Limited Microbial Contribution in Salt Lake Sediment and Water to Each Other’s Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Sample Collection and Physicochemical Measurements
2.3. DNA Extraction and Illumina Sequencing
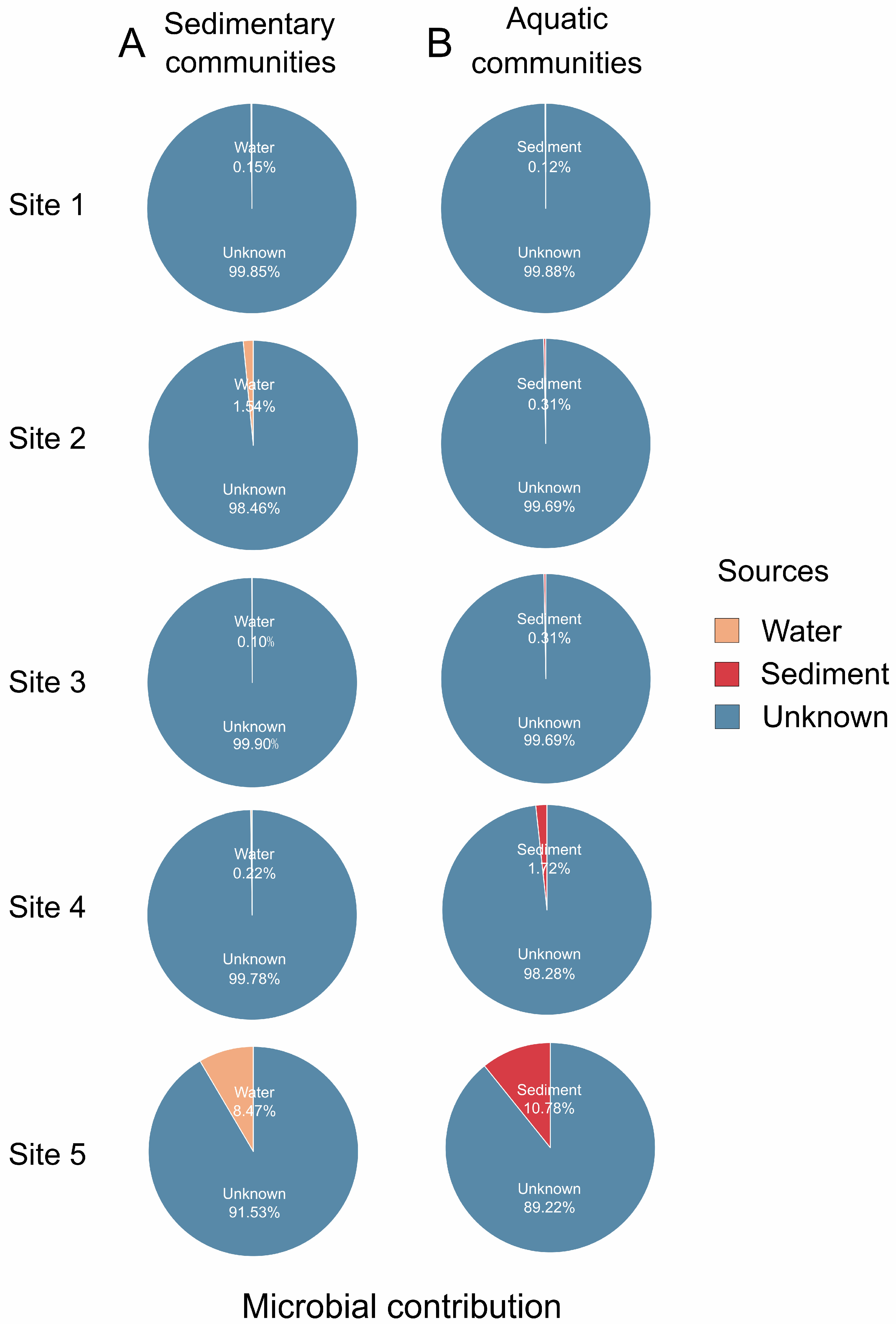
2.4. Microbial Source Tracker
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physiochemical Characteristics in the Sediment and Water Samples
3.2. Microbial Source Tracker in the Sediment and Water Communities
3.3. Diversity and Composition of Microbial Community in the Sediment and Water Samples
3.4. Assembly Mechanisms Qualification of Sedimentary and Aquatic Microbial Community
3.5. Predicted Functional Group Differences Between Sediment and Water Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Contribution of the Lake Water to Microbial Communities in Sediments and Vice Versa
4.2. Distinct Microbial Community Diversity and Compositions Between Saline Lake Sediment and Water
4.3. Relative Contributions of Deterministic and Stochastic Processes in Shaping the Sedimentary and Aquatic Community Structures
4.4. Potential Metabolic Functions of Microbial Players in the Sediment and Water Samples
4.5. Limitations of This Study and Recommendations for Future Microbial Studies in Saline Lakes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nealson, K.H. Sediment bacteria: Who’s there, what are they doing, and what’s new? Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1997, 25, 403–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Jiao, C.; Zhao, D.; Xu, H.; Huang, R.; Cao, X.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Q.L. Patterns and assembly processes of planktonic and sedimentary bacterial community differ along a trophic gradient in freshwater lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Gao, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Ganjurjav, H.; Wang, X. Climate change and human activities altered the diversity and composition of soil microbial community in alpine grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, R.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Zagarese, H.; Baines, S.B.; Hessen, D.O.; Keller, W.; Livingstone, D.M.; Sommaruga, R.; Straile, D.; Van Donk, E. Lakes as sentinels of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Qu, X.; Peng, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, M. Nutrients drive the structures of bacterial communities in sediments and surface waters in the river-lake system of Poyang Lake. Water 2019, 11, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ng, D.H.P.; Wu, Y.; Cao, B. Microbial community composition and putative biogeochemical functions in the sediment and water of tropical granite quarry lakes. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, J.; Guo, L.; Yu, Z. Disentangling the seasonal co-occurrence patterns and ecological stochasticity of planktonic and benthic bacterial communities within multiple lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, A.; Durbin, A.; Ziervogel, K.; Cox, C.; Arnosti, C. Microbial community composition and function in permanently cold seawater and sediments from an arctic fjord of Svalbard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Sun, X.; Huang, J.; Han, M.; Wang, B. Distinct co-occurrence patterns of prokaryotic community between the waters and sediments in lakes with different salinity. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, G.; Yu, B.; Chapman, L.R.; Fields, M.W. Microbial diversity in water and sediment of Lake Chaka, an athalassohaline lake in northwestern China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3832–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Grill, G.; Nedeva, I.; Schmitt, O. Estimating the volume and age of water stored in global lakes using a geo-statistical approach. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; DeRose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002–e00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1326–E1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Hu, A.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Z.; Anslan, S.; Hou, J. Different community assembly mechanisms underlie similar biogeography of bacteria and microeukaryotes in Tibetan lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in subsurface microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Konopka, A.E. Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Jiang, H. Distinct assembly mechanisms for prokaryotic and microeukaryotic communities in the water of Qinghai Lake. J. Earth Sci.-China 2023, 34, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roguet, A.; Laigle, G.S.; Therial, C.; Bressy, A.; Soulignac, F.; Catherine, A.; Lacroix, G.; Jardillier, L.; Bonhomme, C.; Lerch, T.Z.; et al. Neutral community model explains the bacterial community assembly in freshwater lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, fiv125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Wu, Y.; Tu, C.; Soininen, J.; Stegen, J.C.; He, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, E. Phylogenetic beta diversity in bacterial assemblages across ecosystems: Deterministic versus stochastic processes. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Environmental risk characterization and ecological process determination of bacterial antibiotic resistome in lake sediments. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xue, K.; Liang, Y.; Van Nostrand Joy, D.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; Stahl David, A.; et al. Stochasticity, succession, and environmental perturbations in a fluidic ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E836–E845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Ma, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Guo, S.; et al. Metagenomic analysis of the soil microbial composition and salt tolerance mechanism in Yuncheng Salt Lake, Shanxi Province. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1004556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Nan, F.; Feng, J.; Lü, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Xie, S. Transcriptome profile of Dunaliella salina in Yuncheng Salt Lake reveals salt-stress-related genes under different salinity stresses. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 2336–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Howard, K. Groundwater fluoride and arsenic mobilization in a typical deep aquifer system within a semi-arid basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Impact of anthropogenic activities on the enrichment of fluoride and salinity in groundwater in the Yuncheng Basin constrained by Cl/Br ratio, δ18O, δ2H, δ13C and δ7Li isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.; Hyde, E.R.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Ackermann, G.; Humphrey, G.; Parada, A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Caporaso, J.G.; Fuhrman, J.A.; et al. Improved bacterial 16S rRNA gene (V4 and V4-5) and fungal internal transcribed spacer marker gene primers for microbial community surveys. mSystems 2015, 1, e00009–e00015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lai, Q.; He, F.; Zhang, X.; Shui, J.; Yu, M.; Wei, G.; Li, W. Microbial source tracking identifies sources of contamination for a river flowing into the Yellow Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1111297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wu, G.; Xie, Z.; Dong, H. Surviving onshore soil microbial communities differ among the Qing-Tibetan lakes with different salinity. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenhav, L.; Thompson, M.; Joseph, T.A.; Briscoe, L.; Furman, O.; Bogumil, D.; Mizrahi, I.; Pe’er, I.; Halperin, E. FEAST: Fast expectation-maximization for microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Sun, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, Z.; Dong, H. Minerals play key roles in driving prokaryotic and fungal communities in the surface sediments of the Qinghai-Tibetan lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2: An improved and customizable approach for metagenome inference. bioRxiv 2020, 672295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Mai, J.; Cao, X.; Burberry, A.; Cominelli, F.; Zhang, L. ggpicrust2: An R package for PICRUSt2 predicted functional profile analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Wekemo Bioincloud: A user-friendly platform for meta-omics data analyses. iMeta 2024, 3, e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Chu, H. Co-existing water and sediment bacteria are driven by contrasting environmental factors across glacier-fed aquatic systems. Water Res. 2021, 198, 117139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Feng, J.; Xie, S.; Li, X. Distribution patterns and co-occurrence network of eukaryotic algae in different salinity waters of Yuncheng Salt Lake, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comte, J.; Berga, M.; Severin, I.; Logue, J.B.; Lindström, E.S. Contribution of different bacterial dispersal sources to lakes: Population and community effects in different seasons. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2391–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Yan, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K. Habitat-specific patterns of bacterial communities in a glacier-fed lake on the Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2024, 100, fiae018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11436–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Li, M.; Li, F.; Li, H.; Gao, Z. Distinct distribution patterns of prokaryotes between sediment and water in the Yellow River estuary. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9683–9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal variation of planktonic and sediment bacterial assemblages in two plateau freshwater lakes at different trophic status. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4161–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Meng, H.; Xiang, L.; Quan, Z. Bacterial diversity of water and sediment in the Changjiang estuary and coastal area of the East China Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 70, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.A.; Kirkpatrick, J.B.; Rutherford, S.D.; Smith, D.C.; Sogin, M.; D’Hondt, S. Bacterial diversity and community composition from seasurface to subseafloor. ISME J. 2016, 10, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, L.J.; Coffin, R.B.; Sikaroodi, M.; Greinert, J.; Treude, T.; Gillevet, P.M. Ocean currents shape the microbiome of Arctic marine sediments. ISME J. 2013, 7, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Microbial life at high salt concentrations: Phylogenetic and metabolic diversity. Saline Syst. 2008, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran-Reyna, A.; Coker, J.A. The effects of extremes of pH on the growth and transcriptomic profiles of three haloarchaea. F1000Research 2014, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Nagata, T. Alphaproteobacterial dominance in a large mesotrophic lake (Lake Biwa, Japan). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 48, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiano-Labrador, C.; Bland, C.; Miotello, G.; Guérin, P.; Pible, O.; Baena, S.; Armengaud, J. Proteogenomic insights into salt tolerance by a halotolerant alpha-proteobacterium isolated from an Andean saline spring. J. Proteomics 2014, 97, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, F.H.; Meirelles, P.M.; Moreira, A.P.B.; Paranhos, R.P.; Dutilh, B.E.; Thompson, F.L. Niche distribution and influence of environmental parameters in marine microbial communities: A systematic review. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A. Thermodynamic limits to microbial life at high salt concentrations. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1908–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, K.; Marschner, P. Effects of salinity on microbial tolerance to drying and rewetting. Biogeochemistry 2013, 112, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logares, R.; Tesson, S.V.M.; Canbäck, B.; Pontarp, M.; Hedlund, K.; Rengefors, K. Contrasting prevalence of selection and drift in the community structuring of bacteria and microbial eukaryotes. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinger, L.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Horner-Devine, M.C.; Huse, S.M.; Welch, D.B.M.; Martiny, J.B.; Sogin, M.; Boetius, A.; Ramette, A. Global patterns of bacterial beta-diversity in seafloor and seawater ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.K.; Peacock, J.P.; Dodsworth, J.A.; Williams, A.J.; Thompson, D.B.; Dong, H.; Wu, G.; Hedlund, B.P. Sediment microbial communities in Great Boiling Spring are controlled by temperature and distinct from water communities. ISME J. 2013, 7, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Huang, J.; Yang, J. Halotolerant and halophilic microbes and their environmental implications in saline and hypersaline lakes in Qinghai Province, China. In Extremophiles in Eurasian Ecosystems: Ecology, Diversity, and Applications; Egamberdieva, D., Birkeland, N., Panosyan, H., Li, W., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 299–316. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B.; Deocampo, D. Geochemistry of saline lakes. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 5, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearman, J.K.; Adamson, J.; Thomson-Laing, G.; Thompson, L.; Waters, S.; Vandergoes, M.J.; Howarth, J.D.; Wood, S.A. Deterministic processes drive national-scale patterns in lake surface sediment bacteria and eukaryotic assemblage composition. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 68, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, S.; Hou, W.; Feng, K.; Li, F.; Hai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Deng, Y. Temperature and microbial interactions drive the deterministic assembly processes in sediments of hot springs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lian, C.; Wan, W.; Qiu, Z.; Luo, X.; Huang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yu, K. Salinity-triggered homogeneous selection constrains the microbial function and stability in lakes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 6591–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Jeppesen, E.; He, D.; Wang, J.; Liboriussen, L.; Xing, P.; Wu, Q. pH influences the importance of niche-related and neutral processes in lacustrine bacterioplankton assembly. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3104–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, P.; Sommaruga, R. The balance between deterministic and stochastic processes in structuring lake bacterioplankton community over time. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 3117–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, B.; Xiao, H.; Jibin, H. Microbial responses to simulated salinization and desalinization in the sediments of the Qinghai-Tibetan Lakes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Tan, E.; Wang, B.; Gan, Z.; Yang, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Kao, S.; King, G.; Dong, H.; et al. Salinity change induces distinct climate feedbacks of nitrogen removal in saline lakes. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falb, M.; Müller, K.; Königsmaier, L.; Oberwinkler, T.; Horn, P.; von Gronau, S.; Gonzalez, O.; Pfeiffer, F.; Bornberg-Bauer, E.; Oesterhelt, D. Metabolism of halophilic archaea. Extremophiles 2008, 12, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Xia, X. The inhibitory effects of sunlight on nitrogen removal in riverine overlying water with suspended particles. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, M.; Yu, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, H. Limited Microbial Contribution in Salt Lake Sediment and Water to Each Other’s Microbial Communities. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122534
Han M, Yu H, Huang J, Wang C, Li X, Wang X, Xu L, Zhao J, Jiang H. Limited Microbial Contribution in Salt Lake Sediment and Water to Each Other’s Microbial Communities. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122534
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Mingxian, Huiying Yu, Jianrong Huang, Chuanxu Wang, Xin Li, Xiaodong Wang, Liu Xu, Jingjing Zhao, and Hongchen Jiang. 2024. "Limited Microbial Contribution in Salt Lake Sediment and Water to Each Other’s Microbial Communities" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122534
APA StyleHan, M., Yu, H., Huang, J., Wang, C., Li, X., Wang, X., Xu, L., Zhao, J., & Jiang, H. (2024). Limited Microbial Contribution in Salt Lake Sediment and Water to Each Other’s Microbial Communities. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122534






