On the Trail of Stubborn Bacterial Yellowing Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Citrus Little Leaf (LLD)—Citrus Stubborn Disease (CSD) in Israel
3. Bermuda Grass Yellowing Disease (1970–1975)
4. Spiroplasma citri and the Causal Agent of LLD-CSD (1973–1974)
5. Spiroplasma citri Diagnosis Using ELISA (1978)
6. Natural Remission of LLD/CSD Symptoms: Is It Worth Waiting?
7. Attempts to Rescue LLD-Infected Trees by Pruning and Hormonal Treatments
8. Failure to Cure LLD Infected Trees with Antibiotics (1971–1972)
9. Experimenting with Shade Cloth Netting to Prevent LLD Infection
10. Clustering of LLD-Infected Trees
11. Papaya Dieback-Nivun Haamir (1982–1991)
- Insect-proof netting
- 30% shade netting
- 15% shade netting
- 15% shade netting + Temik (aldicarb) soil insecticide
- Whitewash spraying every 10 days
- Uncovered controls
- Dust accumulation on nets significantly reduced light transmission, resulting in plant etiolation.
- Netting interfered with insect pollination, leading to poor-size fruit set.
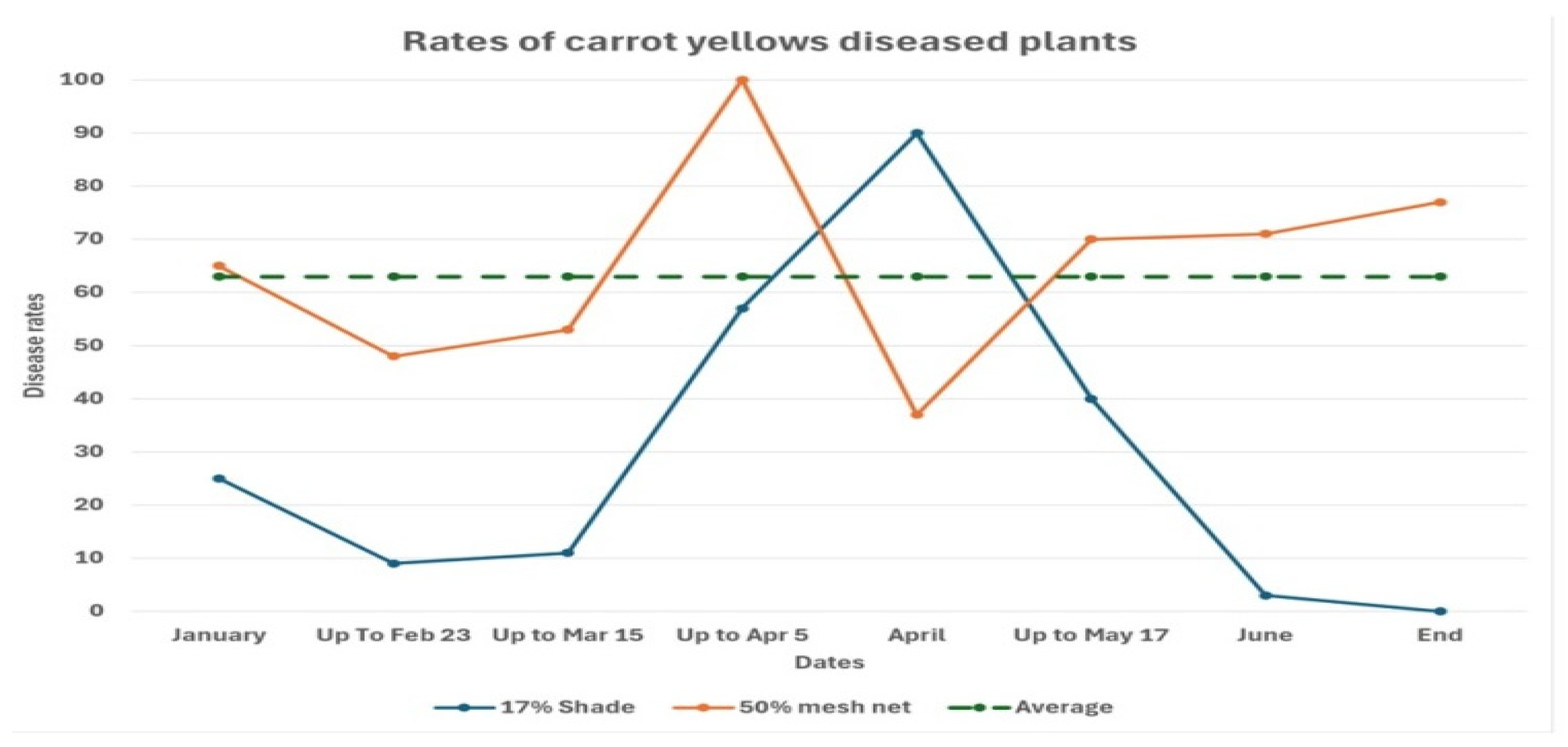
12. Carrot Yellowing and Vector Exclusion Studies
13. Challenges Ahead in Translating Bacterial Genomic Advances into Practical Tools Against Phloem-Invasive Pathogens
14. Epilog
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doi, Y.; Teranaka, M.; Yora, K.; Asuyama, H. Mycoplasma- or PLT group-like microorganisms found in the phloem elements of plants infected with mulberry dwarf, potato witches’ broom, aster yellows, or Paulownia witches’ broom. Jpn. J. Phytopathol. 1967, 33, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiie, T.; Doi, Y.; Yora, K.; Asuyama, H. Suppressive Effects of Antibiotics of Tetracycline Group on Symptom Development of Mulberry Dwarf Disease. Jpn. J. Phytopathol. 1967, 33, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparich, G.E. Spiroplasmas and phytoplasmas: Microbes associated with plant hosts. Biologicals 2010, 38, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.S.; Son, J.; Oren, A. A phylogenomic and molecular markers based taxonomic framework for members of the order Entomoplasmatales: Proposal for an emended order Mycoplasmatales containing the family Spiroplasmataceae and emended family Mycoplasmataceae comprised of six genera. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 561–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirdat, K.; Tiwarekar, B.; Sathe, S.; Yadav, A. From sequences to species: Charting the phytoplasma classification and taxonomy in the era of taxogenomics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1123783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, P.G.; Beanland, L. Insect vectors of phytoplasmas. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 2006, 51, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perilla-Henao, L.M.; Casteel, C.L. Vector-Borne Bacterial Plant Pathogens: Interactions with Hemipteran Insects and Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hosmani, P.S.; Flores-Gonzalez, M.; Shippy, T.; Vosburg, C. Challenging battles of plants with phloem-feeding insects and prokaryotic pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 23390–23397. [Google Scholar]
- Bendix, C.; Lewis, J.D. The enemy within: Phloem-limited pathogens. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Agranovsky, A.A.; Lesemann, D.E. Beet Yellows Virus: Descriptions of Plant Viruses. DPVweb.net. No: 377. 2000. Available online: https://www.dpvweb.net/dpv/showdpv/?dpvno=377 (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Davis, R.E.; Worley, J.F.; Whitcomb, R.F.; Ishijima, T.; Steere, R.L. Helical filaments produced by a mycoplasma-like organism associated with corn stunt disease. Science 1972, 176, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglio, P.; Lhospital, M.; Lafleche, D.; Dupont, G.; Bove, J.M.; Tully, J.G.; Freundt, E.A. Spiroplasma citri gen. and sp. n.: A Mycoplasma-Like Organism Associated with “Stubborn” Disease of Citrus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1973, 23, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.L.; Whitcomb, R.F. Plant Mycoplasmas: A Cultivable Spiroplasma Causes Corn Stunt Disease. Science 1975, 188, 1018–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calavan, E.C.; Bové, J.M. Ecology of Spiroplasma citri. In The Mycoplasmas; Whitcomb, R.F., Tully, J.G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 425–485. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, J.; Melcher, U.; Wayadande, A. The phytopathogenic Spiroplasmas. In The Prokaryotes; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 905–947. ISBN 9780387254944. [Google Scholar]
- Harne, S.; Gayathri, P.; Béven, L. Exploring Spiroplasma Biology: Opportunities and Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.E.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gasparich, G.E.; Gaynor, B.J.; Donofrio, N. Complete Genome Sequence of Spiroplasma citri Strain R8-A2T, Causal Agent of Stubborn Disease in Citrus Species. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00206-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokomi, R.; Rattner, R.; Osman, F.; Maheshwari, Y.; Selvaraj, V.; Pagliaccia, D.; Chen, J.; Vidalakis, G. Whole genome sequence of five strains of Spiroplasma citri isolated from different host plants and its leafhopper vector. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-M.; Davis, R.E.; Gundersen-Rindal, D.E. Phytoplasma: Phytopathogenic mollicutes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 221–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, N.M.; Axelsen, K.B.; Nicolaisen, M.; Schulz, A. Phytoplasmas and their interactions with hosts. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kube, M.; Mitrovic, J.; Duduk, B.; Rabus, R.; Seemüller, E. Current view on phytoplasma genomes and encoded metabolism. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 185942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, S. Molecular and biological properties of phytoplasmas. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2019, 95, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hemmati, C.; Nikooei, M.; Al-Subhi, A.M.; Al-Sadi, A.M. History and Current Status of Phytoplasma Diseases in the Middle East. Biology 2021, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kumari, S.; Nagendran, K.; Rai, A.B.; Singh, B.; Rao, G.P.; Bertaccini, A. Global Status of Phytoplasma Diseases in Vegetable Crops. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, W.; Reyes-Caldas, P.; Mann, M.; Seifbarghi, S.; Kahn, A.; Almeida, R.P.; Béven, L.; Heck, M.; Hogenhout, S.A.; Coaker, G. Bacterial Vector-Borne Plant Diseases: Unanswered Questions and Future Directions. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Bai, B.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L. Phytoplasma: A plant pathogen that cannot be ignored in agricultural production—Research progress and outlook. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 25, e13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bové, J.M. Huanglongbing: A destructive, newly emerging, century-old disease of citrus. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 88, 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, N.A.; Zhang, S.; Setubal, J.C.; Almeida, N.F.; Martins, E.C.; Harakava, R.; Kumar, D.; Rangel, L.T.; Foissac, X.; Bové, J.M.; et al. The complete genome sequence of ‘Candidatus Liberibacter americanus’, associated with Citrus huanglongbing. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2014, 27, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Ghanim, M. Interactions of Liberibacter Species with Their Psyllid Vectors: Molecular, Biological and Behavioural Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Prager, S.M.; Cohen, A.; Cooper, W.R.; Novy, R.; Rashed, A.; Wenninger, E.J.; Wallis, C. A comprehensive review of zebra chip disease in potato and its management through breeding for resistance/tolerance to ‘Candidatus Liberibacter solanacearum’ and its insect vector. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 3731–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killiny, N. Made for Each Other: Vector–Pathogen Interfaces in the Huanglongbing Pathosystem. Phytopatholgy 2022, 112, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.H.; Bassanezi, R.B.; Dawson, W.O.; Dantzler, R. Management of Huanglongbing of Citrus: Lessons from São Paulo and Florida. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2024, 62, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, I.; Perlberger, J. Little leaf disease of citrus trees and its cause. Hadar 1931, 4, 193–194. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.M. Virus and virus like diseases. In The Citrus Industry; Reuther, W., Calavan, E.C., Carman, G.E., Eds.; Division Agricultural Sciences University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1978; Volume 4, pp. 67–184. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, E.O.; Rogers, B. Effects of temperature on expression and transmission of stubborn disease of citrus. Plant Dis. Rep. 1969, 53, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Calavan, E.C.; Blue, R.L.; Harjung, M.K.; Cartia, G.; Granett, A.L.; Rana, G.L.; Gumpf, D.J. Seasonal and geographical variations in natural spread of citrus stubborn disease. In Proceedings of the 7th Conference of the International Organization of Citrus Virologists (IOCV); Calavan, E.C., Ed.; University of California: Riverside, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- DE Almeida, L.; Raccah, B.; Klein, M. Transmission characteristics of Spiroplasma citri and its effect on leafhopper vectors from the Circulifer tenellus complex. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1997, 130, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Raccah, B. The Effect of Temperature and Hosts on the Population Dynamics of Neoaliturus fenestratus (Her-Rich-Schäffer) (Hemiptera: Euscelidae); Bulletin of Entomological Research; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro-Fernández, A.; Hernández-Llópis, D.; Ibáñez, I.; Rodríguez-León, F.; Ferrándiz, J.C.; Sanjuán, S.; Font, M.I. First report of Spi-roplasma citri in celery in Spain. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1175. Available online: http://apsjournals.apsnet.org/loi/pdis (accessed on 1 January 2020). [CrossRef]
- Kyriakou, A.; Eliades, G.; Ioannou, N.; Kapari-Isaia, T. Effect of stubborn disease on growth, yield and fruit quality of Frost Washington Navel and Frost Valencia oranges in Cyprus. J. Hortic. Sci. 1996, 71, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Fatah, W.; Egiza, A.O.; Youssef, S.A.; Shalaby, A.A. Isolation and Identification of Spiroplasma citri Associated with Citrus Stubborn Disease in Egypt. Int. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Sci. 2016, 3, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Çağlar, B.K.; Satar, G.; Baloğlu, S.; Draïs, M.I.; Djelouah, K. Detection of Spiroplasma citri from citrus trees in Turkey by molecular techniques. Mediterr. Agric. Sci. 2020, 33, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calavan, E.C. A review on Stubborn diseases of citrus. Int. Organ. Citrus Virol. Conf. Proc. 1968, 4, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Bové, J.M.; Garnier, M. Stubborn. In Compendium of Citrus Diseases; Timmer, L.W., Garnsey, S.M., Graham, J.H., Eds.; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000; pp. 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sagouti, T.; Belabess, Z.; Rhallabi, N.; Barka, E.A.; Tahiri, A.; Lahlali, R. Citrus Stubborn Disease: Current Insights on an Enigmatic Problem Prevailing in Citrus Orchards. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, A.F.S.; Yokomi, R.K.; Melcher, U.; Chen, J.; Civerolo, E.; Wayadande, A.C.; Fletcher, J. New Perspectives on the Epidemiology of Citrus Stubborn Disease in California Orchards. Plant Health Prog. 2010, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour-Eldin, F. Safargali (stubborn) disease in the U.A.R. and an associated tumor-inducing agent. In Proceedings of the 4th International Organization of Citrus Virologists (IOCV) Conference, Riverside, CA, USA, 1968; Childs, J.F.L., Ed.; University of Florida Press: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1968; p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- Pappo, S.; Bauman, I. A survey of the present status of little leaf (Stubborn0 DISEASE IN Israel). In Proceedings of the First International Citrus Symposium; Riverside, CA, USA, 16–26 March 1968, Chapman, H.D., Ed.; University of California: Riverside, CA, USA, 1968; Volume 3, pp. 1439–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Joseph, M. On the Trail of the Longest Plant RNA Virus: Citrus Tristeza Virus. Viruses 2025, 17, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Raccah, B.; Klein, M. Transmission of the safflower phyllody mollicute by Neolaiturusfenestratus. Phytopathology 1982, 72, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelcer, A.; Bar-Joseph, M.; Loebenstein, G. Mycoplasma-like bodies associated with little-leaf disease of citrus. Israel J. Agric. Res. 1971, 21, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zelcer, A.; Loebenstein, G.; Bar-Joseph, M. Effects of elevated temperature on the ultrastructure of mycoplasmalike or-ganisms in periwinkle. Phytopathology 1972, 62, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.F.; Flegg, C.L.; Bar-Joseph, M.; Rottem, S. The Detection of Spiroplasma citri by Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). J. Phytopathol. 1978, 92, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Joseph, M.; Zelcer, A.; Loebenstein, G. Association of mycoplasmalike organisms with Bermuda grass yellow leaf. Phytopathology 1975, 65, 640–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, Y.; Powell, C.A.; Doud, M.S.; Yang, C.; Duan, Y. Effective antibiotics against ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’ in HLB-affected citrus plants identified via the graft-based evaluation. PLoS ONE 2014, 5, e111032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, S.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. Diversity and functional importance of phytoplasma membrane proteins. Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudl-Allah, A.; Calavan, E.C.; Igwegbe, E.C.K. Culture of a mycoplasma-like organism associated with stubborn disease of citrus. Phytopathology 1972, 62, 729–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, M.J.; Markham, P.G.; Meddins, B.M.; Plaskitt, A.K.; Townsend, R.; Bar-Joseph, M. Axenic culture of a plant path-ogenic spiroplasma. Nature 1973, 244, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, P.G.; Townsend, R.; Bar-Joseph, M.; Daniels, M.J.; Plaskitt, A.; Meddins, B.M. Spiroplasmas are the causal agents of citrus little-leaf disease. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1974, 78, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Gumpf, D.J.; Oldfield, G.N.; Calavan, E. C Transmission of Spriroplasma citri by Circulifer tenellus. Phyto-Pathology 1983, 73, 582–585. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Joseph, M.; Garnsey, S.M. ELISA principles and applications for the diagnosis of plant viruses. In Plant Diseases and Vectors: Ecology and Epidemiology; Maramorosch, K., Harris, K.F., Eds.; NY and London Academic Press: London, UK, 1981; pp. 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Joseph, M. On the Trail of Viroids a Return to Phytosanitary Awareness. Pathogens 2025, 14, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bowyer, J.W. Antibiotic Sensitivity In Vitro of the Mycoplasmalike Organism Associated with Citrus Stubborn Disease. Phytopathology 1974, 64, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, Y.; Shabi, E.; Solel, Z.; Cohen, A. Infiltration and translocation of thaibendazole in apple trees by means of a pressure injection technique. Phytopathology 1973, 63, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck, A.; Bar-Joseph, M. Use of netting and whitewash spray to protect papaya plants against Nivun Haamir (NH)-dieback disease. Crop. Prot. 1992, 11, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Joseph; Nestel, D. Clustering of little-leaf-Stubborn infected citrus trees. Hassadeh 1996, 76, 54–56+59. (In Hebrew) [Google Scholar]
- Glennie, J.D.; Chapman, K.R. A review of die-back-a disorder of the papaw (Carica papaya L.) In Qunsland Queens-Land Department of Primary Industries Division of Plant Industry Bulletin No. 742. Qld. J. Agric. Anim. Sci. 1976, 33, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gibb, K.S.; Persley, D.M.; Schneider, B.; Thomas, J.E. Phytoplasmas associated with papaya diseases in Australia. Plant Dis. 1996, 80, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gera, A.; Maslenin, L.; Weintraub, P.G.; Mawassi, M. Phytoplasma and spiroplasma diseases in open-field crops in Israel. Bull. Insectology 2011, 64, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub, P.G.; Ziedan, M.; Spiegel, S.; Gera, A. A Survey of the Known Phytolasmas in Israel. Bull. Insectology 2007, 60, 143–144. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, A.; Wayadande, A.C.; Yokomi, R.K.; Fletcher, J. Transmission of Different Isolates of Spiroplasma citri to Carrot and Citrus by Circulifer tenellus (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae). J. Econ. Èntomol. 2009, 102, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Joseph, M.; Gera, A. Netting and insecticide spraying effects on Carrot Yellow Disease incidence Section 5. In Management of the Carrot Yellow Disease Report in Ministry of Agriculture Israel; Gera, A., Mawassi, M., Dar, Z., Steinberg, D., Ghanim, M., Dekko, Z., Eds.; Chief Scientist, Research Management System 132-1603-12; Ministry of Agriculture Israel: Beit Dagan, Israel, 2015; pp. 19–21. (In Hebrew) [Google Scholar]
- Musetti, R.; Paolacci, A.; Ciaffi, M.; Tanzarella, O.A.; Polizzotto, R.; Tubaro, F.; Mizzau, M.; Ermacora, P.; Badiani, M.; Osler, R. Phloem Cytochemical Modification and Gene Expression Following the Recovery of Apple Plants from Apple Proliferation Disease. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bar-Joseph, M. On the Trail of Stubborn Bacterial Yellowing Diseases. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102296
Bar-Joseph M. On the Trail of Stubborn Bacterial Yellowing Diseases. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102296
Chicago/Turabian StyleBar-Joseph, Moshe. 2025. "On the Trail of Stubborn Bacterial Yellowing Diseases" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102296
APA StyleBar-Joseph, M. (2025). On the Trail of Stubborn Bacterial Yellowing Diseases. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102296






