Abstract
Bioinvasions constitute both a direct and an indirect threat to ecosystems. Direct threats include pressures on local trophic chains, while indirect threats might take the form of an invasion of a microorganism alongside its host. The marine dinoflagellate Hematodinium perezi, parasitizing blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus), has a worldwide distribution alongside its host. In Greece, fluctuations in the blue crab population are attributed to overexploitation and the effects of climate change. The hypothesis of the present study was that blue crab population reductions cannot only be due to these factors, and that particular pathogens may also be responsible for the fluctuations. To investigate this hypothesis, both lethargic and healthy blue crab specimens were collected from three different fishing sites in order to assess the health status of this important species. Together with the lethargic responses, the hemolymph of the infested crabs presented a milky hue, indicating the first signs of parasitic infestation with H. perezi. The histopathological results and molecular identification demonstrated the effect of the presence of H. perezi in the internal organs and their important role in the mortality of blue crabs. Specifically, H. perezi, in three different tissues examined (heart, gills, hepatopancreas), affected the hemocytes of the species, resulting in alterations in tissue structure. Apart from this dinoflagellate parasite, the epibiotic peritrich ciliate Epistylis sp. was also identified, infecting the gills. This study represents the first detection of H. perezi in the eastern Mediterranean, demonstrating that this is the main causative agent of blue crab mortality on Greek coastlines.
1. Introduction
Global invasions, i.e., the successful establishment, breeding, and spreading of organisms outside of their natural range, may have detrimental consequences on local ecosystems. Invasions in aquatic ecosystems are increasingly frequent and are responsible for pressure on local habitats, posing a risk to biodiversity by spreading pathogenic microorganisms to the new ecosystems [1,2]. Climate change, shipping by the means of ballast waters, global trade, and accidental or intentional (for rearing purposes) releases of non-indigenous species into new ecosystems have intensified the phenomenon in recent years, affecting local flora and fauna [3,4,5,6,7,8]. In parallel with aquatic animals, aquatic pathogens may also invade new ecosystems together with their host, representing another important threat to ecosystems [4,7]. Crustaceans constitute one of the most important examples of global invasions, with more than 240 species recorded and characterized as non-indigenous in the Mediterranean Sea [9].
The Atlantic blue crab, Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1986 (Brachyura: Portunidae), is a highly mobile benthic predator distributed from Nova Scotia, Canada, to Brazil, economically supporting fisheries in the local coastal areas [10,11,12,13]. Beyond its large distribution range of the species in Atlantic coastlines, it has been reported as invader in the Mediterranean Sea [11,12]. C. sapidus invasion was first reported in France in 1900, likely resulting from either ballast waters or having been imported for aquaculture purposes [11,14,15]. Since then, it has invaded many habitats around the Mediterranean Sea, as well as in the Black Sea [11,12]. C. sapidus prefers enclosed environments such as estuaries or lagoons between 0 m and 90 m in depth, mostly on sandy or muddy substrates, regardless of the presence of vegetation [16]. Despite its important status in fisheries in the USA, its exploitation in the Mediterranean Sea is limited mostly to Turkey, Greece, Italy, and Egypt [17,18,19,20]. The blue crab diet consists of a broad spectrum of prey, including mollusks, crustaceans, fish, polychaetes, and marine vegetation [21]. Although the blue crab constitutes an important model organism for studying invasions related to the spread of microorganisms, the majority of scientific research is focused on the population dynamics, structure, and fisheries of the species [12].
During recent years, the blue crab populations across Greek coastlines have been observed to decline, probably on account of high human exploitation and overfishing, resulting in massive population reductions in several circumstances. Additionally, urban pollution and agricultural waste that ends up in marine habitats exerts pressure on the populations and affects the income of many professional fishermen [22]. Regardless of the direct human pressures on habitats and on the organism, mass mortality of the species has emerged, causing a significant deterioration of the populations in Greek coastlines. Mortalities occur mostly in spring and autumn, causing tons of dead individuals to wash ashore in the lagoons or gulfs of the Aegean and Ionian Seas. These phenomena, resulting in blue crab population fluctuations, have only been attributed to the aforementioned factors, i.e., overfishing and pollution. The presence of pathogens, however, has not been investigated so far, even though crustaceans are particularly vulnerable to various parasites [10]. It should also be noted that invasive marine animals may be symptomatic or asymptomatic carriers of invasive microorganisms as well, worsening the negative effects of invasions to biodiversity.
Thus, the main objective of the current research was to investigate blue crab population reductions and mortalities as well as to identify any potential pathogen as the causative agent of the declines in this valuable fisheries resource. Although mortalities of this species occur in several locations in Greece each year, no answer has yet been given concerning the implication of any microorganism towards these events; hence, we hypothesize that the attribution of this phenomenon to overfishing and pollution alone is not correct. The present research attempts to give a holistic overview of the health status of the species in Greece.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Collection
Individuals of C. sapidus were collected from three marine areas across the northern Greek coastlines (Figure 1). Moribund and healthy individuals were collected from the first site, i.e., Porto Lagos lagoon (Vistonikos Gulf, North Aegean), in November 2020, originating from mortality incidents, obtained from local fishermen. The second and the third samplings were performed almost at the same time in November to investigate any potential threat in the local blue crab fisheries in Thermaikos Gulf. Individuals for the second and the third samplings were obtained from two different sites within Thermaikos Gulf to perform a health assessment of the local population. In total, 48 individuals were collected from Porto Lagos lagoon (Vistonikos Gulf, North Aegean), and 40 samples each from Chalastra (Inner Thermaikos Gulf, Figure 1) and Makrygialos (Outer Thermaikos Gulf, Figure 1). An appropriate sample size was calculated using the formula established by Pouhoseingholi et al. [23], where “n” is the recommended sample size, “Z” refers to the corresponding statistic level of confidence, “P” is the expected prevalence of the disease, and “d” represents the precision associated with the effect size. The water temperature during the samplings was 21 °C and 19 °C in Vistonikos Gulf and Thermaikos Gulf, respectively, while the salinity was 37 and 39 PSU, respectively. In the current research, Z was calculated as 0.95, P as 0.9, and d as 0.05, in accordance with Pouhoseingholi et al. [23].
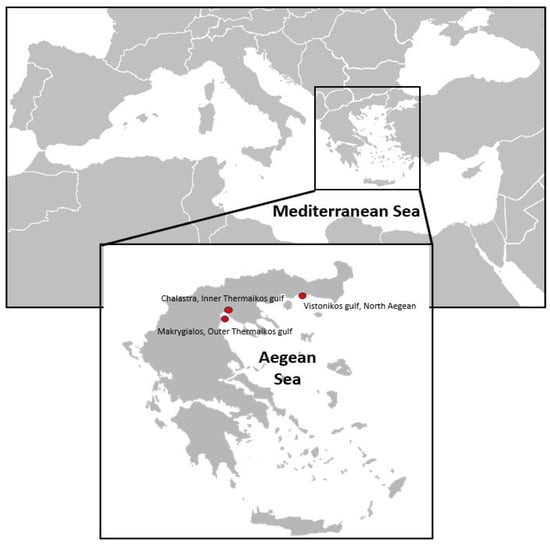
Figure 1.
Sampling sites of C. sapidus individuals for the current study.
2.2. Tissue Sampling
Blue crabs were anesthetized by placement on ice for a 5 min duration. Carapace width (CW) was measured and then target tissues were divided into 2 pieces for further analyses. Target tissues (heart, gills, and hepatopancreas) were collected from each crab and processed for histopathological and molecular analysis. The second half of each tissue, intended for molecular analysis, was stored at −20 °C until DNA extraction.
2.3. Histopathology
Tissues intended for histopathological process were placed in Davidson solution and fixed immediately for 48 h according to Shaw and Battle [24]. After the process of dehydration through graded alcohol, the samples were embedded in paraffin wax and sectioned in a rotary microscope at 4–5 μm. Histological sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin according to the protocol of Howard et al. [25] to monitor the health status of each individual. Finally, the histopathological study was conducted utilizing an optical microscope (iSCOPE, Euromex, Arnhem, The Netherlands) mounted with a CMEX camera (CMEX-5 Pro, Euromex).
2.4. Molecular Detection and Identification of Hematodinium sp. and Ciliates
Genomic DNA was extracted from a piece of tissue (25 mg) from the heart, gills, and hepatopancreas of each crab from all sampling sites. The extraction of DNA was performed using the NucleoSpin Tissue® kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) following the manufacturer’s protocol and, specifically, the guidelines of the standard protocol for human or animal tissue and cultured cells. The purity and concentration of the extracted DNA were evaluated in a Quawell Q-5000 NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Quawell Technology, San Jose, CA, USA) and the DNA samples were stored at −20 °C until PCR application. For the identification of Hematodinium sp. presence, the Hematodinium-specific primer pair HITSF1 5′ CATTCACCGTGAACCTTAGCC 3′ and HITSR1 5′ CTAGTCATACGTTTGAAGAAAGCC 3′ [26,27] was used. This primer pair amplifies a 306 bp region of the parasite’s ITS1 region. For the ciliate detection, the primer set cil-f 5′ TGGTAGTGTATTGGACWACCA 3′ and Cil-r II 5′ TCTRATCGTCTTTGATCCCCTA 3′ developed by Lara et al. [28] was used. This primer set targets a region of approximately 645 bp of the 18S rRNA gene of the ciliate group members. PCR reactions were performed in FastGene Ultra Cycler Gradient (NIPPON Genetics EUROPE, Düren, Germany) in 20 μL final volume containing 10 μL of FastGene Taq 2 × Ready Mix (NIPPON Genetics EUROPE), 0.4 μΜ of each primer, 50 ng of extracted DNA, and PCR-grade water up to the final volume. The thermocycler program for Hematodinium sp. was 95 °C for 3 min followed by 37 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 53 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s and a final extension step of 5 min, while for the ciliates, the annealing temperature was 50.5 °C and the extension time was 45 s. Then, 5 μL of the PCR product was subjected to electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel stained with Midori Green Advance (NIPPON Genetics EUROPE). The agarose gel was observed under UV light, and successfully amplified samples were purified using the NucleoSpin Gel and PCR Clean-up® kit (Macherey Nagel, Düren, Germany) according to the kit protocol. The purified products were then sequenced in both directions using the PCR primers and the Sanger methodology. Chromatograms obtained from Sanger sequencing were visually checked and analyzed using BioEdit [29] and Finch TV 1.4.0 (Geospiza, Seattle, WA, USA). Based on BLAST comparisons and searches of the newly characterized haplotypes on the NCBI website, Maximum Likelihood phylogenetic trees were constructed for both parasites using MEGA software v.7 [30], including various haplotypes belonging to closely related taxa, obtained from the GenBank database.
3. Results
3.1. Gross Signs and Histopathological Results
Among the 128 crabs examined, Hematodinium sp. was detected in 112 samples, resulting in a total prevalence of 87.5%. The total prevalence was calculated based on the molecular identification of the pathogen. Specifically, 40 individuals out of 128 crabs were examined histologically and the presence of the pathogen was confirmed molecularly. For the remaining individuals investigated, molecular detection was conducted in order to calculate the total prevalence and the local prevalence. More specifically, Hematodinium sp. was detected with 87.5% prevalence at the Chalastra sampling site, with 89.6% and 85% prevalence in the Vistonikos Gulf and Makrygialos sampling sites, respectively. The average carapace length size was 11.8 cm, 12.5 cm, and 12.9 cm for the crabs collected from Chalastra, Thermaikos Gulf, Makrygialos, Thermaikos Gulf, and Vistonikos Gulf, respectively.
No characteristic macroscopical sign was observed during the sampling of C. sapidus in each case except from the characteristic “milky” coloration of the hemolymph in infested crabs. However, lethargy was observed in the specimens collected from Vistonikos Gulf in which mortality occurred. Microscopically, parasitic infestation was observed in all tissues assessed for this study (Figure 2).
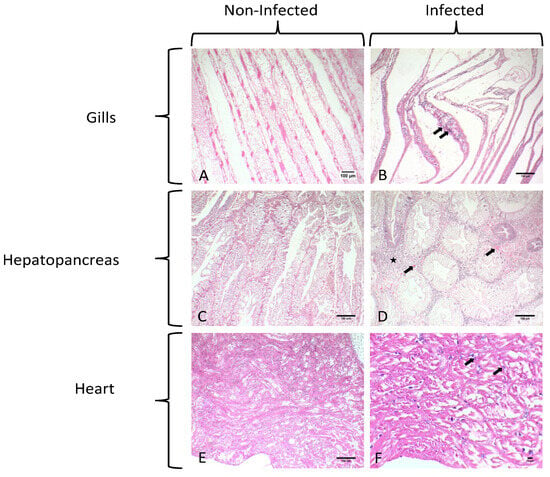
Figure 2.
Histological sections of healthy and infected C. sapidus individuals collected. (A) Histological section of healthy gills of C. sapidus. (B) Uninucleate and multinucleate stages of Hematodinium sp. depicted in gills of an infected individual (arrows). (C) Histological display of Hepatopancreas of a healthy individual. (D) Histological display of hepatopancreas belonging to an infected individual. Heavy parasitism documented in hemal sinus (star) and fewer reserve inclusion cells as a result of the infestation. (E) Histological display of the heart of a healthy individual. (F) Histological micrograph of heart infected with Hematodinium sp. presenting dilations in the hemal sinuses. Myocardium of heart infected with Hematodinium cells (arrows). Total magnification in the microphotographs was ×100, ×100, ×100, ×100, ×100, and ×400 in (A–E) and (F), respectively.
Uninucleate and multinucleate parasites were observed in the gills, hepatopancreas, and heart, typical of previous histological descriptions of the Hematodinium sp. in crustaceans. Specifically, in the gill tissue, ameboid trophonts were detected in the gill lamellae, alongside fouling microorganisms in the space between the lamellae part of the gill (Figure 2B and Figure 3).
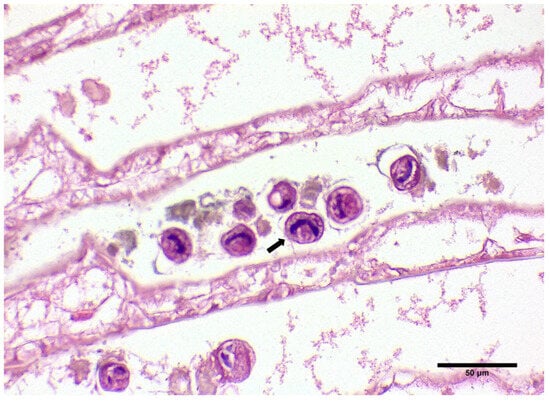
Figure 3.
Histological display of gills infected with ciliates documented in C. sapidus individuals regardless of parasitism with Hematodinium sp. H&E staining. Total magnification ×200.
Hematodinium sp. were also detected in the heart of each infested crab in both the myocardium and pericardium parts as uninucleate trophonts and in multinucleate form with characteristic chromatin (Figure 2F and Figure 4A,B).
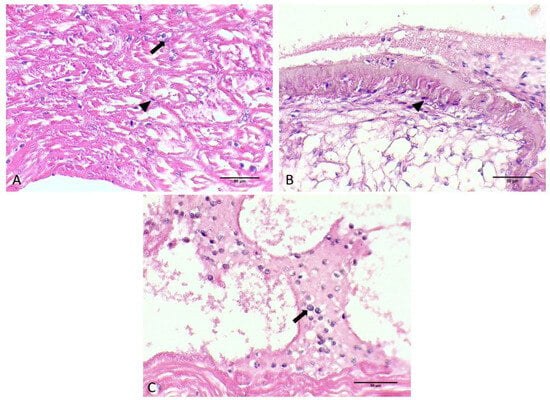
Figure 4.
Histological sections of heart originating from C. sapidus individuals. Myocardium infected with Hematodinium sp. ameboid trophonts (arrow) and filamentous trophont (arrowhead) (A). Filamentous trophonts documented in pericardium of infected C. sapidus (B). Hematodinium sp. cells in pericardium of infected individuals (C). H&E staining. Total magnification ×400.
Hence, Hematodinium sp. cells have been detected in massive numbers in the hemal space of the hepatopancreas alongside several host cells (Figure 2D). Concerning the presence of the parasite in tissues and the pathology in the species of C. sapidus, abnormalities were mostly detected in the digestive gland. Specifically, the concentration of the hemocytes was higher in the infected specimens, which is related to the immune responses of the host to the invasion of the parasite. Additionally, the abnormal development of the epithelial cell wall was detected in infected specimens. Specimens infected with Hematodinium sp. demonstrated thicker epithelium in the digestive tubules, while the lumen of the digestive tubules presented structural abnormalities (Figure 5) that were not observed in healthy individuals (Figure 5A). Finally, reserve inclusion cells were scarce compared with the digestive glands of healthy individuals (Figure 5B).
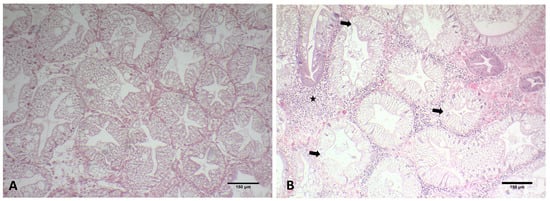
Figure 5.
Histological display of infected hepatopancreas of C. sapidus. (A) No Hematodinium sp. cells were detected in the hemal space in the digestive gland and no atrophic development was observed in the digestive tubule epithelium. (B) Mass presence of Hematodinium sp. trophonts in the hemal space of infected hepatopancreas (star). Atrophic development of epithelium in digestive tubules alongside abnormalities in the structure of the lumen (arrows). H&E staining. Total magnification ×100.
3.2. Molecular Identification of Parasites
The molecular phylogeny of the Hematodinium confirmed its identity as H. perezi, characterizing only one identical haplotype in all analyzed specimens, which was submitted to the GenBank database and assigned the accession number PP056127. It was grouped together with several other H. perezi haplotypes, hosting other crab species (Figure 6). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of this parasite in Greece, providing evidence that it has invaded together with the blue crab.
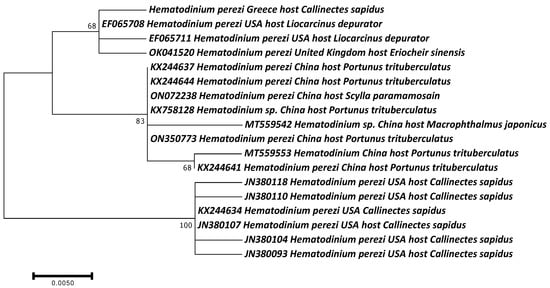
Figure 6.
Maximum Likelihood dendrogram of the H. perezi haplotype found in the Aegean Sea, in comparison with other conspecific and congeneric haplotypes hosting various crab species. Bootstrap values over 60 are shown on each branch.
On the other hand, the molecular analysis did not succeed in identifying the ciliate parasite at the species level, mainly because of the absence of available sequences in the GenBank database. Only one haplotype was defined in all analyzed samples, presenting more than 99.5% sequence similarity with two Epistylis sp. isolates (Figure 7). This haplotype was submitted to the GenBank database and given the accession number PP048746. Two other epibiotic peritrich ciliate parasite genera were very closely genetically related, namely, Myschiston and Zoothamnium.
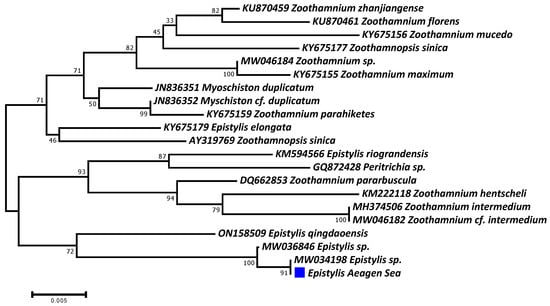
Figure 7.
Phylogenetic dendrogram of the Epistylis isolate (blue square), confirming its taxonomy up to genus level.
4. Discussion
The Mediterranean Sea is considered to be one of the most invaded marine habitats worldwide [31]. Biological invasions tend to become more frequent each year as a result of global climate change and direct human pressures [32,33]. Global climate changes, in combination with direct impacts on marine ecosystems (temperature rise, salinity changes, ocean acidification), are key drivers in shifting the flora and fauna in ecosystems [6,34]. Hence, the impacts of global climate change tend to also affect the physiology of the hosts and the susceptibility of marine species in infectious diseases [35,36,37,38,39]. Elevated temperatures not only impact the host, but also promote the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and their seasonality pattern by prolonging their favored temperature [40]. Keeping in mind the downregulation of the immune responses of the host and the uncontrollable proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, we can assume that the synergy of the aforementioned factors may result in a considerable shift in the biodiversity of marine ecosystems by favoring invasions and pressuring endemic species. Additionally, direct human pressures such as the overexploitation of marine species, commercial shipping with transfers over ballast water, and the opening of pathways to various marine ecosystems (e.g., the Suez canal) could also lead to the shaping of the diversity of species in local ecosystems [40,41,42,43].
The Atlantic blue crab, C. sapidus, was first recorded in Europe in 1901 on the Atlantic coast of France [11]. The invasion in the inner part of the Mediterranean Sea was documented in 1949 and was attributed to ballast waters [14]. Since then, the crab has been reported to invade marine ecosystems in the Iberian Peninsula, in the Italian Peninsula, in Greece, in Turkey, and in Morocco [11,12,37,38,39,40]. Despite the invasive nature and the general ecological traits of the species, including early maturity, rapid growth rates, opportunist diets, and a high reproduction rate, there is a lack of knowledge of this invading species regarding its interactions with the endemic benthic communities and the negative impact of its presence in local ecosystems [14,41]. Despite its territorial presence and the negative impacts that have been recorded in other species [44,45,46,47], the blue crab is considered to be an important species for fisheries in the United States of America and an emerging opportunity for fishery exploitation in Europe [14,48].
In Greece, C. sapidus is commercially exploited, but studies are limited in terms of ecological data and the distribution of the species in new habitats. Blue crab populations are subjected to fluctuations in numbers in almost every habitat on Greek coastlines; however, no research has been conducted to clarify the causes of these fluctuations, attributing population declines to environmental causes and the overexploitation of the species by fishermen. The current study constitutes the first report of Hematodinium perezi, a pathogenic dinoflagellate parasite, in Greece, as well as the ciliate Epistylis sp., both of which infect crustaceans and have been correlated several times with mortalities in C. sapidus. C. sapidus harbors a varied community of parasitic, pathogenic, and commensal microorganisms [49]. Some of these microorganisms are well studied, while others have been proposed for symbiotic traits in the host. The presence of Epistylis sp. is associated with environmental factors such as temperature and salinity fluctuations [49]. The proliferation of fouling microorganisms affects the physiology of the host, resulting in metabolic depression [50].
Infections with H. perezi are fatal and proliferate rapidly at high temperatures and salinities, and there is currently no established and effective method for managing this specific infection [51,52]. Typically, the observable indicators of infected hosts include lethargy and alterations in the hemolymph, tissues, and internal organs [43]. Advanced infection stages manifest as lethargic hosts with noticeable accumulations of parasitic stages in both their hemolymph and tissues [43]. The color of the hemolymph is frequently altered to a white/cream hue, reflecting the substantial presence of parasites [43,53]. Hematodinium infections may cause a profound impact on natural crustacean populations and the fisheries related to them in various ways [54,55]. Immediate consequences involve a decline in harvestable resources and a diminished recruitment rate into the fishery [43]. The parasitic dinoflagellate H. perezi is capable of infecting a broad spectrum of phylogenetically related crustacean hosts [46]. So far, infections attributed to Hematodinium or Hematodinium-like organisms have been documented in more than 40 species of marine crabs, shrimps, lobsters, and amphipods [43,47]. Within the coastal waters of the USA, the dinoflagellate parasite has affected a range of cohabiting wild crab species such as Libinia dubia, Pagurus pollicaris, and Eurypanopeus depressus, in addition to its primary host C. sapidus [56]. Regarding the detection of the parasitic species in China, Hematodinium spp. infections have been recognized as the causative agent of “milky blood disease” and “Yellow water disease” in the cultured species Portunus trituberculatus and Scylla paramamosain on Chinese coasts, respectively [57,58]. Additionally, Hematodinium sp. infection was identified in the shrimps Exopalaemon carinicauda and Penaeus monodon in cultured conditions in coastal areas of China [58,59,60]. Hematodinium sp. infections were also detected on Russian coastlines, infecting crab species such as Paralithodes camtschaticus, Paralithodes platypus, Chinoecertes bairdi, and Paralithodes brevipes [61,62]. On the Atlantic European coast, H. perezi infections have been reported in crab species such as Carcinus maenas, Liocarcinus depurator, Portumnus latipes, Ovalipes ocellatus, C. sapidus, Cancer pagurus, Necorapuber, Pagurus bernhardus, Pagurus prideaux, Minuda rugosa, and Eriphia verrucose [13,63,64,65,66,67,68]. In the inner Mediterranean Sea, H. perezi infections have been documented in the Italian part of the Adriatic Sea and in Akyatan Lagoon, Turkey [13,69].
The present study represents the initial documentation of H. perezi and Epistilys sp. infection in the Aegean Sea, affecting the commercially important species C. sapidus and leading to mortalities. The reported results from this study are in line with other studies concerning the lack of gross signs of infection even in heavily infected individuals of the crab species C. sapidus [70,71]. However, individuals infected with the parasitic dinoflagellate appeared more lethargic in comparison with healthy ones. Although no external sign of the disease was detected in the infected individuals, the hemolymph presented the typical “milky” coloration associated with this infection, as found in other studies [43,62]. Furthermore, the developmental stages of the parasite were recorded in almost all tissues intended for histopathological examination. More precisely, ameboid trophonts in conjunction with filamentous trophonts were observed to parasitize the myocardium and pericardium of the crab and cause the dilation of the hemal sinuses. This finding is corroborated by studies conducted on the dinoflagellate parasite in C. sapidus in which dilations of the heart tissue in mass parasitic infiltration were similarly observed [54,72]. Moreover, the massive infiltration of parasitic cells was documented in the hepatopancreas. A profound infestation of parasites in the hepatopancreas was found to be associated with structural alterations, including the atrophic development of the digestive tubule epithelium, which may ultimately result in epithelial lysis [62]. Structural alterations were additionally identified in the tubule lumen of the hepatopancreas in infected individuals. Specifically, the afflicted crabs exhibited dilations and irregularities in the digestive lumens of the hepatopancreas, often accompanied by the collapse of villi in numerous instances. Alterations in the lumen of the digestive tubules have been previously documented in H. perezi infections, revealing swelling in the tubule villi of mudflat crabs, Helis tientsinensis [73]. The final histopathological observation linked to the infection included a diminished count of hemocytes and reserve inclusion cells in the hepatopancreas. The current result is in line with Huang et al. [65], who observed identical results in H. tientsinensis infected with H. perezi. Regarding the pathological observation in the gills, the massive infiltration of ameboid trophonts was observed in the gill lamellas, which appeared to be swollen with deformities along the structure. The histological results are confirmed by those of Huang et al. [65], who also observed deformities in the gills associated with infections. Furthermore, the presence of parasite cells in all three tissues examined is a typical result, as Hematodinium sp. infection is characterized as a hemolymph disease [70,71,74].
5. Conclusions
Crabs are highly valuable marine resources, serving as a significant part of both commercial fisheries and marine ecosystems [75,76]. The economic importance of the crab trade is underscored by their demand in seafood markets, as is their vital role in supporting livelihoods in coastal communities by their culture or fisheries [77,78]. Nevertheless, the health status of crab populations occasionally faces threats from diverse factors, with disease emerging as a significant concern. The occurrence of mortalities due to disease carries repercussions, contributing to a decline in crab populations and resulting in diminishing productivity in fisheries. Disease outbreaks can stem from a range of pathogens, encompassing parasites, bacteria, and viruses, and can significantly affect the physiological and structural integrity of crab populations. In the current study, a pivotal discovery was made that implicated dinoflagellate H. perezi, for the first time, in the annual decline of the blue crab, C. sapidus, along the Greek coastlines of the North Aegean. While infections of H. perezi are common and extensively studied in numerous crab species and fishery hotspots, the fluctuations in blue crab (C. sapidus) populations originating from the Eastern Mediterranean coastlines remain largely unexplored. H. perezi is an important pathogen infecting a variety of crustacean decapods, resulting in huge mortalities [50,59]. Furthermore, the introduction of non-indigenous species acting as potential hosts for significant pathogens, such as blue crabs, may present a threat to other vital fishery species. In addition, considering the global climate change phenomenon, which can act as a driver for the further introduction of non-indigenous species, we can concur that the management plans for the mitigation of these phenomena are mandatory for the sustainability of fisheries. In recent years, blue crab mortalities in Greece, such as the mortality event that occurred in the Kotychi lagoon in Elis, remained unexplored and the phenomenon was only attributed to the increased water temperature by local authorities. In this research, the identification of an important pathogen such as H. perezi further highlights the fluctuations in the population of crustacean decapods in Greece.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L.; methodology, A.L. and D.K.P.; software, I.A.G. and A.S. validation, A.L., I.A.G. and D.K.; formal analysis, A.L. and D.K.P.; investigation, A.L. and D.K.P.; resources, I.A.G. and D.K.; data curation, I.A.G., A.S. and D.K.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.L.; writing—review and editing, I.A.G. and D.K.; visualization, I.A.G. and D.K.; supervision, I.A.G. and D.K.; project administration, A.L.; funding acquisition, I.A.G. and D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The genomic data produced are available from the GenBank database under the accession numbers PP056127 and PP048746.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lattos, A.; Chaligiannis, I.; Papadopoulos, D.; Giantsis, I.A.; Petridou, E.I.; Vafeas, G.; Staikou, A.; Michaelidis, B. How Safe to Eat Are Raw Bivalves? Host Pathogenic and Public Health Concern Microbes within Mussels, Oysters, and Clams in Greek Markets. Foods 2021, 10, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulme, P.E. Climate change and biological invasions: Evidence, expectations, and response options. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1297–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facon, B.; Genton, B.J.; Shykoff, J.; Jarne, P.; Estoup, A.; David, P. A general eco-evolutionary framework for understanding bioinvasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, L.A.; Doblin, M.A.; Dobbs, F.C. Potential microbial bioinvasions via ships’ ballast water, sediment, and biofilm. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, P.E.; Gardner, T.; Vives, S.P.; Gilligan, M.R.; Courtenay, W.R.; Ray, G.C.; Hare, J.A. Biological invasion of the Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans along the Atlantic coast of North America. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 235, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaveer, H.; Galil, B.S.; Carlton, J.T.; Alleway, H.; Goulletquer, P.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Marchini, A.; Miller, W.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.; Peharda, M.; et al. Historical baselines in marine bioinvasions: Implications for policy and management. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Gastner, M.T.; Blasius, B. The risk of marine bioinvasion caused by global shipping. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giantsis, I.A.; Castells Sierra, J.; Chaskopoulou, A. The distribution of the invasive pest, rice water weevil Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), is expanding in Europe: First record in the Balkans, confirmed by CO1 DNA barcoding. Phytoparasitica 2017, 45, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.L.; Katsanevakis, S.; Zenetos, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Gateways to alien invasions in the European seas. Aquat. Invasions 2014, 9, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H.J.; Huchin-Mian, J.P.; Reece, K.S.; Pagenkopp Lohan, K.M.; Butler, M.J.; Shields, J.D. Parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium perezi prevalence in larval and juvenile blue crabs Callinectes sapidus from coastal bays of Virginia. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2019, 134, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancinelli, G.; Chainho, P.; Cilenti, L.; Falco, S.; Kapiris, K.; Katselis, G.; Ribeiro, F. The Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus in southern European coastal waters: Distribution, impact and prospective invasion management strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampouris, T.E.; Kouroupakis, E.; Batjakas, I.E. Morphometric relationships of the global invader Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 (Decapoda, brachyura, portunidae) from Papapouli lagoon, NW Aegean Sea, Greece. with notes on its ecological preferences. Fishes 2020, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrizia, P.; Giorgio, M. Parasites affect hemocyte functionality in the hemolymph of the invasive Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus from a coastal habitat of the Salento Peninsula (SE Italy). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehring, S. Invasion history and success of the American blue crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 in European and adjacent waters. In In the Wrong Place–Alien Marine Crustaceans: Distribution, Biology and Impacts Invading Nature; Galil, B.S., Clark, P.F., Carlton, J.T., Eds.; Springer Series in Invasion Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 607–624. [Google Scholar]
- Mancinelli, G.; Chainho, P.; Cilenti, L.; Falco, S.; Kapiris, K.; Katselis, G.; Ribeiro, F. On the Atlantic blue crab (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun 1896) in southern European coastal waters: Time to turn a threat into a resource? Fish. Res. 2017, 194, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizerek, T.; Regan, H.M.; Hovel, K.A. Seagrass habitat loss and fragmentation influence management strategies for a blue crab Callinectes sapidus fishery. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 427, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilen, C.T.; Yesilyurt, I.N. Growth of blue crab, Callinectes sapidus, in the Yumurtalik Cove, Turkey: A molt process approach. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2014, 9, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfrin, C.; Turolla, E.; Chung, J.S.; Giulianini, P.G. First occurrence of Callinectes sapidus (Rathbun, 1896) within the Sacca di Goro (Italy) and surroundings. Check List 2015, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Razek, F.A.; Ismaiel, M.; Ameran, M.A.A. Occurrence of the blue crab Callinectes sapidus, Rathbun, 1896, and its fisheries biology in Bardawil Lagoon, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdikaris, C.; Konstantinidis, E.; Gouva, E.; Ergolavou, A.; Klaoudatos, D.; Nathanailides, C.; Paschos, I. Occurrence of the invasive crab species Callinectes sapidus rathbun, 1896, in NW Greece. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 503–510. [Google Scholar]
- Kampouris, T.E.; Porter, J.S.; Sanderson, W.G. Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 (Brachyura: Portunidae): An assessment on its diet and foraging behaviour, Thermaikos Gulf, NW Aegean Sea, Greece: Evidence for ecological and economic impacts. Crustac. Res. 2019, 48, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, S.S.A.E.H.; Abouelatta, M.E.; Abd El Rahman, E.S.K.; Sherif, A.H. Bacterial pathogens causing the blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) mortality at Suez Canal (El-Temsah Lake) in Ismailia Governorate. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Vahedi, M.; Rahimzadeh, M. Sample size calculation in medical studies. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2013, 6, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, B.L.; Battle, H.I. the Gross and Microscopic Anatomy of the Digestive Tract of the Oyster Crassostrea Virginica (Gmelin). Can. J. Zool. 1957, 35, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.W.; Smith, C.S. Histological Techniques for Marine Bivalve Mollusks; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-F/NEC-25; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Woods Hole, MA, USA, 1983; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Small, H.J.; Shields, J.D.; Hudson, K.L.; Reece, K.S. Molecular detection of Hematodinium sp. infecting the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. J. Shellfish Res. 2007, 26, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shields, J.D.; Miller, T.L.; Small, H.J.; Pagenkopp, K.M.; Reece, K.S. Detection and quantification of the free-living stage of the parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium sp. in laboratory and environmental samples. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, E.; Berney, C.; Harms, H.; Chatzinotas, A. Cultivation-independent analysis reveals a shift in ciliate 18S rRNA gene diversity in a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-polluted soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 62, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelist, D.; Rilov, G.; Golani, D.; Carlton, J.T.; Spanier, E. Restructuring the Sea: Profound shifts in the world’s most invaded marine ecosystem. Divers. Distrib. 2013, 19, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Sbragaglia, V.; Cerri, J.; Bariche, M.; Bolognini, L.; Ben Souissi, J.; Busoni, G.; Coco, S.; Chryssanthi, A.; Fanelli, E.; et al. Climate change, biological invasions, and the shifting distribution of Mediterranean fishes: A large-scale survey based on local ecological knowledge. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2779–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.H.; Peck, L.S.; Hughes, K.A.; Aldridge, D.C. Antarctica: The final frontier for marine biological invasions. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2221–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjith, L.; Shukla, S.P.; Vennila, A.; Gashaw, T.D. Bioinvasion in antarctic ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B—Biol. Sci. 2012, 82, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattos, A.; Feidantsis, K.; Georgoulis, I.; Giantsis, I.A.; Karagiannis, D.; Theodorou, J.A.; Staikou, A.; Michaelidis, B. Pathophysiological responses of Pinna nobilis individuals enlightens the etiology of mass mortality situation in the mediterranean populations. Cells 2021, 10, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattos, A.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Feidantsis, K.; Karagiannis, D. Are Marine Heatwaves Responsible for Mortalities of Farmed Mytilus galloprovincialis? A Pathophysiological Analysis of Marteilia infected Mussels from Thermaikos gulf, Greece. Animals 2022, 12, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattos, A.; Feidantsis, K.; Giantsis, I.A.; Theodorou, J.A.; Michaelidis, B. Seasonality in Synergism with Multi-Pathogen Presence Leads to Mass Mortalities of the Highly Endangered Pinna nobilis in Greek Coastlines: A Pathophysiological Approach. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattos, A.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Giantsis, I.A.; Feidantsis, K.; Georgoulis, I.; Karagiannis, D.; Carella, F.; Michaelidis, B. Investigation of the highly endangered Pinna nobilis’ mass mortalities: Seasonal and temperature patterns of health status, antioxidant and heat stress responses. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 188, 105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattos, A.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Feidantsis, K.; Giantsis, I.A.; Georgoulis, I.; Karagiannis, D.; Michaelidis, B. Antioxidant Defense of Mytilus galloprovincialis Mussels Induced by Marine Heatwaves in Correlation with Marteilia Pathogen Presence. Fishes 2023, 8, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattos, A.; Giantsis, I.A.; Tsavea, E.; Kolygas, M.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Bitchava, K. Virulence Genes and In Vitro Antibiotic Profile of Photobacterium damselae Strains, Isolated from Fish Reared in Greek Aquaculture Facilities. Animals 2022, 12, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.W.L.; Lam, V.W.Y.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Kearney, K.; Watson, R.; Pauly, D. Projecting global marine biodiversity impacts under climate change scenarios. Fish Fish. 2009, 10, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, H.K. Marine biodiversity conservation. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R1190–R1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.H.; Halpern, B.S.; Korpinen, S.; Murray, C.; Reker, J. Baltic Sea biodiversity status vs. cumulative human pressures. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 161, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Veríssimo, A. A new record of Callinectes sapidus in a western European estuary (Portuguese coast). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2014, 7, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, P.; Gaspar, M.; Garel, E.; Baptista, V.; Cruz, J.; Cerveira, I.; Leitão, F.; Teodósio, M.A. The Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 expands its non-native distribution into the Ria Formosa lagoon and the Guadiana estuary (SW-Iberian Peninsula, Europe). BioInvasions Rec. 2019, 8, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taybi, A.F.; Mabrouki, Y. The American Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Portunidae) is Rapidly Expanding Through the Mediterranean Coast of Morocco. Thalassas 2020, 36, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchessaux, G.; Mangano, M.C.; Bizzarri, S.; M’Rabet, C.; Principato, E.; Lago, N.; Veyssiere, D.; Garrido, M.; Scyphers, S.B.; Sarà, G. Invasive blue crabs and small-scale fisheries in the Mediterranean sea: Local ecological knowledge, impacts and future management. Mar. Policy 2023, 148, 105461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharov, A.F.; Vølstad, J.H.; Davis, G.R.; Davis, B.K.; Lipcius, R.N.; Montane, M.M. Abundance and exploitation rate of the blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) in Chesapeake Bay. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2003, 72, 543–565. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, E.A.; Bojko, J.; Crowley, C.E.; Gandy, R.L.; Martin, C.W.; Shea, C.P.; Bateman, K.S.; Stentiford, G.D.; Behringer, D.C. Salinity and temperature affect the symbiont profile and host condition of Florida USA blue crabs Callinectes sapidus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2023, 198, 107930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Dunn, A.M. Microsporidia in Aquatic Invertebrates. Microsporidia Pathog. Oppor. First Ed. 2014, 2014, 579–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H.J. Advances in our understanding of the global diversity and distribution of Hematodinium spp.—Significant pathogens of commercially exploited crustaceans. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huchin-Mian, J.P.; Small, H.J.; Shields, J.D. The influence of temperature and salinity on mortality of recently recruited blue crabs, Callinectes sapidus, naturally infected with Hematodinium perezi (Dinoflagellata). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 152, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huchin-Mian, J.P.; Small, H.J.; Shields, J.D. Patterns in the natural transmission of the parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium perezi in American blue crabs, Callinectes sapidus from a highly endemic area. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Shields, J.D. A review of the parasitic dinoflagellates Hematodinium species and Hematodinium-like infections in marine crustaceans. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2005, 66, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, M.; Huang, Q. The parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium infects marine crustaceans. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagenkopp Lohan, K.M.; Reece, K.S.; Miller, T.L.; Wheeler, K.N.; Small, H.J.; Shields, J.D. The role of alternate hosts in the ecology and life history of Hematodinium sp., a parasitic dinoflagellate of the blue crab (Callinectes sapidus). J. Parasitol. 2012, 98, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Xia, X.A.; Wu, Q.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Lin, Y.S. Infection with Hematodinium sp. in mud crabs Scylla serrata cultured in low salinity water in southern China. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2008, 82, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Song, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T. Hematodinium infections in cultured chinese swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus, in northern china. Aquaculture 2013, 396–399, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xie, J.; Shi, H.; Li, C. Hematodinium infections in cultured ridgetail white prawns, Exopalaemon carinicauda, in eastern China. Aquaculture 2010, 300, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, M.; Xiao, J.; Xu, W.J.; Li, C.W. Hematodinium spp. Infections in wild and cultured populations of marine crustaceans along the coast of China. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2017, 124, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryazanova, T.V.; Eliseikina, M.G.; Kukhlevsky, A.D.; Kharlamenko, V.I. Hematodinium sp. infection of red Paralithodes camtschaticus and blue Paralithodes platypus king crabs from the Sea of Okhotsk, Russia. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 105, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryazanova, T.V.; Eliseikina, M.G.; Kukhlevsky, A.D. First detection of Hematodinium sp. In spiny king crab Paralithodes brevipes, and new geographic areas for the parasite in tanner crab Chionoecetes bairdi, and red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 184, 107651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Feist, S.W.; Bateman, K.S.; Hine, P.M. Haemolymph parasite of the shore crab Carcinus maenas: Pathology, ultrastructure and observations on crustacean haplosporidians. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 59, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, K.M.; Shaw, P.W.; Morritt, D. Prevalence and seasonality of Hematodinium (Alveolata: Syndinea) in a Scottish crustacean community. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojko, J.; Stebbing, P.D.; Dunn, A.M.; Bateman, K.S.; Clark, F.; Kerr, R.C.; Stewart-Clark, S.; Johannesen, Á.; Stentiford, G.D. Green crab Carcinus maenas symbiont profiles along a North Atlantic invasion route. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2018, 128, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.E.; Batista, F.M.; Malkin, S.H.; Thomas, J.E.; Bryan, C.C.; Crocombe, P.; Coates, C.J.; Rowley, A.F. Spatial and temporal disease dynamics of the parasite Hematodinium sp. In shore crabs, Carcinus maenas. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigemann, F.; Burmeister, A.; Skovgaard, A. Hematodinium sp. (Alveolata. Syndinea) detected in marine decapod crustaceans from waters of Denmark and Greenland. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 92, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lycett, K.A.; Pitula, J.S. Disease ecology of Hematodinium perezi in a high salinity estuary: Investigating seasonal trends in environmental detection. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2017, 124, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldik, R.; Cengizler, I. The Investigation of Bacteria, Parasite and Fungi in Blue Crabs (Callinectes sapidus, Rathbun 1896) Caught From Akyatan Lagoon in East Mediterranean Sea. J. VetBio Sci. Tech. 2016, 2, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messick, G.A. Hematodinium perezi infections in adult and juvenile blue crabs Callinectes sapidus from coastal bays of Maryland and Virginia, USA. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1994, 19, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, J.D.; Squyars, C.M. Mortality and hematology of blue crabs, Callinectes sapidus, experimentally infected with the parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium perezi. Fish. Bull. 2000, 98, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, J.D.; Sullivan, S.E.; Small, H.J. Overwintering of the parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium perezi in dredged blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus) from Wachapreague Creek, Virginia. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 130, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, F.; Li, C. The parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium perezi infecting mudflat crabs, Helice tientsinensis, in polyculture system in China. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 166, 107229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Xie, G.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Li, A.; Wan, X.; Huang, J.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J. Hematodinium perezi naturally infects Asian brush-clawed crab (Hemigrapsus takanoi). J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, S.A.; Worm, B. Ecological role of large benthic decapods in marine ecosystems: A review. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 469, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanti, D.; Tabalessy, R.; Simatauw, F.; Irwanto, I.; Inayah, I. Fishery Management for Crab Resources Using an Ecosystem Approach. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Economics, Business and Social Humanities, ICONEBS 2020, Madiun, Indonesia, 4–5 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungria, D.B.; dos Santos Tavares, C.P.; Pereira, L.Â.; de Assis Teixeira da Silva, U.; Ostrensky, A. Global status of production and commercialization of soft-shell crabs. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 2213–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Engle, C.; Kumar, G.; van Senten, J. Retail market trends for seafood in the United States. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2023, 54, 603–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).