Comparing Sediment Bacterial Communities of Volcanic Lakes and Surrounding Rivers in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Northeastern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
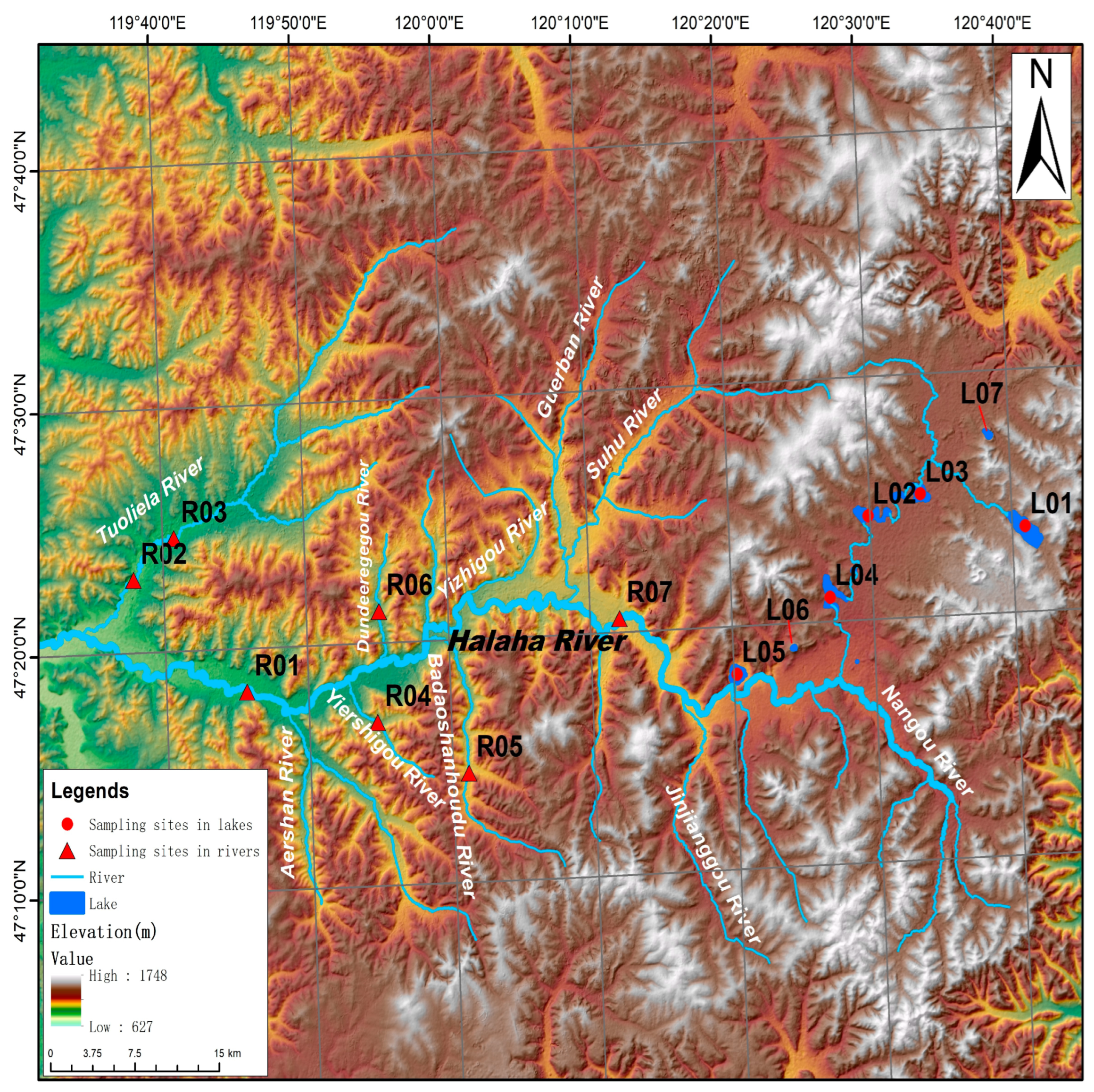
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Sites
2.2. Sampling and Geochemistry Measurements
2.3. DNA Extraction and Illumina Miseq Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis and Network Construction and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Characterization
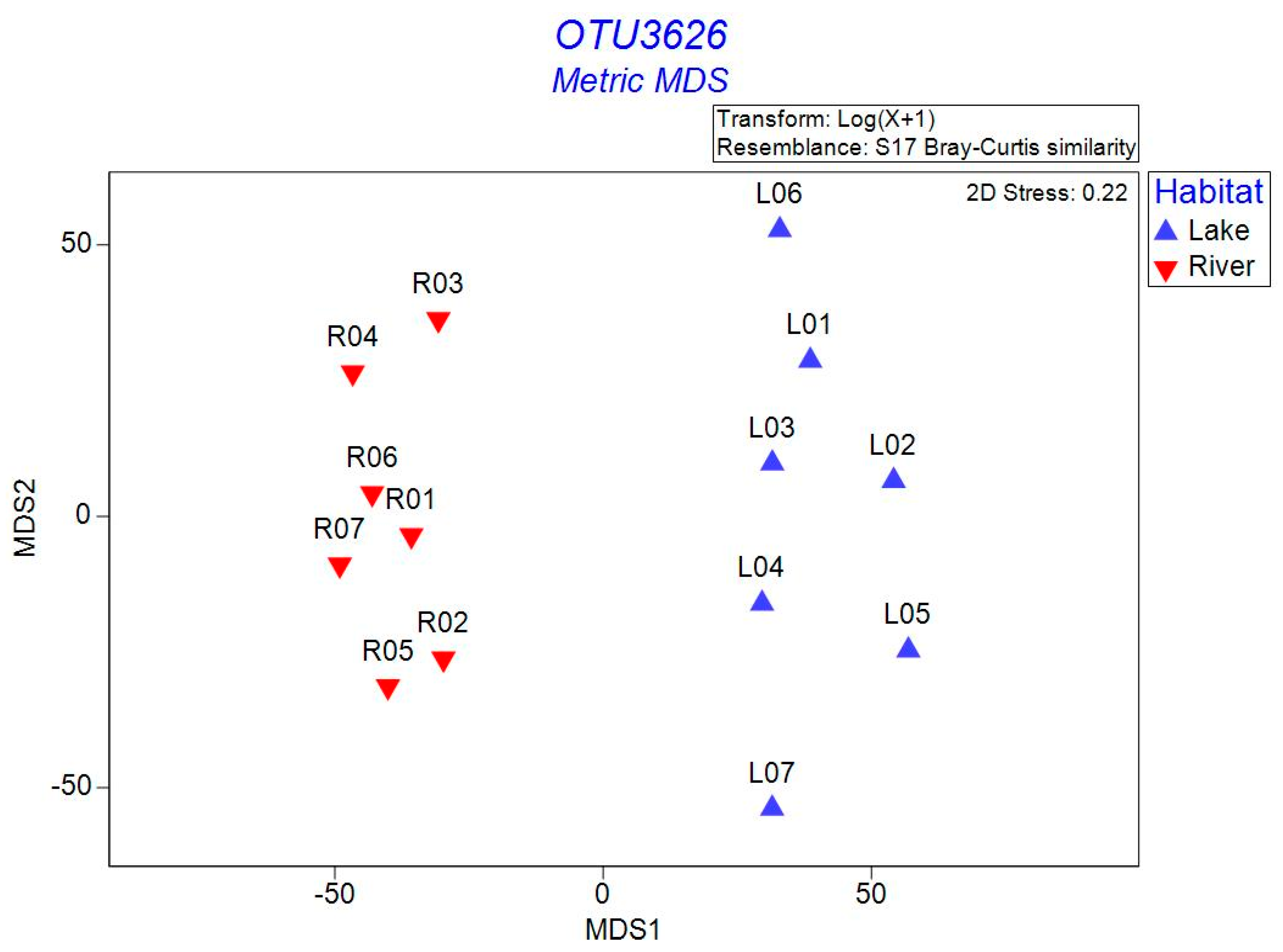
3.2. Bacterial α- and β-Diversity
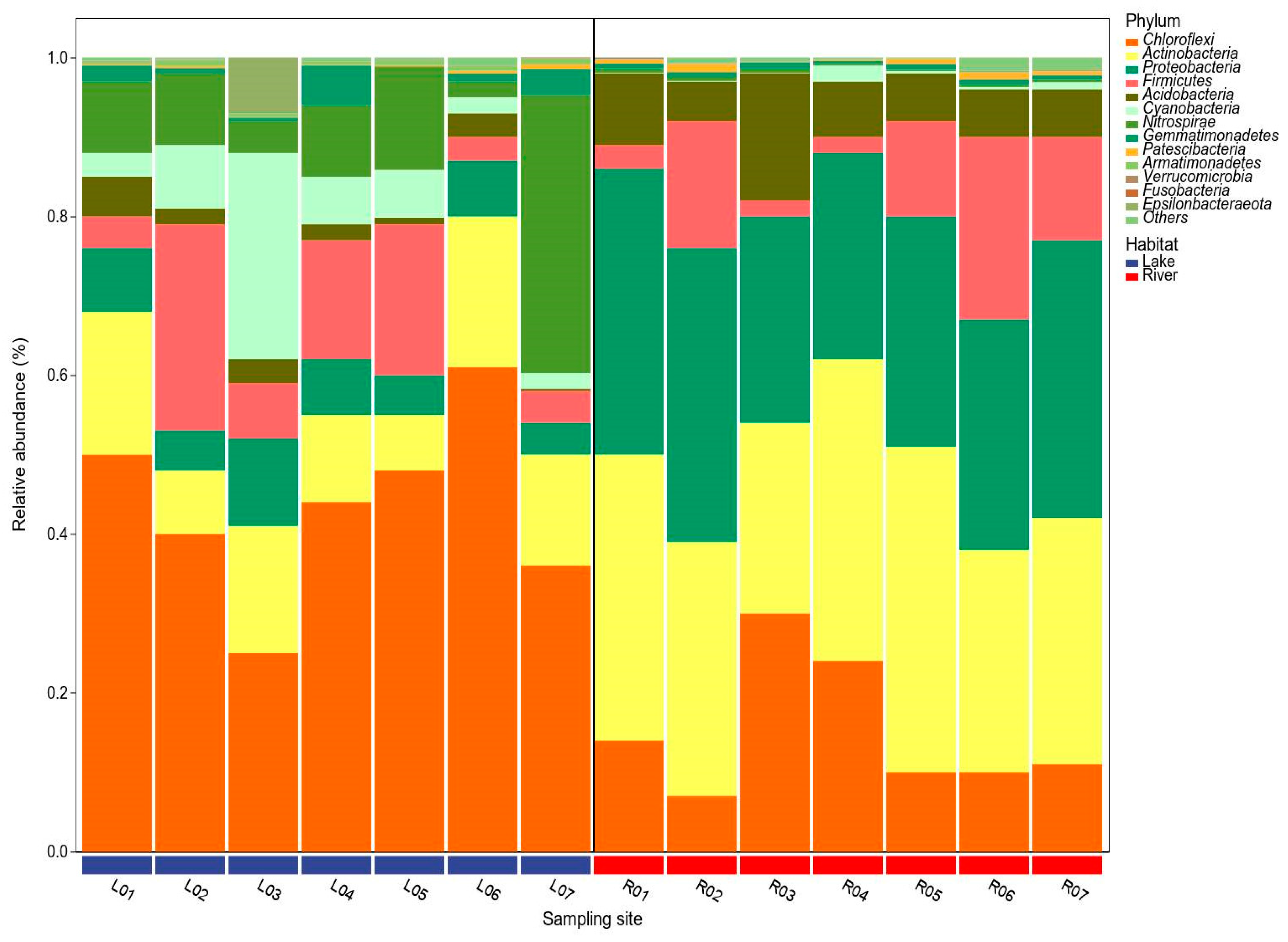
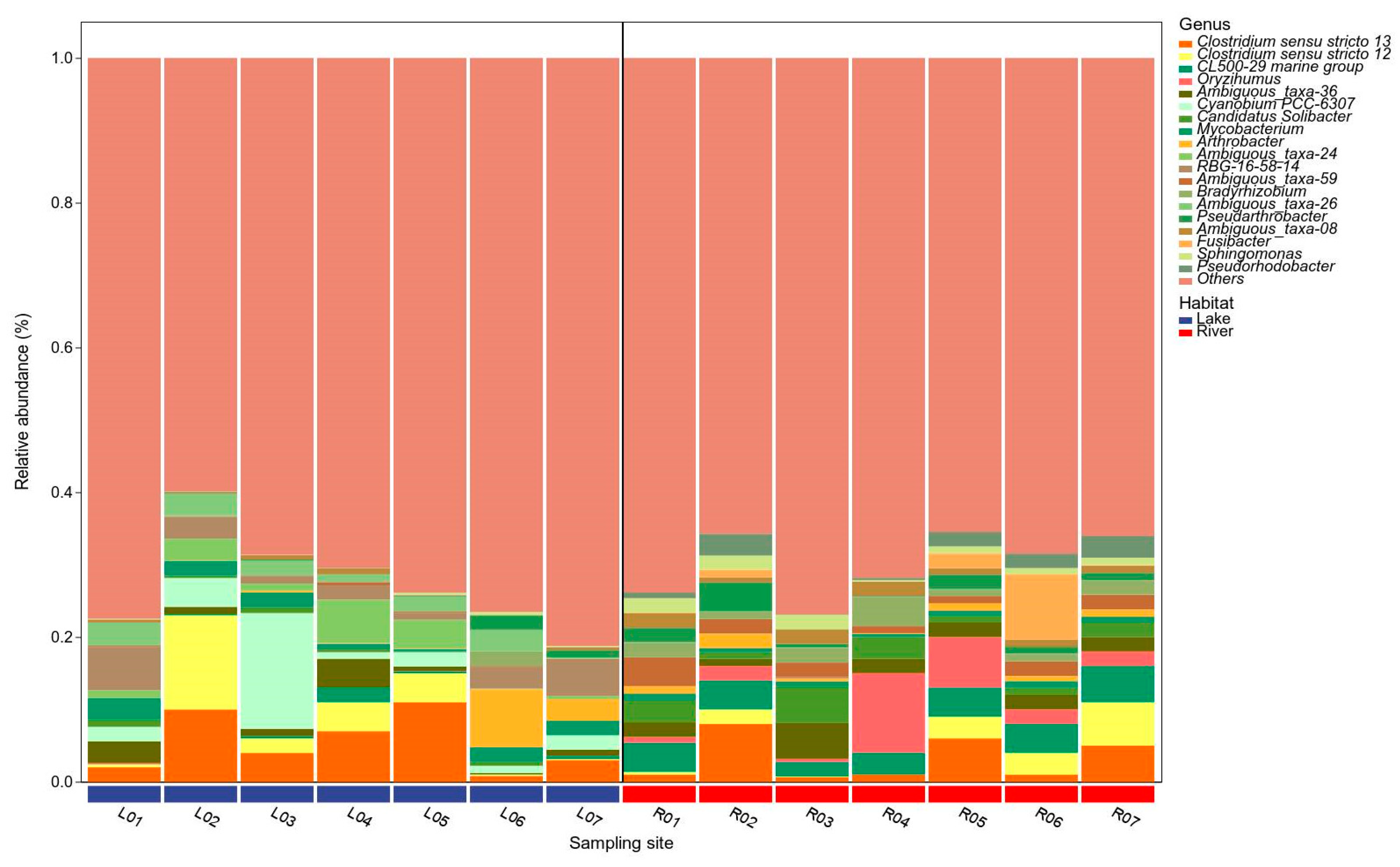
3.3. Bacterial Taxonomy and Community Structure
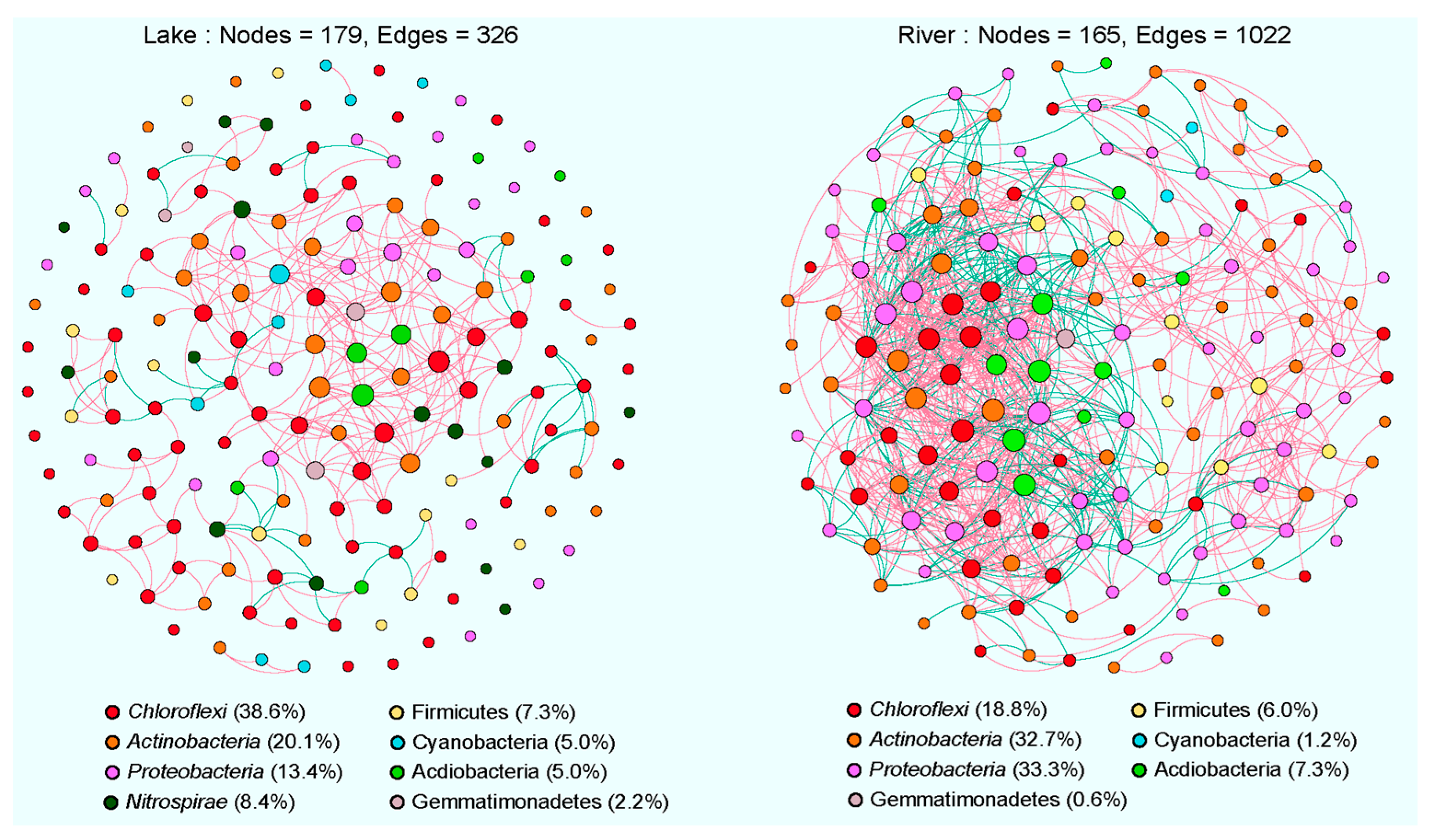
3.4. Co-Occurrence Networks of Sediment Bacterial Communities
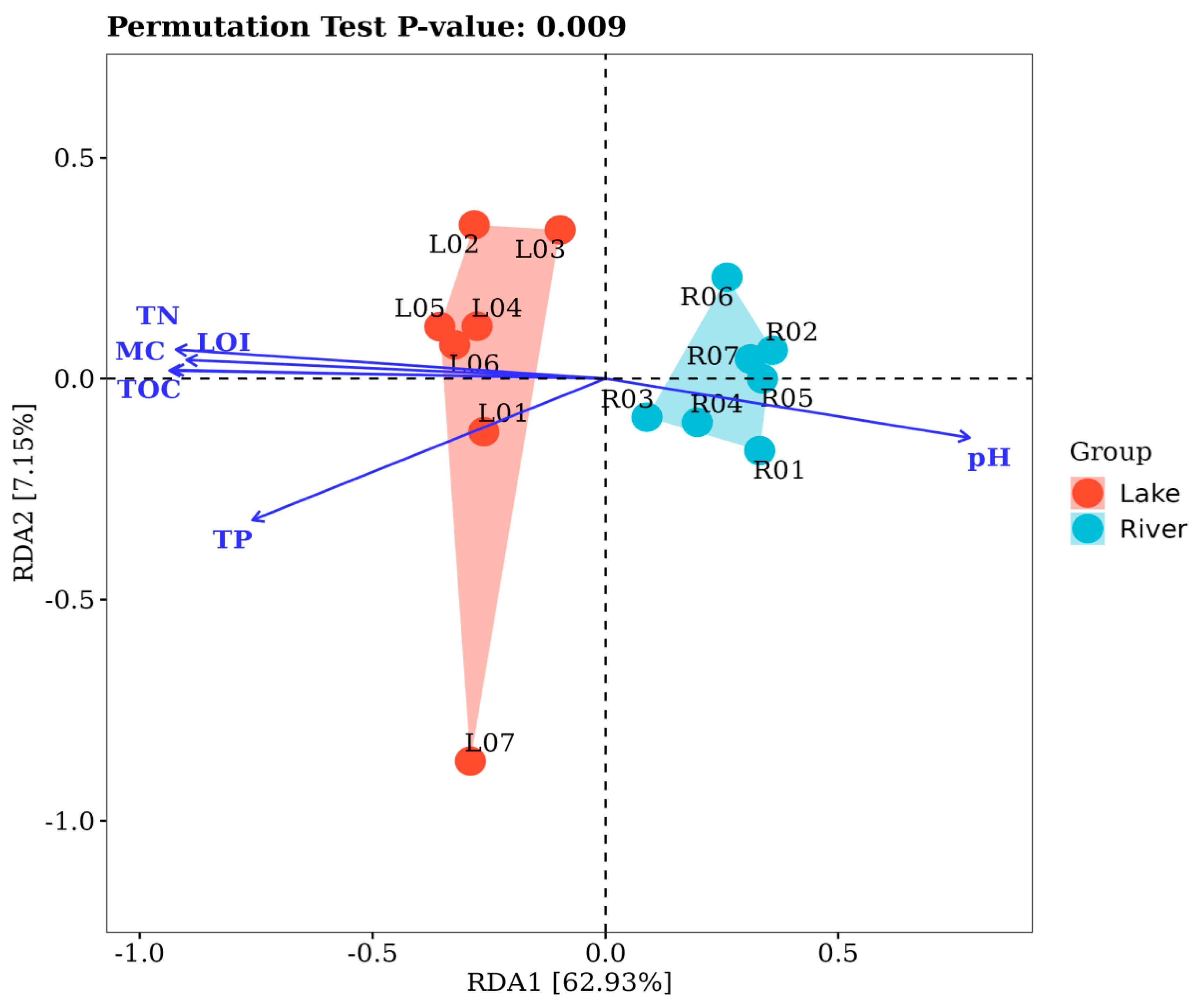
3.5. Environmental Drivers on Sediment Bacterial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Sediment Bacterial Communities between Lake and River Habitats
4.2. Comparison of Co-Occurrence Networks between Lake and River Habitats
4.3. Environmental Factors in Relation to Sediment Microbial Communities
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorokin, D.Y.; Berben, T.; Melton, E.D.; Sorokin, D.Y.; Berben, T.; Melton, E.D.; Overmars, L.; Vavourakis, C.D.; Muyzer, G. Microbial diversity and biogeochemical cycling in soda lakes. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Lakes as sentinels and integrators for the effects of climate change on watersheds, airsheds, and landscapes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.M.; Ohene-Adjei, S.; Hu, F.S.; Cann, I.K.O.; Mackie, R.I. Bacterial diversity and distribution in the Holocene sediments of a northern temperate lake. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 54, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yang, L.Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Xiao, L.; Jiang, L.J.; Zhao, D.Y. Spatial distribution of bacterial communities in sediment of a eutrophic lake revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and multivariate analysis. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.Y.; Li, J.; Kong, M.; Shao, K.Q.; Tang, X.M. Bacterioplankton diversity andpotential health risks in volcanic lakes: A study from Arxan Geopark, China. Environ. Poll. 2024, 342, 123058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, Y.; Kojima, H.; Fukui, M. Dominant microbial composition and its vertical distribution in saline meromictic Lake Kaiike (Japan) as revealed by quantitative oligonucleotide probe membrane hybridization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4930–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, J.P.; Rubin, M. Origin and Age of the Lake Nyos Maar, Cameroon. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 1989, 39, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazieff, H. Mechanisms of the Nyos Carbon Dioxide Disaster and of So-Called Phreatic Steam Eruptions. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 1989, 39, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakabe, M. Evolution of CO2 content in Lakes Nyos and Monoun, and sub-lacustrine CO2-recharge system at Lake Nyos as envisaged from CO2/3 heratios and noble gas signatures. In Volcanic Lakes; Rouwet, D., Christenson, B., Tassi, F., Vandemeulebrouck, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 427–450. [Google Scholar]
- Barberi, F.; Chelini, W.; Marinelli, G.; Martini, M. Rapport de la Mission Technique Italienne au Cameroun a la Suite de la Catastrophe du Lac Nyos (21 aout 1986): Aspects Volcanologiques et Geochemiques; Gruppo Nazionale par la Vulcanologica: Rome, Italy, 1989; 33p. [Google Scholar]
- Kling, G.W.; Evans, W.C.; Tanyileke, G.; Kusakabe, M.; Ohba, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Hell, J.V. Degassing Lakes Nyos and Monoun: Defusing Certain Disaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14185–14190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nana, P.A.; Nola, M.; Bricheux, G.; Fokam, Z.; Ngassam, P.; Enah, D.A.; Colombet, J.; Vellet, A.; Mone, A.; Ravet, V.; et al. Diversity and Structure of the Prokaryotic Communities Indigenous to Two Volcanic Lakes: Nyos and Monoun in Cameroon. Open. J. Ecol. 2020, 10, 632–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Zhao, C.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, C.; Sun, X.; Yan, T.; Zhao, Y. Paleoclimatic changes recorded by n-alkanes from the lacustrine sediments of Arxan Crater Lake, in the central Great Khingan Mountains, Northeast China during the Holocene. Quat. Sci. 2021, 41, 976–985. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.M.; Xie, G.J.; Shao, K.Q.; Tian, W.; Gao, G.; Qin, B. Aquatic bacterial diversity, community composition and assembly in the semi-arid inner mongolia plateau: Combined effects of salinity and nutrient levels. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, H. Introduction to Bioinformatics in Microbiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gotelli, N.J.; McCabe, D.J. Species co-occurrence: A meta-analysis of J. M. Diamond’s assembly rules model. Ecology 2002, 83, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.S.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca. hp R package. Methods. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 4, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.F.; He, Z.L.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J.Z. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Numerical Ecology with R, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; p. 440. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesford, Q.K.; Joyce, K.E.; Hayasaka, S.; Burdette, J.H.; Laurienti, P.J. The ubiquity of small-world networks. Brain. Connect. 2011, 1, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.; Widder, S. Deciphering microbial interactions and detecting keystone species with co-occurrence networks. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-González, C.; Niño-García, J.P.; del Giorgio, P.A. Terrestrial origin of bacterial communities in complex boreal freshwater networks. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptmann, A.L.; Markussen, T.N.; Stibal, M.; Olsen, N.S.; Elberling, B.; Bælum, J.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Jacobsen, C.S. Upstream freshwater and terrestrial sources are differentially reflected in the bacterial community structure along a small Arctic river and its estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño-García, J.P.; Ruiz-González, C.; del Giorgio, P.A. Interactions between hydrology and water chemistry shape bacterioplankton biogeography across boreal freshwater networks. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freilich, S.; Kreimer, A.; Meilijson, I.; Gophna, U.; Sharan, R.; Ruppin, E. The largescale organization of the bacterial network of ecological co-occurrence interactions. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2010, 38, 3857–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial interactions: From networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, Z.B.; Zak, D.R. Atmospheric N deposition alters connectance, but not functional potential among saprotrophic bacterial communities. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 3170–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humayoun, S.B.; Bano, N.; Hollibaugh, J.T. Depth distribution of microbial diversity in Mono Lake, a meromictic soda lake in California. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, H.C.; Grant, W.D.; Jones, B.E.; Heaphy, S. Diversity of Kenyan soda lake alkaliphiles assessed by molecular methods. Extremephiles 2004, 8, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.J.; Liu, X.L.; Lin, S.Q.; Tan, J.; Pan, J.L.; Li, D.T.; Yang, H. The vertical distribution of bacterial and archaeal communities in the water and sediment of Lake Taihu. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 70, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, B.K.; Ehrhardt, C.J.; Reifel, K.M.; Moreno, L.I.; Valentine, D.L. Archaeal and bacterial communities respond differently to environmental gradients in anoxic sediments of a California hypersaline lake the Salton Sea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, L.; Tonolla, M.; Zopfi, J.; Peduzzi, R.; Wildi, W.; Pote, J. Composition of bacterial and archaeal communities in freshwater sediments with different contamination levels (Lake Geneva Switzerland). Water. Res. 2011, 45, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Fang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, H.; Zhang, S. Impact of different types of anthropogenic pollution on bacterial community and metabolic genes in urban river sediments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 793, 148475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.Y.; Cao, X.Y.; Huang, R.; Zeng, J.; Wu, Q.L. Variation of bacterial communities in water and sediments during the decomposition of Microcystis biomass. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, H.; Vinocur, A.; Tell, G. Periphyton on artificial substrata from three lakes of different trophic status at Hope Bay (Antarctica). Polar. Biol. 2002, 25, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, E.L.; Phlips, E.J.; Donnelly, K.A.; Jett, C.H.; Sleszynski, P.; Keller, S. Primary producers and nutrient loading in Silver Springs, FL, USA. Aqu. Bot. 2008, 88, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Z.; Xue, Y.; Xu, J.Q.; Wang, Y. Spatial distribution of epipelic algal biomass and its relationship with the environmental nutrients in Lake Taihu. Acta. Scientiae. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 4178–4186. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Kang, P.; Hu, J.; Song, N. Bacterial community demonstrates stronger network connectivity than fungal community in desert-grassland salt marsh. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 798, 149118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shen, F.; Zeng, J.; Huang, R.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Q.L. Network analysis reveals seasonal variation of co-occurrence correlations between Cyanobacteria and other bacterioplankton. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 573, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbrenner, I.A.; Cernava, T.; Erlacher, A.; Berg, G.; Grube, M. Differential sharing and distinct co-occurrence networks among spatially close bacterial microbia of bark, mosses and lichens. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 2826–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.I.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, S.; Qu, Y.; Ma, Q.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Long-term successional dynamics of microbial association networks in anaerobic digestion processes. Water. Res. 2016, 104, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zeng, J.; Chen, P.; Xiao, F.; He, Z.; Yan, Q. Ecological stability of microbial communities in Lake Donghu regulated by keystone taxa. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.L.; Long, Z.J.; Ren, M.X. Microbial community and functional prediction during the processing of salt production in a 1000-year-old marine solar saltern of South China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 819, 152014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, R.; Velázquez, E.; Willems, A.; Vizcaíno, N.; Subba-Rao, N.S.; Mateos, P.F.; Gillis, M.; Dazzo, F.B.; Martínez-Molina, E. A New Species of Devosia That Forms a Unique Nitrogen-Fixing Root-Nodule Symbiosis with the Aquatic Legume Neptunia natans (L.f.) Druce. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 11, 5217–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, Y.; Inoue, M.; Omae, K.; Yoshida, T.; Sako, Y. Anaerobic and hydrogenogenic carbon monoxide-oxidizing prokaryotes: Versatile microbial conversion of a toxic gas into an available energy. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 110, 99–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Feng, L.; Dong, Y.; Chen, J.; Lan, J.; Hou, H. High-efficiency degradation of phthalic acid esters (paes) by pseudarthrobacter defluvii e5: Performance, degradative pathway, and key genes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 794, 148719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagan, W. Connectivity, fragmentation and extinction risk in dendritic meta-populations. Ecology 2002, 83, 3243–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, F.; Altermatt, F.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; Rinaldo, A. Dendritic connectivity controls biodiversity patterns in experimental metacommunities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5761–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altermatt, F. Diversity in riverine metacommunities: A network perspective. Aquat. Ecol. 2013, 47, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibold, M.A.; Holyoak, M.; Mouquet, N.; Amarasekare, P.; Chase, J.M.; Hoopes, M.F.; Holt, R.D.; Shurin, J.B.; Law, R.; Tilman, D.; et al. The metacommunity concept: A framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besemer, K.; Singer, G.; Quince, C.; Bertuzzo, E.; Sloan, W.; Battin, T.J. Headwaters are critical reservoirs of microbial diversity for fluvial networks. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2013, 280, 20131760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czárán, T.L.; Hoekstra, R.F.; Pagie, L. Chemical warfare between microbes promotes biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widder, S.; Besemer, K.; Singer, G.A.; Ceola, S.; Bertuzzo, E.; Quince, C.; Sloan, W.T.; Rinaldo, A.; Battin, T.J. Fluvial network organization imprints on microbial co-occurrence networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12799–12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macalady, J.L.; Mack, E.E.; Nelson, D.C.; Scow, K.M. Sediment microbial community structure and mercury methylation in mercury-polluted Clear Lake, California. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski-Vähälä, J.; Hartikainen, H.; Tallberg, P. Phosphorus mobilization from various sediment pools in response to increased pH and silicate concentration. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yuan, H.L.; Huang, H.Z. Vertical distribution of phosphorus and P-dissolving/decomposing bacteria in the sediment of Guanting reservoir. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2005, 48 (Suppl. SII), 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Yannarell, A.C.; Triplett, E.W. Geographic and environmental sources of variation in lake bacterial community composition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yang, L.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Jiang, L.J.; Zhao, D.Y. Vertical distribution of bacterial community structure in the sediments of two eutrophic lakes revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and multivariate analysis techniques. World. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.H.; Shi, Q.; Wen, D.H.; Li, Z.; Jefferson, W.A.; Feng, C.; Tang, X. Bacterial communities in the sediments of Dianchi Lake, a partitioned eutrophic waterbody in China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Lin, X.G.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zeng, J.; Hou, J.Z.; Yang, Y.P.; Yao, T.D.; Knight, R.; Chu, H.Y. Geographic distance and pH drive bacterial distribution in alkaline lake sediments across Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.Q.; Gao, G.; Wang, Y.P.; Tang, X.; Qin, B. Vertical diversity of sediment bacterial communities in two different trophic states of the eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Qin, H.; Guo, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Liang, J. Bacterial communities of four adjacent fresh lakes at different trophic status. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2018, 157, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, S.A.; Barbosa da Costa, N.; Shapiro, B.J.; Fradette, M.; Huot, Y.; Walsh, D.A. A large-scale assessment of lakes reveals a pervasive signal of land use on bacterial communities. ISME J. 2020, 14, 3011–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, J.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Bai, C.; Tang, X.; Shao, K. Comparing Sediment Bacterial Communities of Volcanic Lakes and Surrounding Rivers in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Northeastern China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071435
Chao J, Li J, Gao J, Bai C, Tang X, Shao K. Comparing Sediment Bacterial Communities of Volcanic Lakes and Surrounding Rivers in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Northeastern China. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(7):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071435
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, Jianying, Jian Li, Jing Gao, Chengrong Bai, Xiangming Tang, and Keqiang Shao. 2024. "Comparing Sediment Bacterial Communities of Volcanic Lakes and Surrounding Rivers in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Northeastern China" Microorganisms 12, no. 7: 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071435
APA StyleChao, J., Li, J., Gao, J., Bai, C., Tang, X., & Shao, K. (2024). Comparing Sediment Bacterial Communities of Volcanic Lakes and Surrounding Rivers in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Northeastern China. Microorganisms, 12(7), 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071435







