First Isolation and Genomic Characterization of Escherichia ruysiae in Togo from a Five-Year-Old Patient with Gastroenteritis and Bloody Diarrhea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Isolation and Identification
2.3. Susceptibility Testing
2.4. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. Assembly and Annotation
2.6. Resistome, Virulome Genome Sequence Typing
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Case Description
3.2. Phenotypic, Biochemical Characterization and Resistance Profile
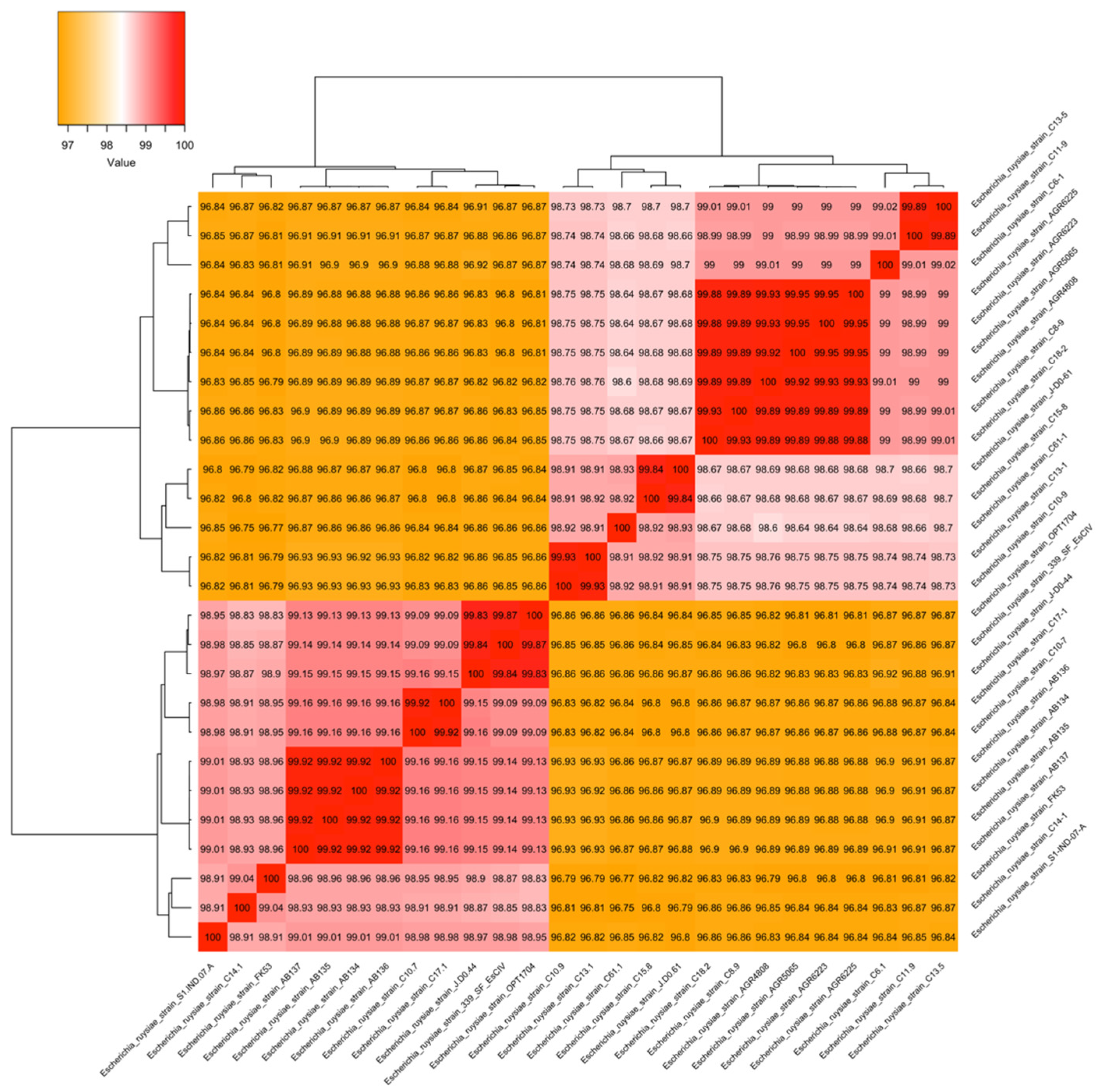
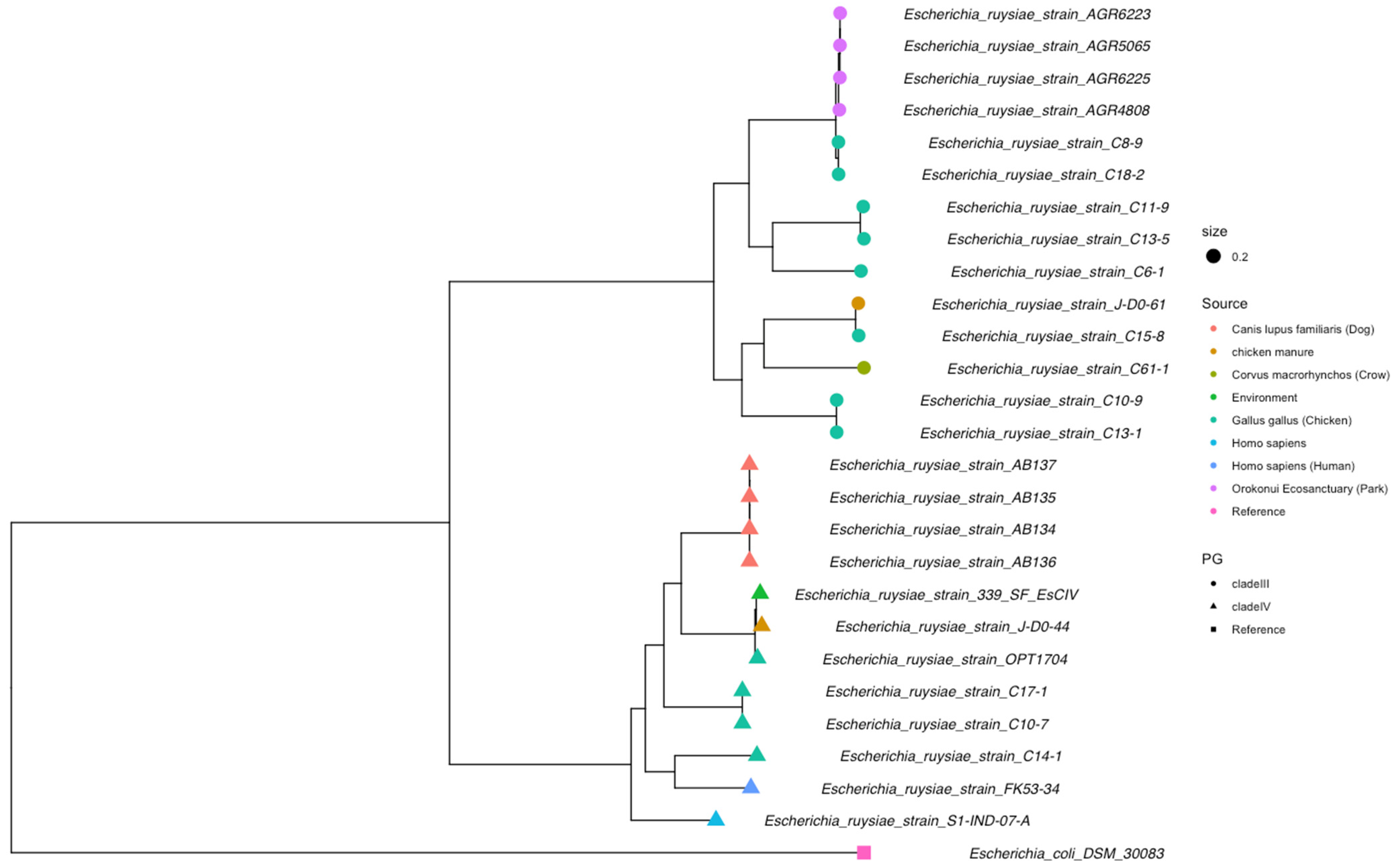
3.3. Genomics Features and Challenges in the Strain Identification
3.4. Resistome, Virulome, and Mobilome of FK53-34
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tenaillon, O.; Skurnik, D.; Picard, B.; Denamur, E. The population genetics of commensal Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMS. Le Genre Escherichia Englobe les Espèces Commensales et Pathogènes. Geneve. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/fr/news-room/fact-sheets (accessed on 18 June 2024).
- Escherich, T. The Intestinal Bacteria of the Neonate and Breast-Fed Infant. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, S.T.; Friedmann, H.C.; Sims, R.H. Theodor Escherich: The First Pediatric Infectious Diseases Physician? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Putten, B.C.L.; Matamoros, S.; Mende, D.R.; Scholl, E.R.; Consortium†, C.; Schultsz, C. Escherichia ruysiae sp. nov., a novel Gram-stain-negative bacterium, isolated from a faecal sample of an international traveller. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.J.; Davis, B.R.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Riddle, C.F.; McWhorter, A.C.; Allen, S.D.; Farmer, J.J.; Saitoh, Y.; Fanning, G.R. Atypical biogroups of Escherichia coli found in clinical specimens and description of Escherichia hermannii sp. nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1982, 15, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, J.J., 3rd; Fanning, G.R.; Davis, B.R.; O’HAra, C.M.; Riddle, C.; Hickman-Brenner, F.W.; Asbury, M.A.; Lowery, V.A., 3rd; Brenner, D.J. Escherichia fergusonii and Enterobacter taylorae, two new species of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from clinical specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 21, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huys, G.; Cnockaert, M.; Janda, J.M.; Swings, J. Escherichia albertii sp. nov., a diarrhoeagenic species isolated from stool specimens of Bangladeshi children. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jin, D.; Lan, R.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Dai, H.; Lu, S.; Hu, S.; Xu, J. Escherichia marmotae sp. nov., isolated from faeces of Marmota himalayana. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2130–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, K.; Tanabe, M.; Takizawa, S.; Kasahara, S.; Denda, T.; Koide, S.; Hayashi, W.; Nagano, Y.; Nagano, N. Zoonotic potential and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia spp. in urban crows in Japan-first detection of E. marmotae and E. ruysiae. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 100, 102040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddi, G.; Piras, F.; Gymoese, P.; Torpdahl, M.; Meloni, M.P.; Cuccu, M.; Migoni, M.; Cabras, D.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; De Santis, E.P.L.; et al. Pathogenic profile and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli, Escherichia marmotae and Escherichia ruysiae detected from hunted wild boars in Sardinia (Italy). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 421, 110790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Madueno, E.I.; Aldeia, C.; Sendi, P.; Endimiani, A. Escherichia ruysiae May Serve as a Reservoir of Antibiotic Resistance Genes across Multiple Settings and Regions. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0175323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, K.; Franz, H. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Anal Chem. 1988, 60, 2299–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Mariani-Kurkdjian, P. Chapitre 15—Diagnostic bactériologique des infections gastro-intestinales. In Bactériologie Médicale; Elsevier Masson: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council (U.S.). Éditeur Biosafety in the Laboratory: Prudent Practices for the Handling and Disposal of Infectious Materials; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J. 301 Control of Hospital Waste; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Avril, J. Technique d’une Coproculture. Med. Mal. Infect. 1979, 9, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K. Microbiology Clinical Laboratory SOPs. GHL. Available online: https://globalhealthlaboratories.tghn.org (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- March, S.B.; Ratnam, S. Sorbitol-MacConkey medium for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with hemorrhagic colitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1986, 23, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.C.; Renaux, C.; Catherinot, E.; Limousin, L.; Couderc, L.J.; Vasse, M. Rapid identification of fungi from respiratory samples by Bruker Biotyper matrix–assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight using ID-FUNGI plates. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 40, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osthoff, M.; Gürtler, N.; Bassetti, S.; Balestra, G.; Marsch, S.; Pargger, H.; Weisser, M.; Egli, A. Impact of MALDI-TOF-MS-based identification directly from positive blood cultures on patient management: A controlled clinical trial. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegger, M.; Leihof, R.F.; Baig, S.; Sieber, R.N.; Thingholm, K.R.; Marvig, R.L.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Nielsen, K.L. A snapshot of diversity: Intraclonal variation of Escherichia coli clones as commensals and pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 310, 151401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. Comité de L’antibiogramme de la Société Française de Microbiologie; Société Française de Microbiologie: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (35e Éd.). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2025. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m100/ (accessed on 29 March 2025).
- Emiyu, K.; Lelisa, K. Review on Illumina Sequencing Technology. Austin J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Husb. 2022, 9, 1088. Available online: https://austinpublishinggroup.com/veterinary-science-research/fulltext/avsah-v9-id1088.php (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Illumina. MiniSeq System Guide. 2023. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/content/dam/illumina-support/documents/documentation/system_documentation/translations/miniseq-system-guide-1000000002695-fra.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Aworh, M.K.; Ekeng, E.; Nilsson, P.; Egyir, B.; Owusu-Nyantakyi, C.; Hendriksen, R.S. Extended-Spectrum ß-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Among Humans, Beef Cattle, and Abattoir Environments in Nigeria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 869314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, G.; Fang, L.; Geng, R.; Shi, S.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Lin, M.; Chen, J.; Si, Y.; et al. The Marine-Origin Exopolysaccharide-Producing Bacteria Micrococcus antarcticus HZ Inhibits Pb Uptake in Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) and Affects Rhizosphere Microbial Communities. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chklovski, A.; Parks, D.H.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM2: A rapid, scalable and accurate tool for assessing microbial genome quality using machine learning. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk v2: Memory friendly classification with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 5315–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Moreira, B.; Vinuesa, P. GET_HOMOLOGUES, a Versatile Software Package for Scalable and Robust Microbial Pangenome Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7696–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marçais, G.; Delcher, A.L.; Phillippy, A.M.; Coston, R.; Salzberg, S.L.; Zimin, A. MUMmer4: A fast and versatile genome alignment system. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1005944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. ABRicate, un Logiciel Combinanr Différentes Bases de Données pour le Dépistage de Masse des Contigs pour la Résistance aux Antimicrobiens ou les Gènes de Virulence. 2020. GGitHub. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/abricate (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Florensa, A.F.; Kaas, R.S.; Clausen, P.T.L.C.; Aytan-Aktug, D.; Aarestrup, F.M. ResFinder—An open online resource for identification of antimicrobial resistance genes in next-generation sequencing data and prediction of phenotypes from genotypes. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000748. Available online: https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/journal/mgen/10.1099/mgen.0.000748 (accessed on 8 October 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcock, B.P.; Raphenya, A.R.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.L.V.; Cheng, A.A.; Liu, S.; et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, gkz935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.; Donnola, S.B.; Sadeghi, Z.; Lu, L.; Erokwu, B.O.; Kavran, M.; Hijaz, A.; Flask, C.A. Intrarenal Injection of Escherichia coli in a Rat Model of Pyelonephritis. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 125, 54649. [Google Scholar]
- Bonin, N.; Doster, E.; Worley, H.; Pinnell, L.J.; Bravo, J.E.; Ferm, P.; Marini, S.; Prosperi, M.; Noyes, N.; Morley, P.S.; et al. MEGARes and AMR++, v3.0: An updated comprehensive database of antimicrobial resistance determinants and an improved software pipeline for classification using high-throughput sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D744–D752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2022: A general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D912–D917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessonov, K.; Laing, C.; Robertson, J.; Yong, I.; Ziebell, K.; Gannon, V.P.J.; Nichani, A.; Arya, G.; Nash, J.H.E.; Christianson, S. ECTyper: In silico Escherichia coli serotype and species prediction from raw and assembled whole-genome sequence data. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000728. Available online: https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/journal/mgen/10.1099/mgen.0.000728 (accessed on 8 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Maiden, M.C.J.; van Rensburg, M.J.J.; Bray, J.E.; Earle, S.G.; Ford, S.A.; Jolley, K.A.; McCarthy, N.D. MLST revisited: The gene-by-gene approach to bacterial genomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tange, O. GNU Parallel 20250222 (Grete Tange’). Zenodo 2025, 22, 10.5281. Available online: https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.14911163 (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Clermont, O.; Gordon, D.; Denamur, E. Guide to the various phylogenetic classification schemes for Escherichia coli and the correspondence among schemes. Microbiology 2015, 161, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, M.; Ekelund, O.; Aarestrup, F.; Canton, R.; Doumith, M.; Giske, C.; Grundman, H.; Hasman, H.; Holden, M.; Hopkins, K.; et al. The role of whole genome sequencing in antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacteria: Report from the EUCAST Subcommittee. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, N.M.; Gilroy, R.; Getino, M.; Foster-Nyarko, E.; van Vliet, A.H.; La Ragione, R.M.; Pallen, M.J. Remarkable genomic diversity among Escherichia isolates recovered from healthy chickens. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dione, N.; Mlaga, K.D.; Liang, S.; Jospin, G.; Marfori, Z.; Alvarado, N.; Scarsella, E.; Uttarwar, R.; Ganz, H.H. Comparative genomic and phenotypic description of Escherichia ruysiae: A newly identified member of the gut microbiome of the domestic dog. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1558802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauget, M.; Valot, B.; Bertrand, X.; Hocquet, D. Can MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Reasonably Type Bacteria? Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, C. Comparative Evaluation of Biochemical and Molecular Techniques for Bacterial Identification, ResearchGate, May 2025. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/391905521_Comparative_Evaluation_of_Biochemical_and_Molecular_Techniques_for_Bacterial_Identification (accessed on 4 November 2025).
- Bajaj, P.; Singh, N.S.; Virdi, J.S. Escherichia coli β-Lactamases: What Really Matters. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 417. Available online: http://journal.frontiersin.org/Article/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00417/abstract (accessed on 25 September 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerson, S.; Betts, J.W.; Lucaßen, K.; Nodari, C.S.; Wille, J.; Josten, M.; Göttig, S.; Nowak, J.; Stefanik, D.; Roca, I.; et al. Investigation of Novel pmrB and eptA Mutations in Isogenic Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Associated with Colistin Resistance and Increased Virulence In Vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01586-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, A.R.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Walkty, A.; Baxter, M.R.; Denisuik, A.J.; McCracken, M.; Mulvey, M.R.; Adam, H.J.; Bay, D.; Zhanel, G.G. Comparison of phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing results and WGS-derived genotypic resistance profiles for a cohort of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli collected from Canadian hospitals: CANWARD 2007–18. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.S.; Jelacic, S.; Habeeb, R.L.; Watkins, S.L.; Tarr, P.I. The Risk of the Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome after Antibiotic Treatment of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yang, W.; Jiang, X.; Yao, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, B. Virulence-related O islands in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1992237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.L.; Low, A.J.; Koziol, A.G.; Thomas, M.C.; Leclair, D.; Tamber, S.; Wong, A.; Blais, B.W.; Carrillo, C.D. Systematic Evaluation of Whole Genome Sequence-Based Predictions of Salmonella Serotype and Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.; Dallman, T.J.; Shabaan, S.; Hanson, M.; Allison, L. Validation of Whole-Genome Sequencing for Identification and Characterization of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli to Produce Standardized Data to Enable Data Sharing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01388-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger, F.O.; Borgwardt, L.; Jespersen, A.S.; Hansen, A.R.; Bertelsen, B.; Kodama, M.; Nielsen, F.C. Whole genome sequencing in clinical practice. BMC Med. Genom. 2024, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, J.; Czeczulin, J.R.; Harrington, S.; Hicks, S.; Henderson, I.R.; Bouguénec, C.; Gounon, P.; Phillips, A.; Nataro, J.P. A novel dispersin protein in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, J.; Sheikh, J.; Mizuguchi, K.; Luisi, B.; Burland, V.; Boutin, A.; Rose, D.J.; Blattner, F.R.; Nataro, J.P. The Export of Coat Protein from Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli by a Specific ATP-binding Cassette Transporter System. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45680–45689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farfan, M.J.; Torres, A.G. Molecular Mechanisms That Mediate Colonization of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, K.S. Role of OmpA and IbeB in Escherichia coli K1 Invasion of Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Pediatr. Res. 2002, 51, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S. Pathogenesis of bacterial meningitis: From bacteraemia to neuronal injury. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick-Cheng, A.E.; Sintsova, A.; Smith, S.N.; Krauthammer, M.; Eaton, K.A.; Mobley, H.L.T. The Gene Expression Profile of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli in Women with Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections Is Recapitulated in the Mouse Model. mBio 2020, 11, e01412-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tested Substrates | FK53-34 (This Study) | E. ruysiae [6] | E. coli [11] |
|---|---|---|---|
| ONPG | + | + | + |
| ADH | − | − | + |
| LDC | − | − | + |
| ODC | + | + | + |
| CIT | + | − | − |
| H2S | − | − | − |
| URE | − | − | − |
| TDA | + | − | − |
| IND | − | +/− | + |
| VP | − | + | − |
| GEL | − | − | − |
| GLU | + | + | + |
| MAN | + | + | + |
| INO | − | − | − |
| SOR | + | + | + |
| RHA | + | + | + |
| SAC | − | − | + |
| MEL | + | − | − |
| AMY | − | − | − |
| ARA | + | + | + |
| Isolate | aadA1-pm | blaLAP-2 | qnrS1 | sul2 | tet(A) | blaCTX-M-15 | blaEC-15 | blaEC-8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABC134 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| ABC135 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| ABC136 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| ABC137 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| C10-7 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| C10-9 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| C11-9 | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | − |
| C13-1 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| C13-5 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| C14-1 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| C15-8 | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | − |
| C17-1 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| C18-2 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| C6-1 | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + |
| C61-1 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| C8-9 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| OPT1704 | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | − |
| S1-IND-07-A | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − |
| FK53-34 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| Isolates | aap/aspU | aatA | aatB | aatC | aatP | agn43 | senB | traJ | traT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABC134 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| ABC135 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| ABC136 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| ABC137 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C10-7 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C10-9 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C11-9 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C13-1 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C13-5 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C14-1 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C15-8 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C17-1 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C18-2 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C6-1 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C61-1 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| C8-9 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| OPT1704 | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| S1-IND-07-A | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| FK53-34 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabo, K.; Dione, N.; Mlaga, K.D.; Tchacondo, T. First Isolation and Genomic Characterization of Escherichia ruysiae in Togo from a Five-Year-Old Patient with Gastroenteritis and Bloody Diarrhea. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122694
Kabo K, Dione N, Mlaga KD, Tchacondo T. First Isolation and Genomic Characterization of Escherichia ruysiae in Togo from a Five-Year-Old Patient with Gastroenteritis and Bloody Diarrhea. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122694
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabo, Kossi, Niokhor Dione, Kodjovi D. Mlaga, and Tchadjobo Tchacondo. 2025. "First Isolation and Genomic Characterization of Escherichia ruysiae in Togo from a Five-Year-Old Patient with Gastroenteritis and Bloody Diarrhea" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122694
APA StyleKabo, K., Dione, N., Mlaga, K. D., & Tchacondo, T. (2025). First Isolation and Genomic Characterization of Escherichia ruysiae in Togo from a Five-Year-Old Patient with Gastroenteritis and Bloody Diarrhea. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122694







