Isolation and Characterization of Carbonosomes from Pseudomonas sp. phDV1 Grown Using Phenol as Carbon Source
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultivation of Pseudomonas sp. phDV1
2.2. Phenol Consumption Measurement
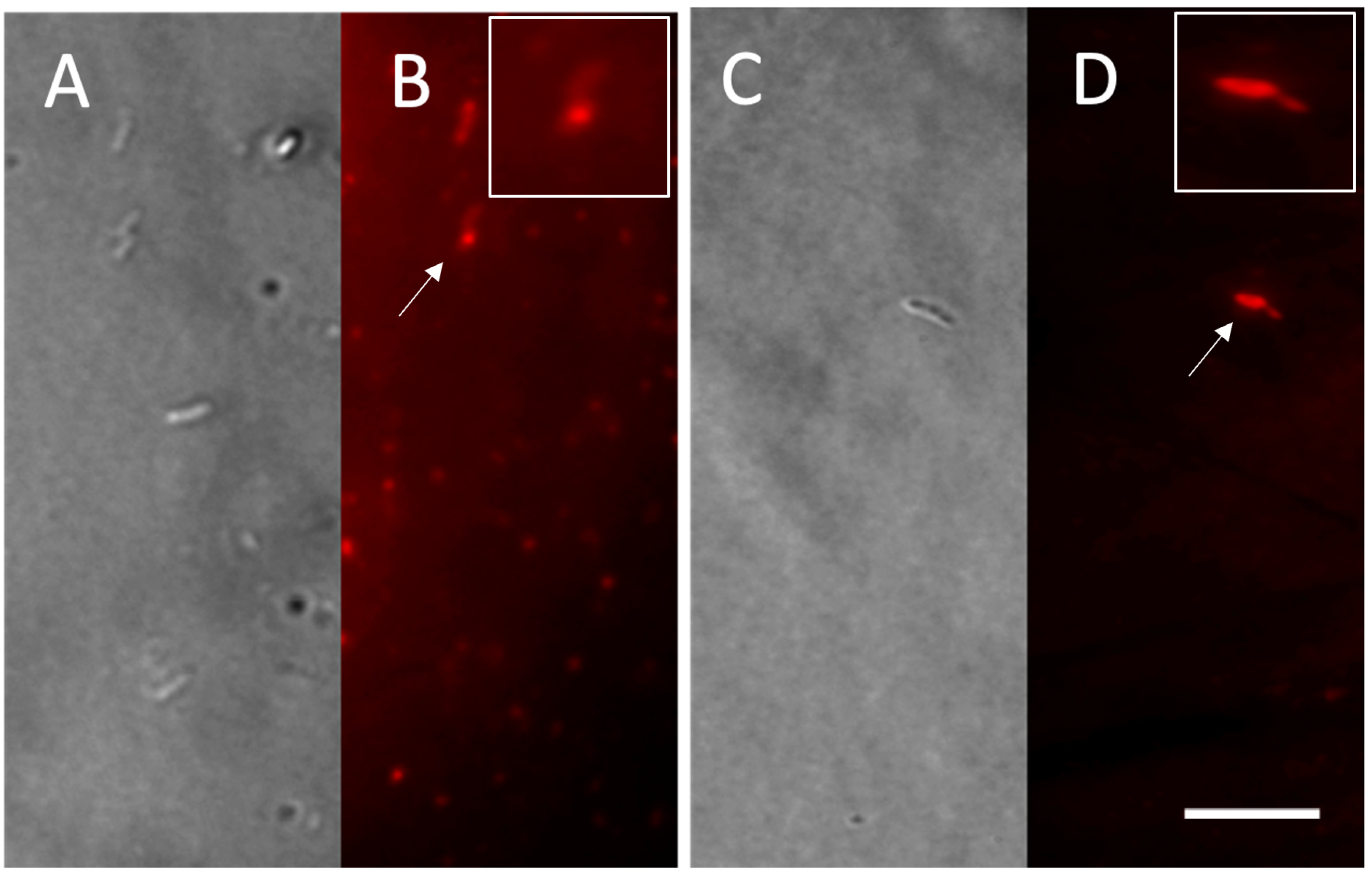
2.3. Nile Red Staining
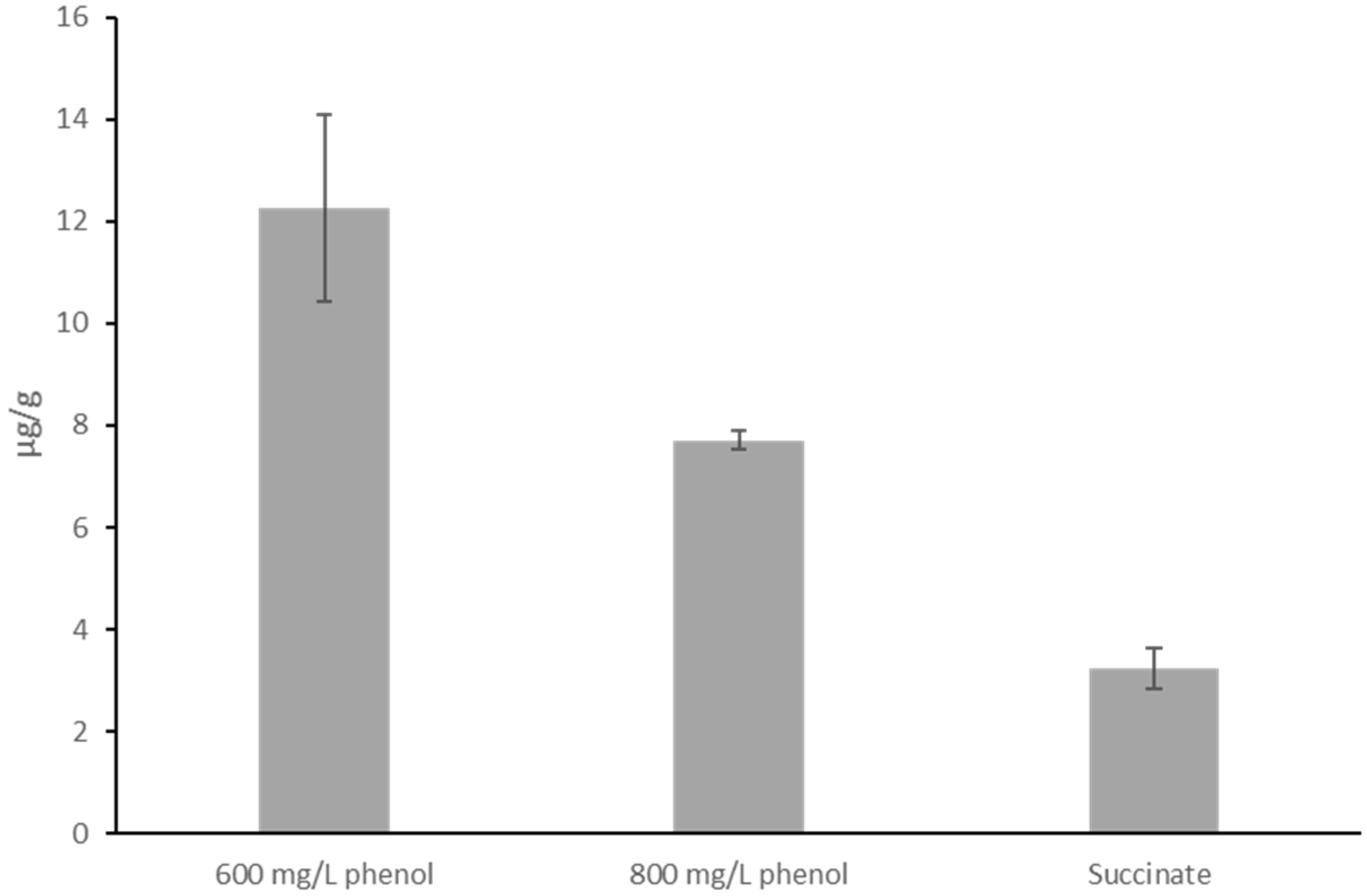
2.4. P(3HB) Quantification by HPLC
2.5. Isolation of P(3HB) Granules
2.6. Sample Preparation for the LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.7. MS/MS Protein Identification and Quantification
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Utilization of Phenol by Pseudomonas sp. phDV1
3.2. Accumulation of PHB Granules
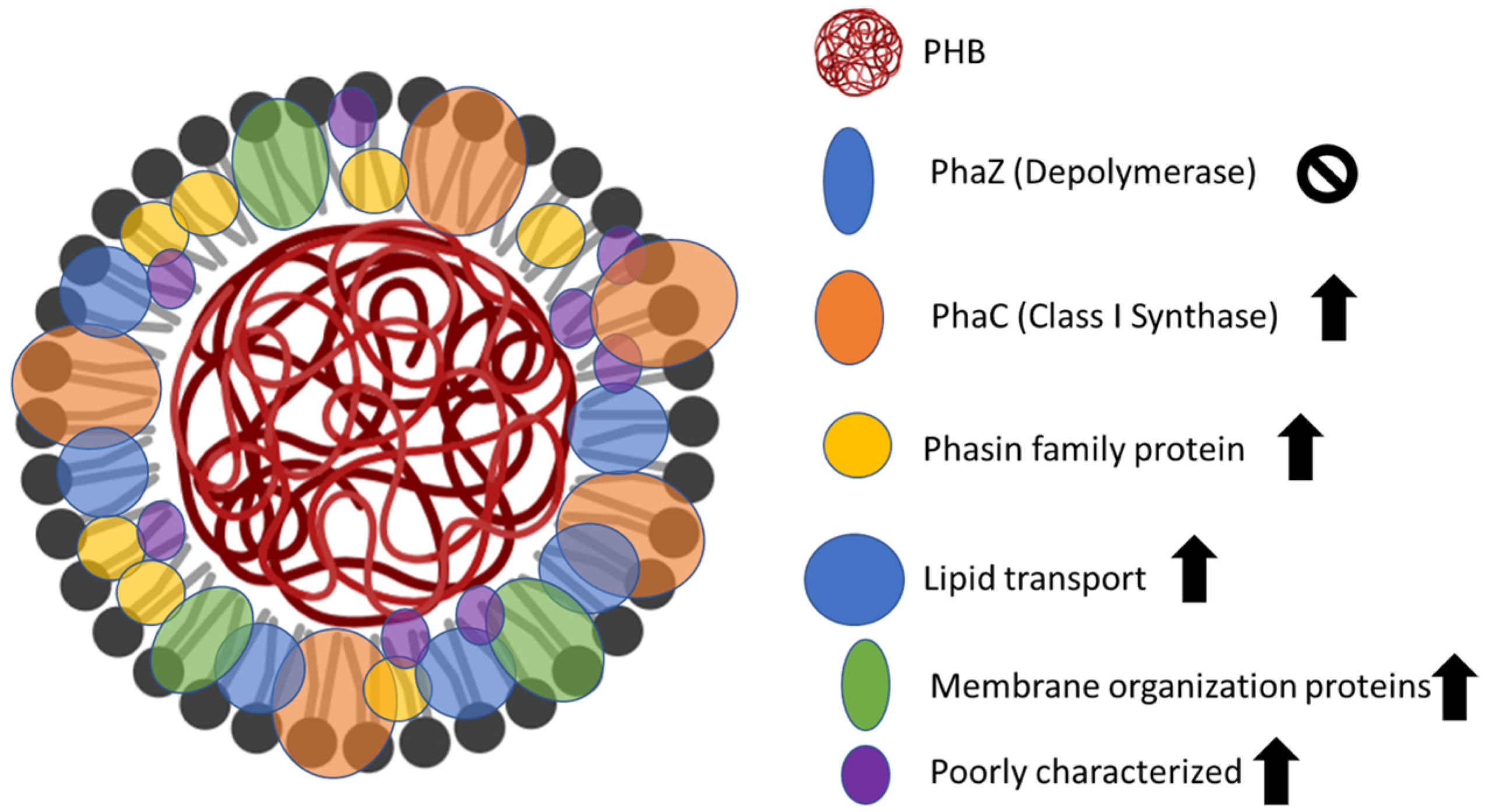
3.3. Isolation and Proteomic Analysis of PHB Granules
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Donno Novelli, L.; Moreno Sayavedra, S.; Rene, E.R. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production via Resource Recovery from Industrial Waste Streams: A Review of Techniques and Perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 331, 124985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoigne, M. Produit de Deshydratation et de Polymerisation de l’acide β-Oxybutyrique. Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol. 1926, 8, 770–782. [Google Scholar]
- Jendrossek, D. Polyhydroxyalkanoate Granules Are Complex Subcellular Organelles (Carbonosomes). J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3195–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradinho, J.C.; Oehmen, A.; Reis, M.A.M. Photosynthetic Mixed Culture Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production from Individual and Mixed Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs): Substrate Preferences and Co-Substrate Uptake. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 185, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, D.M.; Badawy, N.M. Phenol Removal from Wastewater Using Waste Products. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyratzakis, A.; Valsamidis, G.; Kanavaki, I.; Nikolaki, A.; Rupprecht, F.; Langer, J.D.; Tsiotis, G. Proteomic Characterization of the Pseudomonas sp. Strain PhDV1 Response to Monocyclic Aromatic Compounds. Proteomics 2021, 21, e2000003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymenakou, P.N.; Stephanou, E.G. Effect of Temperature and Additional Carbon Sources on Phenol Degradation by an Indigenous Soil Pseudomonad. Biodegradation 2005, 16, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirogianni, E.; Aivaliotis, M.; Papasotiriou, D.G.; Karas, M.; Tsiotis, G. Identification of Inducible Protein Complexes in the Phenol Degrader Pseudomonas sp. Strain PhDV1 by Blue Native Gel Electrophoresis and Mass Spectrometry. Amino Acids 2006, 30, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Valsamidis, G.; Mathioudaki, E.; Tsiotis, G. Complete Genome Sequence of Pseudomonas sp. Strain PhDV1, an Isolate Capable of Efficient Degradation of Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grage, K.; Jahns, A.C.; Parlane, N.; Palanisamy, R.; Rasiah, I.A.; Atwood, J.A.; Rehm, B.H.A. Bacterial Polyhydroxyalkanoate Granules: Biogenesis, Structure, and Potential Use as Nano-/Micro-Beads in Biotechnological and Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbuchel, A.; Aerts, K.; Babel, W.; Follner, C.; Kiebergesell, M.; Madkour, M.H.; Mayer, F.; Pieper-Furst, U.; Pries, A.; Valentin, H.E.; et al. Considerations on the Structure and Biochemistry of Bacterial Polyhydroxyalkanoic Acid Inclusions. Can. J. Microbiol. 1995, 41 (Suppl. 1), 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, N.A.; Hernández-Arriaga, A.M.; Kniewel, R.; Prieto, M.A. Phasin Interactome Reveals the Interplay of PhaF with the Polyhydroxyalkanoate Transcriptional Regulatory Protein PhaD in Pseudomonas Putida. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3922–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchta, K.; Chi, L.; Fuchs, H.; Pötter, M.; Steinbüchel, A. Studies on the Influence of Phasins on Accumulation and Degradation of PHB and Nanostructure of PHB Granules in Ralstonia Eutropha H16. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maehara, A.; Taguchi, S.; Nishiyama, T.; Yamane, T.; Doi, Y. A Repressor Protein, PhaR, Regulates Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Synthesis via Its Direct Interaction with PHA. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 3992–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Yamashita, K.; Wakuda, A.; Ichimura, K.; Maehara, A.; Maeda, M.; Taguchi, S. Autoregulator Protein PhaR for Biosynthesis of Polyhydroxybutyrate [P(3HB)] Possibly Has Two Separate Domains That Bind to the Target DNA and P(3HB): Functional Mapping of Amino Acid Residues Responsible for DNA Binding. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötter, M.; Müller, H.; Steinbüchel, A. Influence of Homologous Phasins (PhaP) on PHA Accumulation and Regulation of Their Expression by the Transcriptional Repressor PhaR in Ralstonia Eutropha H16. Microbiology 2005, 151, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HaileMariam, M.; Eguez, R.V.; Singh, H.; Bekele, S.; Ameni, G.; Pieper, R.; Yu, Y. S-Trap, an Ultrafast Sample-Preparation Approach for Shotgun Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2917–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant Enables High Peptide Identification Rates, Individualized p.p.b.-Range Mass Accuracies and Proteome-Wide Protein Quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Neuhauser, N.; Michalski, A.; Scheltema, R.A.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. Andromeda: A Peptide Search Engine Integrated into the MaxQuant Environment. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanavaki, I.; Drakonaki, A.; Geladas, E.D.; Spyros, A.; Xie, H.; Tsiotis, G. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production in Pseudomonas sp. PhDV1 Strain Grown on Phenol as Carbon Sources. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakonaki, A.; Mathioudaki, E.; Geladas, E.D.; Konsolaki, E.; Vitsaxakis, N.; Chaniotakis, N.; Xie, H.; Tsiotis, G. Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate by Genetically Modified Pseudomonas sp. PhDV1: A Comparative Study of Utilizing Wine Industry Waste as a Carbon Source. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Smet, M.J.; Eggink, G.; Witholt, B.; Kingma, J.; Wynberg, H. Characterization of Intracellular Inclusions Formed by Pseudomonas Oleovorans during Growth on Octane. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 154, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andler, R.; Pino, V.; Moya, F.; Soto, E.; Valdés, C.; Andreeßen, C. Synthesis of Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate (PHB) by Bacillus Cereus Using Grape Residues as Sole Carbon Source. Int. J. Biobased Plast. 2021, 3, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendrossek, D.; Pfeiffer, D. New Insights in the Formation of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Granules (Carbonosomes) and Novel Functions of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate). Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2357–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.; Tham, J.L.; McKeever, K.; Dillon, E.; O’Connell, D.; Scholz, D.; Simpson, J.C.; O’Connor, K.; Narancic, T.; Cagney, G. Comprehensive Proteomics Analysis of Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Biology in Pseudomonas Putida KT2440: The Outer Membrane Lipoprotein OprL Is a Newly Identified Phasin. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2024, 23, 100765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Oh, J.; Jung, J.H.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, S.Y. Three-Dimensional Label-Free Visualization and Quantification of Polyhydroxyalkanoates in Individual Bacterial Cell in Its Native State. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2103956118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirapelle, E.F.; Müller-Santos, M.; Tadra-Sfeir, M.Z.; Kadowaki, M.A.S.; Steffens, M.B.R.; Monteiro, R.A.; Souza, E.M.; Pedrosa, F.O.; Chubatsu, L.S. Identification of Proteins Associated with Polyhydroxybutyrate Granules from Herbaspirillum Seropedicae SmR1—Old Partners, New Players. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauf, W.; Watzer, B.; Roos, N.; Klotz, A.; Forchhammer, K. Photoautotrophic Polyhydroxybutyrate Granule Formation Is Regulated by Cyanobacterial Phasin PhaP in Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC 6803. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4411–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendrossek, D. (Ed.) Bacterial Organelles and Organelle-like Inclusions; Microbiology Monographs; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 34, ISBN 978-3-030-60172-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hokamura, A.; Fujino, K.; Isoda, Y.; Arizono, K.; Shiratsuchi, H.; Matsusaki, H. Characterization and Identification of the Proteins Bound to Two Types of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Granules in Pseudomonas sp. 61-3. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, A.L.; Osorio, A.; Legorreta-Hissner, T.; Lara-Martinez, R.; Jimenez-Garcia, L.F.; Camarena, L.; Poggio, S. A New Type of Phasin Characterized by the Presence of a Helix-Hairpin-Helix Domain Is Required for Normal Polyhydroxybutyrate Accumulation and Granule Organization in Caulobacter Crescentus. Mol. Microbiol. 2023, 120, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, S.; Castellanos, M.; Bedoya-Pérez, L.P.; Canales-Herrerías, P.; Espín, G.; Muriel-Millán, L.F. Outer Membrane Protein i Is Associated with Poly-β-Hydroxybutyrate Granules and Is Necessary for Optimal Polymer Accumulation in Azotobacter Vinelandii on Solid Medium. Microbiology 2019, 165, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sznajder, A.; Pfeiffer, D.; Jendrossek, D. Comparative Proteome Analysis Reveals Four Novel Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Granule-Associated Proteins in Ralstonia Eutropha H16. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1847–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geladas, E.D.; Lyratzakis, A.; Drakonaki, A.; Gkikas, G.; Tsiotis, G. Isolation and Characterization of Carbonosomes from Pseudomonas sp. phDV1 Grown Using Phenol as Carbon Source. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020369
Geladas ED, Lyratzakis A, Drakonaki A, Gkikas G, Tsiotis G. Isolation and Characterization of Carbonosomes from Pseudomonas sp. phDV1 Grown Using Phenol as Carbon Source. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(2):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020369
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeladas, Ermis Dionysios, Alexandros Lyratzakis, Athina Drakonaki, Georgios Gkikas, and Georgios Tsiotis. 2025. "Isolation and Characterization of Carbonosomes from Pseudomonas sp. phDV1 Grown Using Phenol as Carbon Source" Microorganisms 13, no. 2: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020369
APA StyleGeladas, E. D., Lyratzakis, A., Drakonaki, A., Gkikas, G., & Tsiotis, G. (2025). Isolation and Characterization of Carbonosomes from Pseudomonas sp. phDV1 Grown Using Phenol as Carbon Source. Microorganisms, 13(2), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020369





