Excessive Extracellular Ammonium Production by a Free-Living Nitrogen-Fixing Soil Clostridium sp. Strain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Screening of Strains Producing Excessive Extracellular NH4+
2.3. Genomic Analyses
2.4. Morphological and Physiological Analyses
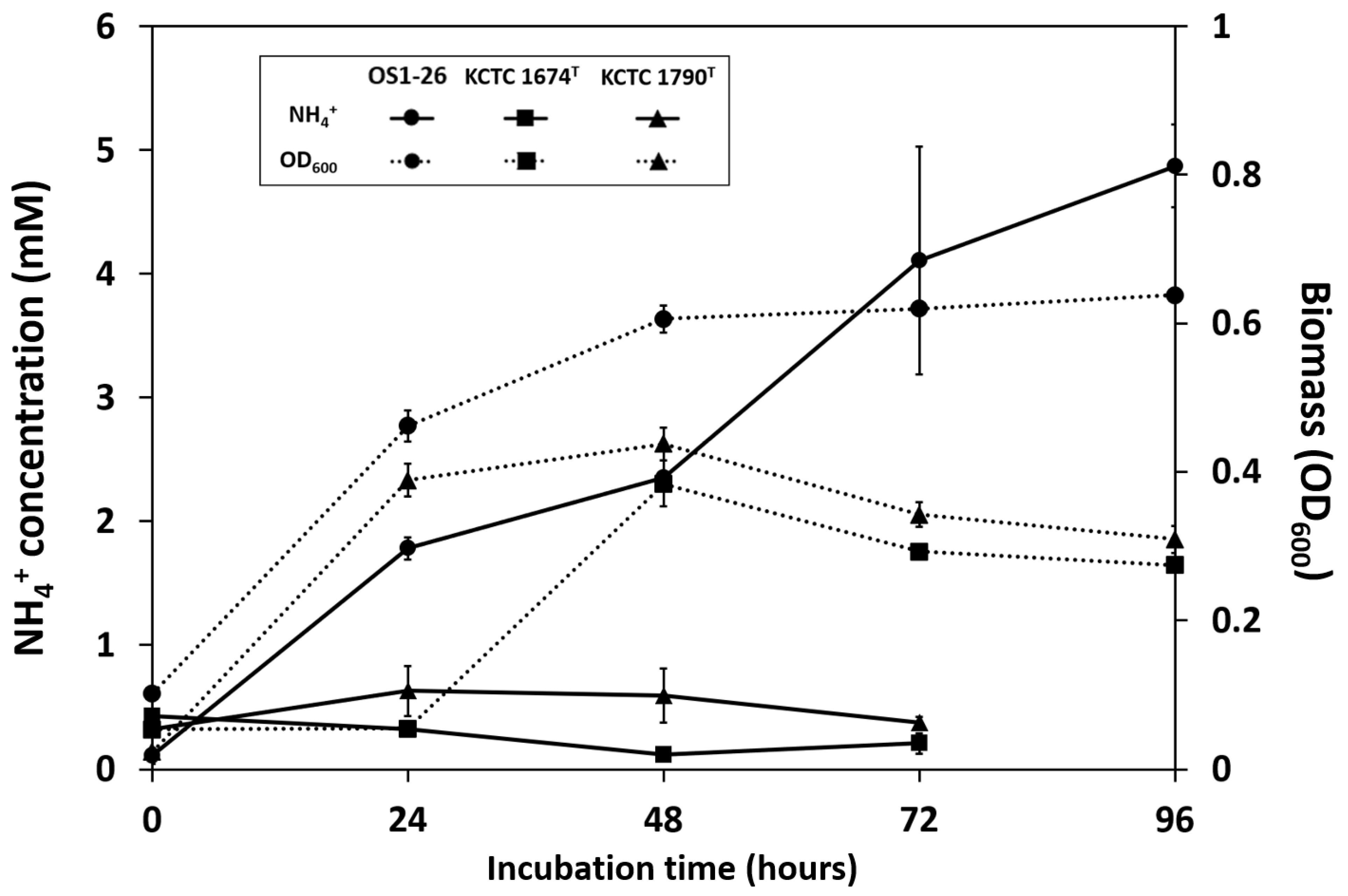
2.5. Extracellular NH4+ Accumulation by Bacteria in the Culture Medium
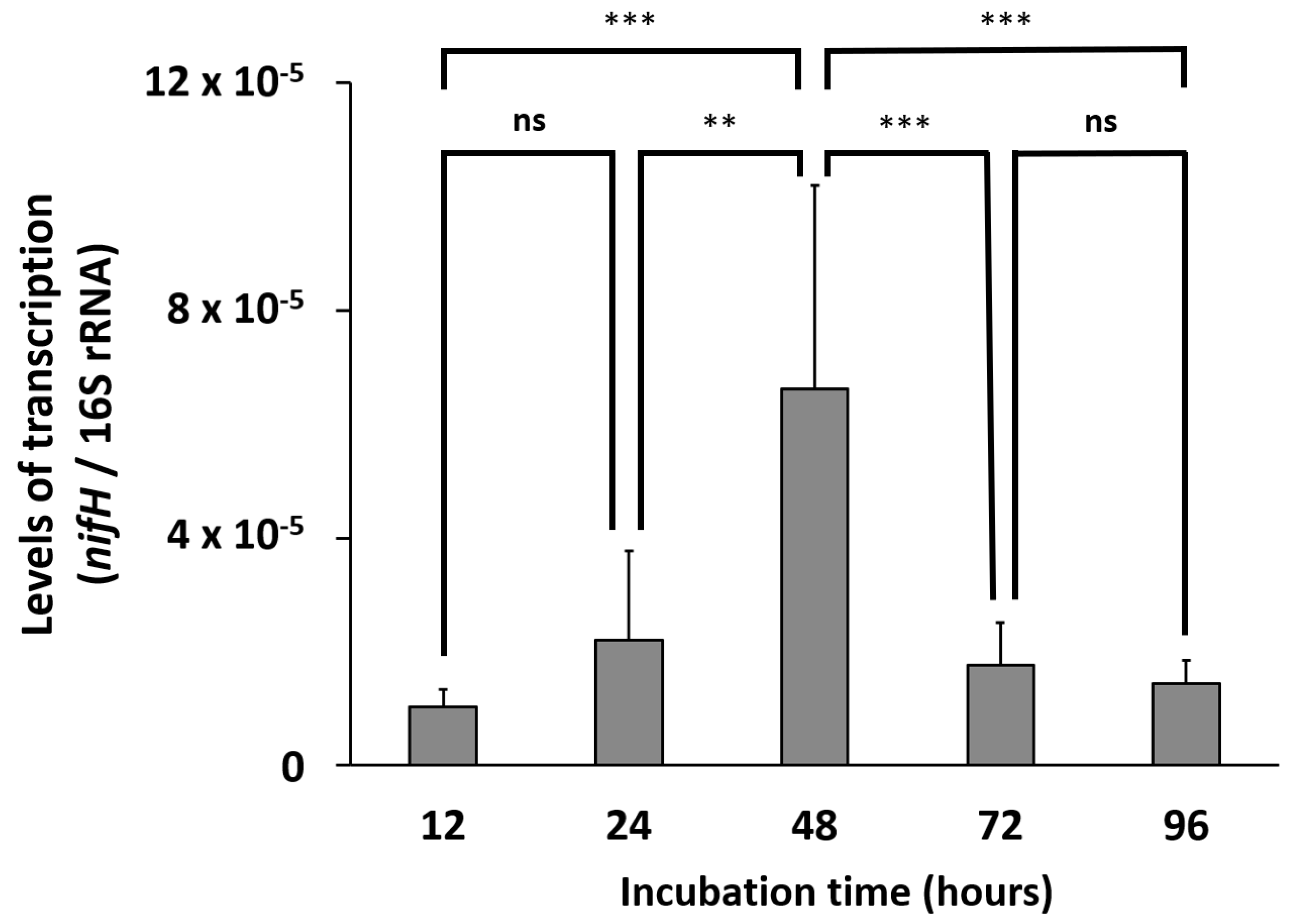
2.6. Transcript Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Genomic Taxonomy
3.2. Phenotypic Traits
3.3. Biological Nitrogen Fixation (BNF)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raymond, J.; Siefert, J.L.; Staples, C.R.; Blankenship, R.E. The Natural History of Nitrogen Fixation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, S.C.; Cleveland, C.C.; Townsend, A.R. Functional Ecology of Free-Living Nitrogen Fixation: A Contemporary Perspective. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2011, 42, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, D.; Cocking, E. Establishing symbiotic nitrogen fixation in cereals and other non-legume crops: The Greener Nitrogen Revolution. Agric. Food Secur. 2017, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, T.E. The presence of nitrogen fixing legumes in terrestrial communities: Evolutionary vs ecological considerations. In New Perspectives on Nitrogen Cycling in the Temperate and Tropical Americas: Report of the International SCOPE Nitrogen Project; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 1999; pp. 233–246. [Google Scholar]
- Menge, D.N.; Hedin, L.O. Nitrogen fixation in different biogeochemical niches along a 120,000-year chronosequence in New Zealand. Ecology 2009, 90, 2190–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, A.R.; Purves, D.W.; Hedin, L.O. Facultative nitrogen fixation by canopy legumes in a lowland tropical forest. Oecologia 2011, 165, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiana, A.; Balle, P.; Kanga, A.G.; Domenach, A.-M. Nitrogen fixation estimated by the 15N natural abundance method in Acacia mangium Willd. inoculated with Bradyrhizobium sp. and grown in silvicultural conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprent, J. Nodulated legume trees. In Nitrogen Fixation in Agriculture, Forestry, Ecology, and the Environment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 113–141. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Townsend, A.R.; Schimel, D.S.; Fisher, H.; Howarth, R.W.; Hedin, L.O.; Perakis, S.S.; Latty, E.F.; Von Fischer, J.C.; Elseroad, A. Global patterns of terrestrial biological nitrogen (N2) fixation in natural ecosystems. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1999, 13, 623–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, G.G.O.; Lopes, V.R.; Romano, T.; Camara, M.C. Chapter 22—Clostridium. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Amaresan, N., Senthil Kumar, M., Annapurna, K., Kumar, K., Sankaranarayanan, A., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 477–491. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Toth, J.; Kasap, M. Nitrogen-fixation genes and nitrogenase activity in Clostridium acetobutylicum and Clostridium beijerinckii. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 27, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-S. Nitrogen Fixation in the Clostridia. In Genetics and Regulation of Nitrogen Fixation in Free-Living Bacteria; Klipp, W., Masepohl, B., Gallon, J.R., Newton, W.E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ribbe, M.W.; Hu, Y.; Hodgson, K.O.; Hedman, B. Biosynthesis of nitrogenase metalloclusters. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4063–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaby, J.C.; Buckley, D.H. A comprehensive aligned nifH gene database: A multipurpose tool for studies of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Database 2014, 2014, bau001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaby, J.C.; Rishishwar, L.; Valderrama-Aguirre, L.C.; Green, S.J.; Valderrama-Aguirre, A.; Jordan, I.K.; Kostka, J.E. Diazotroph community characterization via a high-throughput nifH amplicon sequencing and analysis pipeline. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01512-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smercina, D.N.; Evans, S.E.; Friesen, M.L.; Tiemann, L.K. To fix or not to fix: Controls on free-living nitrogen fixation in the rhizosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02546-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomura, K.; Masuda, T.; Gauglitz, J.M. Active nitrogen fixation by Crocosphaera expands their niche despite the presence of ammonium—A case study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousk, J.; Bengtson, P. Microbial regulation of global biogeochemical cycles. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Robledo, E.; Corzo, A.; Papaspyrou, S. A fast and direct spectrophotometric method for the sequential determination of nitrate and nitrite at low concentrations in small volumes. Mar. Chem. 2014, 162, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.; Kwon, M.; Song, B.; Yoon, S. Involvement of NO3− in ecophysiological regulation of dissimilatory nitrate/nitrite reduction to ammonium (DNRA) is implied by physiological characterization of soil DNRA bacteria isolated via a colorimetric screening method. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01054-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.A.; Reich, C.I.; Sharma, S.; Weisbaum, J.S.; Wilson, B.A.; Olsen, G.J. Critical Evaluation of Two Primers Commonly Used for Amplification of Bacterial 16S rRNA Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E. Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing. Genome biol. 2019, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Ha, S.-m.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, J. A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.-L.; Xie, B.-B.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhou, B.-C.; Zhou, J.; Oren, A.; Zhang, Y.-Z. A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 2210–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasser, M. Bacterial Identification by Gas Chromatographic Analysis of Fatty Acids Methyl Esters (GC-FAME); Microbial ID: Newark, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Muyzer, G.; De Waal, E.C.; Uitterlinden, A. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikitkaew, S.; In-Chan, S.; Singkhala, A.; Tukanghan, W.; Mamimin, C.; Reungsang, A.; Birkeland, N.-K.; O-Thong, S. Clostridium thailandense sp. nov., a novel CO2-reducing acetogenic bacterium isolated from peatland soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Romanek, C.S.; Wiegel, J. Clostridium aciditolerans sp. nov., an acid-tolerant spore-forming anaerobic bacterium from constructed wetland sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Prakash, D.; Rastogi, N.; Jain, R. Clostridium nitrophenolicum sp. nov., a novel anaerobic p-nitrophenol-degrading bacterium, isolated from a subsurface soil sample. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1886–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, D.A.; Smith, P.R.; Lawson, P.A.; Tanner, R.S. Clostridium muellerianum sp. nov., a carbon monoxide-oxidizing acetogen isolated from old hay. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.S.-C.; Balkwill, D.L.; Drake, G.R.; Tanner, R.S. Clostridium carboxidivorans sp. nov., a solvent-producing clostridium isolated from an agricultural settling lagoon, and reclassification of the acetogen Clostridium scatologenes strain SL1 as Clostridium drakei sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.; Hendry, M.; King, J.; Sankaranarayanan, K.; Lawson, P.A. Clostridium tanneri sp. nov., isolated from the faecal material of an alpaca. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 006372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, R.; Kahn, D. Genetic regulation of biological nitrogen fixation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnacka, K.; Moustakas, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Bio-based fertilizers: A practical approach towards circular economy. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, E.S.; Costas, A.M.G.; Hamilton, T.L.; Mus, F.; Peters, J.W. Evolution of molybdenum nitrogenase during the transition from anaerobic to aerobic metabolism. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Huang, K.; Wang, F.; Mei, Z. Molecular mechanism and agricultural application of the NifA–NifL system for nitrogen fixation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soupene, E.; Lee, H.; Kustu, S. Ammonium/methylammonium transport (Amt) proteins facilitate diffusion of NH3 bidirectionally. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3926–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.J.; Stutz, H.E. 11 Nitrogen Assimilation in Clostridia. In Handbook on Clostridia; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 239. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.; Coutts, G.; Merrick, M. The glnKamtB operon: A conserved gene pair in prokaryotes. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compared Genomes | ANI (%) | Genome A Coverage for ANI (%) | Genome B Coverage for ANI (%) | POCP (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genome A | Genome B | ||||
| Clostridium sp. OS1-26 [NZ_CP133264] | C. aciditolerans DSM 17425T [GCA_016316925] | 93.07 | 48.68 | 54.90 | 69.11 |
| C. thailandense PL3T [GCA_019207025] | 80.35 | 30.59 | 28.32 | 24.18 | |
| C. muellerianum P21T [GCA_012926525] | 76.76 | 24.45 | 25.61 | 14.89 | |
| C. carboxidivorans P7T[GCA_001038625] | 76.88 | 25.89 | 26.46 | 15.26 | |
| C. drakei SL1T[GCA_003096175] | 76.67 | 24.63 | 25.43 | 14.84 | |
| C. scatologenes ATCC 25775T [GCA_000968375] | 76.73 | 25.74 | 26.32 | 15.19 | |
| Characteristics | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Apple orchard soil | Constructed wetland sediment | subsurface soil sample | Peatland sediment | Old hay | Agricultural settling lagoon |
| Gram stain | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| Cell size (μm) | 0.8–1.0 × 4.0–10.0 | 0.5–1.0 × 3.0–9.0 | 0.6–0.9 × 3.5–5.0 | 0.8–1.0 × 4.0–10.0 | 0.4 × 5.5–9.2 | 0.5 × 3.0 |
| Growth temperature (optimum; °C) | 25–35 (30–35) | 20–45 (35) | 20–45 (30) | 20–40 (34) | 20–45 (30–40) | 24–42 (37–40) |
| pH (optimum) | 5.0–8.0 (6.0–8.0) | 3.8–8.9 (7.5) | 6.5–8.0 (7.2) | 6.0–7.5 (7.0) | 5.0–8.5 (6.5) | 4.4–7.6 (5.0–7.0) |
| Growth NaCl (optimum; %) | 0–0.5 | 0–1.5 (0) | 0–1 | 0–1.5 (0.5) | 0–20 (0) | NR |
| Catalase activity | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| Substrate utilization: | ||||||
| d-Lactose | - | + | - | + | + | - |
| Maltose | + | + | - | + | - | - |
| d-Raffinose | - | + | - | + | NR | - |
| d-Trehalose | + | - | NR | - | - | + |
| l-Rhamnose | - | - | + | + | - | NR |
| d-Sucrose | + | + | - | - | NR | + |
| d-Sorbitol | weak | - | NR | + | - | - |
| l-Arabinose | - | - | NR | + | NR | NR |
| Glycerol | - | + | NR | + | - | + |
| d-Xylose | - | + | - | + | NR | + |
| d-Ribose | - | + | - | + | NR | + |
| d-Glucose | + | + | - | NR | NR | + |
| Cellobiose | weak | NR | - | NR | NR | + |
| d-Fructose | + | NR | NR | NR | + | + |
| d-Mannose | + | + | - | NR | NR | + |
| Esculin | + | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Jang, J. Excessive Extracellular Ammonium Production by a Free-Living Nitrogen-Fixing Soil Clostridium sp. Strain. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2634. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122634
Park S, Jang J. Excessive Extracellular Ammonium Production by a Free-Living Nitrogen-Fixing Soil Clostridium sp. Strain. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2634. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122634
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Soyeon, and Jeonghwan Jang. 2024. "Excessive Extracellular Ammonium Production by a Free-Living Nitrogen-Fixing Soil Clostridium sp. Strain" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2634. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122634
APA StylePark, S., & Jang, J. (2024). Excessive Extracellular Ammonium Production by a Free-Living Nitrogen-Fixing Soil Clostridium sp. Strain. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2634. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122634






