A Succession of Microbiome Communities in the Early Establishing Process of an Epilithic Algal Matrix in a Fringing Reef
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area and the Experimental Program
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Community Analysis
3. Results
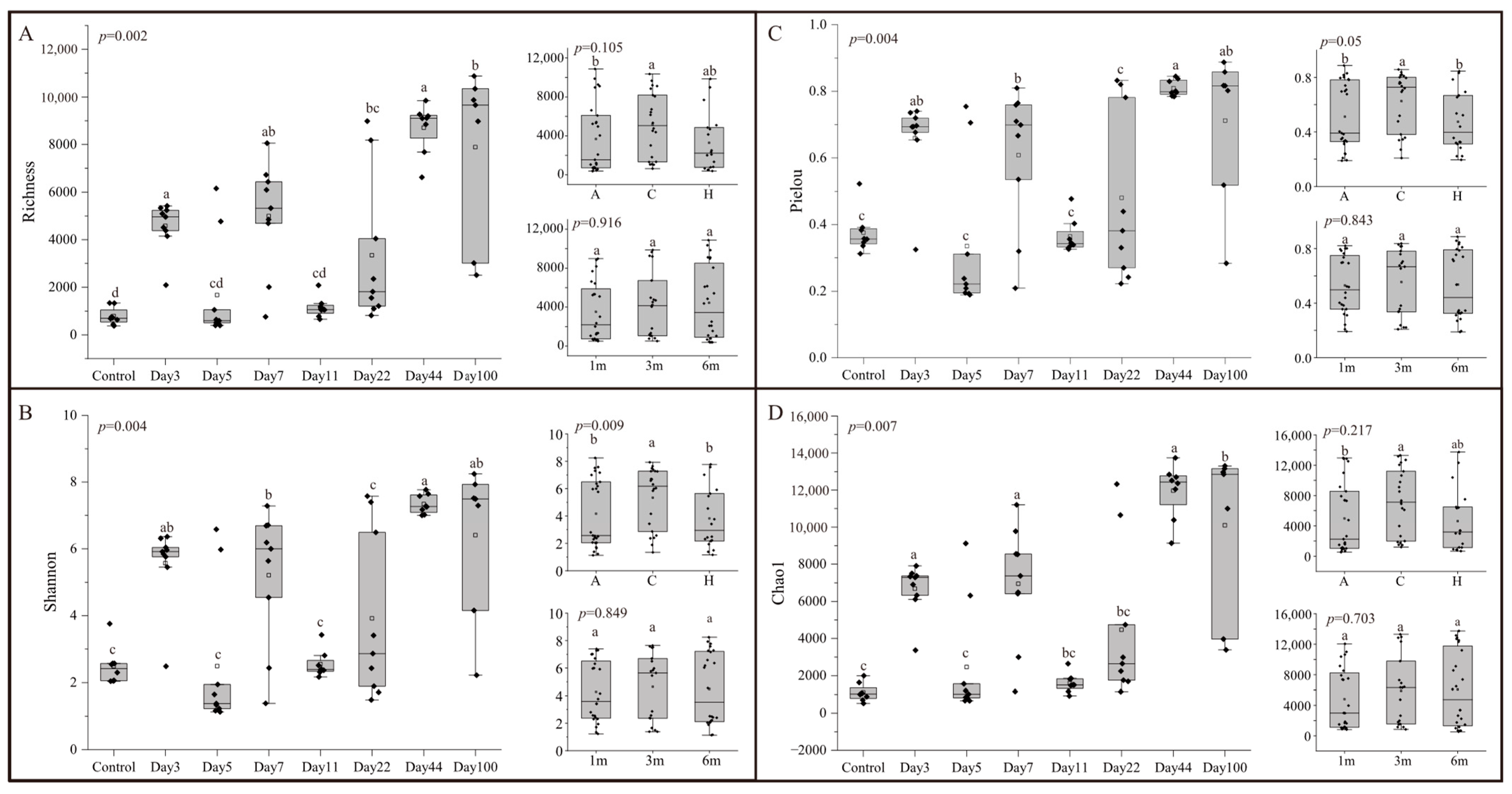
3.1. Alpha-Diversity of Microbial Communities in EAM
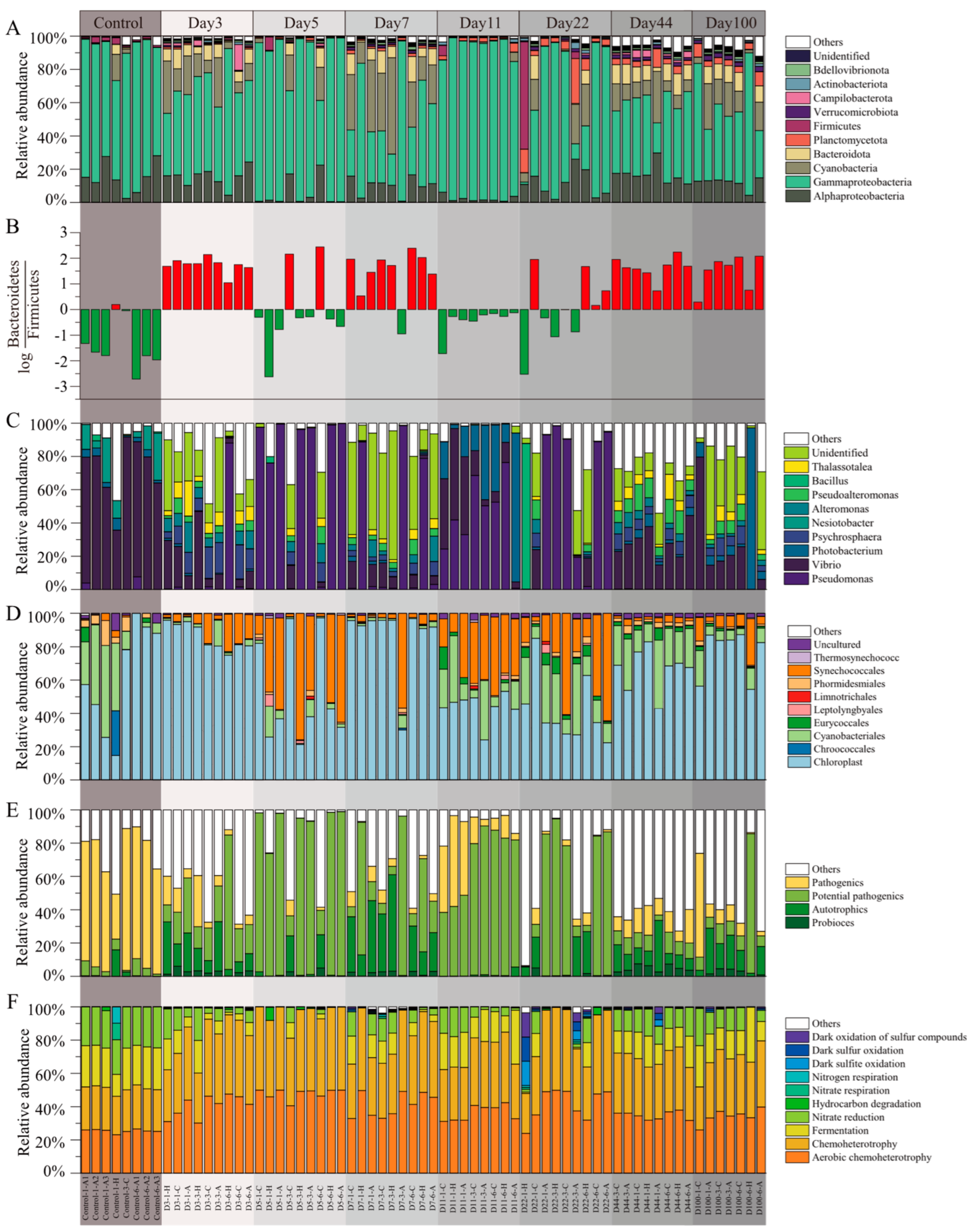
3.2. Microbial Community Compositions in EAMs
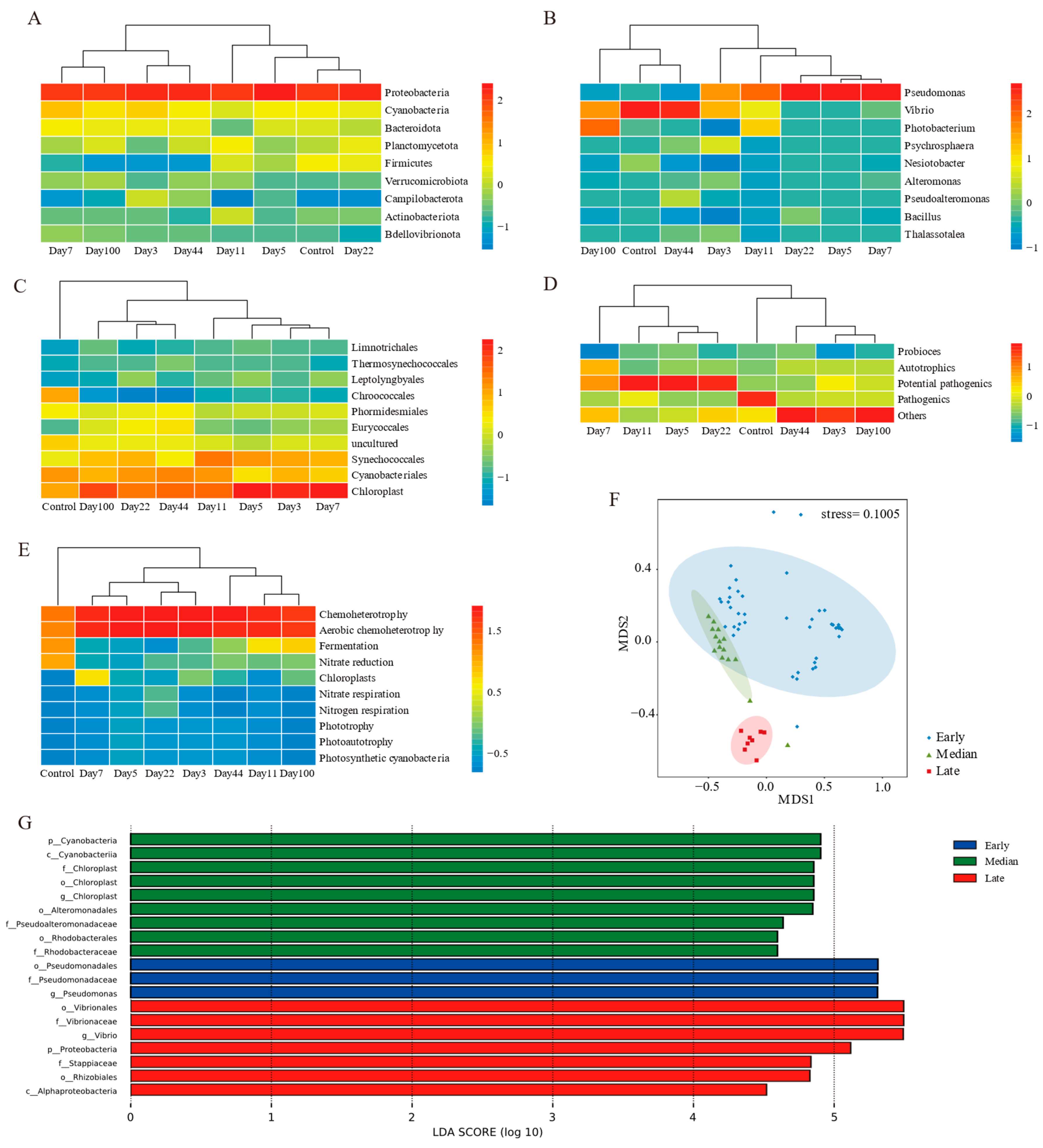
3.3. EAM Microbial Communities Clustered into Three Stages
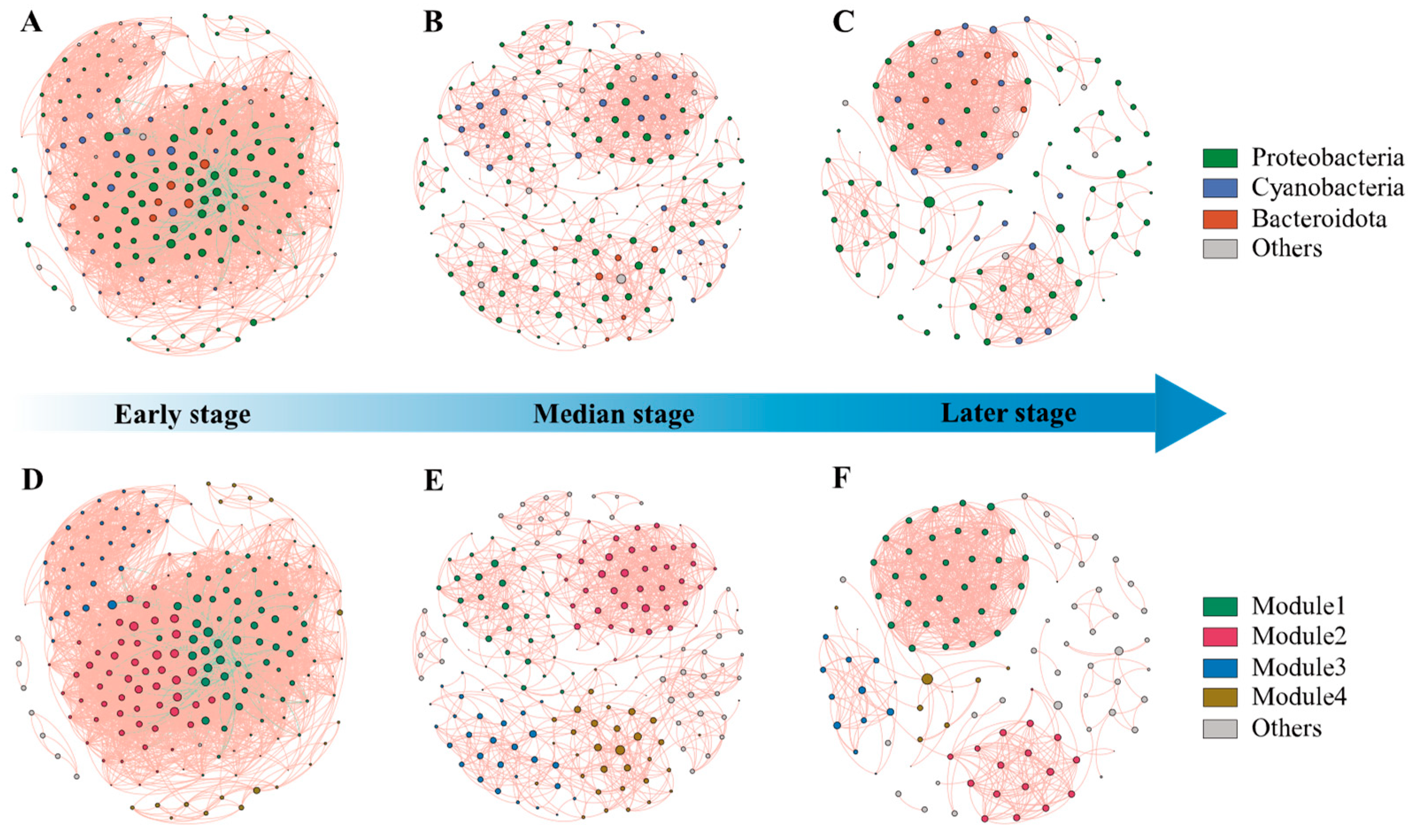
3.4. Network Structure and Biotic Interactions in EAM
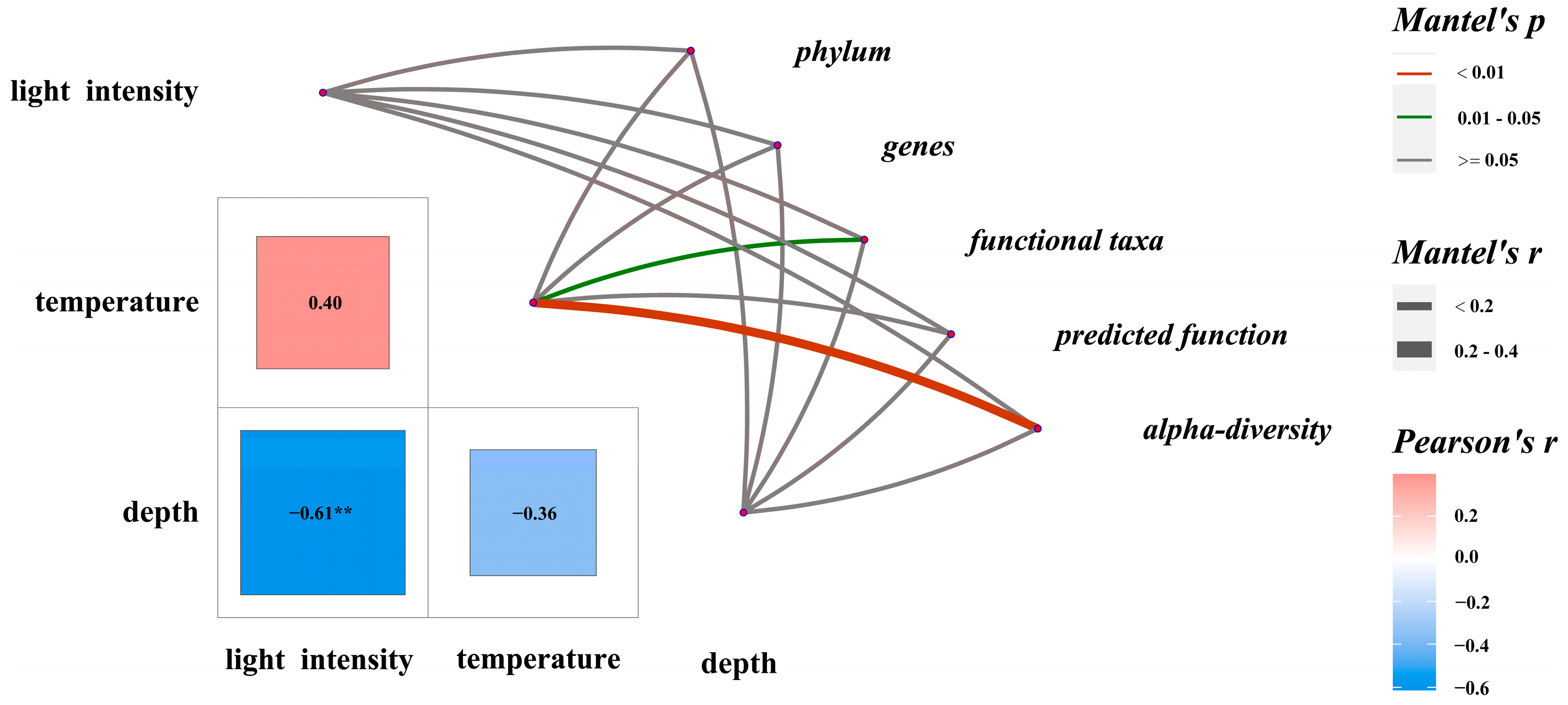
3.5. Relationship Between EAM Microbiota Composition and Environmental Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Microbial Community Succession in EAMs
4.2. Effects of Attached Substrate Type on Microbial Composition
4.3. Effects of Depth on Microbial Composition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wernberg, T.; Bennett, S.; Babcock, R.C.; de Bettignies, T.; Cure, K.; Depczynski, M.; Dufois, F.; Fromont, J.; Fulton, C.J.; Hovey, R.K.; et al. Climate-driven regime shift of a temperate marine ecosystem. Science 2016, 353, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.E.; Brainard, R.; Carter, A.; Grillo, S.; Edwards, C.; Harris, J.; Lewis, L.; Obura, D.; Rohwer, F.; Sala, E.; et al. Re-evaluating the health of coral reef communities: Baselines and evidence for human impacts across the central Pacific. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20151985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbett, S.B.; Bellwood, D.R. Algal turf sediments on coral reefs: What’s known and what’s next. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebbett, S.B.; Bellwood, D.R. Algal turf productivity on coral reefs: A meta-analysis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 168, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, S.D.; Foster, M.S.; Airoldi, L. What are algal turfs? Towards a better description of turfs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 495, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, A.F.; Fairoz, M.F.; Kelly, L.W.; Nelson, C.E.; Dinsdale, E.A.; Edwards, R.A.; Giles, S.; Hatay, M.; Hisakawa, N.; Knowles, B.; et al. Global microbialization of coral reefs. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessarrodona, A.; Filbee-Dexter, K.; Wernberg, T. Recovery of algal turfs following removal. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 192, 106185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DE Carvalho, L.L.; Villaça, R.C. Effect of fine-scale habitat differences on algal colonisation in a coral-dominated subtropical reef. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2021, 93, e20191191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, C.; Sommer, B.; Marzinelli, E.M.; Figueira, W.F. The role of microbial biofilms in range shifts of marine habitat-forming organisms. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.M.; Tschoeke, D.A.; Meirelles, P.M.; de Oliveira, L.; Leomil, L.; Tenorio, M.; Valle, R.; Salomon, P.S.; Thompson, C.C.; Thompson, F.L. Taxonomic and Functional Metagenomic Signature of Turfs in the Abrolhos Reef System (Brazil). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherbini, J.; Corzett, C.; Ravaglioli, C.; Tamburello, L.; Polz, M.; Bulleri, F. Epilithic Bacterial Assemblages on Subtidal Rocky Reefs: Variation Among Alternative Habitats at Ambient and Enhanced Nutrient Levels. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 1552–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, H.F.; Abd-Elgawad, A.; Cai, R.; Luo, Z.; Pie, L.; Xu, C. Microbial community shift on artificial biological reef structures (ABRs) deployed in the South China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barott, K.L.; Rodriguez-Mueller, B.; Youle, M.; Marhaver, K.L.; Vermeij, M.J.; Smith, J.E.; Rohwer, F.L. Microbial to reef scale interactions between the reef-building coral Montastraea annularis and benthic algae. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barott, K.L.; Rohwer, F.L. Unseen players shape benthic competition on coral reefs. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasl, B.; Robbins, S.; Frade, P.R.; Marangon, E.; Laffy, P.W.; Bourne, D.G.; Webster, N.S. Comparative genome-centric analysis reveals seasonal variation in the function of coral reef microbiomes. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1435–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Koren, O.; Reshef, L.; Efrony, R.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, N.R.; Vanwonterghem, I.; Doropoulos, C.; Gouezo, M.; Botte, E.S.; Webster, N.S.; Mumby, P.J. Benthic micro- and macro-community succession and coral recruitment under overfishing and nutrient enrichment. Ecology 2021, 102, e03536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, S.N.T.; Suhaimi, M.N.A.; Maznan, N.A.; Safuan, C.D.M.; Tan, C.H.; Yucharoen, M.; Saidin, J.; Bachok, Z. Isolation and Identification of Bacterial Communities from Coral Tissue Affected by Black Band Disease at Pulau Redang, Terengganu, Malaysia. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2023, 21, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Hu, S.; Jia, N.; Zhang, C.; Huang, H.; Liu, S. Microbial communities associated with epilithic algal matrix with different morphological characters in Luhuitou fringing reef. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 993305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, A.; Teichberg, M.; Nugues, M.M.; Beilfuss, S.; Bischof, K. Effects of depth and ultraviolet radiation on coral reef turf algae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 461, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, A.; Teichberg, M.; Beilfuss, S.; Bischof, K. Succession patterns in algal turf vegetation on a Caribbean coral reef. Bot. Mar. 2011, 54, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadaidi, G.; Ziegler, M.; Shore-Maggio, A.; Jensen, T.; Aeby, G.; Voolstra, C.R. Ecological and molecular characterization of a coral black band disease outbreak in the Red Sea during a bleaching event. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Willis, B.L.; Bourne, D.G. Successional changes in bacterial communities during the development of black band disease on the reef coral, Montipora hispida. ISME J. 2010, 4, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, T.N.F.; Little, M.; Arts, M.G.I.; Huckeba, J.; Haas, A.F.; George, E.E.; Quinn, R.A.; Cobian-Guemes, A.G.; Naliboff, D.S.; Silveira, C.B.; et al. A multiomic analysis of in situ coral-turf algal interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13588–13595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barott, K.L.; Rodriguez-Brito, B.; Janouškovec, J.; Marhaver, K.L.; Smith, J.E.; Keeling, P.; Rohwer, F.L. Microbial diversity associated with four functional groups of benthic reef algae and the reef-building coral Montastraea annularis. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.M.; Connolly, S.R.; Ainsworth, T.D. Coral transplantation triggers shift in microbiome and promotion of coral disease associated potential pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.M.; Ainsworth, T.D.; Choat, J.H.; Connolly, S.R. Farming behaviour of reef fishes increases the prevalence of coral disease associated microbes and black band disease. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.P.; Allen, R.; Agostini, S.; Hoffmann, L.J.; Kon, K.; Summerfield, T.C.; Wada, S.; Hall-Spencer, J.M. Feedback mechanisms stabilise degraded turf algal systems at a CO2 seep site. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messyasz, A.; Maher, R.L.; Meiling, S.S.; Thurber, R.V. Nutrient enrichment predominantly affects low diversity microbiomes in a marine trophic symbiosis between algal farming fish and corals. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, D.; Diaz-Pulido, G.; Dove, S. Warming and acidification promote cyanobacterial dominance in turf algal assemblages. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 517, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpy, L.; Casareto, B.; Langlade, M.-J.; Suzuki, Y. Cyanobacteria in coral reef ecosystems: A review. J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 2012, 259571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, L.; Abbiati, M.; Beck, M.W.; Hawkins, S.J.; Jonsson, P.R.; Martin, D.; Moschella, P.S.; Sundelöf, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Åberg, P. An ecological perspective on the deployment and design of low-crested and other hard coastal defence structures. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulleri, F.; Chapman, M.G. The introduction of coastal infrastructure as a driver of change in marine environments. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Liu, S.; Huang, H.; Huang, L.M.; Jing, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.L. Coral bleaching caused by an abnormal water temperature rise at Luhuitou fringing reef, Sanya Bay, China. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2012, 15, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.H.; Zhou, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, Z.Q.; Deng, W.; Shi, R.G. The mass coral bleaching event of inshore corals form South China Sea witnessed in 2020: Insight into the causes, process and consequence. Coral Reefs 2022, 41, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, L.; Lei, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, L.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, M.; Gan, J.; Zhang, Y. Light availability regulated by particulate organic matter affects coral assemblages on a turbid fringing reef. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 177, 105613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, L.; Yu, X.; Huang, H. Multiple stress-induced mortality of an Acropora coral on the Luhuitou turbid reef in the northern South China Sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieler, R.E.; Gilliam, D.S.; Sherman, R.L. Artificial substrate and coral reef restoration: What do we need to know to know what we need. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2001, 69, 1013–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratte, Z.A.; Longo, G.O.; Burns, A.S.; Hay, M.E.; Stewart, F.J. Contact with turf algae alters the coral microbiome: Contact versus systemic impacts. Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahe, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Gloeckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Fish, J.A.; Chai, B.; McGarrell, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Brown, C.T.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Kuske, C.R.; Tiedje, J.M. Ribosomal Database Project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D633–D642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Xu, Z.Z.; Peddada, S.; Amir, A.; Bittinger, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Lozupone, C.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Birmingham, A.; et al. Normalization and microbial differential abundance strategies depend upon data characteristics. Microbiome 2017, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoodley, P.; Sauer, K.; Davies, D.G.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms as complex differentiated communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.; Kaplan, H.B.; Kolter, R. Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 49–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardus, J.D.; Nedved, B.T.; Huang, Y.; Tran, C.; Hadfield, M.G. Microbial biofilms facilitate adhesion in biofouling invertebrates. Biol. Bull. 2008, 214, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catao, E.C.P.; Pollet, T.; Misson, B.; Garnier, C.; Ghiglione, J.F.; Barry-Martinet, R.; Maintenay, M.; Bressy, C.; Briand, J.F. Shear Stress as a Major Driver of Marine Biofilm Communities in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, T.; Berdjeb, L.; Garnier, C.; Durrieu, G.; Le Poupon, C.; Misson, B.; Jean-Francois, B. Prokaryotic community successions and interactions in marine biofilms: The key role of Flavobacteriia. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejdandžić, M.; Ivanković, T.; Pfannkuchen, M.; Godrijan, J.; Pfannkuchen, D.M.; Hrenović, J.; Ljubešić, Z. Colonization of diatoms and bacteria on artificial substrates in the northeastern coastal Adriatic Sea. Acta Bot. Croat. 2015, 74, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Feng, G.; Moraru, C.I. Micro- and Nanotopography Sensitive Bacterial Attachment Mechanisms: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G. Microbial Colonization in Marine Environments: Overview of Current Knowledge and Emerging Research Topics. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaneveld, J.R.; Burkepile, D.E.; Shantz, A.A.; Pritchard, C.E.; McMinds, R.; Payet, J.P.; Welsh, R.; Correa, A.M.; Lemoine, N.P.; Rosales, S.; et al. Overfishing and nutrient pollution interact with temperature to disrupt coral reefs down to microbial scales. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N.; Tang, Z.; Wu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Mohamed, H.F.; Ou, D.; et al. Identification of quorum sensing-regulated Vibrio fortis as potential pathogenic bacteria for coral bleaching and the effects on the microbial shift. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1116737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchlissin, S.I.; Sabdono, A.; Permata, W.D. Anti-Pathogenic Activity of Coral Bacteria Againts White Plaque Disease of Coral Dipsastraea from Tengah Island, Karimunjawa. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Tropical and Coastal Region Eco Development (ICTCRED), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2–4 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Morrow, K.M.; Paul, V.J.; Liles, M.R.; Chadwick, N.E. Allelochemicals produced by Caribbean macroalgae and cyanobacteria have species-specific effects on reef coral microorganisms. Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G.D.; Santos Ede, O.; Sousa, G.V.; Zingali, R.B.; Thompson, C.C.; Thompson, F.L. Metaproteomics reveals metabolic transitions between healthy and diseased stony coral Mussismilia braziliensis. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4632–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, A.R.; Tait, K.; Parry, H.; de Francisco-Mora, B.; Hicks, N.; Osborn, A.M.; Widdicombe, S.; Stahl, H. Marine Microbial Gene Abundance and Community Composition in Response to Ocean Acidification and Elevated Temperature in Two Contrasting Coastal Marine Sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
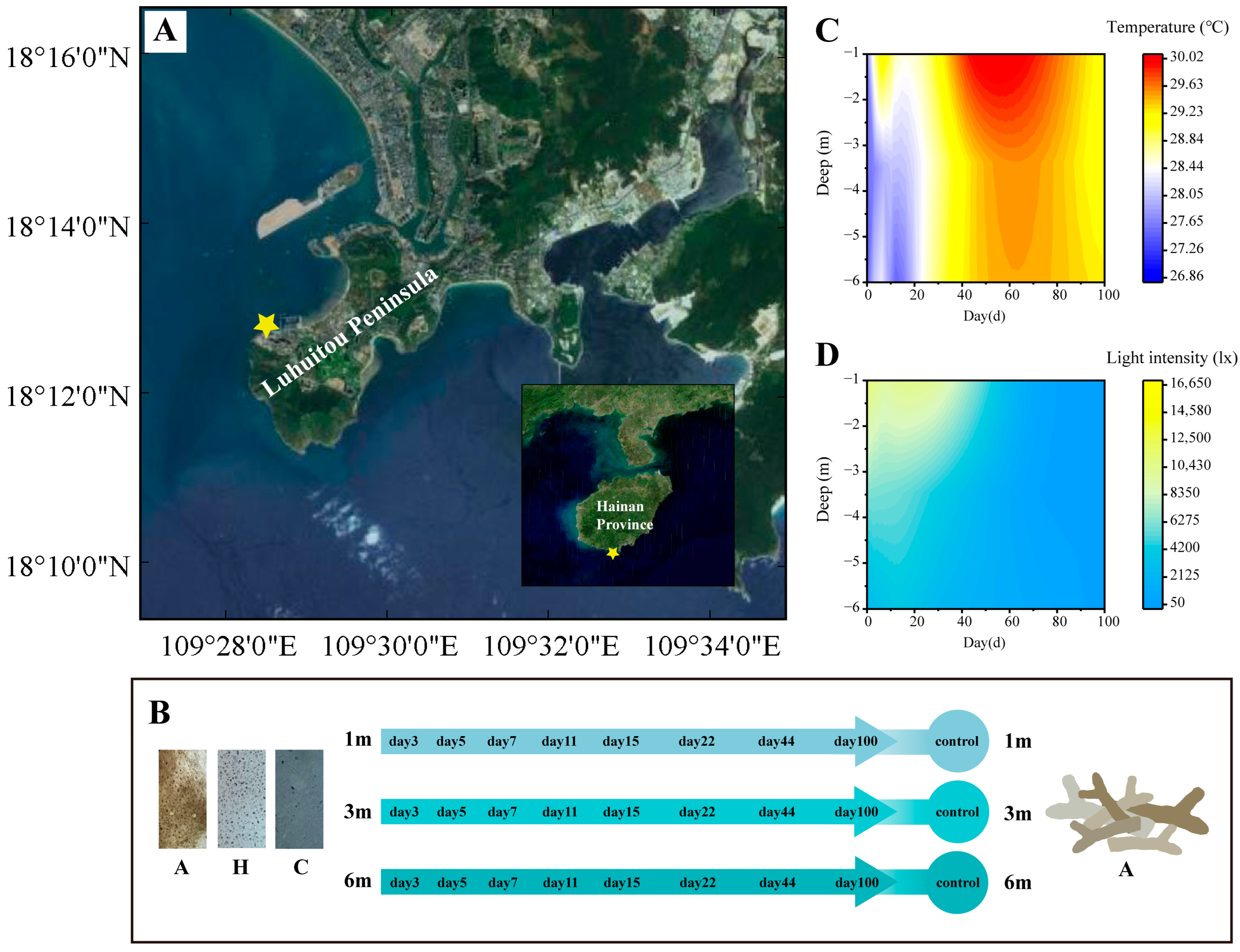
| Attachment Substrate Types | Number of Holes (ind./mm2) | Average Area of Holes (mm2) | Proportion of Hole Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coral rubble (A) | 0.19 | 0.42 | 7.98% |
| Artificial volcanic brick (H) | 0.60 | 0.14 | 8.40% |
| Cement brick (C) | 0.04 | 0.52 | 2.08% |
| Variable | Group | R | p_Value | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| stages | later/early | 0.479 | 0.001 | *** |
| later/median | 0.860 | 0.001 | *** | |
| early/median | 0.175 | 0.001 | *** | |
| depth | 1 m/3 m | 0.016 | 0.252 | |
| 1 m/6 m | 0.029 | 0.143 | ||
| 3 m/6 m | −0.028 | 0.787 | ||
| type | A/H | −0.008 | 0.532 | |
| A/C | −0.016 | 0.666 | ||
| H/C | 0.0552 | 0.100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Hu, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, T.; Li, T.; Huang, H.; Liu, S. A Succession of Microbiome Communities in the Early Establishing Process of an Epilithic Algal Matrix in a Fringing Reef. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030672
Zhang B, Hu S, Zhang C, Zhou T, Li T, Huang H, Liu S. A Succession of Microbiome Communities in the Early Establishing Process of an Epilithic Algal Matrix in a Fringing Reef. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(3):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030672
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Beiye, Simin Hu, Chen Zhang, Tiancheng Zhou, Tao Li, Hui Huang, and Sheng Liu. 2025. "A Succession of Microbiome Communities in the Early Establishing Process of an Epilithic Algal Matrix in a Fringing Reef" Microorganisms 13, no. 3: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030672
APA StyleZhang, B., Hu, S., Zhang, C., Zhou, T., Li, T., Huang, H., & Liu, S. (2025). A Succession of Microbiome Communities in the Early Establishing Process of an Epilithic Algal Matrix in a Fringing Reef. Microorganisms, 13(3), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030672




