Targeting Inflammation and Skin Aging via the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7714-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Measurement of Bacteria-Derived EVs
2.2. Quantification of Bacteria-Derived EVs
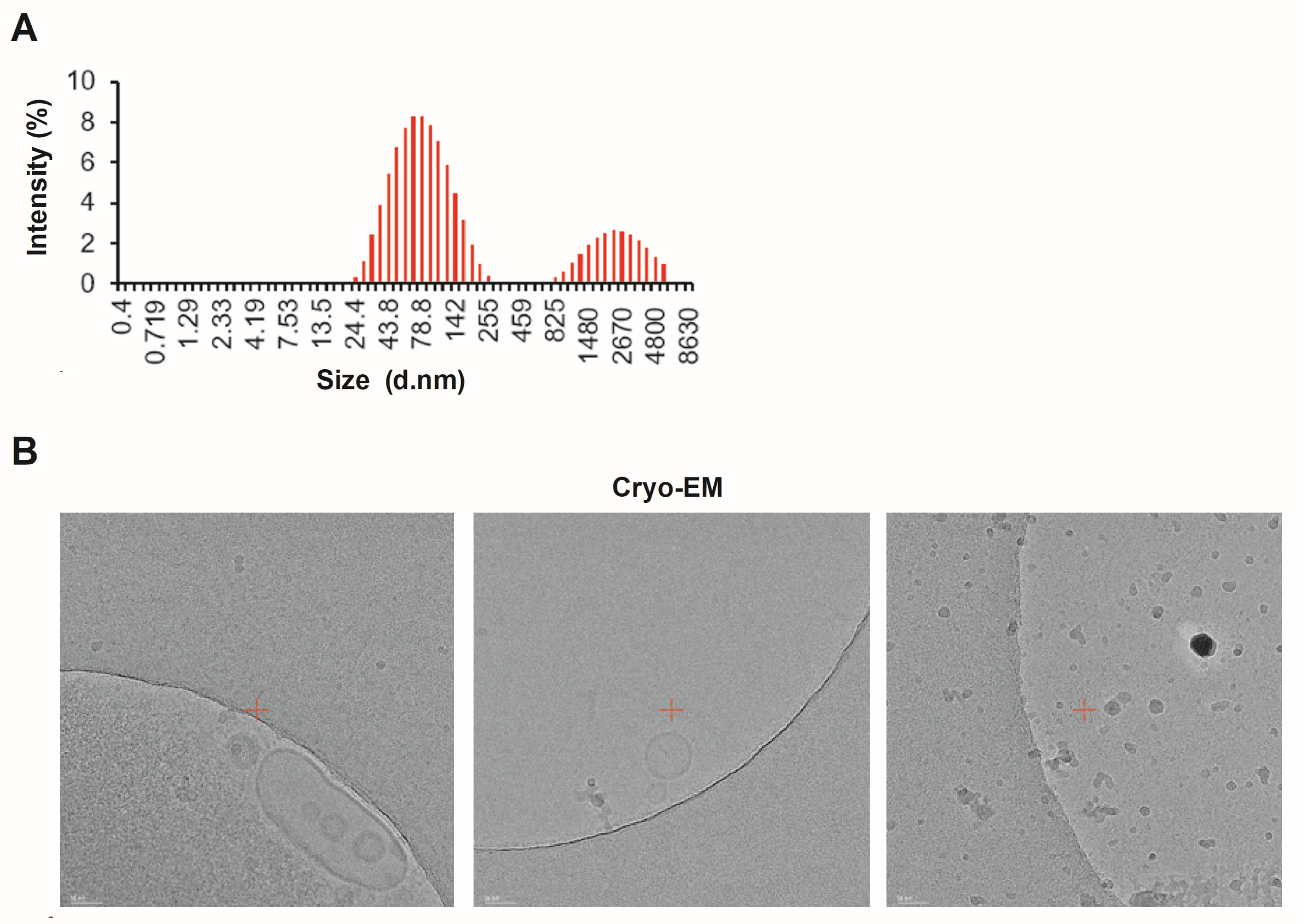
2.3. Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy
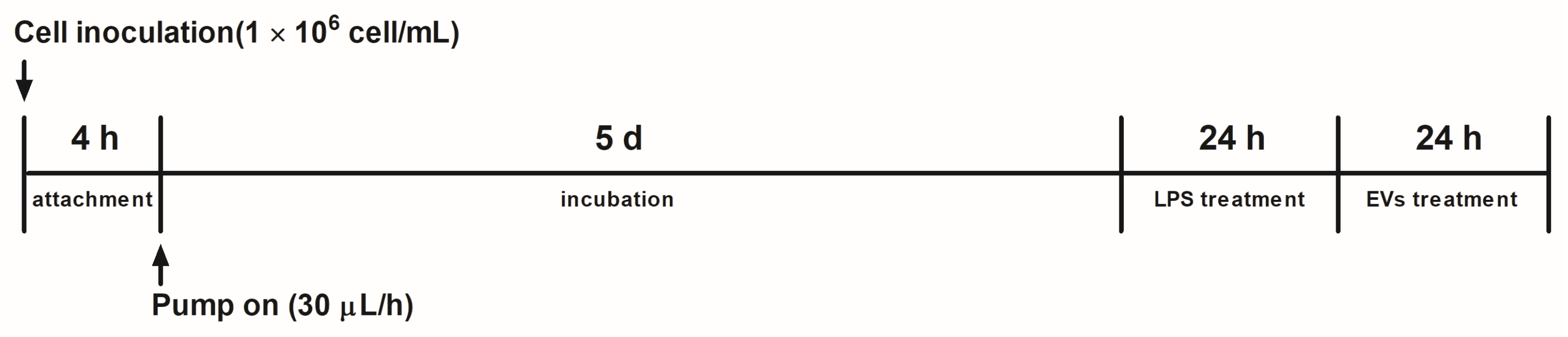
2.4. Gut-on-a-Chip Technique and Cell Preparation
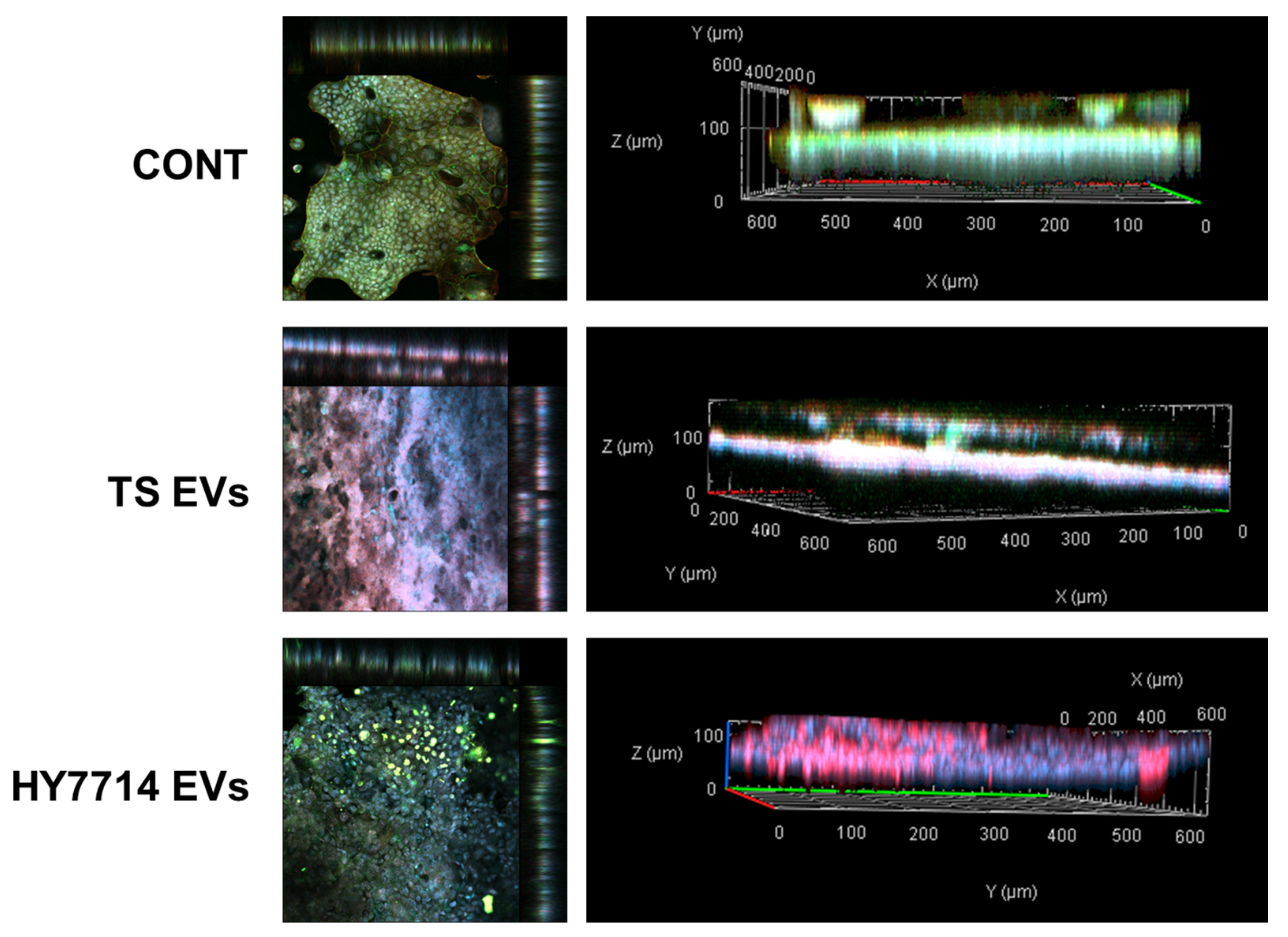
2.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Cell Cultures
2.7. Cell Viability
2.8. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.9. Protein Expression Analysis Through Western Blotting
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characterizing Lpb. plantarum HY7714 EVs
3.2. Quantification of HY7714 EVs
3.3. Effect of Intestinal Barrier Enhancement by EVs on Gut-on-a-Chip
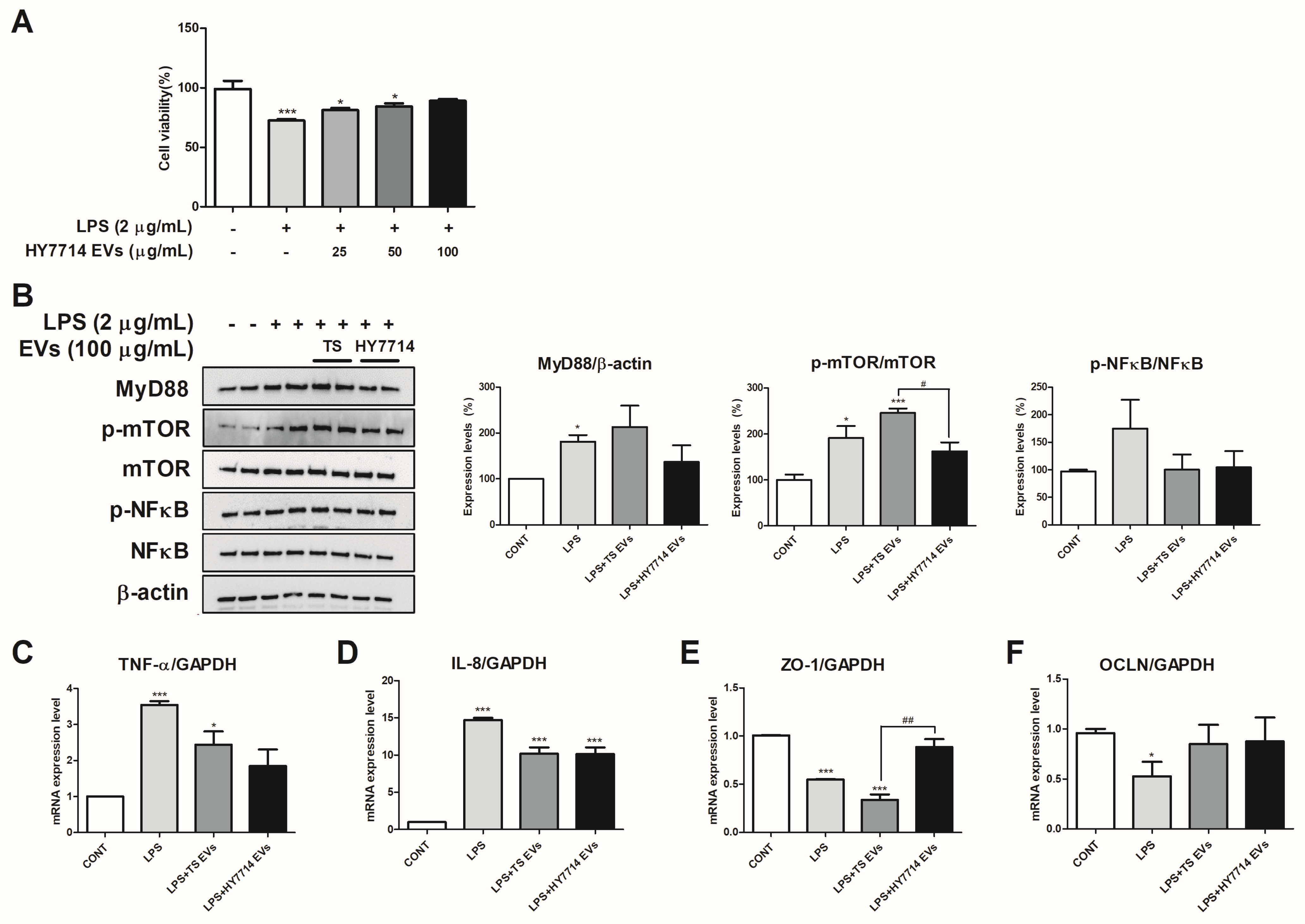
3.4. The Cytoprotective and Intestinal Protective Effect of HY7714 EVs on HT-29 Cells
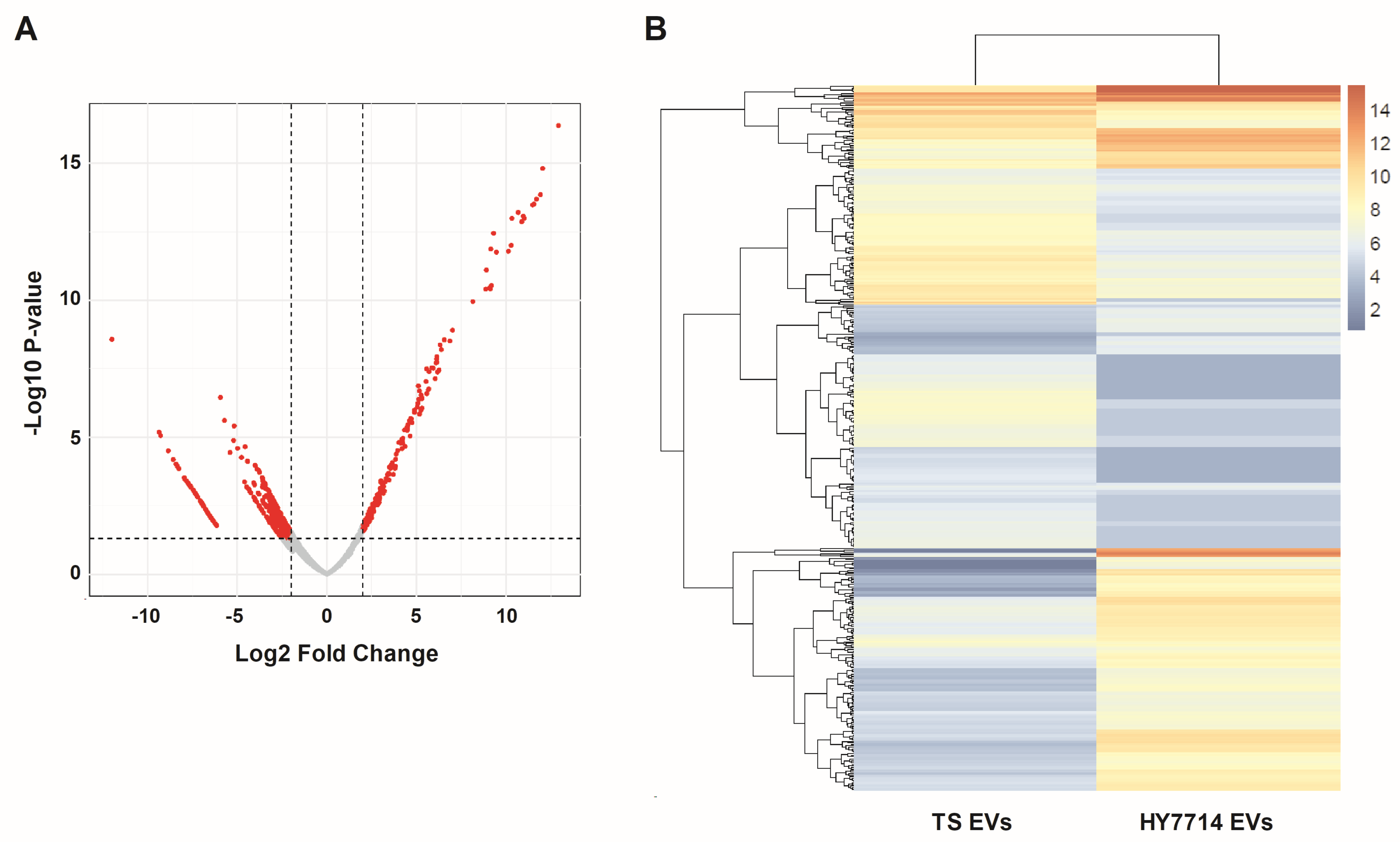
3.5. RNA-Sequencing Analysis of HY7714 EVs
3.6. Effect of HY7714 EVs on ECM-Related Gene Expressions in HS68 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ley, R.E.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 2006, 124, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneethan, U.; Giannella, R.A. Infectious colitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 27, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneethan, U.; Giannella, R.A. Mechanisms of infectious diarrhea. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 5, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Littman, D.R.; Macpherson, A.J. Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science 2012, 336, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Macpherson, A.J. Immune adaptations that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breese, E.J.; Michie, C.A.; Nicholls, S.W.; Murch, S.H.; Williams, C.B.; Domizio, P.; Walker-Smith, J.A.; Macdonald, T.T. Tumor necrosis factor α-producing cells in the intestinal mucosa of children with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1994, 106, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucchelli, L.; Hauser, C.; Zgraggen, K.; Wagner, H.; Hess, M.; Laissue, J.A.; Mueller, C. Expression of interleukin-8 gene in inflammatory bowel disease is related to the histological grade of active inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 144, 997. [Google Scholar]
- Turovskiy, Y.; Noll, K.S.; Chikindas, M.L. The aetiology of bacterial vaginosis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 1105–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, N.; Seo, S.U.; Chen, G.Y.; Núñez, G. Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, W. The skin. Sci. Am. 1965, 212, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Rodriguez, I.A.; Barrosso, L.G.R.; Sánchez, M.L. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017, 17, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon-Lopez, A.; Morales-Penaloza, A.; Martinez-Juarez, V.; Vergas-Torres, A.; Zeugolis, D.; Aguirre-Alvarez, G. Hydrolyzed collagen—Sources and applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The roles of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, F.M.; Fujiwara, H. Cell-extracellular matrix interactions in normal and diseased skin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.C. Molecular mechanisms of skin aging: State of the art. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1119, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Bouladoux, N.; Linehan, J.L.; Han, S.J.; Harrison, O.J.; Wilhelm, C.; Conlan, S.; Himmelfarb, S.; Byrd, A.L.; Deming, C.; et al. Commensal–dendritic-cell interaction specifies a unique protective skin immune signature. Nature 2015, 520, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Nardo, A.D.; Nakatsuji, T.; Leichtle, A.; Yang, Y.; Cogen, A.L.; Wu, Z.-R.; Hooper, L.V.; Schmidt, R.R.; Aulock, S.; et al. Commensal bacteria regulate Toll-like receptor 3–dependent inflammation after skin injury. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, J.S.; Sfyroera, G.; Bartow-McKenney, C.; Gimblet, C.; Bugayev, J.; Horwinski, J.; Kim, B.; Brestoff, J.R.; Tyldsely, A.S.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Commensal microbiota modulate gene expression in the skin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Sugimoto, S.; Izawa, N.; Sone, T.; Chiba, K.; Miyazaki, K. Oral administration of Bifidobacterium breve attenuates UV-induced barrier perturbation and oxidative stress in hairless mice skin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, A.R.; Lee, B.; Kang, D.J.; Chae, S. Skin moisturizing and antiphotodamage effects of tyndallized Lactobacillus acidophilus IDCC 3302. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouilly-Gauthier, D.; Jeannes, C.; Maubert, Y.; Duteil, L.; Queille-Roussel, C.; Piccardi, N.; Montastier, C.; Manissier, P.; Piérard, G.; Ortonne, J.P. Clinical evidence of benefits of a dietary supplement containing probiotic and carotenoids on ultraviolet-induced skin damage. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer-Albers, E.M.; Hill, A.F. Extracellular vesicles: Interneural shuttles of complex messages. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2016, 39, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeun, E.J.; Hong, C.P.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, M.S.; Lee, E.J.; Moon, S.J.; Yun, C.H.; Im, S.H.; Jeong, S.G.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-derived protein from Bifidobacterium longum alleviates food allergy through mast cell suppression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, E.A.; Choi, H.I.; Hong, S.W.; Kang, S.; Jegal, H.Y.; Choi, E.W.; Park, B.S.; Kim, J.S. Extracellular vesicles derived from kefir grain Lactobacillus ameliorate intestinal inflammation via regulation of proinflammatory pathway and tight junction integrity. Biomedicines 2020, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Yu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, D. Exosome-induced regulation in inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clairembault, T.; Leclair-Visonneau, L.; Coron, E.; Bourreille, A.; Le Dily, S.; Vavasseur, F.; Heymann, M.; Neunlist, M.; Derkinderen, P. Structural alterations of the intestinal epithelial barrier in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżek, P.; Marinacci, B.; Vitale, I.; Grande, R. Extracellular vesicles of probiotics: Shedding light on the biological activity and future applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Weng, W.; Jing, Y.; Su, J. Bacterial extracellular vesicles as bioactive nanocarriers for drug delivery: Advances and perspectives. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 14, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Fritz, J.V.; Glaab, E.; Desai, M.S.; Greenhalgh, K.; Frachet, A.; Niegowska, M.; Estes, M.; Jäger, C.; Seguin-Devaux, C.; et al. A microfluidics-based in vitro model of the gastrointestinal human–microbe interface. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.S.; Choi, Y.Y.; Mo, S.J.; Ha, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, H.U.; Park, S.D.; Shim, J.J.; Lee, J.L.; Chung, B.G. Contributions of the microbiome to intestinal inflammation in a gut-on-a-chip. Nano. Converg. 2022, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.E.; Huh, C.S.; Ra, J.; Choi, I.D.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Seo, Y.K.; Koh, J.S.; Lee, J.-H.; et al. Clinical evidence of effects of Lactobacillus plantarum HY7714 on skin aging: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Myoung, K.; Kim, W.; Ko, J.; Kim, K.P.; Cho, E.G. Comparative lipidomic analysis of extracellular vesicles derived from Lactobacillus plantarum APsulloc 331261 living in green tea leaves using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huet, G.; Kim, I.; De Bolos, C.; Lo-Guidice, M.; Hermon, B.; Richet, C.; Delannoy, P.; Real, F.X.; Degand, P. Characterization of mucins and proteoglycans synthesized by a mucin-secreting HT-29 cell subpopulation. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Weirdt, R.; Crabbé, A.; Roos, S.; Vollenweider, S.; Lacroix, C.; Van Pijkeren, J.P.; Britton, R.A.; Sarker, S.; van de Wiele, T.; Nickerson, C.A. Glycerol supplementation enhances L. reuteri’s protective effect against S. Typhimurium colonization in a 3-D model of colonic epithelium. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ge, W.; Wu, J.; Du, P.; Chen, Y. Boosting mTOR-dependent autophagy via upstream TLR4-MyD88-MAPK signalling and downstream NF-κB pathway quenches intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress injury. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Nighot, M.; Al-Sadi, R.; Alhmoud, T.; Nighot, P.; Ma, T.Y. Lipopolysaccharide regulation of intestinal tight junction permeability is mediated by TLR4 signal transduction pathway activation of FAK and MyD88. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4999–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.C.H.; Flynn, A.N.; Turner, J.R.; Buret, A.G. SGLT-1-mediated glucose uptake protects intestinal epithelial cells against LPS-induced apoptosis and barrier defects: A novel cellular rescue mechanism? FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1822–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.R.; Pop, M.; DeBoy, R.T.; Eckburg, P.B.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I.; Relman, D.A.; Fraser-liggett, C.M.; Nelson, K.E. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 2006, 312, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinross, J.M.; Darzi, A.W.; Nicholson, J.K. Gut microbiome-host interactions in health and disease. Genome Med. 2011, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, M.; Mogensen, G.; Fonden, R.; Mättö, J.; Mattila-Sandholm, T. Probiotic bacteria: Safety, functional and technological properties. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 84, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, R.B. Microbial influences in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaffer, M.H.; Holdsworth, C.D.; Duerden, B.I. Virulence properties of Escherichia coli strains isolated from patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1992, 33, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, J.G.; Tattoli, I.; Girardin, S.E. The intestinal epithelial barrier: How to distinguish between the microbial flora and pathogens. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavel, T.; Haller, D. Bacteria-and host-derived mechanisms to control intestinal epithelial cell homeostasis: Implications for chronic inflammation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Komori, H.; Fujita, D.; Tamai, I. Uptake pathway of apple-derived nanoparticle by intestinal cells to deliver its cargo. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Rong, Y.; Teng, Y.; Mu, J.; Zhuang, X.; Tseng, M.; Samykutty, A.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Miller, D.; et al. Broccoli-derived nanoparticle inhibits mouse colitis by activating dendritic cell AMP-activated protein kinase. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1641–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Record, M. Exosome-like nanoparticles from food: Protective nanoshuttles for bioactive cargo. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groschwitz, K.R.; Hogan, S.P. Intestinal barrier function: Molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; He, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. New frontiers in genetics, gut microbiota, and immunity: A rosetta stone for the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8201672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Maras, J.S.; Hussain, M.S.; Sharma, S.; David, P.; Sukriti, S.; Shasthry, S.M.; Maiwall, R.; Trehanpati, N.; Singh, T.P.; et al. Hyperoxidized albumin modulates neutrophils to induce oxidative stress and inflammation in severe alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 2016, 65, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, M.H.W.; Rhee, S.H.; Perkins, D.J.; Medvedev, A.E.; Piao, W.; Fenton, M.J.; Vogel, S.N. TLR4/MyD88/PI3K interactions regulate TLR4 signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Lee, E.J.; Bae, I.H.; Myoung, K.; Kim, S.T.; Park, P.J.; Lee, K.L.; Pham, A.V.Q.; Ko, J.; Oh, S.H.; et al. Lactobacillus plantarum-derived extracellular vesicles induce anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage polarization in vitro. J. Extracell Vesicles 2020, 9, 1793514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.; Zhang, X.; Tong, L.; Liu, Q.; Liang, X.; Bu, Y.; Gong, P.; Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Y.; et al. Effect of extracellular vesicles derived from Lactobacillus plantarum Q7 on gut microbiota and ulcerative colitis in mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 777147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J. Kaempferol alleviates murine experimental colitis by restoring gut microbiota and inhibiting the LPS-TLR4-NF-κB axis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 679897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.K.; Park, E.J.; Ko, S.Y.; Choi, E.W.; Kim, S. Therapeutic effects of kefir grain Lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles in mice with 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced inflammatory bowel disease. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8662–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Moran, G.R. Structural and mechanistic comparisons of the metal-binding members of the vicinal oxygen chelate (VOC) superfamily. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, R.; Pallotta, L.; Cappelletti, M.; Severi, C.; Matarrese, P. The impact of oxidative stress in human pathology: Focus on gastrointestinal disorders. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, M.F.; Hendriks, T. Collagen synthesis in explants from rat intestine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 1989, 993, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilce, M.C.J.; Bond, C.S.; Dixon, N.E.; Freeman, H.C.; Guss, J.M.; Lilley, P.E.; Wilce, J.A. Structure and mechanism of a proline-specific aminopeptidase from Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3472–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Samples | 1 Quantification of EVs |
|---|---|
| Lpb. plantarum HY7714 EVs | 2.97 × 107 |
| Lpb. plantarum KCTC3108 EVs | 3.77 × 107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Hong, D.-K.; Mo, S.-J.; Jeon, S.; Park, S.-D.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, J.-L.; Lee, J.-H. Targeting Inflammation and Skin Aging via the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7714-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122466
Lee H, Lee Y-H, Hong D-K, Mo S-J, Jeon S, Park S-D, Shim J-J, Lee J-L, Lee J-H. Targeting Inflammation and Skin Aging via the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7714-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122466
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hayera, Yun-Ha Lee, Dong-Ki Hong, Sung-Jun Mo, Soomin Jeon, Soo-Dong Park, Jae-Jung Shim, Jeong-Lyoul Lee, and Jae-Hwan Lee. 2024. "Targeting Inflammation and Skin Aging via the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7714-Derived Extracellular Vesicles" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122466
APA StyleLee, H., Lee, Y.-H., Hong, D.-K., Mo, S.-J., Jeon, S., Park, S.-D., Shim, J.-J., Lee, J.-L., & Lee, J.-H. (2024). Targeting Inflammation and Skin Aging via the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7714-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122466





