Sulfurimonas microaerophilic sp. nov. and Sulfurimonas diazotrophicus sp. nov.: Two Novel Nitrogen-Fixing and Hydrogen- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Chemolithoautotrophs Within the Campylobacteria Isolated from Mangrove Sediments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of the Novel Strain and Cultivation
2.2. Phenotypic and Chemotaxonomic Analyses
2.3. Phylogeny Analysis Based on the 16S rRNA Gene Sequences
2.4. Genome Analysis and Functional Annotation
2.5. Characterization of N2 Fixation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological and Phenotypic Characteristics
3.2. Chemotaxonomy
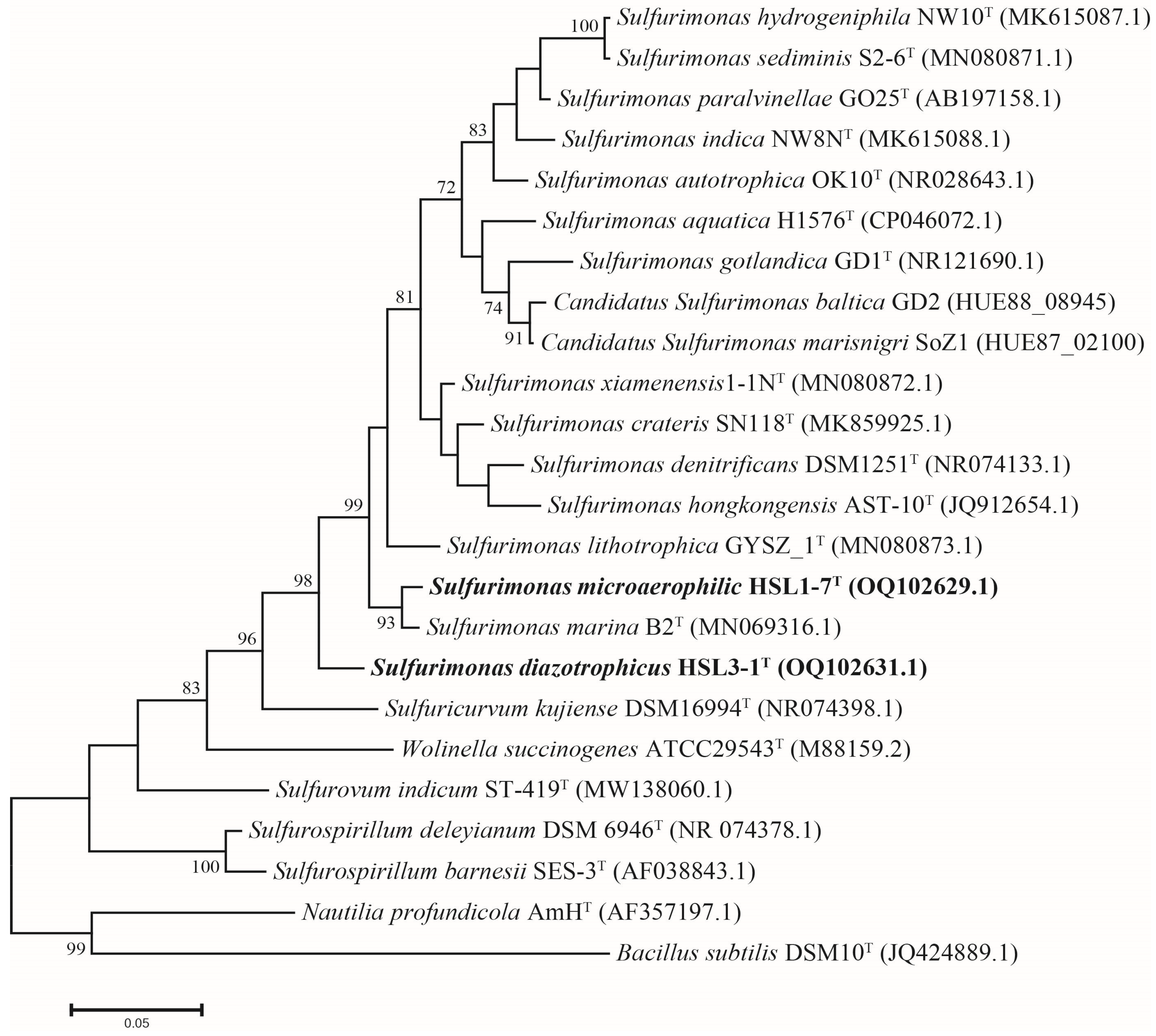
3.3. Phylogeny of 16S rRNA Gene Sequences
3.4. Genomic Properties
3.5. Genomic Functional Analysis
3.5.1. Carbon Metabolism
3.5.2. Hydrogen Metabolism
3.5.3. Sulfur Metabolism
3.5.4. Nitrogen Metabolism
3.6. Nitrogen Fixation Activity
3.7. Taxonomic Conclusion
3.7.1. Description of Sulfurimonas microaerophilic sp. nov.
3.7.2. Description of Sulfurimonas diazotrophicus sp. nov.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duke, N.C.; Meynecke, J.O.; Dittmann, S.; Ellison, A.M.; Anger, K.; Berger, U.; Cannicci, S.; Diele, K.; Ewel, K.C.; Field, C.D.; et al. A world without mangroves? Science 2007, 317, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguin, G.; Vazquez, P.; Bashan, Y. The role of sediment microorganisms in the productivity, conservation, and rehabilitation of mangrove ecosystems: An overview. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 33, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Alain, K.; Cui, L.; Zhong, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lai, Q.; et al. Chemolithoautotrophic diazotrophs dominate dark nitrogen fixation in mangrove sediments. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Chaudhuri, S. Ecology of heterotrophic dinitrogen fixation in the rhizosphere of mangrove plant community at the Ganges river estuary in India. Oecologia 1991, 87, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biderre-Petit, C.; Courtine, D.; Hennequin, C.; Galand, P.E.; Bertilsson, S.; Debroas, D.; Monjot, A.; Lepère, C.; Divne, A.-M.; Hochart, C. A pan-genomic approach reveals novel Sulfurimonas clade in the ferruginous meromictic Lake Pavin. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2024, 24, e13923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, F.; Takai, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Nealson, K.H.; Horikoshi, K. Sulfurimonas autotrophica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel sulfur-oxidizing epsilon-proteobacterium isolated from hydrothermal sediments in the Mid-Okinawa Trough. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, D.W.; Vanwonterghem, I.; Rinke, C.; Parks, D.H.; Zhang, Y.; Takai, K.; Sievert, S.M.; Simon, J.; Campbell, B.J.; Hanson, T.E.; et al. Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Class Epsilonproteobacteria and Proposed Reclassification to Epsilonbacteraeota (phyl. nov.). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 682, Erratum in Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.J.; Engel, A.S.; Porter, M.L.; Takai, K. The versatile epsilon-proteobacteria: Key players in sulphidic habitats. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Perner, M. The globally widespread genus Sulfurimonas: Versatile energy metabolisms and adaptations to redox clines. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievert, S.M.; Scott, K.M.; Klotz, M.G.; Chain, P.S.; Hauser, L.J.; Hemp, J.; Hügler, M.; Land, M.; Lapidus, A.; Larimer, F.W.; et al. Genome of the epsilonproteobacterial chemolithoautotroph Sulfurimonas denitrificans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kubo, K.; Kamei, Y.; Kojima, H.; Fukui, M. Dissimilatory microbial sulfur and methane metabolism in the water column of a shallow meromictic lake. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 45, 126320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, J. Denitrification performance and microbial community analysis of sulfur autotrophic denitrification filter for low-temperature treatment of landfill leachate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, S.; Lai, Q.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, L. Sulfurimonas indica sp. nov., a hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph isolated from a hydrothermal sulfide chimney in the Northwest Indian Ocean. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, K.; Suzuki, M.; Nakagawa, S.; Miyazaki, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Inagaki, F.; Horikoshi, K. Sulfurimonas paralvinellae sp. nov., a novel mesophilic, hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph within the Epsilonproteobacteria isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent polychaete nest, reclassification of Thiomicrospira denitrificans as Sulfurimonas denitrificans comb. nov. and emended description of the genus Sulfurimonas. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Hu, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Shao, Z. Elemental sulfur reduction by a deep-sea hydrothermal vent Campylobacterium Sulfurimonas sp. NW10. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shao, Z.; Lai, Q.; Liu, X.; Xie, S.; Jiang, L.; Yang, S. Sulfurimonas sediminis sp. nov., a novel hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph isolated from a hydrothermal vent at the Longqi system, southwestern Indian ocean. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Shao, M.F.; Zhang, T. Non-contiguous finished genome sequence and description of Sulfurimonas hongkongensis sp. nov., a strictly anaerobic denitrifying, hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph isolated from marine sediment. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2014, 9, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoor, A.T. Energetic aspects of the metabolism of reduced sulphur compounds in Thiobacillus dentrificans. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1976, 42, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Shao, Z. Sulfurimonas xiamenensis sp. nov. and Sulfurimonas lithotrophica sp. nov., hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotrophs within the Epsilonproteobacteria isolated from coastal sediments, and an emended description of the genus Sulfurimonas. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2657–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, J.V.; Vogts, A.; Werner, J.; Neu, T.R.; Spröer, C.; Bunk, B.; Schulz-Vogt, H.N. Candidatus Sulfurimonas marisnigri sp. nov. and Candidatus Sulfurimonas baltica sp. nov., thiotrophic manganese oxide reducing chemolithoautotrophs of the class Campylobacteria isolated from the pelagic redoxclines of the Black Sea and the Baltic Sea. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Kato, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Fukui, M. Sulfurimonas aquatica sp. nov., a sulfur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from water of a brackish lake. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrenz, M.; Grote, J.; Mammitzsch, K.; Boschker, H.T.S.; Laue, M.; Jost, G.; Glaubitz, S.; Jürgens, K. Sulfurimonas gotlandica sp. nov., a chemoautotrophic and psychrotolerant epsilonproteobacterium isolated from a pelagic redoxcline, and an emended description of the genus Sulfurimonas. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 4141–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnikova, N.M.; Slobodkin, A.I.; Merkel, A.Y.; Kopitsyn, D.S.; Kevbrin, V.V.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Slobodkina, G.B. Sulfurimonas crateris sp. nov., a facultative anaerobic sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotrophic bacterium isolated from a terrestrial mud volcano. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Lai, Q.; Wei, S.; Jiang, L.; Shao, Z. Sulfurimonas marina sp. nov., an obligately chemolithoautotrophic, sulphur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a deep-sea sediment sample from the South China Sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lyu, J.; Shao, Z. Sulfur Metabolism of Hydrogenovibrio thermophilus Strain S5 and Its Adaptations to Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Environment. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Hu, Q.; Lyu, J.; Shao, Z. Thiomicrorhabdus indica sp. nov., an obligately chemolithoautotrophic, sulfur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent environment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, K.; Horikoshi, K. Thermosipho japonicus sp. nov., an extremely thermophilic bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent in Japan. Extremophiles 2000, 4, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Ji, B.; Yuan, Q.; Wei, S.; Lai, Q.; Wu, K.; Jiang, L.; Shao, Z. Sulfurovum mangrovi sp. nov., an obligately chemolithoautotrophic, hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium isolated from coastal marine sediments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 006142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiguzel, A.; Ozkan, H.; Baris, O.; Inan, K.; Gulluce, M.; Sahin, F. Identification and characterization of thermophilic bacteria isolated from hot springs in Turkey. J. Microbiol. Methods 2009, 79, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, X.; Wang, F. Vertical distribution and diversity of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes in the Pearl River estuarine sediments, Southern China. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 70, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzhetsky, A.; Nei, M. Statistical properties of the ordinary least-squares, generalized least-squares, and minimum-evolution methods of phylogenetic inference. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 35, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes De Novo Assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Staerfeldt, H.H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNAmmer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcher, A.L.; Harmon, D.; Kasif, S.; White, O.; Salzberg, S.L. Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 4636–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Tran, P.Q.; Breister, A.M.; Liu, Y.; Kieft, K.; Cowley, E.S.; Karaoz, U.; Anantharaman, K. METABOLIC: High-throughput profiling of microbial genomes for functional traits, metabolism, biogeochemistry, and community-scale functional networks. Microbiome 2022, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramaki, T.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Endo, H.; Ohkubo, K.; Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Ogata, H. KofamKOALA: KEGG Ortholog assignment based on profile HMM and adaptive score threshold. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2251–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlar, A.J.; Törönen, P.; Holm, L. AAI-profiler: Fast proteome-wide exploratory analysis reveals taxonomic identity, misclassification and contamination. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W479–W485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.I.; Kim, Y.O.; Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Baek, I.; Chun, J. UBCG: Up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Cai, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): A web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–W592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylinski, D.A.; Morillo, V.; Lefèvre, C.T.; Viloria, N.; Dubbels, B.L.; Williams, T.J. Endothiovibrio diazotrophicus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel nitrogen-fixing, sulfur-oxidizing gammaproteobacterium isolated from a salt marsh. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Dietrich, C.; Radek, R.; Brune, A. Endomicrobium proavitum, the first isolate of Endomicrobia class. nov. (phylum Elusimicrobia)—An ultramicrobacterium with an unusual cell cycle that fixes nitrogen with a Group IV nitrogenase. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Oh, H.-S.; Park, S.-C.; Chun, J. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auch, A.F.; von Jan, M.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2010, 2, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitson, S.M.; Mendz, G.L.; Srinivasan, S.; Hazell, S.L. The tricarboxylic acid cycle of Helicobacter pylori. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 260, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Shi, L.D.; Wei, G.; Hubert, C.R.J.; Wang, Y.; Greening, C. Phylogenetically and catabolically diverse diazotrophs reside in deep-sea cold seep sediments. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Hu, Q.; Cui, L.; Zhu, B.; Fu, X.; Lai, Q.; Shao, Z.; Yang, S. Characterization of Sulfurimonas hydrogeniphila sp. nov., a Novel Bacterium Predominant in Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents and Comparative Genomic Analyses of the Genus Sulfurimonas. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 626705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, L. Genome sequence of Sulfurimonas sp. C5, a potential chemolithoautotrophic, sulfur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a mangrove sediment. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2024, 13, e0047424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, S.; Gros, O.; Heiden, S.E.; Hinzke, T.; Thürmer, A.; Poehlein, A.; Meyer, S.; Vatin, M.; Mbéguié-A-Mbéguié, D.; Tocny, J.; et al. Nitrogen fixation in a chemoautotrophic lucinid symbiosis. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Rods to slightly curved | Rods | Rods | Rods to slightly curved | Rods to slightly curved | Rods | Rods |
| Motility | + | − | + | + | − | − | − |
| Doubling time under optimal (h) | ND | ND | 3.6 | 8 | 12 | 12 | ND |
| Temperature range (Optimal T) (°C) | 10–40 (32) | 4–45 (37) | 10–45 (35) | 4–45 (33) | 10–45 (30) | ND | 15–35 (30) |
| pH range (Optimal pH) | 5.0–8.5 (7.0) | 5.0–8.5 (7.0) | 4.5–9.0 (7.0) | 5.0–8.5 (6.5) | 5.5–8.0 (7.0) | ND (7.0) | 6.5–8.5 (7.0–7.5) |
| NaCl requirement | + | + | + | + | − | − | + |
| Maximum O2 concentration (%) | 10 | 20 | 15 | 20 | 20 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Electron donor | H2, S2O32− | H2, S2O32− | HS−, S0, S2O32− | H2, S0, S2O32−, HS− | H2, S0, S2O32−, S4O62−, HS− | S2O32−, HS− | H2, S2O32−, HS− |
| Organic electron donors | − | − | − | − | − | Formate, fumarate, yeast extract alcohol mix | − |
| Electron acceptor | S0, O2 | S0, O2 | O2 | S0, NO3−, O2 | S0, NO3−, O2 | NO3−, O2, NO2− | NO3− |
| DNA G+C content (%) | 36.1 | 57.3 | 36.0 | 33.2 | 34.5 | 36 | 34.9 |
| Fatty acid (%) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12:0 | 0.3 | 4.0 | 1.3 | 2.6 | - | - | - |
| C14:0 | 10.5 | 11.3 | 9.1 | 3.2 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 4.8 |
| C14:0 3-OH | 2.4 | 4.0 | 6.6 | 4.9 | - | - | - |
| C16:0 | 31.6 | 29.6 | 25.6 | 18.9 | 23.4 | 15.3 | 32.8 |
| C16:1ω7c | 28.7 | 35.0 | 37.7 | 50.5 | 31.8 | 67.9 | - |
| C16:1ω5c | 0.6 | 0.4 | - | - | - | 2.0 | - |
| C18:0 | 2.6 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 10.0 | - | 16.9 |
| C18:1ω7c | 19.5 | 16.7 | 13.2 | 12.1 | 18.7 | 12.1 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Lv, S.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, Q.; Lai, Q.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Sulfurimonas microaerophilic sp. nov. and Sulfurimonas diazotrophicus sp. nov.: Two Novel Nitrogen-Fixing and Hydrogen- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Chemolithoautotrophs Within the Campylobacteria Isolated from Mangrove Sediments. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040713
Zhong Y, Li Y, Wang Z, Cui L, Lv S, Zhu H, Yuan Q, Lai Q, Wang S, Jiang L. Sulfurimonas microaerophilic sp. nov. and Sulfurimonas diazotrophicus sp. nov.: Two Novel Nitrogen-Fixing and Hydrogen- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Chemolithoautotrophs Within the Campylobacteria Isolated from Mangrove Sediments. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040713
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yangsheng, Yufei Li, Zhaodi Wang, Liang Cui, Shiwei Lv, Han Zhu, Qing Yuan, Qiliang Lai, Shasha Wang, and Lijing Jiang. 2025. "Sulfurimonas microaerophilic sp. nov. and Sulfurimonas diazotrophicus sp. nov.: Two Novel Nitrogen-Fixing and Hydrogen- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Chemolithoautotrophs Within the Campylobacteria Isolated from Mangrove Sediments" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040713
APA StyleZhong, Y., Li, Y., Wang, Z., Cui, L., Lv, S., Zhu, H., Yuan, Q., Lai, Q., Wang, S., & Jiang, L. (2025). Sulfurimonas microaerophilic sp. nov. and Sulfurimonas diazotrophicus sp. nov.: Two Novel Nitrogen-Fixing and Hydrogen- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Chemolithoautotrophs Within the Campylobacteria Isolated from Mangrove Sediments. Microorganisms, 13(4), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040713






