Investigating the Biological Characteristics and Pathogenic Potential of Listeria innocua Isolated from Food Through Comparative Genomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Retrieval and Management
2.2. Pan-Genomic Analysis of L. innocua from Different Geographic Origins
2.3. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Functional Features of Core Genes
2.6. Prediction of Virulence Factors Genes and Antibiotic Resistance Genes of L. innocua
2.7. Prediction of Plasmids of L. innocua
2.8. Prediction of LGIs and SSIs of L. innocua
2.9. Prediction of CRISPR-Cas Systems of L. innocua
2.10. Verifying the Pathogenicity of L. innocua Strains
3. Results
3.1. Genome Statistics and General Features
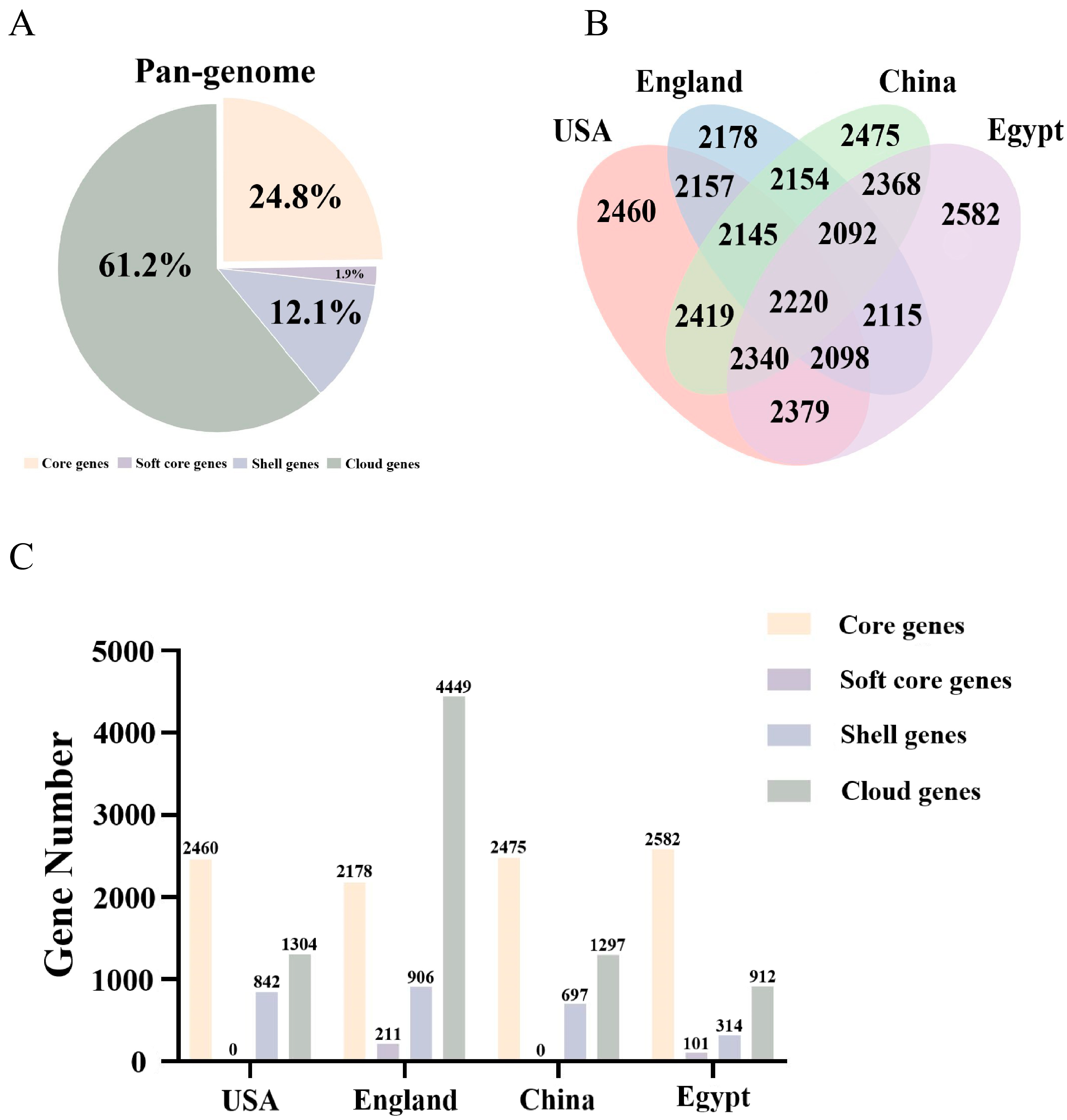
3.2. Pan-Genomic Analysis of L. innocua Strains in Distinct Areas
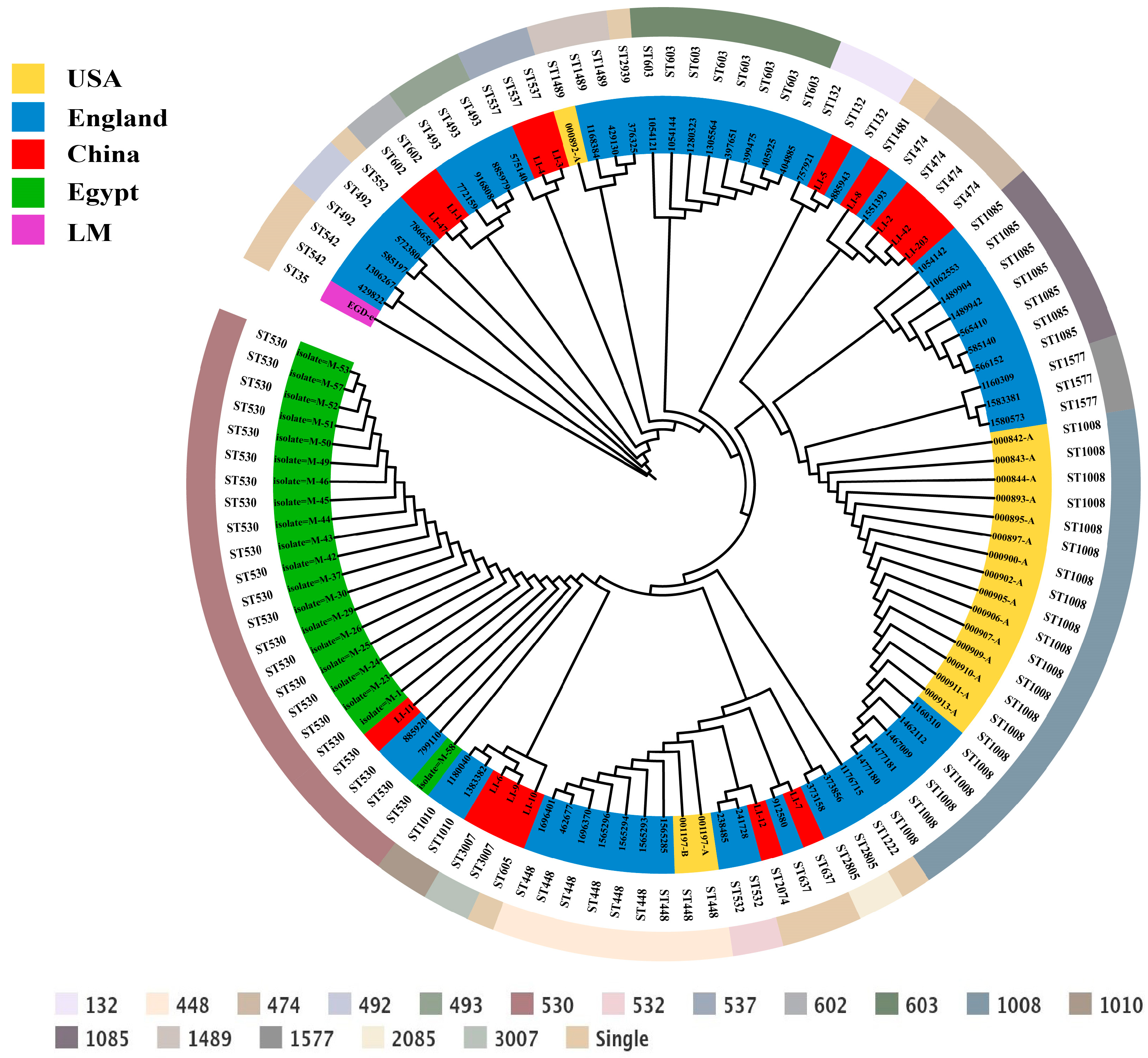
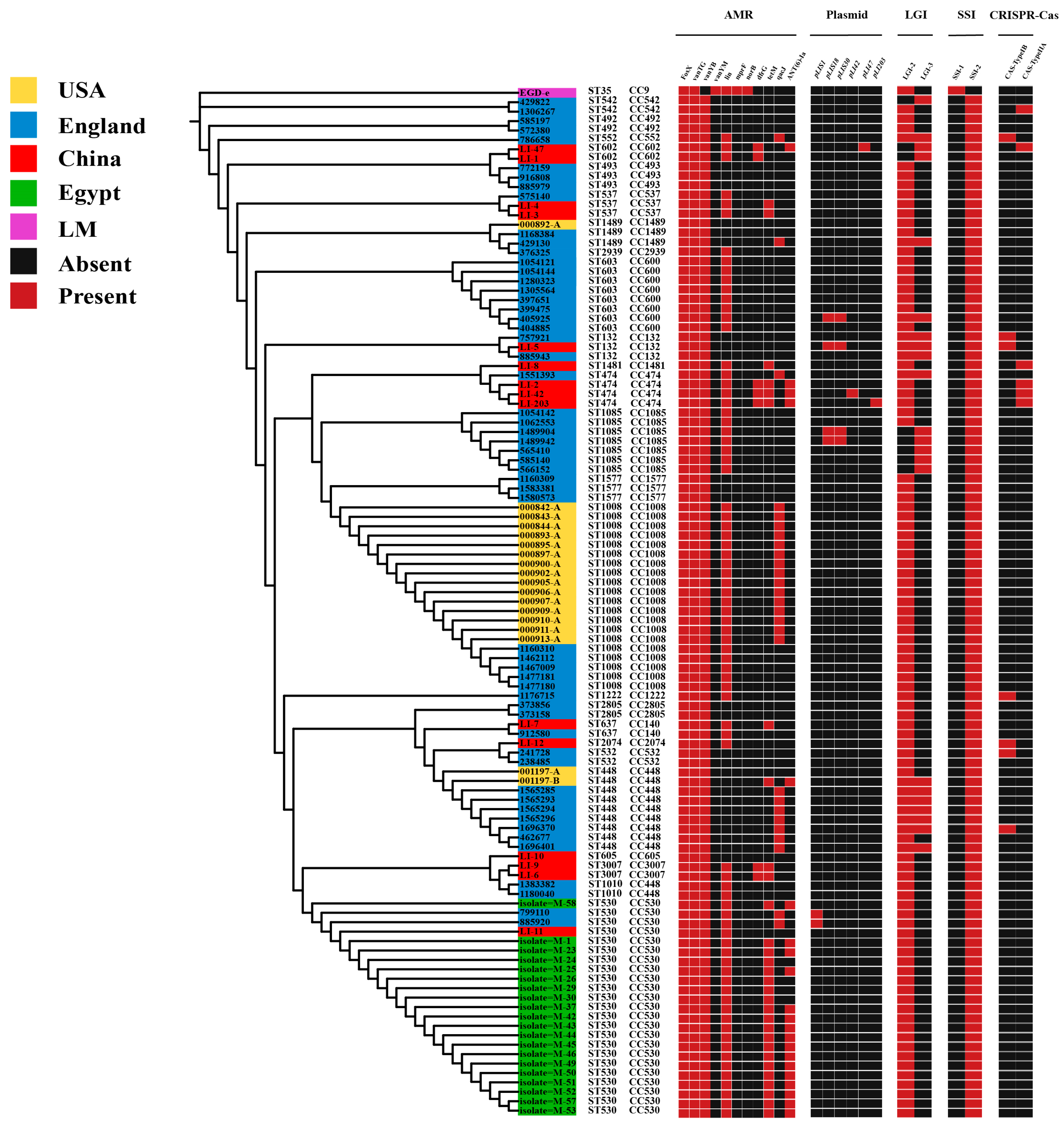
3.3. MLST and Phylogenetic Analysis
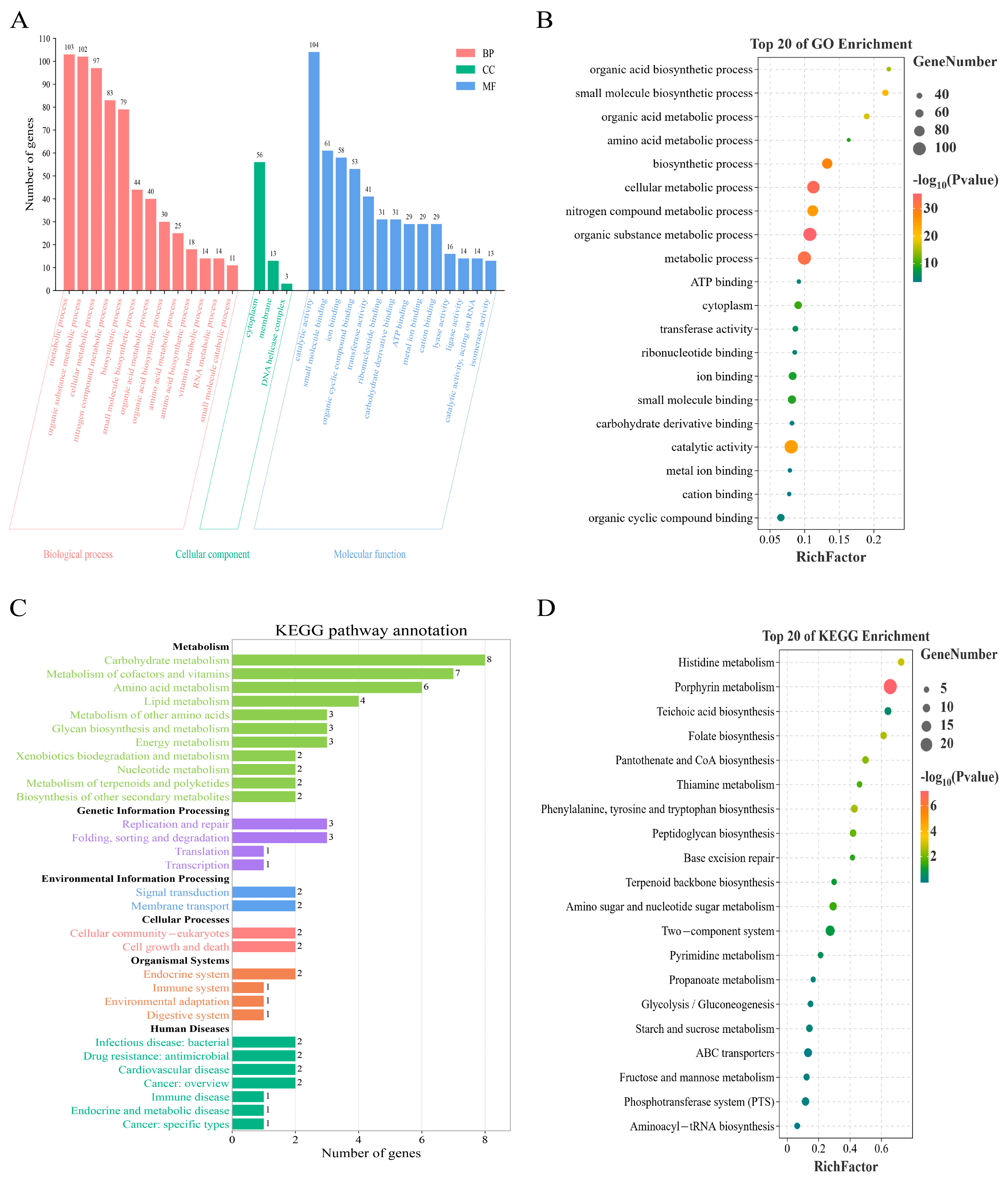
3.4. Enrichment Analysis of the Functional Features of Core Genes with GO and KEGG
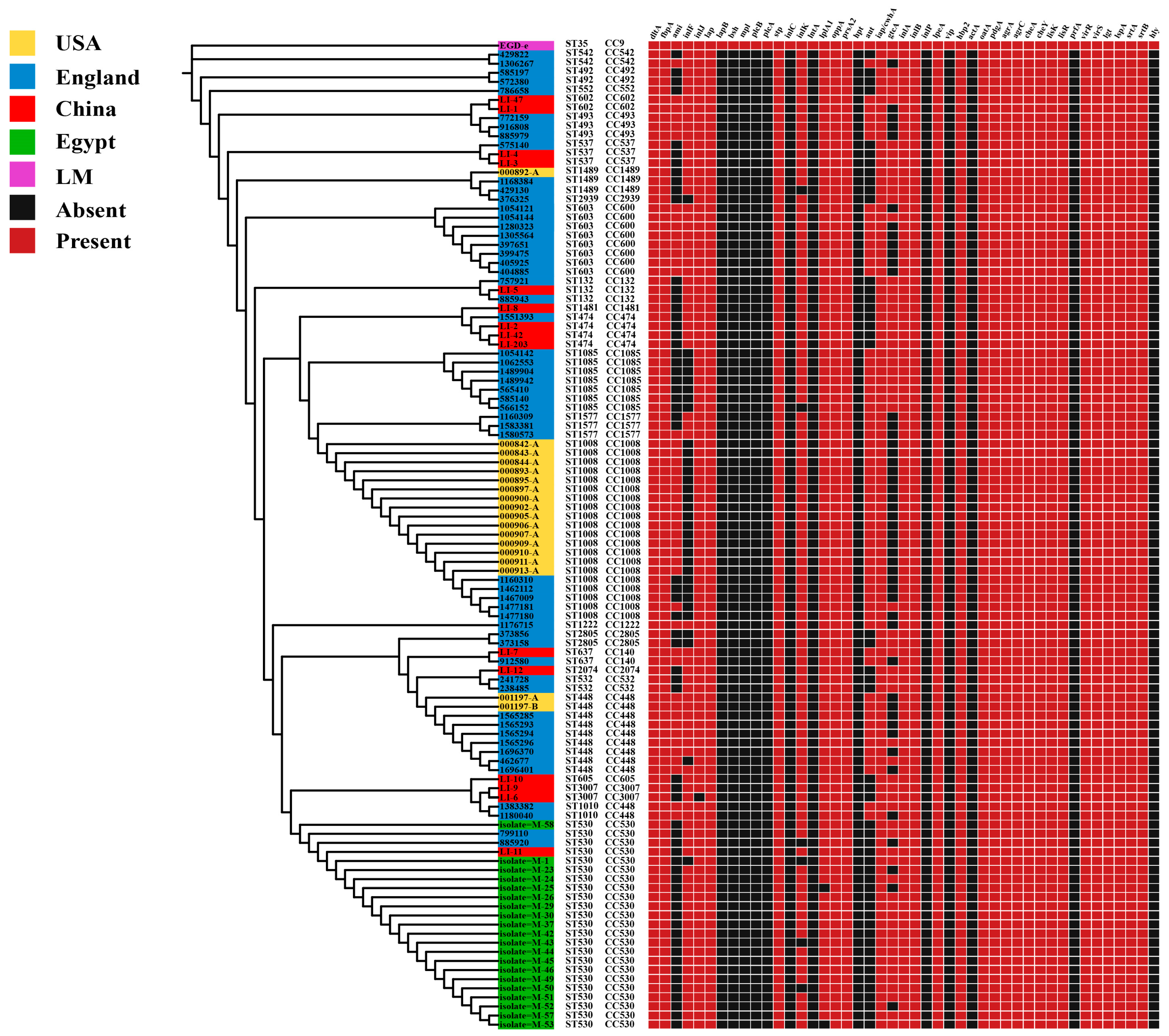
3.5. Distribution of Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in L. innocua Strains in Distinct Areas
3.6. Distribution of Plasmids in L. innocua Strains in Distinct Areas
3.7. Distribution of LGIs in L. innocua Strains in Distinct Areas
3.8. Distribution of SSIs in L. innocua Strains in Distinct Regions
3.9. Distribution of CRISPR-Cas System Types in L. innocua Strains in Distinct Areas
3.10. Results of the Pathogenicity analysis of L. innocua Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Long, Q.; Yi, X.; Yang, A.; Long, X.; Cao, D. Comparative Genomics Reveal the Utilization Ability of Variable Carbohydrates as Key Genetic Features of Listeria Pathogens in Their Pathogenic Lifestyles. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werum, V.; Ehrmann, M.; Vogel, R.; Hilgarth, M. Comparative genome analysis, predicted lifestyle and antimicrobial strategies of Lactococcus carnosus and Lactococcus paracarnosus isolated from meat. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 258, 126982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, F.; Deng, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Jiao, X.; Li, S.; Liu, M. Genomic epidemiology of hypervirulent Listeria monocytogenes CC619: Population structure, phylodynamics and virulence. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 280, 127591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matle, I.; Mbatha, K.R.; Madoroba, E. A review of Listeria monocytogenes from meat and meat products: Epidemiology, virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance and diagnosis. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2020, 87, e1–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Bassey, A.; Huang, J.; Zou, Y.; Ye, K. Expansion of Intestinal Secretory Cell Population Induced by Listeria monocytogenes Infection: Accompanied with the Inhibition of NOTCH Pathway. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 793335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.E.; Abd, E.M.I.; El-Gedawy, A.; Bendary, M.M.; Eltarabili, R.M.; Alhomrani, M.; Alamri, A.S.; Alghamdi, S.A.; Arnout, M.; Binjawha, D.N.; et al. New Insights into Listeria monocytogenes Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Attributes and Their Prospective Correlation. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osek, J.; Wieczorek, K. Listeria monocytogenes—How This Pathogen Uses Its Virulence Mechanisms to Infect the Hosts. Pathogens 2022, 21, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoshevich, L.; Cossart, P. Listeria monocytogenes: Towards a complete picture of its physiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, A.; Disson, O.; Lavina, M.; Thouvenot, P.; Huang, L.; Leclercq, A.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Eshwar, A.K.; Stephan, R.; Lecuit, M. Atypical Hemolytic Listeria innocua Isolates Are Virulent, albeit Less than Listeria monocytogenes. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00758-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Amadoro, C.; Conficoni, D.; Giaccone, V.; Colavita, G. Occurrence, Diversity of Listeria spp. Isolates from Food and Food-Contact Surfaces and the Presence of Virulence Genes. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafuna, T.; Matle, I.; Magwedere, K.; Pierneef, R.E.; Reva, O.N. Whole Genome-Based Characterization of Listeria monocytogenes Isolates Recovered from the Food Chain in South Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matto, C.; Rivero, R.; Mota, M.I.; Braga, V.; Gianneechini, E.; Varela, G. Identification and characterization of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua in bovine listeriosis cases in Uruguay. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2025, 57, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, K.; Gouws, P.; Rip, D. Genetic diversity of Listeria monocytogenes from seafood products, its processing environment, and clinical origin in the Western Cape, South Africa using whole genome sequencing. AIMS Microbiol. 2024, 10, 608–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Ren, H.; Wang, X.; Han, C.; Jin, Y.; Hu, X.; Shi, R.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Comparative genomics analysis to explore the biodiversity and mining novel target genes of Listeria monocytogenes strains from different regions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1424868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Den, B.H.C.; Korlach, J.; Kong, N.; Storey, D.B.; Paxinos, E.E.; Ashby, M.; Clark, T.; Luong, K.; Wiedmann, M.; et al. Comparative Genomics Reveals the Diversity of Restriction-Modification Systems and DNA Methylation Sites in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02091-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Phillippy, A.M.; Li, Z.; Salzberg, S.L.; Zhang, W. Probing the pan-genome of Listeria monocytogenes: New insights into intraspecific niche expansion and genomic diversification. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ye, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Xue, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Zeng, H.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Multiplex PCR for the Identification of Pathogenic Listeria in Flammulina velutipes Plant Based on Novel Specific Targets Revealed by Pan-Genome Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 634255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Xie, T.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Lei, T.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, L.; Chen, M.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis reveals the potential risk of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from ready-to-eat foods in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafuna, T.; Matle, I.; Magwedere, K.; Pierneef, R.E.; Reva, O.N. Comparative Genomics of Listeria Species Recovered from Meat and Food Processing Facilities. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0118922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henri, C.; Félix, B.; Guillier, L.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Michelon, D.; Mariet, J.F.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Mistou, M.Y.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Roussel, S. Population Genetic Structure of Listeria monocytogenes Strains as Determined by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis and Multilocus Sequence Typing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5720–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Zhong, W.; Liu, T.; Zhao, T.; Guo, J. Global Proteomic Analysis of Listeria monocytogenes Response to Linalool. Foods 2021, 10, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.F.; Siow, C.C.; Dutta, A.; Mutha, N.V.; Wee, W.Y.; Heydari, H.; Tan, S.Y.; Ang, M.Y.; Wong, G.J.; Choo, S.W. Development of ListeriaBase and comparative analysis of Listeria monocytogenes. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.; Douillard, F.P.; Korkeala, H.; Lindström, M. Mobile Elements Harboring Heavy Metal and Bacitracin Resistance Genes Are Common among Listeria monocytogenes Strains Persisting on Dairy Farms. mSphere 2021, 6, e0038321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.; Spier, A.; Chaze, T.; Matondo, M.; Cossart, P.; Stavru, F. Listeria monocytogenes Exploits Mitochondrial Contact Site and Cristae Organizing System Complex Subunit Mic10 to Promote Mitochondrial Fragmentation and Cellular Infection. mBio 2020, 11, e03171-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.; Brown, P.; Kathariou, S. Use of Bacteriophage Amended with CRISPR-Cas Systems to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance in the Bacterial Foodborne Pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijokaite, A.; Humbert, M.V.; Borkowski, E.; La Ragione, R.M.; Christodoulides, M. Establishing an invertebrate Galleria mellonella greater wax moth larval model of Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection. Virulence 2021, 12, 1900–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, B.; Anand, S. Environmental persistence of Listeria monocytogenes and its implications in dairy processing plants. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 4573–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowron, K.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Grudlewska, K.; Gajewski, P.; Wiktorczyk, N.; Wietlicka-Piszcz, M.; Dudek, A.; Skowron, K.J.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Disinfectant Susceptibility of Biofilm Formed by Listeria monocytogenes under Selected Environmental Conditions. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.F.; Zhi, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Paoli, G.C.; Cui, Y.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Preliminary comparative genomics revealed pathogenic potential and international spread of Staphylococcus argenteus. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Guo, X.; Li, S.; Anupoju, S.M.B.; Cheng, R.A.; Weller, D.L.; Sullivan, G.; Zhang, H.; Deng, X.; Wiedmann, M. Comparative genomics unveils extensive genomic variation between populations of Listeria species in natural and food-associated environments. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den, B.H.C.; Cummings, C.A.; Ferreira, V.; Vatta, P.; Orsi, R.H.; Degoricija, L.; Barker, M.; Petrauskene, O.; Furtado, M.R.; Wiedmann, M. Comparative genomics of the bacterial genus Listeria: Genome evolution is characterized by limited gene acquisition and limited gene loss. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Types | Cas Genes | Area | Number | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-TypeIB | cas6_TypeI-III, cas8a1b_TypeIB, cas7b_TypeIB, cas5b_TypeIB, cas3_TypeI, cas2_TypeI-II-III | USA | 2 | 7 |
| England | 5 | |||
| China | 0 | |||
| Egypt | 0 | |||
| CAS-type IIA | csn2_TypeIIA, cas2_TypeI-II-III, cas1_TypeII, cas9_TypeII | USA | 2 | 6 |
| England | 1 | |||
| China | 3 | |||
| Egypt | 0 | |||
| Total | 13 |
| No. | Strain Name | Total Number | Number of Deaths | Number of Survivors | Mortality Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LI-1 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 10% |
| 2 | LI-2 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 10% |
| 3 | LI-3 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 90% |
| 4 | LI-4 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100% |
| 5 | LI-5 | 10 | 2 | 8 | 20% |
| 6 | LI-6 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0% |
| 7 | LI-7 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 10% |
| 8 | LI-8 | 10 | 1 | 9 | 10% |
| 9 | LI-9 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0% |
| 10 | LI-10 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0% |
| 11 | LI-11 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0% |
| 12 | LI-12 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100% |
| 13 | PBS | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Cao, R.; Wang, Q.; Hu, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xue, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X. Investigating the Biological Characteristics and Pathogenic Potential of Listeria innocua Isolated from Food Through Comparative Genomics. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112525
Zhang B, Cao R, Wang Q, Hu P, Li Y, Liu Z, Xue Z, Wang W, Zhang S, Wang X. Investigating the Biological Characteristics and Pathogenic Potential of Listeria innocua Isolated from Food Through Comparative Genomics. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112525
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bo, Runlai Cao, Qilin Wang, Pan Hu, Yacong Li, Ziyu Liu, Zhuqing Xue, Weiyang Wang, Shasha Zhang, and Xiaoxu Wang. 2025. "Investigating the Biological Characteristics and Pathogenic Potential of Listeria innocua Isolated from Food Through Comparative Genomics" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112525
APA StyleZhang, B., Cao, R., Wang, Q., Hu, P., Li, Y., Liu, Z., Xue, Z., Wang, W., Zhang, S., & Wang, X. (2025). Investigating the Biological Characteristics and Pathogenic Potential of Listeria innocua Isolated from Food Through Comparative Genomics. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112525






