Sustainable Recycling of Mushroom Residue as an Effective Substitute for Cotton Hull Waste in Volvariella volvacea Cultivation: Evidence from Physicochemical and Microbiome Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Mushroom Strains
2.2. Composting Process and Sampling
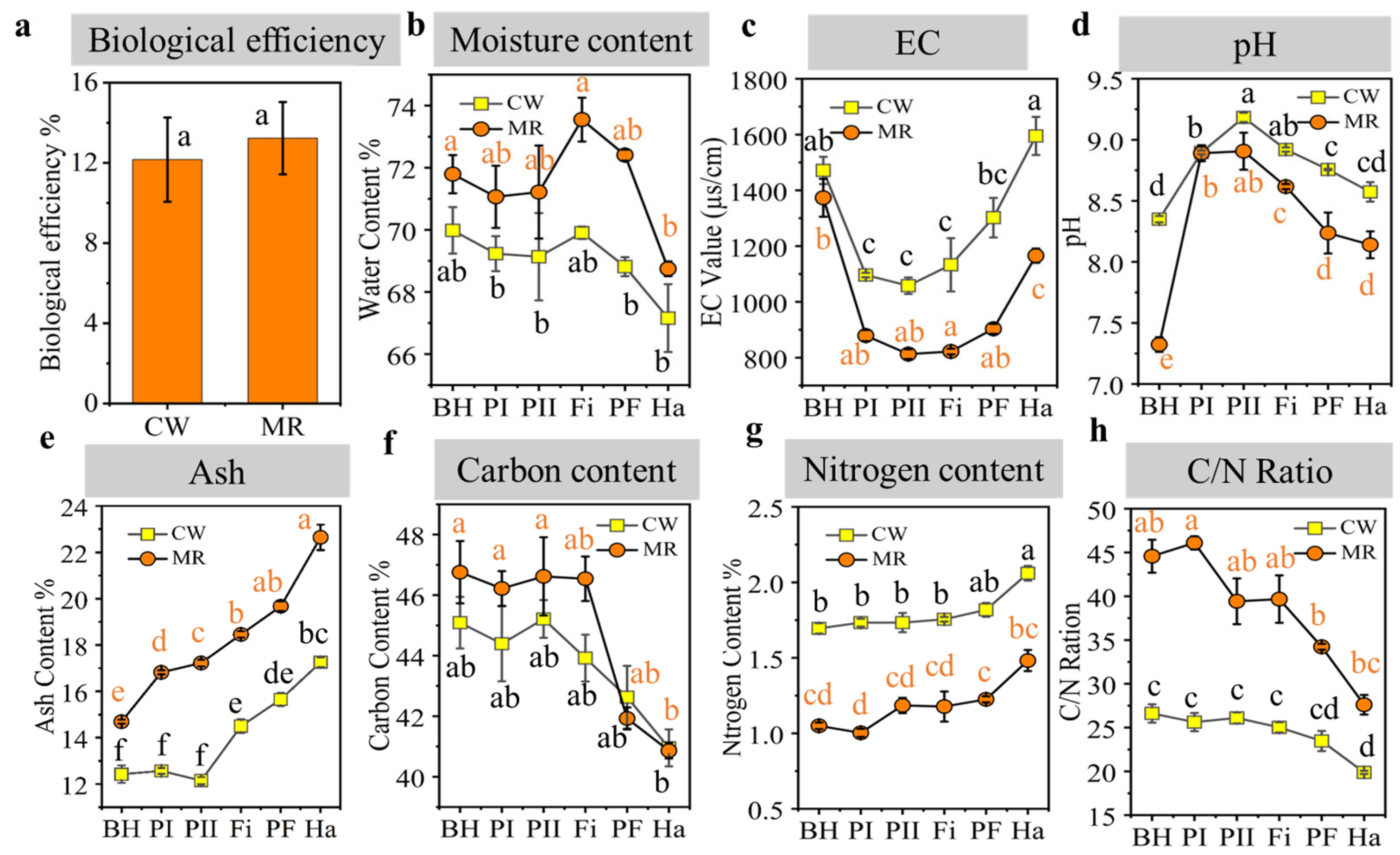
2.3. Determination of Mushroom Yields
2.4. Assays of Physicochemical Properties
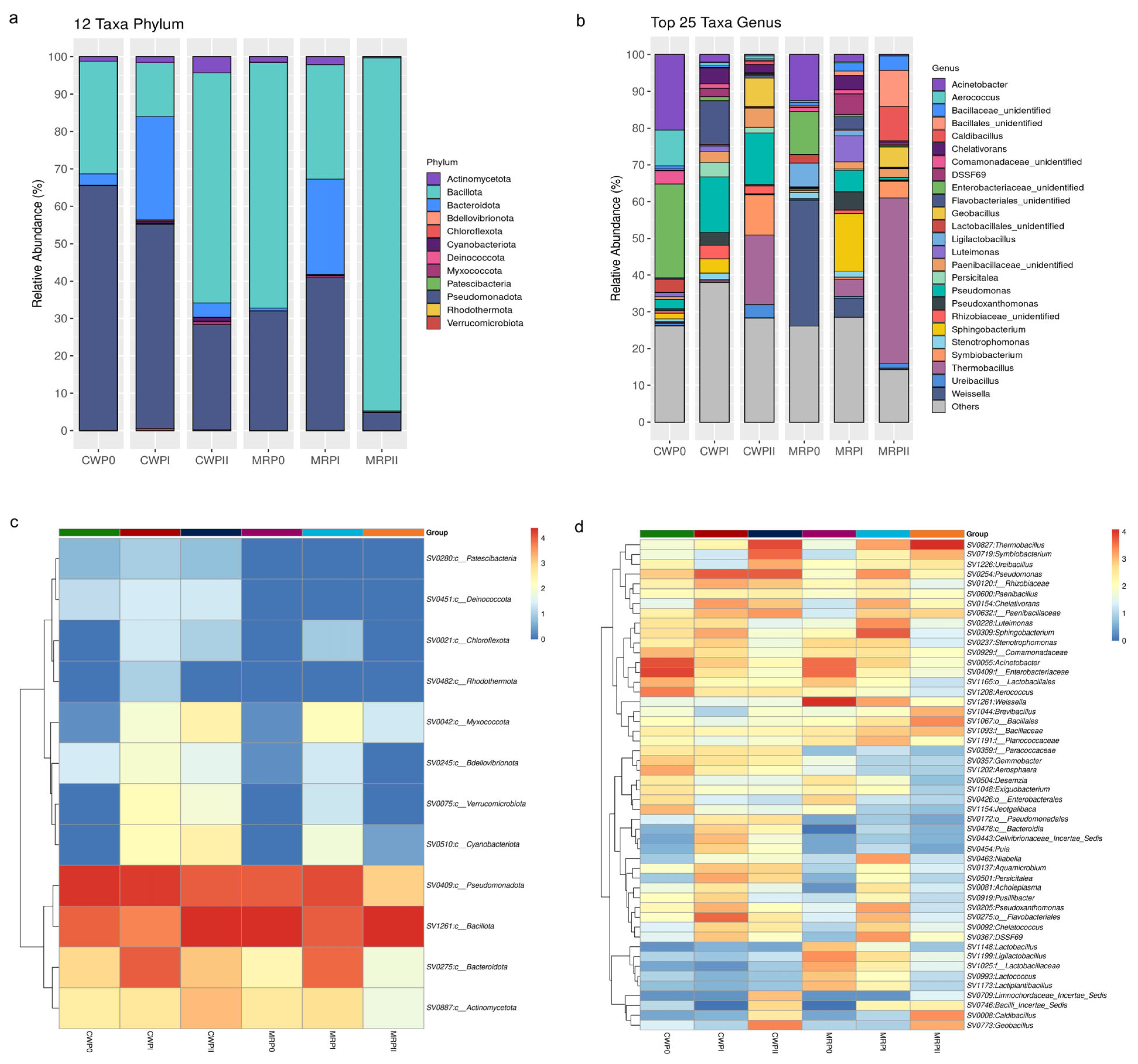
2.5. Bioinformatics Analyses of Bacterial Microbiota Diversity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Changes During Composting
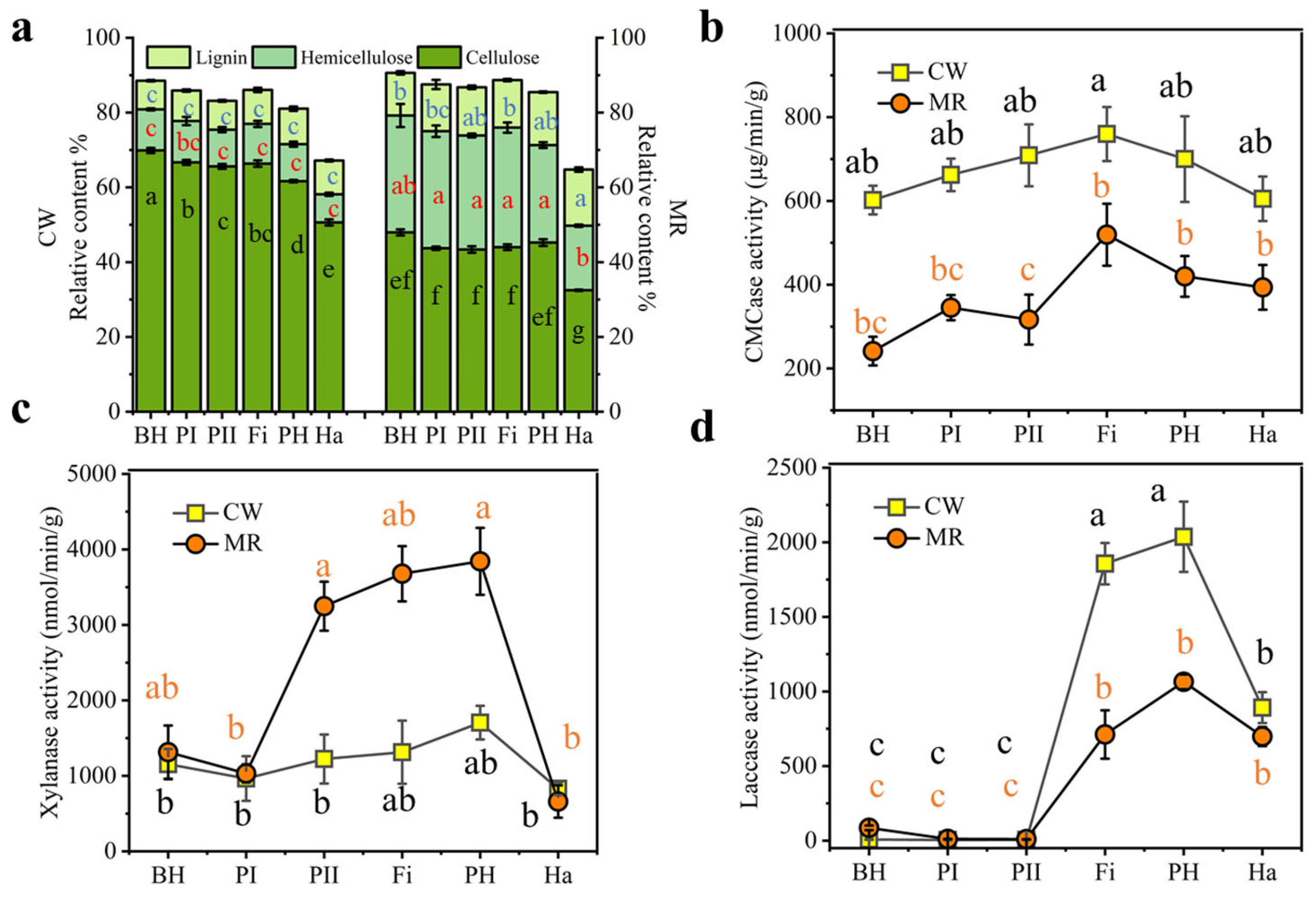
3.2. Changes in Lignocelluloses and Related Degrading Enzymes
3.3. Evolution of the Microbial Community During Composting
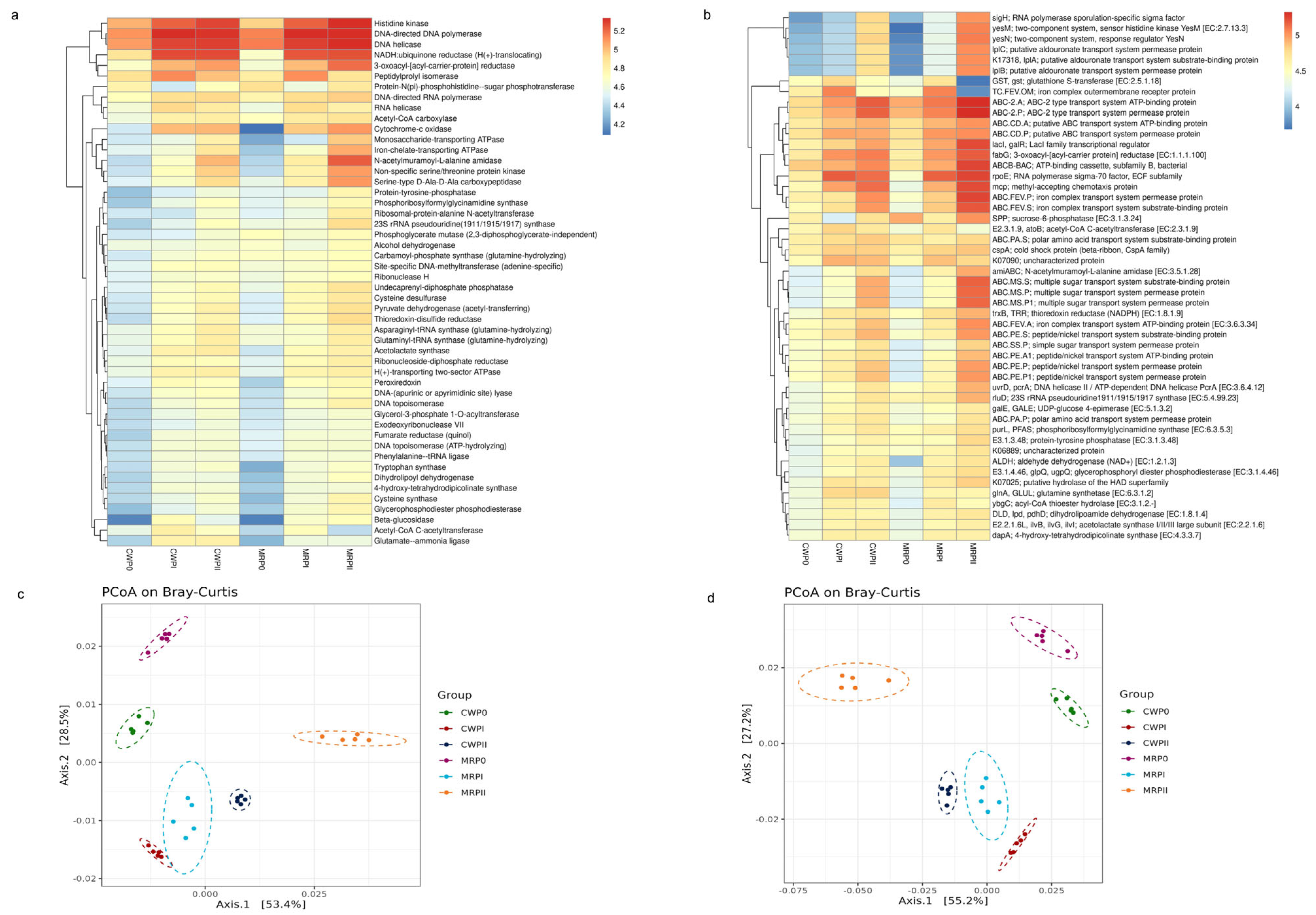
3.4. Analysis of Microbial Community Functions
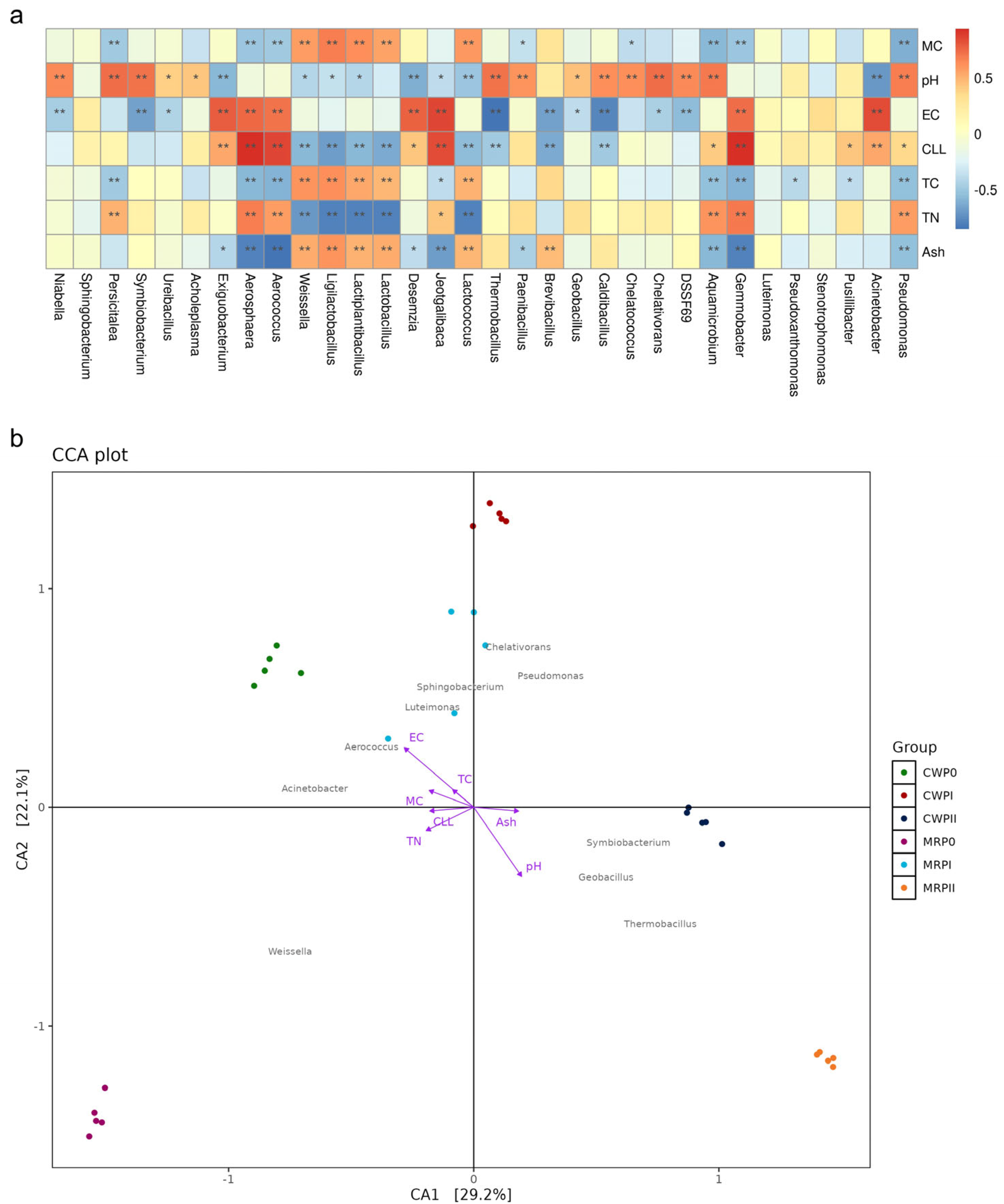
3.5. Correlations Between Microbial Communities and Physiological Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamaliah, N.; Salim, S.; Abdullah, S.; Nobilly, F.; Mat, S.; Norhisham, A.R.; Tohiran, K.A.; Zulkifli, R.; Lechner, A.M.; Azhar, B. Evaluating the experimental cultivation of edible mushroom, Volvariella volvacea underneath tree canopy in tropical agroforestry systems. Agrofor. Syst. 2022, 96, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Cong, C.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, F.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L. Effect of inoculating microorganisms in chicken manure composting with maize straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, X.; Baig, S.A.; Hu, B.; Xu, X. Composition variability of spent mushroom substrates during continuous cultivation, composting process and their effects on mineral nitrogen transformation in soil. Geoderma 2017, 307, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K.; Ma, T.W.; Chang, J.S.; Yang, F.C. Recent advances and future directions on the valorization of spent mushroom substrate (SMS): A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Lv, L. Feasibility of co-composting of sewage sludge, spent mushroom substrate and wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 226, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, C.N.; Philippoussis, A.N.; Diamantopoulou, P.A. Spent mushroom substrate for a second cultivation cycle of Pleurotus mushrooms and dephenolization of agro-industrial wastewaters. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2020, 367, fnaa060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royse, D.J. Recycling of spent shiitake substrate for production of the oyster mushroom, Pleurotus sajor-caju. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 38, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, F.; Li, Z.; Zhao, S.; Song, S.; Rong, C.; Geng, X.; Liu, Y. The spent mushroom substrates of Hypsizigus marmoreus can be an effective component for growing the oyster mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 186, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, C.N.; Diamantopoulou, P.A.; Philippoussis, A.N. Valorization of spent oyster mushroom substrate and laccase recovery through successive solid state cultivation of Pleurotus, Ganoderma, and Lentinula strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5213–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Sun, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, L.; Bao, L.; Liu, S. Metagenomic analysis revealed the succession of microbiota and metabolic function in corncob composting for preparation of cultivation medium for Pleurotus ostreatus. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Xi, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y. Effect of inoculating microbes in municipal solid waste composting on characteristics of humic acid. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely, A.J.; Sipos, R.; Berta, B.; Vajna, B.; Hajdú, C.; Márialigeti, K. DGGE and T-RFLP Analysis of Bacterial Succession during Mushroom Compost Production and Sequence-aided T-RFLP Profile of Mature Compost. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.; Tello, M.L.; De Toro, M.; Tkacz, A.; Poole, P.; Pérez-Clavijo, M.; Preston, G. Casing microbiome dynamics during button mushroom cultivation: Implications for dry and wet bubble diseases. Microbiology 2019, 165, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajna, B.; Nagy, A.; Sajben, E.; Manczinger, L.; Szijártó, N.; Kádár, Z.; Bordás, D.; Márialigeti, K. Microbial community structure changes during oyster mushroom substrate preparation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.X.; Chen, Q.J.; Qin, Y.; Yang, Y.R.; Yang, Q.Z.; Wang, Y.X.; Cheng, Z.; Cao, N.; Zhang, G.Q. Succession of the microbial communities and function prediction during short-term peach sawdust-based composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Dong, P.; Alim, A.; Li, Y.; Qi, Z.; Jacob, M.S.; Su, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Xu, A.; et al. Microbial community succession patterns and assembly mechanisms in the white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) production with corn straw-based compost. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 38, 104135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Cai, W.; Jin, Q.; Feng, W.; Fan, L.; Shen, Y.; Fang, H.; Tian, F. Comparison of microbial communities and histological changes in Phase I rice straw-based Agaricus bisporus compost prepared using two composting methods. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 174, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, G.; Ottesen, A.; Bolten, S.; Ramachandran, P.; Reed, E.; Rideout, S.; Luo, Y.; Patel, J.; Brown, E.; Nou, X. Shifts in spinach microbial communities after chlorine washing and storage at compliant and abusive temperatures. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, X.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, J. Biochar influences the succession of microbial communities and the metabolic functions during rice straw composting with pig manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X. Changes in physical, chemical, and microbiological properties during the two-stage co-composting of green waste with spent mushroom compost and biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, N. Studies on recycling spent compost for mushroom cultivation. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1976, 27, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, Z. Improved fruiting of the straw mushroom (Volvariella volvacea) on cotton waste supplemented with sodium acetate. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 8533–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Hatfield, K.M.; Eric Berson, R. Deactivation of individual cellulase components. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 106, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Awasthi, M.K.; Bao, H.; Bie, J.; Lei, S.; Lv, J. Exploring the microbial mechanisms of organic matter transformation during pig manure composting amended with bean dregs and biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.Z.; Ma, S.C.; Wang, S.P.; Wang, T.T.; Sun, Z.Y.; Tang, Y.Q.; Deng, Y.; Kida, K. A comparative study of composting the solid fraction of dairy manure with or without bulking material: Performance and microbial community dynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.F.; Antunes, L.P.; Pascon, R.C.; De Oliveira, J.C.F.; Digiampietri, L.A.; Barbosa, D.; Peixoto, B.M.; Vallim, M.A.; Viana Niero, C.; Ostroski, E.H.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis of a Tropical Composting Operation at the São Paulo Zoo Park Reveals Diversity of Biomass Degradation Functions and Organisms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.R.; Pecchia, J.A.; Segato, F.; Polikarpov, I. Exploring oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) substrate preparation by varying phase I composting time: Changes in bacterial communities and physicochemical composition of biomass impacting mushroom yields. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Lo, P.K.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; Jiang, Z.; Li, G.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Leong, S.Y.; Li, Q. Molecular mechanisms underlying lignocellulose degradation and antibiotic resistance genes removal revealed via metagenomics analysis during different agricultural wastes composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Guo, D.; Li, D.; Awasthi, S.K.; et al. Evaluation of biochar amended biosolids co-composting to improve the nutrient transformation and its correlation as a function for the production of nutrient-rich compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 237, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pore, S.D.; Engineer, A.; Dagar, S.S.; Dhakephalkar, P.K. Meta-omics based analyses of microbiome involved in biomethanation of rice straw in a thermophilic anaerobic bioreactor under optimized conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Yu, H.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Yu, Q.; Liu, J.; Pei, Z. Microbial succession of lignocellulose degrading bacteria during composting of corn stalk. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 12372–12382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.S.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Fu, X.Y.; Peng, R.H.; Yao, Q.H. Improvement of the Thermostability of Xylanase from Thermobacillus composti through Site-Directed Mutagenesis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, M.; Foda, M.; Shahsavari, E.; Aburto Medina, A.; Adetutu, E.; Ball, A. Commercial feasibility of lignocellulose biodegradation: Possibilities and challenges. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 38, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, Q.; Niu, Q.; Meng, Q.; Yan, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Q. The degradation of organic matter coupled with the functional characteristics of microbial community during composting with different surfactants. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, L.; Hassan, M.; Xie, B. Succession of the functional microbial communities and the metabolic functions in maize straw composting process. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhao, X.; Yang, T.; Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Z. Identifying the key factors that affect the formation of humic substance during different materials composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, Z.; Shi, W.; Li, L.; Tian, R.; Huang, J.; Lin, R.; Wang, B.; Zhou, B. Material conversion, microbial community composition and metabolic functional succession during green soybean hull composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Mao, H.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y. Succession of organics metabolic function of bacterial community in swine manure composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, M.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Siles, J.A.; García-Olmo, J.; Martín, M.A. Chemometric analysis and NIR spectroscopy to evaluate odorous impact during the composting of different raw materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Niu, Q.; Wang, S.; Yan, H.; Li, Q. Understanding the key regulatory functions of red mud in cellulose breakdown and succession of β-glucosidase microbial community during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Hao, R.; Li, Q. Combined analysis of microbial community and microbial metabolites based on untargeted metabolomics during pig manure composting. Biodegradation 2021, 32, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, L. Dynamic changes of the dominant functioning microbial community in the compost of a 90-m3 aerobic solid state fermentor revealed by integrated meta-omics. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loakasikarn, T.; Kubota, Y.; Koyama, M.; Nakasaki, K. Effect of seeding materials on organic matter degradation and microbial community succession during model organic waste composting. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 102182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kakumyan, P.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Saninjuk, K.; Dong, Q.; Pan, X.; Yu, C.; Zhao, Y. Sustainable Recycling of Mushroom Residue as an Effective Substitute for Cotton Hull Waste in Volvariella volvacea Cultivation: Evidence from Physicochemical and Microbiome Analyses. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102372
Kakumyan P, Yang L, Liu S, Saninjuk K, Dong Q, Pan X, Yu C, Zhao Y. Sustainable Recycling of Mushroom Residue as an Effective Substitute for Cotton Hull Waste in Volvariella volvacea Cultivation: Evidence from Physicochemical and Microbiome Analyses. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102372
Chicago/Turabian StyleKakumyan, Pattana, Lin Yang, Shunjie Liu, Kritsakorn Saninjuk, Qin Dong, Xueyu Pan, Changxia Yu, and Yan Zhao. 2025. "Sustainable Recycling of Mushroom Residue as an Effective Substitute for Cotton Hull Waste in Volvariella volvacea Cultivation: Evidence from Physicochemical and Microbiome Analyses" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102372
APA StyleKakumyan, P., Yang, L., Liu, S., Saninjuk, K., Dong, Q., Pan, X., Yu, C., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Sustainable Recycling of Mushroom Residue as an Effective Substitute for Cotton Hull Waste in Volvariella volvacea Cultivation: Evidence from Physicochemical and Microbiome Analyses. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102372






