Variations in the Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities and Their Interactions Within Sediment Affected by the Benthic Organism, Snail Bellamya purificata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Indoor Simulation Experiment Design
2.2. Sediment Sample Collection
2.3. Sediment Properties Determination
2.4. DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diversity and Composition of Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities
3.2. Co-Occurrence Network Patterns of Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities
3.3. Environmental Adaption and Habitat Niche Breadth of Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities
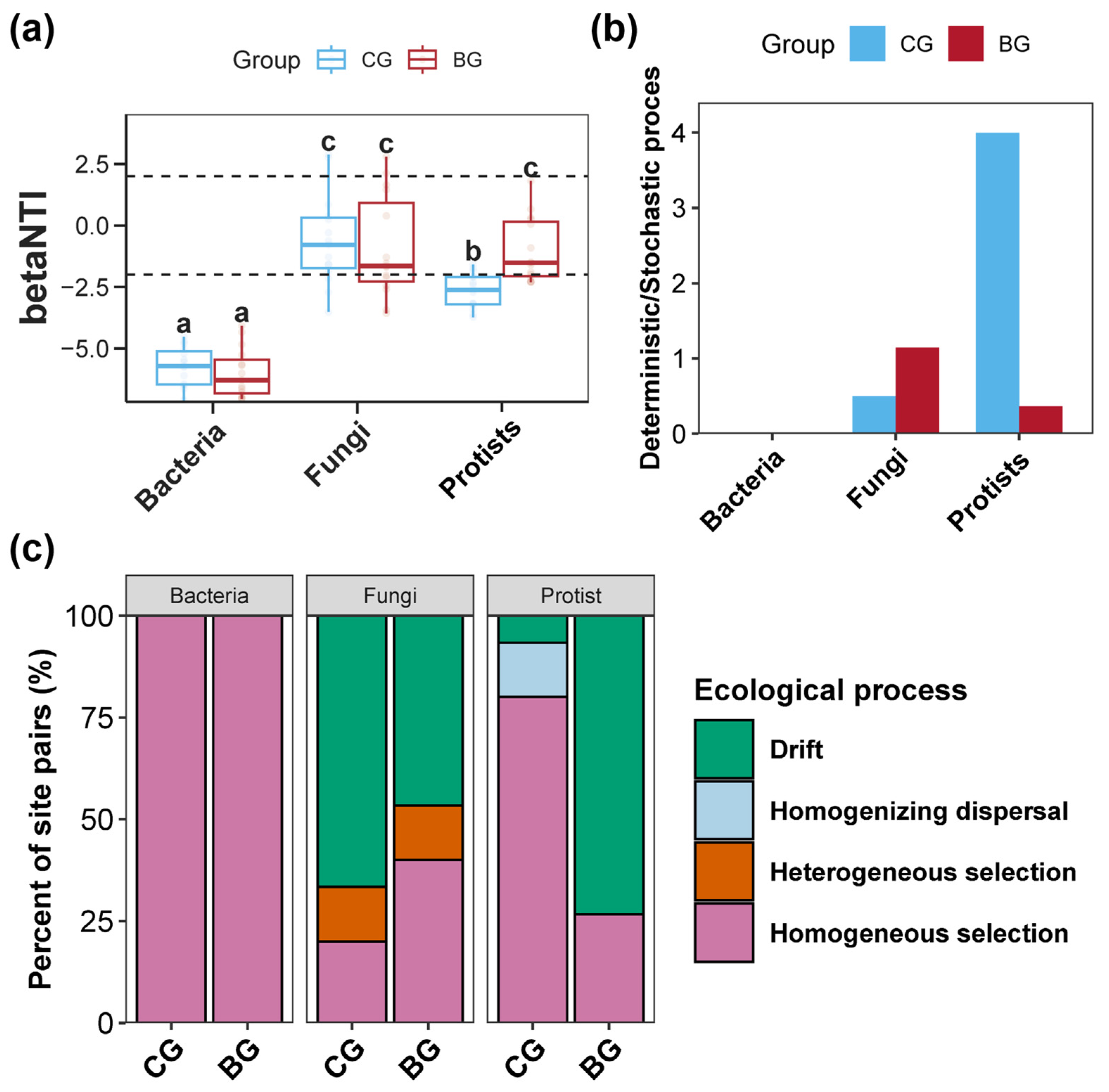
3.4. Assembly Processes of Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities
3.5. Associations Between Sediment Properties and Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Snail B. purificata Presence Altered the Diversity and Composition of Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities
4.2. Snail B. purificata Presence Altered the Co-Occurrence Networks for Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities and Their Intrinsic Interaction Relationships
4.3. Snail B. purificata Presence Altered the Assembly Processes Shaping Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities
4.4. Alterations in Sediment Properties and Their Associations with Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norling, K.; Rosenberg, R.; Hulth, S.; Gremare, A.; Bonsdorff, E. Importance of functional biodiversity and species-specific traits of benthic fauna for ecosystem functions in marine sediment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 332, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.C. Benthic fauna and biogeochemical processes in marine sediments: The role of burrow structures. In Nitrogen Cycling in Coastal Marine Environments; Blackburn, T.H., Sorensen, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 301–338. [Google Scholar]
- Pelegrí, S.P.; Blackburn, T.H. Bioturbation effects of the amphipod Corophium volutator on microbial nitrogen transformations in marine sediments. Mar. Biol. 1994, 121, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.M.H.; Meadows, A.; Meadows, P.S. Biogeomorphological implications of microscale interactions between sediment geotechnics and marine benthos: A review. Geomorphology 2002, 47, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockdale, A.; Davison, W.; Zhang, H. Micro-scale biogeochemical heterogeneity in sediments: A review of available technology and observed evidence. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 92, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Q.; Fan, C.; Zhong, J.; Yin, H. The influence of Tubificid worms bioturbation on the exchange of phosphorus across sediment-water interface in lakes. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 666–674. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz-Lázaro, C.; Marín, A. Diversity patterns of benthic macrofauna caused by marine fish farming. Diversity 2011, 3, 176–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.G.; Liao, Q.J.H.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C.X. The influence of different benthic fauna on inorganic nitrogen flux and denitrification in a large shallow hyper-eutrophic lake. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2014, 184, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.R.; Yang, J.; Han, M.X.; Wang, B.C.; Sun, X.X.; Jiang, H.C. Microbial carbon fixation and its influencing factors in saline lake water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Pan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Gao, S.; Sun, H.; Guan, X.; Wang, B.; et al. Temporal dynamics of bacterial communities in the water and sediments of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) culture ponds. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, V.; Etienne, D.; Masclaux, H.; Essert, V.; Millet, L.; Verneaux, V.; Lyautey, E. Spatial distribution of sediment archaeal and bacterial communities relates to the source of organic matter and hypoxia—A biogeographical study on Lake Remoray (France). Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiab126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Koh, X.P.; Tang, M.L.Y.; Gan, J.; Lau, S.C.K. Microbiological assessment of ecological status in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ma, B.; Stirling, E.; He, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Q. Freshwater trophic status mediates microbial community assembly and interdomain network complexity. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, B.; Yu, Y.; Wang, T.; Xu, N.; Fan, X.; Penuelas, J.; Fu, Z.; Deng, Y.; et al. Global biogeography of microbes driving ocean ecological status under climate change. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, K.A.; Ohsowski, B.M.; Francoeur, S.N.; Neelyb, R.K. Contributions of fungi to carbon flow and nutrient cycling from standing dead Typha angustifolia leaf litter in a temperate freshwater marsh. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.M. The microbial nitrogen cycle. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2903–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, R.E.; Kraemer, S.A.; Onana, V.E.; Huot, Y.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Walsh, D.A. Protist diversity and metabolic strategy in freshwater lakes are shaped by trophic state and watershed land use on a continental scale. Msystems 2022, 7, e00316–e00322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giller, P.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Berninger, U.G.; Gessner, M.O.; Hawkins, S.; Inchausti, P.; Inglis, C.; Leslie, H.; Malmqvist, B.R.; Monaghan, M.T. Biodiversity Effects on Ecosystem Functioning: Emerging Issues and Their Experimental Test in Aquatic Environments. Oikos 2004, 104, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducklow, H. Microbial services: Challenges for microbial ecologists in a changing world. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 53, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Hyde, K.D.; Tsui, K.M. Genera of Freshwater Fungi; Fungal Diversity Press: Hong Kong, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Weisse, T.; Anderson, R.; Arndt, H.; Calbet, A.; Hansen, P.J.; Montagnes, D.J. Functional ecology of aquatic phagotrophic protists–concepts, limitations, and perspectives. Eur. J. Protistol. 2016, 55, 50–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaglia, S.; Bartoli, M.; Gunnarsson, J.S.; Rahm, L.; Raymond, C.; Svensson, O.; Yekta, S.S.; Bruchert, V. Effect of reoxygenation and Marenzelleria spp. bioturbation on Baltic Sea sediment metabolism. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 482, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertics, V.J.; Loscher, C.R.; Salonen, I.; Dale, A.W.; Gier, J.; Schmitz, R.A.; Treude, T. Occurrence of benthic microbial nitrogen fixation coupled to sulfate reduction in the seasonally hypoxic Eckernforde Bay, Baltic Sea. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 1243–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risse-Buhl, U.; Schlief, J.; Mutz, M. Phagotrophic protists are a key component of microbial communities processing leaf litter under contrasting oxic conditions. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 2310–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suberkropp, K.; Klug, M.J. The maceration of deciduous leaf litter by aquatic hyphomycetes. Can. J. Botany. J. Can. Bot. 1980, 58, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, G.R. Interactions between fungi, bacteria and beech leaves in a stream microcosm. Oecologia 1992, 89, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senga, Y.; Yabe, S.; Nakamura, T.; Kagami, M. Influence of parasitic chytrids on the quantity and quality of algal dissolved organic matter (AOM). Water Res. 2018, 145, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, A.; Pinn, D.; Peralta-Maraver, I.; Sweet, M.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Eyice, O.; Bulling, M.; Röthig, T.; Kratina, P. Predation increases multiple components of microbial diversity in activated sludge communities. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, B.; Boysen, A.; Carlson, L.; Groussman, R.; Heal, K.; Cain, K.; Morales, R.; Coesel, S.; Morris, R.; Ingalls, A. Sulfonate-based networks between eukaryotic phytoplankton and heterotrophic bacteria in the surface ocean. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, H.; Ye, J.Y. Purification effects of two eco-ditch systems on Chinese soft-shelled turtle greenhouse culture wastewater pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5610–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, V.; Pant, D. Environmental biomonitoring by snails. Biomarkers 2021, 26, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Taylor, W.D.; Rudstam, L.G. Herbivorous snails can increase water clarity by stimulating growth of benthic algae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24698–24707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.R. Dynamic regulation of ecological water quality in fishery waters based on factorial analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Q.; Yan, S.H.; Chen, K.N.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zed, R.; Zhang, J.Q.; Song, W.; Liu, H.Q. N-15 isotope fractionation in an aquatic food chain: Bellamya aeruginosa (Reeve) as an algal control agent. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Jiang, X. The influence of environmental factors on Bellamya purificate. J. Shanghai Fish. Univ. 1998, 7, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Jin, W.; Wen, H.; Ma, X.; Xue, T.; Sun, C.; He, Y.; Bing, X. Estimation of genetic parameters for growth traits of Bellamya purificata in 60 days. Freshw. Fish. 2018, 48, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Song, G.; Wang, X.; She, L.; Wu, S.; Wu, M.; Ding, F. The efficiency of water purification by different densities of Bellamya aeruginosa and Bellamya purificata. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 11708–11709. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, G.Q.; Chen, M.S.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.P. Experimental study on phosphorus release from sediment with fresh-water snail (Bellamya aeruginosa) bioturbation in eutrophic lakes. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2526–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Lu, K.H.; Liu, X.S. Can the freshwater snail Bellamya aeruginosa (Mollusca) affect phytoplankton community and water quality? Hydrobiologia 2013, 707, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Hou, Y.; Jia, R.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Effects of Bellamya purificata Cultivation at Different Stocking Densities on the Dynamics and Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Sediment. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, B.; Feng, G.; Zhang, C.; He, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, J. Responses of bacterial communities and organic matter degradation in surface sediment to Macrobrachium nipponense bioturbation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Wu, S.; Wu, F.; Sun, S.; Jiang, C.; Tan, W.; Wan, J. Effects of the bioturbation activity of Tubifex tubifex on nitrogen release from sediments. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2011, 31, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Weiwei, J.; Cheng, D.; Xue, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J. Effect of bioturbation of Chironomid larvae and Limno drilus hoffmeiteri on the release of nitrogen, oxygen and phosphate in the sediments from a river. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2015, 35, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Yang, J.; Kang, Q.; Tian, Z.; Wei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X. Determination of Fixed Ammonium in Sediment Using Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry Method. Environ. Sci. Technol. (China) 2014, 37, 340–341. [Google Scholar]
- HJ 634-2012; Soil-Determination of Ammonium, Nitrite and Nitrate by Extraction with Potassium Chloride Solution-Spectrophotometric Methods. MEE: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Peng, G.; Wei, T.; He, J.; Li, R.; Wang, Y. Distinctive patterns of bacterial community succession in the riverine micro-plastisphere in view of biofilm development and ecological niches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoeck, T.; Bass, D.; Nebel, M.; Christen, R.; Jones, M.D.; Breiner, H.W.; Richards, T.A. Multiple marker parallel tag environmental DNA sequencing reveals a highly complex eukaryotic community in marine anoxic water. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Zheng, C.; Suter, H.; Huang, Z. Different responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to nitrogen deposition in a subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; de Vargas, C.; Decelle, J. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarenkov, K.; Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.-H.; Alexander, I.J.; Eberhardt, U.; Erland, S.; Høiland, K.; Kjøller, R.; Larsson, E.; Pennanen, T. The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi–recent updates and future perspectives. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Li, X.; Yan, M.; Lu, J.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, J. Comparable Ecological Processes Govern the Temporal Succession of Gut Bacteria and Microeukaryotes as Shrimp Aged. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 80, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, J.C.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Wilkins, M.J.; Konopka, A.E.; Nelson, W.C.; Arntzen, E.V.; Chrisler, W.B.; Chu, R.K.; Danczak, R.E.; Fansler, S.J.; et al. Groundwater–surface water mixing shifts ecological assembly processes and stimulates organic carbon turnover. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Fan, T.; Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Lu, A.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L. Seasonal changes driving shifts in microbial community assembly and species coexistence in an urban river. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverock, B.; Smith, C.J.; Tait, K.; Osborn, A.M.; Widdicombe, S.; Gilbert, J.A. Bioturbating shrimp alter the structure and diversity of bacterial communities in coastal marine sediments. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermillodblondin, F.; Rosenberg, R.; Francoiscarcaillet, F.; Norling, K.; Mauclaire, L. Influence of bioturbation by three benthic infaunal species on microbial communities and biogeochemical processes in marine sediment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugenski, A.T.; Murria, C.; Whiles, M.R. Tadpoles enhance microbial activity and leaf decomposition in a neotropical headwater stream. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Jiang, W.; Meng, S.; He, W.; Wang, G.; Guo, E.; Yan, Y. Polychaete Bioturbation Alters the Taxonomic Structure, Co-occurrence Network, and Functional Groups of Bacterial Communities in the Intertidal Flat. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusi, M.; Booth, J.M.; Marasco, R.; Merlino, G.; Garcias-Bonet, N.; Barozzi, A.; Garuglieri, E.; Mbobo, T.; Diele, K.; Duarte, C.M.; et al. Bioturbation Intensity Modifies the Sediment Microbiome and Biochemistry and Supports Plant Growth in an Arid Mangrove System. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0111722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Jiang, G.; Wan, X.; Li, H.; Qiao, Y.; Thrush, S.; He, P. Response of the microbial community to bioturbation by benthic macrofauna on intertidal flats. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 488, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Xiao, X.; Liang, J.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, K.; Che, K. Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes as the dominant microorganisms for ammonium nitrogen wastewater treatment with a low C/N ratio in BCOR. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 65, 105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Maria Saez, J.; Davila Costa, J.S.; Leticia Colin, V.; Soledad Fuentes, M.; Antonio Cuozzo, S.; Susana Benimeli, C.; Alejandra Polti, M.; Julia Amoroso, M. Actinobacteria: Current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, O.S.; Fernandes, A.S.; Tupy, S.M.; Ferreira, T.G.; Almeida, L.N.; Creevey, C.J.; Santana, M.F. Insights into plant interactions and the biogeochemical role of the globally widespread Acidobacteriota phylum. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mukhia, S.; Kumar, R. Microbial community dynamics from a fast-receding glacier of Western Himalayas highlight the importance of microbes in primary succession, nutrient recycling, and xenobiotics degradation. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Wang, L.; Du, J.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Hu, L.; Wei, H.; Fang, J.S.; Liu, R.L. Biogeographic distribution, ecotype partitioning and controlling factors of Chloroflexi in the sediments of six hadal trenches of the Paciflc Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Tran, P.Q.; Kieft, K.; Anantharaman, K. Genome diversification in globally distributed novel marine Proteobacteria is linked to environmental adaptation. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2060–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, M.; Behnke, A.; Klier, J.; Buschbaum, C.; Volkenborn, N.; Stoeck, T. Effects of the bioturbating lugworm Arenicola marina on the structure of benthic protistan communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 471, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, H.; Liu, D.; Han, G.; Zhao, P.; Kang, Y. Crab bioturbation significantly alters sediment microbial composition and function in an intertidal marsh. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 249, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, N.; Smith, M.E. Investigating the Ecology, Phylogeny, and Diversity of Zoopagomycota Fungi. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Song, N.; Xu, H.; Yan, Z.; Yang, T.; Wang, C.; Jiang, H.-L. Improved lignin degradation through distinct microbial community in subsurface sediments of one eutrophic lake. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirsová, D.; Wideman, J.G. Integrated overview of stramenopile ecology, taxonomy, and heterotrophic origin. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; He, R.; Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, J.; Huang, R.; Duan, M.; Yu, Z. Composition and co-occurrence patterns of Phragmites australis rhizosphere bacterial community. Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, G.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Jia, R.; Li, Q.; Zhu, J. Dynamic and Assembly of Benthic Bacterial Community in an Industrial-Scale In-Pond Raceway Recirculating Culture System. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 797817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Rui, J.; Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Bai, Y.; Hedenec, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Pei, K.; Liu, C.; et al. Rate-specific responses of prokaryotic diversity and structure to nitrogen deposition in the Leymus chinensis steppe. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 79, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Polz, M.F.; Mazel, F.; Albright, M.B.N.; Huber, J.A.; O’Connor, M.I.; Ackermann, M.; Hahn, A.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Crowe, S.A.; et al. Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D.E.; Ward, C.S. A network-based approach to disturbance transmission through microbial interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.T.-W.; Liu, A.-C.; Weng, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Weng, F.C.-H.; Wang, D.; Chou, C.-Y. A network-based approach to deciphering a dynamic microbiome’s response to a subtle perturbation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Luo, X.; Jiao, J.J.; Li, H.; Kuang, X.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, C. Uncovering the processes of microbial community assembly in the near-surface sediments of a climate-sensitive glacier-fed lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatyer, R.A.; Hirst, M.; Sexton, J.P. Niche breadth predicts geographical range size: A general ecological pattern. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Vandenkoornhuyse, P.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Zhu, C.; Guo, S.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q. Microbial generalists and specialists differently contribute to the community diversity in farmland soils. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 40, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; He, D.; Wan, W. Irreversible community difference between bacterioplankton generalists and specialists in response to lake dredging. Water Res. 2023, 243, 120344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shen, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Jiao, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Ling, J.; Liu, H.; Dong, J.; et al. Specialists regulate microbial network and community assembly in subtropical seagrass sediments under differing land use conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hu, A.; Wan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K. Distinct strategies of the habitat generalists and specialists in sediment of Tibetan lakes. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 4153–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, S.N.; Kolasa, J.; Cottenie, K. Contrasts between habitat generalists and specialists: An empirical extension to the basic metacommunity framework. Ecology 2009, 90, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.A.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Horner-Devine, M.C.; Martiny, J.B.H. Beyond biogeographic patterns: Processes shaping the microbial landscape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellend, M. Conceptual synthesis in community ecology. Q. Rev. Biol. 2010, 85, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.M.; Myers, J.A. Disentangling the importance of ecological niches from stochastic processes across scales. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 2351–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.M.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Liu, J.W. Comparison of assembly process and co-occurrence pattern between planktonic and benthic microbial communities in the Bohai Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1003623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolet, B.L.; Louden, S.I.; Jones, S.E. Microbial community composition, and not pH, influences lake sediment function. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadotte, M.W.; Tucker, C.M. Should Environmental Filtering be Abandoned? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X. Balanced Fertilization Decreases Environmental Filtering on Soil Bacterial Community Assemblage in North China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Stegen, J.C.; Kim, M.; Dong, K.; Adams, J.M.; Lee, Y.K. Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Johnston, E.R.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Han, X. Environmental changes affect the assembly of soil bacterial community primarily by mediating stochastic processes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, R.; Stegen, J.C.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, X. Two key features influencing community assembly processes at regional scale: Initial state and degree of change in environmental conditions. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 5238–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; de Cássia Pereira e Silva, M.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Casamayor, E.O.; van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Dynamics of bacterial community succession in a salt marsh chronosequence: Evidences for temporal niche partitioning. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, J.; Zhang, C.; He, J.; Zhu, J. Effect of Bellamya purificata on organic matter degradation in surface sediment as revealed by amino acids. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2021, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Wong, M.H.; Xu, F.; Yang, X.; Xu, W.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, S. Characteristics of spatial and seasonal bacterial community structures in a river under anthropogenic disturbances. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Gao, S.; Sun, H.; Dong, Y.; Sun, P.; Guan, X.; Zhou, Z. Unrevealing variation of microbial communities and correlation with environmental variables in a full culture-cycle of Undaria pinnatifida. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 139, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Li, L.; Adams, J.M.; Hedenec, P.; Tu, B.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Li, X. Nutrient resource availability mediates niche differentiation and temporal co-occurrence of soil bacterial communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 163, 103965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolukirik, M.; Ince, O.; Cetecioglu, Z.; Celikkol, S.; Ince, B.K. Spatial and temporal changes in microbial diversity of the Marmara Sea Sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Physicochemical Indicator | Measurement Methods |
|---|---|
| Total nitrogen (TN) | Modified Kjeldahl method [45] |
| Fixed ammonium (FA) | Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry method [44] |
| Ammonia | Extraction with potassium chloride solution-spectrophotometric methods [45] |
| Nitrate | |
| Nitrite |
| Category | Amplification Region | Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | 16S rRNA V3-V4 | 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) |
| 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) | ||
| Fungi | ITS1-ITS2 | ITS1F (5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′) |
| ITS2R (5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′) | ||
| Protist | 18S rRNA V4 | TAReuk454FWD1 (5′-CCAGCASCYGCCGTAATTCC-3′) |
| TAReUkREV3 (5′-ACTTTCGTTCTTTGATYRA-3′) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhou, L.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Variations in the Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities and Their Interactions Within Sediment Affected by the Benthic Organism, Snail Bellamya purificata. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122550
Hou Y, Zhang Y, Jia R, Zhou L, Li B, Zhu J. Variations in the Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities and Their Interactions Within Sediment Affected by the Benthic Organism, Snail Bellamya purificata. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122550
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Yiran, Yiyun Zhang, Rui Jia, Linjun Zhou, Bing Li, and Jian Zhu. 2024. "Variations in the Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities and Their Interactions Within Sediment Affected by the Benthic Organism, Snail Bellamya purificata" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122550
APA StyleHou, Y., Zhang, Y., Jia, R., Zhou, L., Li, B., & Zhu, J. (2024). Variations in the Bacterial, Fungal, and Protist Communities and Their Interactions Within Sediment Affected by the Benthic Organism, Snail Bellamya purificata. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122550







