Effects of Dietary Rapeseed Meal on Growth Performance, Intestinal Structure, Gut Microbiota, and Related Gene Expression of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Diets
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Chemical Analysis
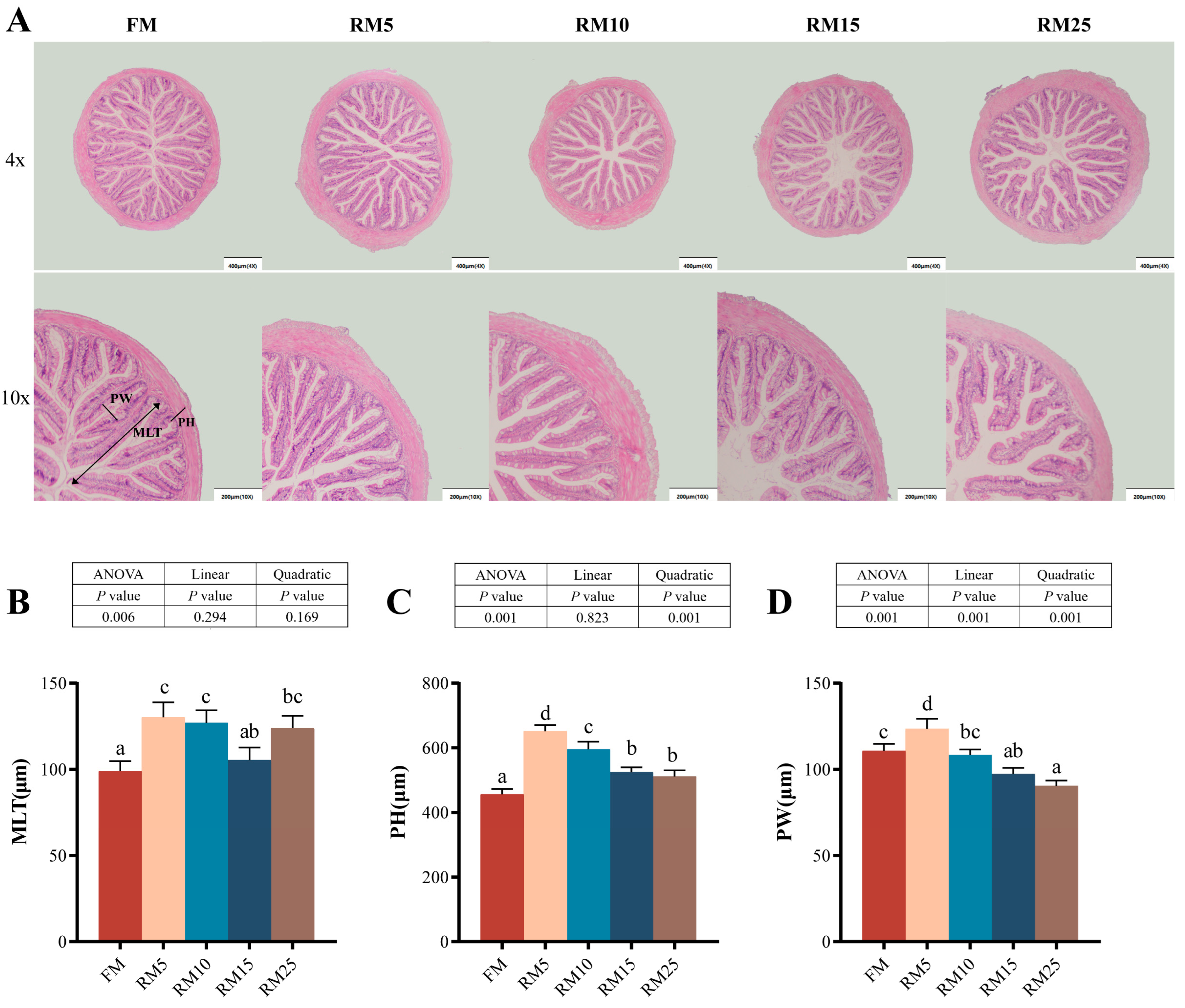
2.5. Intestinal Histological and Morphological Analysis
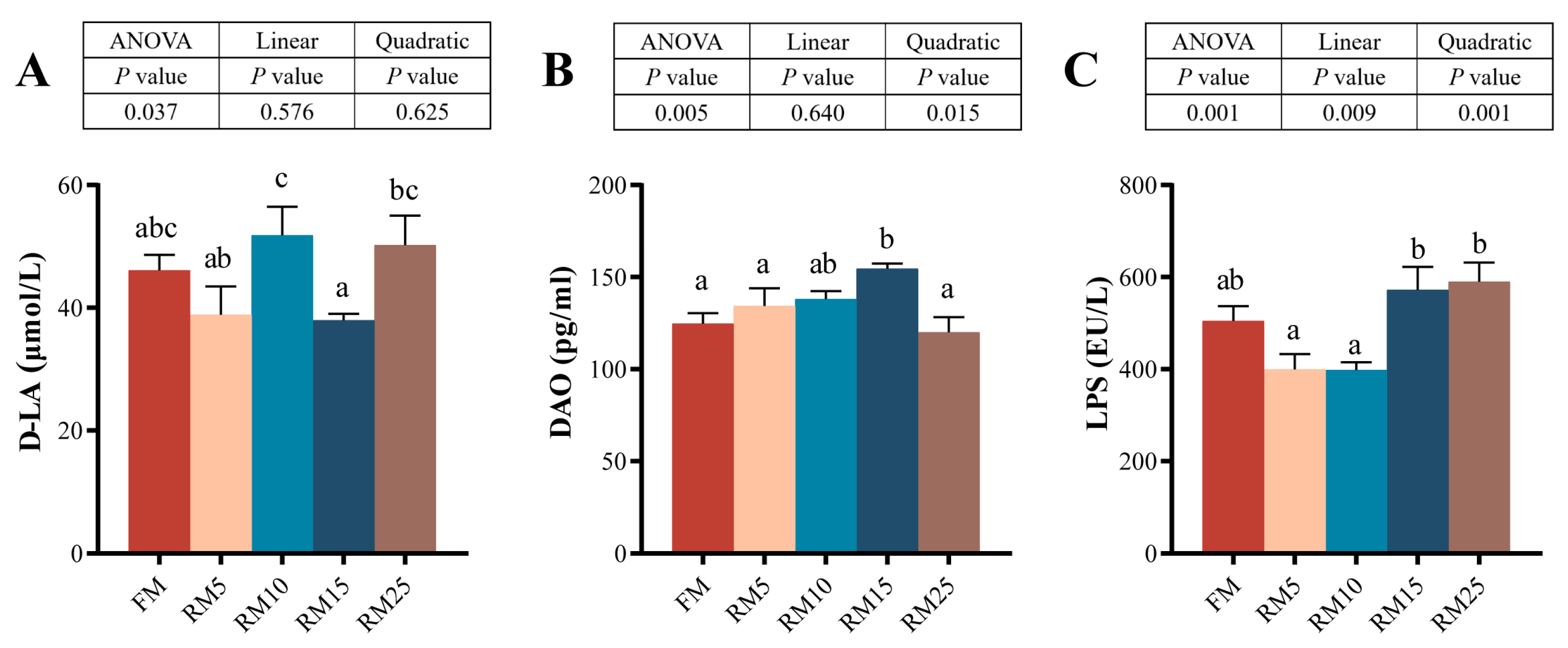
2.6. Intestinal Permeability Assessment
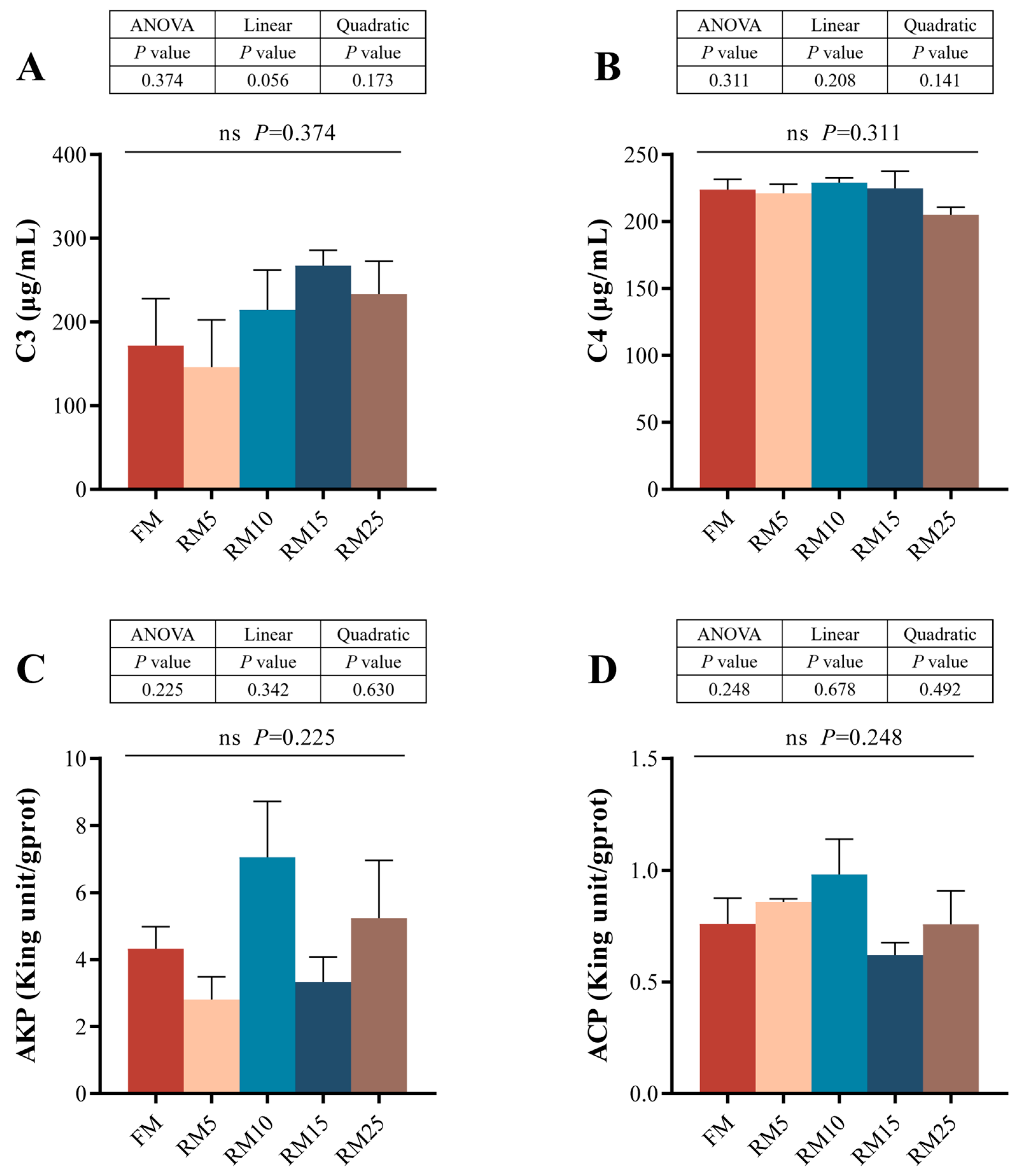
2.7. Physiological and Biochemical Analysis of the Intestine
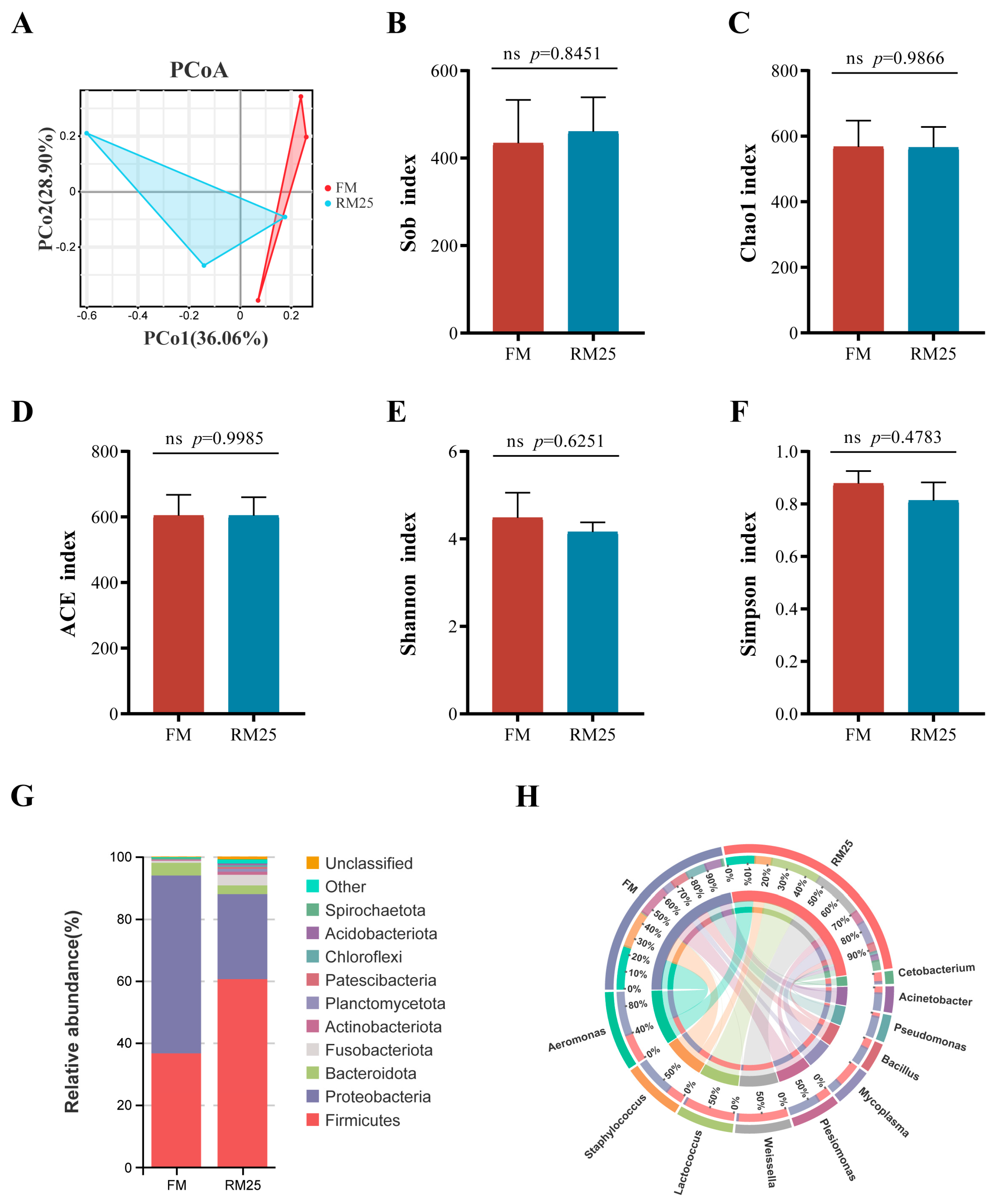
2.8. Intestinal Microbial Analysis
2.9. Intestinal Transcriptomic Analysis
2.10. Quantitative PCR
2.11. Calculations
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Morphology Indices
3.3. Whole-Body Composition
3.4. The Intestinal Structure
3.5. Liver Histology Structure
3.6. The Intestinal Permeability
3.7. The Intestinal Physiological and Biochemical Analysis
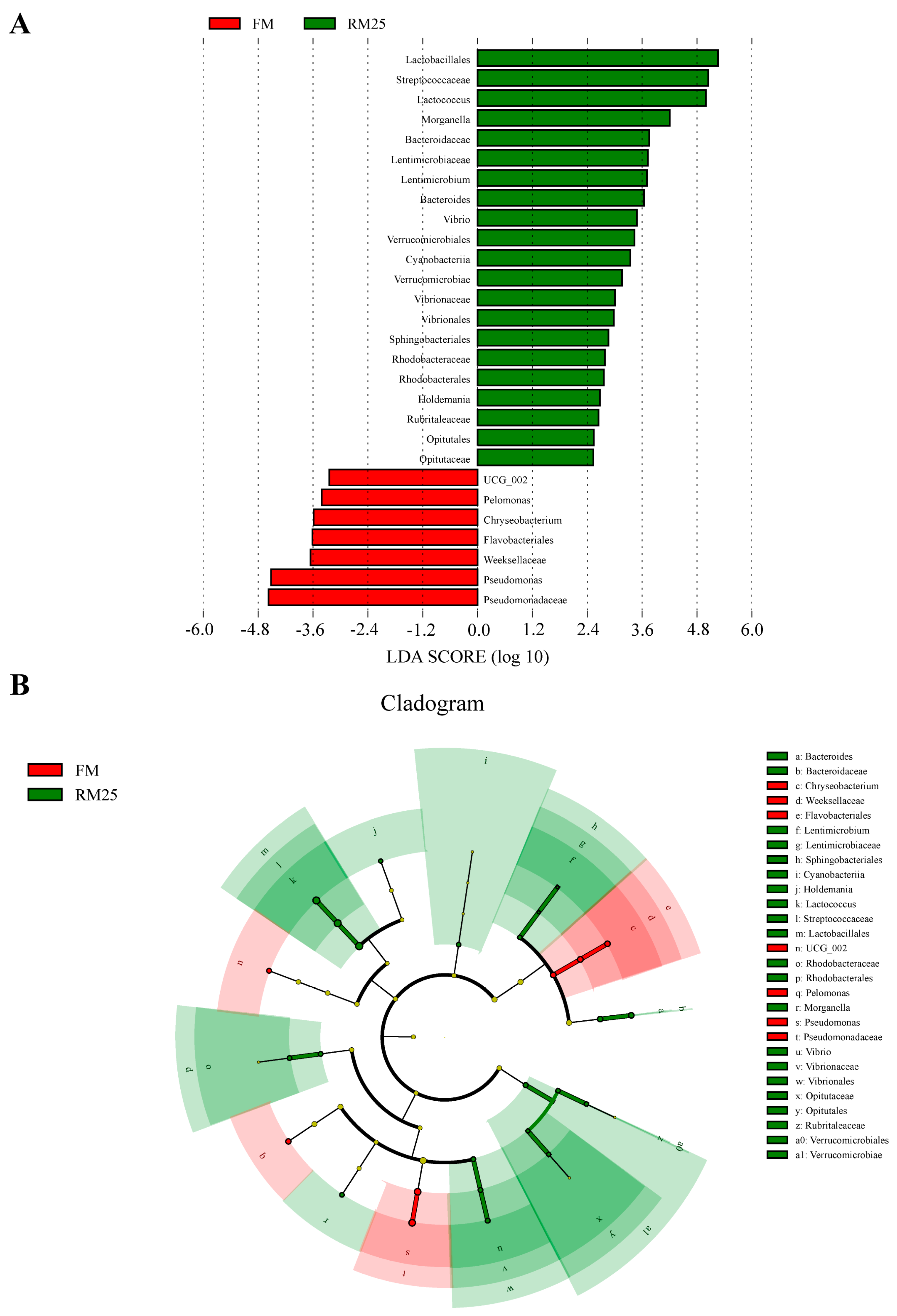
3.8. Analysis of the Intestinal Microbiota
3.9. Analysis of the Intestinal Transcriptome
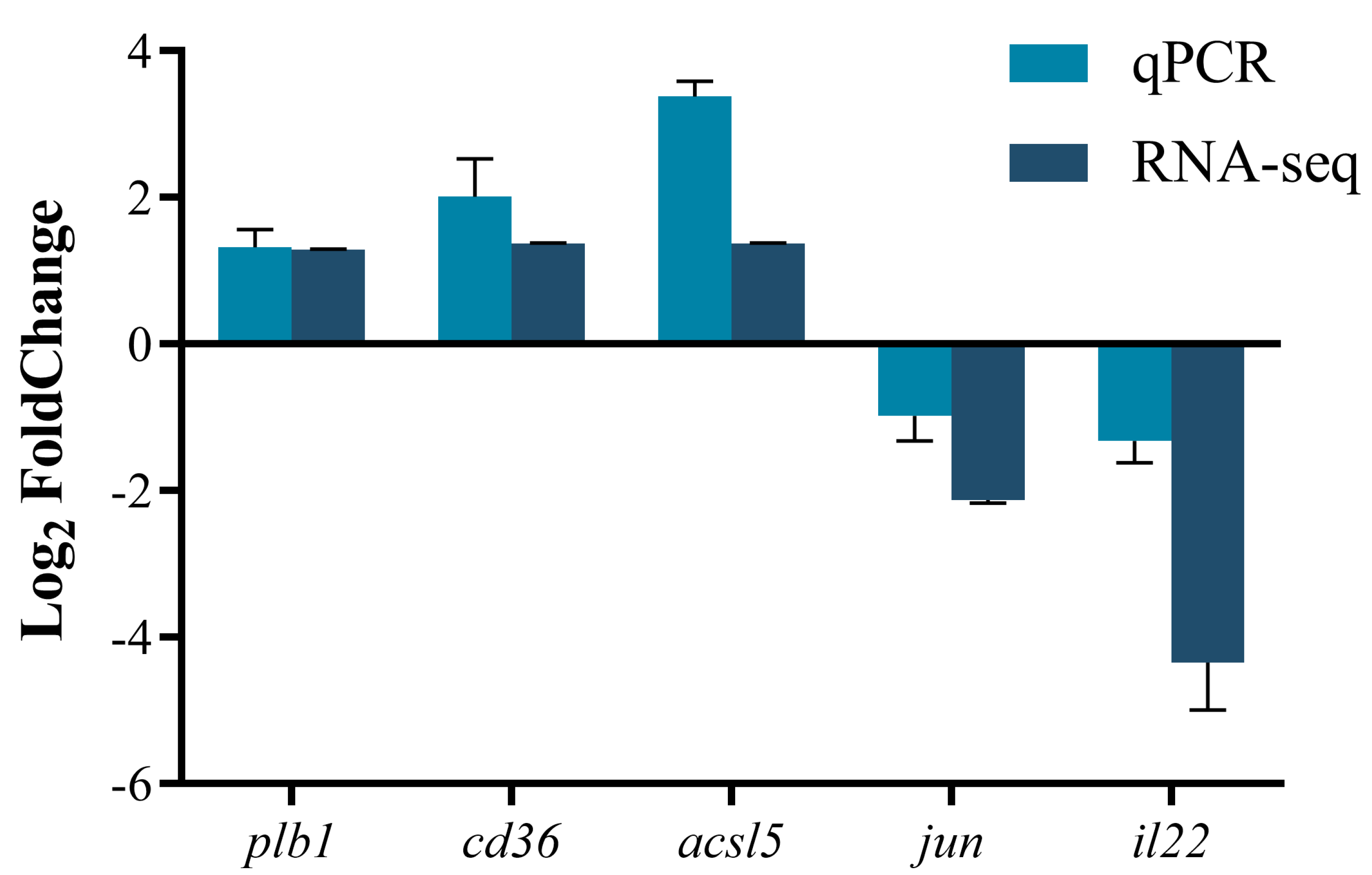
3.10. Verification of the Reliability of Transcriptome Data by qPCR
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Diets Containing Rapeseed Meal on the Growth Performance of Largemouth Bass
4.2. Effects of Diets Containing Rapeseed Meal on the Morphological Indicators and Whole-Body Composition of Largemouth Bass
4.3. Effects of Diets Containing Rapeseed Meal on the Liver Structure of Largemouth Bass
4.4. Effects of Diets Containing Rapeseed Meal on the Intestinal Structure and Biochemical Indicators of Largemouth Bass
4.5. Effects of Diets Containing Rapeseed Meal on the Intestinal Microbiota of Largemouth Bass
4.6. Effects of Diets Containing Rapeseed Meal on the Gene Expression of Largemouth Bass
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| Full Name | Abbreviation |
| Fish meal | FM |
| Rapeseed meal | RM |
| Muscle layer thickness | MLT |
| Plica height | PH |
| Plica width | PW |
| D-Lactic acid | D-LA |
| Diamine oxidase | DAO |
| Lipopolysaccharide | LPS |
| Acid phosphatase | ACP |
| Alkaline phosphatase | AKP |
| Initial body weight | IBW |
| Final body weight | FBW |
| Weight gain rate | WGR |
| Specific growth rate | SGR |
| Protein efficiency ratio | PER |
| Feed conversion ratio | FCR |
| Feed intake | FI |
| Survival rate | SR |
| Visceral somatic index | VSI |
| Hepatosomatic index | HSI |
| Abdominal fat rate | AFR |
| Intestinal weight index | ISI |
| Intestinal length index | ILI |
| Antinutritional factors | ANFs |
References
- Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Pan, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Z. Effect of dietary replacement of fish meal by poultry by-product meal on the growth and hepatic health in loach (Paramisgurnus dabryanus). Aquac. Rep. 2024, 39, 102441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.-X.; Song, K. Replacement of fishmeal with soybean meal and mineral supplements in diets of Litopenaeus vannamei reared in low-salinity water. Aquaculture 2017, 473, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, J.; Feng, J.; He, J.; Lou, Y.; Zhou, Q. Effects of dietary soy protein concentrate meal on growth, immunity, enzyme activity and protein metabolism in relation to gene expression in large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture 2017, 477, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Chen, P.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Huang, D.; Mai, K.; Zhang, W. Dietary cottonseed protein concentrate affected the flesh texture and myofiber characteristics of large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture 2024, 592, 741176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-J.; Dai, J.-H.; Cai, M.-L.; Cheng, K.-M.; Hu, Y.; Luo, Z. Effects of dietary replacement of fishmeal by cottonseed meal on the growth performance, immune and antioxidant responses, and muscle quality of juvenile crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 31, 101639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, F.Y.; Tang, B.B.; Luo, C.Z.; Wang, Y.; Ge, X.P.; Yang, Y.H. An Evaluation of Replacing Fishmeal with Rapeseed Meal in the Diet of Pseudobagrus ussuriensis: Growth, Feed Utilization, Nonspecific Immunity, and Growth-related Gene Expression. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2017, 49, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, F.; Harloff, H.J.; Tressel, R.P.; Kock, T.; Schulz, C. Effects of highly purified rapeseed protein isolate as fishmeal alternative on nutrient digestibility and growth performance in diets fed to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Estrada, U.; González-Alfaro, K.; Shene, C. Replacement of Fish Meal by Solid State Fermented Lupin (Lupinus albus) Meal with Latobacillus plantarum 299v: Effect on Growth and Immune Status of Juvenile Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Ann. Anim. Sci. 2020, 20, 991–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, E.; Lefillanca, J.K.; Carrasco, J.; Davies, S.J.; Hernandez Arias, A.J. Evaluation of andean lupin (Lupinus mutabilis) seed meal as a dietary component on growth performance, feed utilization, nutrient digestibility, and liver histology of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Juveniles. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 34, 101919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke-McKellep, A.M.; Press, C.M.; Baeverfjord, G.; Krogdahl, Å.; Landsverk, T. Changes in immune and enzyme histochemical phenotypes of cells in the intestinal mucosa of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., with soybean meal-induced enteritis. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 23, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatlin, D.M.; Barrows, F.T.; Brown, P.; Dabrowski, K.; Gaylord, T.G.; Hardy, R.W.; Herman, E.; Hu, G.; Krogdahl, Å.; Nelson, R.; et al. Expanding the utilization of sustainable plant products in aquafeeds: A review. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 551–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.D.; Bharadwaj, A.S.; Brown, P.B. Soybean lectins and trypsin inhibitors, but not oligosaccharides or the interactions of factors, impact weight gain of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2010, 306, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.J.; Seiliez, I. Protein and amino acid nutrition and metabolism in fish: Current knowledge and future needs. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, F.; Harbach, H.; Schulz, C. Rapeseed proteins as fishmeal alternatives: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1887–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Raman, H.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. De novo design of future rapeseed crops: Challenges and opportunities. Crop J. 2022, 10, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasundara, J.P.D.; Tan, S.; Alashi, A.M.; Pudel, F.; Blanchard, C. Proteins From Canola/Rapeseed: Current Status. In Sustainable Protein Sources; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 285–304. [Google Scholar]
- Wnęk-Auguścik, K.; Witeska, M.; Niemiec, T.; Piotrowska, I.; Fajkowska, M.; Gomułka, P.; Kondera, E.; Łozicki, A.; Zglińska, K.; Rzepkowska, M. The effects of diets containing rapeseed meal on Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) growth, muscle composition, and physiological performance. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 34, 101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ai, Q.; Mai, K.; Zhang, W.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y. Effects of dietary rapeseed meal on growth performance, digestion and protein metabolism in relation to gene expression of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Aquaculture 2012, 368–369, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masagounder, K.; Ramos, S.; Reimann, I.; Channarayapatna, G. Optimizing nutritional quality of aquafeeds. In Aquafeed Formulation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 239–264. [Google Scholar]
- Dossou, S.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; El Basuini, M.F.; Zaineldin, A.I.; Mzengereza, K.; Moss, A.; Dawood, M.A.O. Effects of replacing fishmeal with fermented and non-fermented rapeseed meal on the growth, immune and antioxidant responses of red sea bream (Pagrus major). Aquac. Nutr. 2019, 25, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, L.; Qian, G.; Gao, Y. Supplying rapeseed meal to the diets with or without potassium iodide for yellow catfish (Tachysurus fulvidraco). Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 2061–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanizza, C.; Trocino, A.; Stejskal, V.; Prokešová, M.D.; Zare, M.; Tran, H.Q.; Brambilla, F.; Xiccato, G.; Bordignon, F. Practical low-fishmeal diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) reared in RAS: Effects of protein meals on fish growth, nutrient digestibility, feed physical quality, and faecal particle size. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 28, 101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.B.; Chen, L.Q.; Qin, J.G. Fishmeal replacement by soybean, rapeseed and cottonseed meals in hybrid sturgeon Acipenser baerii ♀ × Acipenser schrenckii ♂. Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Zheng, D.; Elinav, E. Diet–microbiota interactions and personalized nutrition. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolte, L.A.; Vich Vila, A.; Imhann, F.; Collij, V.; Gacesa, R.; Peters, V.; Wijmenga, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Campmans-Kuijpers, M.J.E.; Fu, J.; et al. Long-term dietary patterns are associated with pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory features of the gut microbiome. Gut 2021, 70, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, K.D.; Angert, E.R.; Montgomery, W.L.; Choat, J.H. Intestinal microbiota in fishes: What’s known and what’s not. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukurba, K.R.; Montgomery, S.B. RNA Sequencing and Analysis. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2015, 2015, 084970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Deng, N.; Xu, J.; Huang, J.; Han, C.; Liu, D.; Liu, S.; Yan, B.; Han, L.; Li, S.; et al. Effects of hyperosmotic stress on the intestinal microbiota, transcriptome, and immune function of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Xue, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, S. Salinity modulates gut microbiota and host transcriptome dynamics in juvenile euryhaline fish yellowfin seabream (Acanthopagrus latus). Aquac. Rep. 2025, 44, 103075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, W.; Allen, K.M.; Habte-Tsion, H.-M.; Meesala, K.-M. Supplementation of glycine, prebiotic, and nucleotides in soybean meal-based diets for largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides): Effects on production performance, whole-body nutrient composition and retention, and intestinal histopathology. Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Fishery Administration (C.F.S.). China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2024; ISBN 978-7-109-32126-7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Pu, C.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Z.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y. Retrospect of fishmeal substitution in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides): A review. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 51, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J.; Karrow, N.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y. Dietary Protein and Lipid Requirements for Juvenile Largemouth Bass, Micropterus salmoides. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2017, 48, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Han, T.; Song, F.; Wu, G. Effects of dietary protein intake on the oxidation of glutamate, glutamine, glucose and palmitate in tissues of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Amino Acids 2020, 52, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Ao, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. Effects of extruded and pelleted diets with different protein levels on growth performance and nutrient retention of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 29, 101479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, S.D.; Tidwell, J.H.; Webster, C.D. Response of Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides to Dietary Supplementation of Lysine, Methionine, and Highly Unsaturated Fatty Acids. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2007, 31, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; AOAC-Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005; Volume 45. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Fan, J.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Bai, J. Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalisation in largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides fed on alternative diets. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Hu, P.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q. Liver Injury and Metabolic Dysregulation in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) after Ammonia Exposure. Metabolites 2023, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dossou, S.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; El Basuini, M.F.; Olivier, A.; Zaineldin, A.I. Growth performance, blood health, antioxidant status and immune response in red sea bream (Pagrus major) fed Aspergillus oryzae fermented rapeseed meal (RM-Koji). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 75, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, F.; von Danwitz, A.; Tusche, K.; Kroeckel, S.; van Bussel, C.G.J.; Schlachter, M.; Adem, H.; Tressel, R.-P.; Schulz, C. Nutritional evaluation of rapeseed protein isolate as fish meal substitute for juvenile turbot (Psetta maxima L.)—Impact on growth performance, body composition, nutrient digestibility and blood physiology. Aquaculture 2012, 356–357, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Che, J.; Zhao, L.; Bu, X.; Yang, Y. Effect of replacing fish meal with soybean meal on growth, feed utilization and nitrogen and phosphorus excretion of juvenile Pseudobagrus ussuriensis. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 3145–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokou, F.; Rigos, G.; Henry, M.; Kentouri, M.; Alexis, M. Growth performance, feed utilization and non-specific immune response of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) fed graded levels of a bioprocessed soybean meal. Aquaculture 2012, 364–365, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tang, J.-w.; Yao, X.-h.; Wu, Y.-f.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Lou, B. Partial substitution of fish meal with fermented cottonseed meal in juvenile black sea bream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii) diets. Aquaculture 2015, 446, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Dong, L.; Peng, D.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Z.; Wen, H.; Tian, J.; Jiang, M. Replacing soybean meal with fermented rapeseed meal in diets: Potential effects on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and liver and intestinal health of juvenile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 50, 1683–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunger, A.N.; Craig, S.R.; McLean, E. Replacement of fish meal in cobia (Rachycentron canadum) diets using an organically certified protein. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzifotis, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Seikai, T. The effect of dietary carnitine supplementation on growth of red sea bream (Pagrus major) fingerlings at two levels of dietary lysine. Aquaculture 1996, 147, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossou, S.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Dawood, M.A.O.; El Basuini, M.F.; El-Hais, A.M.; Olivier, A. Effect of partial replacement of fish meal by fermented rapeseed meal on growth, immune response and oxidative condition of red sea bream juvenile, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishawy, A.T.Y.; Mohammed, H.A.; Zaglool, A.W.; Attia, M.S.; Hassan, F.A.M.; Roushdy, E.M.; Ismail, T.A.; Ibrahim, D. Partial defatted black solider larvae meal as a promising strategy to replace fish meal protein in diet for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Performance, expression of protein and fat transporters, and cytokines related genes and economic efficiency. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefsson, E. Glucosinolate content and amino acid composition of rapeseed (Brassica napus) meal as affected by sulphur and nitrogen nutrition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 21, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnotti, L.J.; Deitch, E.A. Burns, Bacterial Translocation, Gut Barrier Function, and Failure. J. Burn Care Rehabil. 2005, 26, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Tan, B.; Shi, L.; Zhang, S. Effects of replacing fish meal with cottonseed protein concentrate on the growth, immune responses, digestive ability and intestinal microbial flora in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 128, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Zhong, L.; Chen, T.; Shi, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, J.-G.; Liu, H.-Y.; Xu, S.-D. Dietary sanguinarine supplementation on the growth performance, immunity and intestinal health of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fed cottonseed and rapeseed meal diets. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wu, P.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Jiang, W.-D.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, S.-Y.; Tang, L.; Feng, L. Dietary silymarin supplementation enhanced growth performance and improved intestinal apical junctional complex on juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2020, 525, 735311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhou, W.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Olsen, R.E.; Ran, C.; Zhou, Z. Effects of Cetobacterium somerae fermentation product on gut and liver health of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fed diet supplemented with ultra-micro ground mixed plant proteins. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sina, C.; Kemper, C.; Derer, S. The intestinal complement system in inflammatory bowel disease: Shaping intestinal barrier function. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 37, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, N.; Feng, L.; Jiang, W.; Wu, P.; Ren, H.; Shi, H.; Tang, L.; Li, S.; Wu, C.; Li, H.; et al. An emerging role of arecoline on growth performance, intestinal digestion and absorption capacities and intestinal structural integrity of adult grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Anim. Nutr. 2023, 15, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, L.; Hu, Y.; Fu, G. Dietary Clostridium butyricum metabolites mitigated the disturbances in growth, immune response and gut health status of Ctenopharyngodon idella subjected to high cottonseed and rapeseed meal diet. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 154, 109934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Huang, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X. Effect of Bacillus subtilis on Aeromonas hydrophila-induced intestinal mucosal barrier function damage and inflammation in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, X.; Tan, B.; Dong, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S. Partial fishmeal protein replacement with peptides from swine blood modulates the nutritional status, immune response, and intestinal microbiota of hybrid groupers (female Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × male E. lanceolatus). Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Ruenkoed, S.; Li, X.; Leng, X. Dietary effects of supplementing Clostridium butyricum culture or sodium butyrate in low fishmeal diet on growth, serum indicators, intestinal histology and microbiota of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Sperstad, S.; Myklebust, R.; Refstie, S.; Krogdahl, Å. Characterisation of the microbiota associated with intestine of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Aquaculture 2006, 261, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Li, X.; Poolsawat, L.; Guo, Z.; Yao, W.; Zhang, C.; Leng, X. Effects of fish meal replaced by fermented soybean meal on growth performance, intestinal histology and microbiota of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1058–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Sun, H.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Evaluation of extruded full-fat soybean as the substitution for fish meal in diets for juvenile Scophthalmus maximus based on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, and aquaculture water quality. Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-M.; Zhou, X.-M.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Kuang, W.-M.; Chen, Y.-J.; Luo, L.; Dai, F.-Y. Intestinal morphology, immunity and microbiota response to dietary fibers in largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoide. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 103, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Biagi, E.; Nylund, L.; Candela, M.; Ostan, R.; Bucci, L.; Pini, E.; Nikkïla, J.; Monti, D.; Satokari, R.; et al. Through Ageing, and Beyond: Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Status in Seniors and Centenarians. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Bian, Y.; Huang, L.; Lan, Q.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Leng, X. Effects of replacing fish meal with fermented soybean meal on the growth performance, intestinal microbiota, morphology and disease resistance of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 22, 100954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, N.; Gu, M.; Xu, X.; Xu, B.; Krogdahl, Å. Protective effects of mannan oligosaccharides on turbot Scophthalmus maximus suffering from soy enteropathy. Aquaculture 2017, 476, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Fan, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, W.; Deng, J.; Tan, B. Effects of dietary non-starch polysaccharides level on the growth, intestinal flora and intestinal health of juvenile largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Aquaculture 2022, 557, 738343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Li, C.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X. Oral administration of recombinant Lactococcus lactis expressing largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) IFNa3 protein enhances immune response against largemouth bass virus (LMBV) infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 154, 109875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, R.; Dong, W.; Feng, Z.; Jin, T.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S. Effects of three tested medicinal plant extracts on growth, immune function and microflora in juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Rep. 2024, 36, 102075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, M.; Feng, D.; Wang, S.; Li, M. Effects of dietary D-mannose supplementation on growth performance, intestinal digestive capacity, gut microbiota, and ammonia tolerance of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 36, 102054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; Ren, H.-C.; Gu, X.; Liang, Q.-R.; Fei, H.; Yang, Y.-H.; Yang, S.; He, L.-Y.; Liu, L.-L. Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) as adjuvant enhances the immune effects of Aeromonas veronii inactivated vaccine in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, P.X.; Kubes, P. The Neutrophil’s Role During Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1223–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euler, M.; Hoffmann, M.H. The double-edged role of neutrophil extracellular traps in inflammation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uderhardt, S.; Martins, A.J.; Tsang, J.S.; Lämmermann, T.; Germain, R.N. Resident Macrophages Cloak Tissue Microlesions to Prevent Neutrophil-Driven Inflammatory Damage. Cell 2019, 177, 541–555.e517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredients (%) | FM | RM5 | RM10 | RM15 | RM25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5% | 10% | 15% | 25% | |
| Fish meal | 42.00 | 39.90 | 37.80 | 35.70 | 31.50 |
| Rapeseed meal 1 | 0.00 | 3.51 | 7.01 | 10.52 | 17.53 |
| Chicken meal | 13.00 | 13.00 | 13.00 | 13.00 | 13.00 |
| Plasma protein meal | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Pork meal | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Peanut meal | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 |
| Wheat flour | 12.00 | 12.00 | 12.00 | 12.00 | 11.82 |
| Fish oil | 2.00 | 2.10 | 2.30 | 2.50 | 2.70 |
| Soybean oil | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Calcium dihydrogen phosphate | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| Choline chloride | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Vitamin C | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Vitamin and mineral premix | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Ethoxyquin | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Lysine 2 | 0.02 | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 1.05 |
| Methionine 2 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.25 |
| Bentonite | 4.33 | 3.25 | 2.36 | 1.53 | 0.00 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | 4.33 | 3.25 | 2.36 | 1.53 | 0.00 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Proximate composition (%) | |||||
| Crude protein | 48.51 | 49.16 | 49.35 | 49.39 | 49.59 |
| Crude lipid | 10.28 | 10.22 | 10.25 | 10.28 | 10.14 |
| Crude ash | 8.19 | 8.23 | 8.34 | 8.42 | 8.36 |
| Moisture | 8.88 | 8.24 | 7.40 | 7.95 | 7.74 |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) | GenBank |
|---|---|---|---|
| eef1a1 | F: GAAGCTCGAAGACAACCCCA R: TCACGGACTGCAAATCTCCC | 129 | XM_038714535.1 |
| il22 | F: GGGCGAGCGAGGTATAAACA R: GTGGCGGTGGAGTTTTTCAG | 96 | XM_038709272.1 |
| plb1 | F: GCTCAGCTTACAGACACGGT R: GTGAACTGAAGAGGACGGGG | 132 | XM_038729844.1 |
| cd36 | F: TGCTGTAACAGAAGGTGCGG R: CAGGCTCAATGATGACTTCCTTC | 136 | XM_038739146.1 |
| jun | F: GCAC AGAGAGGACGTTTGGA R: GCCGGCGTTGTCGTGTTTTA | 114 | XM_038716392.1 |
| acsl5 | F: TACCCTTACTGTGTGTGCTCC R: AGATAAACATCCTTCACCTGCTCA | 141 | XM_038736141.1 |
| Items | FM | RM5 | RM10 | RM15 | RM25 | ANOVA | Linear | Quadratic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBW (g) | 47.45 ± 1.52 | 45.87 ± 0.77 | 45.45 ± 2.74 | 46.90 ± 2.11 | 43.40 ± 1.83 | 0.626 | 0.233 | 0.485 |
| WGR (%/d) | 331.17 ± 13.54 | 317.02 ± 7.40 | 313.73 ± 24.59 | 326.12 ± 18.89 | 294.54 ± 15.84 | 0.617 | 0.224 | 0.469 |
| SGR (%) | 2.61 ± 0.06 | 2.55 ± 0.03 | 2.53 ± 0.11 | 2.59 ± 0.08 | 2.45 ± 0.07 | 0.598 | 0.209 | 0.447 |
| PER | 1.81 ± 0.04 | 1.76 ± 0.04 | 1.82 ± 0.06 | 1.77 ± 0.06 | 1.77 ± 0.07 | 0.892 | 0.681 | 0.922 |
| FCR | 1.15 ± 0.03 | 1.18 ± 0.03 | 1.19 ± 0.04 | 1.19 ± 0.04 | 1.26 ± 0.05 | 0.453 | 0.072 | 0.186 |
| FI (%/d) | 2.57 ± 0.04 | 2.57 ± 0.04 | 2.59 ± 0.06 | 2.62 ± 0.04 | 2.66 ± 0.05 | 0.637 | 0.102 | 0.248 |
| SR (%) | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 | - | - | - |
| Items | FM | RM5 | RM10 | RM15 | RM25 | ANOVA | Linear | Quadratic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSI (%) | 8.21 ± 0.33 | 7.85 ± 0.23 | 7.61 ± 0.31 | 7.37 ± 0.25 | 7.78 ± 0.25 | 0.290 | 0.124 | 0.103 |
| HSI (%) | 2.46 ± 0.11 b | 2.69 ± 0.10 b | 2.10 ± 0.11 a | 1.96 ± 0.07 a | 2.08 ± 0.12 a | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| AFR (%) | 1.85 ± 0.13 | 1.64 ± 0.12 | 1.66 ± 0.12 | 1.63 ± 0.10 | 1.74 ± 0.11 | 0.682 | 0.540 | 0.362 |
| ISI (%) | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 0.64 ± 0.03 | 0.71 ± 0.06 | 0.70 ± 0.02 | 0.113 | 0.014 | 0.049 |
| ILI (%) | 78.24 ± 2.06 | 79.38 ± 1.15 | 79.01 ± 1.49 | 74.73 ± 2.20 | 76.38 ± 1.74 | 0.308 | 0.137 | 0.303 |
| Items (%) | FM | RM5 | RM10 | RM15 | RM25 | ANOVA | Linear | Quadratic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 72.78 ± 11.29 | 71.75 ± 8.79 | 80.13 ± 0.45 | 79.40 ± 0.74 | 77.75 ± 2.01 | 0.832 | 0.338 | 0.582 |
| Crude Lipid | 8.13 ± 0.61 b | 7.80 ± 0.33 b | 5.92 ± 0.02 a | 5.58 ± 0.11 a | 6.19 ± 0.29 a | 0.010 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| Crude Protein | 15.79 ± 0.16 c | 17.36 ± 0.09 d | 11.74 ± 0.00 a | 12.71 ± 0.07 b | 12.81 ± 0.18 b | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, X.; Wu, H.; Yue, R.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L.; Lin, S.; Ge, H.; He, Y. Effects of Dietary Rapeseed Meal on Growth Performance, Intestinal Structure, Gut Microbiota, and Related Gene Expression of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112535
Hou X, Wu H, Yue R, Zhou X, Chen Y, Luo L, Lin S, Ge H, He Y. Effects of Dietary Rapeseed Meal on Growth Performance, Intestinal Structure, Gut Microbiota, and Related Gene Expression of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112535
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Ximing, Haiqing Wu, Rongyan Yue, Xinghua Zhou, Yongjun Chen, Li Luo, Shimei Lin, Hailong Ge, and Yuanfa He. 2025. "Effects of Dietary Rapeseed Meal on Growth Performance, Intestinal Structure, Gut Microbiota, and Related Gene Expression of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides)" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112535
APA StyleHou, X., Wu, H., Yue, R., Zhou, X., Chen, Y., Luo, L., Lin, S., Ge, H., & He, Y. (2025). Effects of Dietary Rapeseed Meal on Growth Performance, Intestinal Structure, Gut Microbiota, and Related Gene Expression of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Microorganisms, 13(11), 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112535








