium, Under Heavy Metal Stress Conditions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraki, A.; Mohammadi-Sichani, M.; Ranjbar, M. Identification of lead resistant rhizobacteria of Carthamus tinctorius and their effects on lead absorption of Sunflower. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 132, 3073–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Alam, S.; Karim, M.M. Screening of siderophore-producing salt-tolerant rhizobacteria suitable for supporting plant growth in saline soils with iron limitation. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 4, 100150. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Shang, X.; Xue, L.; Ji, G.; Chang, S.; Niu, J.; Emaneghemi, B. Screening of Siderophore-Producing Bacteria and Their Effects on Promoting the Growth of Plants. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Albelda-Berenguer, M.; Monachon, M.; Joseph, E. Siderophores: From natural roles to potential applications. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 106, 193–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saha, M.; Sarkar, S.; Sarkar, B.; Sharma, B.K.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Tribedi, P. Microbial siderophores and their potential applications: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3984–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compant, S.; Samad, A.; Faist, H.; Sessitsch, A. A review on the plant microbiome: Ecology, functions, and emerging trends in microbial application. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 19, 29–37. [Google Scholar]

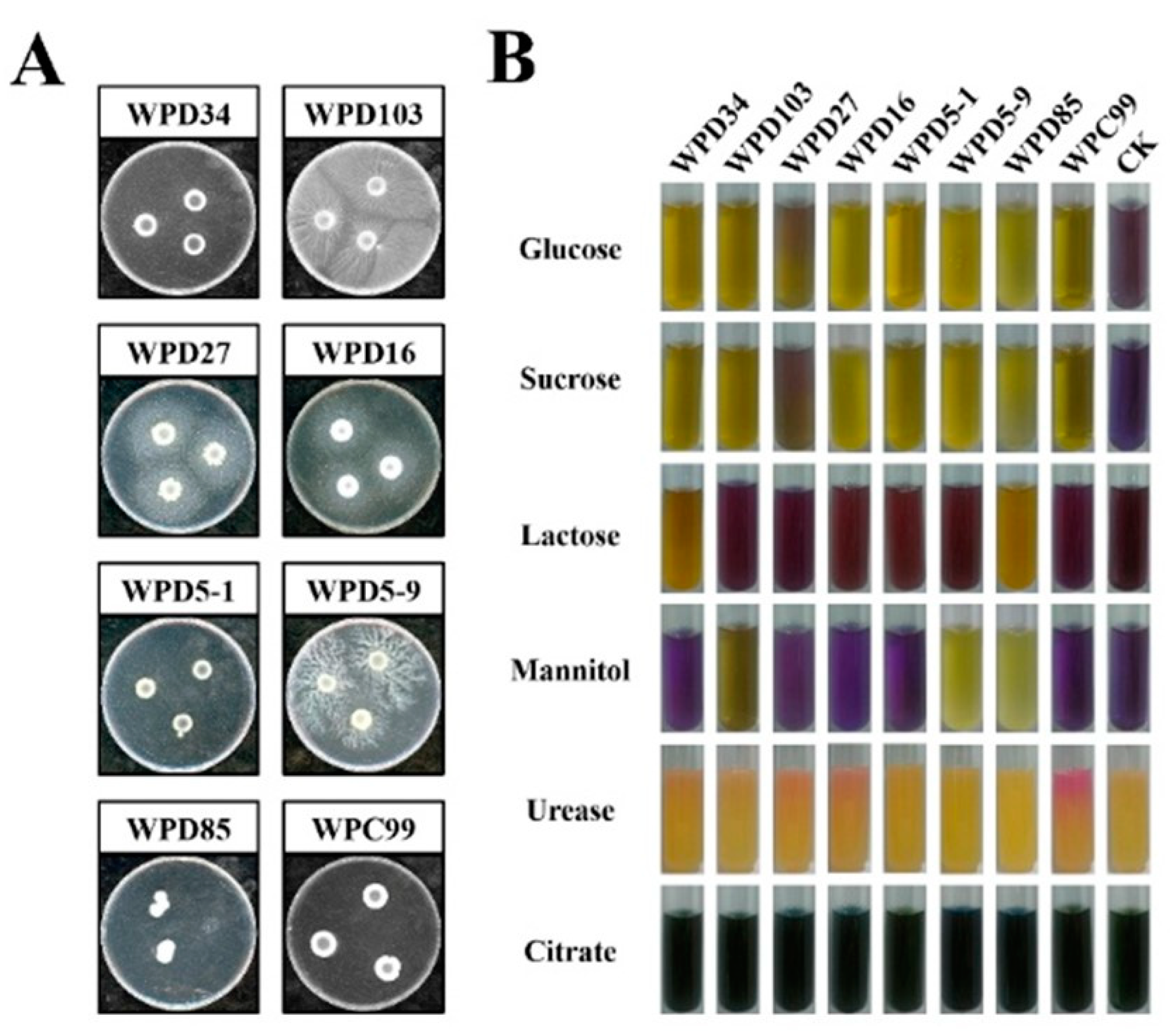
| Strains | Shape | Verge | Colony Morphology | Dryness | Transparency | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPD34 | Orbicular | Undulate | Wrinkled | Dry | Opaque | Bright yellow |
| WPD103 | Orbicular | Undulate | Wrinkled | Moist | Opaque | Bright yellow |
| WPD27 | Orbicular | Neatly | Smooth | Moist | Opaque | Earthy yellow |
| WPD16 | Orbicular | Neatly | Smooth | Moist | Opaque | Yellow |
| WPD5-1 | Orbicular | Undulate | Smooth | Moist | Opaque | Bright yellow |
| WPD5-9 | Orbicular | Undulate | Wrinkled | Moist | Opaque | Light yellow |
| WPD85 | Irregular | Undulate | Wrinkled | Moist | Transparent | White |
| WPC99 | Orbicular | Undulate | Wrinkled | Dry | Opaque | Milky white |
| Strains | Genus | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPD34 | Bacillus sp. | + | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| WPD103 | Bacillus sp. | + | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| WPD27 | Burkholderia sp. | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| WPD16 | Burkholderia sp. | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| WPD5-1 | Pantoea sp. | + | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| WPD5-9 | Pantoea sp. | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | + | − | − | + |
| WPD85 | Paenibacillus sp. | + | + | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| WPC99 | Bacillus sp. | + | + | − | − | + | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Peng, F. Isolation, Characterization and Growth-Promoting Properties of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (PSBs) Derived from Peach Tree Rhizosphere. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040718
Li Z, Li J, Liu G, Li Y, Wu X, Liang J, Wang Z, Chen Q, Peng F. Isolation, Characterization and Growth-Promoting Properties of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (PSBs) Derived from Peach Tree Rhizosphere. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040718
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zixuan, Junyan Li, Guangyuan Liu, Yanyan Li, Xuelian Wu, Jiahui Liang, Zhe Wang, Qiuju Chen, and Futian Peng. 2025. "Isolation, Characterization and Growth-Promoting Properties of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (PSBs) Derived from Peach Tree Rhizosphere" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040718
APA StyleLi, Z., Li, J., Liu, G., Li, Y., Wu, X., Liang, J., Wang, Z., Chen, Q., & Peng, F. (2025). Isolation, Characterization and Growth-Promoting Properties of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (PSBs) Derived from Peach Tree Rhizosphere. Microorganisms, 13(4), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040718






