(Re)Emerging Arboviruses of Public Health Significance in the Brazilian Amazon
Abstract
1. Introduction
Brief History of Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon
2. Arboviruses Associated with Mosquitoes and Humans in Brazil
2.1. Togaviridae
2.1.1. Mayaro Virus (MAYV)
2.1.2. Chikungunya Virus (CHIKV)
2.1.3. Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus (EEEV)
2.1.4. Western Equine Encephalitis Virus (WEEV)
2.1.5. Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus (VEEV)
2.1.6. Mucambo Virus (MUCV)
2.1.7. Pixuna Virus (PIXV)
2.1.8. Una Virus (UNAV)
2.1.9. Aura Virus (AURAV)
2.2. Flaviviridae
2.2.1. Dengue Virus (DENV)
2.2.2. Yellow Fever Virus (YFV)
2.2.3. Zika Virus (ZIKV)
2.2.4. Ilhéus Virus (ILHV)
2.2.5. West Nile Virus (WNV)
2.2.6. St. Louis Encephalitis Virus (SLEV)
2.2.7. Bussuquara Virus (BSQV)
2.2.8. Rocio Virus (ROCV)
2.2.9. Cacipacore Virus (CPCV)
2.3. Peribunyviridae
2.3.1. Tacaiuma Virus (TCMV)
2.3.2. Boracéia Virus (BORV)
2.3.3. Tucunduba Virus (TUCV)
2.3.4. Maguari Virus (MAGV)
2.3.5. Anhembi Virus (AMBV)
2.3.6. Macauã Virus (MCAV)
2.3.7. Guaroa Virus (GROV)
2.3.8. Serra Do Navio Virus (SDNV)
2.3.9. Apeu Virus (APEUV)
2.3.10. Caraparu Virus (CARV)
2.3.11. Itaqui Virus (ITQV)
2.3.12. Marituba Virus (MTBV)
2.3.13. Murucutu Virus (MURV)
2.3.14. Oriboca Virus (ORIV)
2.3.15. Catu Virus (CATUV)
2.3.16. Guamá Virus (GMAV)
2.3.17. Oropouche Virus (OROV)
2.4. Phenuviridae
Itaporanga Virus (ITPV)
2.5. Rhabdoviridae
Jurona Virus (JURV)
| Original Collection Source Information | References | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | Genus | Antigenic Group | Name | Abbreviation | Natural Host or Animal Associations † | In Amazon Forest | Associated Arthropods ‡ | Human Disease | Virus Isolated or Serology | Date | Host Source | Location | |
| Togaviridae | |||||||||||||
| Alphavirus | Group A | Mayaro | MAYV | human; monkeys; wild rodents; opossums; sloths; equines; lizards; wild birds | Y | Haemagogus spp. including Hg. janthinomys; Ae. aegypti; Sabethini spp.; Culex spp. including Cx. quinquefasciatus; Gigantolaelaps spp.; Ixodes spp. | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1954 | human male | Mayaro County, Trinidad | [34,35,36,41,42,43,50,52] | |
| Alphavirus | Group A | Chikungunya | CHIKV | human; monkeys | Y | Ae. aegypti, Ae. albopictus, Ae. fluviatilis; Psorophora albiguenu, Ps. ferox; Cx. quinquefasciatus; Wyeomyia bourrouli | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1953 | human female | Liteho, Newala District, Tanzania | [49,50,51,52,53,56] | |
| Alphavirus | Group A | Eastern Equine encephalitis | EEEV (South American strains) | human; equines; wild birds; wild rodents; opossums; wild boars | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. (Mel.) taeniopus, Cx. (Mel.) pedroi, Cx. (Mel.) spissipes, Cx. quinquefasciatus; Ae. aegypti, Ae. albopictus, Ae. taeniorhynchus | encephalitic | positive isolation and serology | 1933 | horse | Delaware, Virginia, Maryland, USA | [30,41,43,45,51,52,63,64,66] | |
| Alphavirus | Group A | Western Equine encephalitis | WEEV | human; equines; wild birds; sentinel rodents; opossums | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. taeniopus, Cx. portesi, Cx. pedroi; Ae. fulvus | encephalitic | positive serology | 1930 | horse | Merced County, CA, USA | [30,35,41,43,45,76,79,80,81] | |
| Alphavirus | Group A | Mosso das Pedras | VEEV IF | human; wild rodents; bats | Y | Culex spp. | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1978 | Cx. mosquitoes and wild bat | Sitio de Mosso das Pedras, São Paulo, Brazil | [99] | |
| Alphavirus | Group A | Mucambo | MUCV (VEEV IIIA) | human; sentinel capuchin monkey; sentinel rodents; wild rodents; opossums; wild birds | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. (Mel.) portesi; Ae. hortatory, Ae. serratus; Haemagogus spp.; Mansonia spp.; Cq. venezuelnsis; Sabethes spp.; Uranotaenia geometrica | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1954 | sentinel capuchin monkey | Oriboca Forest, Amazonas, Brazil | [41,43,101,102,103,104] | |
| Alphavirus | Group A | Pixuna | PIXV (VEEV IV) | opossums; wild rodents; wild birds | Y | An. nimbus; Trichoprosopon digitatum | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1985 | Tr. digitatum mosquitoes | Belem, Para, Brazil | [30,43,106] | |
| Alphavirus | Group A | Una | UNAV | human; wild rodents, horses, cows; birds | Y | Ps. ferox, Ps. albipes, Ps. lutzii; Ae. serratus, Ae. fulvus, Ae. leucocelaenus; An. nimbus; Coquillettidia arribalzaga; Culex spp.; Wyeomyia spp. | febrile | positive serology | 1959 | Ps. ferox mosquitoes | Belem, Para, Brazil | [30,35,41,109] | |
| Alphavirus | Group A | Aura | AURAV | human; marsupials; wild rodents; horses | Y | Culex spp.; Ae. serratus | unknown | positive serology | 1959 | Cx. Melanoconion mosquitoes | Belem, Pará, Brazil | [30,35,41,110,117] | |
| Flaviviridae | |||||||||||||
| Flavivirus | Group B | Dengue 1 | DENV-1 | human; monkeys; sloths; equines | Y | Aedes aegypti, Ae. albopictus; Haemagogus leucocelaenus | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1943 | human male | Nagasaki, Japan | [30,119,120,129,132,378] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | Dengue 2 | DENV-2 | human; monkeys; sloths; equines | Y | Aedes aegypti, Ae. albopictus; Culex spp. including Cx. vaxus | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1944 | human male | New Guinea | [30,129,132,379,380] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | Dengue 3 | DENV-3 | human; monkeys; sloths; equines | Y | Aedes aegypti, Ae. albopictus | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1954 | human female and Aedes aegypti mosquitoes | Manila, Philippines | [30,124,129,132] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | Dengue 4 | DENV-4 | human; monkeys; sloths; equines | Y | Aedes aegypti; Culex quinquefasciatus, Cx. bidens, Cx. interfor; Psorophora varipes, Ps. albigenu; Sabethes chloropterus | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1954 | human female and Aedes aegypti mosquitoes | Quezon City, Manila, Philippines | [30,124,129,132,135] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | Yellow Fever | YFV | human; monkeys; water buffaloes | Y | Aedes aegypti, Ae. albopictus, Ae. scapularis, Ae. taeniorhynchus, Ae. serratus; Haemagogus janithinomys, Hg. leucocelaemus, Hg. albomaculatus, Hg. capricornii, Hg. spegazzinii; Sabethes chloropterus, Sa. soperi, Sa. cyaneus, Sa. glaucodaemon, Sa. albiprivus, Psorophora ferox | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1927 | human male | Kpeve Village, Ghana | [30,43,144,147,148,172] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | Zika | ZIKV | human; monkeys | Y | Aedes aegypti; Ae. albopictus; Haemagogus leucoelaenus; Culex quinquefasciatus; Anopheles cruzii; Limatus durhamii; Wyeomyia confusa | febrile with neurological and pregnancy complications | positive isolation and serology | 1947 | sentinel rhesus monkey | Zika Forest, Entebbe, Uganda | [51,53,153,154,156,157,172,379,381,382] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | Ilhéus | ILHV | human; sentinel monkeys; bats; rodents; marsupials; sloths; edentate mammals; water buffaloes; cattle; equines; pigs; reptiles; wild birds | Y | Psorophora spp. including Ps. ferox, Ps. albipes, Ps. lutzii; Aedes spp. including Ae. aegypti, Ae. serratus, Ae. fulvus, Ae. leucocelaenus, Ae. scapularis; Culex spp. including Cx. portesi, Cx. coronator; Sabethes chloropterus.; Haemagogus spp. including Hg. leucocelaemus; Trichoprosopon spp. | febrile and encephalitic | positive isolation and serology | 1944 | Aedes and Psorophora mosquitoes, including Ae. serratus and Ps. ferox | Ilhéus, Brazil | [30,41,43,52,72,101,148,175,329,383] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | West Nile | WNV | human; equines; wild birds; domestic birds | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. quinquefasciatus and Cx. pipiens | encephalitic | positive isolation and serology | 1937 | human female | Omogo, West Nile District, Uganda | [195,213,228,232,237,384] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | St. Louis Encephalitis | SLEV | human; equines; wild rodents; wild birds; sentinel rodents, sentinel chickens; sentinel monkeys; wild monkeys; opossums; sloths; water buffaloes | Y | Sabethes spp. including Sa. belisarioi; Culex spp. including Cx. coronator, Cx. declarator, Cx. nigripalpus, Cx. pipiens, Cx. quinquefasciatus; Aedes spp.; Mansonia spp.; Gigantolaelops spp. | Febrile and encephalitic | positive isolation and serology | 1933 | human | St. Louis County, MI, USA | [30,41,43,119,148,233,245,253,254,255,261,385] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | Bussuquara | BSQV | human; sentinel howler monkeys; sentinel rodents; wild rodents; water buffaloes | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. declarator, Cx. portesi, Cx. pedroi, Cx. taeniopus; Cq. venezuelensis, Mansonia titillans | febrile | positive isolation | 1956 | sentinel howler monkey | Belem, Pará, Brazil | [30,35,41,42,101,148,262] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | Rocio | ROCV | human; wild birds; sentinel rodents; wild rodents; equines; water buffaloes; bats; marsupials | Y | Psorophora spp. including Ps. ferox; Aedes spp. including Ae. scapularis; Cx. portesi, Cx. quinquefasciatus | encephalitic | positive isolation and serology | 1975 | human male | Iguape County, Sao Paulo, Brazil | [101,106,233,267,269,270,271] | |
| Flavivirus | Group B | Cacipacore | CPCV | human; monkeys; birds; wild rodents; equines; water buffaloes | Y | Aedes aegypti; Anopheles spp.; Culex spp.; Amblyomma cajennense | unknown | positive isolation and serology | 1977 | black-faced ant bird | Oriximina, Para, Brazil | [30,192,279,280,285] | |
| Peribunyaviridae | |||||||||||||
| Orthobunyavirus | Anopheles A | Tacaiuma | TCMV | human; sentinel capuchin monkeys; equines; small ruminants; wild rodents; birds; bats; water buffaloes | Y | Aedes triannulatus, Ae. scapularis; Anopheles spp. including An. cruzii; Haemagogus spp. including Hg. janthinomys | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1955 | sentinel capuchin monkey | Oriboca Forest, Para, Brazil | [35,43,71,292,294] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Anopheles B | Boraceia | BORV | Human; cattle; equines; dogs; domestic and wild birds; wild rodents; marsupials | N | Anopheles spp. including An. cruzii; Wyeomyia pilicauda | unknown | positive isolation and serology | 1962 | An. cruzii mosquitoes | Casa Grande, São Paulo, Brazil | [292,300,301] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Bunyamwera | Tucunduba | TUCV | human | Y | Anopheles spp. including An. nimbus; Ae. fulvus, Ae. scapularis, Ae. argyrothorax, Ae. serratus, Ae. sexlineatus, Ae. seplemstriatus; Psorophora ferox; Hg. leucoceiaenus; Cx. coronator, Cx. ocellatus; Limatus flavisetosus, Li. durhanii; Wyeomyia spp. including Wy. aporonomo; Sabethes spp. including Sa. quassicyaneus, Sa. interinedius; Trichoprosopon spp. including Tr. digitatum | encephalitic and febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1955 | Wy. spp. mosquitoes | Oriboca Forest, Para, Brazil | [35,41,43,292,297] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Bunyamwera | Maguari | MAGV | human; sentinel rodents; wild rodents; equines; sheep; water buffaloes | Y | Ae. sexlineatus, Ae. fulvus, Ae. leucocelaenus, Ae. scapularis, Ae. serratus; Cx. pedroi; An. nimbus; Psorophora spp. including Ps. ferox, Ps. albipes; Mansonia spp., Limatus spp.; Wyeomyia spp. | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1957 | mixed mosquito pool | Utinga Forest, Belem, Para, Brazil | [41,71,292,294,295] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Bunyamwera | Anhembi | AMBV | human; wild rodents; wild birds | N | Wyeomyia pilicauda; Trichoprosopon pallidiventer | unknown | positive serology | 1965 | Wy. pilicauda mosquitoes | Casa Grande, Brazil | [292,310] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Bunyamwera | Macauã | MCAV | human; wild rodents; wild birds | Y | Sabethes soperi | unknown | positive serology | 1976 | Sa. soperi mosquito | Sena Madureira, Acre, Brazil | [35,42,106,292] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | California | Guaroa | GROV | human; wild birds; water buffaloes; sheep | Y | Anopheles spp. including An. triannulatus, An. nunestovari | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1956 | human female | Guaroa, Colombia | [43,292,303,313] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | California | Serra do Navio | SDNV | human; wild rodents; opossums | Y | Aedes fulvus | unknown | positive serology | 1966 | Ae. fulvus mosquito | Belem, Para, Brazil | [42,79,292,318] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Group C | Apeu | APEUV | human; sentinel capuchin monkeys; opossums; wild non-human primates; sentinel rodents; sheep | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. aikenii, Cx. portesii; Aedes arborealis, Ae. septemstriatus | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1955 | sentinel capuchin monkey | Oriboca Forest, Para, Brazil | [30,41,43,71,292,303,320,321] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Group C | Caraparu | CARV | human; sentinel capuchin monkeys; wild rodents; sentinel rodents; bats; equines; water buffaloes; wild birds | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. aikenii, Cx. vomerifer, Cx. portesi, Cx. sacchettae, Cx. spissipes, Cx. coronator, Cx. nigripalpus, Cx. accelerans, Cx. amazonensis; Ae. scapularis, Ae. serratus; Wyeomyia medioalbipes; Sabethes spp.; Limatus durhamii; Ps. ferox | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1956 | sentinel capuchin monkey | Belem, Para, Brazil | [35,41,43,71,292,319,326] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Group C | Itaqui | ITQV | human; sentinel capuchin monkeys; sentinel rodents; wild rodents; opossums | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. vomerifer, Cx. portesi, Cx. aikenii, Cx. spissipes | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1956 | sentinel capuchin monkey | Belem, Para, Brazil | [35,41,43,292,330] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Group C | Marituba | MTBV | human; sentinel capuchin monkeys; sentinel rodents; opossums | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. aikenii, Cx. portesi | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1954 | sentinel capuchin monkey | Oriboca Forest, Para, Brazil | [35,43,71,292] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Group C | Murucutu | MURV | human; sentinel capuchin monkeys; sentinel rodents; wild rodents; opossums; sloths; birds | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. (Mel.) caudelli, Cx. aikenii. Cx. portesi, Cx. vomerifer; Sabethini spp.; Ixodid ticks | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1955 | sentinel capuchin monkey | Oriboca Forest, Para, Brazil | [41,43,71,106,292] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Group C | Oriboca | ORIV | human; sentinel capuchin monkeys; opossums; sentinel rodents; wild rodents; sheep | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. (Mel.) portesi, Cx. (Mel.) spissipes, Cx. (Mel.) caudelli; Ps. ferox; Sabethini spp.; Aedes spp. including Ae. arborealis, Ae. serratus, Ae. argyrothorax; Cq. arribalgagae, Cq, venezuelnsis, Mansonia spp.; Wyeomyia spp. | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1954 | sentinel capuchin monkey | Oriboca Forest, Para, Brazil | [35,41,43,71,292,303] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Guamá | Catu | CATUV | human; sentinel capuchin monkey; sentinel rodents; wild rodents; opossums; bats | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. (Mel.) portesi, Cx. declarator; An. nimbus; Cq, venezuelensis; Ixodes spp. | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1955 | human male | Oriboca Forest, Para, Brazil | [35,43,71,292] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Guamá | Guamá | GMAV | human; sentinel capuchin and howler monkeys; sentinel rodents; wild rodents; wild birds; opossums; bats; porcupines | Y | Culex spp. including Cx. (Mel.) portesi; Sabethes chloropterus; Cx. (Mel.) spissipes, Cx. (Mel.) pedroi, Cx. (Mel.) taeniopus; Aedes spp. including Ae. serratus, Ae. sexlineatus; Sabethes spp. including Sa. chloropterus; Ma. titillans.; Li. durhamii; Psorophora spp. including Ps. albipes; Cq, venezuelensis; Trichoprosopon spp.; Lutzomyia flaviscutellata; Ixodes spp. | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1955 | sentinel capuchin monkey | Oriboca Forest, Para, Brazil | [35,41,43,71,292] | |
| Orthobunyavirus | Simbu | Oropouche | OROV | human; sloths; domestic and wild birds; sentinel birds; wild rodents; monkeys; sheep; water buffaloes | Y | Ae. serratus; Culex spp. including Cx. quinquefasciatus; Cq. venezuelensis; Culicoides spp. including Cu. paranensis | encephalitic and febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1955 | human male | Sangre Grande, Trinidad | [41,43,52,148,284,292,303,343,345,346,353,354,355,356,357,358,386] | |
| Phenuiviridae | |||||||||||||
| Phlebovirus | Phlebotomus Fever | Itaporanga | ITPV | human; sentinel rodents; opossums; sentinel and wild birds; sentinel monkeys | Y | Culex Melanoconion spp. including Cx. caudelli; Coquillettidia venezuelensis | unknown | positive serology | 1962 | sentinel Swiss mouse | Itapiranga, São Paulo, Brazil | [30,35,41,45,387] | |
| Rhabdoviridae | |||||||||||||
| Vesiculovirus | Vesicular Stomatitis | Jurona | JURV | human | Y | Haemagogus janthinomys | febrile | positive isolation and serology | 1962 | Human male | Costa Marques, Rodônia State, Brazil | [30,35,41,43,297] | |
3. How Has Arbovirus Emergence and Re-Emergence Correlated with Anthropogenic Landscape Changes?
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Yellow Fever. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/yellow-fever (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- WHO. Dengue and Severe Dengue. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dengue-and-severe-dengue (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Marcondes, C.B.; Contigiani, M.; Gleiser, R.M. Emergent and reemergent arboviruses in South America and the Caribbean: Why so many and why now? J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 509–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PAHO. PAHO Health Emergency Appeal 2022; PAHO: Hoonah, AK, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Espinal, M.A.; Andrus, J.K.; Jauregui, B.; Waterman, S.H.; Morens, D.M.; Santos, J.I.; Horstick, O.; Francis, L.A.; Olson, D. Emerging and reemerging Aedes-transmitted arbovirus infections in the region of the Americas: Implications for health policy. Am. J. Public Health 2019, 109, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima-Camara, T.N. Emerging arboviruses and public health challenges in Brazil. Rev. Saude Publica 2016, 50, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, R.; Barcellos, C.; Brasil, P.; Cruz, O.G.; Honório, N.A.; Kuper, H.; Carvalho, M.S. The Zika virus epidemic in Brazil: From discovery to future implications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.F.; Machado, L.C.; Oidtman, R.J.; Siconelli, M.J.L.; Tran, Q.M.; Fauver, J.R.; Carvalho, R.D.d.O.; Dezordi, F.Z.; Pereira, M.R.; de Castro-Jorge, L.A.; et al. Lying in wait: The resurgence of dengue virus after the Zika epidemic in Brazil. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yactayo, S.; Staples, J.E.; Millot, V.; Cibrelus, L.; Ramon-Pardo, P. Epidemiology of Chikungunya in the Americas. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, S441–S445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, G.M.d.; Vieira, V.R. Regional distribution and habitats of Brazilian phlebotomine species. In Brazilian Sand Flies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 251–298. [Google Scholar]
- Gaffigan, T.V.; Wilkerson, R.C.; Pecor, J.E.; Stoffer, J.A.; Anderson, T. Systematic Catalogue of Culicidae. Available online: https://www.mosquitocatalog.org/default.aspx (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Figueiredo, L.T.M. How are so many foreign arboviruses introduced in Brazil? Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2016, 49, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, E.F. Deforestation and land use in the Brazilian Amazon. Hum. Ecol. 1993, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, K.R.; Laurance, W.F.; Albernaz, A.K.; Schroth, G.; Fearnside, P.M.; Bergen, S.; Venticinque, E.M.; Da Costa, C. The future of deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. Futures 2006, 38, 432–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Deforestation in Brazilian Amazonia: History, rates, and consequences. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schielein, J.; Börner, J. Recent transformations of land-use and land-cover dynamics across different deforestation frontiers in the Brazilian Amazon. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepstad, D.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Merry, F.; Lima, A.; Moutinho, P.; Carter, J.; Bowman, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Rodrigues, H.; Schwartzman, S. The end of deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. Science 2009, 326, 1350–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, D.; Chi, D. Amazon deforestation in Brazil: What has not happened and how the global media covered it. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2018, 11, 1940082918794325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, A.M.; de Alencastro Graça, P.M.L.; Ziccardi, L.G.; Escada, M.I.S.; Fearnside, P.M. Brazil’s Amazonian deforestation: The role of landholdings in undesignated public lands. Reg. Environ. Change 2022, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, J.F.; Grace, D. The consequences of human actions on risks for infectious diseases: A review. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 30048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassell, J.M.; Begon, M.; Ward, M.J.; Fèvre, E.M. Urbanization and disease emergence: Dynamics at the wildlife–livestock–human interface. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Dávila, J.D.; Allen, A.; Haklay, M.; Tacoli, C.; Fèvre, E.M. Does urbanization make emergence of zoonosis more likely? Evidence, myths and gaps. Environ. Urban. 2019, 31, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.J.d.S.P.; Thies, S.F.; da Silva, D.J.F.; Kubiszeski, J.R.; Barreto, E.S.; de Oliveira Monteiro, H.A.; Mondini, A.; São Bernardo, C.S.; de Morais Bronzoni, R.V. Ecological aspects of potential arbovirus vectors (Diptera: Culicidae) in an urban landscape of Southern Amazon, Brazil. Acta Trop. 2020, 202, 105276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Kulmann-Leal, B.; Kaminski, V.L.; Valverde-Villegas, J.; VEIGA, A.B.G.; Spilki, F.R.; Fearnside, P.M.; Caesar, L.; Giatti, L.L.; Wallau, G.L.; et al. Beyond diversity loss and climate change: Impacts of Amazon deforestation on infectious diseases and public health. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2020, 92, e20191375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D.I.; Piche-Ovares, M.; Romero-Vega, L.M.; Wagman, J.; Troyo, A. The Impact of Deforestation, Urbanization, and Changing Land Use Patterns on the Ecology of Mosquito and Tick-Borne Diseases in Central America. Insects 2021, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Pessoa Vieira, C.J.; Steiner São Bernardo, C.; Ferreira da Silva, D.J.; Rigotti Kubiszeski, J.; Serpa Barreto, E.; de Oliveira Monteiro, H.A.; Canale, G.R.; Peres, C.A.; Massey, A.L.; Levi, T.; et al. Land-use effects on mosquito biodiversity and potential arbovirus emergence in the Southern Amazon, Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1770–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loaiza, J.R.; Dutari, L.C.; Rovira, J.R.; Sanjur, O.I.; Laporta, G.Z.; Pecor, J.; Foley, D.H.; Eastwood, G.; Kramer, L.D.; Radtke, M.; et al. Disturbance and mosquito diversity in the lowland tropical rainforest of central Panama. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guagliardo, S.A.; Barboza, J.L.; Morrison, A.C.; Astete, H.; Vazquez-Prokopec, G.; Kitron, U. Patterns of geographic expansion of Aedes aegypti in the Peruvian Amazon. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casseb, A.d.R.; Casseb, L.; da Silva, S.; Vasconcelos, P.d.C. Arbovirus: Important zoonoses in the Brazilian Amazon. Veterinária E Zootec. 2013, 20, 391–403. [Google Scholar]
- da Rosa, J.F.S.T.; da Rosa, A.P.d.A.T.; Vasconcelos, P.F.d.C.; Pinheiro, F.d.P.; Dias, L.B.; Cruz, A.C.R. Arboviruses isolated in the Evandro Chagas Institute, including some descibed for the first time in the Brazilian Amazon region, their known hosts, and their pathology for man. In An Overview of Arbovirology in Brazil and Neighbouring Countries; da Rosa, A.P.d.A.T., Vasconcelos, P.F.d.C., da Rosa, J.F.S.T., Eds.; Instituto Evandro Chagas: Belem, Brazil, 1998; pp. 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.W.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Weaver, S.C. Alphaviruses. Clin. Virol. 2009, 1241–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Downs, W.G.; Wattlby, G.; Ahin, N.W.; Beesb, A. Mayaro virus: A new human disease agent. II. Isolation from blood of patients in Trinidad, BWI. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1957, 6, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Navarro, J.C. Mayaro: A re-emerging arbovirus in Venezuela and Latin America. Biomedica 2012, 32, 286–302. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, C.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Chiaravalloti-Neto, F. Mayaro virus distribution in South America. Acta Trop. 2019, 198, 105093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herve, J.; Degallier, N.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.; Pinheiro, F.d.P.; Sa Filho, e.G. Aspectos Ecologicos. In Instituto Evandro Chagas: 50 anos de Contribuição às Ciências Biológicas e à Medicina Tropical; Ministério da Saúde: Belém, Brazil, 1986; Volume 1, pp. 409–437. [Google Scholar]
- Long, K.C.; Ziegler, S.A.; Thangamani, S.; Hausser, N.L.; Kochel, T.J.; Higgs, S.; Tesh, R.B. Experimental transmission of Mayaro virus by Aedes aegypti. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 85, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Rodríguez, Y.; Pacheco, Y.; Anaya, J.-M.; Ramírez-Santana, C. Mayaro: An emerging viral threat? Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsey, E.S.; Siles, C.; Guevara, C.; Vilcarromero, S.; Jhonston, E.J.; Ramal, C.; Aguilar, P.V.; Ampuero, J.S. Mayaro virus infection, Amazon basin region, Peru, 2010–2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slegers, C.; Keuter, M.; Günther, S.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Van der Ven, A.; De Mast, Q. Persisting arthralgia due to Mayaro virus infection in a traveler from Brazil: Is there a risk for attendants to the 2014 FIFA World Cup? J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 60, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, F.W.; Halsey, E.S.; Siles, C.; Vilcarromero, S.; Guevara, C.; Silvas, J.A.; Ramal, C.; Ampuero, J.S.; Aguilar, P.V. Long-term arthralgia after Mayaro virus infection correlates with sustained pro-inflammatory cytokine response. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodall, J.P. Virus research in Amazonia. Atas do Simpósio Sobre a Biota Amazônica (Patologia); Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Travassos da Rosa, A.P.; Shope, R.E.; Pinheiro, F.d.P.; Travassos da Rosa, J.F.; Vasconcelos, P.F.; Herve, J.; Degallier, N. Arbovirus Research in the Brazilian Amazon. In Proceedings of the Proceedings Fifth Symposium, Brisbane, Australia, 28 August–1 September 1989; pp. 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, P.F.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Pinheiro, F.P.; Shope, R.E.; Degallier, N.; Travassos da Rosa, E.S. Arboviruses pathogenic for man in Brazil. In An Overview of Arbovirology in Brazil and Neighbouring Countries; Insituto Evandro Chagas: Belem, Brazil, 1998; pp. 72–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, M.R.T.; Barbosa, T.F.S.; Casseb, L.M.N.; Nunes Neto, J.P.; Segura, N.d.O.; Monteiro, H.A.d.O.; Pinto, E.V.; Casseb, S.M.; Chiang, J.d.O.; Martins, L.C. Eco-epidemiologia dos arbovírus na área de influência da rodovia Cuiabá-Santarém (BR 163), Estado do Pará, Brasil. Cad. Saúde Pública 2009, 25, 2583–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travassos da Rosa, A.; Travassos da Rosa, J.; Hervé, J.-P.; Vasconcelos, P.F.; Dégallier, N.; Rodrigues, S.G. Arboviruses in Serra Norte, Carajás region, Pará, Brazil; Sociedade Brasileira para o Progresso da Ciência: São Paulo, Brazil, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, D.L.A.; Fonseca, B.A.L.d. Will Mayaro virus be responsible for the next outbreak of an arthropod-borne virus in Brazil? Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 21, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, T.L.M.; Santos, C.L.; Suzuki, A.; Petrella, S.; Bisordi, I.; Nagamori, A.H.; Marti, A.T.; Santos, R.N.; Fialho, D.M.; Lavigne, S. Mayaro virus: Imported cases of human infection in São Paulo state, Brazil. In Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo; Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2007; Volume 49, pp. 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Iversson, L.B.; Rosa, A.; Rosa, J.T.d. Estudos sorológicos para pesquisa de anticorpos de arbovírus em população humana da região do Vale do Ribeira: II-inquérito em pacientes do Hospital Regional de Pariquera-Açú, 1980. Rev. Saúde Pública 1981, 15, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.C. An epidemic of virus disease in Southern Province, Tanganyika territory, in 1952–1953. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1955, 49, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzi, L.; Diallo, M.; Rosa-Freitas, M.; Vega-Rua, A.; Ng, L.; Boyer, S.; Drexler, J.F.; Vasilakis, N.; Lourenco-de-Oliveira, R.; Weaver, S. GloPID-R report on chikungunya, o’nyong-nyong and Mayaro virus, part 5: Entomological aspects. Antivir. Res. 2020, 174, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Neves, N.A.; da Silva Ferreira, R.; Morais, D.O.; Pavon, J.A.R.; de Pinho, J.B.; Slhessarenko, R.D. Chikungunya, Zika, Mayaro, and Equine Encephalitis virus detection in adult Culicinae from South Central Mato Grosso, Brazil, during the rainy season of 2018. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Ferreira, R.; de Souza, V.J.; da Silva Neves, N.A.; de Souza, V.C.; Franco Filho, L.C.; da Silva Lemos, P.; de Lima, C.P.S.; Naveca, F.G.; Atanaka, M.; Nunes, M.R.T.; et al. Insect-specific viruses and arboviruses in adult male culicids from Midwestern Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Soto, A.; Carneiro, I.d.O.; Fischer, C.; Feldmann, M.; Kümmerer, B.M.; Silva, N.S.; Santos, U.G.; Souza, B.F.d.C.D.; Liborio, F.d.A.; Valença-Montenegro, M.M.; et al. Limited evidence for infection of urban and peri-urban nonhuman primates with Zika and chikungunya viruses in Brazil. Msphere 2018, 3, e00523-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Jr, J.V.; Ludwig-Begall, L.F.; de Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Oliveira, R.A.; Durães-Carvalho, R.; Lopes, T.R.; Silva, D.E.; Gil, L.H. A scoping review of Chikungunya virus infection: Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, viral co-circulation complications, and control. Acta Trop. 2018, 188, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.R.T.; Faria, N.R.; de Vasconcelos, J.M.; Golding, N.; Kraemer, M.U.; de Oliveira, L.F.; Azevedo, R.d.S.d.S.; da Silva, D.E.A.; da Silva, E.V.P.; da Silva, S.P.; et al. Emergence and potential for spread of Chikungunya virus in Brazil. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo, M.d.F.F.; de Araujo Galvao, J.M.; Inacio, C.L.S.; Silva, V.P.M.E.; do Nascimento Pereira, R.L.; Pinheiro, M.P.G.; de Medeiros Silva, M.M.; Gomes, C.E.S. Arbovirus expansion: New species of culicids infected by the Chikungunya virus in an urban park of Brazil. Acta Trop. 2020, 209, 105538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, W.M.; de Lima, S.T.; Mello, L.M.S.; Candido, D.S.; Buss, L.; Whittaker, C.; Claro, I.M.; Chandradeva, N.; Granja, F.; de Jesus, R.; et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics and recurrence of chikungunya virus in Brazil: An epidemiological study. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e319–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, I.F.; Codeço, C.T.; Lana, R.M.; Bastos, L.S.; de Souza Oliveira, S.; da Cruz Ferreira, D.A.; Godinho, V.B.; Riback, T.I.S.; Cruz, O.G.; Coelho, F.C. The expansion of chikungunya in Brazil. Lancet Reg. Health–Am. 2023, 25, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, N.; Ávila, M.H.T.; Cezarotti, N.M.; Parra, M.C.P.; Banho, C.A.; Sacchetto, L.; Negri, A.F.; Araújo, E.; Bittar, C.; Milhin, B.H.G.d.A.; et al. Cryptic circulation of chikungunya virus in São Jose do Rio Preto, Brazil, 2015–2019. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeck, G.T.; Merrill, M.H. A serological difference between eastern and western equine encephalomyelitis virus. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1933, 31, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giltner, L.; Shahan, M. The 1933 outbreak of infectious equine encephalomyelitis in the eastern states. North Am Vet 1933, 14, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Brault, A.C.; Powers, A.M.; Chavez, C.; Lopez, R.N.; Cachón, M.; Gutierrez, L.; Kang, W.; Tesh, R.B.; Shope, R.E.; Weaver, S.C. Genetic and antigenic diversity among eastern equine encephalitis viruses from North, Central, and South America. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 61, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Winegar, R.; Manger, I.D.; Forrester, N.L. Alphaviruses: Population genetics and determinants of emergence. Antivir. Res. 2012, 94, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turell, M.; O’guinn, M.; Dohm, D.; Zyzak, M.; Watts, D.; Fernandez, R.; Calampa, C.; Klein, T.; Jones, J. Susceptibility of Peruvian mosquitoes to eastern equine encephalitis virus. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigo, N.C.; Adams, A.P.; Watts, D.M.; Newman, P.C.; Weaver, S.C. Cotton rats and house sparrows as hosts for North and South American strains of eastern equine encephalitis virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, L.H.; Magalhaes, T.; Santos, B.S.; Oliveira, L.V.; Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Cunha, J.L.; Fraiha, A.L.; Rocha, B.M.; Longo, B.C.; Ecco, R.; et al. Active Circulation of Madariaga Virus, a Member of the Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus Complex, in Northeast Brazil. Pathogens 2021, 10, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, P.V.; Robich, R.M.; Turell, M.J.; O’GUINN, M.L.; Klein, T.A.; Huaman, A.; Guevara, C.; Rios, Z.; Tesh, R.B.; Watts, D.M.; et al. Endemic eastern equine encephalitis in the Amazon region of Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.L.; Galiza, G.J.; Dantas, A.F.; Oliveira, R.N.; Iamamoto, K.; Achkar, S.M.; Riet-Correa, F. Outbreaks of eastern equine encephalitis in northeastern Brazil. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Novaes Oliveira, R.; Iamamoto, K.; Silva, M.L.C.R.; Achkar, S.M.; Castilho, J.G.; Ono, E.D.; Lobo, R.S.V.; Brandão, P.E.; Carnieli, P.; Carrieri, M.L.; et al. Eastern equine encephalitis cases among horses in Brazil between 2005 and 2009. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2615–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Tavares, F.N.; Costa, E.V.d.; Burlandy, F.M.; Murta, M.; Pellegrin, A.O.; Nogueira, M.F.; Silva, E.E.d. Serologic evidence of the recent circulation of Saint Louis encephalitis virus and high prevalence of equine encephalitis viruses in horses in the Nhecolândia sub-region in South Pantanal, Central-West Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2010, 105, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causey, O.; Causey, C.; Maroja, O.; Macedo, D. The Isolation of Arthropod-Borne Viruses, including Members of Two Hitherto Undescribed Serological Croups, in the Amazon Region of Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.K.M.; Chiang, J.O.; Mendes, F.F.; Andrade, S.L.d.S.; Silva, S.K.S.M.d.; Pereira, W.L.A. Study of Arboviruses in Philander opossum, Didelphis marsupialis and Nectomys rattus captured from forest fragments in the municipality of Belém, Pará, Brazil. Ciência Rural 2021, 51, e20200515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alice, F. Infeccao humana pelo virus “leste” da encefalite equina. Bol. Inst. Biol. Bahia 1956, 3, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza Costa, M.; Maia, L.S.; de Souza, V.C.; Gonzaga, A.; de Azevedo, V.C.; Martins, L.R.; Pavoni, J.C.; Naveca, F.G.; Slhessarenko, R.D. Arbovirus investigation in patients from Mato Grosso during Zika and Chikungunya virus introdution in Brazil, 2015–2016. Acta Trop. 2019, 190, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Causey, O.R.; Theiler, M. Virus antibody survey on sera of residents of the Amazon Valley in Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1958, 7, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.; Haring, C.; Howitt, B. The etiology of epizootic encephalomyelitis of horses in the San Joaquin Valley, 1930. Science 1931, 74, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergren, N.A.; Auguste, A.J.; Forrester, N.L.; Negi, S.S.; Braun, W.A.; Weaver, S.C. Western equine encephalitis virus: Evolutionary analysis of a declining alphavirus based on complete genome sequences. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9260–9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisen, W.K.; Monath, T.P. Western equine encephalomyelitis. In The Arboviruses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 89–138. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, F.P. Situação das arboviroses na Região Amazônica. In Simpósio Internacional Sobre Arbovírus dos Trópicos e Febres hemorrágicas; Academia Brasileira de Ciências: Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, 1980; pp. 27–48. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, P.F.d.C.; Travassos da Rosa, J.F.S.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.d.A.; Dégallier, N.; Pinheiro, F.d.P. Epidemiologia das encefalites por arbovírus na Amazônia brasileira. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 1991, 33, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversson, L.B.; Silva, R.A.; Rosa, A.; Barros, V.L.R. Circulation of eastern equine encephalitis, western equine encephalitis, Ilheus, Maguari and Tacaiuma viruses in equines of the Brazilian Pantanal, South America. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 1993, 35, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.V.; Coffey, R.; Fischer, M.A. Western equine encephalitis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, P.V.; Estrada-Franco, J.G.; Navarro-Lopez, R.; Ferro, C.; Haddow, A.D.; Weaver, S.C. Endemic Venezuelan equine encephalitis in the Americas: Hidden under the dengue umbrella. Future Virol. 2011, 6, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubes, V.; Rios, F.A. The causative agent of infectious equine encephalomyelitis in Venezuela. Science 1939, 90, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.; Wyckoff, R.W. Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis. Science 1938, 88, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Salas, R.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Ludwig, G.V.; Oberste, M.S.; Boshell, J.; Tesh, R.B. Re-emergence of epidemic Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis in South America. Lancet 1996, 348, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán-Terán, C.; Calderón-Rangel, A.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.; Mattar, S. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus: The problem is not over for tropical America. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudia, W.; Newhouse, V.; Beadle, L.; Miller, D.; Johnston Jr, J.; Young, R.; Calisher, C.; Maness, K. Epidemic Venezuelan equine encephalitis in North America in 1971: Vector studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1975, 101, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turell, M.J.; Ludwig, G.V.; Beaman, J.R. Transmission of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus by Aedes sollicitans and Aedes taeniorhynchus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1992, 29, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, L.; Scherer, W. Vector competence of mosquitoes as a marker to distinguish Central American and Mexican epizootic from enzootic strains of Venezuelan encephalitis virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1976, 25, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, M.A.; Galindo, P. Experimental transmission of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus by Deinocerites pseudes Dyar and Knab, 1909. J. Med. Entomol. 1972, 9, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, T. Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis. Equine Vet. Educ. 1996, 8, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, M.; Galindo, P. Ecology of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus in Panama. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1969, 155, 2141–2145. [Google Scholar]
- Barrera, R.; Ferro, C.; Navarro, J.-C.; Freier, J.; Liria, J.; Salas, R.; Ahumada, M.; Vasquez, C.; Gonzalez, M.; Kang, W.; et al. Contrasting sylvatic foci of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus in northern South America. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 67, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, E.; Aguilar, P.V.; Cisneros, J.; Tesh, R.B.; Weaver, S.C. Venezuelan equine encephalitis in Panama: Fatal endemic disease and genetic diversity of etiologic viral strains. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, C.A.; Jaramillo, R.; Martinez, S.; Fernandez, F.; Téllez, H.; Lasso, B.; De Guzmán, R. Sequelae of Venezuelan equine encephalitis in humans: A four year follow-up. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1975, 4, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.; Shelokov, A.; Peralta, P.; Dammin, G.; Young, N. Recovery of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus in Panama. A fatal case in man. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1968, 17, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalin Vilcarromero, V.; Laguna-Torres, A.; Fernández, C.; Gotuzzo, E.; Suárez, L.; Céspedes, M.; Aguilar, P.V.; Kochel, T.J. Venezuelan equine encephalitis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding in child. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H.; Kinney, R.M.; de Souza Lopes, O.; Trent, D.W.; Monath, T.P.; Francy, D.B. Identification of a new Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus from Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1982, 31, 1260–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa, A.P.T.; Vasconcelos, P.F.; Travassos da Rosa, J.F.S.; Rodrigues, D.S. Probable Laboratory-Acquired Infection with VEE (Subtype I F) Virus; Insituto Evandro Chagas: Belem, Brazil, 1990; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, P.A.; Freitas, M.O.; Chiang, J.O.; Silva, F.A.; Chagas, L.L.; Casseb, S.M.; Silva, S.P.; Nunes-Neto, J.P.; Rosa-Júnior, J.W.; Nascimento, B.S.; et al. Investigation about the occurrence of transmission cycles of arbovirus in the tropical forest, amazon region. Viruses 2019, 11, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shope, R.E.; Causey, O.R.; De Andrade, A.; Theiler, M. The Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis complex of group A arthropod-borne viruses, including Mucambo and Pixuna from the Amazon region of Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza-Lopes, O.; de Abreu Sacchetta, L. Isolation of Mucambo virus, a member of the Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus complex in the State of São Paulo, Brasil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 1978, 20, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, F.A.; Ferreira, M.S.; Araújo, P.A.; Casseb, S.M.; Silva, S.P.; Nunes Neto, J.P.; Chiang, J.O.; Rosa Junior, J.W.; Chagas, L.L.; Freitas, M.N.; et al. Serological and molecular evidence of the circulation of the venezuelan equine encephalitis virus subtype IIIA in humans, wild vertebrates and mosquitos in the Brazilian Amazon. Viruses 2022, 14, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Rosário Casseb, A.; Brito, T.C.; da Silva, M.R.M.; Chiang, J.O.; Martins, L.C.; da Silva, S.P.; Henriques, D.F.; Casseb, L.M.N.; da Costa Vasconcelos, P.F. Prevalence of antibodies to equine alphaviruses in the State of Pará, Brazil. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2016, 83, e0202014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabatsos, N. International Catalogue of Arboviruses, 1985: Including Certain Other Viruses of Vertebrates; Subcommittee on Information Exchange of the American Committee on Arthropod: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, C.; Monath, T.; Sabattini, M.; Cropp, C.; Daffner, J.; Calisher, C.; Jakob, W.; Christensen, H. Arbovirus investigations in Argentina, 1977-1980. II. Arthropod collections and virus isolations from Argentine mosquitoes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 34, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, M.B.; Ré, V.E.; Díaz, L.A.; Farias, A.; Stein, M.; Sanchez-Seco, M.P.; Tenorio, A.; Almirón, W.R.; Contigiani, M.S. Enzootic activity of pixuna and Rio Negro viruses (Venezuelan equine encephalitis complex) in a neotropical region of Argentina. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, A.M.; Aguilar, P.V.; Chandler, L.J.; Brault, A.C.; Meakins, T.A.; Watts, D.; Russell, K.L.; Olson, J.; Vasconcelos, P.F.; Da Rosa, A.T.; et al. Genetic relationships among Mayaro and Una viruses suggest distinct patterns of transmission. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Causey, O.R.; Casals, J.; Shope, R.E.; Udomsakdi, S. Aura and Una, two new group A arthropod-borne viruses. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hy. 1963, 12, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, L.A.; Spinsanti, L.I.; Almiron, W.R.; Contigiani, M.S. UNA virus: First report of human infection in Argentina. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2003, 45, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monath, T.; Sabattini, M.; Pauli, R.; Daffner, J.; Mitchell, C.; Bowen, G.; Cropp, C. Arbovirus investigations in Argentina, 1977–1980. IV. Serologic surveys and sentinel equine program. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 34, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabattini, M.S.; Shope, R.E.; Vanella, J.M. Serological survey for arboviruses in Córdoba Province, Argentina. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1965, 14, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabattini, M.S.; Avilés, G.; Monath, T.P. Historical, epidemiological and ecological aspects of arboviruses in Argentina: Togaviridae, Alphavirus. In An Overview of Arbovirology in Brazil and Neighbouring Countries; Instituto Evandro Chagas: Belem, Brazil, 1998; pp. 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Rümenapf, T.; Strauss, E.G.; Strauss, J.H. Aura virus is a New World representative of Sindbis-like viruses. Virology 1995, 208, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rümenapf, T.; Strauss, E.G.; Strauss, J.H. Subgenomic mRNA of Aura alphavirus is packaged into virions. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosimann, A.L.P.; de Siqueira, M.K.; Ceole, L.F.; Nunes Duarte dos Santos, C. A new Aura virus isolate in Brazil shows segment duplication in the variable region of the nsP3 gene. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R. Waiting in the wings: The potential of mosquito transmitted flaviviruses to emerge. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, L.T.M. The brazilian flaviviruses. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, S. Experimental studies on dengue: I. Isolation, identification and modification of the virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1952, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, J.P.; Brady, O.J.; Scott, T.W.; Zou, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Duda, K.A.; Bhatt, S.; Katzelnick, L.; Howes, R.E.; Battle, K.E.; et al. Global spread of dengue virus types: Mapping the 70 year history. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabin, A. The dengue group of viruses and its family relationships. Bacteriol. Rev. 1950, 14, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luang-Suarkia, D.; Ernst, T.; Alpers, M.P.; Garruto, R.; Smith, D.; Imrie, A. Serological evidence for transmission of multiple dengue virus serotypes in Papua New Guinea and West Papua prior to 1963. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammon, W.M.; Rundnick, A.; Sather, G. Viruses associated with epidemic hemorrhagic fevers of the Philippines and Thailand. Science 1960, 131, 1102–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messer, W.B.; Gubler, D.J.; Harris, E.; Sivananthan, K.; De Silva, A.M. Emergence and global spread of a dengue serotype 3, subtype III virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, D.; Kai, I.; Faizah, A.N.; Moi, M.L.; Tajima, S.; Takasaki, T.; Sasaki, T.; Isawa, H. Comparative analysis of the susceptibility of Aedes aegypti and Japanese Aedes albopictus to all dengue virus serotypes. Trop. Med. Health 2023, 51, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, L.; Scott, T.W.; Gubler, D.J. Consequences of the expanding global distribution of Aedes albopictus for dengue virus transmission. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-de-Lima, V.H.; Lima-Camara, T.N. Natural vertical transmission of dengue virus in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus: A systematic review. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwee, S.X.W.; St John, A.L.; Gray, G.C.; Pang, J. Animals as potential reservoirs for dengue transmission: A systematic review. One Health 2021, 12, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, N.E.A.; Quam, M.B.; Wilder-Smith, A. Epidemiology of dengue: Past, present and future prospects. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 5, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, J.M.T.; Sousa, S.C.d.; Tauil, P.L.; Carneiro, M.; Barbosa, D.S. Entry of dengue virus serotypes and their geographic distribution in Brazilian federative units: A systematic review. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2021, 24, e210020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Figueiredo, M.L.; de C Gomes, A.; Amarilla, A.A.; de S Leandro, A.; de S Orrico, A.; de Araujo, R.F.; do SM Castro, J.; Durigon, E.L.; Aquino, V.H.; Figueiredo, L. Mosquitoes infected with dengue viruses in Brazil. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, B.B.; de Jesus Maués, F.C.; Pereira, R.L.; Chiang, J.O.; de Oliveira Freitas, M.N.; Ferreira, M.S.; Martins, L.C.; da Costa Vasconcelos, P.F.; Ganoza, C.; Lalwani, P. Prevalence of arbovirus antibodies in young healthy adult population in Brazil. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, T.P.; Cruz, O.G.; da Silva, K.A.B.; de Castro, M.G.; de Brito, A.F.; Maspero, R.C.; de Alcântra, R.; Dos Santos, F.B.; Honorio, N.A.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R. Dengue serotype circulation in natural populations of Aedes aegypti. Acta Trop. 2017, 176, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, O.P.; Cardoso, B.F.; Ribeiro, A.L.M.; Santos, F.A.L.d.; Slhessarenko, R.D. Mayaro virus and dengue virus 1 and 4 natural infection in culicids from Cuiabá, state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2016, 111, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianchecchi, E.; Cianchi, V.; Torelli, A.; Montomoli, E. Yellow fever: Origin, epidemiology, preventive strategies and future prospects. Vaccines 2022, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, A.; Bauer, J.H.; Hudson, N.P. The transmission of yellow fever to macacus rhesus: Preliminary note. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1928, 90, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, A.; Bauer, J.H.; Hudson, X. Experimental transmission of yellow fever to laboratory animals. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1928, 8, 103–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strode, G.K.; Bugher, J.; Austin-Kerr, J.; Smith, H.; Smithburn, K.; Taylor, R.; Theiler, M.; Warren, A.; Whitman, L. Yellow Fever; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- CR, W. Yellow fever; history of the disease in the eighteenth and nineteenth century. J. Kans. Med. Soc. 1959, 60, 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Gabiane, G.; Yen, P.S.; Failloux, A.B. Aedes mosquitoes in the emerging threat of urban yellow fever transmission. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, N.R.; Kraemer, M.U.; Hill, S.C.; Góes de Jesus, J.; Aguiar, R.d.; Iani, F.C.; Xavier, J.; Quick, J.; du Plessis, L.; Dellicour, S.; et al. Genomic and epidemiological monitoring of yellow fever virus transmission potential. Science 2018, 361, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staples, J.E.; Monath, T.P. Yellow fever: 100 years of discovery. Jama 2008, 300, 960–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.I.O.; Sacchetto, L.; De Rezende, I.M.; Trindade, G.d.S.; LaBeaud, A.D.; De Thoisy, B.; Drumond, B.P. Recent sylvatic yellow fever virus transmission in Brazil: The news from an old disease. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira dos Santos, T.; Roiz, D.; Santos de Abreu, F.V.; Luz, S.L.B.; Santalucia, M.; Jiolle, D.; Santos Neves, M.S.A.; Simard, F.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R.; Paupy, C. Potential of Aedes albopictus as a bridge vector for enzootic pathogens at the urban-forest interface in Brazil. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto-Lima, D.; Madec, Y.; Bersot, M.I.; Campos, S.S.; Motta, M.d.A.; Santos, F.B.d.; Vazeille, M.; Vasconcelos, P.F.d.C.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R.; Failloux, A.-B. Potential risk of re-emergence of urban transmission of Yellow Fever virus in Brazil facilitated by competent Aedes populations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casseb, A.R.; Cruz, A.V.; Jesus, I.S.; Chiang, J.O.; Martins, L.C.; Silva, S.P.; Henriques, D.F.; Casseb, L.; Vasconcelos, P.F.C. Seroprevalence of flaviviruses antibodies in water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) in Brazilian Amazon. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Thoisy, B.; Dussart, P.; Kazanji, M. Wild terrestrial rainforest mammals as potential reservoirs for flaviviruses (yellow fever, dengue 2 and St Louis encephalitis viruses) in French Guiana. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 98, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strier, K.B.; Tabacow, F.P.; de Possamai, C.B.; Ferreira, A.I.; Nery, M.S.; de Melo, F.R.; Mendes, S.L. Status of the northern muriqui (Brachyteles hypoxanthus) in the time of yellow fever. Primates 2019, 60, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmert Jr, H.W.; Kumm, H.W. The Susceptibility of Howler Monkeys. to Yellow Fever Virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1950, 30, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, P. Monkeys and yellow fever. In Nonhuman Primates and Medical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1973; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, M.S.; da Costa, A.C.; de Azevedo Fernandes, N.C.C.; Guerra, J.M.; Dos Santos, F.C.P.; Nogueira, J.S.; D’Agostino, L.G.; Komninakis, S.V.; Witkin, S.S.; Ressio, R.A. Epizootics due to Yellow Fever Virus in São Paulo State, Brazil: Viral dissemination to new areas (2016–2017). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, G.W.; Kitchen, S.F.; Haddow, A.J. Zika virus (I). Isolations and serological specificity. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1952, 46, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorou, R. Zika virus, vectors, reservoirs, amplifying hosts, and their potential to spread worldwide: What we know and what we should investigate urgently. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talero-Gutiérrez, C.; Rivera-Molina, A.; Perez-Pavajeau, C.; Ossa-Ospina, I.; Santos-García, C.; Rojas-Anaya, M.; de-la-Torre, A. Zika virus epidemiology: From Uganda to world pandemic, an update. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.S.; Bersot, M.I.; Castro, M.G.; Telleria, E.L.; Ferreira-de-Brito, A.; Raphael, L.M.; Bonaldo, M.C.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R. Low vector competence in sylvatic mosquitoes limits Zika virus to initiate an enzootic cycle in South America. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.G.; Martinez, N.; Abdalla, L.; Duarte dos Santos, C.N.; Chame, M. Animals in the Zika virus life cycle: What to expect from megadiverse Latin American countries. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, S.R.J.; Bayrami, S.; Moghadam, S.J.; Golrokhi, R.; Pahlaviani, F.G.; SeyedAlinaghi, S. Zika virus: A review of literature. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbi, L.; Coelho, A.V.C.; Alencar, L.C.A.d.; Crovella, S. Prevalence of Guillain-Barré syndrome among Zika virus infected cases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.V.C.; Crovella, S. Microcephaly prevalence in infants born to Zika virus-infected women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, B.D.; Kobylinski, K.C.; Foy, J.L.C.; Blitvich, B.J.; da Rosa, A.T.; Haddow, A.D.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Tesh, R.B. Probable non–vector-borne transmission of Zika virus, Colorado, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanluca, C.; Melo, V.C.A.d.; Mosimann, A.L.P.; Santos, G.I.V.d.; Santos, C.N.D.d.; Luz, K. First report of autochthonous transmission of Zika virus in Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, G.; Bandeira, A.; Sardi, S. Zika virus outbreak, Bahia. Brazil Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1885–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Amorin Vilharba, B.L.; Yamamura, M.; de Azevedo, M.V.; Fernandes, W.d.S.; Santos-Pinto, C.D.B.; de Oliveira, E.F. Disease burden of congenital Zika virus syndrome in Brazil and its association with socioeconomic data. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunali, M.; Radin, A.A.; Başıbüyük, S.; Musah, A.; Borges, I.V.G.; Yenigun, O.; Aldosery, A.; Kostkova, P.; Dos Santos, W.P.; Massoni, T.; et al. A review exploring the overarching burden of Zika virus with emphasis on epidemiological case studies from Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 55952–55966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-de-Brito, A.; Ribeiro, I.P.; Miranda, R.M.d.; Fernandes, R.S.; Campos, S.S.; Silva, K.A.B.d.; Castro, M.G.d.; Bonaldo, M.C.; Brasil, P.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R. First detection of natural infection of Aedes aegypti with Zika virus in Brazil and throughout South America. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2016, 111, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.F.d.; Silva, A.V.d.; Nascimento, V.A.d.; Souza, V.C.d.; Monteiro, D.C.d.S.; Terrazas, W.C.M.; Dos Passos, R.A.; Nascimento, S.; Lima, J.B.P.; Naveca, F.G. Evidence of vertical transmission of Zika virus in field-collected eggs of Aedes aegypti in the Brazilian Amazon. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Silva, J.W.; Nascimento, V.A.d.; Belchior, H.C.M.; Almeida, J.F.; Pessoa, F.A.C.; Naveca, F.G.; Ríos-Velásquez, C.M. First evidence of Zika virus venereal transmission in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2017, 113, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricas Rezende, H.; Malta Romano, C.; Morales Claro, I.; Santos Caleiro, G.; Cerdeira Sabino, E.; Felix, A.C.; Bissoli, J.; Hill, S.; Rodrigues Faria, N.; Cardoso da Silva, T.C.; et al. First report of Aedes albopictus infected by Dengue and Zika virus in a rural outbreak in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, C.T.; Stenn, T.M.; Chen, T.-Y.; Teixeira, M.G.; Queiroz, E.P.; Souza Dos Santos, L.; Queiroz, G.A.; Ribeiro Souza, K.; Kalabric Silva, L.; Shin, D.; et al. Evidence of Zika virus RNA fragments in Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) field-collected eggs from Camaçari, Bahia, Brazil. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.O.; Sacchetto, L.; Teixeira, M.; Chaves, B.A.; Hendy, A.; Mendonça, C.; Guimarães, I.; Linhares, R.; Brito, D.; Valério, D.; et al. Detection of Zika virus in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes collected in urban forest fragments in the Brazilian Amazon. Viruses 2023, 15, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alencar, J.; Ferreira de Mello, C.; Brisola Marcondes, C.; Érico Guimarães, A.; Toma, H.K.; Queiroz Bastos, A.; Olsson Freitas Silva, S.; Lisboa Machado, S. Natural infection and vertical transmission of Zika virus in sylvatic mosquitoes Aedes albopictus and Haemagogus leucocelaenus from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, M.C.P.; Lorenz, C.; de Aguiar Milhim, B.H.G.; Dibo, M.R.; Guirado, M.M.; Chiaravalloti-Neto, F.; Nogueira, M.L. Detection of Zika RNA virus in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes, São Paulo, Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 98, 105226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, D.R.; Paiva, M.H.; Donato, M.M.; Barbosa, P.P.; Krokovsky, L.; Rocha, S.W.d.S.; Saraiva, K.L.; Crespo, M.M.; Rezende, T.M.; Wallau, G.L.; et al. Zika virus replication in the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus in Brazil. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmert Jr, H.W.; Hughes, T.P. The virus of Ilheus encephalitis: Isolation, serological specificity and transmission. J. Immunol. 1947, 55, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Srihongse, S.; Johnson, C.M. The isolation of Ilhéus virus from man in Panamá. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1967, 16, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prías-Landínez, E.; Bernal-Cubides, C.; Morales-Alarcón, A. Isolation of Ilhéus virus from man in Colombia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1968, 17, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.R.; Aitken, T.H.; Downs, W.G. The isolation of Ilhéus virus from wild caught forest mosquitoes in Trinidad. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1956, 5, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grout, H.; Morales, A.; Vidales, H. Virus isolations from forest mosquitoes in San Vicente de Chucuri, Colombia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.A.; Fabbri, C.M.; Zunino, G.E.; Kowalewski, M.M.; Luppo, V.C.; Enría, D.A.; Levis, S.C.; Calderon, G.E. Detection of the mosquito-borne flaviviruses, West Nile, dengue, Saint Louis encephalitis, Ilheus, Bussuquara, and yellow fever in free-ranging black howlers (Alouatta caraya) of northeastern Argentina. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rodaniche, E. Isolation of the Virus of ilheus Encephalitis from Mosquitoes of the Genus Psorophora captured in Honduras. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1956, 5, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rodaniche, E.; Galindo, P. Isolation of the Virus of Ilheus Encephalitis from Mosquitoes captured in Panama. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 393–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turell, M.; O’guinn, M.; Jones, J.; Sardelis, M.; Dohm, D.; Watts, D.; Fernandez, R.; Da Rosa, A.T.; Guzman, H.; Tesh, R. Isolation of viruses from mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) collected in the Amazon Basin region of Peru. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, V.G.; Saivish, M.V.; Lino, N.A.B.; Bittar, C.; de Freitas Calmon, M.; Nogueira, M.L.; Rahal, P. Clinical landscape and rate of exposure to ilheus virus: Insights from systematic review and meta-analysis. Viruses 2022, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F.; Travasos da Rosa, J.; Vasconcelos, P. Aspectos Clínicos-Epidemiológicos: 50 anos do Instituto Evandro Chagas. Belem. Fundação Servidos Saude Publica 1986, 1, 375–407. [Google Scholar]
- Milhim, B.H.; Estofolete, C.F.; Rocha, L.C.d.; Liso, E.; Brienze, V.M.; Vasilakis, N.; Terzian, A.C.; Nogueira, M.L. Fatal outcome of Ilheus virus in the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient diagnosed with encephalitis. Viruses 2020, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Kenney, J.L.; Couto-Lima, D.; Campos, Z.M.; Schatzmayr, H.G.; Nogueira, R.M.; Brault, A.C.; Komar, N. Ilheus virus isolation in the Pantanal, west-central Brazil. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.S.; Luchs, A.; da Costa, A.C.; de Oliveira Ribeiro, G.; Dos Santos, F.C.P.; Nogueira, J.S.; Komninakis, S.V.; Marinho, R.d.S.S.; Witkin, S.S.; Villanova, F. Detection and characterization of Ilheus and Iguape virus genomes in historical mosquito samples from Southern Brazil. Acta Trop. 2020, 205, 105401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.J.d.S.P.; Andrade, C.D.d.; Kubiszeski, J.R.; Silva, D.J.F.d.; Barreto, E.S.; Massey, A.L.; Canale, G.R.; Bernardo, C.S.S.; Levi, T.; Peres, C.A.; et al. Detection of Ilheus virus in mosquitoes from southeast Amazon, Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 113, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, B.A.; Chagas, L.L.D.; de Arruda e Silva, F.; Santos, E.B.d.; Chiang, J.O.; Neto, J.P.N.; Vieira, D.B.R.; Junior, J.W.R.; da Silva, E.V.P.; Freitas, M.N.O. Arboviruses in Free-Ranging Birds and Hematophagous Arthropods (Diptera, Nematocera) from Forest Remnants and Urbanized Areas of an Environmental Protection Area in the Amazon Biome. Viruses 2022, 14, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.G.; Oliva, O.P.; Araujo, F.A.A.; Martins, L.C.; Chiang, J.O.; Henriques, D.F.; da Silva, E.V.P.; Rodrigues, D.S.G.; dos Prazeres, A.d.S.C.; Tavares-Neto, J. Epidemiology of Saint Louis encephalitis virus in the Brazilian Amazon region and in the State of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil: Elevated prevalence of antibodies in horses. Rev. Pan-Amaz. Saúde 2010, 1, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Campos, Z.; Juliano, R.; Velez, J.; Nogueira, R.M.R.; Komar, N. Serological evidence of widespread circulation of West Nile virus and other flaviviruses in equines of the Pantanal, Brazil. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; Suzuki, A.; Coimbra, T.; de Souza, R.; Chamelet, E. Ilheus arbovirus in wild birds (Sporophila caerulescens and Molothrus bonariensis). Rev Saude Publica 2001, 35, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, L.R. Epidemiology of West Nile virus in the United States: Implications for arbovirology and public health. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithburn, K.; Hughes, T.; Burke, A.; Paul, J. A neurotropic virus isolated from the blood of a native of Uganda. Cover The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1940, 20, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnick, J.L.; Paul, J.R.; Riordan, J.T.; Barnett, V.H.; Goldblum, N.; Zabin, E. Isolation from human sera in Egypt of a virus apparently identical to West Nile virus. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1951, 77, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.G. West Nile virus: Uganda, 1937, to New York City, 1999. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.R.; Roehrig, J.T. West Nile virus: A reemerging global pathogen. Rev. Biomédica 2001, 12, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, L.D.; Ciota, A.T.; Kilpatrick, A.M. Introduction, spread, and establishment of West Nile virus in the Americas. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artsob, H.; Gubler, D.; Enria, D.; Morales, M.; Pupo, M.; Bunning, M.; Dudley, J. West Nile Virus in the New World: Trends in the spread and proliferation of West Nile Virus in the Western Hemisphere. Zoonoses Public Health 2009, 56, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turell, M.J.; Dohm, D.J.; Sardelis, M.R.; O’guinn, M.L.; Andreadis, T.G.; Blow, J.A. An update on the potential of North American mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) to transmit West Nile virus. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpatrick, A.M.; Kramer, L.D.; Campbell, S.R.; Alleyne, E.O.; Dobson, A.P.; Daszak, P. West Nile virus risk assessment and the bridge vector paradigm. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciota, A.T. West Nile virus and its vectors. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 22, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sule, W.F.; Oluwayelu, D.O.; Hernández-Triana, L.M.; Fooks, A.R.; Venter, M.; Johnson, N. Epidemiology and ecology of West Nile virus in sub-Saharan Africa. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencattelli, G.; Ndione, M.H.D.; Rosà, R.; Marini, G.; Diagne, C.T.; Diagne, M.M.; Fall, G.; Faye, O.; Diallo, M.; Faye, O.; et al. Epidemiology of West Nile virus in Africa: An underestimated threat. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braack, L.; Gouveia de Almeida, A.P.; Cornel, A.J.; Swanepoel, R.; De Jager, C. Mosquito-borne arboviruses of African origin: Review of key viruses and vectors. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, A.K.; Fuller, D.O.; Haddad, N.; Hassan, A.N.; Gad, A.M.; Beier, J.C. Modeling the distribution of the West Nile and Rift Valley Fever vector Culex pipiens in arid and semi-arid regions of the Middle East and North Africa. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mixão, V.; Bravo Barriga, D.; Parreira, R.; Novo, M.T.; Sousa, C.A.; Frontera, E.; Venter, M.; Braack, L.; Almeida, A.P.G. Comparative morphological and molecular analysis confirms the presence of the West Nile virus mosquito vector, Culex univittatus, in the Iberian Peninsula. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasfi, F.; Dachraoui, K.; Cherni, S.; Bosworth, A.; Barhoumi, W.; Dowall, S.; Chelbi, I.; Derbali, M.; Zoghlami, Z.; Beier, J.; et al. West Nile virus in Tunisia, 2014: First isolation from mosquitoes. Acta Trop. 2016, 159, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, O.; Savini, G.; Papa, A.; Figuerola, J.; Groschup, M.H.; Kampen, H.; Medlock, J.; Vaux, A.; Wilson, A.J.; Werner, D. European surveillance for West Nile virus in mosquito populations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4869–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolsá-García, M.J.; Wehmeyer, M.L.; Lühken, R.; Roiz, D. Worldwide transmission and infection risk of mosquito vectors of West Nile, St. Louis encephalitis, Usutu and Japanese encephalitis viruses: A systematic review. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, J.; Williams, D. The zoonotic flaviviruses of Southern, South-Eastern and Eastern Asia, and Australasia: The potential for emergent viruses. Zoonoses Public Health 2009, 56, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, L.A.M.; da Silva, E.V.P.; Freitas, M.N.O.; Caldeira, R.D.; da Silva Araújo, P.A.; da Silva, F.S.; Junior, J.W.R.; Brandão, R.C.F.; de Almeida Medeiros, D.B.; Martins, L.C.; et al. Vectorial competence potential of Culex quinquefasciatus (Say, 1923) from the Amazon region to transmit West Nile virus isolated in Brazil. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, L.A.M.; Silva, E.V.P.d.; Dias, D.D.; Freitas, M.N.O.; Caldeira, R.D.; Araújo, P.A.d.S.; Silva, F.S.d.; Rosa Junior, J.W.; Brandão, R.C.F.; Nascimento, B.L.S.d. Vector competence of Culex quinquefasciatus from Brazil for West Nile virus. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamino, V.; Escribano-Romero, E.; Blázquez, A.-B.; Gutiérrez-Guzmán, A.-V.; Martín-Acebes, M.-Á.; Saiz, J.-C.; Höfle, U. Experimental North American West Nile virus infection in the red-legged partridge (Alectoris rufa). Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, G.L.; Kitron, U.D.; Goldberg, T.L.; Brawn, J.D.; Loss, S.R.; Ruiz, M.O.; Hayes, D.B.; Walker, E.D. Host selection by Culex pipiens mosquitoes and West Nile virus amplification. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marm Kilpatrick, A.; Daszak, P.; Jones, M.J.; Marra, P.P.; Kramer, L.D. Host heterogeneity dominates West Nile virus transmission. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 2327–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, H.M.; Aggarwal, D.; Apperson, C.S.; Katholi, C.R.; Gordon, E.; Hassan, H.K.; Anderson, M.; Charnetzky, D.; McMillen, L.; Unnasch, E.A.; et al. Host choice and West Nile virus infection rates in blood-fed mosquitoes, including members of the Culex pipiens complex, from Memphis and Shelby County, Tennessee, 2002–2003. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007, 7, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancey, C.; Grinev, A.; Volkova, E.; Rios, M. The global ecology and epidemiology of West Nile virus. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 376230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidaña, B.; Busquets, N.; Napp, S.; Pérez-Ramírez, E.; Jiménez-Clavero, M.Á.; Johnson, N. The role of birds of prey in West Nile virus epidemiology. Vaccines 2020, 8, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taieb, L.; Ludwig, A.; Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, R.L.; Iranpour, M.; Gagnon, C.A.; Bicout, D.J. Bird species involved in West Nile virus epidemiological cycle in Southern Quebec. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.A.; Campbell, G.D.; Pearl, D.L.; Jardine, C.M.; Salgado-Bierman, F.; Nemeth, N.M. A retrospective summary of raptor mortality in Ontario, Canada (1991–2014), including the effects of West Nile virus. J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angenvoort, J.; Brault, A.; Bowen, R.; Groschup, M. West Nile viral infection of equids. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, T.J.; Webb, C.E. A review of the epidemiological and clinical aspects of West Nile virus. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2014, 7, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Thompson, E.A.; Vig, P.J.; Leis, A.A. Current understanding of West Nile virus clinical manifestations, immune responses, neuroinvasion, and immunotherapeutic implications. Pathogens 2019, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granwehr, B.P.; Lillibridge, K.M.; Higgs, S.; Mason, P.W.; Aronson, J.M.; Campbell, G.A.; Barrett, A.D. West Nile virus: Where are we now? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.P.N.; Reis, L.A.M.; Freitas, M.N.O.; do Nascimento, B.L.S.; das Chagas, L.L.; da Costa, H.H.M.; Rodrigues, J.C.P.; Braga, C.M.; da Silva, E.V.P.; Silva, S.P. First Isolation and Genome Sequence Analysis of West Nile Virus in Mosquitoes in Brazil. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ometto, T.; Durigon, E.L.; De Araujo, J.; Aprelon, R.; de Aguiar, D.M.; Cavalcante, G.T.; Melo, R.M.; Levi, J.E.; Júnior, S.M.d.A.; Petry, M.V.; et al. West nile virus surveillance, Brazil, 2008–2010. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 107, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.R.; Medeiros, L.C.d.; Reis, V.P.d.; Chávez, J.H.; Munhoz, T.D.; Borges, G.P.; Soares, O.A.B.; Campos, C.H.C.d.; Machado, R.Z.; Baldani, C.D. Serologic survey of West Nile virus in horses from Central-West, Northeast and Southeast Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Morales, M.A.; Levis, S.; Figueiredo, L.T.M.; Couto-Lima, D.; Campos, Z.; Nogueira, M.F.; Silva, E.E.d.; Nogueira, R.M.R.; Schatzmayr, H.G.; et al. Neutralising antibodies for West Nile virus in horses from Brazilian Pantanal. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melandri, V.; Guimarães, A.É.; Komar, N.; Nogueira, M.L.; Mondini, A.; Fernandez-Sesma, A.; Alencar, J.; Bosch, I. Serological detection of West Nile virus in horses and chicken from Pantanal, Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2012, 107, 1073–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löwen Levy Chalhoub, F.; Maia de Queiroz-Júnior, E.; Holanda Duarte, B.; Eielson Pinheiro de Sá, M.; Cerqueira Lima, P.; Carneiro de Oliveira, A.; Medeiros Neves Casseb, L.; Leal das Chagas, L.; Antônio de Oliveira Monteiro, H.; Sebastião Alberto Santos Neves, M. West Nile virus in the state of ceará, northeast Brazil. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.; Romeiro, M.; Sousa, W.; Munhoz, T.; Borges, G.; Soares, O.; Campos, C.; Machado, R.; Silva, M.; Faria, J. A Saint Louis encephalitis and Rocio virus serosurvey in Brazilian horses. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalhoub, F.L.L.; Horta, M.A.P.; Alcantara, L.C.J.; Morales, A.; Dos Santos, L.M.B.; Guerra-Campos, V.; Rodrigues, C.D.; Santos, C.C.; Mares-Guia, M.A.M.; Pauvolid-Corrêa, A. Serological Evidence of Exposure to Saint Louis Encephalitis and West Nile Viruses in Horses of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Viruses 2022, 14, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Fischer, C.; Berneck, B.S.; Carneiro, I.O.; Kühne, A.; de Almeida Campos, A.C.; Ribas, J.R.; Netto, E.M.; Franke, C.R.; Ulbert, S.; et al. Ecologic determinants of West Nile virus seroprevalence among equids, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.P.; Webster, A.; Zitelli, L.C.; Umeno, K.; Souza, U.A.; Prusch, F.; Anicet, M.; Marsicano, G.; Bandarra, P.; Trainini, G.; et al. Serosurvey of West Nile virus (WNV) in free-ranging raptors from Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.C.; Silva, E.V.P.d.; Casseb, L.M.N.; Silva, S.P.d.; Cruz, A.C.R.; Pantoja, J.A.d.S.; Medeiros, D.B.d.A.; Martins, A.J.; Cruz, E.d.R.M.d.; Araújo, M.T.F.d.; et al. First isolation of West Nile virus in Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2019, 114, e180332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.S.G.; Matos, A.C.D.; da Cunha, M.A.C.R.; Rehfeld, I.S.; Galinari, G.C.F.; Marcelino, S.A.C.; Saraiva, L.H.G.; Martins, N.R.d.S.; Maranhão, R.d.P.A.; Lobato, Z.I.P. West Nile virus associated with equid encephalitis in Brazil, 2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, É.A.; Giovanetti, M.; Silva Catenacci, L.; Fonseca, V.; Aburjaile, F.F.; Chalhoub, F.L.; Xavier, J.; Campos de Melo Iani, F.; da Cunha e Silva Vieira, M.A.; Freitas Henriques, D. West nile virus in brazil. Pathogens 2021, 10, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siconelli, M.J.L.; Jorge, D.M.d.M.; Castro-Jorge, L.A.d.; Fonseca-Júnior, A.A.; Nascimento, M.L.; Floriano, V.G.; Souza, F.R.d.; Queiroz-Júnior, E.M.d.; Camargos, M.F.; Costa, E.D.L.; et al. Evidence for current circulation of an ancient West Nile virus strain (NY99) in Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2021, 54, e0687–e2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, J.; Geraldi, M.; Torres, K.; Torres, M.; Gomes, H.; Mourão, M.; Colella, R.; Wendel, S. Investigaçao molecular da presença do virus do Oeste do Nilo em doadores de sangue e pacientes de três regioes brasileiras. Rev. Bras. Hematol. E Hemoter. 2011, 33, 399. [Google Scholar]
- Muckenfuss, R.S. Clinical observations and laboratory investigations on the 1933 epidemic of encephalitis in St. Louis. Bull. New York Acad. Med. 1934, 10, 444. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, L.T.; Fite, G.L. A virus encountered in the study of material from cases of encephalitis in the St. Louis and Kansas City epidemics of 1933. Science 1933, 78, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, A.; Coffey, L.L.; Burkett-Cadena, N.; Day, J.F. Reemergence of St. Louis encephalitis virus in the Americas. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisen, W.K. Epidemiology of St. Louis encephalitis virus. Adv. Virus Res. 2003, 61, 139–184. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa Costa, G.; Marinho, P.E.S.; Vilela, A.P.P.; Saraiva-Silva, A.T.; Crispim, A.P.C.; Borges, I.A.; Dutra, A.G.S.; Lobato, Z.I.P.; Dos Reis, J.K.P.; de Oliveira, D.B. Silent circulation of the Saint Louis encephalitis virus among humans and equids, Southeast Brazil. Viruses 2019, 11, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Costa, E.A.; Marques, R.E.; Oliveira, T.S.; Furtini, R.; Bomfim, M.R.Q.; Teixeira, M.M.; Paixão, T.A.; Santos, R.L. Isolation of Saint Louis encephalitis virus from a horse with neurological disease in Brazil. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monath, T.P. Epidemiology. In St. Louis Encephalitis; Monath, T.P., Ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; pp. 239–312. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, T.; Mitchell, C. St. Louis Encephalitis. In The Arboviruses: Epidemiology and Ecology; Monath, T.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989; pp. 431–458. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, R.J.; Finley, K.H. SEQUELAE OF ENCEPHALITIS—Report of a Study After the California Epidemic. Calif. Med. 1956, 84, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Brinker, K.R.; Paulson, G.; Monath, T.P.; Wise, G.; Fass, R.J. St Louis encephalitis in Ohio, September 1975: Clinical and EEG studies in 16 cases. Arch. Intern. Med. 1979, 139, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, M.; Downs, W.G. The Arthropod-Borne Viruses of Vertebrates: An Account of the Rockefeller Foundation Virus Program, 1951-1970; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda, W.K.; Martins, L.C.; Malanski, L.d.S.; Shiozawa, M.M.; Spohr, K.A.H.; Hilst, C.L.S.; Aguiar, L.M.; Ludwig, G.; Passos, F.d.C.; Silva, L.R.d.; et al. Serological evidence for Saint Louis encephalitis virus in free-ranging New World monkeys and horses within the upper Paraná River basin region, Southern Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Almeida, M.A.B.d.; Santos, E.d.; Cardoso, J.d.C.; Noll, C.A.; Lima, M.d.M.; Silva, F.d.A.e.; Ferreira, M.S.; Martins, L.C.; Vasconcelos, P.F.d.C.; Bicca-Marques, J.C. Detection of antibodies against Icoaraci, Ilhéus, and Saint Louis Encephalitis arboviruses during yellow fever monitoring surveillance in non-human primates (Alouatta caraya) in southern Brazil. J. Med. Primatol. 2019, 48, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.N.; Mosena, A.C.; Baumbach, L.F.; da Silva, M.S.; Canova, R.; Dos Santos, D.R.; Budaszewski, R.d.F.; de Oliveira, L.V.; Soane, M.M.; Saraiva, N.B.; et al. Serologic evidence of West Nile virus and Saint Louis encephalitis virus in horses from Southern Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, F.P.; LeDuc, J.W.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Leite, O.F. Isolation of St. Louis encephalitis virus from a patient in Belém, Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.L.S.d.; Sallum, M.A.M.; Franco, H.M.; Oshiro, F.M.; Rocco, I.M. Genetic characterization of St. Louis encephalitis virus isolated from human in São Paulo, Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2006, 101, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, I.M.; Santos, C.L.; Bisordi, I.; Petrella, S.M.; Pereira, L.E.; Souza, R.P.; Coimbra, T.L.; Bessa, T.A.; Oshiro, F.M.; Lima, L. St. Louis encephalitis vírus: First isolation from a human in São Paulo state, Brasil. Rev. Do Inst. De Med. Trop. De São Paulo 2005, 47, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, A.; Cardeal, I.L.S.; Lázaro, E.; Nunes, S.H.; Moreira, C.C.; Rahal, P.; Maia, I.L.; Franco, C.; Góngora, D.V.; Góngora-Rubio, F.; et al. Saint louis encephalitis virus, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Pinheiro, F.; Schatzmayr, H.; de Andrade Travassos da Rosa, A.P.; Homma, A.; Bensabath, G. Arbovirus antibodies in children of rural Guanabara, Brazil. Intervirology 1975, 5, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rodrigues, S.G.; Nunes, M.R.; Casseb, S.M.; Prazeres, A.S.; Rodrigues, D.S.; Silva, M.O.; Cruz, A.C.; Tavares-Neto, J.C.; Vasconcelos, P.F. Molecular epidemiology of Saint Louis encephalitis virus in the Brazilian Amazon: Genetic divergence and dispersal. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2420–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.; Causey, O.R. Bussuquara, A New Arthropod-Borne Virus. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1959, 101, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltz, L.A. Zika and Other Neglected and Emerging Flaviviruses-E-Book: The Continuing Threat to Human Health; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, F.; Beran, G. CRC Hand Book Series in Zoonosis, Viral Zoonosis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, O.D.S.; Coimbra, T.L.; Sacchetta, L.D.A.; Calisher, C.H. Emergence of a new arbovirus disease in Brazil: I. Isolation and characterization of the etiologic agent, Rocio virus. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1978, 107, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, O.D.S.; Sacchetta, L.D.A.; Coimbra, T.L.; Pinto, G.H.; GLASSER, C.M. Emergence of a new arbovirus disease in Brazil: II. Epidemiologic studies on 1975 epidemic. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1978, 108, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saivish, M.V.; Gomes da Costa, V.; de Lima Menezes, G.; Alves da Silva, R.; Dutra da Silva, G.C.; Moreli, M.L.; Sacchetto, L.; Pacca, C.C.; Vasilakis, N.; Nogueira, M.L. Rocio virus: An updated view on an elusive flavivirus. Viruses 2021, 13, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lopes, O.S.; de Sacchetta, L.A.; Francy, D.B.; Jakob, W.L.; Calisher, C.H. Emergence of a new arbovirus disease in Brazil: III. Isolation of Rocio virus from Psorophora ferox (Humboldt, 1819). Am. J. Epidemiol. 1981, 113, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forattini, O.P.; Gomes, A.d.C.; Santos, J.L.F.; Galati, E.A.B.; Rabello, E.X.; Natal, D. Observações sobre atividade de mosquitos Culicidae, em mata residual no Vale do Ribeira, S. Paulo, Brasil. Rev. Saúde Pública 1981, 15, 557–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forattini, O.; Gomes, A.; Galati, E.; Rabello, E.; Iversson, L. Ecological studies on Culicidae mosquitoes in the Serra do Mar System, Brazil. 1. Observations in the outdoor environment. Rev. Saude. Publica 1978, 12, 297–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forattini, O.P.; Gomes, A.d.C.; Galati, E.A.B.; Rabello, E.X.; Iversson, L.B. Ecological studies on Culicidae mosquitoes in the Serra do Mar Sistem, Brazil: 2-Observations at the domiciliary environment. Rev. Saúde Pública 1978, 12, 476–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiriba, A.C.; Miziara, A.M.; Lorenco, R.; Costa, C.R.B.; Costa, C.S.; Pinto, G.H. Encefalite humana primária epidêmica por arbovírus observada no litoral sul do Estado de São Paulo: Estudo clínico efetuado em hospital de emergência. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. (1954) 1976, 11, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Iversson, L.; Coimbra, T. Encephalitis in the Valley of Ribeira region, São Paulo, Brazil, in the post-endemic period from 1978 to 1983: Status of the etiological diagnosis and epidemiological characteristics. Rev. Saude Publica 1984, 18, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversson, L.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Rosa, M. Recent occurrence of human infection by Rocio arbovirus in the Valley of Ribeira region. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1989, 31, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano-Lieber, N.S.; Iversson, L.B. Serological survey on arbovirus infection in residents of ecological reserve. Rev. Saúde Pública 2000, 34, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares-Neto, J.; Rosa, A.; Vasconcelos, P.F.; Costa, J.M.L.; Rosa, J.F.S.; Marsden, P.D. Research of antibodies to arbovirus in the serum of residentes of the village of Corte de Pedra, Valença, Bahia. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1986, 81, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saivish, M.V.; da Costa, V.G.; Rodrigues, R.L.; Féres, V.C.; Montoya-Diaz, E.; Moreli, M.L. Detection of Rocio virus SPH 34675 during dengue epidemics, Brazil, 2011–2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Figueiredo, G.G.; Amarilla, A.A.; de Souza, W.M.; Fumagalli, M.J.; de Figueiredo, M.L.G.; Szabó, M.P.J.; Badra, S.J.; Setoh, Y.X.; Khromykh, A.A.; Aquino, V.H. Genetic characterization of Cacipacoré virus from ticks collected in São Paulo State, Brazil. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saivish, M.V.; Nogueira, M.L.; Rossi, S.L.; Vasilakis, N. Beyond Borders: Investigating the Mysteries of Cacipacoré, a Lesser-Studied Arbovirus in Brazil. Viruses 2024, 16, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, M.L.G.d.; Amarilla, A.A.; Figueiredo, G.G.d.; Alfonso, H.L.; Lippi, V.; Maia, F.G.M.; Morais, F.A.; Costa, C.A.d.; Henriques, D.A.; Durigon, E.L.; et al. Cacipacore virus as an emergent mosquito-borne Flavivirus. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2017, 50, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, H.A.d.O. Avaliação da Diversidade de Insetos Hematófagos da Subordem Nematocera e de Vertebrados Silvestres: Transmissão de Arbovírus na área de Influência do Projeto Salobo, Carajás, Pará. Universidade Federal do Pará: Belem, Brazil, 2009. Available online: https://repositorio.ufpa.br/jspui/handle/2011/4748 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Araujo, F.A.A. Inquéritos Sorológicos em Equídeos e aves Silvestres para Detecção de Anticorpos Anti-Arbovírus de Importância em Saúde Pública no Brasil. Tese (Doutorado em Ciências Agrárias)—Universidade Federal de Goiás: Goiânia, Brazil, 2011. Available online: https://repositorio.bc.ufg.br/tede/items/abcfa493-7ca0-4196-814b-a4060c0bab88 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Corrêa, A.P. Investigação para a Circulação do Vírus do oeste do Nilo e Outros Flavivírus no Pantanal de Mato Grosso do Sul. Tese (Doutorado em Medicina Tropical)—Fundação Oswaldo Cruz: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012. Available online: https://www.arca.fiocruz.br/handle/icict/19602 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Batista, P.M.; Andreotti, R.; Almeida, P.S.d.; Marques, A.C.; Rodrigues, S.G.; Chiang, J.O.; Vasconcelos, P.F.d.C. Detection of arboviruses of public health interest in free-living New World primates (Sapajus spp.; Alouatta caraya) captured in Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2013, 46, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, W.C.; Tavares, G.d.S.B.; Vieira, D.S.; Honda, E.R.; Pereira, S.S.; Tada, M.S. Notification of the first isolation of Cacipacore virus in a human in the State of Rondônia, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2011, 44, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahinkesen, İ.; Doğan, F.; Dagalp, S.B. Current classification of Peribunyaviridae family: Genetic diversity and contributing factors. Vet. J. Kastamonu Univ. 2022, 1, 42–58. [Google Scholar]
- Amroun, A.; Priet, S.; de Lamballerie, X.; Quérat, G. Bunyaviridae RdRps: Structure, motifs, and RNA synthesis machinery. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 753–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, H.R.; Adkins, S.; Alkhovskiy, S.; Beer, M.; Blair, C.; Calisher, C.H.; Drebot, M.; Lambert, A.J.; De Souza, W.M.; Marklewitz, M.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Peribunyaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H.; Lazuick, J.S.; Muth, D.J.; Lopes, O.d.S.; Crane, G.T.; Elbel, R.E.; Shope, R.E. Antigenic relationships among Tacaiuma complex viruses of the Anopheles A serogroup (Bunyaviridae). Bull. Pan Am. Health Organ. 1980, 14, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H.; Sasso, D.R.; Maness, K.S.; Gheorghiu, V.N.; Shope, R.E. Relationships of anopheles a group arboviruses. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1973, 143, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dégallier, N.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Hervé, J.-P.; Vasconcelos, P.; Travassos da Rosa, J.; Sa’Filho, G.; Pinheiro, F. Modifications of arbovirus eco-epidemiology in Tucurui, Pará, Brazilian Amazonia, related to the construction of a hydroelectric dam. J. Braz. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 1989, 44, 124–135. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, H.G.; Dos Santos, F.B.; Pauvolid-Corrêa, A. An Overview of Neglected Orthobunyaviruses in Brazil. Viruses 2022, 14, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dégallier, N.; TRAVASSOS DA ROSA, A.A.; DA SILVA, J.C.; Guerreiro Rodrigues, S.; VASCONCELOS, P.C.; TRAVASSOS DA ROSA, J.S. As aves como hospedeiras de arbovírus na Amazônia Brasileira. Bol. Do Mus. Para. Emílio Goeldi. Nova Série. Zool. 1992, 8, 69–111. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.; Dávila, A.; Iversson, L.; de Abreu, U. Equine viral diseases in the Pantanal, Brazil. Studies carried out from 1990 to 1995. Rev. D Elev. Et. Med. Vet. Des. Pays Trop. 1999, 52, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casseb, A.R.; Silva, S.P.; Casseb, L.M.N.; Chiang, J.O.; Martins, L.C.; Vasconcelos, P.F.C. Prevalence of Arbovirus Antibodies Against The Family Bunyaviridae In Water Buffaloes. Ciência Anim. Bras. 2015, 16, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo Junior, A.B.; de Souza, W.M.; Acrani, G.O.; Carvalho, V.L.; Romeiro, M.F.; Tolardo, A.L.; da Silva, S.P.; Cardoso, J.F.; de Oliveira Chiang, J.; Vianez, J.L.d.S.G.; et al. Genomic characterization and evolution of Tacaiuma orthobunyavirus (Peribunyaviridae family) isolated in Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 60, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, P.F.d.C.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Dégallier, N.; Travassos da Rosa, J.; Pinheiro, F.P. Clinical and ecoepidemiological situation of human arboviruses in Brazilian Amazonia. Ciênc. Cult. (Säo Paulo) 1992, 44, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, L.; da Rosa, A.; Fiorillo, A. Arbovirus antibodies levels in subjects of the region of Ribeirao Preto, SP (Brazil). Rev. Saude Publica 1986, 20, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, P.d.C.; Rosa, A.; Rosa, J.; Dégallier, N. Concomitant infections by malaria and arboviruses in the Brazilian Amazon region. Rev. Latinoam. Microbiol. 1990, 32, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza Lopes, O.; Forattini, O.P.; Fonseca, I.E.; Lacerda, J.P.; Sacchetta, L.A.; Rabello, E. Boracéia virus. A new virus related to anopheles B virus. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966, 123, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Lopes, O.; de Abreu Sacchetta, L. Epidemiology of Boraceia virus in a forested area in São Paulo, Brazil. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1974, 100, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamori, A.; Coimbra, T.; Nassar, E.d.S.; Pereira, L.; Souza, L.d.; Kimura, E.; Rocco, I. Presence of bunyaviruses (Bunyamwera serogroup) in São Paulo State, Brazil. Rev. Inst. Adolfo Lutz. 1998, 57, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Campos, Z.; Soares, R.; Nogueira, R.M.R.; Komar, N. Neutralizing antibodies for orthobunyaviruses in Pantanal, Brazil. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Vasconcelos, P. Guaroa and other Bunyamwera group fevers. In Handbook of Zoonoses, Section B: Viral Zoonoses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 217–218. [Google Scholar]
- Groseth, A.; Vine, V.; Weisend, C.; Guevara, C.; Watts, D.; Russell, B.; Tesh, R.B.; Ebihara, H. Maguari virus associated with human disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, L.; Pachal, N.; Mascarenhas, M.; Greig, J.; Harding, S.; Young, I.; Wilhelm, B. Cache Valley virus: A scoping review of the global evidence. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, W.G.; Spence, L.; Aitken, T.H.; Whitman, L. Cache Valley virus, isolated from a Trinidadian mosquito, Aedes scapularis. West Indian Med. J. 1961, 10, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Spence, L.; Jonkers, A.H.; Grant, L.S. Arboviruses in the Caribbean Islands. Progress in Medical virology. Fortschritte der Medizinischen Virusforschung. Prog. En Virol. Medicale 1968, 10, 415–486. [Google Scholar]
- Mettler, N.E.; Parodi, A.S.; Casals, J. Survey for antibodies against arthropod-borne viruses in man in Argentina. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1967, 16, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, R.; Street, C.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Nunes, M.R.; Tee, K.K.; Hutchison, S.K.; Vasconcelos, P.F.; Tesh, R.B.; Lipkin, W.I.; Briese, T. Genetic characterization of the Wyeomyia group of orthobunyaviruses and their phylogenetic relationships. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Lopes, O.; de Abreu Sacchetta, L.; Fonseca, I.; Lacerda, J. Bertioga (Guama group) and Anhembi (Bunyamwera group), two new arboviruses isolated in São Paulo, Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1975, 24, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groseth, A.; Wollenberg, K.R.; Mampilli, V.; Shupert, T.; Weisend, C.; Guevara, C.; Kochel, T.J.; Tesh, R.B.; Ebihara, H. Spatiotemporal analysis of Guaroa virus diversity, evolution, and spread in South America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, H.; Oya, A.; Bernal, C.; Barreto-Reyes, P. Guaroa virus, a new agent isolated in Colombia, South America. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1959, 8, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.H.; Sanmartin, C. Isolations of Guaroa virus from Anopheles (Kerteszia) neivai in the Pacific lowlands of Colombia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1967, 16, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causey, O.; Shope, R.; Rodrigues Filho, A. Isolamento do virus Guaroa do figado por biopsia percutanea de um caso humano com paralisia. Rev. Serv. Espec. Saude Pub. 1962, 12, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, P.V.; Morrison, A.C.; Rocha, C.; Watts, D.M.; Beingolea, L.; Suarez, V.; Vargas, J.; Cruz, C.; Guevara, C.; Montgomery, J.M.; et al. Guaroa virus infection among humans in Bolivia and Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, C.; Elson, W.H.; Vilcarromero, S.; Morrison, A.C.; Hontz, R.D.; Alava, F.; Valdivia, H.; Felices, V.; Guevara, C.; Jenkins, S. Guaroa virus and Plasmodium vivax co-infections, Peruvian Amazon. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDuc, J.W. The ecology of California group viruses. J. Med. Entomol. 1979, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dégallier, N.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Vasconcelos, P.; Travassos da Rosa, J.; Travassos da Rosa, E.; Rodrigues, S. Ecological Aspects of Arboviroses in Brazilian Amazonas, South America. Virus Rev. Res 1996, 1, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shope, R.E.; Woodall, J.P. The epidemiology of diseases caused by viruses in Groups C and Guama (Bunyaviridae). In Arboviruses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; pp. 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, D.B.; Luiz, A.P.M.F.; Fagundes, A.; Pinto, C.A.; Bonjardim, C.A.; Trindade, G.S.; Kroon, E.G.; Abrahão, J.S.; Ferreira, P.C. Evidence of apeu virus infection in wild monkeys, Brazilian Amazon. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gibbs, C.J.; Bruckner, E.A.; Schenker, S. A Case of Apeu Virus Infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auguste, A.J.; Adams, A.P.; Arrigo, N.C.; Martinez, R.; Da Rosa, A.P.T.; Adesiyun, A.A.; Chadee, D.D.; Tesh, R.B.; Carrington, C.V.; Weaver, S.C. Isolation and characterization of sylvatic mosquito-borne viruses in Trinidad: Enzootic transmission and a new potential vector of Mucambo virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, W.F.; Madalengoitia, J.; Flores, W.; Acosta, M. The first isolations of eastern encephalitis, group C, and Guama group arboviruses from the Peruvian Amazon region of western South America. Bull. Pan Am. Health Organ. 1975, 9, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, D.M.; Russell, K.L.; Wooster, M.T.; Sharp, T.W.; Morrison, A.C.; Kochel, T.J.; Bautista, C.T.; Block, K.; Guevara, C.; Aguilar, P.; et al. Etiologies of acute undifferentiated febrile illnesses in and near iquitos from 1993 to 1999 in the amazon river basin of Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 107, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.B.; Pereira, L.E.; Rocco, I.M.; Marti, A.T.; Souza, L.; Iversson, L.B. Surveillance of arbovirus infections in the atlantic forest region, State of São Paulo, Brazil: I. detection of hemagglutination-inhibition antibodies in wild birds between 1978 and 1990. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 1994, 36, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversson, L.B.; Rosa, A.; Coimbra, T.L.M.; Ferreira, I.B.; Nassar, E.d.S. Human disease in Ribeira Valley, Brazil caused by Caraparu, a group C arbovirus-report of a case. In Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo; Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 1987; Volume 29, pp. 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- BENSABATH, B.; ANDRADE, A.d. Anticorpos para arbovírus no sôro de residentes na cidade de Belém, Pará. Rev. Serv. Saúde Públ 1962, 12, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Catenacci, L.S.; Ferreira, M.; Martins, L.C.; De Vleeschouwer, K.; Cassano, C.; Oliveira, L.; Canale, G.; Deem, S.; Tello, J.; Parker, P.; et al. Surveillance of arboviruses in primates and sloths in the Atlantic Forest, Bahia, Brazil. EcoHealth 2018, 15, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shope, R.E.; Causey, C.E.; Causey, O.R. Itaqui virus, a new member of arthropod-borne group C. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walder, R.; Suarez, O.M.; Calisher, C.H. Arbovirus studies in the Guajira region of Venezuela: Activities of eastern equine encephalitis and Venezuelan equine encephalitis viruses during an interepizootic period. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1984, 33, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walder, R.; Suarez, O.M.; Calisher, C.H. Arbovirus studies in southwestern Venezuela during 1973-1981. II. Isolations and further studies of Venezuelan and eastern equine encephalitis, Una, Itaqui, and Moju viruses. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1984, 33, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turell, M.; Dohm, D.; Fernandez, R.; Klein, T. Vector competence of Peruvian mosquitoes for two orthobunyaviruses isolated from mosquitoes captured in Peru. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SHOPE, R.E.; WOODALL, J.P. Ecological interaction of wildlife, man, and a virus of the Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis complex in a tropical forest. J. Wildl. Dis. 1973, 9, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Toda, A.; Shope, R.E. Transmission of Guama and Oriboca viruses by naturally infected mosquitoes. Nature 1965, 208, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.C. Research activities at the Trinidad Regional Virus Laboratory (TRVL). In the Twelfth Meeting of the Advisory Committee on Medical Research. PAHO, ACMR, Washington DC, USA, 25–29 June 1973, pp. 1–11. Available online: https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/47344 (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Panday, R. Mosquito Ecology in Relation to the Transmission of Pathogens in Surinam. Identification, Age Determination, Seasonal Abundance, Statistical Analysis. Proefschrift Universiteit van Suriname: Suriname, 1974. Available online: https://ub1.uvs.edu/cgi-bin/wxis.exe/iah/scripts/?IsisScript=iah.xis&lang=en&base=COLBIB&nextAction=lnk&exprSearch=FYSIOLOGIE%20DER%20DIEREN&indexSearch=DS (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Robin, Y.; Lhuillier, M.; Girault, G.; Pajot, F.; Dégallier, N. Dengue Viruses and Other Arboviruses in French Guiana. In Proceedings of the Internacional Simposium on Tropical Arboviruses and Haemorrhagic Fevers, Academia Brasiliera deficiencias, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–18 April 1980; pp. 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Digoutte, J.P. Ecology of Arboviruses and their diseases in French Guiana. In the Meeting of the Advisory Committee on Medical Research, 14. Pan American Health Organization, 7–10 July 1975. Available online: https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/47375 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Panday, R. Guamá-group virus activity in Surinam. Trop. Geogr. Med. 1981, 33, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Whitman, L.; Casals, J. The Guama Group: A New Serological Group of Hitherto Undescribed Viruses. Immunological Studies. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F.d.P.; Bensabath, G.; Andrade, A.H.P.d.; Lins, Z.; Fraiha, H.; Tang, A.; Lainson, R.; Shaw, J.; Azevedo, M. Infectious diseases along Brazil’s Trans-Amazon highway: Surveillance and research. Bull. Pan Am. Health Organ. 1974, 8, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.R.; Spence, L.; Downs, W.G.; Aitken, T.H. Oropouche virus: A new human disease agent from Trinidad, West Indies. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F.P.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Vasconcelos, P.F.d.C. Oropouche fever. In Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases; Saunders: London, UK, 2004; pp. 2418–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Da Rosa, J.F.T.; De Souza, W.M.; de Paula Pinheiro, F.; Figueiredo, M.L.; Cardoso, J.F.; Acrani, G.O.; Nunes, M.R.T. Oropouche virus: Clinical, epidemiological, and molecular aspects of a neglected Orthobunyavirus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, F.d.P.; Pinheiro, M.; Bensabath, G.; Causey, O.; Shope, R.E. Epidemia de vírus Oropouche em Belém. Rev. Serv. Espec. Saude Publica 1962, 12, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, F.; Travassos da Rosa, A. Arboviral zoonoses of Central and South America. In Handbook of Zoonoses, Section B: Viral Zoonoses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; Volume 210, p. 212. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, F.P.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.; Travassos da Rosa, J.F. Oropouche virus. I. A review of clinical, epidemiological, and ecological findings. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselmann, K.M.; Postigo-Hidalgo, I.; Pezzi, L.; de Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Fischer, C.; de Lamballerie, X.; Drexler, J.F. Emergence of Oropouche fever in Latin America: A narrative review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, e439–e452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilston-Lunel, N.L. Oropouche virus: An emerging orthobunyavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2024, 105, 002027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A. Oropouche virus disease among US travelers—United States, 2024. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2024, 73, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC. Communicable Disease Threats Report, 1-7 June 2024, Week 23; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Solna, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, M.R.T.; Martins, L.C.; Rodrigues, S.G.; Chiang, J.O.; da Silva Azevedo, R.d.S.; Da Rosa, A.P.T.; da Costa Vasconcelos, P.F. Oropouche virus isolation, southeast Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Travassos da Rosa, J.; Bensabath, G. An outbreak of Oropouche virus diease in the vicinity of santarem, para, barzil. Tropenmedizin Und Parasitol. 1976, 27, 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- LeDuc, J.; Hoch, A.; Pinheiro, F.d.P.; Da Rosa, A. Epidemic Oropouche virus disease in northern Brazil. Bull. Pan Am. Health Organ. 1981, 15, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, P.M.; Andreotti, R.; Chiang, J.O.; Ferreira, M.S.; Vasconcelos, P.F.d.C. Seroepidemiological monitoring in sentinel animals and vectors as part of arbovirus surveillance in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2012, 45, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibrail, M.M.; Fiaccadori, F.S.; Souza, M.; Almeida, T.N.V.; Chiang, J.O.; Martins, L.C.; Ferreira, M.S.; Cardoso, D.d.D.d.P. Detection of antibodies to Oropouche virus in non-human primates in Goiânia City, Goiás. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2016, 49, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, M.R.T.; de Souza, W.M.; Savji, N.; Figueiredo, M.L.; Cardoso, J.F.; da Silva, S.P.; de Lima, C.P.d.S.; Vasconcelos, H.B.; Rodrigues, S.G.; Lipkin, W.I.; et al. Oropouche orthobunyavirus: Genetic characterization of full-length genomes and development of molecular methods to discriminate natural reassortments. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 68, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, B.F.; Serra, O.P.; Heinen, L.B.d.S.; Zuchi, N.; Souza, V.C.d.; Naveca, F.G.; Santos, M.A.M.d.; Slhessarenko, R.D. Detection of Oropouche virus segment S in patients and inCulex quinquefasciatus in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Memórias Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, B.; Wise, E.L.; Pullan, S.T.; Logue, C.H.; Bowden, T.A.; Escalera-Zamudio, M.; Trueba, G.; Nunes, M.R.; Faria, N.R.; Pybus, O.G. Evolutionary dynamics of Oropouche virus in South America. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, P.V.; Barrett, A.D.; Saeed, M.F.; Watts, D.M.; Russell, K.; Guevara, C.; Ampuero, J.S.; Suarez, L.; Cespedes, M.; Montgomery, J.M.; et al. Iquitos virus: A novel reassortant Orthobunyavirus associated with human illness in Peru. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Caso, W.; Aguilar-Luis, M.A.; Palomares-Reyes, C.; Mazulis, F.; Weilg, C.; Del Valle, L.J.; Espejo-Evaristo, J.; Soto-Febres, F.; Martins-Luna, J.; del Valle-Mendoza, J. First outbreak of Oropouche Fever reported in a non-endemic western region of the Peruvian Amazon: Molecular diagnosis and clinical characteristics. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 83, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Luna, J.; del Valle-Mendoza, J.; Silva-Caso, W.; Sandoval, I.; Del Valle, L.J.; Palomares-Reyes, C.; Carrillo-Ng, H.; Peña-Tuesta, I.; Aguilar-Luis, M.A. Oropouche infection a neglected arbovirus in patients with acute febrile illness from the Peruvian coast. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillet, M.; Pichard, C.; Restrepo, J.; Lavergne, A.; Perez, L.; Enfissi, A.; Abboud, P.; Lambert, Y.; Ma, L.; Monot, M.; et al. Outbreak of Oropouche virus in French guiana. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernal, S.; Martini, C.C.; da Fonseca, B.A. Oropouche virus–associated aseptic meningoencephalitis, Southeastern Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.O.; Azevedo, R.S.; Justino, M.C.; Matos, H.J.; Cabeça, H.L.; Silva, S.P.; Henriques, D.F.; Silva, E.V.; Andrade, G.S.; Vasconcelos, P.F. Neurological disease caused by Oropouche virus in northern Brazil: Should it be included in the scope of clinical neurological diseases? J. NeuroVirology 2021, 27, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F.; Rocha, A.G.; Freitas, R.; Ohana, B.A.; Rosa, A.; Rogério, J.; Linhares, A.d.C. Meningite associada as infeccoes por virus Oropouche. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Säo Paulo 1982, 24, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- PAHO. Epidemiological Alert Oropouche in the Region of the Americas—1 August 2024; PAHO: Hoonah, AK, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- PAHO. Public Health Risk Assessment related to Oropouche Virus (OROV) in the Region of the Americas—3 August 2024; PAHO: Hoonah, AK, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sah, R.; Srivastava, S.; Mehta, R.; Khan, S.R.; Kumar, S.; Satpathy, P.; Mohanty, A.; Ferraz, C.; Feehan, J.; Apostolopoulos, V.; et al. Oropouche fever fatalities and vertical transmission in South America: Implications of a potential new mode of transmission. Lancet Reg. Health–Am. 2024, 38, 100896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Dashraath, P.; Baud, D. Oropouche Virus (OROV) in pregnancy: An Emerging cause of placental and Fetal Infection Associated with Stillbirth and Microcephaly following Vertical Transmission. Viruses 2024, 16, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaya, T.; Palacios, G.; Briese, T.; Di Serio, F.; Groschup, M.H.; Neriya, Y.; Song, J.-W.; Tomitaka, Y. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Phenuiviridae 2023. J. Gen. Virol. 2023, 104, 001893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Xin, Q.; Tischler, N.D.; Lozach, P.-Y. Entry of phenuiviruses into mammalian host cells. Viruses 2021, 13, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, E.E.; De Andrade, A.H.P.; Shope, R.E. Itaporanga, a newly recognized arbovirus from Sao Paulo state, Brazil. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1965, 118, 421–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaga, S.; Duchemin, J.-B.; Girod, R.; Dusfour, I. The Culex mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) of French Guiana: A comprehensive review with the description of three new species. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 182–221. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, P.J.; Freitas-Astúa, J.; Bejerman, N.; Blasdell, K.R.; Breyta, R.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Fooks, A.R.; Kondo, H.; Kurath, G.; Kuzmin, I.V.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Rhabdoviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rosa, A.P.T.; Mather, T.N.; Takeda, T.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Shope, R.E.; Popov, V.L.; Guzman, H.; Coffey, L.; Araujo, T.P.; Tesh, R.B. Two new rhabdoviruses (Rhabdoviridae) isolated from birds during surveillance for arboviral encephalitis, northeastern United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 616. [Google Scholar]
- Serufo, J.C.; de Oca, H.M.; Tavares, V.A.; Souza, A.M.; Rosa, R.V.; Jamal, M.C.; Lemos, J.R.; Oliveira, M.A.; Nogueira, R.; Schatzmayr, H.G. Isolation of dengue virus type 1 from larvae of Aedes albopictus in Campos Altos City, State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1993, 88, 503–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio-Nuevo, K.M.; Cunha, M.S.; Luchs, A.; Fernandes, A.; Rocco, I.M.; Mucci, L.F.; de Souza, R.P.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; Ceretti-Junior, W.; Marrelli, M.T. Detection of Zika and dengue viruses in wild-caught mosquitoes collected during field surveillance in an environmental protection area in São Paulo, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, V.E.P.; Alencar, C.H.; Kamimura, M.T.; de Carvalho Araujo, F.M.; De Simone, S.G.; Dutra, R.F.; Guedes, M.I.F. Occurrence of natural vertical transmission of dengue-2 and dengue-3 viruses in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzian, A.C.B.; Zini, N.; Sacchetto, L.; Rocha, R.F.; Parra, M.C.P.; Del Sarto, J.L.; Dias, A.C.F.; Coutinho, F.; Rayra, J.; da Silva, R.A.; et al. Evidence of natural Zika virus infection in neotropical non-human primates in Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragan, I.K.; Blizzard, E.L.; Gordy, P.; Bowen, R.A. Investigating the potential role of North American animals as hosts for Zika virus. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.S.; Luchs, A.; Dos Santos, F.C.P.; Caleiro, G.S.; Nogueira, M.L.; Maiorka, P.C. Applying a pan-flavivirus RT-qPCR assay in Brazilian public health surveillance. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.A.; Romano, A.P.; Borba, A.S.; Silva, E.V.; Chiang, J.O.; Eulálio, K.D.; Azevedo, R.S.; Rodrigues, S.G.; Almeida-Neto, W.S.; Vasconcelos, P.F. Case report: West Nile Virus encephalitis: The first human case recorded in Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.M.; Kubiszeski, J.R.; Vieira, C.J.d.S.P.; Gusmao, A.F.; Pratis, T.S.; Colombo, T.E.; Thies, S.F.; do Carmo Araujo, F.; Zanelli, C.F.; Milhim, B.H.G.d.A. Detection of Saint Louis encephalitis virus in two Brazilian states. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, H.G.; de Lima, R.C.; Barbosa, L.S.; Souza, T.M.A.d.; Badolato-Correa, J.; Maia, L.M.S.; Ferreira, R.d.S.; Neves, N.A.d.S.; Costa, M.C.d.S.; Martins, L.R. Retrospective molecular investigation of Mayaro and Oropouche viruses at the human-animal interface in West-central Brazil, 2016–2018. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa, A.P.T.; Vasconcelos, P.F.; da Rosa, J.F.T. An Overview of Arbovirology in Brazil and Neighbouring Countries; Citeseer: Belem, Brazil, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Derraik, J.G.; Slaney, D. Anthropogenic environmental change, mosquito-borne diseases and human health in New Zealand. EcoHealth 2007, 4, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkett-Cadena, N.D.; Vittor, A.Y. Deforestation and vector-borne disease: Forest conversion favors important mosquito vectors of human pathogens. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2018, 26, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, W.M.; Weaver, S.C. Effects of climate change and human activities on vector-borne diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahouli, J.B.; Koudou, B.G.; Müller, P.; Malone, D.; Tano, Y.; Utzinger, J. Effect of land-use changes on the abundance, distribution, and host-seeking behavior of Aedes arbovirus vectors in oil palm-dominated landscapes, southeastern Côte d’Ivoire. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, N. Impact of anthropogenic environmental alterations on vector-borne diseases. Medscape J. Med. 2008, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayer, S.V.; Tesh, R.B.; Vasilakis, N. The emergence of arthropod-borne viral diseases: A global prospective on dengue, chikungunya and zika fevers. Acta Trop. 2017, 166, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, L.A.; Flores, F.S.; Quaglia, A.; Contigiani, M.S. Intertwined arbovirus transmission activity: Reassessing the transmission cycle paradigm. Front. Physiol. 2013, 3, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.D.; Talley, J.L.; Frazier, A.E.; Noden, B.H. Landscape and anthropogenic factors associated with adult Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in small cities in the Southern Great Plains. Insects 2020, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotonirina, A.; Maquart, P.-O.; Flamand, C.; Sokha, C.; Boyer, S. Mosquito diversity (Diptera: Culicidae) and medical importance in four Cambodian forests. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsripong, P.; Green, A.; Kittayapong, P.; Kapan, D.; Wilcox, B.; Bennett, S. Mosquito vector diversity across habitats in central Thailand endemic for dengue and other arthropod-borne diseases. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, A.B.; Vasquez, C.; Carvajal, A.; Moreno, M.; Fuller, D.O.; Cardenas, G.; Petrie, W.D.; Beier, J.C. Urbanization favors the proliferation of Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus in urban areas of Miami-Dade County, Florida. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, R.d.S.S.; Duro, R.L.S.; Mota, M.T.d.O.; Hunter, J.; Diaz, R.S.; Kawakubo, F.S.; Komninakis, S.V. Environmental changes and the impact on the human infections by dengue, chikungunya and Zika viruses in northern Brazil, 2010–2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possas, C.; Lourenço-de-Oliveira, R.; Tauil, P.L.; Pinheiro, F.d.P.; Pissinatti, A.; Cunha, R.V.d.; Freire, M.; Martins, R.M.; Homma, A. Yellow fever outbreak in Brazil: The puzzle of rapid viral spread and challenges for immunisation. Memórias Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2018, 113, e180278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilacqua, R.C.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; Ramos, D.G.; Obara, M.T.; Ceretti-Junior, W.; Mucci, L.F.; Marrelli, M.T.; Laporta, G.Z. Reemergence of yellow fever in Brazil: The role of distinct landscape fragmentation thresholds. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 2021, 8230789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanetti, M.; de Mendonça, M.C.L.; Fonseca, V.; Mares-Guia, M.A.; Fabri, A.; Xavier, J.; de Jesus, J.G.; Gräf, T.; dos Santos Rodrigues, C.D.; Dos Santos, C.C. Yellow fever virus reemergence and spread in Southeast Brazil, 2016–2019. J. Virol. 2019, 94, e01623-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, E.S.; Rocco, I.M.; Bergo, E.S.; Brasil, R.A.; Siciliano, M.M.; Suzuki, A.; Silveira, V.R.; Bisordi, I.; Souza, R.P.d. Reemergence of yellow fever: Detection of transmission in the State of São Paulo, Brazil, 2008. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2011, 44, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da C Cardoso, J.; De Almeida, M.A.; Dos Santos, E.; Da Fonseca, D.F.; Sallum, M.A.; Noll, C.A.; Hamilton, A.d.O.; Cruz, A.C.; Carvalho, V.L.; Pinto, E.V. Yellow fever virus in Haemagogus leucocelaenus and Aedes serratus mosquitoes, southern Brazil, 2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk-da-Silva, R.; Medeiros-Sousa, A.R.; Laporta, G.Z.; Mucci, L.F.; Prist, P.R.; Marrelli, M.T. The influence of landscape structure on the dispersal pattern of yellow fever virus in the state of São Paulo. Acta Trop. 2022, 228, 106333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveca, F.G.; de Almeida, T.A.P.; Souza, V.; Nascimento, V.; Silva, D.; Nascimento, F.; Mejía, M.; de Oliveira, Y.S.; Rocha, L.; Xavier, N.; et al. Human outbreaks of a novel reassortant Oropouche virus in the Brazilian Amazon region. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 3509–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegally, H.; Dellicour, S.; Poongavanan, J.; Mavian, C.; Dor, G.; Fonseca, V.; Tagliamonte, M.S.; Dunaiski, M.; Moir, M.; Wilkinson, E. Dynamics and ecology of a multi-stage expansion of Oropouche virus in Brazil. MedRxiv 2024, MedRxiv:2029.24316328. [Google Scholar]
- IPAM. Amazônia em Chamas 9: O Novo e Alarmante Patamar do Desmatamento na Amazônia; IPAM: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, B.N.; de Souza Ferreira, R.F.P.; do Socorro Athaide, M. Dinâmica do desmatamento na região AMACRO com o sistema de alerta de desmatamento (SAD). In Proceedings of the Anais do XX Simpósio Brasilerio de Sensoriamento Remoto, Florianopolis, Brazil, 2–5 April 2023; pp. 2399–2401. [Google Scholar]
- Gibb, R.; Ryan, S.J.; Pigott, D.; Fernandez, M.d.P.; Muylaert, R.L.; Albery, G.F.; Becker, D.J.; Blackburn, J.K.; Caceres-Escobar, H.; Celone, M. The anthropogenic fingerprint on emerging infectious diseases. MedRxiv 2024, MedRxiv:2024.2005. 2022.24307684. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Alvarez, D.; Escobar, L.E. Vegetation loss and the 2016 Oropouche fever outbreak in Peru. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2017, 112, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Thoisy, B.; Gräf, T.; Mansur, D.S.; Delfraro, A.; Dos Santos, C.N.D. The Risk of Virus Emergence in South America: A Subtle Balance Between Increasingly Favorable Conditions and a Protective Environment. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2024, 11, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côrtes, N.; Lira, A.; Prates-Syed, W.; Dinis Silva, J.; Vuitika, L.; Cabral-Miranda, W.; Durães-Carvalho, R.; Balan, A.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Cabral-Miranda, G. Integrated control strategies for dengue, Zika, and Chikungunya virus infections. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1281667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurgel-Gonçalves, R.; Oliveira, W.K.d.; Croda, J. The greatest dengue epidemic in Brazil: Surveillance, prevention, and control. Rev. Da Soc. Bras. De Med. Trop. 2024, 57, e00203–e02024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leandro, A.; Maciel-de-Freitas, R. Development of an Integrated Surveillance System to Improve Preparedness for Arbovirus Outbreaks in a Dengue Endemic Setting: Descriptive Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024, 10, e62759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlade, S.T.; Adekunle, A.I.; Meehan, M.T.; McBryde, E.S. Quantifying the impact of Wolbachia releases on dengue infection in Townsville, Australia. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utarini, A.; Indriani, C.; Ahmad, R.A.; Tantowijoyo, W.; Arguni, E.; Ansari, M.R.; Supriyati, E.; Wardana, D.S.; Meitika, Y.; Ernesia, I.; et al. Efficacy of Wolbachia-infected mosquito deployments for the control of dengue. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, G.R.; Durovni, B.; Saraceni, V.; Riback, T.I.S.; Pinto, S.B.; Anders, K.L.; Moreira, L.A.; Salje, H. Estimating the effect of the wMel release programme on the incidence of dengue and chikungunya in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: A spatiotemporal modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.B.; Riback, T.I.; Sylvestre, G.; Costa, G.; Peixoto, J.; Dias, F.B.; Tanamas, S.K.; Simmons, C.P.; Dufault, S.M.; Ryan, P.A. Effectiveness of Wolbachia-infected mosquito deployments in reducing the incidence of dengue and other Aedes-borne diseases in Niterói, Brazil: A quasi-experimental study. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, D.; Power, G.M.; Jones, R.T.; Massad, E.; Iriart, J.B.; Preet, R.; Kinsman, J.; Logan, J.G. Vector control strategies in Brazil: A qualitative investigation into community knowledge, attitudes and perceptions following the 2015–2016 Zika virus epidemic. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e050991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possas, C.; Martins, R.M.; Oliveira, R.L.d.; Homma, A. Urgent call for action: Avoiding spread and re-urbanisation of yellow fever in Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2017, 113, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
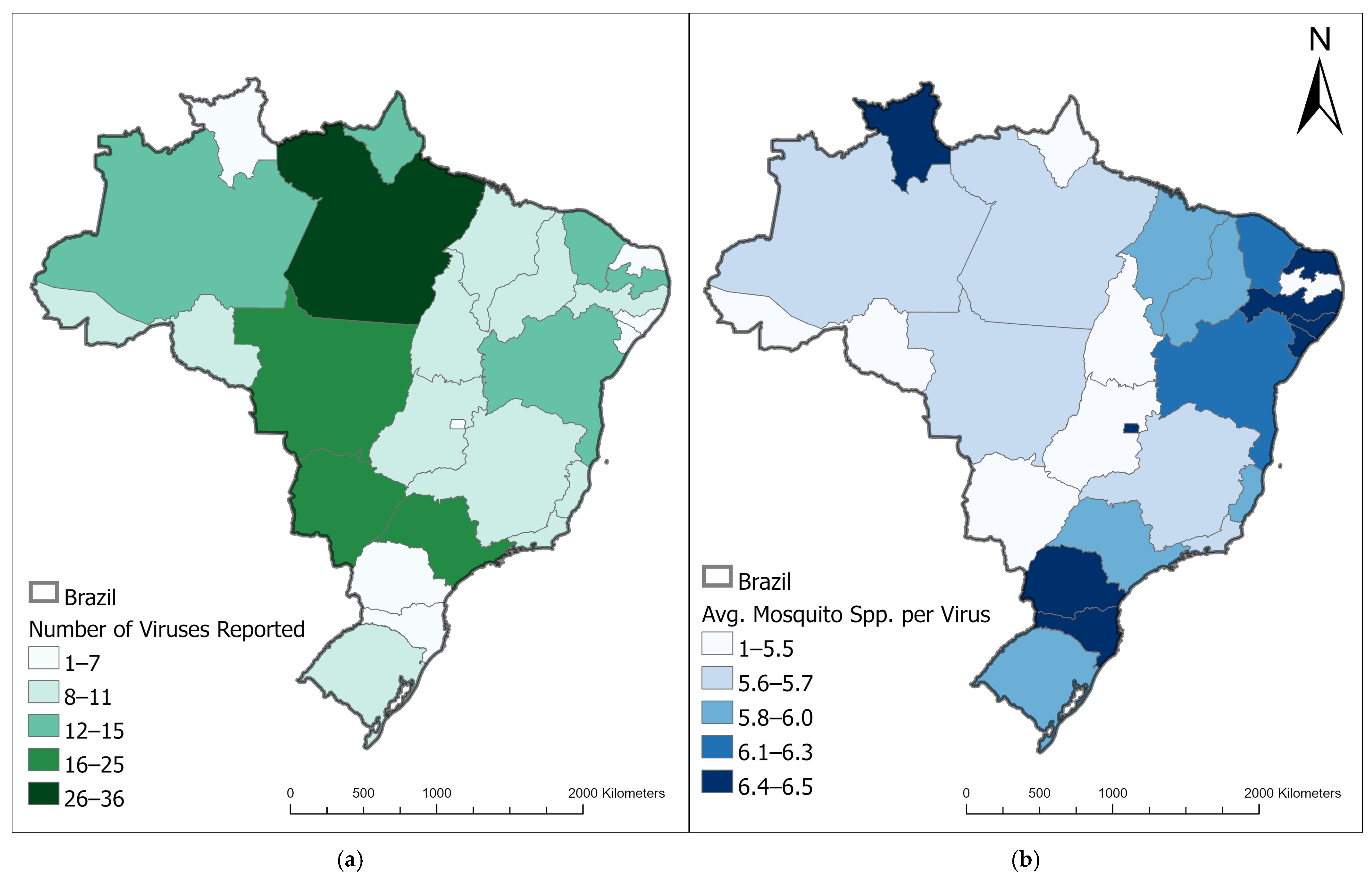

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dye-Braumuller, K.C.; Prisco, R.A.; Nolan, M.S. (Re)Emerging Arboviruses of Public Health Significance in the Brazilian Amazon. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030650
Dye-Braumuller KC, Prisco RA, Nolan MS. (Re)Emerging Arboviruses of Public Health Significance in the Brazilian Amazon. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(3):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030650
Chicago/Turabian StyleDye-Braumuller, Kyndall C., Rebecca A. Prisco, and Melissa S. Nolan. 2025. "(Re)Emerging Arboviruses of Public Health Significance in the Brazilian Amazon" Microorganisms 13, no. 3: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030650
APA StyleDye-Braumuller, K. C., Prisco, R. A., & Nolan, M. S. (2025). (Re)Emerging Arboviruses of Public Health Significance in the Brazilian Amazon. Microorganisms, 13(3), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030650






