Variation in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Soils from Three Major Apple Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) Orchards
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sample Collection and Soil Physiochemical Property Determination
2.2. Soil DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Data Analysis
2.3. Statistical Methods
2.4. Network Construction and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
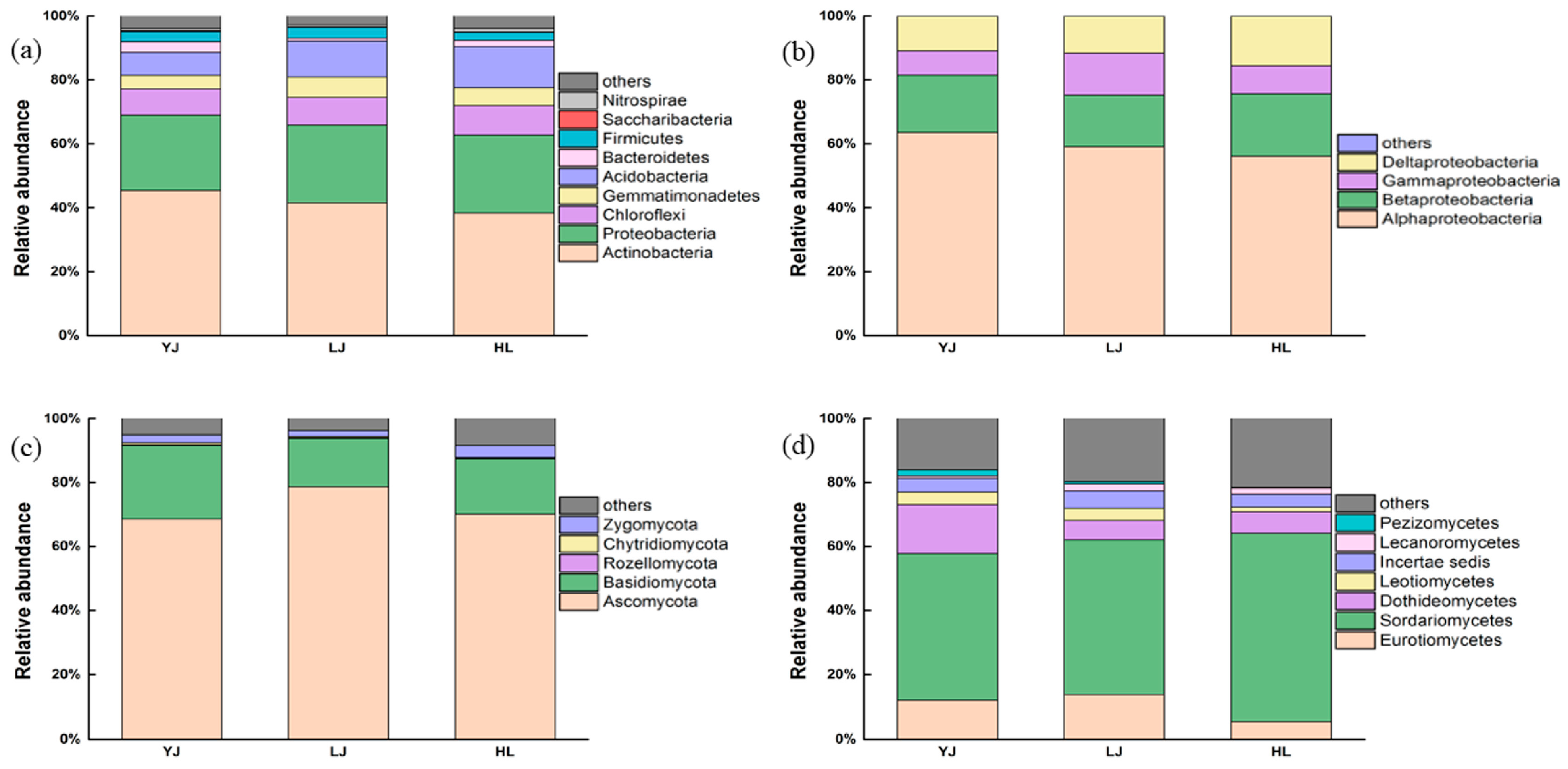
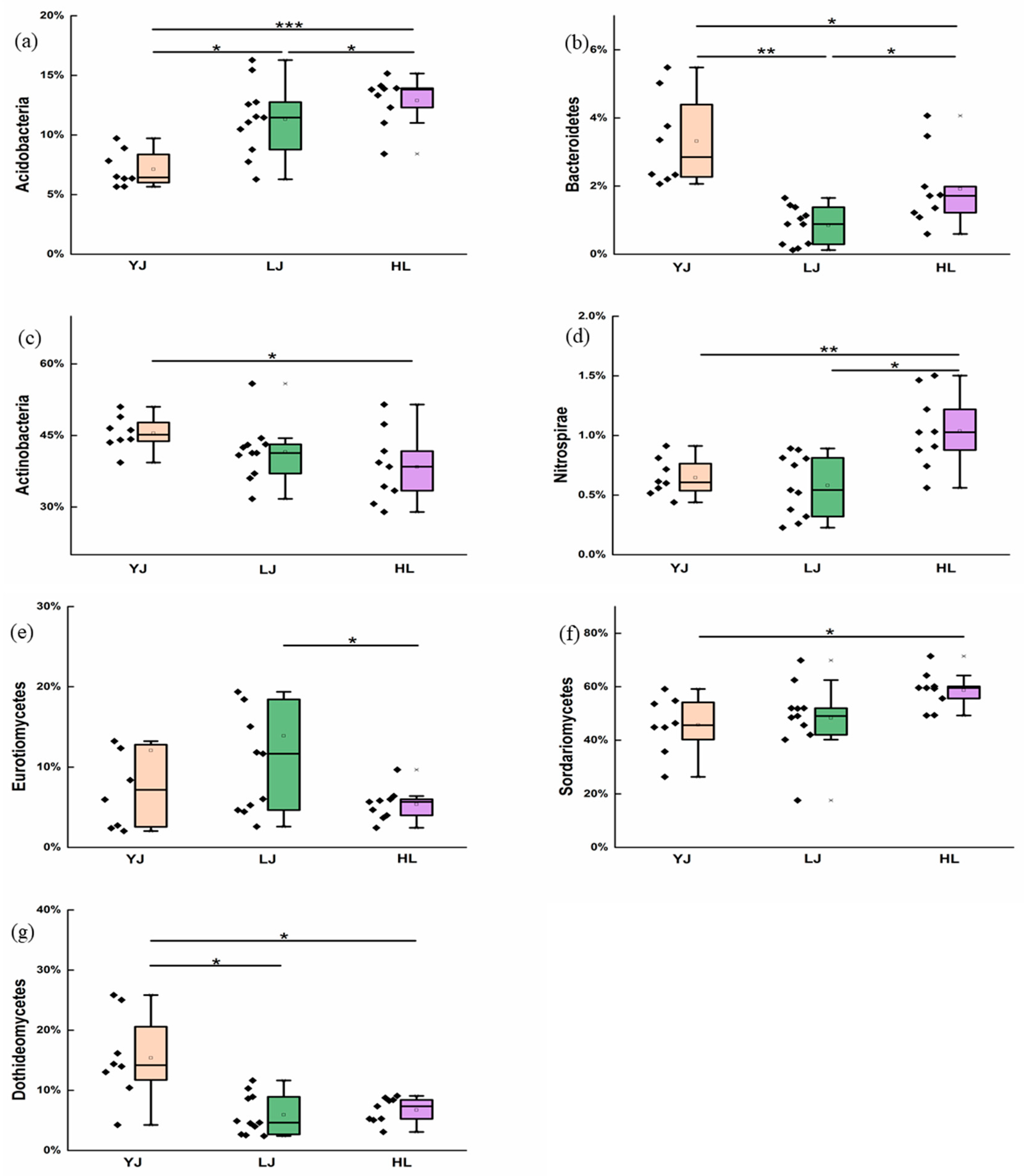
3.1. Bacterial and Fungal Community Composition
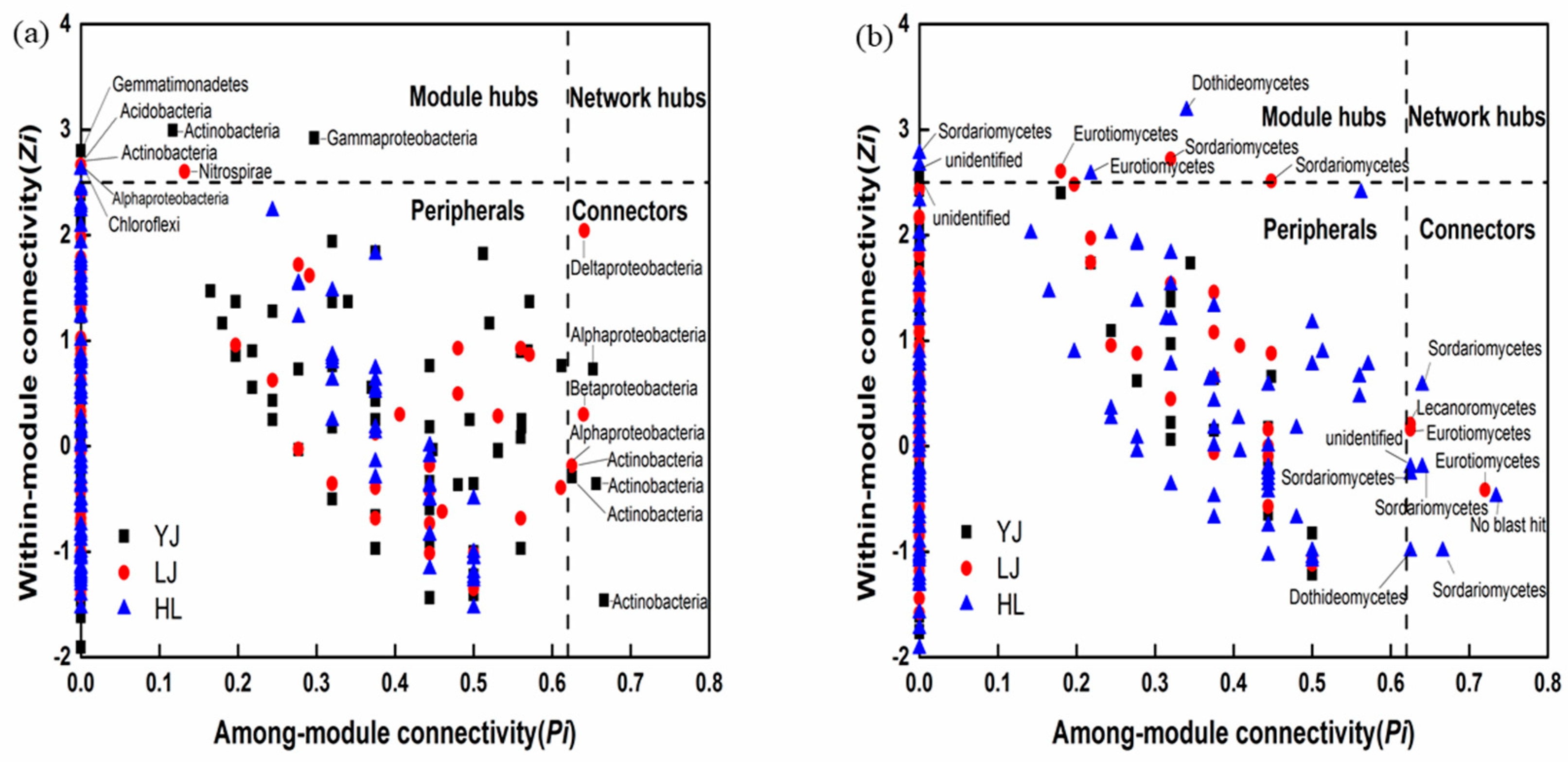
3.2. Network Analysis
3.3. Relationship of Microbial Communities to Physicochemical Properties and Geographic Distance
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Microbial Composition and Keystone Taxa
4.2. Effects of Soil Properties on Microbial Communities
4.3. Interactions between Bacterial Taxa as Revealed by Co-Occurrence Networks
4.4. Effects of Geographic Distance on Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piao, Y.; Liu, B.; Piao, Y.; Yang, L. Study on the Nutritional Status of Apple-Pear Orchard at Yanbian Area. J. Anhui Agric. 2015, 43, 59–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Liao, Y. Mulching Practices Altered Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Improved Orchard Productivity and Apple Quality after Five Growing Seasons. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 172, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, D.; Oliverio, A.M.; Brewer, T.E.; Benavent-González, A.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Maestre, F.T.; Singh, B.K.; Fierer, N.A. Global Atlas of the Dominant Bacteria Found in Soil. Science 2018, 359, 320–325. [Google Scholar]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Freeman, C.; Ostle, N.J. Microbial Contributions to Climate Change through Carbon Cycle Feedbacks. ISME J. 2008, 8, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torsvik, V.; Goksøyr, J.; Daae, F.L. High Diversity in DNA of Soil Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Bender, S.F.; Widmer, F.; Van Der Heijden, M.G. Soil Biodiversity and Soil Community Composition Determine Ecosystem Multifunctionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, J.; Lynch, D.H.; Owen, J. Quantification of Nitrogen Inputs from Biological Nitrogen Fixation to Whole Farm Nitrogen Budgets of Two Dairy Farms in Atlantic Canada. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2013, 96, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmatiski, A.; Beard, K.H.; Stevens, J.R.; Cobbold, S.M. Plant–Soil Feedbacks: A Meta-Analytical Review. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockett, B.F.; Prescott, C.E.; Grayston, S.J. Soil Moisture Is the Major Factor Influencing Microbial Community Structure and Enzyme Activities across Seven Biogeoclimatic Zones in Western Canada. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, B. Global Dispersal of Free-Living Microbial Eukaryote Species. Science 2002, 296, 1061–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, J.B.H.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Brown, J.H.; Colwell, R.K.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Green, J.L.; Horner-Devine, M.C.; Kane, M.; Krumins, J.A.; Kuske, C.R.; et al. Microbial Biogeography: Putting Microorganisms on the Map. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, Y.; Xiong, W.; Ran, W.; Shen, B.A.; Shen, Q.R.; Zhang, R.F. Responses of Bacterial Communities in Arable Soils in a Rice-Wheat Cropping System to Different Fertilizer Regimes and Sampling Times. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Nergui, S.; Han, Z.M.; Huang, G.N.; Li, H.R.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, L.Y.; Liao, J.F. The Variation of the Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Is Linked to Land Use Types in Northeast China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalnina, K.; Dias, R.; de Quadros, P.D.; Davis-Richardson, A.; Camargo, F.A.O.; Clark, I.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Triplett, E.W. Soil pH Determines Microbial Diversity and Composition in the Park Grass Experiment. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constancias, F.; Terrat, S.; Saby, N.P.A.; Horrigue, W.; Villerd, J.; Guillemin, J.P.; Biju-Duval, L.; Nowak, V.; Dequiedt, S.; Ranjard, L. Mapping and Determinism of Soil Microbial Community Distribution across an Agricultural Landscape. Microbiologyopen 2015, 4, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities across a pH Gradient in an Arable Soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Guan, D.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Cao, F.; Shen, D.; et al. Thirty Four Years of Nitrogen Fertilization Decreases Fungal Diversity and Alters Fungal Community Composition in Black Soil in Northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Zheng, Y.M.; Hu, H.W.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; He, J.Z. Soil pH Determines the Alpha Diversity but Not Beta Diversity of Soil Fungal Community Along Altitude in a Typical Tibetan Forest Ecosystem. J. Soil Sediments 2015, 5, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjard, L.; Richaume, A.S. Quantitative and Qualitative Microscale Distribution of Bacteria in Soil. Res. Microbiol. 2001, 152, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Deng, M.; Yuan, A.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Ma, J. Vertical Variation of a Black Soil’s Properties in Response to Freeze-Thaw Cycles and Its Links to Shift of Microbial Community Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essel, E.; Xie, J.; Deng, C.; Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Xie, J.; Coulter, J.A.; Li, L. Bacterial and Fungal Diversity in Rhizosphere and Bulk Soil under Different Long-Term Tillage and Cereal/Legume Rotation. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitea, M.A.; Gitea, D.; Tit, D.M.; Purza, L.; Samuel, A.D.; Bungau, S.; Badea, G.E.; Aleya, L. Orchard Management under the Effects of Climate Change: Implications for Apple, Plum, and Almond Growing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 9908–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Gast, C.J.; Gosling, P.; Tiwari, B.; Bending, G.D. Spatial Scaling of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Diversity Is Affected by Farming Practice. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, J.; Hou, J.; Yang, Y.; Yao, T.; Knight, R.; Chu, H. Geographic Distance and pH Drive Bacterial Distribution in Alkaline Lake Sediments across Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, T. Biosorption and Biomineralization of Uranium by Saccharomyces cerevisiae-Crystal Formation of Chernikovite. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Murray, P.; Hendershot, W.H. Trace Metal Speciation and Bioavailability in Urban Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 107, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Li, J.; Han, Z.; Lyu, G.; Ibekwe, A.M.; Ma, J. Persistence of Salmonella Typhimurium in Apple-Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) Orchard Soils Influenced by Bacterial Communities and Soil Properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-High-Throughput Microbial Community Analysis on the Illumina Hiseq and Miseq Platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. Qiime Allows Analysis of High-Throughput Community Sequencing Data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and Clustering Orders of Magnitude Faster Than Blast. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.F.; He, Z.L.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J.Z. Molecular Ecological Network Analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, J.; Gao, H.; Khan, L.; Thompson, D.K.; Zhou, J. Constructing Gene Co-Expression Networks and Predicting Functions of Unknown Genes by Random Matrix Theory. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Yang, Y. Phylogenetic Molecular Ecological Network of Soil Microbial Communities in Response to Elevated CO2. mBio 2011, 2, e00122-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Tu, Q.; Zhi, X. Functional Molecular Ecological Networks. mBio 2010, 1, e00169-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S.; Dong, J. Geometric Interpretation of Gene Coexpression Network Analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimera, R.; Sales-Pardo, M.; Amaral, L.A.N. Classes of Complex Networks Defined by Role-to-Role Connectivity Profiles. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimera, R.; Amaral, L.A.N. Functional Cartography of Complex Metabolic Networks. Nature 2005, 433, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The Modularity of Pollination Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, S.G.; Magbanua, Z.V.; Williams, M.A.; Jangid, K.; Whitman, W.B.; Peterson, D.G.; Kingery, W.L. Bacterial Diversity Patterns Differed in Two Developing Ecosystems. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 73, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Xiong, W.; Huang, T.; Ran, W.; Li, D.; Shen, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R. Swine Manure and Quicklime Have Different Impacts on Chemical Properties and Composition of Bacterial Communities of an Acidic Soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 100, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egidi, E.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Plett, J.M.; Wang, J.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Maestre, F.T.; Singh, B.K. A Few Ascomycota Taxa Dominate Soil Fungal Communities Worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelle, D.; Ralph, J.; Lu, F.; Hammel, K.E. Evidence for Cleavage of Lignin by a Brown Rot Basidiomycete. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beimforde, C.; Feldberg, K.; Nylinder, S.; Rikkinen, J.; Tuovila, H.; Dorfelt, H.; Gube, M.; Jackson, D.J.; Reitner, J.; Seyfullah, L.J.; et al. Estimating the Phanerozoic History of the Ascomycota Lineages: Combining Fossil and Molecular Data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 78, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Nie, J.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, J. Differentiated surface fungal communities at point of harvest on apple fruits from rural and peri-urban orchards. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2165. [Google Scholar]
- Franke-Whittle, I.H.; Manici, L.M.; Insam, H.; Stres, B. Rhizosphere bacteria and fungi associated with plant growth in soils of three replanted apple orchards. Plant Soil 2015, 395, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xiao, J.; Liang, T.; He, W.; Tan, H. Response of soil biological properties and bacterial diversity to different levels of nitrogen application in sugarcane fields. Amb Express 2021, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, X.-M.; Du, Y.-M.; Zong, H.; Shen, G.-m. Effects of tobacco-peanut relay intercropping on soil bacteria community structure. Ann. Microbioly. 2019, 69, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xing, Z.; Su, X.; Dong, L.; Zhao, T.; Li, J. Investigation of microbial community structures in typical landfill cover soils of China. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 71, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Schlaeppi, K.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Keystone Taxa as Drivers of Microbiome Structure and Functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.; Schaeffer, S. Microbial Control over Carbon Cycling in Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.A.; Hugenholtz, F.; Lahti, L.; Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M. Intestinal Microbiome Landscaping: Insight in Community Assemblage and Implications for Microbial Modulation Strategies. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Darveau, R.P.; Curtis, M.A. The Keystone-Pathogen Hypothesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.-W.; Kwon, T.-H.; Dai, S. Clay-bacteria interaction: Effect of bacterial cell density on sedimentation behavior and fabric map of kaolinite clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 241, 106973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.A.; McLendon, T.; Paschke, M.W.; Redente, E.F. Nitrogen Availability and Fungal-Bacterial Responses in Successional Semiarid Steppe Soils. Arid Soil Res. Rehab. 1996, 10, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Marschner, P.; Tscherko, D.; Gahoonia, T.S.; Nielsen, N.E. Microbial Community Composition and Functional Diversity in the Rhizosphere of Maize. Plant Soil 2002, 238, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xia, B.; Treves, D.S. Spatial and Resource Factors Influencing High Microbial Diversity in Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. High Throughput Sequencing Analysis of Biogeographical Distribution of Bacterial Communities in the Black Soils of Northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beales, N. Adaptation of Microorganisms to Cold Temperatures, Weak Acid Preservatives, Low pH, and Osmotic Stress: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2004, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, D. Responses of Soil Aggregates and Bacterial Communities to Soil-Pb Immobilization Induced by Biofertilizer. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, R.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, Y. Responses of Soil Microbial Traits to Ground Cover in Citrus Orchards in Central China. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Ibekwe, A.M.; Yang, C.H.; Crowley, D.E. Bacterial Diversity and Composition in Major Fresh Produce Growing Soils Affected by Physiochemical Properties and Geographic Locations. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Shen, J.P.; Di, H.J.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhang, C.; He, J.Z. Variation of Soil Nitrate and Bacterial Diversity Along Soil Profiles in Manure Disposal Maize Field and Adjacent Woodland. J. Soil Sediments 2020, 20, 3557–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Bai, Y.; Lv, M.L.; Tian, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.M.; Ge, S.F. Soil Fertility, Microbial Biomass, and Microbial Functional Diversity Responses to Four Years Fertilization in an Apple Orchard in North China. Hortic. Plant J. 2020, 6, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Wang, J.T.; Deng, Y.; He, J.Z.; Feng, K.; Zhang, L.M. Microbial Community and Functional Structure Significantly Varied among Distinct Types of Paddy Soils but Responded Differently Along Gradients of Soil Depth Layers. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Sui, Y.; Suvannang, N.; Zhou, J.; Sun, B. Crop Rotations Alter Bacterial and Fungal Diversity in Paddy Soils across East Asia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yin, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Gu, T.; Shen, Q.; Qiu, H. Fungal Networks in Yield-Invigorating and -Debilitating Soils Induced by Prolonged Potato Monoculture. Soil Biolol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, E.L.; Timothy, W.J.; Stefano, A.; Stuart, B. What Can Interaction Webs Tell Us About Species Roles? PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.M.; Pimm, S.L.; Solé, R.V. Ecological Networks and Their Fragility. Nature 2006, 442, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, S.; Behl, T.; Aleya, L.; Bourgeade, P.; Aloui-Sosse, B.; Purza, A.L.; Abid, A.; Samuel, A.D. Expatiating the Impact of Anthropogenic Aspects and Climatic Factors on Long-Term Soil Monitoring and Management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30528–30550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Mrpp | Adonis | Anosim | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ | p | F | p | R | p | |
| bacteria | 0.684 | 0.001 | 2.193 | 0.002 | 0.407 | 0.001 |
| fungi | 0.656 | 0.001 | 2.789 | 0.001 | 0.369 | 0.001 |
| Bacterial Community | Fungal Community | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YJ | LJ | HL | YJ | LJ | HL | ||
| Empirical networks | st | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.9 |
| Network size | 275 | 177 | 324 | 201 | 157 | 253 | |
| link | 491 | 287 | 383 | 252 | 216 | 403 | |
| avgK | 3.57 | 3.24 | 2.36 | 2.51 | 2.75 | 3.19 | |
| GD | 7.33 | 5.65 | 9.86 | 6.73 | 6.23 | 5.62 | |
| avgCC | 0.28 | 0.2 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.14 | |
| Modularity | 0.71 | 0.7 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.78 | 0.74 | |
| R2 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.8 | 0.87 | 0.84 | 0.89 | |
| Random networks | GD ± SD | 4.23 ± 0.06 | 4.07 ± 0.08 | 6.60 ± 0.18 | 5.40 ± 0.16 | 4.80 ± 0.14 | 4.45 ± 0.08 |
| avgCC ± SD | 0.019 ± 0.006 | 0.023 ± 0.008 | 0.005 ± 0.003 | 0.009 ± 0.006 | 0.014 ± 0.008 | 0.016 ± 0.006 | |
| Modularity ± SD | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.74 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | |
| Bacterial Community | Fungal Community | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mantel | Partial | Mantel | Partial | |
| clay | 0.232 ** | 0.117 | 0.172 * | 0.152 |
| silt | 0.352 *** | 0.284 * | 0.158 | 0.140 |
| sand | 0.335 ** | 0.236 * | 0.177 | 0.159 |
| pH | 0.555 *** | 0.573 *** | 0.277 * | 0.277 * |
| WSOC | 0.236 ** | 0.174 * | 0.082 | 0.063 |
| NO3−-N | 0.263 * | 0.042 | 0.054 | −0.020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, G.; Hu, J.; Ma, J. Variation in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Soils from Three Major Apple Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) Orchards. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091751
Lyu G, Hu J, Ma J. Variation in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Soils from Three Major Apple Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) Orchards. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(9):1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091751
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Guangze, Jiayang Hu, and Jincai Ma. 2024. "Variation in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Soils from Three Major Apple Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) Orchards" Microorganisms 12, no. 9: 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091751
APA StyleLyu, G., Hu, J., & Ma, J. (2024). Variation in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Soils from Three Major Apple Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) Orchards. Microorganisms, 12(9), 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12091751






