Central Nervous System Disorders with Auto-Antibodies in People Living with HIV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, M.E.; Stein, D.J.; Joska, J.A.; Naudé, P.J.W. Cerebrospinal fluid immune markers and HIV-associated neurocognitive impairments: A systematic review. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 358, 577649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulfhammer, G.; Edén, A.; Mellgren, Å.; Fuchs, D.; Zetterberg, H.; Hagberg, L.; Nilsson, S.; Yilmaz, A.; Gisslén, M. Persistent central nervous system immune activation following more than 10 years of effective HIV antiretroviral treatment. AIDS 2018, 32, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunill, V.; Arboleya, S.; Jiménez, M.d.L.R.; Campins, A.; Herbera, P.; Mestre, L.; Clemente, A.; Barceló, M.I.; Leyes, M.; Canellas, F.; et al. Neuronal surface antibodies in HIV-infected patients with isolated psychosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 301, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneche, F.; Demeret, S.; Psimaras, D.; Katlama, C.; Pourcher, V. An anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis mimicking an HIV encephalitis. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 193, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, P.B.; Hutchinson, S.; Heskin, J.; Mulcahy, F.; Langan, Y.; Conlon, N.P.; Linas, B.P.; Takahashi, C.; Cervantes-Arslanian, A.M. Possible N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibody-mediated encephalitis in the setting of HIV cerebrospinal fluid escape. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchayaram, N.; Nagabushana, D.; Nishamol, T.; Bhattacharya, K.; Saini, J.; Chowdary, R.; Mahadevan, A.; Polavarapu, K. Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate-receptor Encephalitis as a Harbinger of Pediatric HIV Infection. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2021, 16, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, L.M.; Valadares, E.A.; Ferreira-Júnior, C.U.; Santos, M.F.; Albergaria, B.-H.; Rosa-Júnior, M. CD8 + T-lymphocyte Encephalitis: A Systematic Review. AIDS Rev. 2020, 22, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, A.C.; Parker, R.; Allinson, K.; Scoffings, D. CD8 encephalitis presenting as autoimmune encephalitis in HIV-1 infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e246290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.; Goldacre, R.; Maruszak, H.; Giovannoni, G.; Yeates, D.; Goldacre, M. HIV and lower risk of multiple sclerosis: Beginning to unravel a mystery using a record-linked database study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, L.; Bengoufa, D.; Taulera, O.; Rami, A.; Lascoux-Combe, C.; Day, N.; Parrinello, M.; Sellier, P.-O.; Molina, J.-M.; Mahr, A. Nonorgan-specific autoantibodies in HIV-infected patients in the HAART era. Medicine 2017, 96, e6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkiewicz, J.; Smolewska, E. Kaleidoscope of autoimmune diseases in HIV infection. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 36, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratton, R.; Slapak, G.; Mahungu, T.; Kinloch-de Loes, S. Autoimmunity and HIV. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 22, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sempere, J.M.; Soriano, V.; Benito, J.M. T regulatory cells and HIV infection. AIDS Rev. 2007, 9, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, H.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, D.H.; Lee, J.M. A Case of Paraneoplastic Neurological Syndrome Expressing Dual Antineuronal Antibodies: Anti-Hu and Recoverin. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2020, 23, 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T.P.; Nath, A. Biotypes of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders based on viral and immune pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 35, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataller, L.; Wade, D.F.; Graus, F.; Stacey, H.D.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Dalmau, J. Antibodies to Zic4 in paraneoplastic neurologic disorders and small-cell lung cancer. Neurology 2004, 62, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armangue, T.; Spatola, M.; Vlagea, A.; Mattozzi, S.; Cárceles-Cordon, M.; Llufriu, S.; Muchart, J.; Erro, M.E.; Abraira, L.; Moris, G.; et al. Frequency, symptoms, risk factors, and outcomes of autoimmune encephalitis after herpes simplex encephalitis: A prospective observational study and retrospective analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.C.; Partridge, A.T.; Sell, C.; Torres, C.; Martín-García, J. Fate of microglia during HIV-1 infection: From activation to senescence? Glia 2017, 65, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudich, S.S. Immune activation in the central nervous system throughout the course of HIV infection. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2016, 11, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, A.; Turrini, F.; de Zan, V.; Caccia, R.; Gerevini, S.; Cinque, P. Symptomatic cerebrospinal fluid escape. AIDS 2019, 33 (Suppl. S2), S159–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.; Busovaca, E.; Foley, J.M.; Allen, I.E.; Schwarz, C.G.; Jahanshad, N.; Nir, T.M.; Esmaeili-Firidouni, P.; Milanini, B.; Rosen, H.; et al. White matter hyperintensities correlate to cognition and fiber tract integrity in older adults with HIV. J. Neurovirol. 2017, 23, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, H.B.; Perron, H.; Clausen, J. Do endogenous retroviruses have etiological implications in inflammatory and degenerative nervous system diseases? Acta Neurol. Scand. 1993, 88, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornevik, K.; Cortese, M.; Healy, B.C.; Kuhle, J.; Mina, M.J.; Leng, Y.; Elledge, S.J.; Niebuhr, D.W.; Scher, A.I.; Munger, K.L.; et al. Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis. Science 2022, 375, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, W.; Tang, S.J. HIV-1 gp120Bal down-Regulates Phosphorylated NMDA Receptor Subunit 1 in Cortical Neurons via Activation of Glutamate and Chemokine Receptors. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupia, T.; Milia, M.G.; Atzori, C.; Gianella, S.; Audagnotto, S.; Imperiale, D.; Mighetto, L.; Pirriatore, V.; Gregori, G.; Lipani, F.; et al. Presence of Epstein–Barr virus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid is associated with greater HIV RNA and inflammation. AIDS 2020, 34, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.D.; Fugate, J.E.; Rabinstein, A.A. The spectrum of acute encephalitis: Causes, management, and predictors of outcome. Neurology 2015, 84, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gable, M.S.; Sheriff, H.; Dalmau, J.; Tilley, D.H.; Glaser, C.A. The frequency of autoimmune N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis surpasses that of individual viral etiologies in young individuals enrolled in the California Encephalitis Project. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Bharucha, T.; Breuer, J. Encephalitis diagnosis using metagenomics: Application of next generation sequencing for undiagnosed cases. J. Infect. 2018, 76, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pender, M.P.; Csurhes, P.A.; Smith, C.; Douglas, N.L.; Neller, M.A.; Matthews, K.K.; Beagley, L.; Rehan, S.; Crooks, P.; Hopkins, T.J.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-specific T cell therapy for progressive multiple sclerosis. JCI Insight. 2018, 3, e124714, Erratum in JCI Insight. 2020, 5, e144624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud, H.; Probasco, J.C.; Irani, S.; Ances, B.; Benavides, D.R.; Bradshaw, M.; Christo, P.P.; Dale, R.C.; Fernandez-Fournier, M.; Flanagan, E.P.; et al. Autoimmune Encephalitis Alliance Clinicians Network. Autoimmune encephalitis: Proposed best practice recommendations for diagnosis and acute management. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
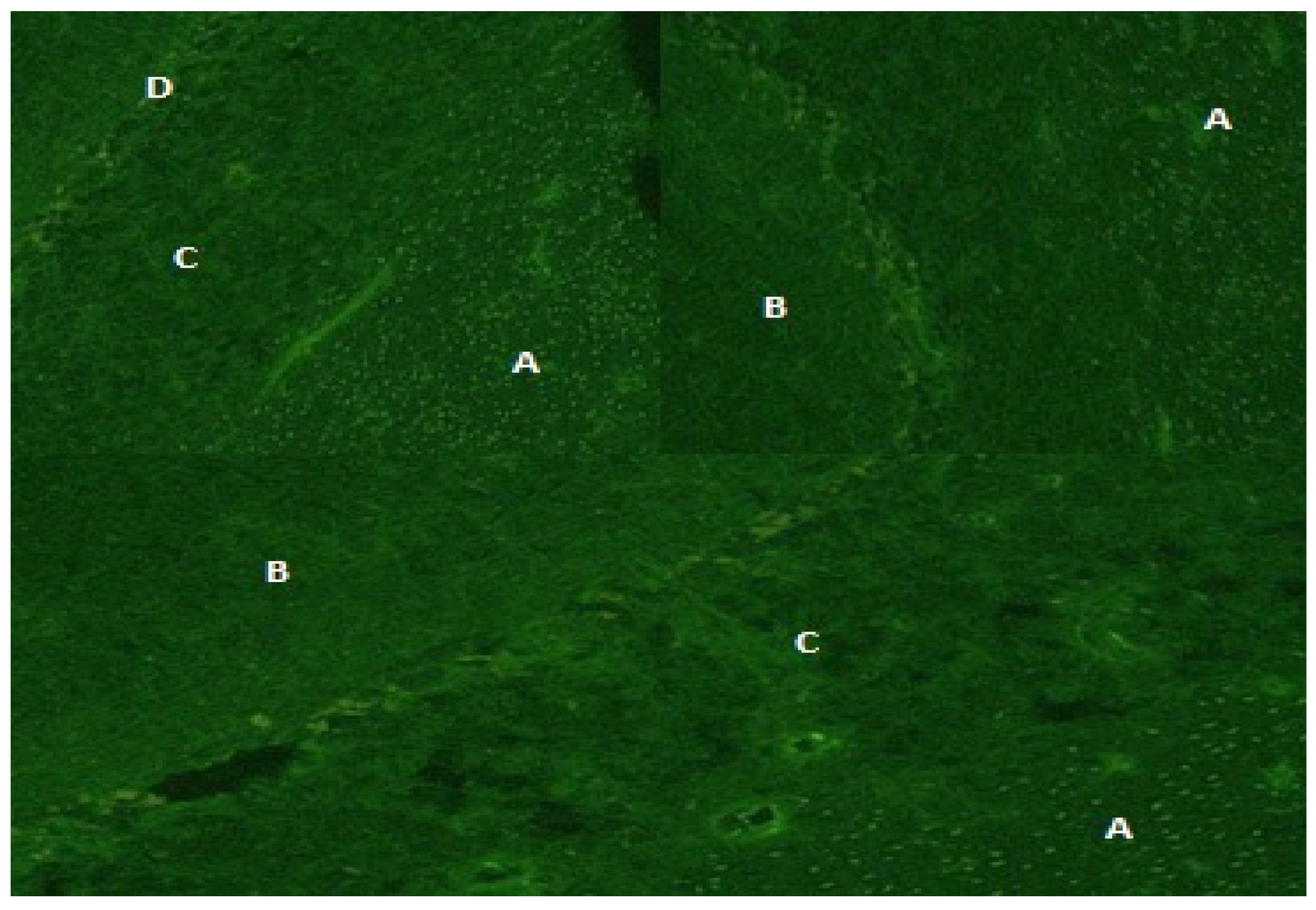
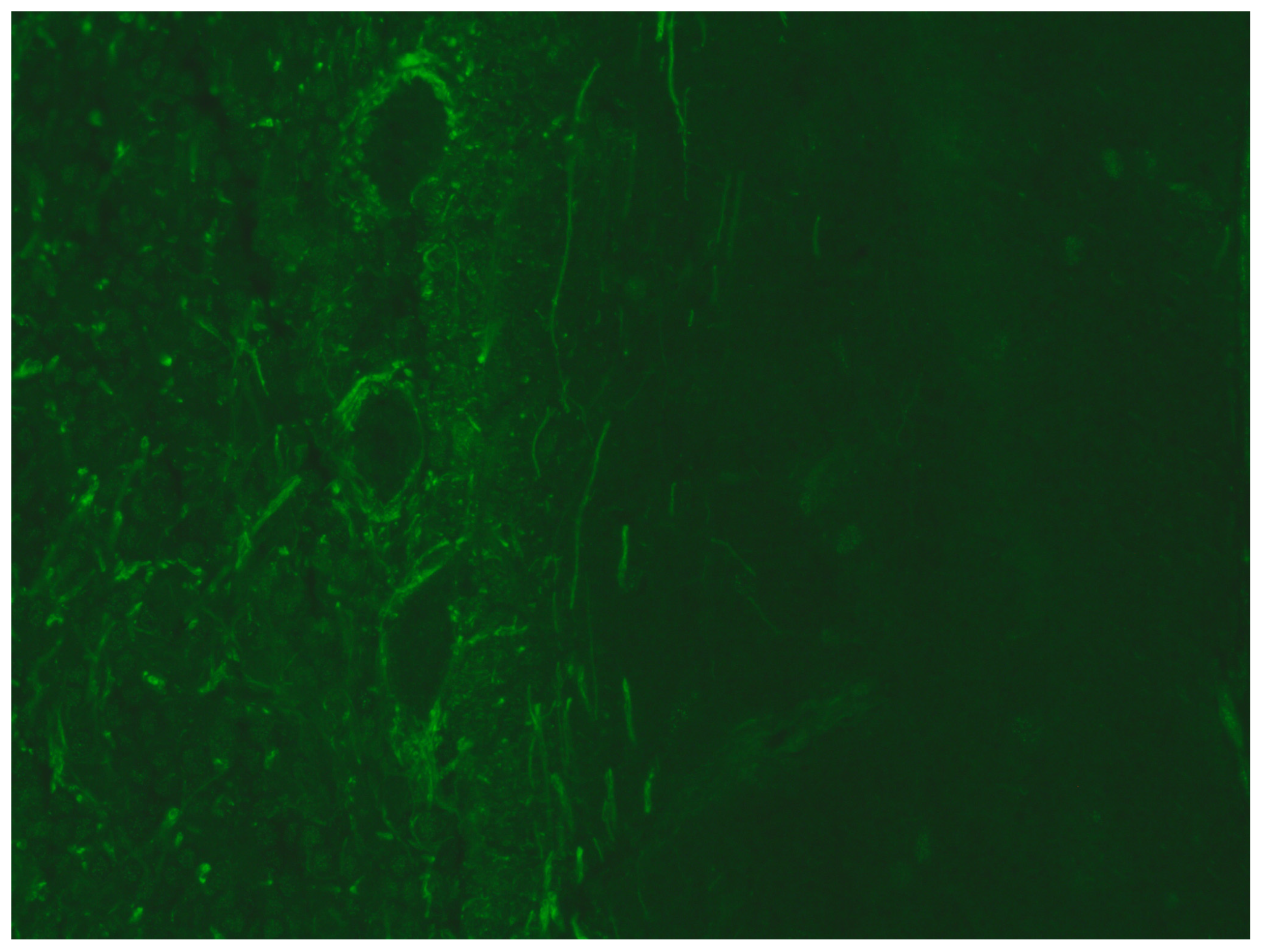
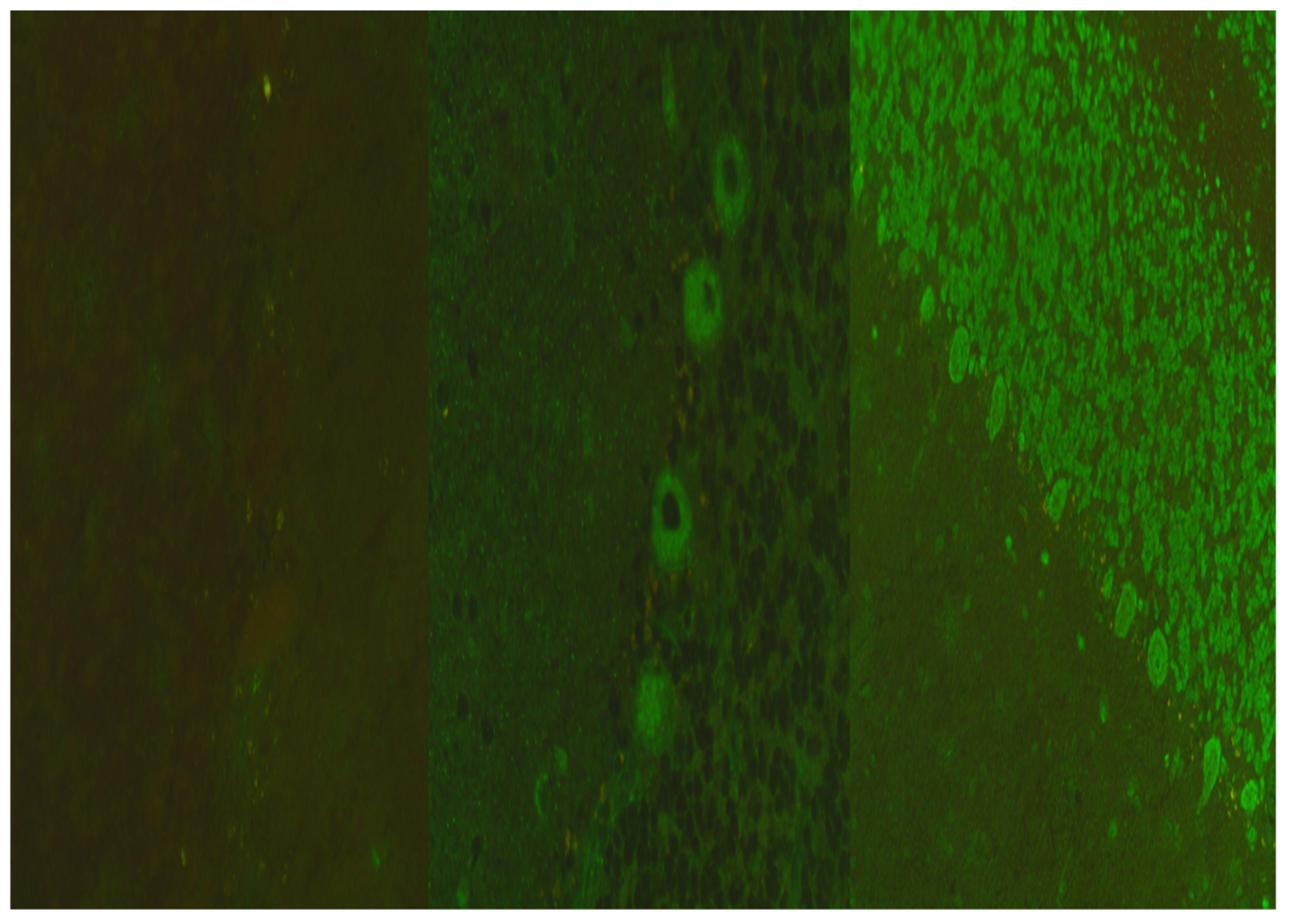
| Patient n° | Age | Gender | Imaging Pattern | Onset Symptoms | CD4+ | HIV RNA Plasma (cp/mL) | HIV RNA CSF (cp/mL) | EBV DNA CSF (cp/mL) | CSF Ab Pattern | EEG | Altered Neuromarkers | HAART | Final Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 52 | M | Demyelinating | Sensory and dysautonomic disorders | 285 | 6679 | 4466 | N/A | Synaptic | Normal | 14.3.3, Neopterin, BBBp, CSAR, and IgG index | Treated | Myelitis |
| 2 | 55 | M | Normal | Asymptomatic, control in previous neurolue, and VDRL serum positivity | 436 | Negative | Negative | N/A | Nuclear | Normal | None | Naïve | None |
| 3 | 28 | M | Inflammatory/demyelinating | Confusion | 251 | 16,197 | 1064 | N/A | Nuclear | Normal | 14.3.3, Tau, and Beta Amyloid | Naïve | Balo concentric sclerosis |
| 4 | 60 | F | Demyelinating | Sensory and extrapyramidal disorders | 111 | Negative | 160 | 54 | Nuclear and Synpatic | Normal | Intrathecal synthesis | Treated | PML-IRIS |
| 5 | 50 | F | Inflammatory/demyelinating | Extrapiramidal disorders and vertigo | 516 | Negative | 7566 | 82 | Aspecific | Normal | Intrathecal synthesis, CSAR, BBBp, Neopterin, and Beta Amyloid | Treated | CNS viral escape |
| 6 | 41 | M | Normal | Cefalea and sensory disorders | 147 | 395 | 71 | Negative | Nuclear | Normal | None | Naïve | HAART neurotoxicity |
| 7 | 41 | M | Demyelinating | Vertigo, sensory and extrapyramidal disorders, and ataxia | 19 | 36,676 | 16,030 | Negative | Synaptic | Normal | Neopterin, BBBp, and CSAR | Naïve | PML |
| 8 | 44 | F | Inflammatory | Dysautonomic and extrapuramidal disorders, confusion, and agitation | 320 | Negative | Negative | 315 | Aspecific | Altered | BBBp and intrathecal synthesis | Treated | None |
| 9 | 60 | F | Inflammatory | Movement disorders and ataxia | 429 | 88,982 | 330,273 | N/A | Aspecific | Altered | Intrathecal synthesis, BBBp, Neopterin, and Beta Amyloid | Treated | CSF viral escape |
| 10 | 44 | M | Demyelinating, inflammatory, and mass effect | Dysautonomic, sensory, and motor disorders | 37 | 758,988 | 23,762 | N/A | Synaptic | Normal | Tau, Neopterin, 14.3.3, and BBBp | Naïve | PCNSL |
| 11 | 50 | M | Atrophic | Extrapyramidal and movement disorders, ataxia, and confusion | 379 | Negative | Negative | Negative | Nuclear | Normal | None | Treated | None |
| 12 | 55 | M | Normal | Sensory disorders | 715 | 1450 | 330,000 | Negative | Nuclear, Recoverin, and Zic 4 on Blot | Normal | BBBp and Intrathecal synthesis | Naïve | None |
| Altered Neuromarkers and Correspondances with Antibody Patterns | Nuclear | Synaptic | Aspecific | Zic4 | Recoverine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neopterin | |||||
| 1–42 Beta Amyloid | |||||
| BBB damage | |||||
| Intrathecal synthesis | |||||
| CSAR | |||||
| Tau | |||||
| FTau | |||||
| 14.3.3. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stroffolini, G.; Atzori, C.; Imperiale, D.; Trunfio, M.; Di Perri, G.; Calcagno, A. Central Nervous System Disorders with Auto-Antibodies in People Living with HIV. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091758
Stroffolini G, Atzori C, Imperiale D, Trunfio M, Di Perri G, Calcagno A. Central Nervous System Disorders with Auto-Antibodies in People Living with HIV. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(9):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091758
Chicago/Turabian StyleStroffolini, Giacomo, Cristiana Atzori, Daniele Imperiale, Mattia Trunfio, Giovanni Di Perri, and Andrea Calcagno. 2024. "Central Nervous System Disorders with Auto-Antibodies in People Living with HIV" Microorganisms 12, no. 9: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091758
APA StyleStroffolini, G., Atzori, C., Imperiale, D., Trunfio, M., Di Perri, G., & Calcagno, A. (2024). Central Nervous System Disorders with Auto-Antibodies in People Living with HIV. Microorganisms, 12(9), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091758






