Phylogenetic Analysis of Alphacoronaviruses Based on 3c and M Gene Sequences Isolated from Cats with FIP in Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Coronavirus Antibodies
2.3. RNA Extraction from Effusions and Faecal Samples
2.4. RNA Extraction from Organ Samples
2.5. Amplification Using Real-Time RT-qPCR
2.6. Amplification Using RT-PCR
2.7. Sequencing
2.8. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Coronavirus Antibodies Titre
3.2. Amplification, Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Results for the 3c Gene
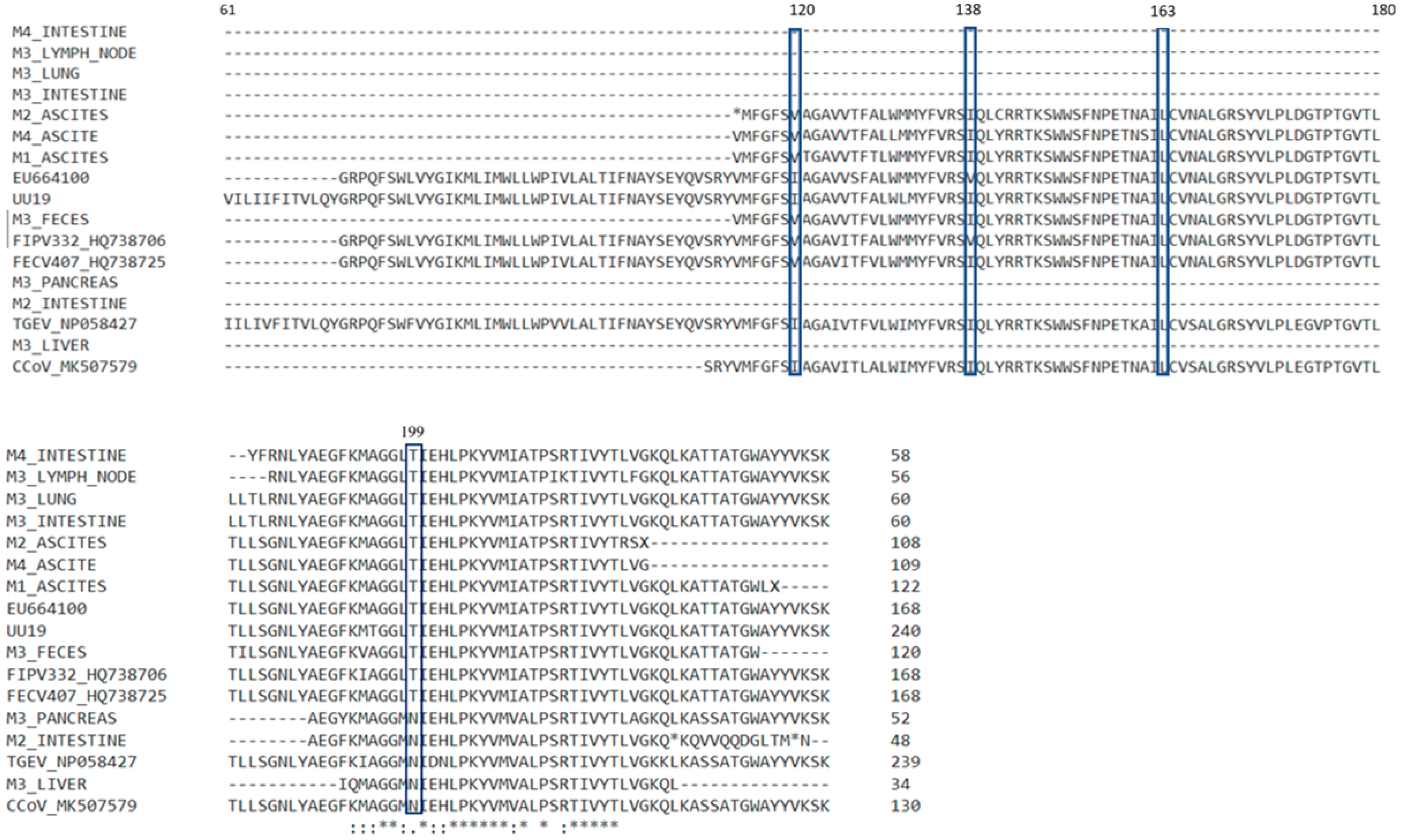
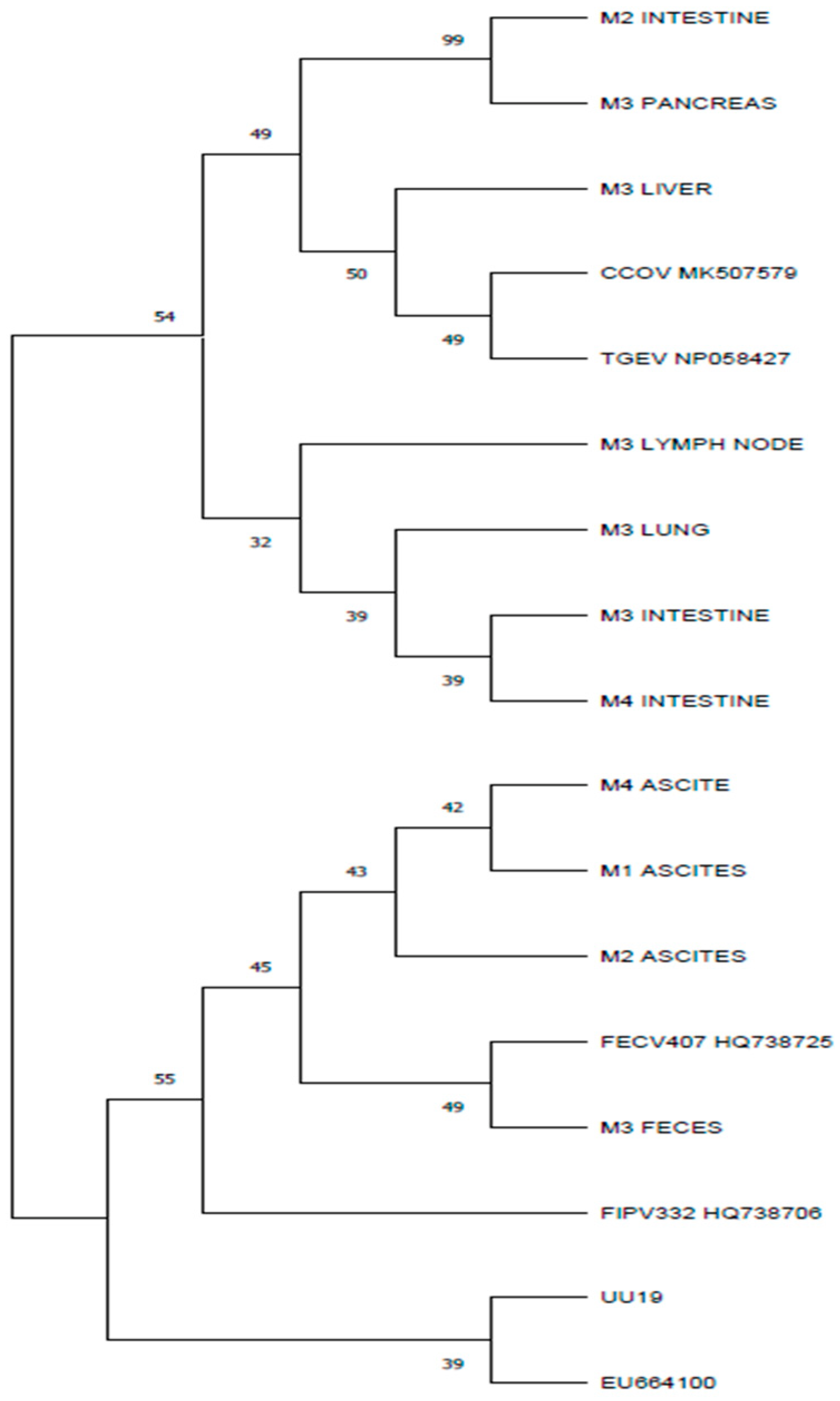
3.4. Results for M Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Huang, Y.; Yuen, K.Y. Coronavirus diversity, phylogeny and interspecies jumping. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 234, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 588, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaro, N.; Mari, V.; Campolo, M.; Lorusso, A.; Camero, M.; Elia, G.; Martella, V.; Cordioli, P.; Enjuanes, L.; Buonavoglia, C. Recombinant canine coronaviruses related to transmissible gastroenteritis virus of Swine are circulating in dogs. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Poder, S.; Pham-Hung d’Alexandryd’Orangiani, A.L.; Duarte, L.; Fournier, A.; Horhogea, C.; Pinhas, C.; Vabret, A.; Eloit, M. Infection of cats with atypical feline coronaviruses harbouring a truncated form of the canine type I non-structural ORF3 gene. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 20, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, Y.; Matsui, N.; Noguchi, K.; Kuwata, R.; Shimoda, H.; Soma, T.; Mochizuki, M.; Maeda, K. Emergence of Pathogenic Coronaviruses in Cats by Homologous Recombination between Feline and Canine Coronaviruses. PLoS ONE. 2014, 9, e106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1282, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borschensky, C.M.; Reinacher, M. Mutations in the 3c and 7b genes of feline coronavirus in spontaneously affected FIP cats. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrrha, L.W.; Silva, F.M.F.; Vidigal, P.M.P.; Resende, M.; Bressan, G.C.; Fietto, J.L.R.; Santos, M.R.; Silva, L.M.N.; Assao, V.S.; Silva-JúNior, A.; et al. Feline coronavirus isolates from a part of Brazil: Insights into molecular epidemiology and phylogeny inferred from the 7b gene. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Egberink, H.F.; Halpin, R.; Spiro, D.J.; Rottier, P.J. Spike protein fusion peptide and feline coronavirus virulence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; de Groot, R.J.; Egberink, H.F.; Rottier, P.J. Feline infectious peritonitis: Insights into feline coronavirus pathobiogenesis and epidemiology based on genetic analysis of the viral 3c gene. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91 Pt 2, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hora, A.S.; Tonietti, P.O.; Taniwaki, S.A.; Asano, K.M.; Maiorka, P.; Richtzenhain, L.J.; Brandão, P.E. Feline Coronavirus 3c Protein: A Candidate for a Virulence Marker? Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8560691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Troyer, J.L.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Roelke, M.E.; O’Brien, S.J. Genetics and pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrewegh, A.A.; Smeenk, I.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J.; de Groot, R.J. Feline coronavirus type II strains 79-1683 and 79–1146 originate from a double recombination between feline coronavirus type I and canine coronavirus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4508–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennema, H.; Poland, A.; Foley, J.; Pedersen, N.C. Feline infectious peritonitis viruses arise by mutation from endemic feline enteric coronaviruses. Virology 1998, 243, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrewegh, A.A.; de Groot, R.J.; Cepica, A.; Egberink, H.F.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J. Detection of feline coronavirus RNA in feces, tissues, and body fluids of naturally infected cats by reverse transcriptase PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.S.; Porter, E.; Matthews, D.; Kipar, A.; Tasker, S.; Helps, C.R.; Siddell, S.G. Genotyping coronaviruses associated with feline infectious peritonitis. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96 Pt 6, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguma, K.; Ohno, M.; Yoshida, M.; Sentsui, H. Mutation of the S and 3c genes in genomes of feline coronaviruses. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chang, H.W.; Egberink, H.F.; Rottier, P.J. Sequence analysis of feline coronaviruses and the circulating virulent/avirulent theory. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazán, F.; González, J.M.; Pénzes, Z.; Izeta, A.; Calvo, E.; Plana-Durán, J.; Enjuanes, L. Engineering the largest RNA virus genome as an infectious bacterial artificial chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5516-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felten, S.; Klein-Richers, U.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Bergmann, M.; Unterer, S.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Hartmann, K. Correlation of Feline Coronavirus Shedding in Feces with Coronavirus Antibody Titer. Pathogens 2020, 9, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Liu, H.; Dodd, K.A.; Pesavento, P.A. Significance of coronavirus mutants in feces and diseased tissues of cats suffering from feline infectious peritonitis. Viruses 2009, 1, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank-Wolf, B.R.; Stallkamp, I.; Wiese, S.; Moritz, A.; Tekes, G.; Thiel, H.J. Mutations of 3c and spike protein genes correlate with the occurrence of feline infectious peritonitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hora, A.S.; Asano, K.M.; Guerra, J.M.; Mesquita, R.G.; Maiorka, P.; Richtzenhain, L.J.; Brandão, P.E. Intrahost diversity of feline coronavirus: A consensus between the circulating virulent/avirulent strains and the internal mutation hypotheses? Sci. World J. 2013, 27, 572325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, C.; Siddell, S.G. Genomic RNA sequence of feline coronavirus strain FCoV C1Je. J. Feline. Med. Surg. 2007, 9, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addie, D.D.; Schaap, I.A.T.; Nicolson, L.; Jarrett, O. Persistence and transmission of natural type I feline coronavirus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84 Pt 10, 2735–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Liu, H.; Scarlett, J.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Golovko, L.; Kennedy, H.; Kamal, F.M. Feline infectious peritonitis: Role of the feline coronavirus 3c gene in intestinal tropism and pathogenicity based upon isolates from resident and adopted shelter cats. Virus Res. 2012, 165, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekes, G.; Thiel, H.J. Feline Coronaviruses: Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Adv. Virus Res. 2016, 96, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, V.; Thiel, H.J.; Tekes, G. Tackling feline infectious peritonitis via reverse genetics. Bioengineered 2014, 5, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Coronavirus Strain | GenBank Accession No | Year of Collection | Host | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIPV332 | HQ738706 | 2009 | cat | [19] |
| FECV407 | HQ738725 | 2010 | cat | [19] |
| TGEV_NP058427 | NP_058427 | Tissue culture adapted clone of the TGEV Purdue strain | pig | [20] |
| CCoV_MK507579 | MK507579 | 2018 | dog | Not available |
| EU664100 (FIPV) | EU664100 | 2004 | cat | [13] |
| UU19 (FECV-complete genome) | HQ392470 | 2007 | cat | [18] |
| Coronavirus Strain | GenBank Accession No | Year of Collection | Host | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feline Coronavirus isolate 26 M | KP143512 | 2013 | cat | [17] |
| Feline coronavirus isolate 27C | KP143507 | 2013 | cat | [17] |
| Feline coronavirus isolate 28O | KP143508 | 2013 | cat | [17] |
| UU19 (FECV-complete genome) | HQ392470 | 2007 | cat | [18] |
| Canine coronavirus strain 119/08 | EU924791 | 2008 | dog | [4] |
| Cat | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Real-Time-RT-PCR | RT-PCR | Sequencing | real-Time-RT-PCR | RT-PCR | Sequencing | Real-Time-RT-PCR | RT-PCR | Sequencing | Real-Time--RT-PCR | RT-PCR | Sequencing |
| ascites | + | - | - | + | + | 471 pb | NA | NA | NA | + | + | 390 pb |
| feces | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | 727 pb | + | - | - |
| heart | NA | NA | NA | + | - | - | + | - | - | NA | NA | NA |
| kidney | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - |
| large intestine | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | - | - | NA | - | - |
| liver | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - |
| lung | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | NA | NA |
| lymph node | + | + | 430 pb | NA | NA | NA | + | + | 442 pb | + | + | - |
| pancreas | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | 405 pb | NA | NA | NA |
| small intestine | + | - | - | + | + | 432 pb | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| spleen | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | NA | NA |
| Cat | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Real-Time-RT-PCR | RT-PCR | Sequencing | Real-Time-RT-PCR | RT-PCR | Sequencing | Real-Time-RT-PCR | RT-PCR | Sequencing | Real-Time- RT-PCR | RT-PCR | Sequencing |
| ascites | + | + | 374 pb | + | + | 373 pb | NA | NA | NA | + | + | 368 pb |
| feces | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | 382 pb | + | NA | NA |
| heart | NA | NA | NA | + | NA | NA | + | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| kidney | + | NA | NA | + | + | - | + | NA | NA | + | NA | NA |
| large intestine | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | 201 pb | + | NA | NA |
| liver | + | NA | NA | + | NA | NA | + | + | 104 pb | + | NA | NA |
| lung | + | NA | NA | + | NA | NA | + | + | 200 pb | + | NA | NA |
| lymph node | + | + | - | NA | NA | NA | + | + | 189 pb | NA | + | - |
| pancreas | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | 194 pb | + | NA | NA |
| small intestine | + | NA | NA | + | + | 181 pb | + | NA | NA | + | + | 263 pb |
| spleen | + | NA | NA | + | NA | NA | - | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popovici, I.; Le Poder, S.; Rîmbu, C.-M.; Horhogea, C.-E. Phylogenetic Analysis of Alphacoronaviruses Based on 3c and M Gene Sequences Isolated from Cats with FIP in Romania. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081557
Popovici I, Le Poder S, Rîmbu C-M, Horhogea C-E. Phylogenetic Analysis of Alphacoronaviruses Based on 3c and M Gene Sequences Isolated from Cats with FIP in Romania. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(8):1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081557
Chicago/Turabian StylePopovici, Ivona, Sophie Le Poder, Cristina-Mihaela Rîmbu, and Cristina-Elena Horhogea. 2024. "Phylogenetic Analysis of Alphacoronaviruses Based on 3c and M Gene Sequences Isolated from Cats with FIP in Romania" Microorganisms 12, no. 8: 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081557
APA StylePopovici, I., Le Poder, S., Rîmbu, C.-M., & Horhogea, C.-E. (2024). Phylogenetic Analysis of Alphacoronaviruses Based on 3c and M Gene Sequences Isolated from Cats with FIP in Romania. Microorganisms, 12(8), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081557





