Development of Duplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Hydroxynaphthol Blue for Detection of Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus and Aeromonas hydrophila in Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation of DNA Templates
2.2. Primer Design and Synthesis
2.3. LAMP for ISKNV and A. hydrophila with Pre-Additional Hydroxynapthol Blue
2.4. Optimization of LAMP-HNB
2.5. Specificity of the Duplex LAMP-HNB
2.6. Identification of Duplex LAMP-HNB Reaction Products by Enzymatic Digestion
2.7. Sensitivity of the Duplex LAMP-HNB
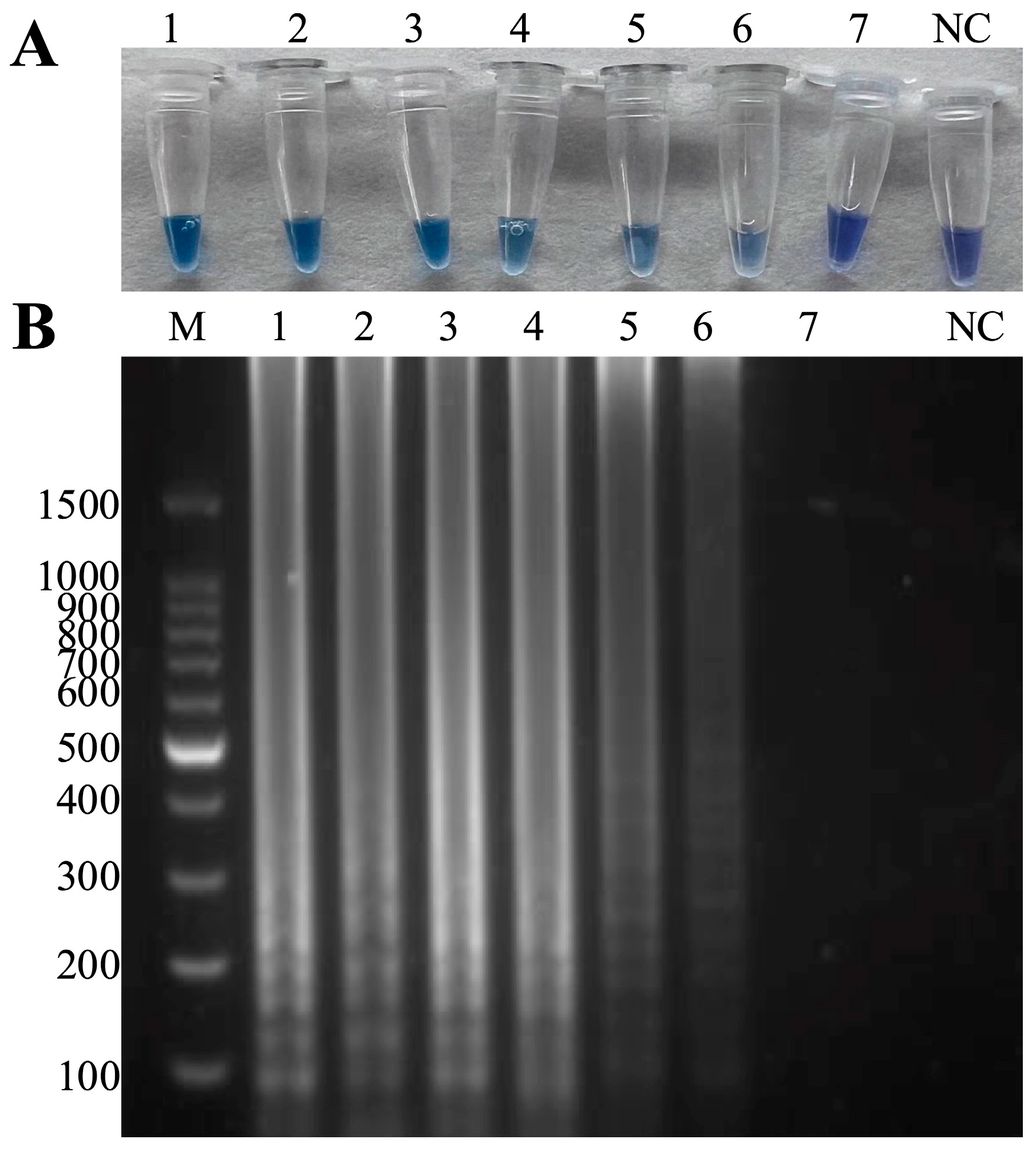
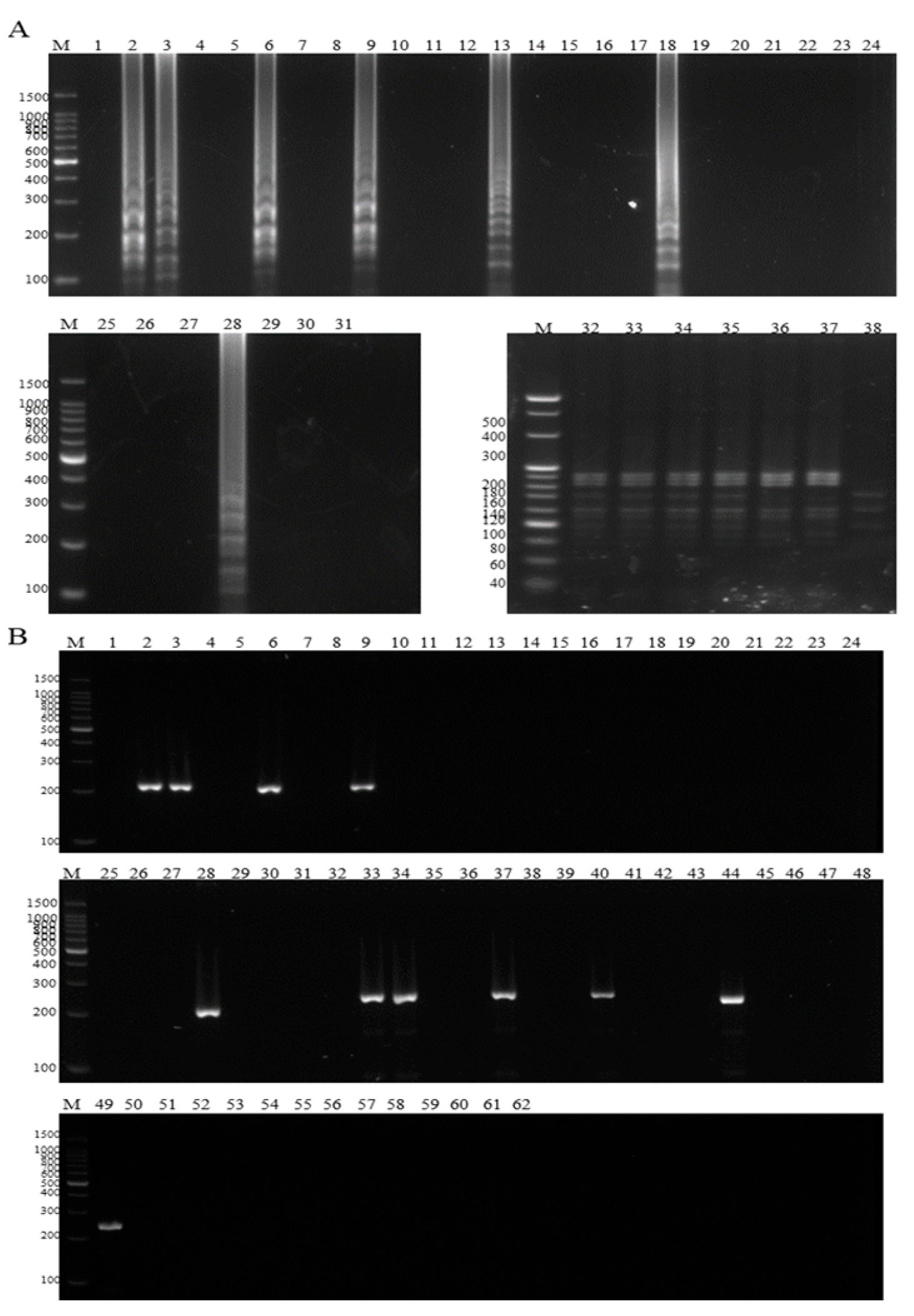
2.8. Clinical Tests of the Duplex LAMP-HNB
3. Results
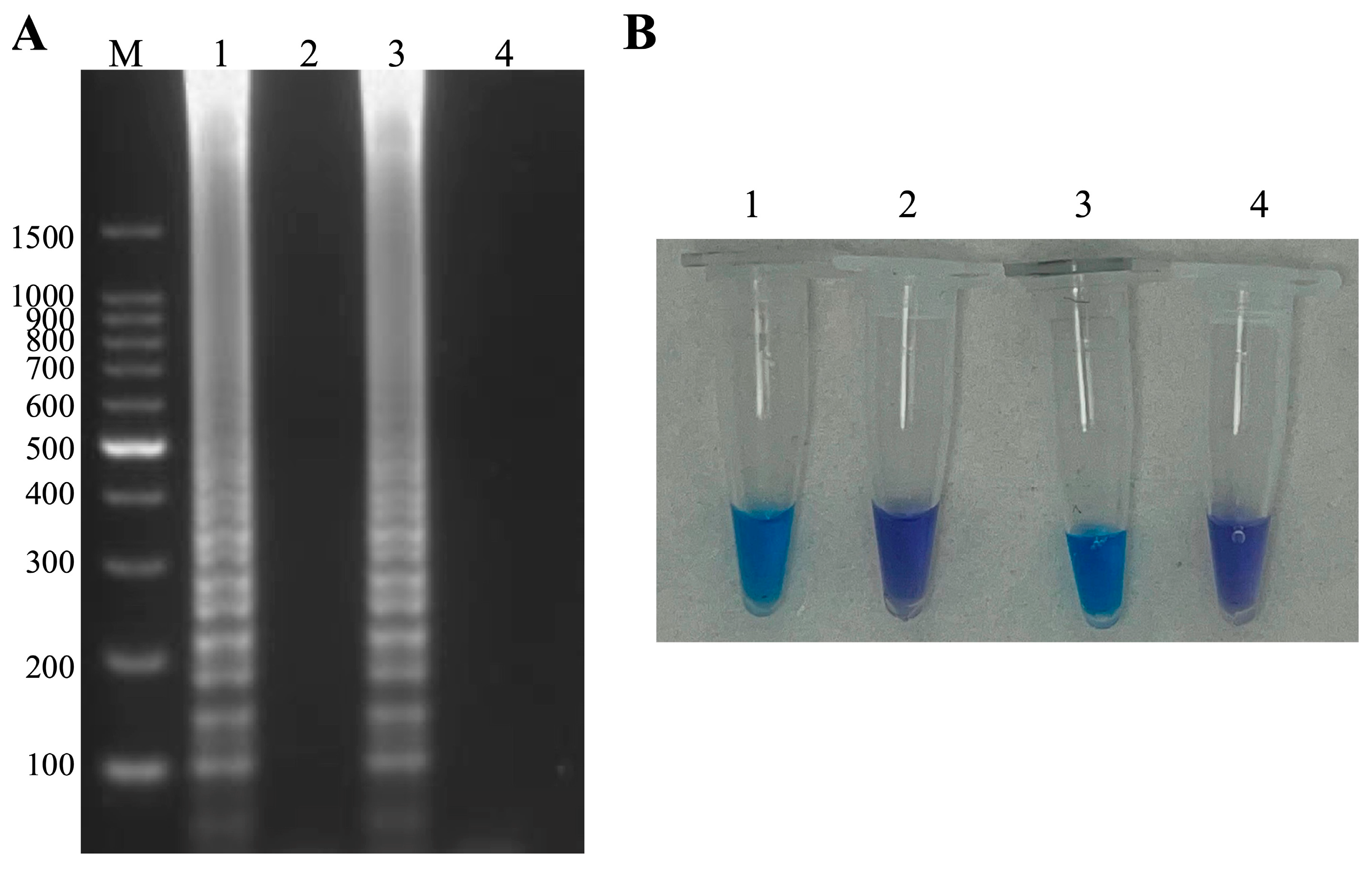
3.1. LAMP of ISKNV and A. hydrophila with Pre-Additional Hydroxynapthol Blue
3.2. Establishment of ISKNV and A. hydrophila Duplex LAMP-HNB
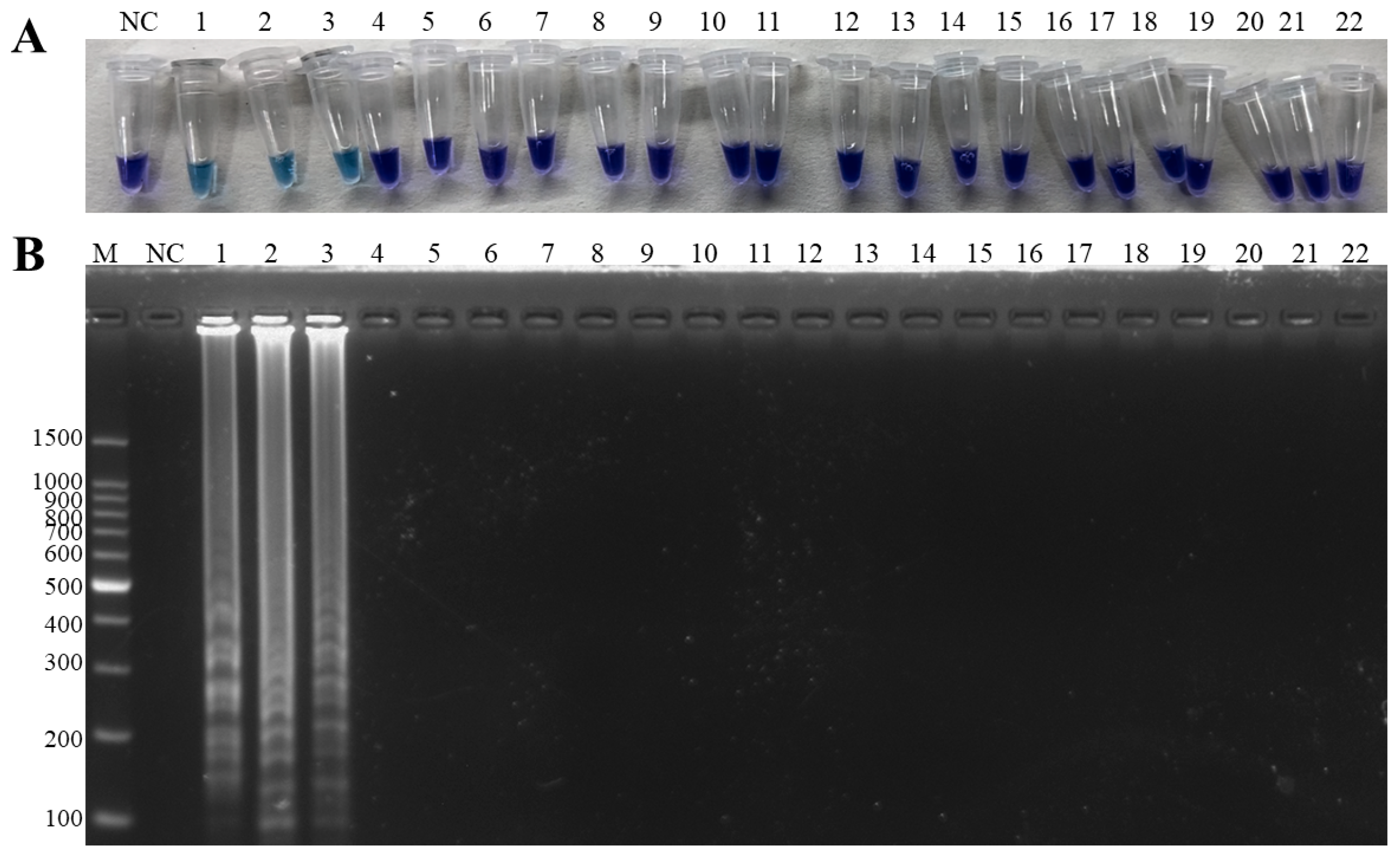
3.3. Specificity Tests of the Duplex LAMP-HNB
3.4. Identification of Duplex LAMP-HNB Enzymatic Digestion Products
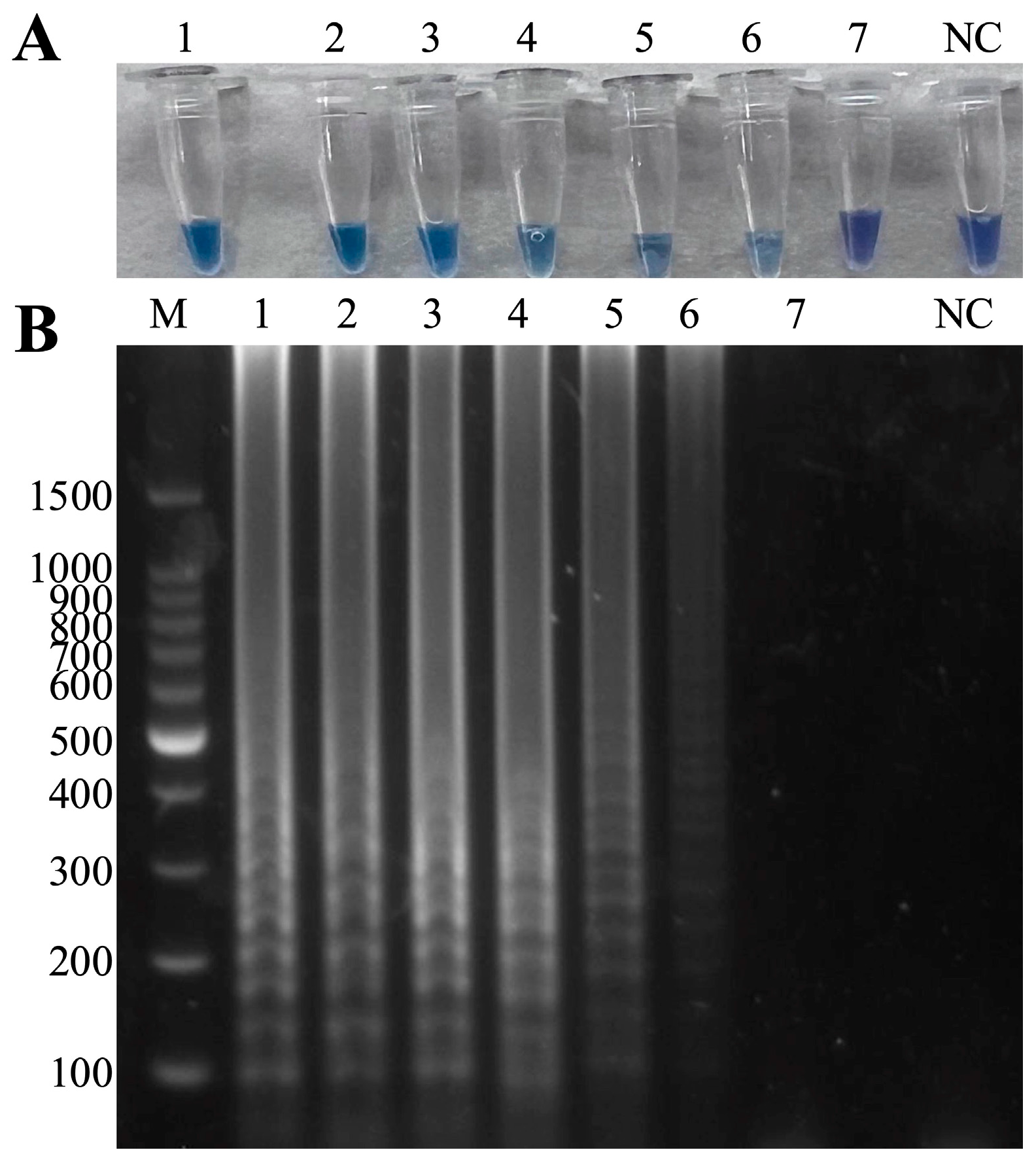
3.5. Sensitivity Tests of the Duplex LAMP-HNB
3.6. Comparison of the Duplex LAMP-HNB and Conventional PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ReferencesSong, Y.Q.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, S.S.; Xie, S.G. Ontogenetic development and otolith microstructure in the larval and juvenile stages of mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi. Ichthyol. Res. 2019, 66, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.P.; Zheng, W.D.; He, S.; Ye, X.; Xiao, G.C.; Yang, X.L. Identification of a Vibrio cholerae Isolate as the Causal Agent of Ascites Disease in Cultured Mandarin Fish Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky). Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2013, 65, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.F.; Duan, C.; Zhang, H.T.; Weng, S.P.; He, J.G.; Dong, C.F. Widespread outbreaks of the emerging mandarinfish ranavirus (MRV) both in natural and ISKNV-FKC vaccinated mandarinfish Siniperca chuatsi in Guangdong, South China, 2017. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, J. Studies on virulence and isolation of pathogenic bacteria causing bacterial septicemia in mandarinfish Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky). J. Huazhong Cent. China Agric. Univ. 1996, 15, 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.Z.; Li, N.Q.; Liu, L.H.; Lin, Q.; Wang, F.; Lai, Y.T.; Jiang, H.M.; Pan, H.J.; Shi, C.B.; Wu, S.Q. Genotype and host range analysis of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV). Virus Genes 2011, 42, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Izawa, T.; Kuwamura, M.; Higashiguchi, N.; Kezuka, C.; Kurata, O.; Wada, S.; Yamate, J. The first case of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) infection in aquarium-maintained mandarin fish, Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky), in Japan. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, J.; Nakajima, K. Megalocytiviruses. Viruses 2012, 4, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Lü, L.; Weng, S.P.; Huang, J.N.; Chan, S.M.; He, J.G. Molecular epidemiology and phylogenetic analysis of a marine fish infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus-like (ISKNV-like) virus. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung-Schroers, V.; Adamek, M.; Wohlsein, P.; Wolter, J.; Wedekind, H.; Steinhagen, D. First outbreak of an infection with infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) in ornamental fish in Germany. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2016, 119, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Weng, S.; Huang, Z.; Lu, J.; Lan, D.; Zhong, X.; Yu, X.; Xu, A.; He, J. A zebrafish (Danio rerio) model of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) infection. Virology 2008, 376, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, P.; Moody, N.; Williams, L.; Hoad, J.; Cummins, D.M.; Davies, K.; Crane, M. Molecular confirmation of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) in farmed and imported ornamental fish in Australia. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 116, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.T.; Jitrakorn, S.; Kayansamruaj, P.; Pirarat, N.; Rodkhum, C.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S.; Saksmerprome, V. Infectious spleen and kidney necrosis disease (ISKND) outbreaks in farmed barramundi (Lates calcarifer) in Vietnam. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.L.; Shaw, J.G. Aeromonas spp. clinical microbiology and disease. J. Infect. 2011, 62, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerigano, N.K.; Chibsa, T.R.; Molla, Y.G.; Mohammed, A.A.; Tamiru, M.; Bulto, A.O.; Wodaj, T.K.; Gebreweld, D.S.; Abdi, A.K. Phenotypic, molecular detection and antibiogram analysis of Aeromonas hydrophila from Oreochromis niloticus (Nile Tilapia) and Ready-To-eat fish products in selected Rift Valley lakes of Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awan, F.; Dong, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Ma, K.; Liu, Y. The fight for invincibility: Environmental stress response mechanisms and Aeromonas hydrophila. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Pillai, D. Prevalence and characterization of virulence-associated genes and antimicrobial resistance in Aeromonas hydrophila from freshwater finfish farms in Andhra Pradesh, India. Biologia 2023, 78, 2931–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.E.; Høi, L.; Schmidt, A.S.; Qian, D.; Shimada, T.; Shen, J.Y.; Larsen, J.L. Is Aeromonas hydrophila the dominant motile Aeromonas species that causes disease outbreaks in aquaculture production in the Zhejiang Province of China? Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2001, 46, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, C.; He, X.; Tan, R.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y. The Success of Yellow Catfish Aquaculture in China: From Rare Wild Fish to Popular Farmed Fish. In Aquaculture in China; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 270–282. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, N.; Xi, B.; Xie, J. A Study on Bacterial Etiology and Histopathology Associated With Hemorrhagic Disease in American Shad Alosa sapidissima. Aquac. Res. 2024, 2024, 8869167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, S.; Tong, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X. Pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila causing mass mortalities of Procambarus clarkia and its induced host immune response. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakijkosol, O.; Owens, L.; Picard, J. Case report of bacterial infections in a redclaw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) hatchery. Aquaculture 2017, 475, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.-y.; Abdallah, G.; Zhang, B.-y.; Wang, S.; Yao, Q.; Chen, Y.-k.; Wang, Q.-j.; Zhang, D.-m. Effect of infection with Aeromonas hydrophila on antioxidant capacity, inflammation response, and apoptosis proteins in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 252, 109220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchill, S.A.; Perebolte, L.; Johnston, C.; Top, B.; Selby, P. Comparison of the RNA-amplification based methods RT-PCR and NASBA for the detection of circulating tumour cells. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, G.T.; Little, M.C.; Nadeau, J.G.; Shank, D.D. Isothermal in vitro amplification of DNA by a restriction enzyme/DNA polymerase system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizardi, P.M.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Bray-Ward, P.; Thomas, D.C.; Ward, D.C. Mutation detection and single-molecule counting using isothermal rolling-circle amplification. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, D.; Li, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Wu, G.; Wu, G.; Tan, G.; Zheng, Z.; Li, L.; et al. Hemolysin from Aeromonas hydrophila enhances the host’s serum enzyme activity and regulates transcriptional responses in the spleen of Cyprinus rubrofuscus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katata, M.; Okuyama, Y. Development of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Methods for Detection of the Enteric Myxosporeans Causing Myxosporean Emaciation Disease. Fish Pathol. 2017, 52, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Phusantisampan, T.; Yamkasem, J.; Tattiyapong, P.; Sriariyanun, M.; Surachetpong, W. Specific and rapid detection of tilapia parvovirus using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Gao, Z.X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhao, X.P.; Liu, Y. Development of a quadruplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for field detection of four Vibrio species associated with fish disease. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.G.; Weng, S.P.; Huang, Z.J.; Zeng, K. Identification of Outbreak and Infectious Diseases Pathogen of Siniperca chuatsi. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1998, 5, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, W. Research On The Pathogen Of The Outbreak-Infective Disease Of Siniperca Chuastsi. J. Fish. China 1997, 21, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Lin, Q.; Liu, L.; Liang, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, N. Display of ISKNV orf086 protein on the surface of Aeromonas hydrophila and its immunogenicity in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Impact of Aeromonas hydrophila and infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus infections on susceptibility and host immune response in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 105, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Figueras, M.J.; McGarey, D.; Liles, M.R. Virulence Factors of Aeromonas hydrophila: In the Wake of Reclassification. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X. Analysis of pathogenicity factors in the highly virulent Aeromonas hydrophila strain LP-2. Aquaculture 2025, 598, 741982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, K.; Shariff, M.; Omar, A.R.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Ong, B.L. Use of Acridine Orange to Visually Improve the Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification for Detection of Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus. Fish Pathol. 2014, 49, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Deng, R.Q.; Wang, X.Z.; Huang, Y.S.; Xing, K.; Feng, J.H.; He, J.G.; Long, Q.X. Cladistic analysis of iridoviruses based on protein and DNA sequences. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.W.; Cha, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; An, E.J.; Park, M.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, M.A.; Park, J.W. Sequence variation in the gene encoding the major capsid protein of Korean fish iridoviruses. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, K.; Shariff, M.; Omar, A.R.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Ong, B.L. Detection and molecular characterization of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus from major ornamental fish breeding states in Peninsular Malaysia. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, K.; Rathore, R.S.; Thomas, P.; Arun, T.R.; Viswas, K.N.; Dhama, K.; Agarwal, R.K. New closed tube loop mediated isothermal amplification assay for prevention of product cross-contamination. MethodsX 2014, 1, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suebsing, R.; Pradeep, P.J.; Jitrakorn, S.; Sirithammajak, S.; Kampeera, J.; Turner, W.A.; Saksmerprome, V.; Withyachumnarnkul, B.; Kiatpathomchai, W. Detection of natural infection of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus in farmed tilapia by hydroxynapthol blue-loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kuang, W.; Zheng, Q.; Cao, J. Establishment of a Rapid LAMP Assay for Aeromonas hydrophila and Comparison with the Application of qPCR. Metabolites 2023, 13, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.J.; Lu, J.F.; Su, X.R.; Jin, J.L.; Li, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Shao, X.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Yan, M.C.; et al. Simultaneous detection of multiple bacterial and viral aquatic pathogens using a fluorogenic loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based dual-sample microfluidic chip. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Fu, X.Z.; Liu, L.H.; Liang, H.R.; Niu, Y.J.; Wen, Y.Y.; Huang, Z.B.; Li, N.Q. Development and application of a sensitive droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) for the detection of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Lu, J.; Wu, S.; Lin, X.; Zheng, L.; Lou, Y.; Xiao, X. A novel detection method for the pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila expressing aerA gene and/or hlyA gene based on dualplex RAA and CRISPR/Cas12a. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 973996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.T.; Teh, C.S.; Thong, K.L. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 895816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupama, K.P.; Nayak, A.; Karunasagar, I.; Maiti, B. Rapid visual detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood samples by loop-mediated isothermal amplification with hydroxynaphthol blue dye. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trakhna, F.; Harf-Monteil, C.; Abdelnour, A.; Maaroufi, A.; Gadonna-Widehem, P. Rapid Aeromonas hydrophila identification by TaqMan PCR assay: Comparison with a phenotypic method. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Fu, X.; Liu, L.; Liang, H.; Guo, H.; Yin, S.; Kumaresan, V.; Huang, Z.; Li, N. Application and development of a TaqMan real-time PCR for detecting infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus in Siniperca chuatsi. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.A.; Jeyasekaran, G.; Shakila, R.J.; Raj, K.T.; Jeevithan, E. Detection of hemolytic strains of Aeromonas hydrophila and A. sobria along with other Aeromonas spp. from fish and fishery products by multiplex PCR. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.C.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.H.; Lu, X.J.; Li, M.Y. Rapid and sensitive detection of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, N.; Cain, K.; Zeng, L. Development of cross-priming amplification coupled with vertical flow visualization for rapid detection of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) in mandarin fish, Siniperca chuatsi. J Virol. Methods 2018, 253, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primers | Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Target Amplification |
|---|---|---|
| MCP F3 | GCCCGCAGACAATTCCTTG | 211 bp |
| MCP B3 | CCGAGGGGTGTTCTCGTAA | |
| MCP FIP | TTGCGGTGGGTGACGTTCTTTAGTGCATCTGGACCTCAGGT | |
| MCP BIP | CGTGCAAAGCAACTACACCGCGGGATTGGTGGCCATCAAAG |
| Primers | Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Target Amplification |
|---|---|---|
| hlyA F3 | GGGGTCGAGGTGAACAAGG | 250 bp |
| hlyA B3 | AGCTGAGCGGCTGGATGC | |
| hlyA FIP | TTCGACCCGGTAATCCTGGGTGGAGGCGTCGGCCAAGT | |
| hlyA BIP | GCGCCCAGAAGGTGAGTTTCAAGGAGAGCAGGGACTCCG |
| Components | Content (μL) |
|---|---|
| MCP F3 (10 μM) | 0.5 |
| MCP B3 (10 μM) | 0.5 |
| MCP FIP (100 μM) | 0.4 |
| MCP BIP (100 μM) | 0.4 |
| 10 × IsothermalAmp Buffer | 2.5 |
| MgSO4 (100 mM) | 1.5 |
| Hydroxynaphthol blue (1.5 mM) | 2 |
| dNTPs mix (10 mM) | 3.5 |
| Bst II DNA Polymerase Large Fragment (8 U/μL) | 1 |
| DNA template | 1 |
| ddH2O | 11.7 |
| Components | Content (μL) |
|---|---|
| hlyA F3 (10 μM) | 0.5 |
| hlyA B3 (10 μM) | 0.5 |
| hlyA FIP (100 μM) | 0.4 |
| hlyA BIP (100 μM) | 0.4 |
| 10 × IsothermalAmp Buffer | 2.5 |
| MgSO4 (100 mM) | 1.5 |
| Hydroxynaphthol blue (1.5 mM) | 2 |
| dNTPs mix (10 mM) | 3.5 |
| Bst II DNA Polymerase Large Fragment (8 U/μL) | 1 |
| DNA template | 1 |
| ddH2O | 11.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Wu, J.; Tan, X.; Xu, S.; Kong, W.; Liu, X. Development of Duplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Hydroxynaphthol Blue for Detection of Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus and Aeromonas hydrophila in Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Microorganisms 2025, 13, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030586
He X, Wu J, Tan X, Xu S, Kong W, Liu X. Development of Duplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Hydroxynaphthol Blue for Detection of Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus and Aeromonas hydrophila in Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Microorganisms. 2025; 13(3):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030586
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiao, Jingyi Wu, Xu Tan, Sunan Xu, Weiguang Kong, and Xiaodan Liu. 2025. "Development of Duplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Hydroxynaphthol Blue for Detection of Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus and Aeromonas hydrophila in Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi)" Microorganisms 13, no. 3: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030586
APA StyleHe, X., Wu, J., Tan, X., Xu, S., Kong, W., & Liu, X. (2025). Development of Duplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Hydroxynaphthol Blue for Detection of Infectious Spleen and Kidney Necrosis Virus and Aeromonas hydrophila in Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Microorganisms, 13(3), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030586







