Mapping Staphylococcus aureus at Early and Late Stages of Infection in a Clinically Representative Hip Prosthetic Joint Infection Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Preparation of S. aureus
2.2. Cemented Hip HA PJI Animal Model
2.3. In Vivo Luminescent Imaging
2.4. Bacterial Load in Tissue
2.5. Histology Analysis
2.5.1. Fixation and Processing of Femur and Acetabulum
2.5.2. IHC Staining
2.5.3. Analysis of Histology Slides
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Establishing Infection
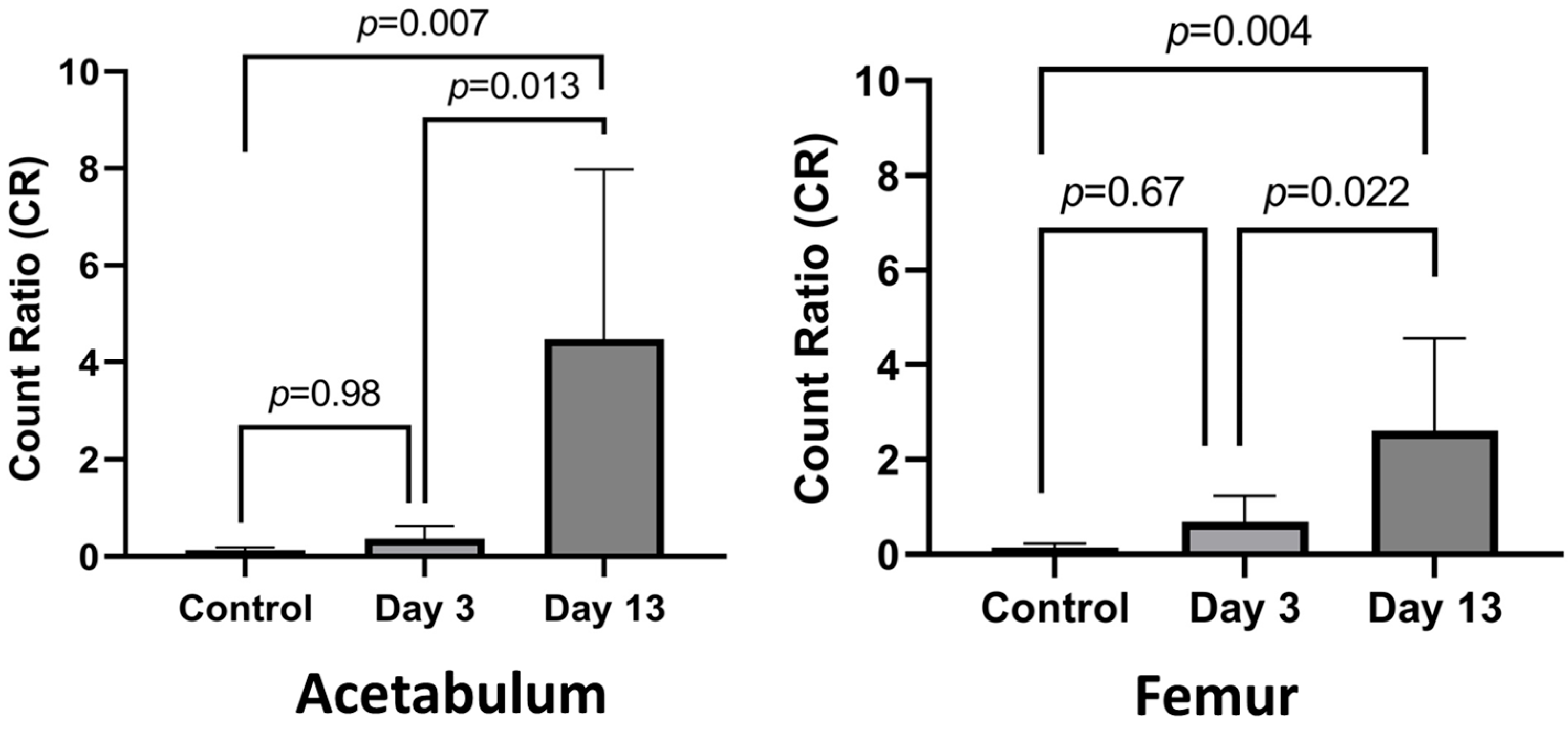
3.2. Histological Analysis of Acetabulum
3.3. Histologic Analysis of Femur
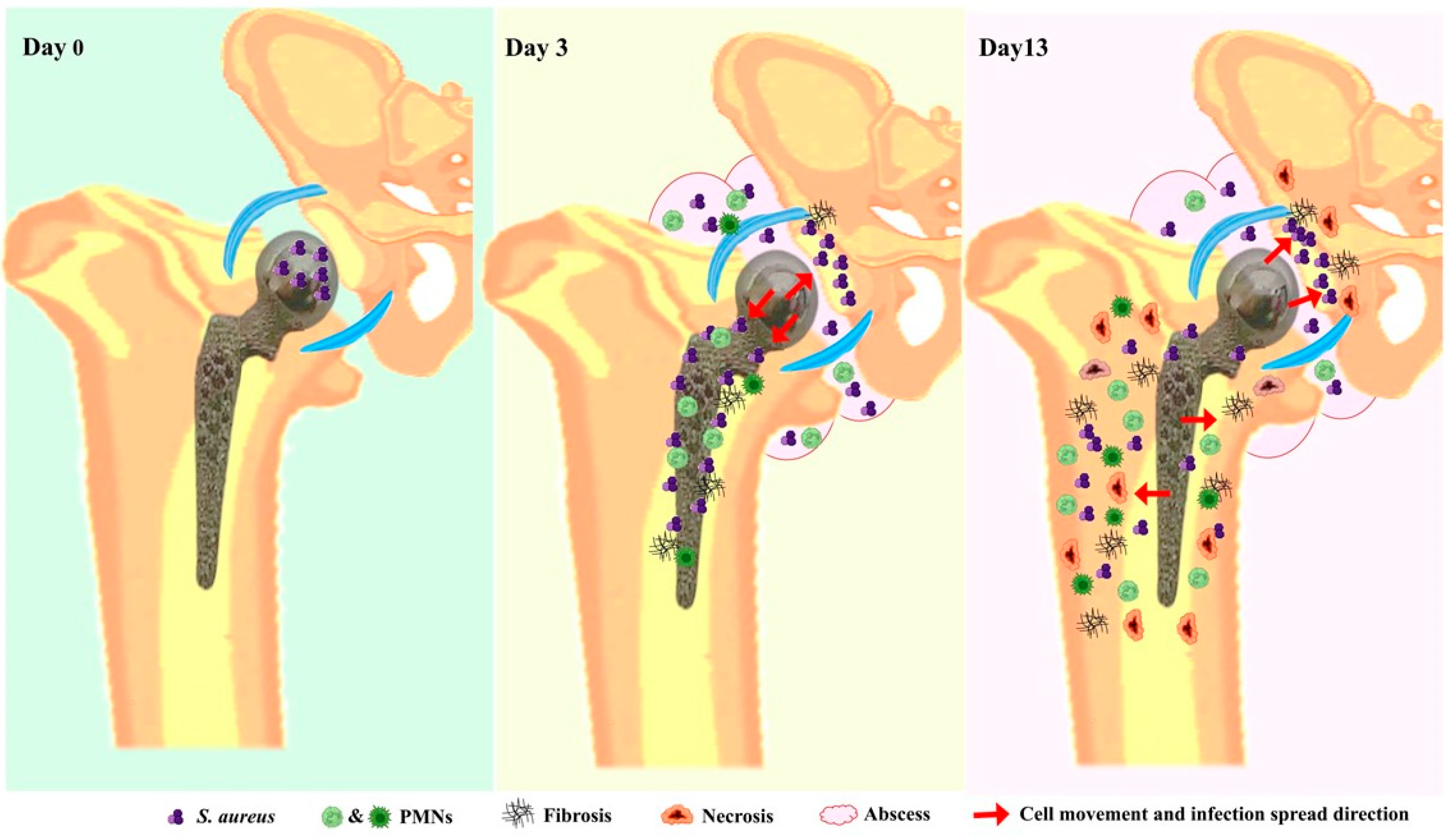
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, C.; Counsell, A.; Boulton, C.; Moran, C.G. Early infection after hip fracture surgery: Risk factors, costs and outcome. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2008, 90, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, T.C.; Newman, J.E.; Barlow, N.J.; Price, J.D.; Willett, K.M. Deep wound infection after proximal femoral fracture: Consequences and costs. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 63, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourget-Murray, J.; Bansal, R.; Soroceanu, A.; Piroozfar, S.; Railton, P.; Johnston, K.; Johnson, A.; Powell, J. Assessment of risk factors for early-onset deep surgical site infection following primary total hip arthroplasty for osteoarthritis. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2021, 6, 443–450, Erratum in J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2022, 7, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, J.; Metcalfe, D.; Ha, J.S.; Judge, A.; Costa, M.L. Surgical site infection after hip fracture surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies published in the UK. Bone Jt. Res. 2020, 9, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster Arthroplasty, C. Risk Factors for Periprosthetic Joint Infection Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: A 15-Year, Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2020, 102, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, A.F.; Ong, K.L.; Lau, E.; Chan, V.; Vail, T.P.; Rubash, H.E.; Berry, D.J.; Bozic, K.J. Quantifying the Burden of Revision Total Joint Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2015, 30, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Whitehouse, M.R.; Blom, A.W.; Board, T.; Kay, P.; Wroblewski, B.M.; Zeller, V.; Chen, S.Y.; Hsieh, P.H.; Masri, B.A.; et al. One- and two-stage surgical revision of peri-prosthetic joint infection of the hip: A pooled individual participant data analysis of 44 cohort studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, C.L.; Tsuchiya, H.; Morelli, I.; Battaglia, A.G.; Drago, L. Antibacterial coating of implants: Are we missing something? Bone Jt. Res. 2019, 8, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, W.Y.; Jafari, S.M.; Restrepo, C.; Austin, M.; Purtill, J.J.; Parvizi, J. Preventing infection in total joint arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2010, 92 (Suppl. 2), 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartzler, M.A.; Li, K.; Geary, M.B.; Odum, S.M.; Springer, B.D. Complications in the treatment of prosthetic joint infection. Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102 (Suppl. B), 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassim, S.A.; Limoges, R.G. Natural solution to antibiotic resistance: Bacteriophages ‘The Living Drugs’. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2153–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson Malchau, K.; Tillander, J.; Zaborowska, M.; Hoffman, M.; Lasa, I.; Thomsen, P.; Malchau, H.; Rolfson, O.; Trobos, M. Biofilm properties in relation to treatment outcome in patients with first-time periprosthetic hip or knee joint infection. J. Orthop. Transl. 2021, 30, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, T.; Li, B. Differential responses of osteoblasts and macrophages upon Staphylococcus aureus infection. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosse, M.J.; Gruber, H.E.; Ramp, W.K. Internalization of bacteria by osteoblasts in a patient with recurrent, long-term osteomyelitis. A case report. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2005, 87, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, W.J.; Ibrahim, M.; Taha, M.; Ure, K.; Liu, Y.; Paish, A.D.M.; Holdsworth, D.W.; Abdelbary, H. 2021 Frank Stinchfield Award: A novel cemented hip hemiarthroplasty infection model with real-time in vivo imaging in rats: An animal study. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103 (Suppl. B), 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paish, A.D.M.; Nikolov, H.N.; Welch, I.D.; El-Warrak, A.O.; Teeter, M.G.; Naudie, D.D.R.; Holdsworth, D.W. Image-based design and 3D-metal printing of a rat hip implant for use in a clinically representative model of joint replacement. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, A.V.; Ross, F.P.; Bhimani, S.J.; Nodzo, S.R.; Bostrom, M.P. Developing a Clinically Representative Model of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2016, 98, 1666–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, M.; Abdelbary, H.; Ross, F.P.; Carli, A.V. New Innovations in the Treatment of PJI and Biofilms-Clinical and Preclinical Topics. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2018, 11, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, S.; Wang, T.; Bolam, S.M.; Alvares, S.; Swift, S.; Cornish, J.; Williams, D.L.; Ashton, N.N.; Matthews, B.G. Rat model of recalcitrant prosthetic joint infection using biofilm inocula. J. Orthop. Res. 2023, 41, 2462–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poilvache, H.; Van Bambeke, F.; Cornu, O. Development of an innovative in vivo model of PJI treated with DAIR. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 984814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribaz, J.R.; Bernthal, N.M.; Billi, F.; Cho, J.S.; Ramos, R.I.; Guo, Y.; Cheung, A.L.; Francis, K.P.; Miller, L.S. Mouse model of chronic post-arthroplasty infection: Noninvasive in vivo bioluminescence imaging to monitor bacterial burden for long-term study. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaise, O.; Leseigneur, C.; Cokelaer, T.; Capuzzo, E.; Frescaline, N.; Dussurget, O. Complete Genome Sequences of Bioluminescent Staphylococcus aureus Strains Xen31 and Xen36, Derived from Two Clinical Isolates. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2023, 12, e0002423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzana, J.A.; Schwarz, E.M.; Kates, S.L.; Awad, H.A. A novel murine model of established Staphylococcal bone infection in the presence of a fracture fixation plate to study therapies utilizing antibiotic-laden spacers after revision surgery. Bone 2015, 72, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishitani, K.; Sutipornpalangkul, W.; de Mesy Bentley, K.L.; Varrone, J.J.; Bello-Irizarry, S.N.; Ito, H.; Matsuda, S.; Kates, S.L.; Daiss, J.L.; Schwarz, E.M. Quantifying the natural history of biofilm formation in vivo during the establishment of chronic implant-associated Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis in mice to identify critical pathogen and host factors. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mesy Bentley, K.L.; Trombetta, R.; Nishitani, K.; Bello-Irizarry, S.N.; Ninomiya, M.; Zhang, L.; Chung, H.L.; McGrath, J.L.; Daiss, J.L.; Awad, H.A.; et al. Evidence of Staphylococcus Aureus Deformation, Proliferation, and Migration in Canaliculi of Live Cortical Bone in Murine Models of Osteomyelitis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Ure, K.; Hall, C.W.; Mah, T.F.; Abdelbary, H. Establishment of a Novel Rat Model of Gram-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infection Using Cementless Hip Hemiarthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2023, 105, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.K.; Jensen, H.E.; Gottlieb, H. Intraoperative tissue sampling for histology in chronic osteomyelitis shows high neutrophil infiltration centrally and low remains in debrided presumed infection-free regions. Injury 2024, 55, 111178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.F.; Caterina, P.; Filion, P.; van Heerden, P.V.; Ilett, K.F. The ratio of polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN) to non-PMN cells—A novel method of assessing acute lung inflammation. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2002, 54, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restall, I.J.; Parolin, D.A.; Daneshmand, M.; Hanson, J.E.; Simard, M.A.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Kumar, R.; Lavictoire, S.J.; Lorimer, I.A. PKCiota depletion initiates mitotic slippage-induced senescence in glioblastoma. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2938–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gunther, F.; Wabnitz, G.H.; Stroh, P.; Prior, B.; Obst, U.; Samstag, Y.; Wagner, C.; Hansch, G.M. Host defence against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms infection: Phagocytosis of biofilms by polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN). Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, D.L.; Claassen, B.; Black, J. The rat as an animal model for total hip replacement arthroplasty. J. Invest. Surg. 1995, 8, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, R.A.; Leid, J.G.; Calhoun, J.H.; Costerton, J.W.; Shirtliff, M.E. Osteomyelitis and the role of biofilms in chronic infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 52, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora-Tamayo, J.; Euba, G.; Ribera, A.; Murillo, O.; Pedrero, S.; Garcia-Somoza, D.; Pujol, M.; Cabo, X.; Ariza, J. Infected hip hemiarthroplasties and total hip arthroplasties: Differential findings and prognosis. J. Infect. 2013, 67, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, A.; Bourget-Murray, J.; Azad, M.A.; Abdelbary, H.; Grammatopoulos, G.; Garceau, S.P. Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infections After Hemiarthroplasty of the Hip: A Critical Analysis Review. JBJS Rev. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourget-Murray, J.; Horton, I.; Morris, J.; Bureau, A.; Garceau, S.; Abdelbary, H.; Grammatopoulos, G. Periprosthetic joint infection following hip hemiarthroplasty: Factors associated with infection and treatment outcome. Bone Jt. Open 2022, 3, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Toro, M.D.; Nieto, I.; Guerrero, F.; Corzo, J.; del Arco, A.; Palomino, J.; Nuno, E.; Lomas, J.M.; Natera, C.; Fajardo, J.M.; et al. Are hip hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty infections different entities? The importance of hip fractures. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craxford, S.; Marson, B.A.; Nightingale, J.; Ikram, A.; Agrawal, Y.; Deakin, D.; Ollivere, B. Deep infection after hip hemiarthroplasty: Risk factors for infection and outcome of treatments. Bone Jt. Open 2021, 2, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergkvist, M.; Mukka, S.S.; Johansson, L.; Ahl, T.E.; Sayed-Noor, A.S.; Skoldenberg, O.G.; Eisler, T. Debridement, antibiotics and implant retention in early periprosthetic joint infection. Hip Int. 2016, 26, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, J.K.; Harris, M.; Hudson, M.C.; Vishin, S.; Webb, L.X.; Sherertz, R. Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus and antibiotic resistance: Implications for treatment of staphylococcal osteomyelitis. J. Orthop. Res. 2006, 24, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, S.S.; Hudson, M.C.; Kellam, J.F.; Ramp, W.K. In vivo internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by embryonic chick osteoblasts. Bone 2000, 26, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poultsides, L.A.; Papatheodorou, L.K.; Karachalios, T.S.; Khaldi, L.; Maniatis, A.; Petinaki, E.; Malizos, K.N. Novel model for studying hematogenous infection in an experimental setting of implant-related infection by a community-acquired methicillin-resistant S. aureus strain. J. Orthop. Res. 2008, 26, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.M.; Miller, R.J.; Ashbaugh, A.G.; Dillen, C.A.; Pickett, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Ortines, R.V.; Sterling, R.S.; Francis, K.P.; Bernthal, N.M.; et al. Mouse model of Gram-negative prosthetic joint infection reveals therapeutic targets. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e121737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, J.M.; Pannu, T.S.; Theeb, I.; Buttaro, M.A.; Onativia, J.I.; Carbo, L.; Rienzi, D.H.; Fregeiro, J.I.; Kornilov, N.N.; Bozhkova, S.A.; et al. International Organism Profile of Periprosthetic Total Hip and Knee Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taha, M.; AlDuwaisan, A.; Daneshmand, M.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Bourget-Murray, J.; Grammatopoulos, G.; Garceau, S.; Abdelbary, H. Mapping Staphylococcus aureus at Early and Late Stages of Infection in a Clinically Representative Hip Prosthetic Joint Infection Rat Model. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091895
Taha M, AlDuwaisan A, Daneshmand M, Ibrahim MM, Bourget-Murray J, Grammatopoulos G, Garceau S, Abdelbary H. Mapping Staphylococcus aureus at Early and Late Stages of Infection in a Clinically Representative Hip Prosthetic Joint Infection Rat Model. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(9):1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091895
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaha, Mariam, Abdullah AlDuwaisan, Manijeh Daneshmand, Mazen M. Ibrahim, Jonathan Bourget-Murray, George Grammatopoulos, Simon Garceau, and Hesham Abdelbary. 2024. "Mapping Staphylococcus aureus at Early and Late Stages of Infection in a Clinically Representative Hip Prosthetic Joint Infection Rat Model" Microorganisms 12, no. 9: 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091895
APA StyleTaha, M., AlDuwaisan, A., Daneshmand, M., Ibrahim, M. M., Bourget-Murray, J., Grammatopoulos, G., Garceau, S., & Abdelbary, H. (2024). Mapping Staphylococcus aureus at Early and Late Stages of Infection in a Clinically Representative Hip Prosthetic Joint Infection Rat Model. Microorganisms, 12(9), 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091895





