Occurrence, Impact, and Multilocus Sequence Analysis of Alder Yellows Phytoplasma Infecting Common Alder and Italian Alder in Southern Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Samples, Symptom Evaluation, and Phytoplasma Reference Strains
2.2. DNA Isolation and PCR Amplification
2.3. Actual and Virtual RFLP Analyses
2.4. DNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Incidence and Impact of ALY Phytoplasma Infections
3.2. Actual and Virtual RFLP Analyses
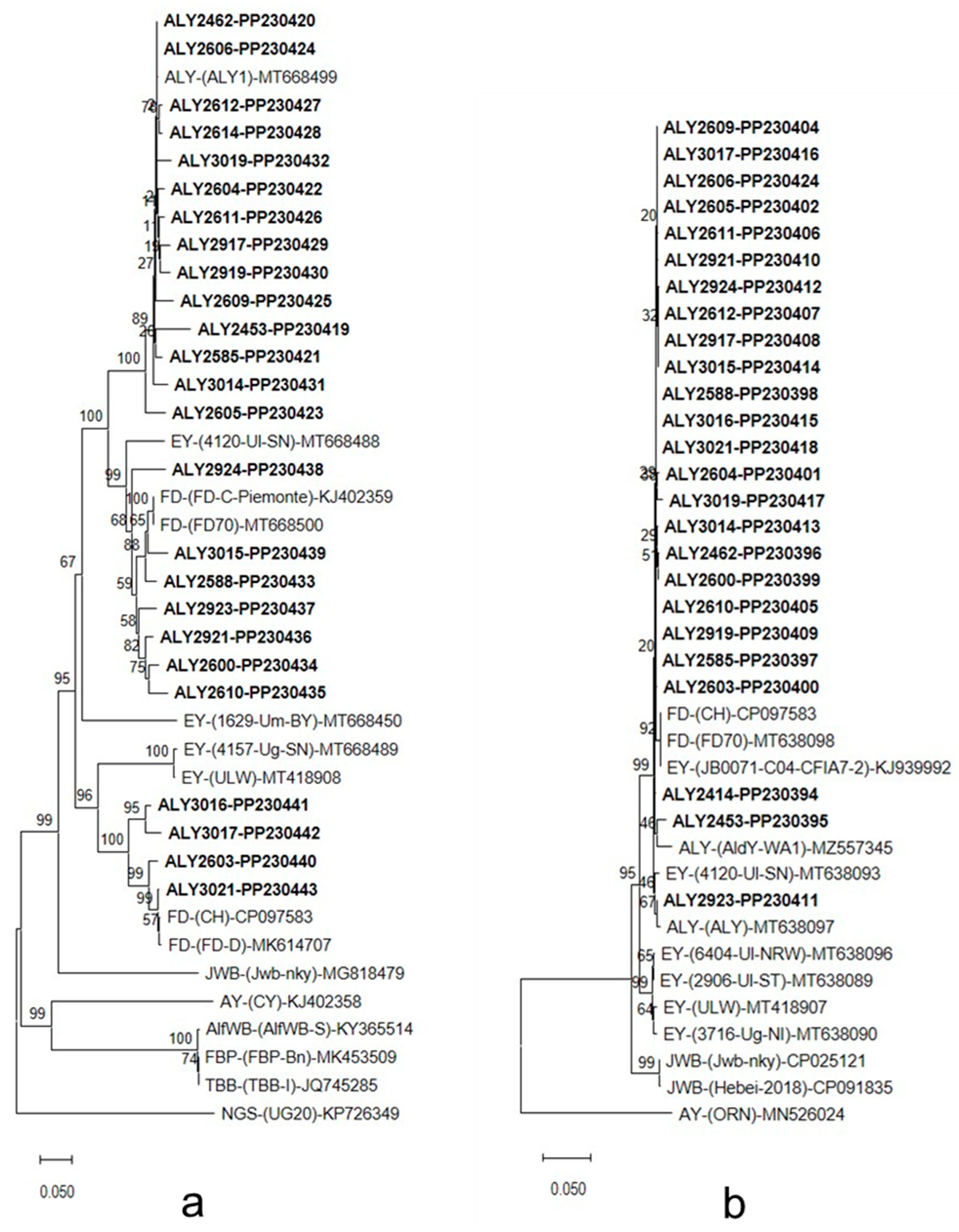
3.3. DNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IRPCM Phytoplasma/Spiroplasma Working Team—Phytoplasma taxonomy group. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’, a taxon for the wall-less, non-helical prokaryotes that colonize plant phloem and insects. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Zhao, Y. Phytoplasma Taxonomy: Nomenclature, Classification, and Identification. Biology 2022, 11, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertaccini, A.; Arocha-Rosete, Y.; Contaldo, N.; Duduk, B.; Fiore, N.; Guglielmi Montano, H.; Kube, M.; Kuo, C.-H.; Martini, M.; Oshima, K.; et al. Revision of the ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ species description guidelines. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcone, C. Current status of phytoplasma diseases of forest and landscape trees and shrubs. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 97, 9–36. [Google Scholar]
- Marcone, C.; Valiunas, D.; Mondal, S.; Sundararaj, R. On some significant phytoplasma diseases of forest trees: An update. Forests 2021, 12, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, W.; Seemüller, E. Occurrence of mycoplasma-like organisms in diseased and non-symptomatic alder trees (Alnus spp.). Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1991, 21, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäurer, R.; Seemüller, E.; Sinclair, W.A. Genetic relatedness of mycoplasmalike organisms affecting elm, alder, and ash in Europe and North America. Phytopathology 1993, 83, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foissac, X.; Salar, P.; Olivier, C.; Malembic-Maher, S. Proposal to establish a common taxon for 16SrV-C and 16SrV-D phytoplasmas and three genetic clades based on combined 16S rDNA signatures and variability of housekeeping genes. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 2019, 9, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Nunziata, S.O.; Srivastava, S.K.; Wilson, T.; Chambers, N.; Rivera, Y.; Nakhla, M.; Costanzo, S. Draft genome sequence resource of AldY-WA1, a phytoplasma strain associated with alder yellows of Alnus rubra in Washington, U.S.A. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1971–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemüller, E.; Lederer, W. MLO-associated decline of Alnus glutinosa, Populus tremula and Crataegus monogyna. J. Phytopathol. 1988, 121, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, C.; Firrao, G.; Ragozzino, A.; Locci, R. Detection of MLOs in declining alder trees in Southern Italy and their characterization by RFLP analysis. Eur. J. For. Path. 1994, 24, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiunas, D.; Alminaite, A.; Staniulis, J.; Jomantiene, R.; Davis, R.E. First report of alder yellows phytoplasma in the eastern Baltic Region. Plant Dis. 2001, 85, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvrković, T.; Jović, J.; Mitrović, M.; Petrović, A.; Krnjajić, S.; Malembic-Maher, S.; Toševski, I. First report of alder yellows phytoplasma on common alder (Alnus glutinosa) in Serbia. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radonjić, S.; Hrnčic, S.; Krstić, O.; Cvrković, T.; Mitrović, M.; Jović, J.; Toševski, I. First report of alder yellows phytoplasma infecting common and grey alder (Alnus glutinosa and A. incana) in Montenegro. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasova, B.; Spasov, D.; Jakovljević, M.; Jović, J.; Krstić, O.; Mitrović, M.; Cvrković, T. First report of alder yellows phytoplasma associated with common alder (Alnus glutinosa) in the Republic of Macedonia. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanovic, M.; Stepanovic, J.; Rekanovic, E.; Kube, M.; Duduk, B. Alder yellows phytoplasmas in Alnus species in Serbia. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 2019, 9, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kube, M.; Furch, A.C.U. Symptomless phytoplasmosis of black alder (Alnus glutinosa): A model for host tolerance. Plant Physiol. Rep. 2019, 24, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-M.; Martini, M.; Marcone, C.; Zhu, S.F. Classification of phytoplasma strains in the elm yellows group (16SrV) and proposal of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma ulmi’ for the phytoplasma associated with elm yellows. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Song, C.S.; Ren, Z.G.; Lin, C.L.; Xu, Q.C.; Li, Y.; Piao, C.G.; Yu, S.S.; Guo, M.W.; Tian, G.Z. Molecular characterization of a new member of the 16SrV group of phytoplasma associated with Bischofia polycarpa (Levl.) airy shaw witches’-broom disease in China by a multiple gene-based analysis. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2014, 43, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fránová, J.; de Sousa, E.; Koloniuk, I.; Mimoso, C.; Matos, J.; Cardoso, F.; Contaldo, N.; Paltrinieri, S.; Bertaccini, E. Multigene characterization of a new ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma rubi’-related strain associated with blackberry witches’ broom. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, C. Elm yellows: A phytoplasma disease of concern in forest and landscape ecosystems. For. Pathol. 2017, 47, e12324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertaccini, A.; Lee, I.-M. Phytoplasmas: An update. In Phytoplasmas: Plant Pathogenic Bacteria-I. Characterization and Epidemiology of Phytoplasma-Associated Diseases; Rao, G.P., Bertaccini, A., Fiore, N., Liefting, L., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Wei, W.; Davis, R.E.; Tan, Y.; Lee, I.-M.; Zhu, D.; Wei, H.; Zhao, Y. Multilocus genotyping identifies a highly homogeneous phytoplasma lineage associated with sweet cherry virescence disease in China and its carriage by an erythroneurine leafhopper. Crop Prot. 2018, 106, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malembic-Maher, S.; Desqué, D.; Khalil, D.; Salar, P.; Bergey, B.; Danet, J.-L.; Duret, S.; Dubrana-Ourabah, M.-P.; Beven, L.; Ember, I.; et al. When a Palearctic bacterium meets a Nearctic insect vector: Genetic and ecological insights into the emergence of the grapevine Flavescence doreé epidemics in Europe. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1007967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, G.; Malembic-Maher, S.; Salar, P.; Bonnet, P.; Maixner, M.; Marcone, C.; Boudon-Padieu, E.; Foissac, X. Multilocus sequence typing confirms the close genetic interrelatedness of three distinct flavescence dorée phytoplasma strain clusters and group 16SrV phytoplasmas infecting grapevine and alder in Europe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4001–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, S.; Duduk, B.; Büttner, C.; Kube, M. Genetic variability of alder yellows phytoplasma in Alnus glutinosa in its natural Spreewald habitat. For. Pathol. 2016, 46, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurga, M.; Zwolińska, A. Artemisia vulgaris, a new host of 16SrV-C phytoplasma related strains infecting black alder in Poland. J. Phytopathol. 2020, 168, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, O.; Cvrković, T.; Marinković, S.; Jakovljević, M.; Mitrović, M.; Toševski, I.; Jović, J. Genetic diversity of flavescence dorée phytoplasmas in vineyards of serbia: From the widespread occurrence of autochthonous map-M51 to the emergence of endemic map-FD2 (vectotype II) and new map-FD3 (vectotype III) epidemic genotypes. Agronomy 2022, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maixner, M.; Reinert, W. Oncopsis alni (Schrank) (Auchenorrhyncha: Cicadellidae) as a vector of the alder yellows phytoplasma of Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1999, 105, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoli, A.; Belgeri, E.; Jermini, M.; Conedera, M.; Filippin, L.; Angelini, E. Alnus glutinosa and Orientus ishidae (Matsumura, 1902) share phytoplasma genotypes linked to the ‘Flavescence dorée’ epidemics. J. Appl. Entomol. 2021, 145, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarausch, B.; Markheiser, A.; Jarausch, W.; Biancu, S.; Kugler, S.; Runne, M.; Maixner, M. Risk assessment for the spread of flavescence dorée-related phytoplasmas from alder to grapevine by alternative insect vectors in Germany. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maixner, M.; Rüdel, M.; Daire, X.; Boudon-Padieu, E. Diversity of grapevine yellows in Germany. Vitis 1995, 34, 235–236. [Google Scholar]
- Maixner, M.; Reinert, W.; Darimont, H. Transmission of grapevine yellows by Oncopsis alni (Schrank) (Auchenorrhynca: Macropsinae). Vitis 2000, 39, 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Angelini, E.; Clair, D.; Borgo, M.; Bertaccini, A.; Boudon-Padieu, E. Flavescence dorée in France and Italy—Occurrence of closely related phytoplasma isolates and their near relationships to Palatinate grapevine yellows and an alder yellows phytoplasma. Vitis 2001, 40, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Casati, P.; Jermini, M.; Quaglino, F.; Corbani, G.; Schaerer, S.; Passera, A.; Bianco, P.A.; Rigamonti, I.E. New insights on Flavescence dorée phytoplasma ecology in the vineyard agro-ecosystem in southern Switzerland. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2017, 171, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigamonti, I.E.; Salvetti, M.; Girgenti, P.; Bianco, P.A.; Quaglino, F. Investigation on Flavescence dorée in north-western Italy identifies map-M54 (16SrV-D/map-FD2) as the only phytoplasma genotype in Vitis vinifera L. and reveals the presence of new putative reservoir plants. Biology 2023, 12, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M.; Kirk, S.M.; Declan, J.; Cooke, D.E.L.; Jung, T.; Man In’t Veld, W.E. “Phytophthora alni sp. nov. and its variants: Designation of emerging heteroploid hybrid pathogens spreading on Alnus trees”. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moricca, S. Phomopsis alnea, the cause of dieback of black alder in Italy. Plant Pathol. 2002, 51, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surico, G.; Mugnai, L.; Pastorelli, R.; Giovannetti, L.; Stead, D.E. Erwinia alni, a new species causing bark cankers of alder (Alnus Miller) species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, C.; Ragozzino, A.; Seemüller, E. Identification and characterization of the phytoplasma associated with elm yellows in southern Italy and its relatedness to other phytoplasmas of the elm yellows group. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1997, 27, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemüller, E.; Marcone, C.; Lauer, U.; Ragozzino, A.; Göschl, M. Current status of molecular classification of the phytoplasmas. J. Plant Pathol. 1998, 80, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Marcone, C.; Ragozzino, A.; Seemüller, E. Dodder transmission of the alder yellows phytoplasma to the experimental host Catharanthus roseus (periwinkle). Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1997, 27, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, C.; Hergenhahn, F.; Ragozzino, A.; Seemüller, E. Dodder transmission of pear decline, European stone fruit yellows, rubus stunt, picris echioides yellows and cotton phyllody phytoplasmas to periwinkle. J. Phytopathol. 1999, 147, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, C.; Ragozzino, A.; Schneider, B.; Lauer, U.; Smart, C.D.; Seemüller, E. Genetic characterization and classification of two phytoplasmas associated with spartium witches’-broom disease. Plant Dis. 1996, 80, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, U.; Seemüller, E. Detection of mycoplasmalike organisms in declining oaks by polymerase chain reaction. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1994, 24, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, U.; Seemüller, E. Detection of DNA of plant pathogenic mycoplasmalike organisms by a polymerase chain reaction that amplifies a sequence of the 16S rRNA gene. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.; Seemüller, E.; Smart, C.D.; Kirkpatrick, B.C. Phylogenetic classification of plant pathogenic mycoplasma-like organisms or phytoplasmas. In Molecular and Diagnostic Procedures in Mycoplasmology; Razin, S., Tully, J.G., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995; Volume I, pp. 369–380. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, C.D.; Schneider, B.; Blomquist, C.L.; Guerra, L.J.; Harrison, N.A.; Ahrens, U.; Lorenz, K.-H.; Seemüller, E.; Kirkpatrick, B.C. Phytoplasma-specific PCR primers based on sequences of the 16S/23S rRNA spacer region. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 2988–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-M.; Gundersen, D.E.; Hammond, R.W.; Davis, R.E. Use of mycoplasmalike organism (MLO) group-specific oligonucleotide primers for nested-PCR assays to detect mixed-MLO infections in a single host plant. Phytopathology 1994, 84, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.; Hüttel, B.; Zübert, C.; Kube, M. Genetic variation, phylogenetic relationship and spatial distribution of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma ulmi’ strains in Germany. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Lee, I.-M.; Bottner, K.D.; Zhao, Y.; Botti, S.; Bertaccini, A.; Harrison, N.A.; Carraro, L.; Marcone, C.; Khan, A.J.; et al. Ribosomal protein gene-based phylogeny for finer differentiation and classification of phytoplasmas. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2037–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Bottner-Parker, K.D.; Lee, I.-M. PCR-based sequence analysis on multiple genes other than 16S rRNA gene for differentiation of phytoplasmas. In Phytoplasmas: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology; Musetti, R., Pagliari, L., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1875, pp. 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Lee, I.-M.; Shao, J.; Suo, X.; Davis, R.E. Construction of an interactive online phytoplasma classification tool, iPhyClassifier, and its application in analysis of the peach X-disease phytoplasma group (16SrIII). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2582–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA 11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berges, R.; Cousin, M.T.; Roux, J.; Seemüller, E. Detection of phytoplasma infections in declining Populus nigra ‘Italica’ trees and molecular differentiation of the aster yellows phytoplasmas identified in various Populus species. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1997, 27, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berges, R.; Rott, M.; Seemüller, E. Range of phytoplasma concentrations in various plant hosts as determined by competitive polymerase chain reaction. Phytopathology 2000, 90, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertaccini, A.; Paltrinieri, S.; Contaldo, N. Standard detection protocol: PCR and RFLP analyses based on 16S rRNA gene. In Phytoplasmas: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology; Musetti, R., Pagliari, L., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1875, pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zwitter, Z.K.; Seljak, G.; Jakomin, T.; Brodarić, J.; Vućurović, A.; Pedemay, S.; Salar, P.; Malembic-Maher, S.; Foissac, X.; Mehle, N. Epidemiology of flavescence dorée and hazelnut decline in Slovenia: Geographical distribution and genetic diversity of the associated 16SrV phytoplasmas. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1217425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ember, I.; Acs, Z.; Salar, P.; Danet, J.-L.; Foissac, X.; Kölber, M.; Malembic-Maher, S. Survey and genetic diversity of phytoplasmas from the 16SrV-C and -D subgroups in Hungary. Bull. Insectol. 2011, 64, 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mehle, N.; Rupar, M.; Seljak, G.; Ravnikar, M.; Dermastia, M. Molecular diversity of ‘flavescence dorée’ phytoplasma strains in Slovenia. Bull. Insectol. 2011, 64, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Desqué, D.; Salar, P.; Danet, J.-L.; Lusseau, T.; Garcion, C.; Moreau, E.; Dubus, C.; Dureuil, J.; Delbac, L.; Binet, D.; et al. Impact of Orientus ishidae on “flavescence dorée” emergence in the vineyards of riparian ecosystems. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 2019, 9, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berges, R.; Seemüller, E. Impact of phytoplasma infection of common alder (Alnus glutinosa) depends on strain virulence. For. Pathol. 2002, 32, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, W.A.; Griffiths, H.M. Variation in aggressiveness of ash yellows phytoplasmas. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemüller, E.; Kiss, E.; Sule, S.; Schneider, B. Multiple infection of apple trees by distinct strains of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma mali’ and its pathological relevance. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Vallino, M.; Galetto, L.; Marzachì, C. Competitive exclusion of flavescence dorée phytoplasma strains in Catharanthus roseus plants. Plants 2020, 9, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belli, G.; Bianco, P.A.; Conti, M. Grapevine yellows in Italy: Past, present and future. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 92, 303–326. [Google Scholar]
- Gentili, A.; Ferretti, L.; Costantini, E.; Zoina, A.; Cozzolino, I.; Spigno, P.; Pasquini, G. Identification of ‘flavescence dorée’ strain FD-D in viticultural areas of Ischia island (Campania, Italy). Petria 2013, 23, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Danet, J.L.; Balakishiyeva, G.; Cimerman, A.; Sauvion, N.; Marie-Jeanne, V.; Labonne, G.; Laviňa, A.; Battle, A.; Križanac, I.; Škorić, D.; et al. Multilocus sequence analysis reveals the genetic diversity of European fruit tree phytoplasmas and supports the existence of inter-species recombination. Microbiology 2011, 157, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrović, J.; Kakizawa, S.; Duduk, B.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S.; Bertaccini, A. The groEL gene as an additional marker for finer differentiation of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris’-related strains. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2011, 159, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siampour, M.; Izadpanah, K.; Galetto, L.; Salehi, M.; Marzachì, C. Molecular characterization, phylogenetic comparison and serological relationship of the Imp protein of several ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma aurantifolia’ strains. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrović, J.; Smiljković, M.; Seemüller, E.; Reinhardt, R.; Hüttel, B.; Büttner, C.; Bertaccini, A.; Kube, M.; Duduk, B. Differentiation of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma cynodontis’ based on 16S rRNA and groEL genes and identification of a new subgroup, 16SrXIV-C. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohunická, M.; Valentová, L.; Suchá, J.; Nečas, T.; Eichmeier, A.; Kiss, T.; Cmejla, R. Identification of 17 ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma pyri’ genotypes based on the diversity of the imp gene sequence. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermastia, M.; Dolanc, D.; Mlinar, P.; Mehle, N. Molecular diversity of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma mali’ and ‘Ca. P. prunorum’ in orchards in Slovenia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 152, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muirhead, K.; Pérez-López, E.; Bahder, B.W.; Hill, J.E.; Dumonceaux, T. The CpnClassiPhyR is a resource for cpn 60 universal target-based classification of phytoplasmas. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2494–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcone, C.; Pierro, R.; Palmieri, C. Occurrence, Impact, and Multilocus Sequence Analysis of Alder Yellows Phytoplasma Infecting Common Alder and Italian Alder in Southern Italy. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061140
Marcone C, Pierro R, Palmieri C. Occurrence, Impact, and Multilocus Sequence Analysis of Alder Yellows Phytoplasma Infecting Common Alder and Italian Alder in Southern Italy. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(6):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061140
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcone, Carmine, Roberto Pierro, and Carmine Palmieri. 2024. "Occurrence, Impact, and Multilocus Sequence Analysis of Alder Yellows Phytoplasma Infecting Common Alder and Italian Alder in Southern Italy" Microorganisms 12, no. 6: 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061140
APA StyleMarcone, C., Pierro, R., & Palmieri, C. (2024). Occurrence, Impact, and Multilocus Sequence Analysis of Alder Yellows Phytoplasma Infecting Common Alder and Italian Alder in Southern Italy. Microorganisms, 12(6), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061140






