Comprehensive Genomics Investigation of Neboviruses Reveals Distinct Codon Usage Patterns and Host Specificity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Whole-Genome NeV Dataset and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.2. Nucleotide Composition Analysis
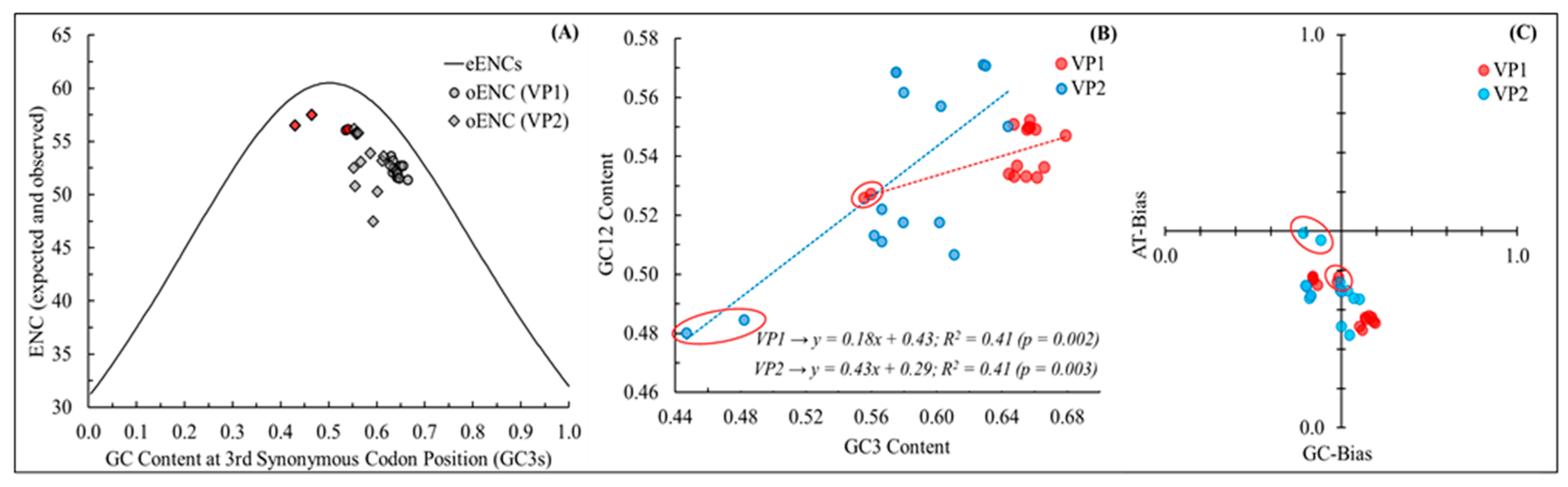
2.3. Effective Number of Codons (ENC) and ENC-GC3 Plot Analysis
2.4. Neutrality Plot (Neutral Evolution) and PR2-Bias Plot
2.5. Relative Synonymous Codon Usage (RSCU)
2.6. Codon Adaptation Index (CAI)
2.7. Relative Codon Deoptimization Index (RCDI)
2.8. Recombination Analysis of NeVs
3. Results
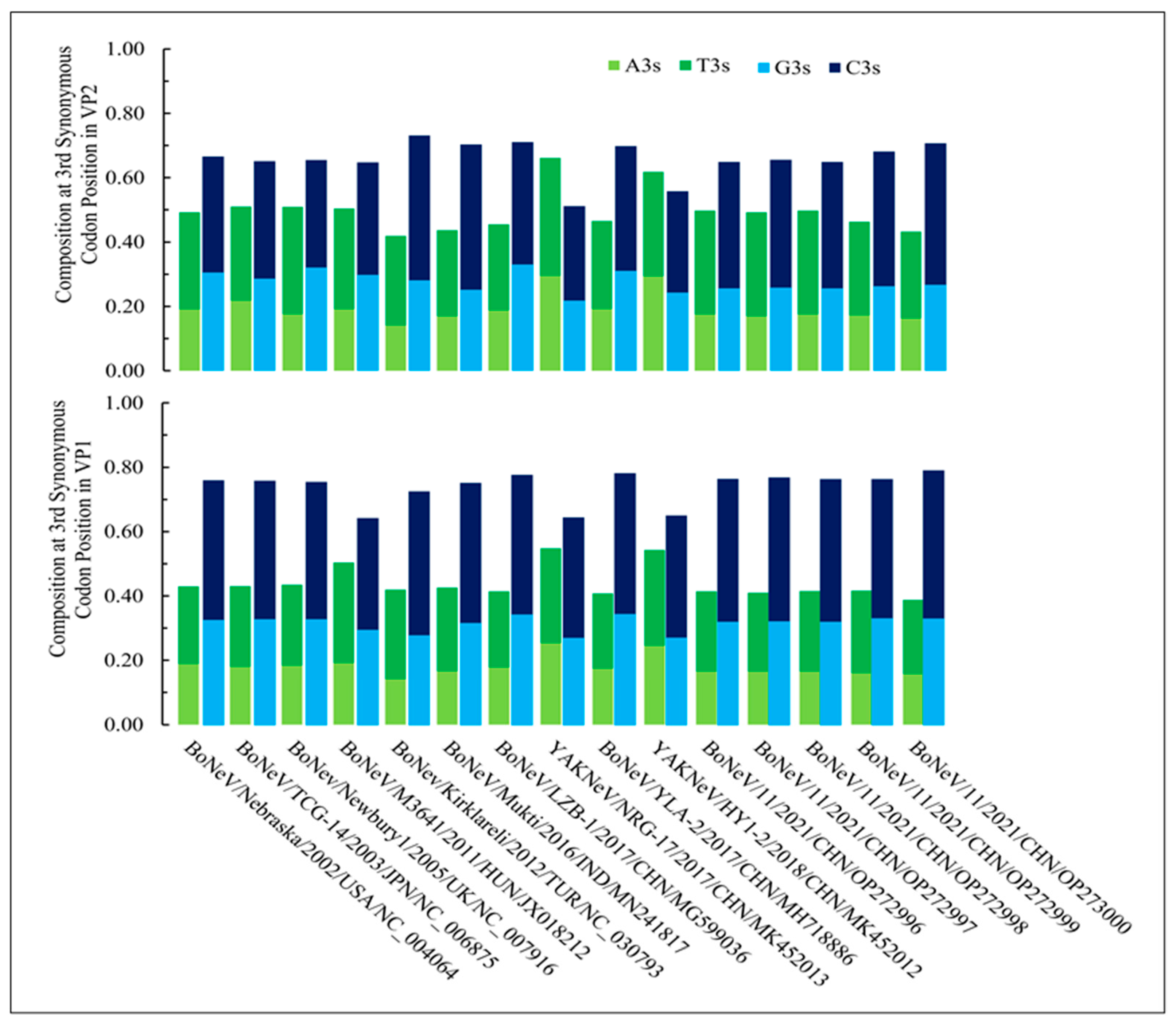
3.1. Nucleotide Composition and Codon Usage Bias Are Significantly Different in NeVs Infecting Yaks than Those of Bovines
3.2. Both Mutational Pressure and Natural Selection Govern the Codon Usage Patterns Differently across the NeV Genes as Well as Host Species
3.3. Most Common Codons across NeVs Have Abundant G/C at the Third Position
3.4. Codon Adaptation Index Showed Marginal Variations among NeVs
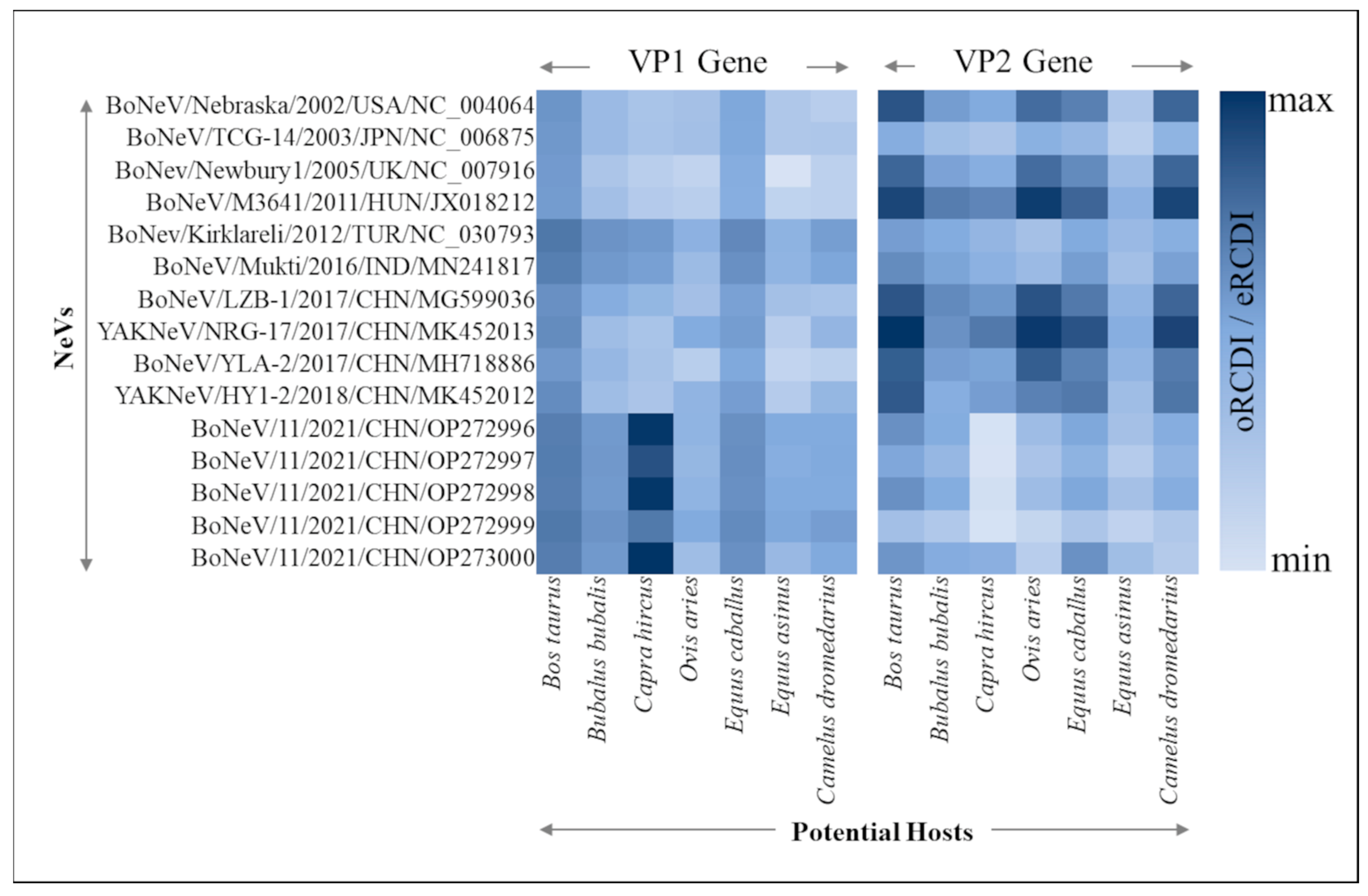
3.5. Viral Adaptability to Different Hosts through RCDI
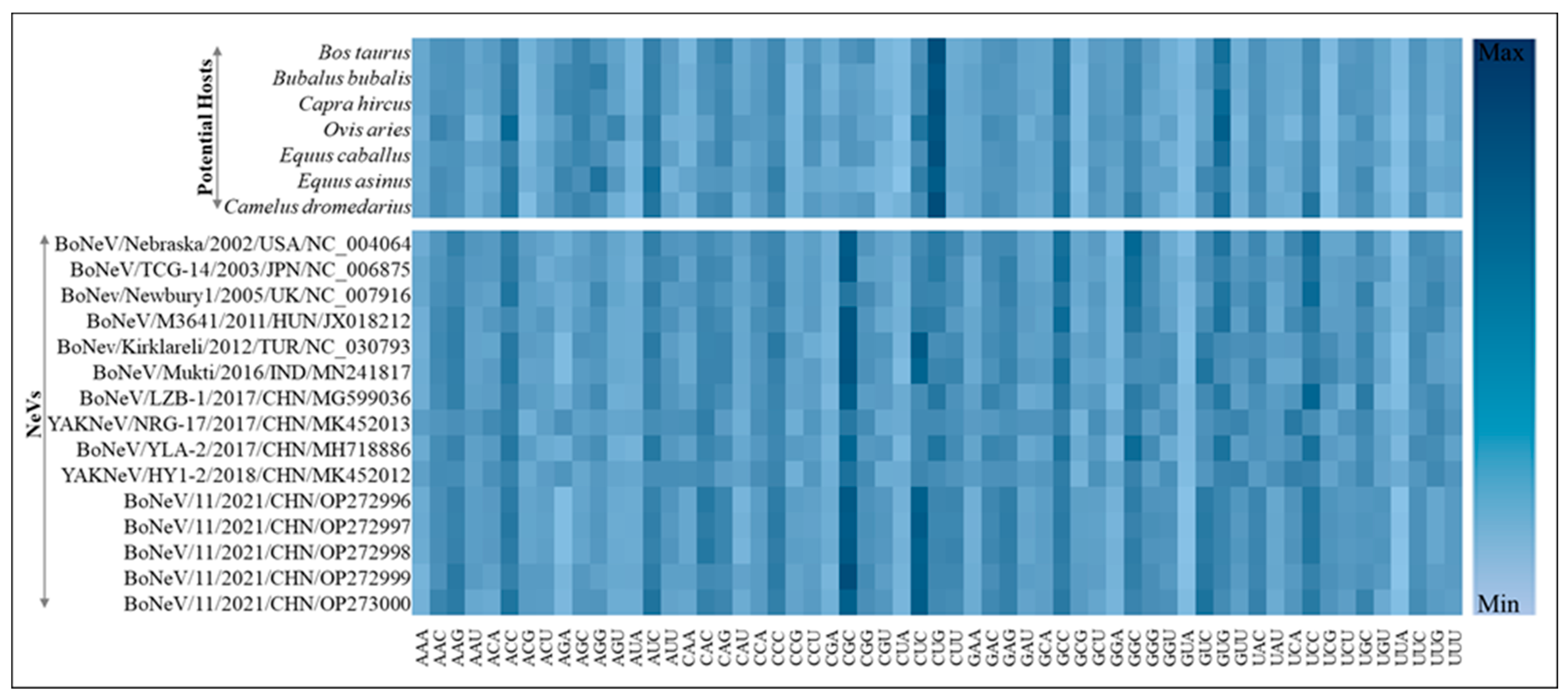
3.6. Isoacceptor tRNA Pool Analysis of Different Hosts
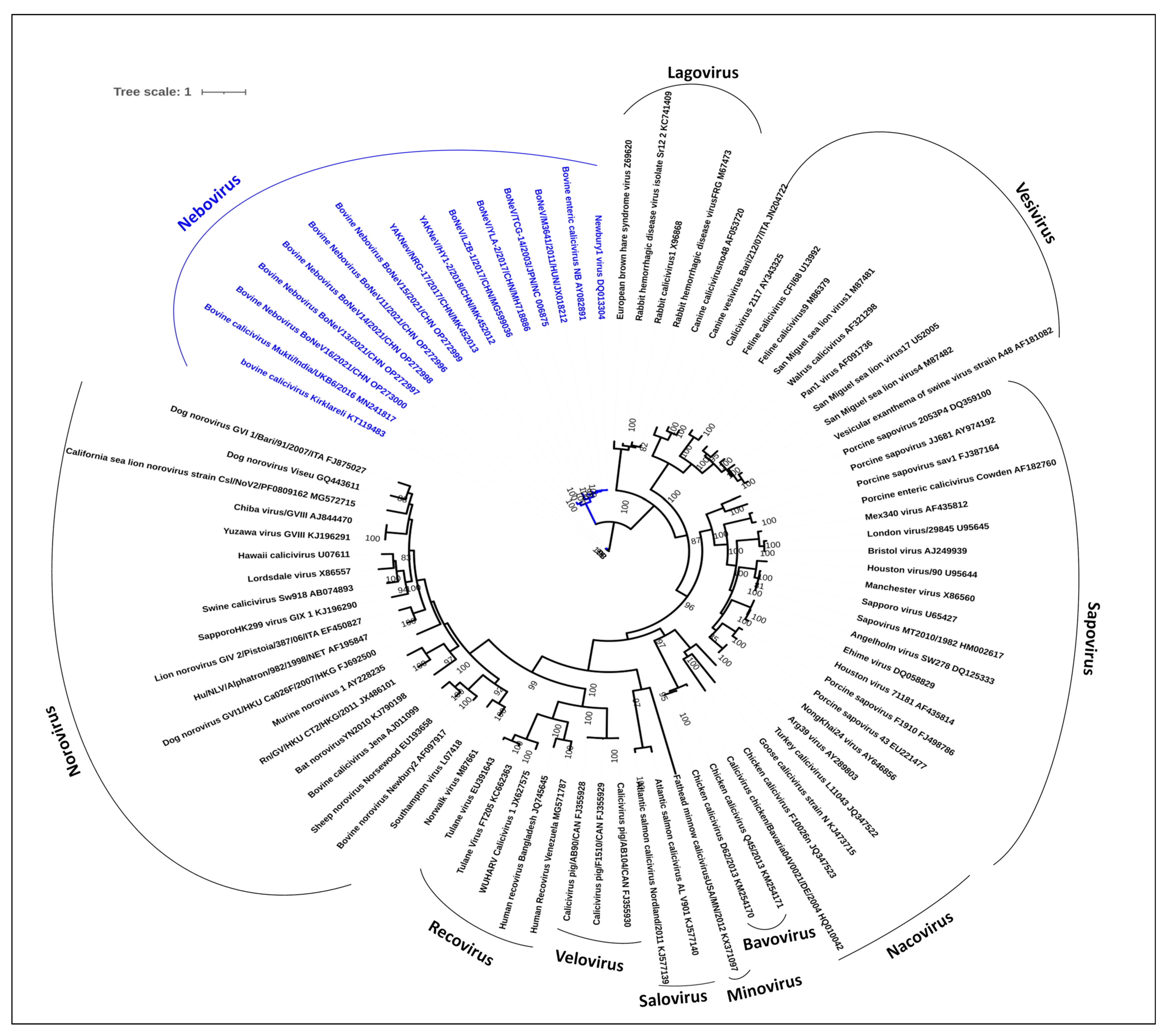
3.7. Phylogenetic Analysis of NeVs Revealed Two Distinct Clusters
3.8. Recombination Analysis Indicated Four Potential Recombination Events in NeVs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, N.; Kaushik, R.; Singh, A.; Uversky, V.N.; Zhang, K.Y.J.; Sahu, U.; Bhatia, S.; Sanyal, A. Bayesian Molecular Dating Analyses Combined with Mutational Profiling Suggest an Independent Origin and Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 Sub-Lineages. Viruses 2022, 14, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Kaushik, R.; Tennakoon, C.; Uversky, V.N.; Longhi, S.; Zhang, K.Y.J.; Bhatia, S. Insights into the evolutionary forces that shape the codon usage in the viral genome segments encoding intrinsically disordered protein regions. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, Y.S.; Ansari, M.I.; Kattoor, J.J.; Kaushik, R.; Sircar, S.; Subbaiyan, A.; Tiwari, R.; Dhama, K.; Ghosh, S.; Tomar, S.; et al. Evolutionary and codon usage preference insights into spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1006–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkan, F.; Karayel, İ.; Catella, C.; Bodnar, L.; Lanave, G.; Bányai, K.; Di Martino, B.; Decaro, N.; Buonavoglia, C.; Martella, V. Identification of a Bovine Enteric Calicivirus, Kırklareli Virus, Distantly Related to Neboviruses, in Calves with Enteritis in Turkey. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3614–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castells, M.; Victoria, M.; Colina, R.; Musto, H.; Cristina, J. Genome-wide analysis of codon usage bias in Bovine Coronavirus. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Felice, E.; Mauroy, A.; Pozzo, F.D.; Thiry, D.; Ceci, C.; Di Martino, B.; Marsilio, F.; Thiry, E. Bovine noroviruses: A missing component of calf diarrhoea diagnosis. Vet. J. 2016, 207, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Krupovic, M.; Varsani, A.; Wolf, Y.I.; Yutin, N.; Zerbini, F.M.; Kuhn, J.H. Global Organization and Proposed Megataxonomy of the Virus World. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.M.; Dalton, K.P.; Magalhães, M.J.; Parra, F.; Esteves, P.J.; Holmes, E.C.; Abrantes, J. Full genomic analysis of new variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus revealed multiple recombination events. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, M.; Alencar, A.L.; Almeida-Queiroz, S.R.; Buzinaro, M.G.; Munin, F.S.; Godoy, S.H.; Livonesi, M.C.; Fernandes, A.M.; Sousa, R.L. First detection and molecular characterization of Nebovirus in Brazil. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 1876–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pendu, J.; Abrantes, J.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guitton, J.S.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lopes, A.M.; Marchandeau, S.; Alda, F.; Almeida, T.; Célio, A.P.; et al. Proposal for a unified classification system and nomenclature of lagoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martella, V.; Pinto, P.; Lorusso, E.; Di Martino, B.; Wang, Q.; Larocca, V.; Cavalli, A.; Camero, M.; Decaro, N.; Bányai, K.; et al. Detection and Full-Length Genome Characterization of Novel Canine Vesiviruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1433–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, T.; Stoltzfus, G.T.; Zhu, C.; Jung, K.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.J. Attempts to grow human noroviruses, a sapovirus, and a bovine norovirus in vitro. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0178157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, T.; Wang, Q.; Katayama, K.; Saif, L.J. Comprehensive review of human sapoviruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 32–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; He, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yue, H.; Tang, C. Detection and molecular characteristics of neboviruses in dairy cows in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, T.; Işıdan, H.; Atasoy, M.O.; Irehan, B. Detection and Molecular Analysis of Bovine Enteric Norovirus and Nebovirus in Turkey. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexaki, A.; Kames, J.; Holcomb, D.D.; Athey, J.; Santana-Quintero, L.V.; Lam, P.V.N.; Hamasaki-Katagiri, N.; Osipova, E.; Simonyan, V.; Bar, H.; et al. Codon and Codon-Pair Usage Tables (CoCoPUTs): Facilitating Genetic Variation Analyses and Recombinant Gene Design. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 2434–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.F.; Yedloutschnig, R.J.; Dardiri, A.H.; Callis, J.J. Vesicular exanthema of swine virus: Isolation and serotyping of field samples. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1987, 51, 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Padidam, M.; Sawyer, S.; Fauquet, C.M. Possible emergence of new geminiviruses by frequent recombination. Virology 1999, 265, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Elliott, J.B.; Glasgow, A.; Poland, A.; Keel, K. An isolated epizootic of hemorrhagic-like fever in cats caused by a novel and highly virulent strain of feline calicivirus. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 73, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiley, J.R.; Chang, K.O.; Hayes, J.; Vinjé, J.; Saif, L.J. Characterization of an enteropathogenic bovine calicivirus representing a potentially new calicivirus genus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10089–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.W.; Iversen, P.L.; Skilling, D.E.; Stein, D.A.; Bok, K.; Matson, D.O. Vesivirus viremia and seroprevalence in humans. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.H.; Soliman, M.; Alfajaro, M.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Seo, J.Y.; Park, J.G.; Kim, D.S.; Baek, Y.B.; Kang, M.I.; Park, S.I.; et al. Bovine Nebovirus Interacts with a Wide Spectrum of Histo-Blood Group Antigens. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez-Valcarce, M.; Castro, C.J.; Marine, R.L.; Halasa, N.; Mayta, H.; Saito, M.; Tsaknaridis, L.; Pan, C.Y.; Bucardo, F.; Becker-Dreps, S.; et al. Genetic diversity of human sapovirus across the Americas. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 104, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; He, Q.; Yue, H.; Zhang, B.; Tang, C. First detection of Nebovirus and Norovirus from cattle in China. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.I.; Jeong, C.; Park, S.J.; Kim, H.H.; Jeong, Y.J.; Hyun, B.H.; Chun, Y.H.; Kang, M.I.; Cho, K.O. Molecular detection and characterization of unclassified bovine enteric caliciviruses in South Korea. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 130, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourasgari, F.; Kaplon, J.; Sanchooli, A.; Fremy, C.; Karimi-Naghlani, S.; Otarod, V.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Mojgani, N.; Pothier, P. Molecular prevalence of bovine noroviruses and neboviruses in newborn calves in Iran. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kaushik, R.; Yadav, P.; Sircar, S.; Shete-Aich, A.; Singh, A.; Malik, Y.S. A novel highly divergent enteric calicivirus in a bovine calf, India. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Bera, B.C.; Greenbaum, B.D.; Bhatia, S.; Sood, R.; Selvaraj, P.; Anand, T.; Tripathi, B.N.; Virmani, N. Revelation of Influencing Factors in Overall Codon Usage Bias of Equine Influenza Viruses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kulkarni, D.D.; Lee, B.; Kaushik, R.; Bhatia, S.; Sood, R.; Pateriya, A.K.; Bhat, S.; Singh, V.P. Evolution of Codon Usage Bias in Henipaviruses Is Governed by Natural Selection and Is Host-Specific. Viruses 2018, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordstein, C.; Cano, L.; Morales, A.C.; Young, B.; Ho, A.T.; Rice, A.M.; Liss, M.; Hurst, L.D.; Kudla, G. Transcription, mRNA Export, and Immune Evasion Shape the Codon Usage of Viruses. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thioulouse, J.; Chevenet, F. NetMul, a World-Wide Web user interface for multivariate analysis software. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 1996, 21, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuglsang, A. The ‘effective number of codons’ revisited. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 317, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglsang, A. Accounting for background nucleotide composition when measuring codon usage bias: Brilliant idea, difficult in practice. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, F. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archetti, M. Codon usage bias and mutation constraints reduce the level of error minimization of the genetic code. J. Mol. Evol. 2004, 59, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulmer, M. The selection-mutation-drift theory of synonymous codon usage. Genetics 1991, 129, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Lee, W.; Hottes, A.K.; Shapiro, L.; McAdams, H.H. Codon usage between genomes is constrained by genome-wide mutational processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3480–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, J.; Moreno, P.; Moratorio, G.; Musto, H. Genome-wide analysis of codon usage bias in Ebolavirus. Virus Res. 2015, 196, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Reis, M.; Savva, R.; Wernisch, L. Solving the riddle of codon usage preferences: A test for translational selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 5036–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, R.D.; Freeland, S.J.; Landweber, L.F. A simple model based on mutation and selection explains trends in codon and amino-acid usage and GC composition within and across genomes. Genome Biol. 2001, 2, Research0010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komar, A.A. The Yin and Yang of codon usage. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, R77–R85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershberg, R.; Petrov, D.A. Selection on codon bias. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunec, D.; Osterrieder, N. Codon Pair Bias Is a Direct Consequence of Dinucleotide Bias. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.; Libchaber, A. Degeneracy of the genetic code and stability of the base pair at the second position of the anticodon. RNA 2008, 14, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovesan, A.; Pelleri, M.C.; Antonaros, F.; Strippoli, P.; Caracausi, M.; Vitale, L. On the length, weight and GC content of the human genome. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeron, J.M.; Aguadé, M. An evaluation of measures of synonymous codon usage bias. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 47, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2653–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Translation-coupled violation of Parity Rule 2 in human genes is not the cause of heterogeneity of the DNA G+C content of third codon position. Gene 1999, 238, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueoka, N. Near homogeneity of PR2-bias fingerprints in the human genome and their implications in phylogenetic analyses. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 53, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, C.; Govindarajan, S.; Minshull, J. Codon bias and heterologous protein expression. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalina, S.A.; Spiridonov, N.A.; Kashina, A. Sounds of silence: Synonymous nucleotides as a key to biological regulation and complexity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 2073–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. An evolutionary perspective on synonymous codon usage in unicellular organisms. J. Mol. Evol. 1986, 24, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Stenico, M.; Peden, J.F.; Lloyd, A.T. Codon usage: Mutational bias, translational selection, or both? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B.; Wei, W. Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage Bias of Zika Virus and Its Adaption to the Hosts. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puigbò, P.; Bravo, I.G.; Garcia-Vallve, S. CAIcal: A combined set of tools to assess codon usage adaptation. Biol. Direct 2008, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belalov, I.S.; Lukashev, A.N. Causes and implications of codon usage bias in RNA viruses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Zinovyev, A.; Képès, F. Codon adaptation index as a measure of dominating codon bias. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, K.A.; Goodenbour, J.M.; Pan, T. Tissue-specific differences in human transfer RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. The codon Adaptation Index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Gojobori, T.; Ikemura, T. Codon usage tabulated from international DNA sequence databases: Status for the year 2000. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigbò, P.; Aragonès, L.; Garcia-Vallvé, S. RCDI/eRCDI: A web-server to estimate codon usage deoptimization. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Rybicki, E. RDP: Detection of recombination amongst aligned sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löytynoja, A.; Goldman, N. An algorithm for progressive multiple alignment of sequences with insertions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10557–10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, S. Statistical tests for detecting gene conversion. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1989, 6, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Evaluation of methods for detecting recombination from DNA sequences: Computer simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13757–13762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.W. Problems of translating heterologous genes in expression systems: The role of tRNA. Biotechnol. Prog. 1996, 12, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, M.F.; Posada, D.; Feldman, M.W. An exact nonparametric method for inferring mosaic structure in sequence triplets. Genetics 2007, 176, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, M.O.; Carr, J.K.; Burke, D.S.; McCutchan, F.E. Identification of breakpoints in intergenotypic recombinants of HIV type 1 by bootscanning. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1995, 11, 1423–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, M.J.; Armstrong, J.S.; Gibbs, A.J. Sister-scanning: A Monte Carlo procedure for assessing signals in recombinant sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietel, A.K.; Merker, H.; Kaltenpoth, M.; Kost, C. Selective advantages favour high genomic AT-contents in intracellular elements. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.M.; Nasrullah, I.; Qamar, R.; Tong, Y. Evolution of codon usage in Zika virus genomes is host and vector specific. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Zhou, T.; Ma, J.; Sun, X.; Lu, Z. Analysis of synonymous codon usage in SARS Coronavirus and other viruses in the Nidovirales. Virus Res. 2004, 101, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Ramírez, E.E.; Salazar, M.I.; López-López Mde, J.; Salas-Benito, J.S.; Sánchez-Varela, A.; Guo, X. Large-scale genomic analysis of codon usage in dengue virus and evaluation of its phylogenetic dependence. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 851425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, L.F.; Naylor, M.; Clifford, P. Heterogeneity in codon usages of sobemovirus genes. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 1591–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoe, T.A.; de Koning, A.P.; Kim, H.M.; Gu, W.; Noonan, B.P.; Naylor, G.; Jiang, Z.J.; Parkinson, C.L.; Pollock, D.D. Evidence for an ancient adaptive episode of convergent molecular evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8986–8991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, A.; Shackelton, L.A.; Holmes, E.C. Family level phylogenies reveal modes of macroevolution in RNA viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Y.S.; Kumar, N.; Sharma, K.; Dhama, K.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Ganesh, B.; Kobayashi, N.; Banyai, K. Epidemiology, phylogeny, and evolution of emerging enteric Picobirnaviruses of animal origin and their relationship to human strains. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 780752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompei, S.; Loreto, V.; Tria, F. Phylogenetic properties of RNA viruses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivailler, P.; Mao, N.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, W. Recombination analysis of Human mastadenovirus C whole genomes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon-Loriere, E.; Holmes, E.C. Why do RNA viruses recombine? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worobey, M.; Holmes, E.C. Evolutionary aspects of recombination in RNA viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80 Pt 10, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Kaushik, R.; Tennakoon, C.; Uversky, V.N.; Mishra, A.; Sood, R.; Srivastava, P.; Tripathi, M.; Zhang, K.Y.J.; Bhatia, S. Evolutionary Signatures Governing the Codon Usage Bias in Coronaviruses and Their Implications for Viruses Infecting Various Bat Species. Viruses 2021, 13, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Gu, W.; Ma, J.; Sun, X.; Lu, Z. Analysis of synonymous codon usage in H5N1 virus and other influenza A viruses. Biosystems 2005, 81, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.M.; Nasrullah, I.; Tong, Y. Genome-wide analysis of codon usage and influencing factors in chikungunya viruses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandia, R.; Singhal, S.; Kumar, U.; Ansari, A.; Tiwari, R.; Dhama, K.; Das, J.; Munjal, A.; Singh, R.K. Analysis of Nipah Virus Codon Usage and Adaptation to Hosts. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moratorio, G.; Iriarte, A.; Moreno, P.; Musto, H.; Cristina, J. A detailed comparative analysis on the overall codon usage patterns in West Nile virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 14, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. Mutation pressure shapes codon usage in the GC-Rich genome of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virus Genes 2007, 35, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goñi, N.; Iriarte, A.; Comas, V.; Soñora, M.; Moreno, P.; Moratorio, G.; Musto, H.; Cristina, J. Pandemic influenza A virus codon usage revisited: Biases, adaptation and implications for vaccine strain development. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, I.; Yamaki, Y.; Detroja, R.; Tagore, S.; Moore, H.; Maharjan, S.; Nakano, Y.; Christian, T.; Matsubara, R.; Lowe, T.M.; et al. tRNA methylation resolves codon usage bias at the limit of cell viability. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, M.C.; Pryszcz, L.P.; Medina, R.; Milenkovic, I.; Camacho, N.; Marchand, V.; Motorin, Y.; Ribas de Pouplana, L.; Novoa, E.M. Quantitative analysis of tRNA abundance and modifications by nanopore RNA sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.; Cullen, B.R. Epigenetic and epitranscriptomic regulation of viral replication. Nature reviews. Microbiology 2020, 18, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NeVs | Accession ID | Method | Size (bp) | Source (PMID) | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BoNeV/Nebraska/2002/USA/NC_004064 | NC_004064 | NA | 7453 | 12239283 | USA |
| BoNeV/TCG-14/2003/JPN/NC_006875 | NC_006875 | NA | 7453 | NCBI | Japan |
| BoNev/Newbury1/2005/UK/NC_007916 | NC_007916 | NA | 7454 | 16574184 | UK |
| BoNeV/M3641/2011/HUN/JX018212 | JX018212 | Sanger | 7453 | NCBI | Hungary |
| BoNev/Kirklareli/2012/TUR/NC_030793 | NC_030793 | Sanger | 7484 | 26292294 | Turkey |
| BoNeV/Mukti/2016/IND/MN241817 | MN241817 | Sanger | 7484 | NCBI | India |
| BoNeV/LZB-1/2017/CHN/MG599036 | MG599036 | Sanger | 7453 | 31500726 | China |
| YAKNeV/NRG-17/2017/CHN/MK452013 | MK452013 | Sanger | 7459 | 31500726 | China |
| BoNeV/YLA-2/2017/CHN/MH718886 | MH718886 | Sanger | 7453 | 30444471 | China |
| YAKNeV/HY1-2/2018/CHN/MK452012 | MK452012 | Sanger | 7460 | 31500726 | China |
| BoNeV/11/2021/CHN/OP272996 | OP272996 | Illumina | 7485 | 38108282 | China |
| BoNeV/11/2021/CHN/OP272997 | OP272997 | Illumina | 7453 | 38108282 | China |
| BoNeV/11/2021/CHN/OP272998 | OP272998 | Illumina | 7462 | 38108282 | China |
| BoNeV/11/2021/CHN/OP272999 | OP272999 | Illumina | 7466 | 38108282 | China |
| BoNeV/11/2021/CHN/OP273000 | OP273000 | Illumina | 7463 | 38108282 | China |
| REs | Recomb | Major Parent | Minor Parent | RDP | GCn | BSc | MCh | Chm | SiS | 3SQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MG599036 | JX018212 | NC_007916 * | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 2 | NC_007916 | MH718886 * | NC_004064 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3 | NC_004064 | NC_007916 | MH718886 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 4 | JX018212 | MH718886 | NC_004064 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaushik, R.; Kumar, N.; Yadav, P.; Sircar, S.; Shete-Aich, A.; Singh, A.; Tomar, S.; Launey, T.; Malik, Y.S. Comprehensive Genomics Investigation of Neboviruses Reveals Distinct Codon Usage Patterns and Host Specificity. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040696
Kaushik R, Kumar N, Yadav P, Sircar S, Shete-Aich A, Singh A, Tomar S, Launey T, Malik YS. Comprehensive Genomics Investigation of Neboviruses Reveals Distinct Codon Usage Patterns and Host Specificity. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(4):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040696
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaushik, Rahul, Naveen Kumar, Pragya Yadav, Shubhankar Sircar, Anita Shete-Aich, Ankur Singh, Shailly Tomar, Thomas Launey, and Yashpal Singh Malik. 2024. "Comprehensive Genomics Investigation of Neboviruses Reveals Distinct Codon Usage Patterns and Host Specificity" Microorganisms 12, no. 4: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040696
APA StyleKaushik, R., Kumar, N., Yadav, P., Sircar, S., Shete-Aich, A., Singh, A., Tomar, S., Launey, T., & Malik, Y. S. (2024). Comprehensive Genomics Investigation of Neboviruses Reveals Distinct Codon Usage Patterns and Host Specificity. Microorganisms, 12(4), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040696










